Deck 1: Medicine
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/1702
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 1: Medicine
1
A group of investigators is studying the relationship between a particular 5-lipoxygenase genotype and atherosclerosis. A random sample of patients from a local university hospital is invited to participate in the study. Blood samples for leukocyte genotyping are obtained, and ultrasonography to assess carotid intima-media thickness (CIMT), a marker of atherosclerosis, is performed. Results show that the particular 5-lipoxygenase genotype is associated with abnormally increased CIMT, a predisposition to atherosclerosis. Which of the following best describes this study design?
A)Case-control study
B)Cross-sectional study
C)Prospective cohort study
D)Randomized clinical trial
E)Retrospective cohort study
A)Case-control study
B)Cross-sectional study
C)Prospective cohort study
D)Randomized clinical trial
E)Retrospective cohort study
B
Explanation:
![B Explanation: A <strong>cross-sectional</strong> study is an <strong>observational</strong> study design that may be employed to estimate the <strong>prevalence</strong> of disease, or to examine <strong>associations</strong> between risk factors and disease as they exist in a well-defined population at <strong>one particular time</strong>. This type of design typically takes a <strong>snapshot</strong> and measures prevalence of risk factor and outcome simultaneously. In this case, subjects are classified according to their risk factor (ie, presence or absence of the particular 5-lipoxygenase genotype) and disease status (ie, presence or absence of abnormally increased carotid intima-media thickness [CIMT]) <strong>at the same time</strong> (ie, snapshot). Then, the association between the presence of the risk factor and the disease is estimated. A major <strong>limitation</strong> of cross-sectional studies is that the temporal relationship between risk factor and disease is not always clear. In this example, however, demonstrating a temporal relationship is possible due to the nature of the risk factor (acquiring a particular genotype precedes atherosclerosis). <strong>(Choice A)</strong> A case-control study is designed by selecting both patients with a particular disease (cases) and patients without that disease (controls), and then determining their previous exposure status. In this case, the researchers selected a single sample from the target population and categorized subjects according to their presence or absence of the risk factor (ie, a particular 5-lipoxygenase genotype) and disease (ie, CIMT status) at a single point in time. <strong>(Choices C and E)</strong> In cohort studies, a group of exposed and unexposed subjects is followed over time for development of the outcome of interest. Contrary to the prospective cohort study, in the retrospective case, exposure and outcome have already occurred at the beginning of the study; therefore, exposure and outcome status are ascertained retrospectively. In both prospective and retrospective cohort studies, however, there is a follow-up of exposed and unexposed individuals across time. By contrast, in this example, a snapshot of the subjects was obtained at one particular time. <strong>(Choice D)</strong> A randomized clinical trial is an experimental study that directly compares ≥2 treatments or interventions. Typically, the subjects are randomly assigned to an intervention (eg, a medication) or placebo, and then followed for the development of the outcome of interest (eg, disease). <strong>Educational objective:</strong> In a cross-sectional study, risk factor and outcome are measured simultaneously at a particular point in time (snapshot study). In other study designs, a certain period separates the exposure from the outcome.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/MD0003/11ec25c8_d091_b6e1_bc81_6be8acbe60ff_MD0003_00.jpg) A cross-sectional study is an observational study design that may be employed to estimate the prevalence of disease, or to examine associations between risk factors and disease as they exist in a well-defined population at one particular time. This type of design typically takes a snapshot and measures prevalence of risk factor and outcome simultaneously.
A cross-sectional study is an observational study design that may be employed to estimate the prevalence of disease, or to examine associations between risk factors and disease as they exist in a well-defined population at one particular time. This type of design typically takes a snapshot and measures prevalence of risk factor and outcome simultaneously.
In this case, subjects are classified according to their risk factor (ie, presence or absence of the particular 5-lipoxygenase genotype) and disease status (ie, presence or absence of abnormally increased carotid intima-media thickness [CIMT]) at the same time (ie, snapshot). Then, the association between the presence of the risk factor and the disease is estimated. A major limitation of cross-sectional studies is that the temporal relationship between risk factor and disease is not always clear. In this example, however, demonstrating a temporal relationship is possible due to the nature of the risk factor (acquiring a particular genotype precedes atherosclerosis).
(Choice A) A case-control study is designed by selecting both patients with a particular disease (cases) and patients without that disease (controls), and then determining their previous exposure status. In this case, the researchers selected a single sample from the target population and categorized subjects according to their presence or absence of the risk factor (ie, a particular 5-lipoxygenase genotype) and disease (ie, CIMT status) at a single point in time.
(Choices C and E) In cohort studies, a group of exposed and unexposed subjects is followed over time for development of the outcome of interest. Contrary to the prospective cohort study, in the retrospective case, exposure and outcome have already occurred at the beginning of the study; therefore, exposure and outcome status are ascertained retrospectively. In both prospective and retrospective cohort studies, however, there is a follow-up of exposed and unexposed individuals across time. By contrast, in this example, a snapshot of the subjects was obtained at one particular time.
(Choice D) A randomized clinical trial is an experimental study that directly compares ≥2 treatments or interventions. Typically, the subjects are randomly assigned to an intervention (eg, a medication) or placebo, and then followed for the development of the outcome of interest (eg, disease).
Educational objective:
In a cross-sectional study, risk factor and outcome are measured simultaneously at a particular point in time (snapshot study). In other study designs, a certain period separates the exposure from the outcome.
Explanation:
![B Explanation: A <strong>cross-sectional</strong> study is an <strong>observational</strong> study design that may be employed to estimate the <strong>prevalence</strong> of disease, or to examine <strong>associations</strong> between risk factors and disease as they exist in a well-defined population at <strong>one particular time</strong>. This type of design typically takes a <strong>snapshot</strong> and measures prevalence of risk factor and outcome simultaneously. In this case, subjects are classified according to their risk factor (ie, presence or absence of the particular 5-lipoxygenase genotype) and disease status (ie, presence or absence of abnormally increased carotid intima-media thickness [CIMT]) <strong>at the same time</strong> (ie, snapshot). Then, the association between the presence of the risk factor and the disease is estimated. A major <strong>limitation</strong> of cross-sectional studies is that the temporal relationship between risk factor and disease is not always clear. In this example, however, demonstrating a temporal relationship is possible due to the nature of the risk factor (acquiring a particular genotype precedes atherosclerosis). <strong>(Choice A)</strong> A case-control study is designed by selecting both patients with a particular disease (cases) and patients without that disease (controls), and then determining their previous exposure status. In this case, the researchers selected a single sample from the target population and categorized subjects according to their presence or absence of the risk factor (ie, a particular 5-lipoxygenase genotype) and disease (ie, CIMT status) at a single point in time. <strong>(Choices C and E)</strong> In cohort studies, a group of exposed and unexposed subjects is followed over time for development of the outcome of interest. Contrary to the prospective cohort study, in the retrospective case, exposure and outcome have already occurred at the beginning of the study; therefore, exposure and outcome status are ascertained retrospectively. In both prospective and retrospective cohort studies, however, there is a follow-up of exposed and unexposed individuals across time. By contrast, in this example, a snapshot of the subjects was obtained at one particular time. <strong>(Choice D)</strong> A randomized clinical trial is an experimental study that directly compares ≥2 treatments or interventions. Typically, the subjects are randomly assigned to an intervention (eg, a medication) or placebo, and then followed for the development of the outcome of interest (eg, disease). <strong>Educational objective:</strong> In a cross-sectional study, risk factor and outcome are measured simultaneously at a particular point in time (snapshot study). In other study designs, a certain period separates the exposure from the outcome.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/MD0003/11ec25c8_d091_b6e1_bc81_6be8acbe60ff_MD0003_00.jpg) A cross-sectional study is an observational study design that may be employed to estimate the prevalence of disease, or to examine associations between risk factors and disease as they exist in a well-defined population at one particular time. This type of design typically takes a snapshot and measures prevalence of risk factor and outcome simultaneously.
A cross-sectional study is an observational study design that may be employed to estimate the prevalence of disease, or to examine associations between risk factors and disease as they exist in a well-defined population at one particular time. This type of design typically takes a snapshot and measures prevalence of risk factor and outcome simultaneously.In this case, subjects are classified according to their risk factor (ie, presence or absence of the particular 5-lipoxygenase genotype) and disease status (ie, presence or absence of abnormally increased carotid intima-media thickness [CIMT]) at the same time (ie, snapshot). Then, the association between the presence of the risk factor and the disease is estimated. A major limitation of cross-sectional studies is that the temporal relationship between risk factor and disease is not always clear. In this example, however, demonstrating a temporal relationship is possible due to the nature of the risk factor (acquiring a particular genotype precedes atherosclerosis).
(Choice A) A case-control study is designed by selecting both patients with a particular disease (cases) and patients without that disease (controls), and then determining their previous exposure status. In this case, the researchers selected a single sample from the target population and categorized subjects according to their presence or absence of the risk factor (ie, a particular 5-lipoxygenase genotype) and disease (ie, CIMT status) at a single point in time.
(Choices C and E) In cohort studies, a group of exposed and unexposed subjects is followed over time for development of the outcome of interest. Contrary to the prospective cohort study, in the retrospective case, exposure and outcome have already occurred at the beginning of the study; therefore, exposure and outcome status are ascertained retrospectively. In both prospective and retrospective cohort studies, however, there is a follow-up of exposed and unexposed individuals across time. By contrast, in this example, a snapshot of the subjects was obtained at one particular time.
(Choice D) A randomized clinical trial is an experimental study that directly compares ≥2 treatments or interventions. Typically, the subjects are randomly assigned to an intervention (eg, a medication) or placebo, and then followed for the development of the outcome of interest (eg, disease).
Educational objective:
In a cross-sectional study, risk factor and outcome are measured simultaneously at a particular point in time (snapshot study). In other study designs, a certain period separates the exposure from the outcome.
2
A 46-year-old man comes to the physician due to exertional dyspnea and dry cough. He also has occasional episodes of suffocating nighttime cough that is relieved only by sitting up. Medical history is significant for myocardial infarction 6 months ago and hypercholesterolemia. Current medications include metoprolol, aspirin, and rosuvastatin. The patient drinks alcohol on social occasions but does not use tobacco or illicit drugs. His father died of a stroke and his mother has type 2 diabetes mellitus. Blood pressure is 150/100 mm Hg and pulse is 60/min. Chest examination shows bibasilar crackles. The cardiac apex is palpated in the left sixth intercostal space. Bilateral pitting leg edema is present. Which of the following is most likely to be associated with this patient's condition?
A)Constriction of the renal efferent arterioles
B)Decreased plasma colloid pressure
C)Decreased renal venous pressure
D)Dilation of the renal afferent arterioles
E)High sodium delivery to the distal tubule
F)Increased chloride delivery to the macula densa
A)Constriction of the renal efferent arterioles
B)Decreased plasma colloid pressure
C)Decreased renal venous pressure
D)Dilation of the renal afferent arterioles
E)High sodium delivery to the distal tubule
F)Increased chloride delivery to the macula densa
A
Explanation:
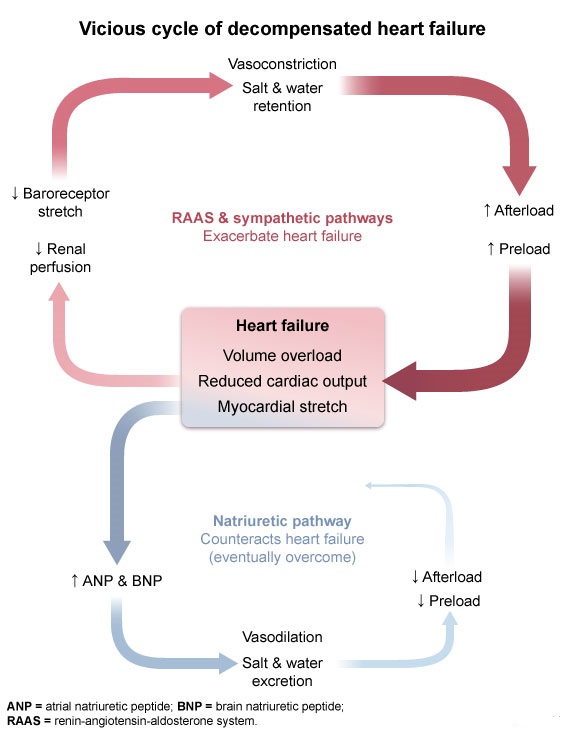 This patient's presentation with exertional dyspnea, cough, orthopnea, and evidence of pulmonary and peripheral edema following recent myocardial infarction is consistent with decompensated heart failure (DHF). The initial disturbance in heart failure is usually a reduction in left ventricular function that leads to reduced cardiac output. The reduced cardiac output causes decreased organ and tissue perfusion that is sensed by arterial baroreceptors and the juxtaglomerular apparatus of the kidneys, which triggers compensatory activation of the sympathetic nervous system and renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS). These systems stimulate both vasoconstriction and sodium retention (ie, increased blood volume) to maintain organ and tissue perfusion. Specifically, angiotensin II causes vasoconstriction of both the afferent and efferent renal arterioles (more prominent of the efferent arterioles) to maintain the glomerular filtration rate.
This patient's presentation with exertional dyspnea, cough, orthopnea, and evidence of pulmonary and peripheral edema following recent myocardial infarction is consistent with decompensated heart failure (DHF). The initial disturbance in heart failure is usually a reduction in left ventricular function that leads to reduced cardiac output. The reduced cardiac output causes decreased organ and tissue perfusion that is sensed by arterial baroreceptors and the juxtaglomerular apparatus of the kidneys, which triggers compensatory activation of the sympathetic nervous system and renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS). These systems stimulate both vasoconstriction and sodium retention (ie, increased blood volume) to maintain organ and tissue perfusion. Specifically, angiotensin II causes vasoconstriction of both the afferent and efferent renal arterioles (more prominent of the efferent arterioles) to maintain the glomerular filtration rate.
RAAS
Ultimately, these compensatory mechanisms are maladaptive as vasoconstriction increases afterload and sodium retention increases preload, both of which place additional strain on the failing heart and further reduce cardiac output. A vicious cycle ensues, eventually progressing to clinical decompensation with overt volume overload.
(Choice B) Plasma colloid pressure is mostly driven by albumin concentration. It is low in nephrotic syndrome and decompensated cirrhosis, but it is typically normal in DHF. Edema in DHF results from elevated venous hydrostatic pressure.
(Choice C) Renal venous pressure is increased in DHF as elevated pressure is transmitted back from the heart to the vena cava and to the renal veins (ie, central venous pressure is elevated).
(Choices D, E, and F) The release of natriuretic peptides is triggered by myocardial stretch; these peptides stimulate renal afferent arteriole vasodilation and sodium excretion to counteract the sympathetic and RAAS pathways and offset the downward spiral of DHF. However, the natriuretic pathway is eventually overcome. Renal arteriolar vasoconstriction predominates with reduced renal blood flow and reduced glomerular filtration (ie, reduced sodium delivery to the distal tubule, reduced chloride delivery to the macula densa).
Educational objective:
Decompensated heart failure involves the activation of compensatory mechanisms in the form of the sympathetic nervous system and renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. These systems stimulate vasoconstriction and sodium retention to maintain organ and tissue perfusion in the setting of reduced cardiac output. The compensatory mechanisms are ultimately maladaptive as they further decrease cardiac output and perpetuate a downward spiral of clinical decompensation.
References:
Congestive heart failure: pathophysiologic consequences of neurohormonal activation and the potential for recovery: part I.
(http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22030844)
Explanation:
 This patient's presentation with exertional dyspnea, cough, orthopnea, and evidence of pulmonary and peripheral edema following recent myocardial infarction is consistent with decompensated heart failure (DHF). The initial disturbance in heart failure is usually a reduction in left ventricular function that leads to reduced cardiac output. The reduced cardiac output causes decreased organ and tissue perfusion that is sensed by arterial baroreceptors and the juxtaglomerular apparatus of the kidneys, which triggers compensatory activation of the sympathetic nervous system and renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS). These systems stimulate both vasoconstriction and sodium retention (ie, increased blood volume) to maintain organ and tissue perfusion. Specifically, angiotensin II causes vasoconstriction of both the afferent and efferent renal arterioles (more prominent of the efferent arterioles) to maintain the glomerular filtration rate.
This patient's presentation with exertional dyspnea, cough, orthopnea, and evidence of pulmonary and peripheral edema following recent myocardial infarction is consistent with decompensated heart failure (DHF). The initial disturbance in heart failure is usually a reduction in left ventricular function that leads to reduced cardiac output. The reduced cardiac output causes decreased organ and tissue perfusion that is sensed by arterial baroreceptors and the juxtaglomerular apparatus of the kidneys, which triggers compensatory activation of the sympathetic nervous system and renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS). These systems stimulate both vasoconstriction and sodium retention (ie, increased blood volume) to maintain organ and tissue perfusion. Specifically, angiotensin II causes vasoconstriction of both the afferent and efferent renal arterioles (more prominent of the efferent arterioles) to maintain the glomerular filtration rate.RAAS
Ultimately, these compensatory mechanisms are maladaptive as vasoconstriction increases afterload and sodium retention increases preload, both of which place additional strain on the failing heart and further reduce cardiac output. A vicious cycle ensues, eventually progressing to clinical decompensation with overt volume overload.
(Choice B) Plasma colloid pressure is mostly driven by albumin concentration. It is low in nephrotic syndrome and decompensated cirrhosis, but it is typically normal in DHF. Edema in DHF results from elevated venous hydrostatic pressure.
(Choice C) Renal venous pressure is increased in DHF as elevated pressure is transmitted back from the heart to the vena cava and to the renal veins (ie, central venous pressure is elevated).
(Choices D, E, and F) The release of natriuretic peptides is triggered by myocardial stretch; these peptides stimulate renal afferent arteriole vasodilation and sodium excretion to counteract the sympathetic and RAAS pathways and offset the downward spiral of DHF. However, the natriuretic pathway is eventually overcome. Renal arteriolar vasoconstriction predominates with reduced renal blood flow and reduced glomerular filtration (ie, reduced sodium delivery to the distal tubule, reduced chloride delivery to the macula densa).
Educational objective:
Decompensated heart failure involves the activation of compensatory mechanisms in the form of the sympathetic nervous system and renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. These systems stimulate vasoconstriction and sodium retention to maintain organ and tissue perfusion in the setting of reduced cardiac output. The compensatory mechanisms are ultimately maladaptive as they further decrease cardiac output and perpetuate a downward spiral of clinical decompensation.
References:
Congestive heart failure: pathophysiologic consequences of neurohormonal activation and the potential for recovery: part I.
(http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22030844)
3
A study evaluated the relationship between the common cold and the number of cigarettes smoked per day. The research was conducted among fourth-year medical students and sponsored by the public health department of the medical school. Medical students with symptoms of common cold were asked to fill out a questionnaire about their smoking status, number of packs smoked per day, and duration of smoking. Which of the following factors would most likely invalidate the findings of this study?
A)Admission rate bias
B)Lead-time bias
C)Nonresponse bias
D)Regression to the mean
E)Response bias
A)Admission rate bias
B)Lead-time bias
C)Nonresponse bias
D)Regression to the mean
E)Response bias
E
Explanation:
Response bias occurs when participants in cross-sectional studies (eg, surveys, polls, questionnaires) purposely give desirable responses to questions about topics perceived to be sensitive (eg, health behaviors). Biased responses become less useful as they are inaccurate and may lead to incorrect conclusions (eg, lower than expected prevalence of disease or frequency of risk factors).
In this example, medical students likely know the risk of smoking and may purposely not reveal their smoking status, especially to interviewers from the public health department of their institution. They may also report smoking a lesser number of cigarettes than they truly smoke, significantly affecting the results of the study.
(Choice A) Admission rate bias occurs when a distortion in risk ratio exists due to hospitals' differing admission rates for certain cases. For instance, patients with cardiac diseases may be admitted to hospitals with more specialized cardiology services.
(Choice B) Lead-time bias occurs when a screening test diagnoses a disease earlier than it would have appeared by natural history alone, so that the time from diagnosis until death appears prolonged even though there might actually be no improvement in survival.
(Choice C) Nonresponse bias occurs when respondents differ from nonrespondents in such meaningful ways that threaten the generalizability of study results. It most often occurs when data is collected by mailed surveys or questionnaires. The study in this question provides no information to evaluate nonresponse bias.
(Choice D) Regression to the mean refers to a set of data where the first assessment of a variable reveals an extreme value but repeat assessment reveals values closer to the center of the distribution of that variable.
Educational objective:
Response bias occurs when participants purposely give desirable responses to questions about topics perceived to be sensitive (eg, health behaviors). This practice results in responses that are inaccurate and may lead to incorrect conclusions (eg, lower than expected prevalence of disease or frequency of risk factors).
Explanation:
Response bias occurs when participants in cross-sectional studies (eg, surveys, polls, questionnaires) purposely give desirable responses to questions about topics perceived to be sensitive (eg, health behaviors). Biased responses become less useful as they are inaccurate and may lead to incorrect conclusions (eg, lower than expected prevalence of disease or frequency of risk factors).
In this example, medical students likely know the risk of smoking and may purposely not reveal their smoking status, especially to interviewers from the public health department of their institution. They may also report smoking a lesser number of cigarettes than they truly smoke, significantly affecting the results of the study.
(Choice A) Admission rate bias occurs when a distortion in risk ratio exists due to hospitals' differing admission rates for certain cases. For instance, patients with cardiac diseases may be admitted to hospitals with more specialized cardiology services.
(Choice B) Lead-time bias occurs when a screening test diagnoses a disease earlier than it would have appeared by natural history alone, so that the time from diagnosis until death appears prolonged even though there might actually be no improvement in survival.
(Choice C) Nonresponse bias occurs when respondents differ from nonrespondents in such meaningful ways that threaten the generalizability of study results. It most often occurs when data is collected by mailed surveys or questionnaires. The study in this question provides no information to evaluate nonresponse bias.
(Choice D) Regression to the mean refers to a set of data where the first assessment of a variable reveals an extreme value but repeat assessment reveals values closer to the center of the distribution of that variable.
Educational objective:
Response bias occurs when participants purposely give desirable responses to questions about topics perceived to be sensitive (eg, health behaviors). This practice results in responses that are inaccurate and may lead to incorrect conclusions (eg, lower than expected prevalence of disease or frequency of risk factors).
4
A 68-year-old woman comes to the office for follow-up after a recent emergency department visit. Two weeks ago, the patient experienced palpitations and mild dizziness; ECG showed atrial fibrillation with rapid ventricular response. The episode resolved spontaneously in 2 hours, and she has had no symptoms since then. The patient has a history of hypertension treated with valsartan and hydrochlorothiazide. She is a lifetime nonsmoker and does not drink alcohol. Her exercise tolerance is good. Blood pressure is 128/72 mm Hg, and pulse is 74/min and regular. Physical examination is unremarkable. TSH is 1.6, creatinine is 1.1 mg/dL, and fasting glucose is 85 mg/dL. Echocardiography shows preserved left ventricular ejection fraction and no significant valvular abnormalities. Which of the following is the best next step in management of this patient?
A)Ambulatory heart rhythm monitoring
B)Amiodarone
C)Apixaban
D)Aspirin
E)Carotid ultrasound
F)Clinical follow-up only
A)Ambulatory heart rhythm monitoring
B)Amiodarone
C)Apixaban
D)Aspirin
E)Carotid ultrasound
F)Clinical follow-up only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 1702 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A group of investigators plans to conduct a study to assess the relationship between colon cancer and elevated plasma C-reactive protein (CRP) levels. The study design involves determining the prevalence of elevated plasma CRP levels (based on prespecified cutoff values) and of colon cancer in a sample of individuals at a given point in time. The prevalence of elevated CRP levels is compared between patients with and without colon cancer. Which of the following is the best statement of the null hypothesis for this study?
A)Colon cancer is more prevalent among subjects with elevated CRP levels
B)Having a diagnosis of colon cancer does not affect plasma CRP levels
C)Subjects with elevated plasma CRP levels are prone to colon cancer
D)The risk of colon cancer is the same for subjects with and without elevated plasma CRP levels
E)There is no association between elevated plasma CRP level and colon cancer
A)Colon cancer is more prevalent among subjects with elevated CRP levels
B)Having a diagnosis of colon cancer does not affect plasma CRP levels
C)Subjects with elevated plasma CRP levels are prone to colon cancer
D)The risk of colon cancer is the same for subjects with and without elevated plasma CRP levels
E)There is no association between elevated plasma CRP level and colon cancer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 1702 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A 76-year-old man with coronary artery disease comes to the office for follow-up 6 months after an uncomplicated coronary artery bypass surgery. The exertional chest pain that was bothering the patient before the surgery has completely resolved. He reports no palpitations, shortness of breath, light-headedness, or syncope. The patient has a history of hypertension, diet-controlled type 2 diabetes mellitus, and gout. Medications include low-dose aspirin, metoprolol, and rosuvastatin. He has a 30-pack-year smoking history but quit 5 years ago. The patient does not use alcohol or illicit drugs. Physical examination shows an irregular pulse. The chest surgical incision is well healed. There are no heart murmurs, and the lungs are clear on auscultation. There is no peripheral edema. ECG obtained in the office is shown in the exhibit.
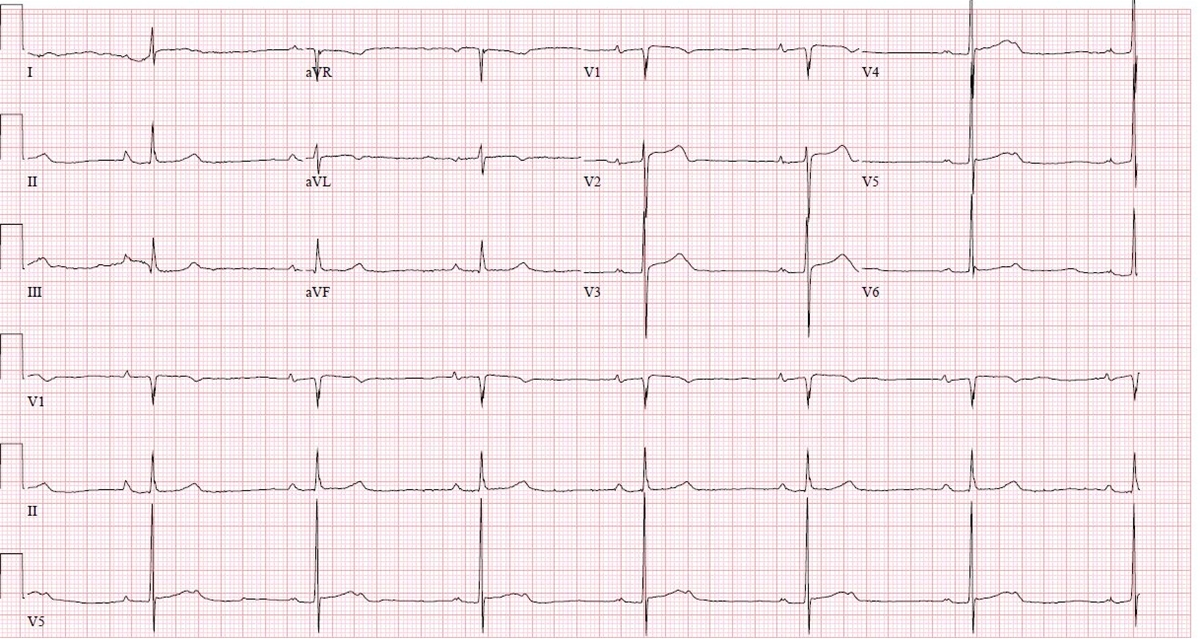
Which of the following is the best management for this patient?
A)Atrioventricular nodal slow pathway ablation
B)Atrioventricular nodal reentrant tachycardia
C)Flecainide initiation
D)Oral anticoagulant therapy
E)Routine follow-up in 6 months

Which of the following is the best management for this patient?
A)Atrioventricular nodal slow pathway ablation
B)Atrioventricular nodal reentrant tachycardia
C)Flecainide initiation
D)Oral anticoagulant therapy
E)Routine follow-up in 6 months

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 1702 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A 65-year-old man is found to have an abnormal reading during screening tonometry. The patient has no visual symptoms or headache. Medical history is significant for asthma, for which he takes inhaled fluticasone/salmeterol routinely and inhaled albuterol on most days to control the symptoms. Vital signs are within normal limits. Eye examination shows normal conjunctivae, corneas, and lenses. Intraocular pressure is 28 mm Hg (normal: 8-21). Funduscopy reveals thinning of the optic disc rim and asymmetry of the cup/disc ratio between the eyes. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management of this patient's ocular condition?
A)Advise to stop glucocorticoid therapy
B)Begin atropine eye drops
C)Prescribe oral acetazolamide therapy
D)Recommend treatment only if symptomatic
E)Start latanoprost ophthalmic solution
A)Advise to stop glucocorticoid therapy
B)Begin atropine eye drops
C)Prescribe oral acetazolamide therapy
D)Recommend treatment only if symptomatic
E)Start latanoprost ophthalmic solution

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 1702 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A prospective cohort study revealed a strong positive association between smoking and liver cirrhosis (relative risk = 2.8). The researchers then divided the cohort into two groups: alcohol consumers and non-consumers. Subsequent statistical analysis did not reveal any association between smoking and liver cirrhosis with either group. The scenario described above is an example of which of the following?
A)Selection bias
B)Observer's bias
C)Measurement bias
D)Recall bias
E)Confounding
A)Selection bias
B)Observer's bias
C)Measurement bias
D)Recall bias
E)Confounding

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 1702 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A group of investigators conducted a randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial to assess the effect of a new aldosterone receptor antagonist on the progression of chronic heart failure. The primary outcome was all-cause mortality. A decrease in all-cause mortality in the treatment group was reported, with a relative risk of 0.71 (p = 0.001). Which of the following statements is the best interpretation of the reported association?
A)The 95% confidence interval for the relative risk of all-cause mortality includes 1.0
B)There is a 0.1% probability of observing the given relative risk (or more extreme) by chance alone assuming no differences in mortality
C)There is a 71% decrease in all-cause mortality in the new aldosterone receptor antagonist compared to the placebo group
D)There is only a 0.1% chance that the relative risk calculated is biased in favor of the aldosterone receptor antagonist group
E)The results obtained are not statistically significant
A)The 95% confidence interval for the relative risk of all-cause mortality includes 1.0
B)There is a 0.1% probability of observing the given relative risk (or more extreme) by chance alone assuming no differences in mortality
C)There is a 71% decrease in all-cause mortality in the new aldosterone receptor antagonist compared to the placebo group
D)There is only a 0.1% chance that the relative risk calculated is biased in favor of the aldosterone receptor antagonist group
E)The results obtained are not statistically significant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 1702 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
An 82-year-old man comes to the office for evaluation of chronic back pain. On physical examination, he is found to have a blood pressure of 160/85 mm Hg while supine and 135/70 mm Hg while standing. He is otherwise healthy; his only medicine is occasional ibuprofen for back pain. Which of the following age-related changes best explains the observed finding?
A)Increased left ventricular wall stiffness
B)Decreased left ventricular contractility
C)Decreased baroreceptor responsiveness
D)Decreased stress-mediated adrenal catecholamine release
E)Decreased glomerular filtration rate
A)Increased left ventricular wall stiffness
B)Decreased left ventricular contractility
C)Decreased baroreceptor responsiveness
D)Decreased stress-mediated adrenal catecholamine release
E)Decreased glomerular filtration rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 1702 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A 44-year-old man comes to the office for follow-up after a recent hospitalization. The patient went to the emergency department with palpitations 2 weeks ago and was found to have atrial fibrillation with rapid ventricular response. He was admitted to the hospital, where he spontaneously converted to normal sinus rhythm overnight and was discharged home the next day. Prior to this episode, the patient had gone on an alcohol drinking binge during a friend's bachelor party. He otherwise rarely drinks alcohol. Medical history is unremarkable. He is a lifetime nonsmoker. Blood pressure is 124/70 mm Hg and pulse is 78/min and regular. Estimated jugular venous pressure is normal. Examination shows no abnormalities. Review of laboratory results from the hospital admission shows normal creatinine level, liver function tests, thyroid studies, and lipid panel. Echocardiogram shows normal left and right ventricular function and no valvular abnormalities. Which of the following is the best next step in managing this patient?
A)Amiodarone
B)Aspirin and clopidogrel
C)No additional therapy
D)Rivaroxaban
E)Warfarin
A)Amiodarone
B)Aspirin and clopidogrel
C)No additional therapy
D)Rivaroxaban
E)Warfarin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 1702 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A 76-year-old woman comes to the office due to intermittent palpitations for the last 6 months. The patient describes episodes of her heart beating fast. These happen on average once a week, last up to an hour, and resolve spontaneously. She cannot identify any provoking factors but thinks they occur typically when she is tired. The patient has had no chest pain, dyspnea, syncope, or lower extremity swelling. She has a history of hypertension. The patient is a lifetime nonsmoker. Blood pressure is 145/85 mm Hg, and pulse is 75/min and regular. There are no heart murmurs. The lungs are clear on auscultation. Peripheral pulses are full and symmetric. ECG shows normal sinus rhythm. Echocardiogram shows moderate left atrial enlargement, left ventricular hypertrophy, ejection fraction of 65%, and no valvular abnormalities. Further workup is most likely to identify which of the following in this patient?
A)Atrial fibrillation
B)Atrioventricular nodal reentrant tachycardia
C)Intermittent second-degree atrioventricular block
D)Sinus node dysfunction
E)Ventricular tachycardia
A)Atrial fibrillation
B)Atrioventricular nodal reentrant tachycardia
C)Intermittent second-degree atrioventricular block
D)Sinus node dysfunction
E)Ventricular tachycardia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 1702 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A study is undertaken to evaluate a new serological screening test for the diagnosis of tuberculosis infection. In the study, 1000 people were randomly selected from the population and given the new diagnostic test, and positive and negative results were recorded. Each study participant also was given the gold standard diagnostic procedure to determine the true infection state of the individual. The findings are as follows: 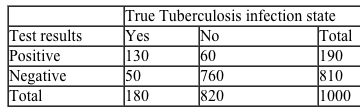 Which of the following is the positive predictive value of the screening test under study?
Which of the following is the positive predictive value of the screening test under study?
A)130/180
B)130/190
C)50/810
D)760/810
E)60/190
 Which of the following is the positive predictive value of the screening test under study?
Which of the following is the positive predictive value of the screening test under study?A)130/180
B)130/190
C)50/810
D)760/810
E)60/190

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 1702 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A 29-year-old man comes to clinic 2 weeks after an emergency department visit for epistaxis requiring anterior nasal packing. In the emergency department, his blood pressure was 170/110 mm Hg. He has occasional headaches and fatigue but no chest pain, palpitations, or syncope. His past medical history is unremarkable and he does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs. The patient's current blood pressure is 180/112 mm Hg and pulse is 78/min and regular. Cardiac auscultation in the supine position reveals no murmurs or additional sounds. Abdominal examination shows no periumbilical bruits. ECG shows normal sinus rhythm, high-voltage QRS complexes, downsloping ST-segment depression, and T wave inversion in leads V5 and V6. Laboratory results are as follows:  Which of the following is the best next step in evaluation of this patient?
Which of the following is the best next step in evaluation of this patient?
A)Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring
B)Bilateral arm and leg blood pressure measurements
C)Cardiac auscultation in squatting and standing positions
D)Carotid sinus massage
E)Exercise stress testing
 Which of the following is the best next step in evaluation of this patient?
Which of the following is the best next step in evaluation of this patient?A)Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring
B)Bilateral arm and leg blood pressure measurements
C)Cardiac auscultation in squatting and standing positions
D)Carotid sinus massage
E)Exercise stress testing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 1702 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Two cross-sectional studies were conducted using different questionnaires to determine the prevalence of over-the-counter analgesics use in a population. The first study showed a prevalence of 7.5% (95% confidence interval 6.0 - 9.0), and the second study demonstrated a prevalence of 7.3% (95% confidence interval 6.9 - 7.6). If the true prevalence of over-the-counter analgesics use in the population is 7.4%, which of the following statements about the results of the study is the most accurate?
A)The first study results are more specific
B)The second study results are more sensitive
C)The first study results are more valid
D)The first study results are more accurate
E)The second study results are more precise
A)The first study results are more specific
B)The second study results are more sensitive
C)The first study results are more valid
D)The first study results are more accurate
E)The second study results are more precise

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 1702 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A 33-year-old man comes to the physician reporting mild exertional shortness of breath and a "pounding" heart over the last 5 months. He is uncomfortably aware of his heartbeat while lying on his left side. Vital signs include blood pressure of 150/45 mm Hg and pulse of 73/min. Which of the following is most likely responsible for his symptoms?
A)Aortic regurgitation
B)Aortic stenosis
C)Mitral stenosis
D)Pulmonic regurgitation
E)Tricuspid stenosis
A)Aortic regurgitation
B)Aortic stenosis
C)Mitral stenosis
D)Pulmonic regurgitation
E)Tricuspid stenosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 1702 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A cohort study was conducted to assess the relationship between high saturated fat consumption and the occurrence of colorectal carcinoma among women. A group of women aged 40-65 was selected. The baseline saturated fat consumption was calculated using a food questionnaire, and the cohort was followed for seven years for the development of colon cancer. The study showed that women with high baseline saturated fat consumption have four times the risk of colorectal cancer in a 7-year period, compared to women with low fat consumption (RR = 4.0, 95% CI = 1.5 - 6.5). According to the study results, what percent of colorectal carcinoma in women with high fat consumption could be attributed to their diet?
A)25%
B)50%
C)75%
D)90%
E)100%
A)25%
B)50%
C)75%
D)90%
E)100%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 1702 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A new screening test was devised to detect pancreatic cancer at early stages using a serum marker (CA19-9) of the disease. A study of this new test showed that its use prolongs the survival of patients with pancreatic cancer by several months. The researchers concluded that use of the test improves the prognosis of patients with pancreatic cancer. Which of the following is a potential problem with this conclusion?
A)Observer's bias
B)Measurement bias
C)Lead-time bias
D)Confounding
E)Ascertainment bias
A)Observer's bias
B)Measurement bias
C)Lead-time bias
D)Confounding
E)Ascertainment bias

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 1702 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A 59-year-old woman comes to the office for a routine visit. She reports no symptoms. She has no medical problems and takes no medications. She grew up in the United States and has not traveled outside the country. The patient does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs. Her blood pressure is 120/70 mm Hg, pulse is 88/min, and respirations are 14/min. Physical examination shows a firm, nontender mass in the right upper quadrant. The remainder of the examination is within normal limits. Laboratory testing is unremarkable. Abdominal CT scan is shown in the image below. 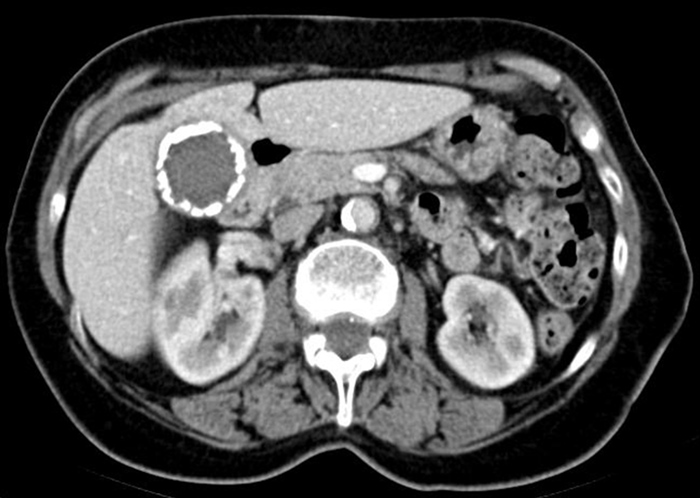 This patient is at greatest risk for which of the following conditions?
This patient is at greatest risk for which of the following conditions?
A)Anaphylactic shock
B)Gallbladder adenocarcinoma
C)Hepatic abscess
D)Intestinal perforation
E)Liver cirrhosis
F)Renal cell carcinoma
 This patient is at greatest risk for which of the following conditions?
This patient is at greatest risk for which of the following conditions?A)Anaphylactic shock
B)Gallbladder adenocarcinoma
C)Hepatic abscess
D)Intestinal perforation
E)Liver cirrhosis
F)Renal cell carcinoma

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 1702 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A study was conducted to assess the relationship between race and end-stage renal disease. Two groups of pathologists independently studied specimens from 1,000 kidney biopsies. The first group of pathologists was aware of the race of the patient from whom the biopsy came, while the second group was blinded from the patient's race. The first group reported "hypertensive nephropathy" much more frequently for Black patients than the second group. This study best demonstrates which of the following types of bias?
A)Confounding
B)Respondent bias
C)Recall bias
D)Selection bias
E)Observer bias
A)Confounding
B)Respondent bias
C)Recall bias
D)Selection bias
E)Observer bias

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 1702 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A 52-year-old woman comes to the clinic for follow-up of type 2 diabetes mellitus that was diagnosed 6 months ago after she was hospitalized for cellulitis of the right lower leg. The patient's diabetes is managed with insulin in addition to diet and exercise. Her only other medical condition is hypertension, for which she takes antihypertensive medication. The patient's mother had systemic lupus erythematosus and died at age 60. Serum creatinine is 1.7 mg/dL. Urine albumin/creatinine ratio is elevated at 190 mg/g and was also elevated 3 months ago. Which of the following additional findings would most strongly support a diagnosis of diabetic nephropathy in this patient?
A)Discrepancy in right and left kidney size
B)Left ventricular hypertrophy
C)Microscopic hematuria
D)Rapidly progressive renal dysfunction
E)Retinal neovascularization
A)Discrepancy in right and left kidney size
B)Left ventricular hypertrophy
C)Microscopic hematuria
D)Rapidly progressive renal dysfunction
E)Retinal neovascularization

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 1702 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A 27-year-old primigravida at 8 weeks gestation is found to have a thyroid nodule during her initial prenatal visit. She has fatigue and frequent nausea with vomiting. The patient has no heat or cold intolerance and no skin changes. She has no dysphagia to solids or liquids, although she has been eating more carbohydrates since becoming pregnant. Medical history is otherwise not significant. The patient does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs. Temperature is 36.7 C (98.1 F), blood pressure is 110/70 mm Hg, pulse is 86/min, and respirations are 18/min. Physical examination shows a small, 1.5-cm nodule in her right thyroid gland. Pelvic examination reveals a slightly enlarged uterus consistent with 8 weeks gestation. Serum TSH is normal. Ultrasound of her thyroid reveals a 1.5-cm hypoechoic nodule in her right thyroid lobe with irregular margins, internal microcalcifications, and internal vascularity. Which of the following is the next most appropriate step in management of this patient?
A)Fine-needle aspiration biopsy
B)MRI of the neck
C)Radionuclide scan
D)Reassurance and follow-up after delivery
E)Serum thyroglobulin
F)Total thyroidectomy in the second trimester
A)Fine-needle aspiration biopsy
B)MRI of the neck
C)Radionuclide scan
D)Reassurance and follow-up after delivery
E)Serum thyroglobulin
F)Total thyroidectomy in the second trimester

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 1702 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A 65-year-old woman comes to the office due to a 2-month history of shortness of breath and lower extremity edema. The patient reports no chest pain, palpitations, or syncope. She takes chlorthalidone and lisinopril for chronic hypertension. The patient has a sedentary lifestyle. She drinks 1-2 glasses of wine with dinner most days of the week. Blood pressure is 145/94 mm Hg and pulse is 80/min. BMI is 40 kg/m2. Estimated jugular venous pressure is 9 cm H2O. Cardiac examination reveals a regular rate and rhythm with no murmurs. Crackles are heard bilaterally in the lung bases. Bilateral pitting pedal edema is present. Chest x-ray shows a normal cardiac silhouette with pulmonary vascular congestion. Echocardiogram demonstrates left atrial enlargement, mild concentric left ventricular (LV) hypertrophy, mild mitral regurgitation, and no pericardial effusion. LV ejection fraction is 65% and there are no wall motion abnormalities. Serum creatinine is 0.8 mg/dL. Serum lipid studies show a total cholesterol of 208 mg/dL, HDL cholesterol of 35 mg/dL, and LDL cholesterol of 136 mg/dL. Which of the following is the strongest predisposing factor to this patient's current condition?
A)Alcohol use
B)Hereditary mutation in sarcomere gene
C)Hypercholesterolemia
D)Obesity and sedentary lifestyle
E)Valvular heart disease
F)Viral infection
A)Alcohol use
B)Hereditary mutation in sarcomere gene
C)Hypercholesterolemia
D)Obesity and sedentary lifestyle
E)Valvular heart disease
F)Viral infection

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 1702 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A 50-year-old woman comes to the office due to lower extremity edema. The edema started about 6 weeks ago and has slowly progressed . Medical history is significant for hypertension, treated with metoprolol for 3 years. Two months ago, amlodipine was added because of inadequate blood pressure control with metoprolol alone. The patient does not use tobacco or alcohol. She has no known drug allergies. Blood pressure is 130/80 mm Hg and pulse is 64/min. Physical examination reveals bilateral symmetric 3+ pitting edema of both lower extremities, without any skin changes or varicosities. Her neck vein pulsation is normal. The rest of the examination is unremarkable. Laboratory results are as follows:  Urinalysis is within normal limits. What is the most likely cause of the edema in this patient?
Urinalysis is within normal limits. What is the most likely cause of the edema in this patient?
A)Heart failure
B)Liver disease
C)Renal disease
D)Venous insufficiency
E)Medication side effect
 Urinalysis is within normal limits. What is the most likely cause of the edema in this patient?
Urinalysis is within normal limits. What is the most likely cause of the edema in this patient?A)Heart failure
B)Liver disease
C)Renal disease
D)Venous insufficiency
E)Medication side effect

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 1702 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A 55-year-old man comes to the office due to left-sided facial numbness. His symptoms began a month ago with tingling over his left mid-face and have progressively worsened to complete numbness on that side. The patient has also had 2 months of headaches, nasal congestion with intermittent epistaxis, and left ear fullness. He has had no fever, rhinorrhea, or purulent nasal discharge. The patient has taken over-the-counter allergy medications, but these have provided no relief. He has no other medical problems and does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs. He recently immigrated to the United States from southern China to be closer to his son. Temperature is 37 C (98.6 F), blood pressure is 126/80 mm Hg, and pulse is 84/min. Examination reveals sensory loss to touch and pain on the left side of the face. No facial muscle weakness or other neurological findings are present. Enlarged, nontender, and mobile cervical lymph nodes are palpable bilaterally. No oropharyngeal or nasal lesions are visualized. Otoscopy of the left ear demonstrates clear fluid behind the retracted tympanic membrane, but the right ear is normal. Nasopharyngoscopy reveals a soft-tissue mass in the nasopharynx. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A)Granulomatosis with polyangiitis
B)Mucormycosis
C)Nasal polyposis
D)Nasopharyngeal carcinoma
E)Tertiary syphilis
A)Granulomatosis with polyangiitis
B)Mucormycosis
C)Nasal polyposis
D)Nasopharyngeal carcinoma
E)Tertiary syphilis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 1702 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A 43-year-old woman complains of fatigue and shortness of breath over the last 2 weeks. She has no chest pain, nausea, vomiting, or weight loss. She reports a recent upper respiratory tract infection. The patient does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs. Her blood pressure is 98/55 mm Hg and pulse is 105/min. Jugular veins are distended with the patient in the seated position. Lungs are clear to auscultation. Chest x-ray is shown below. 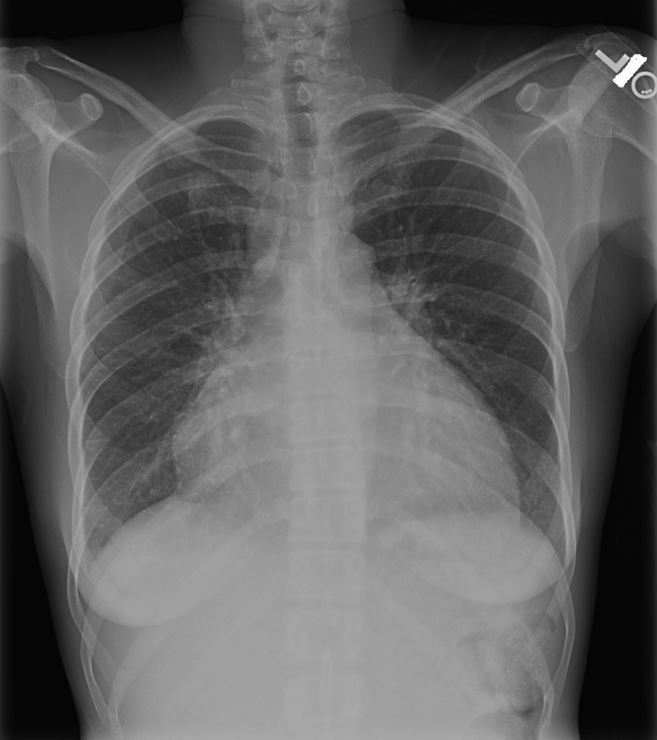 Which of the following is the most likely additional finding in this patient?
Which of the following is the most likely additional finding in this patient?
A)Audible fourth heart sound
B)Fixed splitting of the second heart sound
C)Intermittent ptosis
D)Nonpalpable point of maximal impulse
E)Opening snap
F)Pulsus bisferiens
 Which of the following is the most likely additional finding in this patient?
Which of the following is the most likely additional finding in this patient?A)Audible fourth heart sound
B)Fixed splitting of the second heart sound
C)Intermittent ptosis
D)Nonpalpable point of maximal impulse
E)Opening snap
F)Pulsus bisferiens

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 1702 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A 38-year-old woman comes to the office with a 3-week history of weight loss, nausea, abdominal pain, and postural dizziness. She traveled to Thailand 6 months ago and has felt fatigued since then. Medical history is notable for moderate persistent asthma treated with an inhaled beta-2 agonist and inhaled corticosteroid. Over the last 2 years, the patient has had several asthma exacerbations requiring oral prednisone. She also has hypothyroidism treated with levothyroxine. The patient is married and is a stay-at-home mother. Blood pressure is 90/60 mm Hg and pulse is 96/min. Pharyngeal examination shows bilateral tonsillar enlargement. Skin examination shows increased pigmentation at the palmar creases and mucous membranes as well as a few patches of vitiligo. Initial laboratory testing shows mild hyponatremia and hyperkalemia with normal renal function. Complete blood count is normal, but differential shows moderate eosinophilia. Follow-up testing confirms a low 8 AM serum cortisol. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's adrenal insufficiency?
A)Adrenal hemorrhage
B)Adrenal tumor
C)Autoimmune adrenalitis
D)Exogenous glucocorticoid use
E)HIV infection
F)Tuberculosis
A)Adrenal hemorrhage
B)Adrenal tumor
C)Autoimmune adrenalitis
D)Exogenous glucocorticoid use
E)HIV infection
F)Tuberculosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 1702 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A 75-year-old man comes to the clinic due to a 6-month history of periodic substernal chest pressure, which he experiences when walking uphill or climbing 2 flights of stairs. His medical history is significant for hyperlipidemia, for which he takes atorvastatin. The patient smokes a pack of cigarettes daily and occasionally consumes alcohol. Blood pressure is 120/78 mm Hg and pulse is 75/min. Physical examination shows no abnormalities. Resting ECG is normal. A treadmill stress test shows a horizontal ST-segment depression in leads V1-V4 at 73% of predicted maximal heart rate. Echocardiography demonstrates normal resting left ventricular systolic function. The patient prefers medical management. He is prescribed sublingual nitroglycerin to take as needed when anginal pain occurs and he is also prescribed a daily medication to help prevent anginal episodes. The daily medication most likely functions through which of the following mechanisms?
A)Altered myocardial calcium level
B)Coronary artery vasodilation
C)Decreased cardiac afterload
D)Decreased cardiac preload
E)Decreased myocardial contractility
A)Altered myocardial calcium level
B)Coronary artery vasodilation
C)Decreased cardiac afterload
D)Decreased cardiac preload
E)Decreased myocardial contractility

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 1702 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A 23-year-old man comes to the clinic for a physical examination prior to joining a professional soccer team. The patient goes on a 10-mile run 3 or 4 times per week, during which he experiences no chest pain, lightheadedness, or shortness of breath. Medical history is unremarkable. He does not smoke or drink alcohol. The patient lives in Texas and has not traveled recently. Family history includes myocardial infarction in his father at age 56. Blood pressure is 114/62 mm Hg and pulse is 54/min. Cardiac examination reveals normal heart sounds with no murmurs. The lungs are clear to auscultation. ECG shows sinus bradycardia with occasional dropped QRS complexes preceded by progressive lengthening of the PR interval. No ST-segment abnormalities are present, and the QTc interval is normal. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in the management of this patient?
A)Exercise stress testing
B)Lyme serology
C)Pacemaker placement
D)Reassurance with no further intervention
E)Transthoracic echocardiography
A)Exercise stress testing
B)Lyme serology
C)Pacemaker placement
D)Reassurance with no further intervention
E)Transthoracic echocardiography

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 1702 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A 55-year-old woman comes to the office due to persistent shortness of breath. Over the last year, she has had difficulty climbing the stairs to her bedroom and performing household chores. The patient also feels fatigued at the end of the day. She has no chest pain, cough, syncope, or lower extremity swelling. Medical history is significant for carpal tunnel syndrome and hypothyroidism, for which she takes levothyroxine. The patient is a lifetime nonsmoker. She has no family history of early coronary artery disease. Blood pressure is 133/75 mm Hg and pulse is 85/min and regular. Lungs are clear on auscultation. The apical impulse is displaced to the left, and there is a palpable systolic thrill. A 4/6 blowing and high-pitched holosystolic murmur is heard at the apex. Which of the following additional physical findings would most likely be present in this patient?
A)Clubbed fingers
B)Opening snap
C)S3
D)S4
E)Uvular pulsation
F)Wide and fixed splitting of S2
A)Clubbed fingers
B)Opening snap
C)S3
D)S4
E)Uvular pulsation
F)Wide and fixed splitting of S2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 1702 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A 60-year-old man comes to the office for evaluation of a 6-month history of intermittent chest pain. He describes substernal tightness and pain that occur when he walks quickly or climbs stairs. The symptoms last about 10 minutes and slowly fade away with rest. These episodes do not happen at rest. The patient has a known history of coronary artery disease with coronary artery bypass grafting surgery 7 years ago. Other medical problems include hypertension and hyperlipidemia. Blood pressure is 140/78 mm Hg and pulse is 78/min and regular. There are no murmurs on cardiac auscultation. Lungs are clear bilaterally. Treadmill stress test is performed. Seven minutes into the test, the patient develops chest pain and the treadmill is stopped. Sublingual nitroglycerin is administered, which almost immediately relieves the patient's pain. What is the predominant mechanism responsible for the rapid pain relief in this patient?
A)Coronary vasodilation
B)Decreased left ventricular contractility
C)Decreased left ventricular wall stress
D)Dilation of small arteries
E)Negative chronotropic effect
A)Coronary vasodilation
B)Decreased left ventricular contractility
C)Decreased left ventricular wall stress
D)Dilation of small arteries
E)Negative chronotropic effect

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 1702 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A 60-year-old woman comes to the office due to several months of lower extremity swelling. Medical history is significant for hypertension, type 2 diabetes mellitus, and hepatitis C infection. The patient was also diagnosed with latent tuberculosis 10 years ago, but she declined antibiotic therapy. Blood pressure is 120/80 mm Hg and pulse is 90/min. Physical examination shows symmetric pitting edema of the lower extremities. The liver is palpated 4 cm below the costal margin, and ascites is present. The tip of the spleen is palpated on deep inspiration. Hepatojugular reflux is present when sustained pressure is applied to the upper abdomen. The lungs are clear on auscultation. Which of the following findings is most suggestive of a cardiac cause for this patient's edema?
A)Ascites
B)Clear lungs
C)Hepatojugular reflux
D)Hepatomegaly
E)Lower extremity edema
F)Splenomegaly
A)Ascites
B)Clear lungs
C)Hepatojugular reflux
D)Hepatomegaly
E)Lower extremity edema
F)Splenomegaly

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 1702 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A 31-year-old woman comes to the office due to a 6.8-kg (15-lb) weight gain over the last few months. She has been unable to lose weight despite rigorous dieting and regular exercise. The patient also has experienced weakness and cannot lift weights that she was able to lift before the onset of her symptoms. Her menstrual periods have been irregular for the last few months, and she has had increasing anxiety and insomnia for which she has started seeing a clinical psychologist. Medical history is unremarkable. She drinks wine only on rare occasions and quit smoking 7 years ago after a 5-pack-year history. On examination, blood pressure is 160/100 mm Hg and pulse is 88/min and regular. Neurologic examination shows proximal muscle weakness. Dark terminal hair is present on the lower abdomen. Fasting laboratory results are as follows:  Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in evaluating this patient's condition?
Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in evaluating this patient's condition?
A)Early-morning cortisol level
B)Overnight low-dose dexamethasone suppression test
C)Serum ACTH level
D)Serum aldosterone to plasma renin activity ratio
E)Serum testosterone level
 Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in evaluating this patient's condition?
Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in evaluating this patient's condition?A)Early-morning cortisol level
B)Overnight low-dose dexamethasone suppression test
C)Serum ACTH level
D)Serum aldosterone to plasma renin activity ratio
E)Serum testosterone level

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 1702 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A 54-year-old man comes to the physician because of edema of his right ankle. He reports heaviness and cramping in the same leg that is worse after a long day at work. The swelling is usually reduced significantly when he wakes up in the morning and worsens progressively throughout the day. He denies any other symptoms. He has no significant medical problems except hypertension, for which he takes atenolol. His temperature is 36.7° C (98° F), blood pressure is 120/76 mm Hg, pulse is 80/min and respirations are 16/min. JVP is normal. Lungs are clear to auscultation. There are no murmurs. There is no hepatosplenomegaly. Examination shows edema of the right ankle. Doppler examination of the leg shows no evidence of thrombosis. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his edema?
A)Lymphatic obstruction
B)Impaired cardiac contraction
C)Reduced diastolic filling of the heart
D)Increased urinary loss of protein
E)Venous valve incompetence
F)Decreased liver protein synthesis
G)Arterial occlusion
A)Lymphatic obstruction
B)Impaired cardiac contraction
C)Reduced diastolic filling of the heart
D)Increased urinary loss of protein
E)Venous valve incompetence
F)Decreased liver protein synthesis
G)Arterial occlusion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 1702 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
A 54-year-old homeless man comes to the emergency department 24 hours after the onset of substernal chest pain and is diagnosed with an anterior wall myocardial infarction. The patient has no history of hypertension or diabetes mellitus and has had no previous chest pain, dyspnea, palpitations, syncope, or leg swelling. He has a 40-pack-year smoking history. Echocardiography shows normal left ventricular size and left ventricular anterior wall hypokinesis, as well as an ejection fraction of 40%. The patient refuses pharmacologic therapy on discharge and is scheduled for an outpatient clinic visit but never shows up. Two years later, the patient is found dead in the street. Autopsy reveals a dilated left ventricle with a globular shape and thinned walls with a scar on the anterior wall. Which of the following would most likely have helped prevent this patient's pathologic findings?
A)Amlodipine
B)Apixaban
C)Aspirin
D)Enalapril
E)Isosorbide dinitrate
F)Prasugrel
A)Amlodipine
B)Apixaban
C)Aspirin
D)Enalapril
E)Isosorbide dinitrate
F)Prasugrel

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 1702 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A 35-year-old woman is seen in the outpatient clinic due to palpitations. Over the past 6 months, she has noticed decreased exercise tolerance and episodes of her heart "racing in my chest." Temperature is 37.2 C (98.9 F) and blood pressure is 125/75 mm Hg. On examination, there is an early diastolic sound followed by a middiastolic murmur. The rest of the examination is unremarkable. ECG is shown in the exhibit.
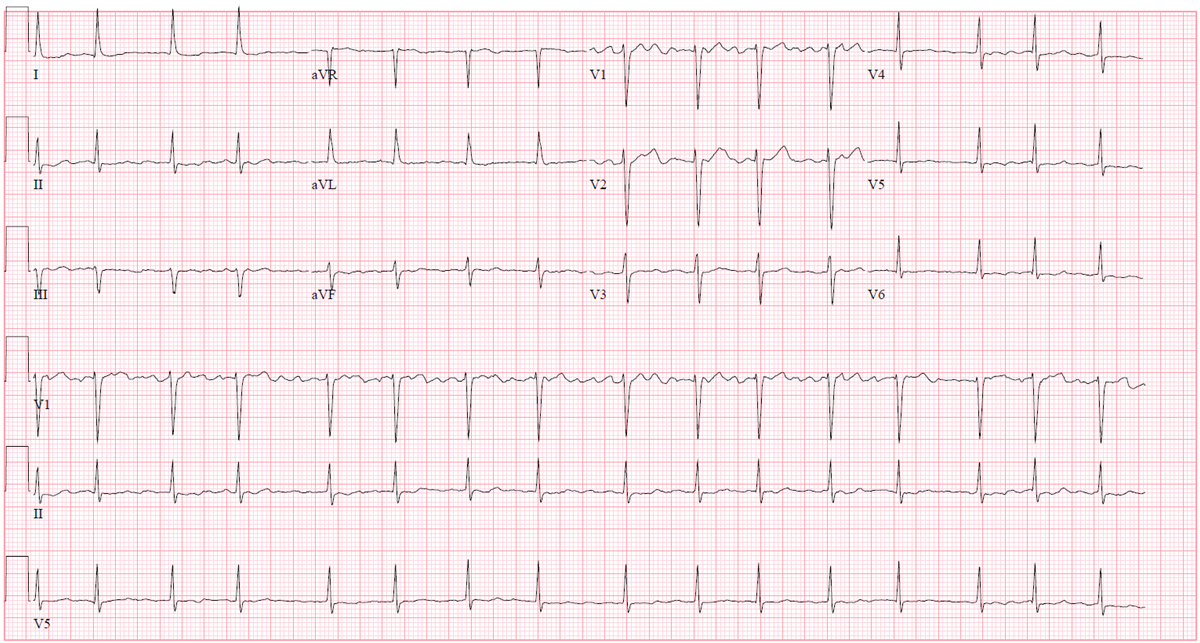
Which of the following is the most likely finding on echocardiography?
A)Atrial septal defect
B)Left atrial dilation
C)Left atrial mass attached to interatrial septum
D)Left ventricular dilation
E)Left ventricular hypertrophy

Which of the following is the most likely finding on echocardiography?
A)Atrial septal defect
B)Left atrial dilation
C)Left atrial mass attached to interatrial septum
D)Left ventricular dilation
E)Left ventricular hypertrophy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 1702 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A 56-year-old woman comes to the office due to left lower extremity pain and swelling. One year ago, the patient had a provoked left femoropopliteal deep venous thrombosis and completed 6 months of antithrombotic therapy. Over the past 3 months, she has had slowly worsening intermittent pain, fatigue, and swelling of the left leg, especially toward the end of the day. Medical history is significant for obesity and tobacco use. Temperature is 36.6 C (97.9 F), blood pressure is 122/74 mm Hg, pulse is 83/min, and respirations are 14/min. Oxygen saturation is 98% on room air. Mild pitting edema is noted on left lower extremity examination. There are scattered dilated superficial veins, but no skin erythema or calf tenderness is present. The right lower extremity has no abnormalities. Lower extremity venous ultrasonography is negative for thrombus. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management of this patient?
A)Arterial Doppler ultrasonography
B)Exercise and compression therapy
C)Inferior vena cava filter placement
D)Long-term antithrombotic therapy
E)Salt restriction and diuretics
F)Smoking cessation and cilostazol
A)Arterial Doppler ultrasonography
B)Exercise and compression therapy
C)Inferior vena cava filter placement
D)Long-term antithrombotic therapy
E)Salt restriction and diuretics
F)Smoking cessation and cilostazol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 1702 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A 28-year-old man comes to the office for evaluation of white lesions over the tongue that he recently noticed while brushing his teeth. The lesions are not painful or itchy. Review of systems is negative for dysphagia and positive for both fatigue and unintentional weight loss over the past 4 months. The patient smokes a pack of cigarettes daily and does not drink alcohol. Vital signs are within normal limits. BMI is 22 kg/m2. Examination shows bilateral corrugated, adherent plaques located on the lateral tongue surfaces; the lesions cannot be scraped off. Dentition is normal without any caries or decayed tooth. There are multiple enlarged cervical lymph nodes bilaterally that are mobile and nontender. What is the most appropriate next step in management?
A)Obtain HIV testing
B)Obtain lymph node biopsy
C)Perform laryngoscopy
D)Prescribe oral nystatin swish and swallow
E)Recommend tobacco cessation and reevaluate in 3 months
A)Obtain HIV testing
B)Obtain lymph node biopsy
C)Perform laryngoscopy
D)Prescribe oral nystatin swish and swallow
E)Recommend tobacco cessation and reevaluate in 3 months

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 1702 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A 28-year-old woman comes to the office due to persistent nasal congestion and stuffiness. The patient has a constant sensation of dripping in the back of her throat and states that food has tasted bland to her recently. A year ago, she came to the emergency department due to severe wheezing after taking naproxen for menstrual cramping. The patient has no history of head trauma. Family history is significant for asthma in her sister. She does not smoke cigarettes but occasionally smokes marijuana. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's current symptoms?
A)Allergic rhinitis
B)Fungal rhinosinusitis
C)Nasal polyposis
D)Nasopharyngeal angiofibroma
E)Perforated nasal septum
F)Pyogenic granuloma
A)Allergic rhinitis
B)Fungal rhinosinusitis
C)Nasal polyposis
D)Nasopharyngeal angiofibroma
E)Perforated nasal septum
F)Pyogenic granuloma

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 1702 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A 38-year-old woman comes to the physician complaining of occasional palpitations. She describes a fast and irregular heartbeat. She has had 3 such episodes over the past 2 months, each lasting about 2 hours. The patient has no associated chest pain, shortness of breath, cough, or ankle swelling. She drinks alcohol on social occasions and does not smoke. She has no other medical problems and takes no medications. Her temperature is 37.1°C (98.9°F), blood pressure is 130/70 mm Hg, pulse is 80/min, and respirations are 14/min. The apical impulse is displaced to the left, and a third heart sound is heard at the apex in the left decubitus position. There is also a holosystolic murmur that is loudest at the apex and radiates to the axilla. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's condition?
A)Bacterial infection of the mitral valve
B)Mitral annular calcification
C)Myocardial ischemia
D)Myxomatous degeneration of the mitral valve
E)Rheumatic mitral valve disease
A)Bacterial infection of the mitral valve
B)Mitral annular calcification
C)Myocardial ischemia
D)Myxomatous degeneration of the mitral valve
E)Rheumatic mitral valve disease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 1702 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A 31-year-old woman, gravida 3 aborta 3, comes to the office for an annual examination and discussion of contraceptive options. Seven months ago, she experienced her third spontaneous miscarriage and underwent a recurrent miscarriage workup. Results were consistent with antiphospholipid antibody syndrome, and the patient was informed that she is at increased risk for another miscarriage. Due to these risks, the patient and her husband have elected to adopt. She takes no medications and does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs. Her blood pressure is 115/60 mm Hg and pulse is 88/min. BMI is 22 kg/m2. Physical examination is normal. Which of the following is the best contraceptive option for this patient?
A)Combined hormonal patch
B)Combined oral contraceptive pills
C)Condom with spermicide
D)Copper intrauterine device
E)Medroxyprogesterone injection
A)Combined hormonal patch
B)Combined oral contraceptive pills
C)Condom with spermicide
D)Copper intrauterine device
E)Medroxyprogesterone injection

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 1702 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
A 31-year-old woman comes to the office with a 3-month history of palpitations and weight loss. She weighs 110 kg (243 lb); 3 months ago, she weighed 118 kg (260 lb). There is no associated dysphagia, neck pain, or hoarseness, and her menstrual periods have been regular. The patient was previously healthy and her family history is unremarkable. She does not use tobacco or alcohol. The patient is sexually active with one partner and uses a barrier method for contraception. Temperature is 36.7 C (98.1 F), blood pressure is 140/90 mm Hg, pulse is 102/min, and respirations are 20/min. The thyroid gland cannot be clearly felt on examination due to body habitus. Ocular examination is unremarkable. Laboratory tests show an elevated serum free triiodothyronine and thyroxine and low TSH. A urine pregnancy test is negative. Radioactive iodine scan reveals uptake of tracer only in the right thyroid lobe, as shown in the image below. 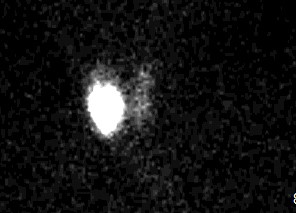 Which of the following processes is responsible for this patient's elevated thyroid hormone levels?
Which of the following processes is responsible for this patient's elevated thyroid hormone levels?
A)Antibody-stimulated thyroid hormone production
B)Autonomous thyroid hormone production
C)Exogenous thyroid hormone intake
D)Pituitary dysfunction
E)Release of preformed thyroid hormone
 Which of the following processes is responsible for this patient's elevated thyroid hormone levels?
Which of the following processes is responsible for this patient's elevated thyroid hormone levels?A)Antibody-stimulated thyroid hormone production
B)Autonomous thyroid hormone production
C)Exogenous thyroid hormone intake
D)Pituitary dysfunction
E)Release of preformed thyroid hormone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 1702 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
A 36-year-old man comes to the office after experiencing intermittent episodes of rectal bleeding over the past 2 months. Initially, he noted only small streaks of blood on the tissue when wiping, but yesterday he dripped bright red blood after defecating and the stool was coated with blood. He has had no anal or abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, anorexia, or weight loss. The patient has been having bowel movements every 2 or 3 days, which is unchanged from his previous routine. He has no other medical concerns and takes no medications. The patient's father was diagnosed with colon cancer at age 54. Blood pressure is 130/70 mm Hg, and pulse is 80/min with no orthostatic changes. Physical examination shows a soft and nontender abdomen with no masses or organomegaly. Inspection of the perianal skin shows no abnormalities. No mass or tenderness is palpable on digital rectal examination. Anoscopy reveals purplish mucosal bulges. Which of the following is the best next step in management of this patient?
A)Biopsy of the anal lesions
B)High-fiber diet and follow-up
C)Referral for colonoscopy
D)Referral for surgical evaluation
E)Topical nifedipine therapy
A)Biopsy of the anal lesions
B)High-fiber diet and follow-up
C)Referral for colonoscopy
D)Referral for surgical evaluation
E)Topical nifedipine therapy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 1702 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A 55-year-old man comes to the clinic for follow-up of hypertension. The patient was diagnosed with hypertension 3 months ago after an episode of transient vision loss in his right eye. He has occasional headaches and general fatigue but otherwise feels well. His current medications include aspirin, lisinopril, and low-dose hydrochlorothiazide. His blood pressure is 157/95 mm Hg and pulse is 69/min. BMI is 26 kg/m2. Cardiac examination shows a fourth heart sound on auscultation. There are no bruits in the carotids or abdomen. Pulses are 2+ in all extremities. Laboratory results are as follows: 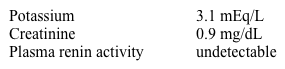 Which of the following best explains this patient's laboratory findings?
Which of the following best explains this patient's laboratory findings?
A)Lisinopril side effect
B)Malignant hypertension
C)Primary hyperaldosteronism
D)Thiazide side effect
E)Unilateral renal artery stenosis
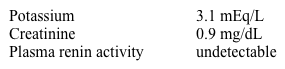 Which of the following best explains this patient's laboratory findings?
Which of the following best explains this patient's laboratory findings?A)Lisinopril side effect
B)Malignant hypertension
C)Primary hyperaldosteronism
D)Thiazide side effect
E)Unilateral renal artery stenosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 1702 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
A 36-year-old man comes to the office for a routine preventive visit. The patient feels well, but for the past 2 days he has occasionally noticed blood on the tissue paper after defecation. Otherwise, his bowel movements have remained normal in consistency and frequency. He has no melena, vomiting, abdominal pain, or unexpected weight changes. Medical history is unremarkable, and the patient has no family history of malignancy. Vital signs are normal. The abdomen is soft and nontender with normal bowel sounds and no hepatosplenomegaly or masses. Digital rectal examination is unremarkable except for traces of red blood visible on the glove. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
A)Anoscopy
B)Colonoscopy
C)CT colonography
D)Fecal DNA testing
E)Reassurance and periodic follow-up
A)Anoscopy
B)Colonoscopy
C)CT colonography
D)Fecal DNA testing
E)Reassurance and periodic follow-up

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 1702 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
A 17-year-old girl comes to the office for evaluation of irregular menses. The patient reports irregular menses since menarche at age 13, and her menstrual cycle has become increasingly unpredictable. Over the past year, she has had 5 menstrual periods. Her most recent period was 6 weeks ago and it lasted 10 days, with heavy bleeding and large clots. The patient has also gained 10 kg (22 lb) over the last year and has been unable to lose weight despite changes in her diet. She has no medical problems and has had no surgeries. She does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs. Blood pressure is 130/80 mm Hg and pulse is 76/min. BMI is 28 kg/m2. Physical examination shows coarse hair along the chin. There is no thyromegaly or palpable neck masses. The abdomen is soft and nontender, with no striae or palpable masses. Deep tendon reflexes of the extremities are normal, and no pedal edema is present. Hemoglobin is 10.2 g/dL. TSH and prolactin levels are normal. A urine pregnancy test is negative. Which of the following is the best next step for addressing this patient's irregular menses?
A)Order CT scan of the adrenal gland
B)Prescribe combined oral contraceptives
C)Prescribe letrozole
D)Prescribe leuprolide
E)Prescribe levothyroxine
F)Prescribe spironolactone
A)Order CT scan of the adrenal gland
B)Prescribe combined oral contraceptives
C)Prescribe letrozole
D)Prescribe leuprolide
E)Prescribe levothyroxine
F)Prescribe spironolactone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 1702 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A 46-year-old man comes to the office to discuss type 2 diabetes mellitus and obesity. The patient has poorly controlled diabetes despite multiple oral medications and previous attempts at dietary change. He reports that his endocrinologist has recommended insulin therapy, but he has declined because he wishes to avoid injected medications. The patient says, "I found a new diet on the Internet that I am thinking of trying. I know my weight is bad for me, but if I can get the weight off, maybe I won't have to go on insulin." Which of the following is the most appropriate response to this patient's statement?
A)"Don't worry about any specific diet. Just do whatever it takes to lose weight."
B)"If you can get your diabetes under control with insulin, that will make losing weight easier."
C)"Let's talk about the diet you found and discuss the pros and cons."
D)"Small steps are usually best for weight loss. Maybe try to lose 5 pounds in the first few weeks."
E)"You are right about your weight. Obesity makes it hard to control diabetes."
A)"Don't worry about any specific diet. Just do whatever it takes to lose weight."
B)"If you can get your diabetes under control with insulin, that will make losing weight easier."
C)"Let's talk about the diet you found and discuss the pros and cons."
D)"Small steps are usually best for weight loss. Maybe try to lose 5 pounds in the first few weeks."
E)"You are right about your weight. Obesity makes it hard to control diabetes."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 1702 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A 45-year-old man from Guatemala comes to the office due to persistent nausea and vomiting of partially digested food. He has had these symptoms for the past 1 month. He has also lost 2.3 kg (5 lb) during this period of time. His appetite is good, but he mentions early satiety. He has not had any hematemesis, black stools, difficulty swallowing, and chest pain. Other medical problems include type 2 diabetes for the past 1 year and a suicide attempt 3 months ago in which he ingested acid. He has a history of peptic ulcer disease and often takes antacids for heartburn. He drinks alcohol and smokes one pack of cigarettes daily. His temperature is 36.8 C (98.2 F), blood pressure is 110/65 mm Hg, pulse is 110/min, and respirations are 16/min. Mucous membranes are dry. Abdominal examination shows succussion splash on the epigastrium. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A)Achalasia
B)Chronic pancreatitis
C)Diabetic gastroparesis
D)Esophageal stricture
E)Portal hypertension
F)Pyloric stricture
A)Achalasia
B)Chronic pancreatitis
C)Diabetic gastroparesis
D)Esophageal stricture
E)Portal hypertension
F)Pyloric stricture

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 1702 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A 25-year-old woman comes to the office due to "chest pain" that began 2 days ago. The pain is described as a constant soreness across the chest, and the patient is unable to sleep prone because of the pain. She is an avid runner and kickboxer and has been unable to maintain her normal exercise routine due to discomfort wearing a sports bra. The patient is sexually active with her husband and recently stopped taking oral contraceptives because the couple are trying to have a child. Her last menstrual period was 3 weeks ago; menses are regular, occur approximately every 28 days, and last for 6 days. The patient takes a daily folic acid supplement and no other medications. Vitals signs are normal. Palpation demonstrates bilateral, nonfocal chest tenderness and diffusely nodular, dense breasts. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
A)Costochondritis
B)Cyclic mastalgia
C)Fat necrosis
D)Fibroadenoma
E)Fibrocystic changes
F)Phyllodes tumor
A)Costochondritis
B)Cyclic mastalgia
C)Fat necrosis
D)Fibroadenoma
E)Fibrocystic changes
F)Phyllodes tumor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 1702 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A 65-year-old woman comes to the office to follow up for osteoporosis, which was diagnosed by a screening bone mineral density scan. The patient was prescribed alendronate, but she stopped taking it due to intense stomach pain from the medication. She saw a television advertisement about raloxifene and is interested in this treatment option. The patient has a history of deep venous thrombosis in her left leg while on an oral contraceptive at age 38 that was treated with several months of heparin. She currently takes medications for hypertension and hyperlipidemia diagnosed after a minor heart attack at age 63. Her mother had breast cancer at age 52 and died from ovarian cancer at age 61. A maternal aunt died from endometrial cancer at age 72. Blood pressure is 125/80 mm Hg, and physical examination is normal. Which of the following is a contraindication to raloxifene in this patient?
A)History of breast cancer in her mother
B)History of endometrial cancer in her maternal aunt
C)History of myocardial infarction
D)History of ovarian cancer in her mother
E)History of venous thrombosis
A)History of breast cancer in her mother
B)History of endometrial cancer in her maternal aunt
C)History of myocardial infarction
D)History of ovarian cancer in her mother
E)History of venous thrombosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 1702 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A 34-year-old woman comes to the office due to diarrhea, weight loss, and fatigue over the past year. The diarrhea occurs 2 or 3 times daily and is accompanied by crampy abdominal pain. She has diarrhea occasionally at night but no tenesmus or blood in the stool. The patient describes her stools as very foul smelling and floating. Associated symptoms include diffuse bone pain. Physical examination is unremarkable. Laboratory results show hemoglobin of 9.8 g/dL with a mean corpuscular volume of 72 µm3. Which of the following serum laboratory findings would be expected in this patient?


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 1702 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A 38-year-old woman comes to the office due to jaundice. Her eyes have been yellow for the past 8 days, and she has also had pruritus, fever, nausea, and vomiting. The patient has had no unexpected weight loss or bloody stools. Medical history is significant for hypertension; current medications include amlodipine and an oral contraceptive. The patient works in a day care center, where some of the children were recently ill. She drinks alcohol but does not use illicit drugs and is in a monogamous relationship with her husband. Family history is unremarkable. Temperature is 38.7 C (101.7 F), blood pressure is 125/80 mm Hg, and pulse is 80/min. Scleral icterus is present. Oropharyngeal and cardiopulmonary examinations are unremarkable. The neck is supple without lymphadenopathy. The abdomen is nontender and nondistended. The liver edge is smooth and palpable below the right costal margin. Laboratory evaluation reveals the following:  Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A)Alcoholic hepatitis
B)Bacterial liver abscess
C)Budd-Chiari syndrome
D)Hepatitis A infection
E)Infectious mononucleosis
F)Primary biliary cholangitis
G)Ruptured hepatic adenoma
 Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?A)Alcoholic hepatitis
B)Bacterial liver abscess
C)Budd-Chiari syndrome
D)Hepatitis A infection
E)Infectious mononucleosis
F)Primary biliary cholangitis
G)Ruptured hepatic adenoma

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 1702 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
A 62-year-old man comes to the office for a follow-up visit. He recently had episodes of sweating, headache, tremor, and palpitation while working in his backyard; his wife has noticed that he seems confused during these episodes. Medical history is notable for long-standing type 2 diabetes mellitus treated with insulin glargine and glipizide, hypertension, peripheral vascular disease, and hyperlipidemia. The patient also has chronic kidney disease, and his renal function has declined significantly over the past 2 years despite optimal glycemic control. Which of the following is most likely responsible for this patient's symptoms?
A)Angina pectoris
B)Catecholamine-secreting tumor
C)Insulin excess
D)Orthostatic hypotension
E)Panic attacks
F)Thyroid hormone overproduction
G)Vasovagal reaction
A)Angina pectoris
B)Catecholamine-secreting tumor
C)Insulin excess
D)Orthostatic hypotension
E)Panic attacks
F)Thyroid hormone overproduction
G)Vasovagal reaction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 1702 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
A 45-year-old man comes to the office due to progressive shortness of breath on exertion and fatigue for the past several weeks. Two years ago, the patient was diagnosed with alcoholic cirrhosis and esophageal varices after presenting with hematemesis. He underwent banding of the varices. Several months ago, the patient came to the office with massive ascites and a large-volume paracentesis was performed. His current medications include furosemide, spironolactone, and nadolol. He has had no alcohol for the past 2 years. The patient does not use tobacco or illicit drugs. Blood pressure is 114/72 mm Hg and pulse is 63/min. Pulse oximetry shows 95% on room air. There is no change in dyspnea on lying down or moving into an upright position. His neck veins are flat. Heart sounds are normal with no murmur or gallop. Dullness and decreased breath sounds are present on the right. Left-sided breath sounds are normal with no added sounds. The abdomen is moderately distended with shifting dullness. Bowel sounds are normal. Stool guaiac is negative. He has 1+ bilateral lower extremity pitting edema. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's current symptoms?
A)Alcohol-induced cardiac dysfunction
B)Decreased diaphragmatic excursion
C)Fluid passage through diaphragmatic defects
D)Intrapulmonary vascular dilations
E)Medication adverse effects
F)Recurrent variceal bleeding
A)Alcohol-induced cardiac dysfunction
B)Decreased diaphragmatic excursion
C)Fluid passage through diaphragmatic defects
D)Intrapulmonary vascular dilations
E)Medication adverse effects
F)Recurrent variceal bleeding

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 1702 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A 19-year-old woman comes to the office due to severe acne. She had expected the acne to improve after high school, but instead, it is worsening. The patient has tried multiple remedies without significant improvement. She is concerned that the acne is scarring her face. Since the patient started college last year, she has gained 13.6 kg (30 lb). She sings in a local church choir and has not noticed any voice changes. The patient has no chronic medical conditions, has had no surgeries, and takes no medications. BMI is 29 kg/m2. Physical examination shows nodulocystic acne on the face, arms, back, and forehead. The scalp is normal, with no alopecia. Tanner stage is 5. There is no skin discoloration or striae. No masses are palpable on abdominal examination. A urine pregnancy test is negative. Which of the following additional information is required to establish the most likely diagnosis?
A)Family history of hypothyroidism
B)Food intake diary
C)History of an eating disorder
D)Intravenous drug use
E)Menstrual history
F)Number of lifetime sexual partners
A)Family history of hypothyroidism
B)Food intake diary
C)History of an eating disorder
D)Intravenous drug use
E)Menstrual history
F)Number of lifetime sexual partners

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 1702 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
A 66-year-old woman comes to the office due to 4 days of watery diarrhea and abdominal cramps. The patient has had 7-10 loose stools daily with no blood or mucus. She has a history of constipation requiring frequent laxative use but last took a laxative 6 days ago. The patient received oral antibiotics for acute sinusitis 3 weeks ago. She has a history of gastroesophageal reflux disease and type 2 diabetes mellitus. The patient takes omeprazole and metformin daily. She smokes a pack of cigarettes daily. Temperature is 38 C (100.4 F). The abdomen is soft with mild distension and mild diffuse tenderness. No guarding or rebound tenderness is present. Stool testing for Clostridioides difficile is positive. In addition to recent antibiotic use, which of the following most likely predisposed this patient to her current condition?
A)Chronic laxative use
B)Chronic metformin use
C)Cigarette smoking
D)Gastric acid suppression
E)Small bowel dysmotility
A)Chronic laxative use
B)Chronic metformin use
C)Cigarette smoking
D)Gastric acid suppression
E)Small bowel dysmotility

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 1702 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A 45-year-old woman comes to the clinic due to fatigue, weakness, and diffuse bone pain. She was diagnosed with celiac disease 5 years ago but continues to consume gluten-containing foods on occasion. The patient takes over-the-counter folic acid and iron supplements. Laboratory results are as follows:  Which of the following is directly responsible for this patient's bone pain?
Which of the following is directly responsible for this patient's bone pain?
A)Accelerated focal bone remodeling
B)Defective formation of collagen
C)Impaired osteoid matrix mineralization
D)Low bone mass with normal mineralization
E)Lytic lesions due to malignant cell infiltration
 Which of the following is directly responsible for this patient's bone pain?
Which of the following is directly responsible for this patient's bone pain?A)Accelerated focal bone remodeling
B)Defective formation of collagen
C)Impaired osteoid matrix mineralization
D)Low bone mass with normal mineralization
E)Lytic lesions due to malignant cell infiltration

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 1702 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
A 55-year-old Caucasian male presents to the office for a routine check-up. He has no present complaints. His past medical history is significant for a long history of hypertension. He does not smoke or consume alcohol. His current medications are enalapril and hydrochlorothiazide. His blood pressure is 140/90 mm Hg and heart rate is 80/min. Physical examination reveals a moderately overweight man (BMI = 27 kg/m2) with a waist circumference of 41 inches. The laboratory studies show:
 Which of the following is the most important pathogenic factor for this patient's condition?
Which of the following is the most important pathogenic factor for this patient's condition?
A)Impaired secretion of insulin
B)Low absolute values of insulin
C)Insulin resistance
D)Sympathetic hyperactivity
E)Insulin-mediated vasodilatation
 Which of the following is the most important pathogenic factor for this patient's condition?
Which of the following is the most important pathogenic factor for this patient's condition?A)Impaired secretion of insulin
B)Low absolute values of insulin
C)Insulin resistance
D)Sympathetic hyperactivity
E)Insulin-mediated vasodilatation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 1702 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
A 34-year-old man comes to the office due to lack of sexual desire and erectile dysfunction for 3 months. Medical history is significant for opioid use disorder, for which he has been taking methadone for 2 years. The patient has gained 4.5 kg (10 lb) over the past 6 months. Vital signs are normal. BMI is 24.5 kg/m2. On examination, the testes are small and soft. There is no gynecomastia. Visual field and thyroid examination findings are normal. Laboratory results are as follows:  Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's symptoms?
Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's symptoms?
A)Klinefelter syndrome
B)Medication adverse effect
C)Pituitary tumor
D)Rapid weight gain
 Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's symptoms?
Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's symptoms?A)Klinefelter syndrome
B)Medication adverse effect
C)Pituitary tumor
D)Rapid weight gain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 1702 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
A 45-year-old man comes to the office due to loss of sexual desire and failure to attain satisfactory erections during intercourse. He has no morning erections. The patient has no leg or buttock pain with exertion but has had intermittent bilateral hand pain. Medical history is significant for type 2 diabetes mellitus and recent-onset peripheral neuropathy. He does not use tobacco or alcohol. The patient has a 12-year-old child from a previous marriage and now lives with his second wife. Blood pressure is 120/70 mm Hg and pulse is 70/min. BMI is 24 kg/m2. The neck is supple with no thyromegaly or lymphadenopathy. Cardiopulmonary examination is normal. The abdomen is soft and nontender with palpable hepatomegaly. Genital examination shows small testes bilaterally but otherwise normal secondary sexual characteristics. Peripheral pulses are 2+, and capillary refill in the feet is normal. Neurologic examination demonstrates normal deep tendon reflexes and muscle strength; sensation is mildly decreased in both ankles. Visual field testing is normal. What is the best next step in management of this patient?
A)Karyotype analysis
B)Nocturnal polysomnography
C)Phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor therapy
D)Scrotal ultrasound
E)Serum ferritin level
F)Testosterone replacement therapy
A)Karyotype analysis
B)Nocturnal polysomnography
C)Phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor therapy
D)Scrotal ultrasound
E)Serum ferritin level
F)Testosterone replacement therapy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 1702 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
A 46-year-old woman comes to the clinic due to left lower extremity swelling for the past 2 years. She has had several episodes of cellulitis involving the left leg. During the most recent episode 6 months ago, she underwent treatment with intravenous antibiotics that was complicated by a catheter-related axillary vein thrombosis requiring 3 months of anticoagulation therapy. Her medical history is also significant for diet-controlled type 2 diabetes mellitus. BMI is 34 kg/m2. Physical examination shows firm edema of the left lower extremity. There is no erythema or warmth. The examiner cannot lift the skin from the dorsum of the toes on the left foot but is able to do so with the toes on the right foot. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's symptoms?
A)Albuminuria
B)Disruption of lymphatics
C)Increased central venous pressure
D)Systemic sclerosis
E)Venous valve incompetence
A)Albuminuria
B)Disruption of lymphatics
C)Increased central venous pressure
D)Systemic sclerosis
E)Venous valve incompetence

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 1702 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
A 57-year-old man comes to the office due to several months of persistent tingling in both legs. The patient also says he feels clumsy and often bumps into furniture. He has a history of hip osteoarthritis, but the pain is well controlled with acetaminophen and occasional ibuprofen and does not limit his mobility. The patient also has a history of gastroesophageal reflux disease and Barrett esophagus; he has used omeprazole for the past several years and has had no recent heartburn or dysphagia. He does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs. The patient consumes a balanced diet and walks 1 or 2 miles every other day. Vital signs are within normal limits. Lower extremity muscle strength is intact. Sensation to light touch and vibration are diminished in the feet bilaterally. The remainder of the physical examination shows no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in evaluation of this patient's symptoms?
A)Serologic testing for HIV
B)Serum protein electrophoresis
C)Serum vitamin B12 level test
D)Urine analysis for heavy metals
E)Viral hepatitis serology
A)Serologic testing for HIV
B)Serum protein electrophoresis
C)Serum vitamin B12 level test
D)Urine analysis for heavy metals
E)Viral hepatitis serology

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 1702 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
A 21-year-old man comes to the office due to recent irritability and aggressive behavior. He is a star college football linebacker and is training for his senior season. The patient does not use tobacco or alcohol. His mother has diabetes and his father has basal cell skin cancer. Blood pressure is 132/84 mm Hg and pulse is 62/min. The patient is muscular and well appearing. There is no lymphadenopathy in the cervical or supraclavicular chains. Cardiopulmonary examination is normal. Mild gynecomastia is present. The abdomen is soft and nontender. Liver span is 8 cm, and the spleen is not palpable. Laboratory results are as follows:  Which of the following is the best single explanation for this patient's presentation?
Which of the following is the best single explanation for this patient's presentation?
A)Anabolic steroid abuse
B)Autologous blood transfusion
C)Erythropoietin abuse
D)Intensive exercise schedule
E)Polycythemia vera
 Which of the following is the best single explanation for this patient's presentation?
Which of the following is the best single explanation for this patient's presentation?A)Anabolic steroid abuse
B)Autologous blood transfusion
C)Erythropoietin abuse
D)Intensive exercise schedule
E)Polycythemia vera

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 1702 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
A 62-year-old man comes to the office due to several months of fatigue. The patient has no chest pain, vomiting, diarrhea, weight loss, or back pain. Review of systems is significant for occasional leg cramps. He takes lisinopril for hypertension and atorvastatin for hyperlipidemia. The patient no longer smokes cigarettes but has a 30-pack-year history. He does not consume alcohol. Blood pressure is 132/80 mm Hg and pulse is 95/min. Conjunctiva are pale. Cardiopulmonary auscultation reveals clear lungs and a soft 2/6 ejection murmur at the right upper sternal border. The abdomen is soft and nontender without palpable masses. There are no skin rashes or peripheral edema. Laboratory results are as follows:  Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management of this patient?
Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management of this patient?
A)Bone marrow biopsy
B)Discontinuation of atorvastatin
C)Endoscopic evaluation
D)Serum C-reactive protein
E)Serum erythropoietin level
F)Serum free monoclonal light chains
 Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management of this patient?
Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management of this patient?A)Bone marrow biopsy
B)Discontinuation of atorvastatin
C)Endoscopic evaluation
D)Serum C-reactive protein
E)Serum erythropoietin level
F)Serum free monoclonal light chains

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 1702 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
A 65-year-old woman comes to the office due to a month of back pain. The pain is primarily in her lumbar and thoracic spine and is partially relieved with acetaminophen. It is worse with activity and has limited her ability to take restorative yoga classes. The patient has a history of hypertension, type 2 diabetes mellitus, and osteopenia. She takes over-the-counter calcium and vitamin D supplements in addition to prescription medications. The patient had her yearly physical examination 4 months ago; physical and laboratory examinations were normal at that time. Temperature is 36.6 C (97.8 F), blood pressure is 148/82 mm Hg, and pulse is 94/min. The patient is thin but appears well. Mucous membranes are moist. There is no lymphadenopathy in the cervical or supraclavicular chains. Cardiopulmonary and abdominal examinations are normal. There is no focal tenderness over the spine. Muscle strength is 5/5 in all 4 extremities. Laboratory results are as follows:  Urine dipstick is negative and urine sediment is bland except for a few granular casts. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's current condition?
Urine dipstick is negative and urine sediment is bland except for a few granular casts. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's current condition?
A)Acetaminophen toxicity
B)Diabetes mellitus
C)Monoclonal protein
D)Primary hyperparathyroidism
E)Systemic lupus erythematosus
F)Vitamin D toxicity
 Urine dipstick is negative and urine sediment is bland except for a few granular casts. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's current condition?
Urine dipstick is negative and urine sediment is bland except for a few granular casts. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's current condition?A)Acetaminophen toxicity
B)Diabetes mellitus
C)Monoclonal protein
D)Primary hyperparathyroidism
E)Systemic lupus erythematosus
F)Vitamin D toxicity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 1702 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
A 42-year-old man who recently emigrated from Northern Africa comes to the clinic due to a 1-month history of abdominal pain and watery diarrhea. He has also had a skin rash for the last 2 months that gets worse with sun exposure. In addition, the patient has felt depressed recently and has loss of appetite with mild weight loss. Medical history is notable for latent tuberculosis, for which he is currently taking isoniazid and pyridoxine. The patient takes no other medications and does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs. He is vegetarian, and his diet consists mostly of corn and other cereal grains. On examination, there is a pigmented scaly skin rash in the malar distribution of his face, on his neck, and on the back of his hands. He also has mild, diffuse abdominal tenderness. Neurologic examination, including distal sensation and gait, is normal. Liver function tests are normal. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A)Acute intermittent porphyria
B)Isoniazid hypersensitivity
C)Pellagra
D)Seborrheic dermatitis
E)Systemic lupus erythematosus
F)Ulcerative colitis
A)Acute intermittent porphyria
B)Isoniazid hypersensitivity
C)Pellagra
D)Seborrheic dermatitis
E)Systemic lupus erythematosus
F)Ulcerative colitis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 1702 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
A 62-year-old man comes to the office for evaluation of a lump in his neck. The patient first noticed the lump under the right side of his jaw about 4 months ago when he cut himself while shaving. The lump is slowly getting larger. He has also had occasional deep-seated right ear pain. The patient has had no fevers, chills, cough, or shortness of breath. He has had no change in his diet and no weight loss. Medical history is significant for hypertension and type 2 diabetes mellitus. The patient smokes 2 packs of cigarettes daily and uses alcohol occasionally. Physical examination shows a firm, nontender, right-sided submandibular mass that is 3 cm in diameter. Ear examination is normal. There are no abnormal skin lesions. Oral cavity examination shows poor dentition and no mucosal lesions. The tonsils are small and soft with no lesions. Chest examination is unremarkable. The abdomen is soft and nontender with no hepatosplenomegaly. There is no other lymphadenopathy. Complete blood count is within normal limits. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's condition?
A)Chronic lymphocytic leukemia
B)Granulomatous polyangiitis
C)Hodgkin lymphoma
D)Infectious mononucleosis
E)Medullary thyroid carcinoma
F)Mycobacterial lymphadenitis
G)Squamous cell carcinoma
A)Chronic lymphocytic leukemia
B)Granulomatous polyangiitis
C)Hodgkin lymphoma
D)Infectious mononucleosis
E)Medullary thyroid carcinoma
F)Mycobacterial lymphadenitis
G)Squamous cell carcinoma

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 1702 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
A 25-year-old African American woman comes to the office after experiencing increasingly heavy menstrual cycles for 3 months. The patient has also noticed that her gums frequently bleed when she brushes her teeth. Review of systems is positive for ongoing pain and stiffness in her hands and wrists that is partially responsive to ibuprofen. She is not taking any medications and has no known medical conditions. The patient is afebrile, blood pressure is 149/79 mm Hg, and pulse is 87/min. A nonpainful oral ulcer is present. Multiple petechiae are present on the upper arms and shins. The wrists and hands are tender to palpation and demonstrate reduced range of motion. Laboratory results are as follows:  Which of the following is the most likely cause of thrombocytopenia in this patient?
Which of the following is the most likely cause of thrombocytopenia in this patient?
A)Aberrant splenic sequestration
B)Bone marrow invasion by malignancy
C)Dilutional cytopenia
D)Ineffective hematopoiesis
E)Peripheral destruction
 Which of the following is the most likely cause of thrombocytopenia in this patient?
Which of the following is the most likely cause of thrombocytopenia in this patient?A)Aberrant splenic sequestration
B)Bone marrow invasion by malignancy
C)Dilutional cytopenia
D)Ineffective hematopoiesis
E)Peripheral destruction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 1702 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
A 62-year-old man comes to the office due to fatigue and weight loss. Over the last 6 months, he has lost 9 kg (20 lb) and can no longer walk long distances without sitting down to rest. The patient has not seen a physician in 15 years. He has smoked a pack of cigarettes daily for the last 35 years but does not use alcohol or illicit drugs. He has not recently traveled. Temperature is 36.9 C (98.4 F), blood pressure is 130/80 mm Hg, pulse is 88/min, and respirations are 12/min. Lungs are clear to auscultation, and abdominal examination shows a liver span of 14 cm with no tenderness. Rectal examination reveals normal sphincter tone but a slightly enlarged prostate that is nontender to palpation. Chest x-ray is unremarkable. CT scan of the abdomen with contrast is shown in the image below.  Which of the following is most likely to establish the diagnosis in this patient?
Which of the following is most likely to establish the diagnosis in this patient?
A)Alpha-fetoprotein measurement
B)Aspiration and culture of the liver lesions
C)Bone marrow biopsy
D)Colonoscopy
E)Prostate-specific antigen measurement
F)Stool test for ova and parasites
 Which of the following is most likely to establish the diagnosis in this patient?
Which of the following is most likely to establish the diagnosis in this patient?A)Alpha-fetoprotein measurement
B)Aspiration and culture of the liver lesions
C)Bone marrow biopsy
D)Colonoscopy
E)Prostate-specific antigen measurement
F)Stool test for ova and parasites

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 1702 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
A 32-year-old woman comes to the office due to intermittent abdominal pain and nonbloody diarrhea for the past 3-4 months. She describes the pain as crampy and located in the mid-abdomen and right lower quadrant. The patient thinks she has lost some weight during this period. She modified her diet several times in an attempt to decrease the symptoms, believing that heavy meals exacerbate the pain and diarrhea. The patient underwent appendectomy with abscess debridement one year ago. She has no other medical issues and takes no medication other than oral contraceptives. She has not traveled outside the United States and does not use tobacco, alcohol, or recreational drugs. Temperature is 36.7 C (98 F), blood pressure is 120/70 mm Hg, pulse is 85/min, and respirations are 14/min. A few shallow ulcers are present in her mouth. Abdominal examination shows mild tenderness in the right lower quadrant without rebound. Laboratory results are as follows:  Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis for this patient?
Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis for this patient?
A)Celiac disease
B)Crohn disease
C)Giardia infection
D)Irritable bowel syndrome
E)Lactose intolerance
F)Ulcerative colitis
G)Yersinia infection
 Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis for this patient?
Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis for this patient?A)Celiac disease
B)Crohn disease
C)Giardia infection
D)Irritable bowel syndrome
E)Lactose intolerance
F)Ulcerative colitis
G)Yersinia infection

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 1702 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
A 70-year-old man comes to the office due to 6 months of progressive fatigue and dyspnea. He has had no fever, night sweats, or weight loss. The patient's medical history is significant for benign prostatic hyperplasia, hypertension, and mechanical aortic valve replacement for severe aortic stenosis. The patient currently takes warfarin, tamsulosin, and amlodipine. He does not drink alcohol. Temperature is 36.4 C (97.5 F), blood pressure is 150/99 mm Hg, and pulse is 68/min. BMI is 27 kg/m2. The patient appears well nourished and fit. No scleral icterus is present, but the mucosa is pale. There is no jugular venous distension or lymphadenopathy. Cardiac examination reveals a normal S1 and a mechanical S2. Pulmonary examination is normal. Both the liver and the spleen are palpable. The remainder of the examination shows no abnormalities. Laboratory results are as follows:  Which of the following is the best next step in management?
Which of the following is the best next step in management?
A)ADAMTS-13 assay
B)Bone marrow biopsy
C)Colonoscopy
D)Echocardiogram
E)Liver biopsy
 Which of the following is the best next step in management?
Which of the following is the best next step in management?A)ADAMTS-13 assay
B)Bone marrow biopsy
C)Colonoscopy
D)Echocardiogram
E)Liver biopsy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 1702 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
A 52-year-old woman comes to the office due to intense itching and fatigue. She is unable to specify when her symptoms started as they developed gradually. Past medical history is significant for hypothyroidism and carpal tunnel syndrome. Current medications include levothyroxine. The patient lives with her husband and 3 children. She does not smoke and drinks wine on social occasions. Vital signs are normal. Cardiopulmonary examination shows no abnormalities. The abdomen is soft with normal bowel sounds. Hepatomegaly is present. There is no scleral icterus or jaundice, but bilateral xanthelasma and skin excoriations are evident. Laboratory results are as follows:  A right upper quadrant ultrasound shows a normal common bile duct. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management of this patient?
A right upper quadrant ultrasound shows a normal common bile duct. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management of this patient?
A)Check anti-mitochondrial antibodies
B)Check anti-smooth muscle antibodies
C)Discontinue levothyroxine
D)Obtain MRI scan of the abdomen
E)Prescribe oral glucocorticoids
 A right upper quadrant ultrasound shows a normal common bile duct. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management of this patient?
A right upper quadrant ultrasound shows a normal common bile duct. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management of this patient?A)Check anti-mitochondrial antibodies
B)Check anti-smooth muscle antibodies
C)Discontinue levothyroxine
D)Obtain MRI scan of the abdomen
E)Prescribe oral glucocorticoids

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 1702 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
A 67-year-old woman comes to the office due to progressive fatigue and anorexia over the last 6 months. She has lost 4 kg (8.8 lb), which she attributes to early satiety. She has had no abdominal pain, night sweats, or fevers. The patient's past medical history is significant for hypothyroidism, hypertension, and gout. She does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs and is compliant with her medications. Temperature is 37.3 C (99.2 F), blood pressure is 128/82 mm Hg, and pulse is 88/min. The patient is slightly thin but well nourished. Mild mucosal pallor is present. There is no lymphadenopathy in the cervical or supraclavicular chains. Cardiopulmonary examination is normal. A spleen tip is palpable with deep exhalation. Laboratory results are as follows: 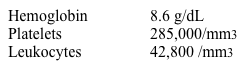 Florescence in situ hybridization reveals an abnormality in chromosome 22. Which of the following is the most important target in treating this patient's disease?
Florescence in situ hybridization reveals an abnormality in chromosome 22. Which of the following is the most important target in treating this patient's disease?
A)DNA methylation mutations
B)Folic acid metabolism
C)Retinoic acid receptor
D)Thymidine synthesis
E)Tyrosine kinase
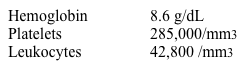 Florescence in situ hybridization reveals an abnormality in chromosome 22. Which of the following is the most important target in treating this patient's disease?
Florescence in situ hybridization reveals an abnormality in chromosome 22. Which of the following is the most important target in treating this patient's disease?A)DNA methylation mutations
B)Folic acid metabolism
C)Retinoic acid receptor
D)Thymidine synthesis
E)Tyrosine kinase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 1702 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
A 54-year-old woman comes to the office due to fatigue, anorexia, and weight loss. Over the past 3 months, she has lost 10 kg (22 lb) but has not changed her diet or activity level. The patient has a history of hypertension and type 2 diabetes mellitus. She does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs. Temperature is 36.9 C (98.4 F), blood pressure is 120/80 mm Hg, pulse is 80/min, and respirations are 16/min. BMI is 31 kg/m2. Mild temporal wasting is noted. The abdomen is soft, the flanks are full, and shifting dullness is present. There is hepatomegaly and a single palpable liver nodule. Trace edema is present in the bilateral lower extremities. Laboratory results are as follows:  Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A)Focal nodular hyperplasia
B)Hepatic adenoma
C)Hepatocellular carcinoma
D)Hydatid cyst
E)Pyogenic liver abscess
 Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?A)Focal nodular hyperplasia
B)Hepatic adenoma
C)Hepatocellular carcinoma
D)Hydatid cyst
E)Pyogenic liver abscess

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 1702 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
A 58-year-old man comes to the office due to yellowish discoloration of the skin, anorexia, and unintentional weight loss of 6 kg (13.2 lb) over the past 3 months. He also reports dark urine and pale stools. The patient has had no fever, abdominal pain, constipation, or diarrhea. He has a history of hypertension and hyperlipidemia. The patient does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs. Vital signs are within normal limits. BMI is 32 kg/m2. Scleral icterus is present. An enlarged, nontender gallbladder is palpated below the right costal margin. There is no ascites. Abdominal imaging in this patient is most likely to reveal which of the following findings?
A)Cystic lesion at the tail of the pancreas
B)Gallstone obstructing the cystic duct
C)Intra- and extra-hepatic biliary duct dilation
D)Multiloculated hypoechoic hepatic lesions
E)Peripancreatic fluid collection
F)Thrombus within the portal vein
A)Cystic lesion at the tail of the pancreas
B)Gallstone obstructing the cystic duct
C)Intra- and extra-hepatic biliary duct dilation
D)Multiloculated hypoechoic hepatic lesions
E)Peripancreatic fluid collection
F)Thrombus within the portal vein

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 1702 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
A 43-year-old woman comes to the office due to elevated aminotransferase levels, which were identified during routine blood work. She feels well and reports no symptoms. She has no known medical conditions, and her family history is unremarkable. She used heroin 10 years ago but completed rehabilitation and has not used it since. She does not use tobacco or alcohol. Temperature is 37.5 C (99.5 F), blood pressure is 120/80 mm Hg, and pulse is 87/min. BMI is 24.5 kg/m2. There is no scleral icterus or asterixis. Skin and cardiopulmonary examinations are unremarkable. The abdomen is soft and nontender; there is no ascites. Laboratory results are as follows:  Abdominal ultrasonography reveals a nodular, shrunken liver without evidence of ascites. Upper endoscopy is negative for esophageal or gastric varices. In addition to providing antiviral therapy to treat this patient's hepatitis C infection, which of the following would be recommended at this time?
Abdominal ultrasonography reveals a nodular, shrunken liver without evidence of ascites. Upper endoscopy is negative for esophageal or gastric varices. In addition to providing antiviral therapy to treat this patient's hepatitis C infection, which of the following would be recommended at this time?
A)Antiviral therapy for hepatitis B
B)Daily lactulose
C)Daily spironolactone
D)Hepatitis A vaccination
E)Hepatitis B vaccination
F)No additional intervention
 Abdominal ultrasonography reveals a nodular, shrunken liver without evidence of ascites. Upper endoscopy is negative for esophageal or gastric varices. In addition to providing antiviral therapy to treat this patient's hepatitis C infection, which of the following would be recommended at this time?
Abdominal ultrasonography reveals a nodular, shrunken liver without evidence of ascites. Upper endoscopy is negative for esophageal or gastric varices. In addition to providing antiviral therapy to treat this patient's hepatitis C infection, which of the following would be recommended at this time?A)Antiviral therapy for hepatitis B
B)Daily lactulose
C)Daily spironolactone
D)Hepatitis A vaccination
E)Hepatitis B vaccination
F)No additional intervention

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 1702 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
A 56-year-old man comes to the office due to fatigue. He has a 20-year history of diabetes mellitus treated with daily insulin therapy. The patient also has end-stage renal disease and receives hemodialysis 3 times a week. He has been receiving erythropoietin therapy for anemia (pretreatment hemoglobin: 8.0 g/dL). Physical examination shows pale conjunctiva. Laboratory results are as follows:  Which of the following is the most appropriate intervention to improve this patient's symptoms?
Which of the following is the most appropriate intervention to improve this patient's symptoms?
A)Blood transfusion
B)Change erythropoietin to darbepoetin
C)Folic acid supplementation
D)Iron supplementation
E)Tighter blood glucose control
 Which of the following is the most appropriate intervention to improve this patient's symptoms?
Which of the following is the most appropriate intervention to improve this patient's symptoms?A)Blood transfusion
B)Change erythropoietin to darbepoetin
C)Folic acid supplementation
D)Iron supplementation
E)Tighter blood glucose control

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 1702 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
A 53-year-old man comes to the office due to a 3-day history of right leg swelling and pain. He has had no chest pain or dyspnea. The patient describes himself as healthy, and his last visit to the doctor was 10 years ago. He has had no weight loss or abdominal pain. The patient smokes and has a 30-pack-year history. He has an active lifestyle and has not recently traveled. The patient's mother died of breast cancer, and his father has congestive heart failure. Temperature is 37 C (98.6 F), blood pressure is 140/80 mm Hg, pulse is 70/min, and respirations are 14/min. Oxygen saturation is 97% on room air. Normal vesicular breath sounds and cardiac sounds are heard on chest auscultation. Abdominal examination is unremarkable. The right leg is swollen and tender up to midthigh. Results of complete blood cell count and coagulation studies are within normal limits. Duplex ultrasonography demonstrates incompressible popliteal and femoral veins, and anticoagulation is started immediately. Chest x-ray is unremarkable. Which of the following is most appropriate in evaluation of this patient's current condition?
A)Age-appropriate cancer screening
B)CT scan of the abdomen
C)Positron emission tomography of the chest
D)Protein C, protein S, and antithrombin tests
E)Serum carbohydrate antigen (CA) 19-9 and carcinoembryonic antigen tests
A)Age-appropriate cancer screening
B)CT scan of the abdomen
C)Positron emission tomography of the chest
D)Protein C, protein S, and antithrombin tests
E)Serum carbohydrate antigen (CA) 19-9 and carcinoembryonic antigen tests

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 1702 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
A 45-year-old Asian-American woman comes to the physician due to bloating, flatulence, abdominal cramps and explosive watery diarrhea. These symptoms occur after ingesting dairy products. She has not had any weight loss. She has not had bone pain or easy bruising. Physical examination shows abdominal distention and borborygmi. You decide to investigate the patient further. Which of the following test results is most likely to be observed?
A)Positive urine test for reducing substances
B)Decreased stool osmotic gap
C)Positive hydrogen breath test
D)Alkaline stool pH
E)Positive acid steatocrit test
A)Positive urine test for reducing substances
B)Decreased stool osmotic gap
C)Positive hydrogen breath test
D)Alkaline stool pH
E)Positive acid steatocrit test

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 1702 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
A 32-year-old Italian-American man comes to the office for a routine checkup. The patient is a business executive and has been under significant stress recently. He drinks alcohol occasionally and has a 10-pack-year smoking history. Laboratory results are as follows:  Serial fecal occult blood tests are negative. Peripheral blood smear is shown in the image below.
Serial fecal occult blood tests are negative. Peripheral blood smear is shown in the image below.
 Which of the following is the best treatment for this patient?
Which of the following is the best treatment for this patient?
A)Cobalamin
B)Deferoxamine
C)Erythropoietin
D)Folic acid
E)Hydroxyurea
F)Iron
G)Prednisone
H)Reassurance with no specific therapy required
I)Splenectomy
 Serial fecal occult blood tests are negative. Peripheral blood smear is shown in the image below.
Serial fecal occult blood tests are negative. Peripheral blood smear is shown in the image below. Which of the following is the best treatment for this patient?
Which of the following is the best treatment for this patient?A)Cobalamin
B)Deferoxamine
C)Erythropoietin
D)Folic acid
E)Hydroxyurea
F)Iron
G)Prednisone
H)Reassurance with no specific therapy required
I)Splenectomy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 1702 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



