Deck 3: Biochemistry
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/102
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 3: Biochemistry
1
A physiologist is studying the mechanisms of signal transduction involved in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Their research focuses on the intracellular signaling cascade that begins when insulin binds to the insulin receptor. In a series of experiments, they demonstrate that pre-treatment with tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alph A) results in decreased insulin-mediated glucose uptake. This effect of TNF-alpha is most likely mediated through upregulation of which of the following processes?
A)Cyclic AMP hydrolyzation
B)Phosphatidylinositol cleavage
C)Proline residue hydroxylation
D)Serine residue phosphorylation
E)Stimulation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor
A)Cyclic AMP hydrolyzation
B)Phosphatidylinositol cleavage
C)Proline residue hydroxylation
D)Serine residue phosphorylation
E)Stimulation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor
Serine residue phosphorylation
2
A pharmaceutical researcher develops a new drug that affects bacterial protein synthesis. In an experiment, Escherichia coli is exposed to the drug and serially cultured in media containing tagged nucleotides and amino acids. It is found that the drug inhibits molecules that recognize the highlighted codon in the bacterial mRNA fragment shown in the image below.  Which of the following molecules is the most likely target of this drug?
Which of the following molecules is the most likely target of this drug?
A)Charged tRNA
B)Elongation factor 2
C)Releasing factor 1
D)snRNP
E)Transcription factor II D
F)Uncharged tRNA
 Which of the following molecules is the most likely target of this drug?
Which of the following molecules is the most likely target of this drug?A)Charged tRNA
B)Elongation factor 2
C)Releasing factor 1
D)snRNP
E)Transcription factor II D
F)Uncharged tRNA
Releasing factor 1
3
A 20-year-old man arrives to the emergency department complaining of lethargy, malaise, and black urine. Several days earlier, the patient was treated for a bacterial skin infection. Scleral icterus is discovered during a physical examination. Anemia with an increased reticulocyte count is revealed by laboratory findings. On a peripheral smear, abnormal erythrocytes might be observed. Which of the following substrate flow routes in this patient is most likely deficient? 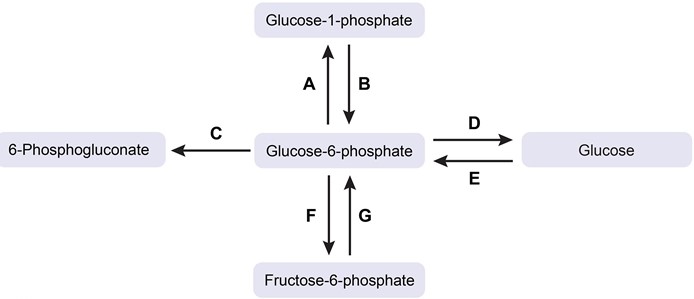
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E
F)F
G)G

A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E
F)F
G)G
C
4
Due to insufficient exercise endurance, a 15-year-old kid is taken to the clinic. He just begun weight lifting with pals but has struggled to complete the routines. According to the sufferer, his arms "feel like jello after just a few repetitions." He also experiences significant muscle cramps and sometimes urine staining following training sessions. Further testing showed that ingesting an oral glucose solution before commencing a demanding activity can significantly increase the patient's exercise tolerance. The vital signs are normal, and the exam is ordinary. Which of the following transformations is most likely catalyzed by this patient's deficiency in an enzyme? 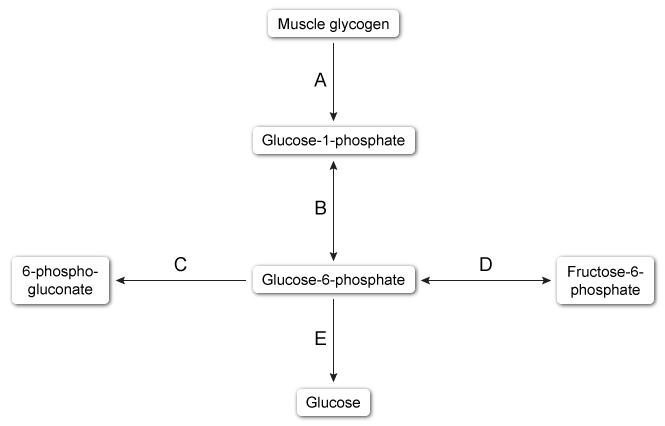
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Hepatocytes are isolated from biopsy samples acquired from patients getting standard treatment at a local tertiary referral center as part of a research project studying enzyme activity in both normal and sick liver tissue. To remove membrane components and organelles, the cells are homogenized and centrifuged. Following several centrifugation rounds, the residual supernatant comprises solely cytosol and cytosolic proteins. Which of the following enzymes' activity is most likely to be detectable in the supernatant of healthy liver cells? A)3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA lyase
B)Ornithine transcarbamylase
C)Pyruvate carboxylase
D)Succinate dehydrogenase
E)Transketolase
B)Ornithine transcarbamylase
C)Pyruvate carboxylase
D)Succinate dehydrogenase
E)Transketolase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Hepatocytes are isolated from biopsy samples acquired from patients getting standard treatment at a local tertiary referral center as part of a research project studying enzyme activity in both normal and sick liver tissue. To remove membrane components and organelles, the cells are homogenized and centrifuged. Following several centrifugation rounds, the residual supernatant comprises solely cytosol and cytosolic proteins. Which of the following enzymes' activity is most likely to be detectable in the supernatant of healthy liver cells? A)3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA lyase
B)Ornithine transcarbamylase
C)Pyruvate carboxylase
D)Succinate dehydrogenase
E)Transketolase
B)Ornithine transcarbamylase
C)Pyruvate carboxylase
D)Succinate dehydrogenase
E)Transketolase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
After his truck breaks down while searching for gold in Arizona, a 43-year-old man finds stranded in the desert. He carried plenty of water, but only a few granola bars for nourishment. He is able to flag down a passing car and gain transportation to the next village after three days. His liver begins to produce significant amounts of glucose from source molecules such as alanine, lactate, and glycerol throughout this experience. Phosphoenolpyruvate is synthesized from oxaloacetate in a reaction that needs a particular nucleoside triphosphate as a cofactor. Which of the following processes produces this cofactor directly? 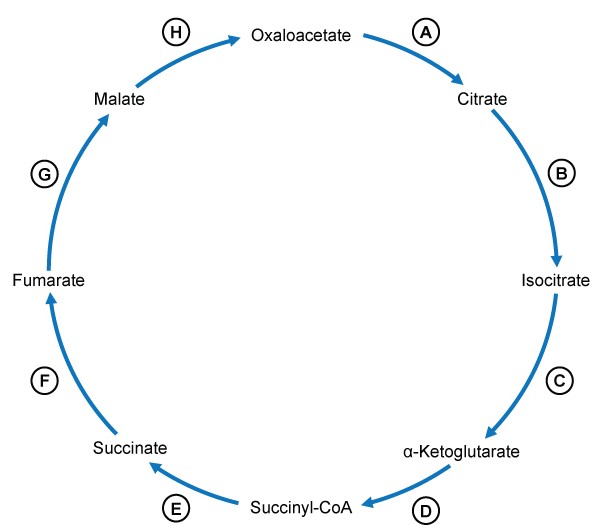
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E
F)F
G)G
H)H

A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E
F)F
G)G
H)H

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A scientist is investigating the structure of several hormone receptors. From a homogenized tissue sample, receptor proteins are extracted and purified. According to detailed structural study, one of the proteins has a 30-amino acid pattern that coordinates a zinc molecule, as illustrated in the picture below. 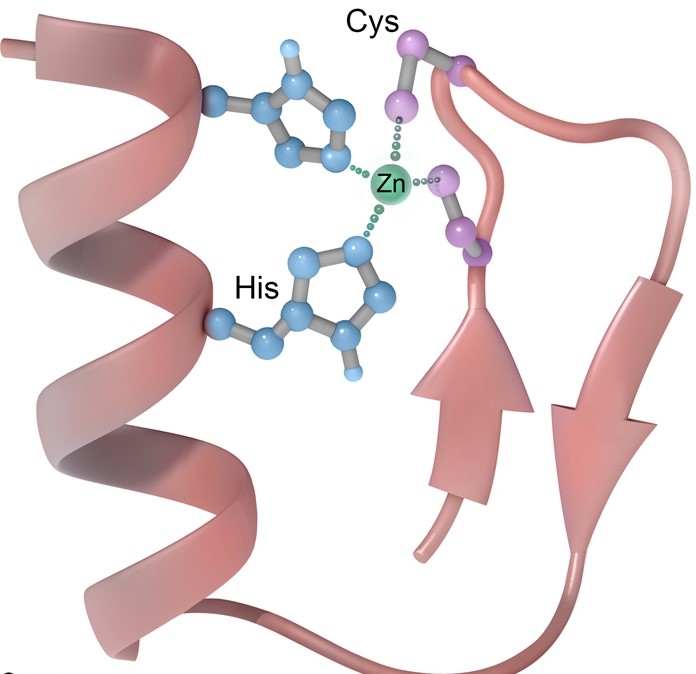 A receptor for which of the following hormones was most likely isolated in this experiment?
A receptor for which of the following hormones was most likely isolated in this experiment?
A)Adrenocorticotropic hormone
B)Antidiuretic hormone
C)Epinephrine
D)Glucagon
E)Growth hormone
F)Insulin
G)Thyroid hormone
 A receptor for which of the following hormones was most likely isolated in this experiment?
A receptor for which of the following hormones was most likely isolated in this experiment?A)Adrenocorticotropic hormone
B)Antidiuretic hormone
C)Epinephrine
D)Glucagon
E)Growth hormone
F)Insulin
G)Thyroid hormone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Following a car collision, paramedics transport a 23-year-old man to the emergency room. He was an unconstrained front-seat passenger. His fluid volume and plasma osmolarity are measured several days after his admission and are depicted in the figure below (solid line, normal; dotted line, patient). 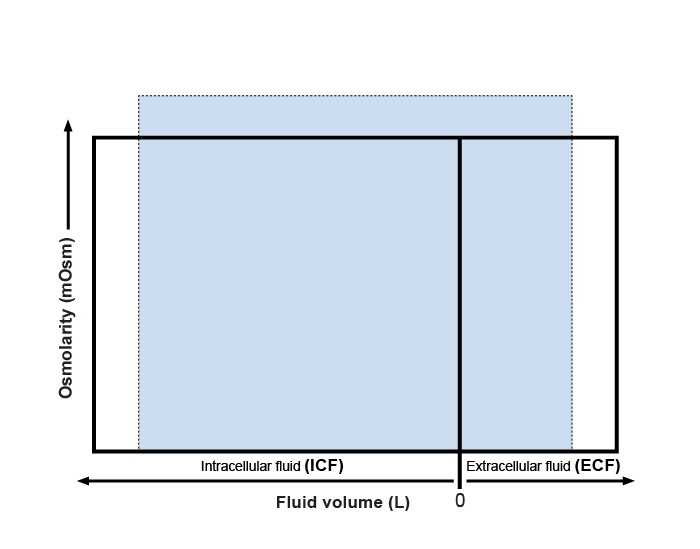 Which of the following conditions is most likely to cause the findings shown in the image?
Which of the following conditions is most likely to cause the findings shown in the image?
A)Acute gastrointestinal hemorrhage
B)Adrenal insufficiency
C)Diabetes insipidus
D)Hypertonic saline infusion
E)Primary polydipsia
F
 Which of the following conditions is most likely to cause the findings shown in the image?
Which of the following conditions is most likely to cause the findings shown in the image?A)Acute gastrointestinal hemorrhage
B)Adrenal insufficiency
C)Diabetes insipidus
D)Hypertonic saline infusion
E)Primary polydipsia
F

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A 34-year-old woman arrives at the emergency department in the early morning, confused, trembling, and sweating. Her spouse claims she did not wake up to her alarm clock and was difficult to awaken. The patient has experienced comparable experiences in the morning before eating and after exercising in the last week. The patient's medical history is ordinary. The blood pressure is 135/95 mm Hg, the pulse is 110 beats per minute, and the respirations are 24/ minute. The patient is receptive to voice but does not obey directions. The assessment of the cranial nerves, muscular tone, and deep tendon reflexes are all normal. The glucose level on a bedtime fingerstick is 35 mg/dL. The patient receives an intravenous infusion of glucose, which improves her mental condition quickly. Further evaluation reveals that her episodes of hypoglycemia are due to increased levels of an endogenous hormone. This hormonal imbalance is most likely causing the patient's symptoms by stimulating which of the following conversions? 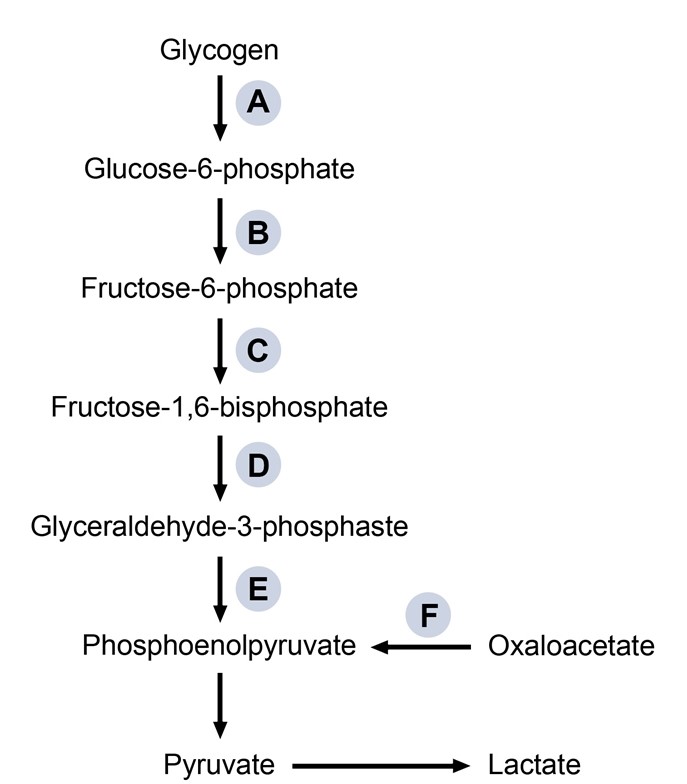
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E
F)F

A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E
F)F

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A couple visits the clinic for preconception advice. Because they are of Ashkenazi Jewish origin, they are given genetic testing. Both are carriers for a lysosomal enzyme deficiency condition, which results in reduced metabolic breakdown of a phospholipid substrate to ceramide, resulting in phospholipid accumulation. They are advised about the possibility that their children would be afflicted by this condition. The couple is interested in learning about the clinical characteristics of a sick child. Which of the following results is most likely to be associated with this condition?
A)Abnormally shaped bones and corneal clouding
B)Coarse facial features and cardiac dysfunction
C)Neuropathic pain and angiokeratomas
D)Retinal opacification and splenomegaly
E)Small stature and infertility
A)Abnormally shaped bones and corneal clouding
B)Coarse facial features and cardiac dysfunction
C)Neuropathic pain and angiokeratomas
D)Retinal opacification and splenomegaly
E)Small stature and infertility

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A kid aged 18 months is being tested for neurologic regression. He had a typical newborn and early development track till the age of 5 months. The kid then had steady regression of developmental milestones, and he is now unable to sit without assistance, has poor head control, and has lost his social grin. Weight and height are both lower than the 5th percentile. The physical examination reveals an enlarged liver and spleen, as well as decreased deep tendon reflexes in both limbs and hypotonia. The display includes funduscopic results. 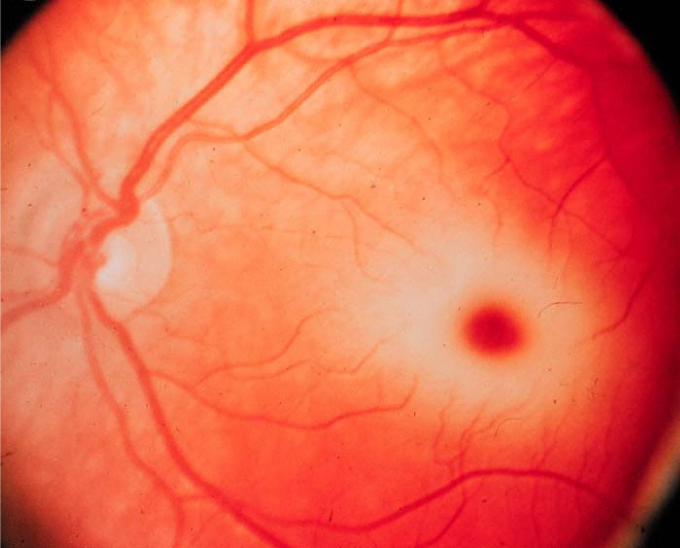 This patient most likely has an accumulation of which of the following substrates?
This patient most likely has an accumulation of which of the following substrates?
A)Cerebroside sulfate
B)Galactocerebroside
C)Globotriaosylceramide
D)Glucocerebroside
E)GM2 ganglioside
F)Sphingomyelin
 This patient most likely has an accumulation of which of the following substrates?
This patient most likely has an accumulation of which of the following substrates?A)Cerebroside sulfate
B)Galactocerebroside
C)Globotriaosylceramide
D)Glucocerebroside
E)GM2 ganglioside
F)Sphingomyelin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A group of researchers is looking at how catecholamine production is regulated in response to extreme stress. Subject rats are randomly allocated to either an experimental or a control group in the experiments. The pituitary gland is resected in the experimental rats, while the control rats get a craniotomy without pituitary resection. When compared to control animals, the experimental animals produce less epinephrine from the adrenal medulla and less cortisol from the adrenal cortex. Which of the following enzymes' decreased activity is most likely responsible for the reduced epinephrine levels in the experimental animals?
A)Catechol-O-methyl transferase
B)Dopa decarboxylase
C)Dopamine beta-hydroxylase
D)Monoamine oxidase
E)Phenylalanine hydroxylase
F)Phenylethanolamine-N-methyltransferase
G)Tyrosine hydroxylase
A)Catechol-O-methyl transferase
B)Dopa decarboxylase
C)Dopamine beta-hydroxylase
D)Monoamine oxidase
E)Phenylalanine hydroxylase
F)Phenylethanolamine-N-methyltransferase
G)Tyrosine hydroxylase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A 17-year-old child was discovered unconscious at home after being diagnosed with type 1 diabetes mellitus. According to his family, the patient did not feel well last night and skipped supper, but he nevertheless took his customary insulin dosage. His fingerstick blood glucose level is 32 mg/dL, so paramedics promptly give intramuscular glucagon. In hepatocytes, glucagon interacts to a transmembrane receptor, promoting intracellular GTP binding to a particular receptor-associated protein. This results in further downstream signaling and fast metabolic changes inside hepatocytes, such as a rapid depletion in intracellular glycogen reserves and glucose release into the blood. Which of the following is the most likely cause of these effects?
A)cGMP-dependent protein kinase
B)Janus tyrosine kinase
C)Phosphodiesterase
D)Protein kinase A
E)Tyrosine-specific protein kinase
A)cGMP-dependent protein kinase
B)Janus tyrosine kinase
C)Phosphodiesterase
D)Protein kinase A
E)Tyrosine-specific protein kinase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
In an animal experiment, mouse proerythroblasts are cultivated in two distinct growth conditions; the first is lacking in folate, while the second (control) is enriched with folic acid. Both media contain large levels of erythropoietin. Over 48 hours, cells in the control medium proliferate and differentiate into reticulocytes, but cell proliferation is low in the folate-deficient media, with the majority of cells suffering apoptosis. In another experiment, a chemical is introduced to the folate-deficient medium that inhibits apoptosis and allows proerythroblasts to proliferate. Which of the following substances is most likely to be added to the growing medium?
A)Cobalamin
B)Cytosine
C)Glutamine
D)Homocysteine
E)Thymidine
A)Cobalamin
B)Cytosine
C)Glutamine
D)Homocysteine
E)Thymidine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A 2-year-old kid from daycare is sent to the emergency room with diarrhea, exhaustion, and stomach pains. He also has foul-smelling, foamy feces, according to his parents. The youngster is brought to the hospital for rehydration and is later diagnosed with giardiasis, which is treated with metronidazole. He recovers and is sent home. One week after discharge, the youngster is examined by his primary care physician for recurring symptoms of frothy, loose feces, as well as stomach bloating and cramps. Which of the following phases in this route is most likely to be faulty in this patient? 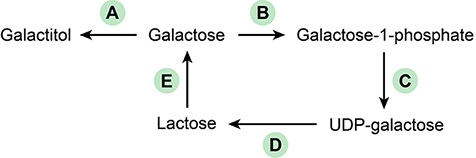
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A 79-year-old woman arrives at the office for an examination of walking difficulties caused by weariness and bilateral leg discomfort. The pain began in her lower legs three weeks ago and has now spread to her thighs' muscles. She has also seen red blotches on her legs. The patient has been living alone since her spouse died three years ago and is mostly housebound. Her diet is primarily comprised of bread and tinned meat items. The gums are swollen and sensitive on inspection. The exhibit depicts the patient's skin results. 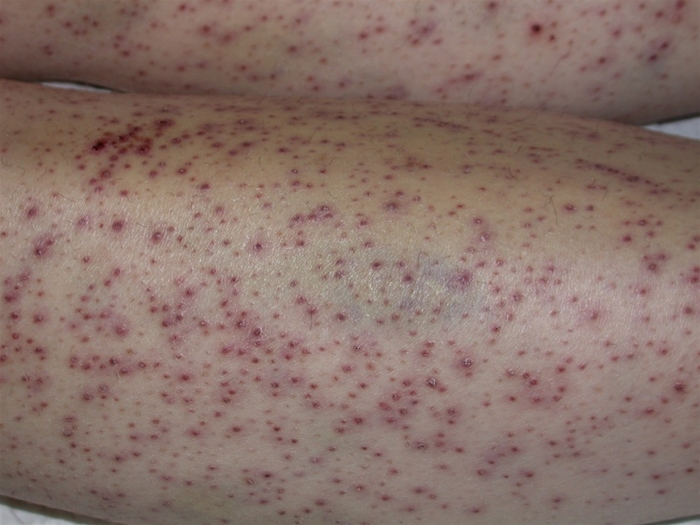 Muscles of the lower limbs are tender to palpation. Imaging studies reveal a tibial subperiosteal hematoma. Which of the following nutrient deficiencies is most likely responsible for this patient's symptoms?
Muscles of the lower limbs are tender to palpation. Imaging studies reveal a tibial subperiosteal hematoma. Which of the following nutrient deficiencies is most likely responsible for this patient's symptoms?
A)Ascorbic acid
B)Biotin
C)Folic acid
D)Linoleic acid
E)Pyridoxine
F)Riboflavin
G)Thiamine
H)Vitamin K
I)Zinc
 Muscles of the lower limbs are tender to palpation. Imaging studies reveal a tibial subperiosteal hematoma. Which of the following nutrient deficiencies is most likely responsible for this patient's symptoms?
Muscles of the lower limbs are tender to palpation. Imaging studies reveal a tibial subperiosteal hematoma. Which of the following nutrient deficiencies is most likely responsible for this patient's symptoms?A)Ascorbic acid
B)Biotin
C)Folic acid
D)Linoleic acid
E)Pyridoxine
F)Riboflavin
G)Thiamine
H)Vitamin K
I)Zinc

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A 6-year-old African American youngster is brought to the doctor because he is easily fatigable. Splenomegaly is discovered on physical examination, and his complete blood count confirms slight anemia. On a cellulose acetate strip, hemoglobin electrophoresis is conducted at an alkaline pH. The patient's results are displayed below in comparison to those with normal hemoglobin and known sickle cell illness. 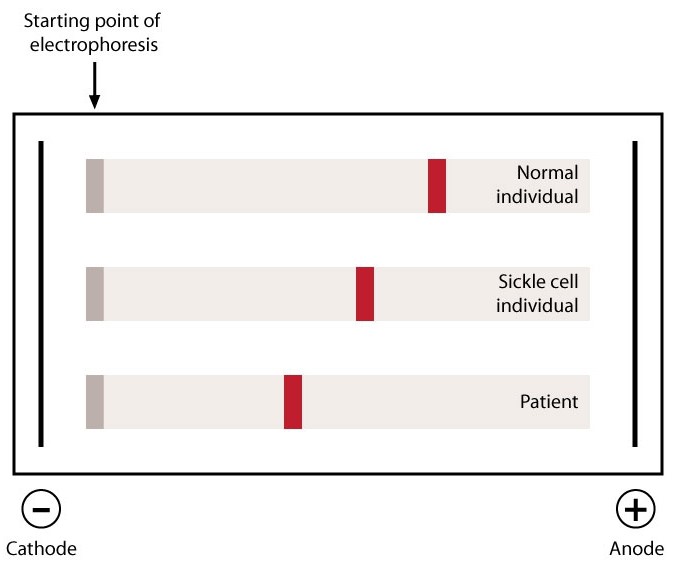 Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's condition?
Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's condition?
A)Alpha globin gene deletion
B)Missense mutation
C)Nonsense mutation
D)Silent mutation
E)Trinucleotide expansion
 Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's condition?
Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's condition?A)Alpha globin gene deletion
B)Missense mutation
C)Nonsense mutation
D)Silent mutation
E)Trinucleotide expansion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A group of researchers is looking at the changes in oxygen-hemoglobin binding that occur under different clinical settings. They are particularly interested in circumstances that change the form and location of the oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curve. Which of the following procedures would most likely cause the blue curve in the graph below to move to the red curve? 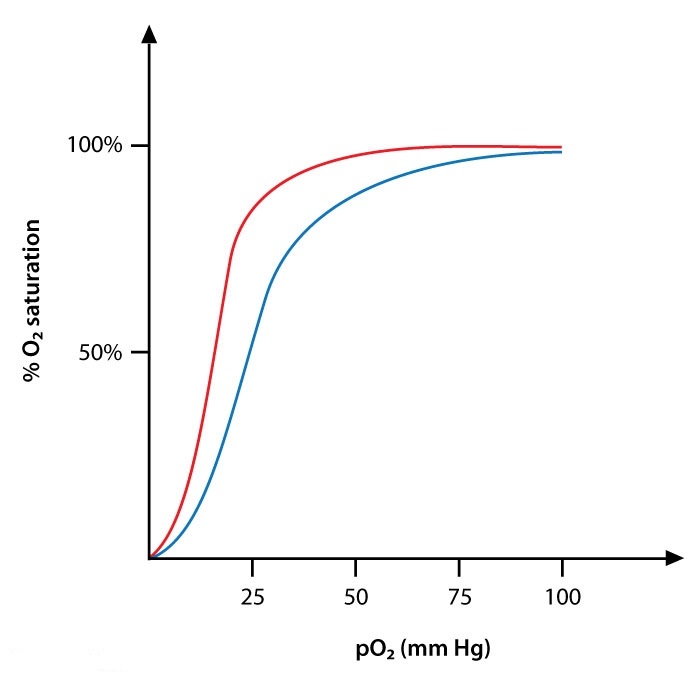
A)Chronic high-altitude adaptation
B)Hypothermia
C)Hypoventilation
D)Severe anemia
E)Strenuous exercise

A)Chronic high-altitude adaptation
B)Hypothermia
C)Hypoventilation
D)Severe anemia
E)Strenuous exercise

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Researchers investigating the fundamentals of oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation have effectively separated hemoglobin tetramers into individual alpha and beta subunits. Under physiological settings, a solution containing exclusively monomeric beta-hemoglobin subunits is generated during an experiment. The oxygen dissociation curve of dissolved beta subunits will most likely resemble which of the following lines if measured? 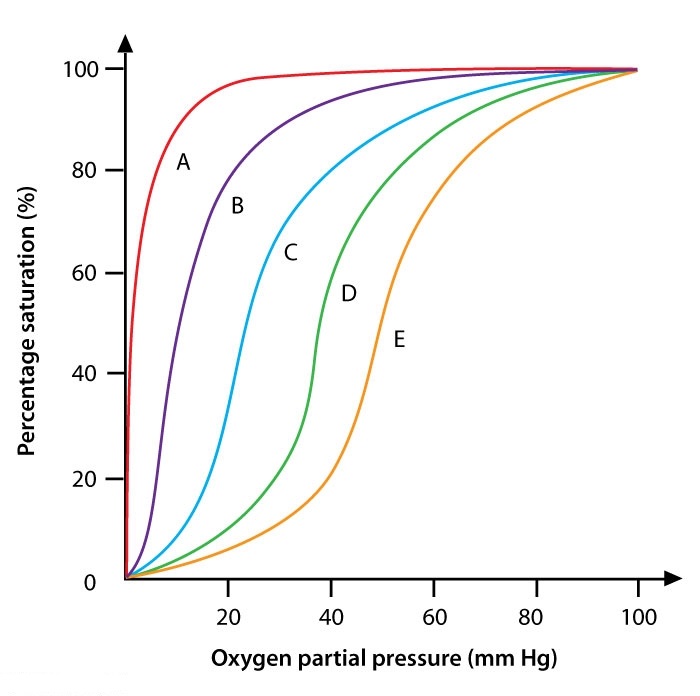
A)Line A
B)Line B
C)Line C
D)Line D
E)Line E

A)Line A
B)Line B
C)Line C
D)Line D
E)Line E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A 55-year-old farmer is taken to the emergency room after his daughter discovered him confused and disoriented in his home tool shed. He is otherwise healthy and does not require any drugs. On physical examination, the blood pressure is 110/70 mm Hg and the pulse rate is 50 / minute. The patient's pupils are symmetric, 2 mm in diameter, and light reactive. His eyes are crying up a lot. On lung auscultation, there are scattered wheezes bilaterally. The patient's skin is clammy, and he is excessively sweating. Which of the following stages at the neuromuscular junction is most likely impaired in his presentation? 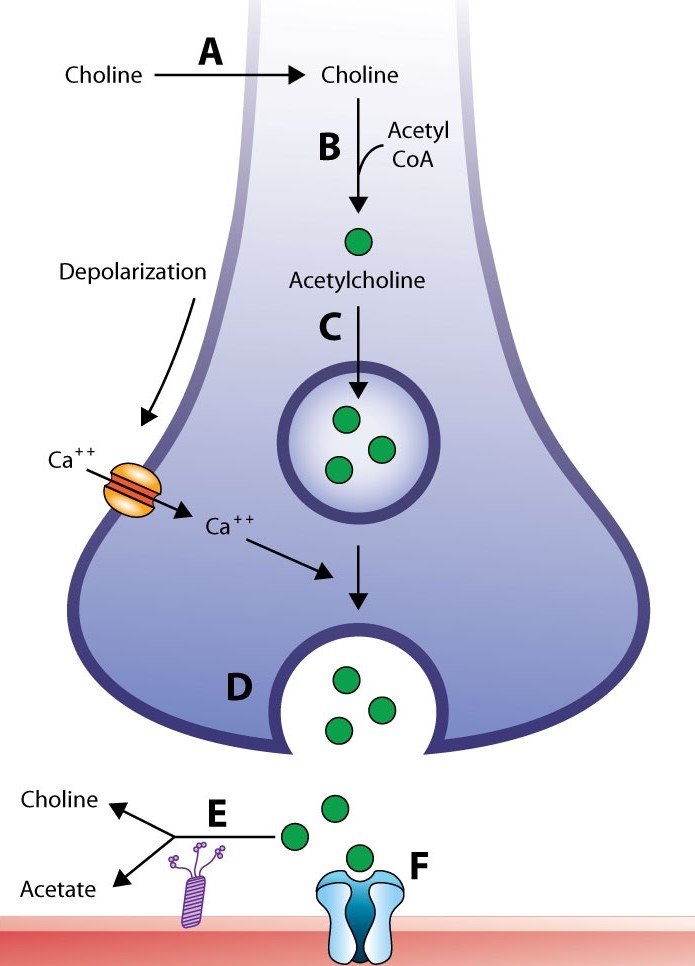
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E
F)F

A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E
F)F

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A 7-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department due to lethargy and vomiting. He hasn't eaten for approximately 24 hours because he had been on an overnight hiking trip with his family. During the trip, the family lost their food pack while canoeing and had to hike back to their car. The child became weak and was carried for the last mile. None of the family On examination, the patient appears listless. Mild hepatomegaly is noted. Laboratory results are as follows:  The patient begins seizing shortly after arriving at the emergency department. Which of the following enzymes is most likely deficient in this patient?
The patient begins seizing shortly after arriving at the emergency department. Which of the following enzymes is most likely deficient in this patient?
A)Acetyl-CoA carboxylase
B)Acid alpha-glucosidase
C)Acyl-CoA dehydrogenase
D)Glucose 6-phosphatase
E)Glycogen phosphorylase
 The patient begins seizing shortly after arriving at the emergency department. Which of the following enzymes is most likely deficient in this patient?
The patient begins seizing shortly after arriving at the emergency department. Which of the following enzymes is most likely deficient in this patient?A)Acetyl-CoA carboxylase
B)Acid alpha-glucosidase
C)Acyl-CoA dehydrogenase
D)Glucose 6-phosphatase
E)Glycogen phosphorylase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A 6-year-old girl is brought to office due to prolonged fatigue and difficulty walking. Her childhood developmental growth was normal but rapidly becomes weak and tired. The patient has not been ill recently and is usually happy and playful. She has a history of mild motor delays but is otherwise developmentally normal. Vital signs are within normal limits. Examination shows mildly decreased power in all extremities but no ataxia. Cardiac auscultation reveals a 1/6 systolic murmur and an S3 gallop. Laboratory results are as follows: 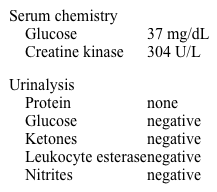 Muscle biopsy shows a very low carnitine content. This patient most likely has deficient synthesis of which of the following substances?
Muscle biopsy shows a very low carnitine content. This patient most likely has deficient synthesis of which of the following substances?
A)Acetoacetate
B)Arachidonic acid
C)Glutathione
D)Homocysteine
E)Lactate
F)Palmitate
 Muscle biopsy shows a very low carnitine content. This patient most likely has deficient synthesis of which of the following substances?
Muscle biopsy shows a very low carnitine content. This patient most likely has deficient synthesis of which of the following substances?A)Acetoacetate
B)Arachidonic acid
C)Glutathione
D)Homocysteine
E)Lactate
F)Palmitate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A research scientist studying the metabolic pathways that contribute to obesity feeds experimental animals a high-carbohydrate, high-protein diet for a prolonged period. A sample of liver tissue is then obtained from the animals, and the activity of various enzymes involved in fatty acid metabolism is measured and recorded. It is determined that beta-oxidation of fatty acids is inhibited within these cells as a result of the diet. An increase in which of the following substances is most likely responsible for the observed effect?
A)Acetoacetate
B)Carnitine
C)Citrate
D)Malonyl-CoA
E)NADPH
A)Acetoacetate
B)Carnitine
C)Citrate
D)Malonyl-CoA
E)NADPH

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A 62-year-old man comes to the office due to an enlarging mole on his left forearm. The patient works as a farmer and has a significant amount of sun exposure daily. On examination, he has a black-brown macular lesion on the dorsum of his right forearm measuring approximately 1 cm in diameter with an irregular border. Excisional biopsy is performed and histopathology reveals malignant melanoma. Immunohistochemical analysis indicates that the malignant cells have decreased integrin expression. These cells are most likely to exhibit poor adhesion to which of the following components of the extracellular matrix?
A)Actin
B)Fibronectin
C)Hyaluronic acid
D)Keratan sulfate
E)Keratin
A)Actin
B)Fibronectin
C)Hyaluronic acid
D)Keratan sulfate
E)Keratin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Researchers are investigating the specifics underlying glucose transport across adipose cell membranes. One of their experiments shows that, in the presence of insulin, D-glucose transport across the plasma membrane of adipocytes is much faster than L-glucose transport. Which of the following transport processes best describes the mechanism for glucose entry into these cells?
A)Simple diffusion
B)Receptor-mediated endocytosis
C)Carrier-mediated transport
D)Primary active transport
E)Co-transport
A)Simple diffusion
B)Receptor-mediated endocytosis
C)Carrier-mediated transport
D)Primary active transport
E)Co-transport

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Two graphs illustrating the transport rate of solutes across the plasma membrane are shown on the slide below. 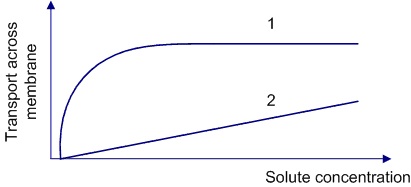 Which of the following best explains the difference in the shape of the curves?
Which of the following best explains the difference in the shape of the curves?
A)Different amounts of membrane surface area for diffusion
B)Different degrees of membrane thickness
C)The 2 solutes have different molecular weights
D)The 2 solutes have different oil/water partition coefficients
E)The presence of a protein transporter
 Which of the following best explains the difference in the shape of the curves?
Which of the following best explains the difference in the shape of the curves?A)Different amounts of membrane surface area for diffusion
B)Different degrees of membrane thickness
C)The 2 solutes have different molecular weights
D)The 2 solutes have different oil/water partition coefficients
E)The presence of a protein transporter

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A 55-year-old man comes to the office with a long history of fatigue and exertional dyspnea. He has early satiety and frequent upper abdominal discomfort. On physical examination, the patient has palpable splenomegaly but no lymphadenopathy. Laboratory tests are as follows: 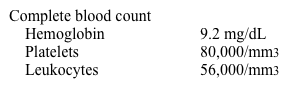 Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction is used to diagnose chronic myelogenous leukemia in this patient. Which of the following is most likely to be detected by this test?
Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction is used to diagnose chronic myelogenous leukemia in this patient. Which of the following is most likely to be detected by this test?
A)Chromosomal position of the BCR and ABL genes
B)DNA rearrangement in the BCR promoter region
C)Fusion protein containing BCR and ABL domains
D)Messenger RNA transcript containing BCR and ABL exons
E)Point mutation in the ABL enhancer region
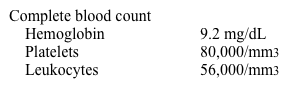 Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction is used to diagnose chronic myelogenous leukemia in this patient. Which of the following is most likely to be detected by this test?
Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction is used to diagnose chronic myelogenous leukemia in this patient. Which of the following is most likely to be detected by this test?A)Chromosomal position of the BCR and ABL genes
B)DNA rearrangement in the BCR promoter region
C)Fusion protein containing BCR and ABL domains
D)Messenger RNA transcript containing BCR and ABL exons
E)Point mutation in the ABL enhancer region

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A 54-year-old woman is evaluated for progressive constipation, anorexia, and a 5.4-kg (12-lb) weight loss over the past several months. Physical examination is unremarkable. Stool guaiac test is positive, and a colonoscopy is performed. An exophytic mass is identified in the sigmoid colon. The patient undergoes a left hemicolectomy, and histopathology of the surgical specimen is positive for adenocarcinoma. Molecular testing of the cancer cells reveals a mutation in the KRAS gene that results in constitutive activation of the Ras protein. Under normal circumstances, this protein is only active when bound to which of the following substances?
A)ATP
B)Ca2+
C)cAMP
D)GTP
E)IP3
A)ATP
B)Ca2+
C)cAMP
D)GTP
E)IP3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
An 8-year-old boy is brought to his pediatrician for developing multiple bruises over the course of the school year. The patient's mother believes the child is being bullied at school. The patient is otherwise healthy. Family history is significant for his father expiring at 38 yearas of age due to a severe subarachnoid hemorrhage. On physical exam, there are ecchymoses and hematomas over the shins and knees. The skin also appears fragile and thin, which demonstrates a venous pattern in the extremities. A skin biopsy is performed, and histochemical evaluation of the biopsy reveals a defect in extracellular processing of collagen. Which of the following steps of collagen synthesis is most likely impaired in this patient?
A)Glycosylation of hydroxylysine residues
B)Interchain C-terminal disulfide bond formation
C)N-terminal propeptide removal
D)Proline residue hydroxylation
E)Triple helix formation
A)Glycosylation of hydroxylysine residues
B)Interchain C-terminal disulfide bond formation
C)N-terminal propeptide removal
D)Proline residue hydroxylation
E)Triple helix formation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A 20-year-old male with no significant medical history comes to you with a urine positive for fructose. When asked about his past medical history, he says that he has no significant medical problems. However, his mother told him that he was born with "a problem metabolizing sugar." The patient maintains no dietary restrictions and regularly eats vegetables, fruits, meats, and processed foods. Urine samples show a repeatedly positive copper reduction test, but glucose oxidase dipstick testing is negative. Which of the following enzymes is most likely to be deficient in this patient?
A)Acid alpha-glucosidase
B)Aldolase B
C)Fructokinase
D)Galactose-1-phosphate uridyl transferase
E)Lactase
A)Acid alpha-glucosidase
B)Aldolase B
C)Fructokinase
D)Galactose-1-phosphate uridyl transferase
E)Lactase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A 54-year-old woman is brought to the physician by her brother because of abdominal pain and vomiting. She had similar episodes which resolved without treatment. Laboratory tests show high serum amylase which she is admitted, and treatment with bowel rest and intravenous fluids is begun. In the next morning she is evaluated for a new confusion and agitation. She is unable to personally give a history. On mental status examination, she is confused and oriented only to person. She recalls 0 out of 3 words after 5 minutes. Neurologic examination shows horizontal nystagmus on lateral gaze. She has difficulty walking without assistance. Which of the following most likely precipitated this patient's current neurologic condition?
A)Abrupt alcohol cessation
B)Excessive hydration
C)Glucose infusion
D)Hypotonic fluid administration
E)Lack of anticoagulant use
F)Vitamin supplementation
A)Abrupt alcohol cessation
B)Excessive hydration
C)Glucose infusion
D)Hypotonic fluid administration
E)Lack of anticoagulant use
F)Vitamin supplementation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A 6-month-old infant male is brought to the emergency department with a 1-hour history of vomiting and convulsions. He was born at home and had sporadic prenatal care though his parents say that he appeared healthy at birth. He initially fed well; however, his parents have noticed that he has been feeding poorly and is very irritable since they moved on to baby foods. They have also noticed mild yellowing of his skin but assumed it would go away over time. On presentation, he is found to be very sleepy, and physical exam reveals an enlarged liver and spleen. The rest of the physical exam is normal. Which of the following enzymes is most likely to be deficient in this patient?
A)Galactose-1-phosphate uridyl transferase
B)Aldolase B
C)Fructokinase
D)Galactokinase
E)Acid alpha-glucosidase
A)Galactose-1-phosphate uridyl transferase
B)Aldolase B
C)Fructokinase
D)Galactokinase
E)Acid alpha-glucosidase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Nutrition researchers investigating the relationship between fructose consumption and cardiovascular disease conduct a prospective cohort study on a population of randomly selected young adults. Study participants undergo semiannual measurement of waist circumference, blood pressure, and serum cholesterol and triglyceride concentrations. Dietary fructose consumption is assessed through the use of questionnaires and by measuring urinary fructose excretion. A 23-year-old man enrolled in the study is found to excrete large amounts of fructose in his urine compared to other study participants despite maintaining a moderate fructose intake. Further evaluation shows a hereditary defect in fructose metabolism, but he is asymptomatic and has no other medical problems. This patient most likely remains able to metabolize fructose due to the compensatory activity of which of the following enzymes?
A)Aldolase B
B)Aldose reductase
C)Fructokinase
D)Hexokinase
E)UDP-galactose-4-epimerase
A)Aldolase B
B)Aldose reductase
C)Fructokinase
D)Hexokinase
E)UDP-galactose-4-epimerase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
A 6-month-old boy is brought to the emergency department by his mother because of recent onset of vomiting, irritability, and jaundice. The infant was born at term and had been healthy until the onset of these symptoms. All of his vaccinations are up-to-date. He had been breast-fed exclusively until 1 week ago, when cereals and fruit juices were introduced into his diet. Further evaluation reveals hepatomegaly and abnormal liver function tests. Serum glucose is 30 mg/dL. Diagnostic testing confirms aldolase B deficiency. Which of the following should be removed from this patient's diet?
A)Amylose
B)Cellulose
C)Galactose
D)Glucose
E)Lactose
F)Maltose
G)Sucrose
A)Amylose
B)Cellulose
C)Galactose
D)Glucose
E)Lactose
F)Maltose
G)Sucrose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Erythroblasts isolated from a bone marrow biopsy sample of a patient with neonatal jaundice are incubated in a medium containing radiolabeled glucose. The cells are unable to generate NADPH from glucose metabolism but are able to convert fructose-6-phosphate to ribose-5-phosphate, which is required for nucleic acid synthesis. Which of the following enzymes is essential for the latter conversion?
A)Aconitase
B)Enolase
C)Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase
D)Glutathione reductase
E)Transketolase
A)Aconitase
B)Enolase
C)Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase
D)Glutathione reductase
E)Transketolase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A 3-week-old male is brought to the emergency department because of increasing lethargy. He was born at home without prenatal care or neonatal screening and appeared to be normal at birth. Despite this, his parents noticed that he would vomit after breastfeeding. He then progressively became more lethargic and began to have a few episodes of diarrhea after feeding. His parents do not recall any significant family history and neither of his siblings have had similar symptoms. Upon presentation, the infant is found to be generally unresponsive with mild hepatomegaly. Physical exam further reveals signs of clouding in the lenses of his eyes bilaterally. Which of the following steps in metabolism is most likely impaired in this patient? 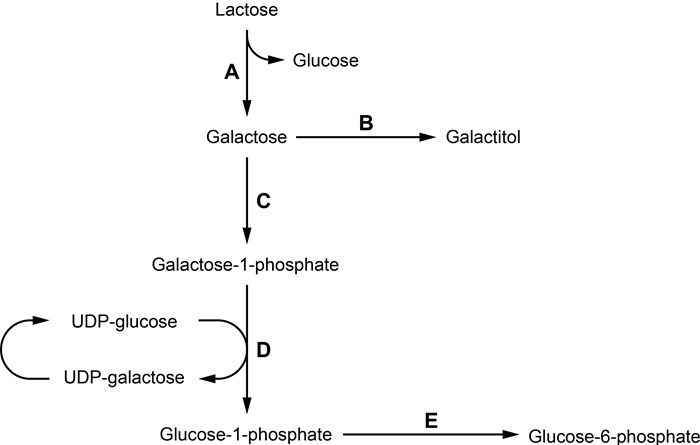
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A 3-week-old male is brought to the emergency department because of increasing lethargy. He was born at home without prenatal care or neonatal screening and appeared to be normal at birth. Despite this, his parents noticed that he would vomit after breastfeeding. He then progressively became more lethargic and began to have a few episodes of diarrhea after feeding. His parents do not recall any significant family history and neither of his siblings have had similar symptoms. Upon presentation, the infant is found to be generally unresponsive with mild hepatomegaly. Physical exam further reveals signs of clouding in the lenses of his eyes bilaterally. Which of the following steps in metabolism is most likely impaired in this patient? 
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
An 11-year-old girl is evaluated for blurry vision. The patient was adopted internationally at age 9. She has no history of head or eye trauma or exposure to ionizing radiation. Motor and cognitive milestones have been achieved at the appropriate age. She has a good appetite and does not follow any specific diet. The patient takes no medications and has no allergies. Vaccinations are up to date. Vital signs are normal. She is at the 40th percentile for height and weight. Other than bilateral lens opacities, the rest of her examination is normal. Urine is positive for reducing substances. Deficient activity of which of the following enzymes is the most likely cause of this patient's eye condition?
A)Aldolase B
B)Alpha-galactosidase A
C)Fructokinase
D)Galactokinase
E)Glucose-6-phosphatase
F)Hexosaminidase A
G)Sphingomyelinase
A)Aldolase B
B)Alpha-galactosidase A
C)Fructokinase
D)Galactokinase
E)Glucose-6-phosphatase
F)Hexosaminidase A
G)Sphingomyelinase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A 69-year-old woman with Alzheimer disease is brought to the emergency department after getting lost while taking a walk in her neighborhood. Her son has been unable to contact the patient for the last 2 days, and today the police found her wandering in a park. The patient says that she drank water from a park fountain but has not had anything to eat for over 24 hours. On physical examination, she is mildly confused with dry mucous membranes. Laboratory studies show a blood glucose level of 92 mg/dL. Which of the following hormones binds to an intracellular receptor to help maintain this patient's laboratory findings within the normal range?
A)Cortisol
B)Epinephrine
C)Glucagon
D)Growth hormone
E)Insulin
F)Norepinephrine
A)Cortisol
B)Epinephrine
C)Glucagon
D)Growth hormone
E)Insulin
F)Norepinephrine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A 30-year-old woman comes to the emergency department due to vomiting, and fever. Her symptoms began 24 hours ago, and she has been unable to eat or drink anything since. She has a 2-year-old daughter who had similar symptoms 2 days earlier but is now fine. Laboratory studies show a blood glucose level of 72 mg/dL despite her 24-hour fast. Maintenance of this patient's blood glucose levels is facilitated by hepatic conversion of pyruvate into glucose. Which of the following substances directly stimulates the first enzyme involved in this process?
A)Acetyl-CoA
B)Alanine
C)Citrate
D)Fructose 2,6-bisphosphate
E)Lactate
F)Oxaloacetate
A)Acetyl-CoA
B)Alanine
C)Citrate
D)Fructose 2,6-bisphosphate
E)Lactate
F)Oxaloacetate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
A 26-year-old man is brought to the emergency department due to progressive confusion. His roommate says that he has been binge drinking for the last 5 days and probably has had very little to eat. The patient's medical history is significant for alcohol-related seizures 1 year ago. He had been sober until 2 weeks ago, when he started drinking again. The patient's past medical history is otherwise unremarkable. On examination, he responds to voice but does not follow commands. Fingerstick glucose is 35 mg/dL and urine is strongly positive for ketones. Suppression of which of the following is the primary cause of this patient's hypoglycemia?
A)Gluconeogenesis
B)Glycogenolysis
C)Insulin clearance
D)Insulin sensitivity
E)Lipolysis
A)Gluconeogenesis
B)Glycogenolysis
C)Insulin clearance
D)Insulin sensitivity
E)Lipolysis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
A 26-year-old man is brought to the emergency department due to progressive confusion. His roommate says that he has been binge drinking for the last 5 days and probably has had very little to eat. The patient's medical history is significant for alcohol-related seizures 1 year ago. He had been sober until 2 weeks ago, when he started drinking again. The patient's past medical history is otherwise unremarkable. On examination, he responds to voice but does not follow commands. Fingerstick glucose is 35 mg/dL and urine is strongly positive for ketones. Suppression of which of the following is the primary cause of this patient's hypoglycemia?
A)Gluconeogenesis
B)Glycogenolysis
C)Insulin clearance
D)Insulin sensitivity
E)Lipolysis
A)Gluconeogenesis
B)Glycogenolysis
C)Insulin clearance
D)Insulin sensitivity
E)Lipolysis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A 4-month-old boy is brought to the office due to difficulty feeding. His mother says that he has difficulty holding his head up while breastfeeding and his suckling seems weaker than usual. Weight is at the 5th percentile. Length and head circumference are tracking along the 25th percentile. Physical examination shows hepatomegaly and hypotonia in all 4 limbs. Cardiac auscultation shows a gallop rhythm, and chest x-ray reveals severe cardiomegaly. Muscle biopsy shows enlarged lysosomes containing periodic acid-Schiff (PAS)-positive material. Which of the following enzymes is most likely deficient in this patient?
A)Acid alpha-glucosidase
B)Galactokinase
C)Glucose-6-phosphatase
D)Glycogen debrancher enzyme
E)Glycogen phosphorylase
F)Pyruvate kinase
A)Acid alpha-glucosidase
B)Galactokinase
C)Glucose-6-phosphatase
D)Glycogen debrancher enzyme
E)Glycogen phosphorylase
F)Pyruvate kinase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
A 5-month-old girl is brought to the office by her mother for a health checkup. The mother states, "My baby doesn't seem to be growing much despite feeding as often as my previous children. I am worried that something is wrong with her." Physical examination shows hepatomegaly, hypotonia, and height and weight below the 10th percentile. Laboratory studies show hypoglycemia and ketoacidosis. A liver biopsy shows hepatic fibrosis without fat accumulation. Further analysis reveals abundant quantities of a multibranched polysaccharide with abnormally short outer chains within the cytosol of the hepatocytes. Which of the following enzymes is most likely deficient in this patient?
A)Acid maltase
B)Debranching enzyme
C)Glucose-6-phosphatase
D)Liver glycogen phosphorylase
E)Muscle glycogen phosphorylase
F)Pyruvate kinase
A)Acid maltase
B)Debranching enzyme
C)Glucose-6-phosphatase
D)Liver glycogen phosphorylase
E)Muscle glycogen phosphorylase
F)Pyruvate kinase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
An 8-year-old boy is evaluated for exercise intolerance. The patient experiences fatigue, muscle pain, and cramps during exercise as well as severe muscle stiffness following strenuous activity. Physical examination is unremarkable. A forearm ischemic exercise test is performed by applying a blood pressure cuff on the patient's exercising forearm and sampling blood lactate several minutes after the exercise. The patient's blood samples show no rise in lactate levels. Biochemical analysis of a muscle biopsy reveals absent lactate dehydrogenase activity. In this patient, strenuous exercise leads to inhibition of glycolysis in skeletal muscle due to intracellular depletion of which of the following substances?
A)AMP
B)Carnitine
C)Citrate
D)FADH2
E)NAD+
F)Pyruvate
A)AMP
B)Carnitine
C)Citrate
D)FADH2
E)NAD+
F)Pyruvate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A 22-year-old previously healthy man is brought to the emergency department by his mother because of crushing chest pain, nausea, and vomiting for the past 2 hours. The pain is constant and radiates to his left shoulder. Over the past year, he has been admitted to the hospital twice for deep vein thrombosis. He has a history of learning disability and has been held back three grades. The patient is at the 99th percentile for height and the 45th percentile for weight. His pulse is 110/min, respirations are 21/min, and blood pressure is 128/84 mm Hg. His fingers are long and slender, and his arm span exceeds his body height. Electrocardiography shows ST-segment elevation in leads V1 and V2. His serum troponin I concentration is 2.0 ng/mL. Coronary angiography shows 90% occlusion of the proximal left anterior descending artery. Further testing reveals a homozygous mutation in the methylene tetrahydrofolate reductase gene that leads to decreased enzymatic activity. Due to this defect, the patient most likely has impairment converting homocysteine to which of the following?
A)Cystathionine
B)Cysteine
C)Methionine
D)Methylmalonyl-CoA
E)Succinyl-CoA
A)Cystathionine
B)Cysteine
C)Methionine
D)Methylmalonyl-CoA
E)Succinyl-CoA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A 13-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department with severe chest pain. He has had intermittent substernal chest pain for the past few months that typically occurs after heavy activity. The boy's activities have been limited due to the chest pain, and he is no longer able to play on the soccer team. The patient does not use tobacco or illicit drugs. His temperature is 36.7 C (98 F), blood pressure is 130/80 mm Hg, pulse is 132/min, respirations are 24/min, and pulse oximetry is 98% on room air. BMI is 17 kg/m2. Physical examination shows an anxious-appearing boy with a rapid but regular pulse. No abnormalities are seen. Troponin is elevated, and ECG reveals ST segment elevations in leads II, III, and aVF. After acute stabilization and treatment, further laboratory workup shows an increased serum methionine level. Which of the following amino acids is most likely essential in this patient?
A)Asparagine
B)Cysteine
C)Isoleucine
D)Leucine
E)Tyrosine
F)Valine
A)Asparagine
B)Cysteine
C)Isoleucine
D)Leucine
E)Tyrosine
F)Valine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Researchers lyse human cells and isolate a specific messenger RNA template using gel electrophoresis. Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction is then used to synthesize complementary DNA (cDN A) from the RNA template. Next, the cDNA is modified into an expression vector containing an optimized bacterial promoter, ribosomal binding site, and terminator sequence. After insertion of the vector into appropriate bacterial hosts, the transformed bacteria are cultured in a bioreactor and produce large quantities of a protein containing a domain that binds to a specific DNA sequence. This protein is most likely the receptor for which of the following hormones?
A)Glucagon
B)Growth hormone
C)Insulin
D)Insulin-like growth factor
E)Parathyroid hormone
F)Progesterone
A)Glucagon
B)Growth hormone
C)Insulin
D)Insulin-like growth factor
E)Parathyroid hormone
F)Progesterone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A 15-year-old boy comes to the office for health check-up. The patient is incidentally found to have mild hypercalcemia on laboratory testing. Further questioning reveals that several of his family members also have mild hypercalcemia. Subsequent laboratory studies show a borderline high parathyroid hormone concentration, very low urinary calcium level, and normal 25-hydroxyvitamin D level. A mutation in which of the following receptors is most likely responsible for this patient's laboratory abnormalities?
A)Intracellular receptor with a DNA-binding domain
B)Membrane-bound receptor coupled with a G protein
C)Transmembrane ligand-gated ion channel
D)Transmembrane receptor associated with intrinsic tyrosine kinase activity
E)Transmembrane receptor causing activation of Janus kinase/STAT pathway
A)Intracellular receptor with a DNA-binding domain
B)Membrane-bound receptor coupled with a G protein
C)Transmembrane ligand-gated ion channel
D)Transmembrane receptor associated with intrinsic tyrosine kinase activity
E)Transmembrane receptor causing activation of Janus kinase/STAT pathway

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A 18-month-old boy is brought to the office due to developmental delay and failure to thrive. his mother states that he has recurrent ear infections since 6 months of age. Physical examination shows corneal clouding, hepatosplenomegaly, and restricted joint mobility. Further evaluation shows deficient phosphorylation of mannose residues on certain glycoproteins in the Golgi apparatus. In unaffected patients, these proteins are normally transported to which of the following cellular locations?
A)Endoplasmic reticulum
B)Extracellular space
C)Lysosome
D)Mitochondria
E)Plasma membrane
A)Endoplasmic reticulum
B)Extracellular space
C)Lysosome
D)Mitochondria
E)Plasma membrane

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A 9-month-old boy is brought to the clinic for a routine follow-up. His mother is concerned because the patient is not yet able to sit up unsupported. He was born at term and has had muscle weakness since birth. Vital signs are normal. The patient is alert but has diminished tone. Examination shows a prominent forehead with a depressed nasal bridge. Eye examination shows epicanthal folds. Analysis of lysosomal acid hydrolases shows an increased concentration within the serum and a decreased level within the cultured skin fibroblast cells. This patient most likely has a defect in which of the following steps of enzyme production?
A)DNA methylation
B)Posttranslational modification
C)Protein folding
D)Splicing
E)Translation
A)DNA methylation
B)Posttranslational modification
C)Protein folding
D)Splicing
E)Translation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
An autopsy is being performed on a 4-year-old boy who recently died from a myocardial infarction. The child had a history of intellectual disability. Autopsy shows a prominent forehead and broad nose. There is a diffuse haze over the corneas bilaterally. The heart, liver, and spleen are enlarged. Sampling of the coronary arteries is most likely to reveal intimal accumulation of which of the following substances?
A)Cholesterol
B)Glucocerebroside
C)Glycogen
D)Heparan sulfate
E)Sphingomyelin
A)Cholesterol
B)Glucocerebroside
C)Glycogen
D)Heparan sulfate
E)Sphingomyelin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
An autopsy is being performed on a 4-year-old boy who recently died from a myocardial infarction. The child had a history of intellectual disability. Autopsy shows a prominent forehead and broad nose. There is a diffuse haze over the corneas bilaterally. The heart, liver, and spleen are enlarged. Sampling of the coronary arteries is most likely to reveal intimal accumulation of which of the following substances?
A)Cholesterol
B)Glucocerebroside
C)Glycogen
D)Heparan sulfate
E)Sphingomyelin
A)Cholesterol
B)Glucocerebroside
C)Glycogen
D)Heparan sulfate
E)Sphingomyelin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A 64-year-old man comes to the emergency department due to severe abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting. He has a history of hypertension, myocardial infarction, and systolic heart failure. His blood pressure is 100/60 mm Hg, pulse is 116/min and irregular, and respirations are 24/min. Examination shows a soft, mildly distended, and tender abdomen. Laboratory results are as follows:  CT scan of the abdomen reveals distal ileal wall thickening and lack of enhancement with intravenous contrast. Decreased activity of which of the following enzymes best explains the acid-base disorder in this patient?
CT scan of the abdomen reveals distal ileal wall thickening and lack of enhancement with intravenous contrast. Decreased activity of which of the following enzymes best explains the acid-base disorder in this patient?
A)Enolase
B)Lactate dehydrogenase
C)Pyruvate carboxylase
D)Pyruvate dehydrogenase
E)Pyruvate kinase
 CT scan of the abdomen reveals distal ileal wall thickening and lack of enhancement with intravenous contrast. Decreased activity of which of the following enzymes best explains the acid-base disorder in this patient?
CT scan of the abdomen reveals distal ileal wall thickening and lack of enhancement with intravenous contrast. Decreased activity of which of the following enzymes best explains the acid-base disorder in this patient?A)Enolase
B)Lactate dehydrogenase
C)Pyruvate carboxylase
D)Pyruvate dehydrogenase
E)Pyruvate kinase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
A 13-year-old boy is brought to the office due to gait instability and pruritic skin rash for the past several weeks. His mother reports that he has also been irritable and had loose stools during this time. The patient's childhood development has been unremarkable except for several episodes of similar skin rash that resolved spontaneously. Examination shows scaly, erythematous skin lesions in sun-exposed areas and cerebellar ataxia. Laboratory evaluation shows increased levels of neutral amino acids in the urine. This patient's symptoms would most likely respond to which of the following supplements?
A)Ascorbate
B)Folic acid
C)Niacin
D)Pyridoxine
E)Riboflavin
F)Thiamine
G)Tocopherol
A)Ascorbate
B)Folic acid
C)Niacin
D)Pyridoxine
E)Riboflavin
F)Thiamine
G)Tocopherol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A 55-year-old man is brought to the emergency department for abdominal pain associated with watery diarrhea. His symptoms have been progressive over the last month. He says that he is depressed and often has difficulty remembering things. The patient has a 20-year history of alcohol use disorder. On examination, he appears disheveled. A pigmented scaly skin rash is present in the malar distribution of his face, neck, and back of his hands. The rash has been present for several months and worsens on exposure to sunlight. It is determined that the patient's symptoms are secondary to lack of a specific nutrient. Activity of which of the following enzymes is most likely decreased in the patient as a result of this deficiency?
A)Citrate synthase
B)Hexokinase
C)Isocitrate dehydrogenase
D)Phosphoglycerate kinase
E)Succinate dehydrogenase
A)Citrate synthase
B)Hexokinase
C)Isocitrate dehydrogenase
D)Phosphoglycerate kinase
E)Succinate dehydrogenase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
An 8-day-old neonate born to a 25-year-old woman is brought to the office due to progressive lethargy, vomiting, and poor feeding. The mother reports an uneventful pregnancy and perinatal course. She exclusively breastfeeds the infant and has no medical problems in any of her other children. On examination, the infant is somnolent and dehydrated with decreased muscle tone. Laboratory studies reveal metabolic acidosis with an elevated anion gap, ketosis, and hypoglycemia. Further evaluation reveals a markedly elevated propionic acid level due to defective conversion of propionyl-CoA to methylmalonyl-CoA. This patient is most likely unable to use which of the following amino acids for energy production?
A)Alanine
B)Aspartate
C)Glutamate
D)Lysine
E)Phenylalanine
F)Valine
A)Alanine
B)Aspartate
C)Glutamate
D)Lysine
E)Phenylalanine
F)Valine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
A 3-year-old boy who recently immigrated to the United States is brought to the physician by his parents because he has not yet begun to walk or speak. Assessment of his developmental milestones shows severe intellectual disability. He dies 6 months later from refractory seizures resulting in respiratory failure. Autopsy shows pallor of the substantia nigra, locus ceruleus, and vagal nucleus dorsalis. The underlying condition responsible for this patient's death is most likely caused by a deficiency of which of the following enzymes?
A)Branched-chain ketoacid dehydrogenase
B)Dopamine hydroxylase
C)Homogentisic acid oxidase
D)Phenylalanine hydroxylase
E)Tyrosinase
A)Branched-chain ketoacid dehydrogenase
B)Dopamine hydroxylase
C)Homogentisic acid oxidase
D)Phenylalanine hydroxylase
E)Tyrosinase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
A 4-month-old boy is brought to the office for his first visit since arriving in the United States. The patient was recently adopted, and his adoptive mother says the boy is tremulous compared to her biological children. Over the past week, the boy has also had episodes of upward eye deviation and bilateral arm and leg shaking for approximately 2 minutes at a time. Biological family history is not available. His temperature is 36.7 C (98.1 F), blood pressure is 90/40 mm Hg, pulse is 120/min, and respirations are 30/min. Examination shows a fair-skinned infant with blue eyes and a musty body odor. Which of the following amino acids is most likely essential in this patient?
A)Cysteine
B)Isoleucine
C)Leucine
D)Phenylalanine
E)Tyrosine
F)Valine
A)Cysteine
B)Isoleucine
C)Leucine
D)Phenylalanine
E)Tyrosine
F)Valine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
A 5-month-old boy is brought by his parent for follow up. He was diagnosed with hyperphenylalaninemia by newborn screening on day one of age. He was placed on a special phenylalanine-restricted diet with tyrosine supplementation. laboratory test results indicate that the infant has a normal serum phenylalanine level. Careful examination, however, reveals some neurological abnormalities, including axial hypotonia and microcephaly. Further workup is notable for elevated prolactin, and his physician suspects a cofactor deficiency. Which of the following enzymes is most likely deficient in this patient?
A)Dihydrobiopterin reductase
B)Dopamine Beta-hydroxylase
C)Phenylalanine hydroxylase
D)Phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase
E)Tyrosinase
A)Dihydrobiopterin reductase
B)Dopamine Beta-hydroxylase
C)Phenylalanine hydroxylase
D)Phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase
E)Tyrosinase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
A 33-year-old man comes to the office for a health checkup. He has no prior medical problems and does not take any medications. The patient works as a fitness trainer and lifts weights recreationally. He has been consuming carbohydrate-rich food prior to his weightlifting sessions and claims that it increases muscle strength. A literature review shows that the rate of glycogenolysis within myocytes increases several hundredfold during active skeletal muscle contraction. Which of the following substances is most likely responsible for increasing the reaction rate during active contraction?
A)ATP
B)Ca2+
C)cAMP
D)Glucose-6-phosphate
E)Lactate
A)ATP
B)Ca2+
C)cAMP
D)Glucose-6-phosphate
E)Lactate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
A dermatology researcher is studying the role of different amino acids in wound healing. She cultures mature dermal fibroblasts in growth media. After several days, the fibroblasts begin synthesizing polypeptide chains that assemble into triple helical structures, followed by fibrils. The fibrillar proteins are hydrolyzed and separated into their constituent amino acids via paper chromatography. Which of the following amino acids is most likely to be found in highest quantity in these proteins?
A)Alanine
B)Cysteine
C)Glycine
D)Leucine
E)Lysine
F)Proline
A)Alanine
B)Cysteine
C)Glycine
D)Leucine
E)Lysine
F)Proline

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
A pharmaceutical researcher is studying a target protein involved in the signal transduction and cellular response to TSH. The protein is isolated and purified from thyroid follicular cells. Further analysis reveals that the protein contains multiple alpha-helical regions. Each of these regions is composed of approximately 20 amino acid residues consisting primarily of valine, alanine, and isoleucine. This particular region of the protein most likely performs which of the following functions?
A)Anchoring to the cell membrane
B)Binding to an extracellular ligand
C)Binding to intranuclear DNA
D)Interacting with metal ions in transporting proteins
E)Phosphorylating tyrosine residues
A)Anchoring to the cell membrane
B)Binding to an extracellular ligand
C)Binding to intranuclear DNA
D)Interacting with metal ions in transporting proteins
E)Phosphorylating tyrosine residues

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Biologists investigating the morphologic changes associated with reversible cellular injury perform a procedure on anesthetized mice to assess the effects of transient hepatic ischemia. During the experiment, they clamp the hepatic artery and obtain liver biopsy samples at varying intervals. The samples are then examined by electron microscopy. Cells that are exposed to longer ischemic periods are found to have reduced numbers of ribosomes attached to the endoplasmic reticulum. This structural change is most likely to impair which of the following cellular functions?
A)ATP production
B)Drug detoxification
C)Synthesis of cell membrane proteins
D)Synthesis of cytosolic proteins
E)Synthesis of steroid hormones
A)ATP production
B)Drug detoxification
C)Synthesis of cell membrane proteins
D)Synthesis of cytosolic proteins
E)Synthesis of steroid hormones

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Biologists investigating the morphologic changes associated with reversible cellular injury perform a procedure on anesthetized mice to assess the effects of transient hepatic ischemia. During the experiment, they clamp the hepatic artery and obtain liver biopsy samples at varying intervals. The samples are then examined by electron microscopy. Cells that are exposed to longer ischemic periods are found to have reduced numbers of ribosomes attached to the endoplasmic reticulum. This structural change is most likely to impair which of the following cellular functions?
A)ATP production
B)Drug detoxification
C)Synthesis of cell membrane proteins
D)Synthesis of cytosolic proteins
E)Synthesis of steroid hormones
A)ATP production
B)Drug detoxification
C)Synthesis of cell membrane proteins
D)Synthesis of cytosolic proteins
E)Synthesis of steroid hormones

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
A 13-month-old boy is evaluated for failure to thrive and delayed physical and mental development. His mother reports that at 12 months he could barely lift his head and had difficulty sitting unsupported. The toddler has not started babbling or forming words. He is at the 10th percentile for height and 5th percentile for weight. Laboratory results show Megaloblastic anemia and normal ammonia level. Urine specimens reveal increase orotic acid . Supplementation with which of the following substances would most likely benefit this patient?
A)Ascorbic acid
B)Folic acid
C)Guanine
D)Iron
E)Pyridoxine
F)Uridine
A)Ascorbic acid
B)Folic acid
C)Guanine
D)Iron
E)Pyridoxine
F)Uridine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
A research scientist develops an agent that specifically blocks the interaction of inositol triphosphate with its intracellular receptor. A study is then performed in which vascular smooth muscle cells are divided into 2 groups: an experimental group treated with the receptor blocker and an untreated control group. Both groups are exposed to phenylephrine. Compared to the control cells, decreased activity of which of the following enzymes is most likely to be observed in the experimental cells?
A)Adenylate cyclase
B)Lipoxygenase
C)Phosphodiesterase
D)Phospholipase C
E)Protein kinase C
A)Adenylate cyclase
B)Lipoxygenase
C)Phosphodiesterase
D)Phospholipase C
E)Protein kinase C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
A biologist is studying signal transduction apply an agent to human cells that activates G-protein- dependent phospholipase C. Which of the following intracellular substances is most likely to increase immediately after exposure to this agent?
A)Ca2+
B)cAMP
C)cGMP
D)Cl-
E)mRNA
F)NO
A)Ca2+
B)cAMP
C)cGMP
D)Cl-
E)mRNA
F)NO

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
An 8-month-old boy is evaluated for developmental delay, failure to thrive, and episodic seizures. Physical examination shows ophthalmoplegia and hypotonia. Laboratory studies reveal an elevated serum lactate level. Further histochemical studies show severely reduced pyruvate dehydrogenase enzyme activity in both freshly isolated peripheral blood lymphocytes and cultured fibroblasts. Increasing which of the following substances in his diet is most likely to help this patient generate energy without further elevating lactate levels?
A)Alanine
B)Asparagine
C)Galactose
D)Glycerol
E)Lysine
F)Serine
A)Alanine
B)Asparagine
C)Galactose
D)Glycerol
E)Lysine
F)Serine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
As part of an experiment, healthy volunteers undergo a 12-hour fast and then drink a solution containing radiolabeled alanine. Consecutive blood samples are drawn every 15 minutes for the next 3 hours. Initial blood samples detect the radiolabeled alanine, but analysis of later samples shows that the radiotracer is present in blood primarily in the form of glucose. Before alanine can be converted to glucose, its amino group is transferred to which of the following?
A)alpha-Ketoglutarate
B)L-citrulline
C)Malate
D)Citrate
E)Oxaloacetate
A)alpha-Ketoglutarate
B)L-citrulline
C)Malate
D)Citrate
E)Oxaloacetate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
A 40-year-old homeless man comes to the emergency department due to a "pins-and-needles" sensation in his legs. He also has painful lesions on his lips and corners of his mouth. He has had no loss of consciousness, nausea, vomiting, or diplopia. The patient drinks alcohol heavily on a daily basis and has a history of intravenous heroin use. On physical examination, he appears unkempt and ill appearing. Temperature is 36.8 C (98.2 F), blood pressure is 146/90 mm Hg, and pulse is 106/min. He has glossitis and angular stomatitis. Abdominal examination reveals hepatomegaly. Laboratory evaluation shows very low urinary riboflavin excretion. Activity of which of the following enzymes is most likely directly impaired in this patient?
A)Fumarase
B)Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase
C)HMG-CoA reductase
D)Isocitrate dehydrogenase
E)Malate dehydrogenase
F)Succinate dehydrogenase
G)Succinate thiokinase
A)Fumarase
B)Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase
C)HMG-CoA reductase
D)Isocitrate dehydrogenase
E)Malate dehydrogenase
F)Succinate dehydrogenase
G)Succinate thiokinase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
A 40-year-old woman is enrolled in a research study. She has a 10-year history of Parkinson's disease with resting tremor, bradykinesia, and cogwheel rigidity . One of her siblings recently started having similar symptoms. Genetic analysis is performed on the patient and her affected sibling. The results show a loss-of-function mutation in a gene that leads to an accumulation of misfolded proteins. Which of the following biochemical processes is most likely defective in this patient?
A)Acetylation
B)Gamma-carboxylation
C)Glucuronidation
D)Phosphorylation
E)Ubiquitination
A)Acetylation
B)Gamma-carboxylation
C)Glucuronidation
D)Phosphorylation
E)Ubiquitination

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
A 3-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department due to altered mental status with fever. He had multiple episodes of emesis this morning, and his mother was unable to wake him from his afternoon nap. The boy has had mild rhinorrhea and fever for the past 3 days. Since the newborn period, the parents say that the patient has had multiple illnesses characterized by vomiting and sleepiness. Prior laboratory testing revealed increased blood ammonia levels during these episodes and markedly increased orotic acid excretion in the urine. Physical examination shows a tachypneic boy who is unresponsive to all stimuli. Which of the following enzymes is most likely to be deficient in this patient?
A)Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I
B)Hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase
C)N-acetylglutamate synthetase
D)Ornithine transcarbamylase
E)Uridine monophosphate synthetase
A)Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I
B)Hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase
C)N-acetylglutamate synthetase
D)Ornithine transcarbamylase
E)Uridine monophosphate synthetase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
A 5-day-old boy born to a 24-year-old woman is brought to the office for evaluation of poor feeding and vomiting. The pregnancy was uneventful and the mother had a normal delivery. Family history is noncontributory. The patient's temperature is 37.2 C (99 F), blood pressure is 60/30 mm Hg, pulse is 110/min, and respirations are 56/min. Physical examination reveals a lethargic newborn with exaggerated deep tendon reflexes and clonus. Further investigation reveals that the patient has an inherited condition that results in impaired transport of ornithine from the cytosol to the mitochondria. Nutritional restriction of which of the following substances can improve this patient's condition?
A)Branched-chain amino acids
B)Fructose
C)Galactose
D)Medium-chain triglycerides
E)Phenylalanine
F)Proteins
G)Pyridoxine
A)Branched-chain amino acids
B)Fructose
C)Galactose
D)Medium-chain triglycerides
E)Phenylalanine
F)Proteins
G)Pyridoxine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
A 3-year-old boy is brought to the office due to abnormal motor development. He was born at 40 weeks gestation and had an unremarkable perinatal course. The boy developed normally during the first year of life. However, for the past 2 years, he has had progressive bilateral leg stiffness and abnormal involuntary movements. His cognitive and motor development is also delayed. There is no significant family history of neurological or muscular disorders. The patient's height, weight, and head circumference are below the 3rd percentile. Examination shows bilateral spastic paresis of his lower extremities and frequent choreoathetoid movements. Comprehensive laboratory testing reveals significantly elevated arginine levels in plasma and cerebrospinal fluid. The deficient enzyme in this patient is normally involved in the production of which of the following?
A)Gamma-aminobutyric acid
B)Glutamine
C)Homocysteine
D)Orotic acid
E)Serotonin
F)Urea
A)Gamma-aminobutyric acid
B)Glutamine
C)Homocysteine
D)Orotic acid
E)Serotonin
F)Urea

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
A pharmacist is studying the mechanism of action of verapamil on the muscle tissue in the pathients who have a hypertension. He found that verapamil affects cardiac contractility but has a minimal effect on skeletal muscle. Which of the following properties of skeletal muscle is responsible for its resistance to the medication?
A)Calmodulin-independent excitation-contraction coupling
B)Decreased troponin affinity to intracellular calcium
C)Elaborate T-tubular system
D)Lack of internal automaticity
E)Little dependence on extracellular calcium influ
A)Calmodulin-independent excitation-contraction coupling
B)Decreased troponin affinity to intracellular calcium
C)Elaborate T-tubular system
D)Lack of internal automaticity
E)Little dependence on extracellular calcium influ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
A 70-year-old man comes to the office due to four weeks history of increase dyspnea, generalized weakness, lethargy, and palpitations. He also reports tingling and numbness in both lower limbs. His daughter, who is visiting from another state, adds that since his wife's death a year ago, the patient has not been taking care of himself. Blood pressure is 105/50 mm Hg and pulse is 104/min. Cardiovascular examination shows a displaced apical impulse at the sixth intercostal space, a third heart sound, and high-volume, collapsing carotid pulses. Bilateral basal crackles, 2+ bilateral pedal edema, and mild hepatomegaly are also present. Neurologic examination shows decreased light touch and vibration sense in the feet, with decreased knee and ankle reflexes bilaterally. Laboratory evaluation shows normal blood counts. Deficiency of which of the following nutrients is most likely responsible for this patient's symptoms?
A)Ascorbic acid
B)Cobalamin
C)Niacin
D)Pyridoxine
E)Retinol
F)Riboflavin
G)Thiamine
A)Ascorbic acid
B)Cobalamin
C)Niacin
D)Pyridoxine
E)Retinol
F)Riboflavin
G)Thiamine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
A 3-year-old boy is brought to the office by his parents due to a concern of abnormal urine color. After he urinated in the toilet last night, his parents forgot to flush the toilet and noticed that the boy's urine turned black overnight. The child has no significant past medical history and takes no medications. He has no abnormal growth and developmental milestone. Examination shows a well-nourished child with no swelling or tenderness of any joints. Urinalysis results are as follows:  Which of the following conversion pathways is most likely deficient in this patient?
Which of the following conversion pathways is most likely deficient in this patient?
A)Leucine to acetoacetate
B)Phenylalanine to tyrosine
C)Serine to cysteine
D)Tyrosine to fumarate
E)Valine to glutamic acid
 Which of the following conversion pathways is most likely deficient in this patient?
Which of the following conversion pathways is most likely deficient in this patient?A)Leucine to acetoacetate
B)Phenylalanine to tyrosine
C)Serine to cysteine
D)Tyrosine to fumarate
E)Valine to glutamic acid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
A 56-year-old man is evaluated for progressive visual impairment. The patient works as part of the grounds crew at an airport, and says he has trouble identifying aircraft at a distance and with filling out paperwork at the end of his shift. His medical history includes poorly controlled diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and gout. A year ago, the patient underwent an uncomplicated repair of a right inguinal hernia. Physical examination shows bilateral clouding of the lens. The remainder of the examination is unremarkable. Which of the following metabolic conversions is most likely contributing to this patient's current condition?
A)Galactitol to tagatose
B)Galactose to galactitol
C)Glucose to sorbitol
D)Glucose-6-phosphate to 6-phosphogluconolactone
E)Pyruvate to lactate
A)Galactitol to tagatose
B)Galactose to galactitol
C)Glucose to sorbitol
D)Glucose-6-phosphate to 6-phosphogluconolactone
E)Pyruvate to lactate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



