Deck 8: Immunology
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/147
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 8: Immunology
1
A 7-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department by his parents for arthralgias. He had a cough and runny nose last week but otherwise has been in good health. Temperature is 37 C (98.6 F), blood pressure is 95/65 mm Hg, pulse is 92/min, and respirations are 20/min. Physical examination shows raised, red-purple papules, some of which have coalesced, over the patient's buttocks and thighs. Auscultation of the lungs and heart is normal. The abdomen is soft with normal bowel sounds. The knees are tender but do not appear warm or swollen. Urinalysis results are as follows:  Which of the following mechanisms is the most likely underlying cause of this patient's renal findings?
Which of the following mechanisms is the most likely underlying cause of this patient's renal findings?
A)Autoantibodies against podocyte antigens
B)Autoantibodies to host cell basement membranes
C)Immune complex deposition in glomerular mesangium
D)Thrombosis of glomerular capillaries
E)T-lymphocyte cytotoxicity against virally-infected mesangial cells
 Which of the following mechanisms is the most likely underlying cause of this patient's renal findings?
Which of the following mechanisms is the most likely underlying cause of this patient's renal findings?A)Autoantibodies against podocyte antigens
B)Autoantibodies to host cell basement membranes
C)Immune complex deposition in glomerular mesangium
D)Thrombosis of glomerular capillaries
E)T-lymphocyte cytotoxicity against virally-infected mesangial cells
Immune complex deposition in glomerular mesangium
2
A 7-year-old boy is brought to the clinic by his parents after developing red urine earlier in the day. The patient has asthma, allergic rhinitis, and atopic dermatitis. He was recently treated for a skin infection. Blood pressure is 140/90 mm Hg. On physical examination, there is periorbital edema as well as pitting edema on both feet. Laboratory results are as follows:  Which of the following is most likely responsible for this patient's renal injury?
Which of the following is most likely responsible for this patient's renal injury?
A)CD8+ T lymphocytes
B)Histamine release
C)IgG autoantibodies
D)IgG immune complexes
E)Macrophages
 Which of the following is most likely responsible for this patient's renal injury?
Which of the following is most likely responsible for this patient's renal injury?A)CD8+ T lymphocytes
B)Histamine release
C)IgG autoantibodies
D)IgG immune complexes
E)Macrophages
IgG immune complexes
3
A 28-year-old man comes to the office with a 2-month history of dull low back pain and morning stiffness. The pain had an insidious onset, and the patient does not recall any recent trauma. He attempted treatment with acetaminophen and spinal manipulation, which did not provide relief. The patient has usually slept on his back but now must lie on his side to fall asleep easily. Past medical history is unremarkable. Vital signs are normal. Physical examination shows limited anterior flexion of the spine. There is no swelling or warmth of any peripheral joints. X-rays reveal narrowing of the sacroiliac joints. Which of the following is most strongly associated with this patient's disease?
A)A specific human leukocyte antigen class I serotype
B)A specific human leukocyte antigen class II serotype
C)Auto-reactive immunoglobulin M antibodies
D)Deficient complement component
E)Selective immunoglobulin deficiency
A)A specific human leukocyte antigen class I serotype
B)A specific human leukocyte antigen class II serotype
C)Auto-reactive immunoglobulin M antibodies
D)Deficient complement component
E)Selective immunoglobulin deficiency
A specific human leukocyte antigen class I serotype
4
A 22-year-old woman comes to the office because of a 6-month history of increasing neck and low back pain that is most severe in the morning. Her pain improves as the day passes. The patient has no history of trauma, rashes, or urinary symptoms. Vital signs are within normal limits. Examination shows tenderness over the lumbosacral area and at the insertion site of the Achilles tendon. Forward flexion is reduced. This patient's symptoms are most likely attributable to upregulation of which of the following cytokines?
A)IL-2 and interferon gamma
B)IL-4 and interferon alpha
C)IL-5 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha
D)IL-10 and transforming growth factor-beta
E)IL-17 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha
A)IL-2 and interferon gamma
B)IL-4 and interferon alpha
C)IL-5 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha
D)IL-10 and transforming growth factor-beta
E)IL-17 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A 38-year-old woman comes to the office due to abdominal pain. For the last 2-3 weeks, she has had increasingly severe abdominal pain associated with watery diarrhea. The patient has a history of Crohn disease treated for the last year with adalimumab, which has controlled the symptoms until now. Vital signs are normal except for a temperature of 37.8 C (100 F). Examination shows moderate tenderness in the right lower quadrant with no peritoneal signs. Laboratory results show an undetectable trough adalimumab level. Which of the following is the most likely explanation for this patient's worsening symptoms?
A)Development of antidrug antibodies
B)Formation of insoluble complexes at the injection site
C)Increased enterohepatic drug recirculation
D)Increased renal drug elimination
E)Induction of cytochrome P-450 enzymes
A)Development of antidrug antibodies
B)Formation of insoluble complexes at the injection site
C)Increased enterohepatic drug recirculation
D)Increased renal drug elimination
E)Induction of cytochrome P-450 enzymes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A 2-year-old boy is brought to the office due to recurrent infections. He was born at term after an uncomplicated pregnancy. His mother states, "My boy is always sick with something and is constantly on antibiotics." The patient has had multiple episodes of otitis media, skin infections, and pneumonia. Incision and drainage of his skin infections revealed Staphylococcus aureus on bacterial culture but no purulence. The infections usually resolve with prolonged antibiotic courses. Laboratory testing reveals absent CD18 antigens on the surface of leukocytes. This patient's underlying condition is most likely associated with which of the following?
A)Infection following live-virus vaccines
B)Infection with Neisseria
C)Persistent leukocytosis
D)Small or absent lymph nodes
E)Thrombocytopenia and eczema
A)Infection following live-virus vaccines
B)Infection with Neisseria
C)Persistent leukocytosis
D)Small or absent lymph nodes
E)Thrombocytopenia and eczema

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A 45-year-old woman comes to the office due to a long history of joint pain, swelling, and stiffness. She recently immigrated to the United States and had little access to medical care in her original country. On physical examination, her proximal interphalangeal and metacarpophalangeal joints are tender and swollen bilaterally, and her fingers appear significantly deformed. Subcutaneous nodules are palpated near the elbow. Laboratory studies are obtained to confirm the diagnosis. This patient's serum is most likely to contain IgM antibodies against which of the following substances?
A)Centromeres
B)Double-stranded DNA
C)Fc portion of human IgG
D)Mitochondrial extract
E)Nuclear basic proteins
F)Phospholipids
G)Sheep erythrocytes
A)Centromeres
B)Double-stranded DNA
C)Fc portion of human IgG
D)Mitochondrial extract
E)Nuclear basic proteins
F)Phospholipids
G)Sheep erythrocytes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A 2-month-old girl is brought to the office for a well-child visit. The patient was born at term with no complications. She is exclusively formula fed and gaining weight well. Examination is unremarkable today. The mother is informed that several vaccinations are due at this visit. She becomes upset and mentions that her older son, who did follow a standard vaccine schedule, had a "bad reaction" to his last set of shots and had a cough for weeks. She wants to defer immunizations for her daughter at this time. The mother says, "I know you won't agree with me, but I have been reading that these reactions are actually very harmful to the immune system." Which of the following is the most appropriate response?
A)"I understand your concern, and I believe that ensuring your children's health and safety is our shared goal."
B)"I want to reassure you that immunizations are safe, and we should proceed with vaccination today."
C)"I would like to provide you with a list of resources on vaccine safety so you can make the best decision for your child."
D)"I'm sorry that this is a stressful topic. Let's talk about this again at the next visit."
E)"This must be hard. I know you are concerned about vaccine side effects, but the risk of vaccine-preventable disease is far greater."
A)"I understand your concern, and I believe that ensuring your children's health and safety is our shared goal."
B)"I want to reassure you that immunizations are safe, and we should proceed with vaccination today."
C)"I would like to provide you with a list of resources on vaccine safety so you can make the best decision for your child."
D)"I'm sorry that this is a stressful topic. Let's talk about this again at the next visit."
E)"This must be hard. I know you are concerned about vaccine side effects, but the risk of vaccine-preventable disease is far greater."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A 34-year-old man is admitted to the intensive care unit due to fever, chills, shortness of breath, and altered mental status. His symptoms began 3 days ago and have progressively worsened over the last 24 hours. His past medical history is significant for a motor vehicle accident 2 years ago in which he sustained blunt abdominal trauma and required emergency laparotomy due to internal bleeding. His blood pressure is 81/44 mm Hg and pulse is 122/min. He is started on broad-spectrum antibiotics, intravenous fluids, and vasopressors. His condition continues to deteriorate and he dies in the hospital several hours later despite extensive resuscitation efforts. Blood cultures obtained on admission grow Streptococcus pneumoniae. Impairment of which of the following mechanisms most likely contributed to the severity of this patient's infection?
A)Complement production
B)Immediate hypersensitivity
C)Intracellular killing
D)Systemic bacterial clearance
E)Type I interferon release
A)Complement production
B)Immediate hypersensitivity
C)Intracellular killing
D)Systemic bacterial clearance
E)Type I interferon release

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A 58-year-old asymptomatic woman comes to the office for a health checkup prior to starting volunteer work at a hospital. She has a history of hypothyroidism and takes levothyroxine. She does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs. Her examination findings are unremarkable. During a laboratory test, her white blood cells are incubated with mycobacterial antigens. Compared to the control, a large amount of interferon-gamma is detected in her blood sample. Which of the following cell types is most directly responsible for this finding?
A)B lymphocytes
B)Basophils
C)Eosinophils
D)Monocytes
E)Neutrophils
F)T lymphocytes
A)B lymphocytes
B)Basophils
C)Eosinophils
D)Monocytes
E)Neutrophils
F)T lymphocytes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A 45-year-old woman comes to the office due to several weeks of nonproductive cough and dyspnea. She underwent lung transplantation 7 months ago because she has a history of primary pulmonary hypertension. She takes her medications regularly. Pulmonary function testing demonstrates a forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1), 67% of her best posttransplant FEV1. Her forced vital capacity remains largely unchanged. A lung biopsy shows areas of total fibrotic obstruction in the terminal bronchioles. This patient's condition is most likely caused by which of the following?
A)Acute transplant rejection
B)Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
C)Chronic transplant rejection
D)Ischemia-reperfusion injury
E)Opportunistic infection
F)Recurrence of pulmonary hypertension
A)Acute transplant rejection
B)Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
C)Chronic transplant rejection
D)Ischemia-reperfusion injury
E)Opportunistic infection
F)Recurrence of pulmonary hypertension

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A 44-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a 6-month history of fatigue, intermittent fever, a 4.0-kg (9-lb) weight loss, and a progressive, nonproductive cough. She does not smoke. Physical examination shows mild wheezing over bilateral lung fields. Chest x-ray demonstrates enlarged hilar lymph nodes, and laboratory testing reveals an elevated ACE level. Purified protein derivative testing is negative. A bronchoscopy is scheduled to help determine the diagnosis. Which of the following is most likely to be the predominant cell type in this patient's bronchoalveolar lavage fluid?
A)CD4+ lymphocytes
B)CD8+ lymphocytes
C)CD22+ lymphocytes
D)Eosinophils
E)Mast cells
F)Neutrophils
A)CD4+ lymphocytes
B)CD8+ lymphocytes
C)CD22+ lymphocytes
D)Eosinophils
E)Mast cells
F)Neutrophils

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A 68-year-old man with bilateral percutaneous nephrostomy tubes is brought to the emergency department by his wife because of confusion. She adds that he complained of right flank pain yesterday. He has prostate cancer and receives leuprolide injections every 3 months. He is oriented to person but not to place or time. Temperature is 38.9 C (102 F), blood pressure is 80/50 mm Hg, pulse is 130/min, and respirations are 20/min. The right nephrostomy bag contains a small amount of cloudy urine; the left nephrostomy bag contains clear urine. Laboratory results are as follows: 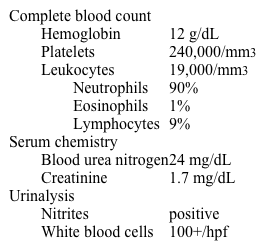 Which of the following is most likely decreased in this patient?
Which of the following is most likely decreased in this patient?
A)C-reactive protein
B)Endotoxin
C)IL-1
D)Nitric oxide
E)Vasopressin
 Which of the following is most likely decreased in this patient?
Which of the following is most likely decreased in this patient?A)C-reactive protein
B)Endotoxin
C)IL-1
D)Nitric oxide
E)Vasopressin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A 5-year-old boy is brought to the physician by his mother because of a generalized pruritic rash for 2 weeks. The itchiness often causes him to wake up at night. His father has a history of asthma. His immunizations are up-to-date. He is at the 75th percentile for length and the 70th percentile for weight. Examination shows dry and scaly patches on the face and extensor surfaces of the extremities. The groin is spared. First-line therapy for this patient's condition works by which of the following mechanisms of action?
A)Blockade of leukotriene receptors in inflamed tissue
B)Increasing the number of resident dendritic cells
C)Induction of keratinocyte apoptosis
D)Inhibition of phospholipase A2 activity in cell membranes
E)Reduction of serum IgE levels
A)Blockade of leukotriene receptors in inflamed tissue
B)Increasing the number of resident dendritic cells
C)Induction of keratinocyte apoptosis
D)Inhibition of phospholipase A2 activity in cell membranes
E)Reduction of serum IgE levels

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A 32-year-old man comes to the clinic for follow-up due to Crohn disease. The patient was initially diagnosed 3 years ago and achieved disease remission following a course of high-dose glucocorticoids. He remained in remission until 2 months ago, when he experienced an acute flare of diarrhea and abdominal pain that required a brief hospitalization and another course of high-dose glucocorticoids. The patient completed a prescribed glucocorticoid taper earlier this week and says that his symptoms have returned to "about normal." Azathioprine maintenance therapy is started to help prevent future flares. Which of the following most accurately describes the expected effects of this new medication on immune function? 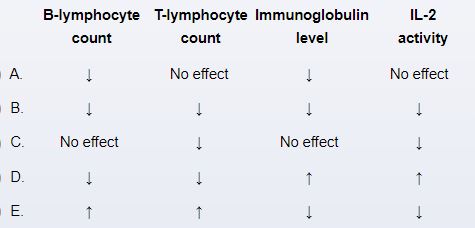


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A 21-year-old woman comes to the office due to recurrent episodes of self-limited, colicky abdominal pain. She also had an episode of facial swelling that resolved spontaneously. The patient has no other significant past medical history and takes no medications. Examination is unremarkable. Evaluation shows that her complement protein C1, even when not attached to an antigen-antibody complex, is excessively cleaving C2 and C4. Which of the following is most likely increased in this patient?
A)Antinuclear antibody titer
B)Antistreptolysin O titer
C)Bradykinin
D)Free hemoglobin
E)Renin
A)Antinuclear antibody titer
B)Antistreptolysin O titer
C)Bradykinin
D)Free hemoglobin
E)Renin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A 43-year-old man is hospitalized with recent-onset oliguria and a high serum creatinine level. He has been seen in clinic several times for an intranasal ulcer that has failed to heal. This patient's condition is most likely associated with antibodies against which of the following?
A)Glomerular basal membrane
B)Smooth muscle cells
C)Neutrophils
D)Erythrocytes
E)Platelets
F)Mitochondria
A)Glomerular basal membrane
B)Smooth muscle cells
C)Neutrophils
D)Erythrocytes
E)Platelets
F)Mitochondria

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
An 18-year-old woman comes to the emergency department for evaluation of a rash. The patient developed mild aches involving her knees and ankles 2 days ago. Before going to sleep last night, she noticed purplish spots around her right knee. Today, the rash involves both of the lower extremities. She has had no fever, weight loss, sore throat, abdominal pain, vomiting, or diarrhea. The patient has no chronic medical conditions and takes no medications. Temperature is 37 C (98.6 F), blood pressure is 146/90 mm Hg, pulse is 90/min, and respirations are 20/min. Cardiopulmonary examination is unremarkable. The patient has pain with passive range of motion of the knees and ankles. Skin examination is seen in the exhibit.Laboratory results are as follows:  Histologic examination of the rash is most likely to show which of the following?
Histologic examination of the rash is most likely to show which of the following?
A)Abundant intravascular fibrin without inflammatory cells
B)Obliterative endarteritis with lymphocytes and plasma cells
C)Perivascular necrotizing granulomas with eosinophilic infiltration
D)Small vessels damaged by perivascular neutrophil accumulation
E)Vessels with transmural granulomatous infiltration and fragmentation of elastic fibers
 Histologic examination of the rash is most likely to show which of the following?
Histologic examination of the rash is most likely to show which of the following?A)Abundant intravascular fibrin without inflammatory cells
B)Obliterative endarteritis with lymphocytes and plasma cells
C)Perivascular necrotizing granulomas with eosinophilic infiltration
D)Small vessels damaged by perivascular neutrophil accumulation
E)Vessels with transmural granulomatous infiltration and fragmentation of elastic fibers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A 24-year-old man comes to the urgent care clinic due to painful swelling in his left groin. The patient noticed the swelling 2 days ago, and it has progressively become more tender and painful. He has no chronic medical conditions, but he recently sustained a puncture wound to the sole of his left foot. Physical examination shows an enlarged, tender, and nonfluctuant left inguinal lymph node with erythematous overlying skin. There is a small puncture wound on the sole of the left foot, which expresses pus upon mild pressure. Which of the following histologic findings is most likely responsible for this patient's groin mass?
A)Atypical B-cell proliferation
B)Diffuse granulomatous reaction
C)Extensive lymph node necrosis
D)Marked paracortical cell expansion
E)Formation of multiple germinal centers
A)Atypical B-cell proliferation
B)Diffuse granulomatous reaction
C)Extensive lymph node necrosis
D)Marked paracortical cell expansion
E)Formation of multiple germinal centers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A 42-year-old woman comes to the emergency department due to worsening jaw pain over the past week. She is unable to chew solid foods on the left side because of severe throbbing pain. The patient has had several "tooth infections" over the last year despite meticulous oral hygiene. Physical examination shows facial edema over the left mandible. Multiple teeth have decay and gingival recession, and gentle tapping of the left second molar elicits pain. This patient's current disease process is most likely to develop secondary to which of the following underlying conditions?
A)Acromegaly
B)Crohn disease
C)Riboflavin deficiency
D)Selective IgA deficiency
E)Sjögren syndrome
A)Acromegaly
B)Crohn disease
C)Riboflavin deficiency
D)Selective IgA deficiency
E)Sjögren syndrome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A 42-year-old woman comes to the emergency department due to worsening jaw pain over the past week. She is unable to chew solid foods on the left side because of severe throbbing pain. The patient has had several "tooth infections" over the last year despite meticulous oral hygiene. Physical examination shows facial edema over the left mandible. Multiple teeth have decay and gingival recession, and gentle tapping of the left second molar elicits pain. This patient's current disease process is most likely to develop secondary to which of the following underlying conditions?
A)Acromegaly
B)Crohn disease
C)Riboflavin deficiency
D)Selective IgA deficiency
E)Sjögren syndrome
A)Acromegaly
B)Crohn disease
C)Riboflavin deficiency
D)Selective IgA deficiency
E)Sjögren syndrome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A 5-month-old boy is brought to the physician because of fever and a cough for 3 days. His mother reports that he has had multiple episodes of loose stools over the past 3 months. He has been treated for otitis media 4 times and bronchiolitis 3 times during the past 3 months. He was born at 37 weeks' gestation and the neonatal period was uncomplicated. He is at the 10th percentile for height and 3rd percentile for weight. His temperature is 38.3°C (100.9°F), pulse is 126/min, and respirations are 35/min. Examination shows an erythematous scaly rash over the trunk and extremities. There are white patches on the tongue and buccal mucosa that bleed when scraped.Auscultation of the lungs shows expiratory wheezing. Cardiac examination is within normal limits. Laboratory results are as follows:  Serum protein electrophoresis shows a very low gamma globulin level. Chest x-ray reveals an absent thymic shadow. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Serum protein electrophoresis shows a very low gamma globulin level. Chest x-ray reveals an absent thymic shadow. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A)Common variable immunodeficiency
B)DiGeorge syndrome
C)Severe combined immunodeficiency
D)Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome
E)X-linked agammaglobulinemia
 Serum protein electrophoresis shows a very low gamma globulin level. Chest x-ray reveals an absent thymic shadow. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Serum protein electrophoresis shows a very low gamma globulin level. Chest x-ray reveals an absent thymic shadow. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?A)Common variable immunodeficiency
B)DiGeorge syndrome
C)Severe combined immunodeficiency
D)Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome
E)X-linked agammaglobulinemia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A 2-year-old boy is brought to the physician by his mother for evaluation of recurrent infections and easy bruising. He has been hospitalized 3 times for severe skin and respiratory infections, which responded to treatment with antibiotics. Examination shows sparse silvery hair. The skin is hypopigmented and there are diffuse petechiae. Laboratory studies show a hemoglobin concentration of 8 g/dL, leukocyte count of 3000/mm3, and platelet count of 45,000/mm3. Peripheral blood smear is shown in the image below: 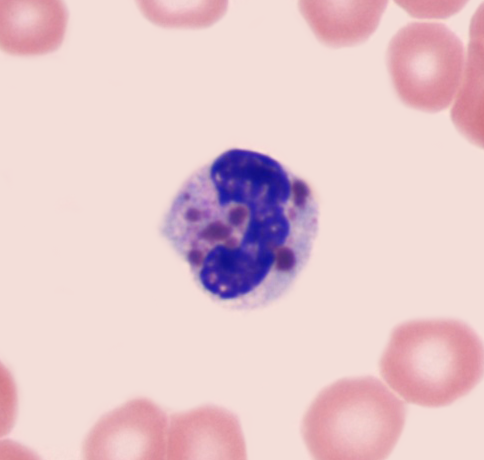 This patient most likely has which of the following disorders?
This patient most likely has which of the following disorders?
A)Ataxia telangiectasia
B)Chédiak-Higashi syndrome
C)Chronic granulomatous disease
D)Gaucher disease
E)Leukocyte adhesion deficiency
F)Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome
 This patient most likely has which of the following disorders?
This patient most likely has which of the following disorders?A)Ataxia telangiectasia
B)Chédiak-Higashi syndrome
C)Chronic granulomatous disease
D)Gaucher disease
E)Leukocyte adhesion deficiency
F)Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A 7-month-old boy is brought to the physician by his parents due to irritability and white patches in his mouth. His past medical history is significant forchronic diarrhea and failure to thrive. The child is small for his age and ill-appearing. He is found to have a low blood T-lymphocyte count and severely decreased serum immunoglobulin. After thorough evaluation, an experimental treatment is proposed to his parents. The therapy consists of infecting the patient's cells with a retroviral vector containing the gene for a protein that is deficient in this patient. Which of the following proteins is most likely coded by this gene?
A)Adenosine deaminase
B)Myeloperoxidase
C)NADPH oxidase
D)Reverse transcriptase
E)Xanthine oxidase
A)Adenosine deaminase
B)Myeloperoxidase
C)NADPH oxidase
D)Reverse transcriptase
E)Xanthine oxidase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A 7-month-old boy is brought to the physician by his parents due to irritability and white patches in his mouth. His past medical history is significant forchronic diarrhea and failure to thrive. The child is small for his age and ill-appearing. He is found to have a low blood T-lymphocyte count and severely decreased serum immunoglobulin. After thorough evaluation, an experimental treatment is proposed to his parents. The therapy consists of infecting the patient's cells with a retroviral vector containing the gene for a protein that is deficient in this patient. Which of the following proteins is most likely coded by this gene?
A)Adenosine deaminase
B)Myeloperoxidase
C)NADPH oxidase
D)Reverse transcriptase
E)Xanthine oxidase
A)Adenosine deaminase
B)Myeloperoxidase
C)NADPH oxidase
D)Reverse transcriptase
E)Xanthine oxidase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A 2-year-old boy is brought to the physician for the evaluation of fever, difficulty breathing, and coughing for the past week. In the past year, he has had four sinus infections, three upper respiratory tract infections, and an episode of severe bronchiolitis requiring hospitalization. is born with facial dysmorphia and a cleft palate. Further evaluation reveals a heart condition with a right-to-left shunt and the absence of a thymic shadow on x-ray. Examination of this patient's lymph nodes will most likely show poor development of which of the following structures?
A)Cortical follicles
B)Medullary sinuses
C)Medullary cords
D)Paracortex region
E)Subcapsular sinuses
A)Cortical follicles
B)Medullary sinuses
C)Medullary cords
D)Paracortex region
E)Subcapsular sinuses

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A 3-year-old boy is brought to the physician for the evaluation of recurrent skin lesions. The lesions first appeared at the age of 2 months and multiple treatment options have been attempted without success. He has also had several episodes of respiratory tract infections, enlarged lymph nodes, and recurrent fevers since birth. The patient's immunizations are up-to-date. He is at the 5th percentile for length and 10th percentile for weight. He appears ill. His temperature is 38°C (100.4°F), pulse is 100/min, and blood pressure is 100/60 mm Hg. Examination shows several raised, erythematous lesions of different sizes over the face, neck, groin, and extremities; some secrete pus. Cervical and axillary lymph nodes are enlarged bilaterally. This patient most likely has an increased risk of infection with which of the following organisms?
A)Burkholderia cepacia
B)Enterococcus faecalis
C)Giardia lamblia
D)Herpes simplex virus type 1
E)Streptococcus pyogenes
A)Burkholderia cepacia
B)Enterococcus faecalis
C)Giardia lamblia
D)Herpes simplex virus type 1
E)Streptococcus pyogenes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A 28-year-old woman, gravida 2 para 2, brings her healthy 6-day-old girl to the office for her first well-baby checkup. The infant was born full-term, with a birth weight of 4.2 kg (9.3 lb) and a length of 51 cm (20 in). She was discharged from the nursery with no concerns. Physical examination is normal. The infant's blood type is A negative, whereas the mother's is B negative. High circulating levels of anti-A antibodies are found in the mother's blood. Hemolysis did not occur in the infant because these maternal antibodies are most likely of which class?
A)IgA
B)IgD
C)IgE
D)IgG
E)IgM
A)IgA
B)IgD
C)IgE
D)IgG
E)IgM

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A 5-year-old boy is undergoing a lymphadenoctomy to treat a poorly draining lymph node abscess. He has a history of recurrent skin abscesses. Cultures from his abscess are growing Staphylococcus aureus, which is sensitive to the current antibiotic regimen, but the abscess has failed to improve. Evaluation of the patient's neutrophils by dihydrorhodamine flow cytometry shows an absence of fluorescence. This patient's condition is most likely due to impaired activity of which of the following enzymes?
A)Adenosine deaminase
B)Cytochrome c oxidase
C)Lysozyme
D)Myeloperoxidase
E)NADPH oxidase
A)Adenosine deaminase
B)Cytochrome c oxidase
C)Lysozyme
D)Myeloperoxidase
E)NADPH oxidase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A 44-year-old woman comes to the emergency department after waking up with facial swelling and with difficulties speaking and swallowing. She states that she does not have allergies or recently had insect bites. She has a 4-year history of hypertension and type 2 diabetes mellitus controlled with medication. Her pulse is 110/min, respirations are 20/min, and blood pressure is 140/90 mm Hg. Pulse oximetry on room air shows an oxygen saturation of 97%. On physical examination, she appears uncomfortable, with notable swelling of the lips and tongue. The remainder of the examination shows no abnormalities. Serum C4 levels are within normal limits. Which of the following is the most likely mechanism responsible for this patient's symptoms?
A)Bradykinin accumulation
B)Hereditary C1-esterase inhibitor deficiency
C)IgE-dependent mast cell degranulation
D)Increased renin secretion
E)Nonimmune mediated mast cell degranulation
A)Bradykinin accumulation
B)Hereditary C1-esterase inhibitor deficiency
C)IgE-dependent mast cell degranulation
D)Increased renin secretion
E)Nonimmune mediated mast cell degranulation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A mother of a 12-month boy is calling the office due to a concern of her son temperature after a he received the first dose of the subcutaneous measles-mumps-rubella vaccine. His temperature is 38 C (100.4 F) and has been irritable since the vaccination. He has had no prior vaccine-related adverse events. He has no known allergies. The immunization site is mildly red, swollen, and tender; there is no other skin rash. Which of the following cells and effector mechanisms is most likely involved in pathogenesis of this patient's current condition?
A)CD4+ T cells and CD40 ligand
B)CD8+ T cells and perforins
C)Dendritic cells and MHC II
D)Macrophages and IL-6
E)Plasma cells and IgM
A)CD4+ T cells and CD40 ligand
B)CD8+ T cells and perforins
C)Dendritic cells and MHC II
D)Macrophages and IL-6
E)Plasma cells and IgM

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A 75-year-old man is hospitalized due to respiratory distress. The patient developed fever, cough, and muscle aches 4 days prior to admission. He is otherwise healthy and has no chronic medical conditions. The patient has received all recommended vaccinations, including a yearly flu vaccine. Temperature is 39 C (102.2 F), blood pressure is 110/65 mm Hg, pulse is 115/min, and respirations are 29/min. Chest x-ray shows bilateral infiltrates. Reverse transcriptase PCR of a specimen from a nasopharyngeal swab reveals a strain of influenza A virus that was included in the seasonal trivalent flu vaccine. The patient lives with his 50-year-old son, who received the same vaccine but did not develop the infection. Which of the following factors most likely increased this patient's risk of vaccine failure compared with that of his son?
A)Decreased overall quality of antibodies
B)Decreased production of naive B lymphocytes
C)Diminished levels of memory T lymphocytes
D)Increased apoptosis induced by neutrophils
E)Increased phagocytosis by macrophages
A)Decreased overall quality of antibodies
B)Decreased production of naive B lymphocytes
C)Diminished levels of memory T lymphocytes
D)Increased apoptosis induced by neutrophils
E)Increased phagocytosis by macrophages

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A 5-year-old child is brought to the emergency department by his parents for right arm pain. The patient reports that he was playing hide and seek outside and felt a sharp pain on his arm while hiding in some thick bushes. His parents suspect that something had stung him. Physical examination shows an edematous and erythematous plaque with mild central pallor. A residual stinger, located central to the lesion, is readily extracted. The physical examination is otherwise not significant. Which of the following substances is most likely directly responsible for the skin findings observed in this patient?
A)C3b
B)IL-2
C)Histamine
D)Lysozyme
E)TNF-Alpha
A)C3b
B)IL-2
C)Histamine
D)Lysozyme
E)TNF-Alpha

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A 14-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department by his parents for joint pain following the acute onset of a diffuse, pruritic rash for the past 24 hours. A week ago, he was diagnosed with pharyngitis after returning home from summer camp and is currently taking antibiotics. There is no family history of serious illness. His temperature is 38.5°C (101.3°F), pulse is 90/min, and blood pressure is 110/70 mm Hg. Physical examination shows periorbital edema, generalized lymphadenopathy, and well-circumscribed, erythematous, confluent skin lesions of variable sizes up to several centimeters in width over his entire body. There is pain on passive movement of wrists and ankle joints bilaterally. Urine dipstick shows 1+ proteinuria. There is no hematuria. Which of the following findings is most likely to accompany this patient's condition?
A)Candida antigen anergy
B)Decreased serum C3 level
C)Increased serum IgE level
D)Low serum IgA level
E)Neutrophilia
F)Severe thrombocytopenia
A)Candida antigen anergy
B)Decreased serum C3 level
C)Increased serum IgE level
D)Low serum IgA level
E)Neutrophilia
F)Severe thrombocytopenia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
A 52-year-old woman comes to the emergency department with pain and redness affecting her left leg. The patient's symptoms began 2 days ago and have progressed to the point where she cannot walk without experiencing severe pain. Physical examination shows a large, erythematous area with indistinct margins over her left leg. The area feels hot and indurated and is exquisitely tender. She is admitted to the hospital for severe left leg cellulitis and is started on intravenous cefazolin. Several minutes after the infusion is started, she experiences shortness of breath, diffuse itching, and dizziness. Her blood pressure is 64/38 mm Hg and heart rate is 130/min. On examination, there is a diffuse erythematous skin rash and bilateral wheezing is heard on lung auscultation. Which of the following is most likely to be elevated in this patient's serum as a result of her medication reaction?
A)Alkaline phosphatase
B)Calcitonin
C)Collagenase
D)Myeloperoxidase
E)Tryptase
A)Alkaline phosphatase
B)Calcitonin
C)Collagenase
D)Myeloperoxidase
E)Tryptase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A 23-year-old woman comes to the emergency department because of a diffuse, itchy rash and swollen face for 6 hours. That morning, she was diagnosed with an abscess of the lower leg. She underwent treatment with incision and drainage as well as oral antibiotics. She has no history of serious illness. She is not in acute distress. Her temperature is 37.2°C (99°F), pulse is 78/min, and blood pressure is 128/84 mm Hg. Physical examination shows mild swelling of the eyelids and lips. There are multiple erythematous patches and wheals over her upper extremities, back, and abdomen. The lungs are clear to auscultation. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's hypotension?
A)Chemical mediator-induced decreased myocardial contractility
B)Chemical mediator-induced increased vascular permeability
C)Impaired endogenous sympathetic nerve activity
D)Toxin-mediated decreased myocardial contractility
E)Toxin-mediated increased capillary permeability
A)Chemical mediator-induced decreased myocardial contractility
B)Chemical mediator-induced increased vascular permeability
C)Impaired endogenous sympathetic nerve activity
D)Toxin-mediated decreased myocardial contractility
E)Toxin-mediated increased capillary permeability

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The patient's anaphylactic reaction is determined to be mediated by antigen-specific IgE antibodies attached to high-affinity receptors on the surface of mast cells and basophils. Which of the following mechanisms is most likely to trigger vasoactive substance release by these cells?
A)Antibody-receptor covalent binding
B)Antibody-receptor dissociation
C)Receptor aggregation
D)Receptor detachment from the cell surface
E)Receptor internalization
A)Antibody-receptor covalent binding
B)Antibody-receptor dissociation
C)Receptor aggregation
D)Receptor detachment from the cell surface
E)Receptor internalization

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A 7-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department by his mother because of difficulty breathing for 20 minutes. He was having lunch with his mother when she noticed a rash and swelling of his tongue and lips. His temperature is 37°C (98.6°F), pulse is 169/min, respirations are 28/min, and blood pressure is 90/50 mmHg. Pulse oximetry on room air shows an oxygen saturation of 92%. Examination shows generalized hives, swelling of his tongue and lips, and labored breathing with intercostal retractions. Which of the following is most responsible for this patient's current condition?
A)Gram-negative bacterial endotoxin
B)Gram-positive bacterial exotoxin
C)Kallikrein-generated bradykinin
D)Mast cell-derived histamine
E)Vasoactive intestinal peptide
A)Gram-negative bacterial endotoxin
B)Gram-positive bacterial exotoxin
C)Kallikrein-generated bradykinin
D)Mast cell-derived histamine
E)Vasoactive intestinal peptide

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A 12-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department by his mother because of progressive shortness of breath, difficulty speaking, and diffuse, colicky abdominal pain for the past 3 hours. Yesterday he underwent a tooth extraction. His father and a paternal uncle have a history of repeated hospitalizations for upper airway and orofacial swelling. The patient takes no medications. His blood pressure is 112/62 mm Hg. Examination shows edematous swelling of the lips, tongue, arms, and legs; there is no rash. Which of the following studies is most likely to be abnormal?
A)Eosinophil count
B)Serum C4 level
C)Serum C8 level
D)Serum IgA level
E)Serum IgE level
A)Eosinophil count
B)Serum C4 level
C)Serum C8 level
D)Serum IgA level
E)Serum IgE level

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A 15-month-old boy is brought to the emergency room with a fever and edema in his feet. Four days ago, the patient had edema in his right foot and a fever. Swelling of the left foot has also occurred today. A 9-month-old perianal abscess has a considerable medical history. Imaging examinations indicate osteomyelitis in both feet's metatarsal bones. Although intravenous antibiotics are given, the patient still has a fever and bilateral foot edema two weeks later. A laboratory examination reveals chronic neutrophilic leukocytosis. Staphylococcus aureus develops in bone biopsy cultures. The search for an underlying diagnosis begins; the patient's peripheral blood is stimulated with phorbol myristate acetate (PM A) and compared to a control using a rhodamine derivative. 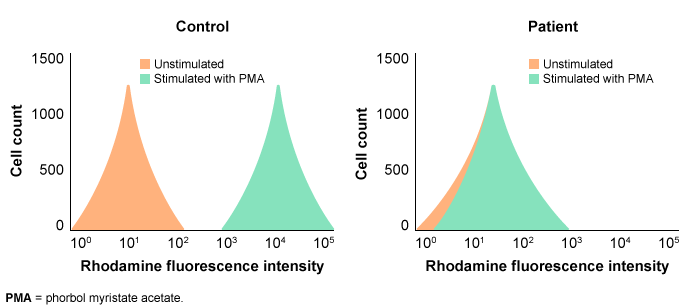 Which of the following processes is most likely impaired in this patient?
Which of the following processes is most likely impaired in this patient?
A)Chemotaxis
B)Complement production
C)Opsonization
D)Phagocytic metabolism
E)T-lymphocyte function
 Which of the following processes is most likely impaired in this patient?
Which of the following processes is most likely impaired in this patient?A)Chemotaxis
B)Complement production
C)Opsonization
D)Phagocytic metabolism
E)T-lymphocyte function

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A 57-year-old woman comes to the emergency department due to cough and hemoptysis. The patient also reports several months of fatigue and joint pain. Physical examination is notable for crusting of the nasal mucosa, lung crackles, and scattered palpable purpura over the lower extremities. Chest x-ray reveals bilateral, diffuse alveolar infiltrates. Laboratory studies show normocytic anemia, red blood cell casts and protein in the urine, and positive c-ANCA. After a confirmatory biopsy, treatment with rituximab infusion is planned. This medication is most likely to improve this patient's condition via which of the following mechanisms?
A)Blockade of T-cell costimulation
B)Depletion of B cells
C)Disruption of leukocyte migration
D)Inhibition of cytoplasmic kinase
E)Interruption of cytokine function
A)Blockade of T-cell costimulation
B)Depletion of B cells
C)Disruption of leukocyte migration
D)Inhibition of cytoplasmic kinase
E)Interruption of cytokine function

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
A 56-year-old woman with a history of heart failure is admitted to the hospital for orthotopic cardiac transplantation. The patient developed biventricular failure due to idiopathic myocarditis. She has had persistent New York Heart Association class IV symptoms refractory to maximal medical therapy and was placed on the transplant waiting list. An ABO-compatible cadaveric heart is available for transplant with partial human leukocyte antigen (HL A) mismatch. Cardiac transplantation is performed and the patient's T lymphocytes quickly recognize the foreign HLA molecules of the transplant cells. Inhibition of which of the following substances would specifically reduce the proliferation and differentiation of these T lymphocytes?
A)Bcl-2
B)Calcineurin
C)E-cadherin
D)Neurofibromin
E)p53
A)Bcl-2
B)Calcineurin
C)E-cadherin
D)Neurofibromin
E)p53

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
A 23-year-old woman comes to the physician with migratory joint pains involving her hands and knees. Physical examination shows bilateral tenderness in her wrists and proximal interphalangeal joints. There is also a malar skin rash and generalized lymphadenopathy. A urinalysis reveals proteinuria. Further evaluation shows that the patient's lymphocytes contain a mutated and functionally defective Fas gene product. Which of the following immunologic mechanisms is most likely impaired in this patient as a result of this molecular defect?
A)Activation-induced T lymphocyte death
B)Affinity maturation of B lymphocytes
C)Clonal anergy of T lymphocytes
D)Isotype switching of B lymphocytes
E)TH1 and TH2 lymphocyte differentiation
A)Activation-induced T lymphocyte death
B)Affinity maturation of B lymphocytes
C)Clonal anergy of T lymphocytes
D)Isotype switching of B lymphocytes
E)TH1 and TH2 lymphocyte differentiation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A 33 year-old female is being followed by her neurologist for her multiple sclerosis. She was initially diagnosed with relapsing remitting subtype after an episode of visual disturbance and an episode of paralysis. In her study of autoimmune diseases she encounters the topic of lymphocyte development and comes across a question which she poses to her neurologist during a routine follow-up visit: During the process of T-lymphocyte maturation, T cell receptors of many lymphocytes demonstrate a very high-affinity interaction with MHC molecules expressed on thymic medullary epithelial and dendritic cells. What process do these lymphocytes undergo at this time?
A)Affinity maturation
B)Isotype switching
C)Negative selection
D)Positive selection
E)TCR DNA rearrangement
A)Affinity maturation
B)Isotype switching
C)Negative selection
D)Positive selection
E)TCR DNA rearrangement

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Different kinds of immunoglobulins have distinct structures. Some immunoglobulins contain lengthy hinge areas between the Fab and Fc regions, whereas others do not, as seen in the graphic below: 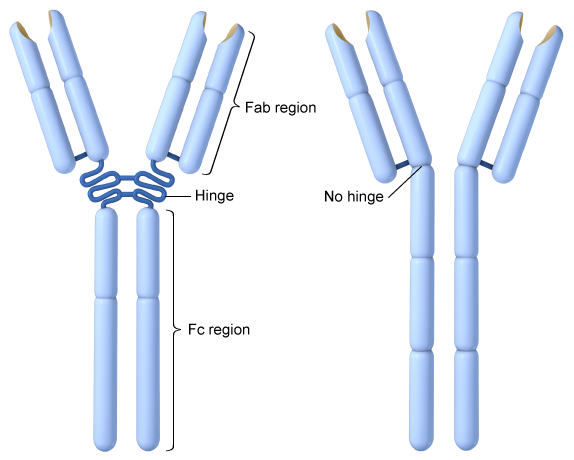 The hinge region provides movement flexibility to the Fab regions. This is most likely to affect which of the following immunoglobulin properties?
The hinge region provides movement flexibility to the Fab regions. This is most likely to affect which of the following immunoglobulin properties?
A)Affinity to antigen
B)Antibody polymerization
C)Avidity to antigen
D)Effector cell interaction
E)Effector cell specificity
 The hinge region provides movement flexibility to the Fab regions. This is most likely to affect which of the following immunoglobulin properties?
The hinge region provides movement flexibility to the Fab regions. This is most likely to affect which of the following immunoglobulin properties?A)Affinity to antigen
B)Antibody polymerization
C)Avidity to antigen
D)Effector cell interaction
E)Effector cell specificity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
On flow cytometric analysis of a sample of fetal thymus, a certain population of cells is identified that is positive for both CD4 and CD8 cell surface antigens. These cells are best characterized as which of the following cells?
A)Immature cortical T lymphocytes
B)Mature cytotoxic T lymphocytes
C)Mature helper T lymphocytes
D)Antigen presenting cells
E)Natural killer (NK) cells
F)Thymic epithelial cells
A)Immature cortical T lymphocytes
B)Mature cytotoxic T lymphocytes
C)Mature helper T lymphocytes
D)Antigen presenting cells
E)Natural killer (NK) cells
F)Thymic epithelial cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A researcher is comparing surface antigens X and Y from two distinct viruses. He acquires antigen X antibodies from an animal that has previously been exposed to the virus encoding this antigen. After that, the antibodies are added to test plates. Following that, a set amount of radiolabeled X antigen is applied to the plates. Unlabeled Y antigens are then given to each plate in escalating quantities, and the plates are washed to eliminate unbound antigens. The graph below depicts radioactivity as a function of Y antigen concentration. . 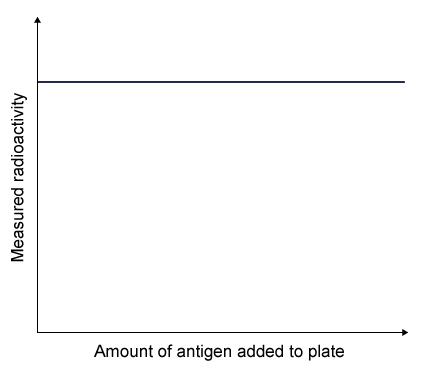 Which of the following best describes the results of this experiment?
Which of the following best describes the results of this experiment?
A)Antigen X and antigen Y have no epitopes in common
B)Antigen X and antigen Y have the same epitopes
C)Antigen Y shares most of the epitopes of antigen X
D)Antigen Y shares some of the epitopes of antigen X
 Which of the following best describes the results of this experiment?
Which of the following best describes the results of this experiment?A)Antigen X and antigen Y have no epitopes in common
B)Antigen X and antigen Y have the same epitopes
C)Antigen Y shares most of the epitopes of antigen X
D)Antigen Y shares some of the epitopes of antigen X

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A researcher identifies a group of malignant epithelial cells in the sigmoid colon that have decreased their surface expression of MHC class I antigen. Which of the following immune effector cell types is most likely to kill the transformed epithelial cells?
A)Neutrophils
B)Macrophages
C)Dendritic cells
D)CD4+ T lymphocytes
E)Plasma cells
F)Natural killer cells
A)Neutrophils
B)Macrophages
C)Dendritic cells
D)CD4+ T lymphocytes
E)Plasma cells
F)Natural killer cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A 10-month-old kid is admitted to the hospital with respiratory distress caused by Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia. The kid has had many bouts of otitis media and thrush, and his weight is below the fifth percentile. An examination in the laboratory indicates normal levels of circulating B and T cells as well as low levels of all immunoglobulins. A uncommon autosomal recessive mutation results in a failure in the control of human leukocyte antigen gene transcription, according to genetic testing. The figure below depicts flow cytometry of the patient's peripheral blood compared to a healthy control: 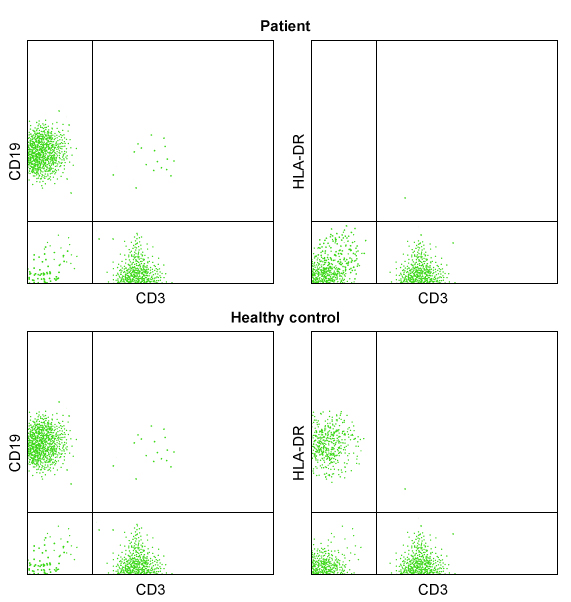 Which of the following processes is most likely to be impaired by this patient's mutation?
Which of the following processes is most likely to be impaired by this patient's mutation?
A)Development of pharyngeal pouches
B)Capability of activated CD4+ T cells to express CD40L
C)Maturation of pro-B cells into pre-B cells
D)Presentation of antigens processed in lysosomes
E)Transport of cytosolic proteins into the endoplasmic reticulum
 Which of the following processes is most likely to be impaired by this patient's mutation?
Which of the following processes is most likely to be impaired by this patient's mutation?A)Development of pharyngeal pouches
B)Capability of activated CD4+ T cells to express CD40L
C)Maturation of pro-B cells into pre-B cells
D)Presentation of antigens processed in lysosomes
E)Transport of cytosolic proteins into the endoplasmic reticulum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A 23-year-old man comes to the physician with dysuria and increased urinary frequency. He is an active duty member of the US military and recently returned from sub-Saharan Africa, where he had been stationed for the last year. The patient's symptoms have persisted for several months and have failed to resolve following antibiotic treatment. His blood eosinophil count is elevated. Urine microscopy shows schistosome eggs. He is started on praziquantel and experiences improvement in his symptoms. The elevated eosinophils in this patient contribute to the host defense against schistosomiasis through which of the following mechanisms?
A)Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity
B)B lymphocyte chemotaxis
C)Complement activation
D)Immediate hypersensitivity
E)MHC class I antigen processing
A)Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity
B)B lymphocyte chemotaxis
C)Complement activation
D)Immediate hypersensitivity
E)MHC class I antigen processing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A 5-year-old boy with severe, recurrent respiratory infections is undergoing evaluation. Sputum studies reveal intracellular bacteria. Further testing shows that the patient's T cells lack the IL-12 receptor. Supplementation with which of the following substances would most likely improve this patient's condition?
A)Early complement components
B)GM-CSF
C)Immunoglobulins
D)Interferon-gamma
E)Interleukin-4
A)Early complement components
B)GM-CSF
C)Immunoglobulins
D)Interferon-gamma
E)Interleukin-4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A 62-year-old man arrives to the office with a severe pruritic face rash that has persisted for three days. The patient does not use any face cosmetics but has coloured his hair regularly in the last year; he recently dyed his hair 5 days ago and recalls experiencing a similar reaction the prior time he used hair dye. The patient has a history of asthma, high blood pressure, and type 2 diabetes. He does not smoke, drink, or use illegal drugs. The vital indicators are within normal ranges. The presentation depicts the results of the physical examination. 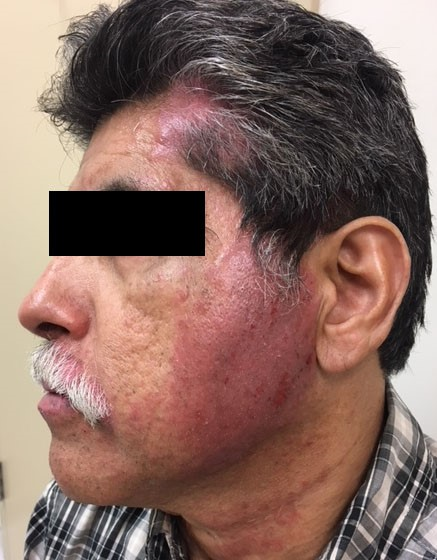 Which of the following are primarily involved in the pathogenesis of this patient's rash?
Which of the following are primarily involved in the pathogenesis of this patient's rash?
A)CD8+ T cells and interferon gamma
B)Mast cells and histamine
C)Neutrophils and myeloperoxidase
D)Plasma cells and immunoglobulins
E)Regulatory T cells and interleukin-10
 Which of the following are primarily involved in the pathogenesis of this patient's rash?
Which of the following are primarily involved in the pathogenesis of this patient's rash?A)CD8+ T cells and interferon gamma
B)Mast cells and histamine
C)Neutrophils and myeloperoxidase
D)Plasma cells and immunoglobulins
E)Regulatory T cells and interleukin-10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
A 1-year-old boy is brought to the office for medical evaluation. The patient was recently diagnosed with type 1 diabetes mellitus. He has also had chronic diarrhea, failure to thrive, and eczematous dermatitis since early infancy. Small bowel biopsy reveals villous atrophy and extensive lymphocytic infiltration. Immunologic testing shows significantly increased serum immunoglobulins and decreased IL-10 and transforming growth factor-beta levels. Genetic testing reveals a missense mutation affecting FOXP3. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's current condition?
A)Defective B-cell differentiation into plasma cells
B)Dysfunction of regulatory T cells
C)Dysfunction of T-helper cell type 17
D)Impaired immunoglobulin isotype switching
E)Impaired positive selection of thymic T cells
A)Defective B-cell differentiation into plasma cells
B)Dysfunction of regulatory T cells
C)Dysfunction of T-helper cell type 17
D)Impaired immunoglobulin isotype switching
E)Impaired positive selection of thymic T cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
A 32-year-old woman visits an allergy clinic because she has a recurring skin problem. Over the last few months, the patient has experienced many episodes of itchy, erythematous, vesicular eruptions on her hands. She works at a hair salon, where she is frequently exposed to hair color and other beauty products. There are no additional medical issues or drugs that the patient is taking. Several allergens detected in common cosmetic items are placed on nonocclusive tape strips applied to her upper back during patch testing. The exhibit depicts skin results that occurred after two days of treatment. 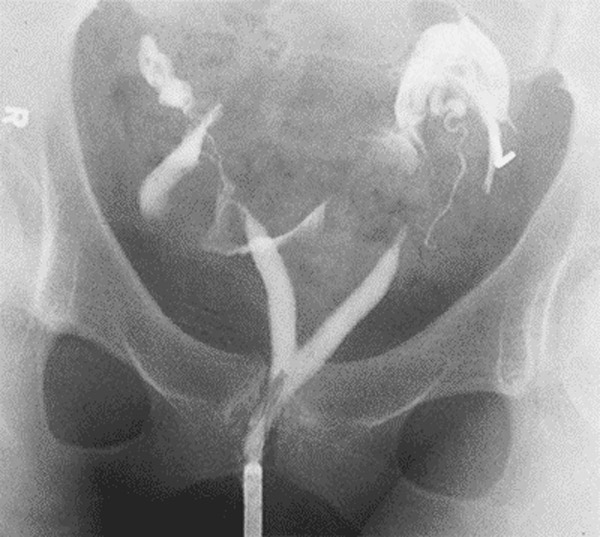 Which of the following processes most likely occurred in this patient to enable the development of the observed skin reaction?
Which of the following processes most likely occurred in this patient to enable the development of the observed skin reaction?
A)B-cell binding with helper T cells via CD40 and CD40 ligand
B)Formation of autoantibodies against keratinocyte cell surface antigens
C)Immune complex formation and deposition in the small cutaneous vessels
D)Migration of hapten-activated Langerhans cells to regional lymph nodes
E)Release of vasoactive peptides from IgE-bound mast cells
 Which of the following processes most likely occurred in this patient to enable the development of the observed skin reaction?
Which of the following processes most likely occurred in this patient to enable the development of the observed skin reaction?A)B-cell binding with helper T cells via CD40 and CD40 ligand
B)Formation of autoantibodies against keratinocyte cell surface antigens
C)Immune complex formation and deposition in the small cutaneous vessels
D)Migration of hapten-activated Langerhans cells to regional lymph nodes
E)Release of vasoactive peptides from IgE-bound mast cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A 19-year-old man comes to the office due to eye pain and blurry vision in both eyes for the last several days. He sustained an open globe injury to the right eye 3 months ago after being struck during an altercation and was treated with surgical repair and prophylactic antibiotics. The left eye was unaffected. At the patient's last follow-up appointment, visual acuity in the right eye had improved from 20/400 to 20/80. He is otherwise healthy. Temperature is 37.1 C (98.8 F). Examination is unremarkable apart from bilateral conjunctival injection and decreased visual acuity in both eyes. Analysis of vitreous samples from both eyes demonstrates multinucleated giant cells. Which of the following mechanisms is most likely causing this patient's current manifestations?
A)Granulomatous response to reactivation of a latent viral infection
B)Mixed inflammatory reaction triggered by a gastrointestinal pathogen
C)Neutrophilic response to an intraocular infection
D)T-cell response to previously sequestered antigens
E)Type IV hypersensitivity reaction to an antibiotic
A)Granulomatous response to reactivation of a latent viral infection
B)Mixed inflammatory reaction triggered by a gastrointestinal pathogen
C)Neutrophilic response to an intraocular infection
D)T-cell response to previously sequestered antigens
E)Type IV hypersensitivity reaction to an antibiotic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
A 65-year-old woman is enrolled in a clinical trial to test a new medication for rheumatoid arthritis. The patient's condition has been poorly controlled despite prolonged treatment with multiple disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs. The new medication is a CTLA4-Ig fusion protein that prevents CD28 from binding to CD80/86 on antigen-presenting cells. A month after treatment begins, the patient reports a significant reduction in joint pain and stiffness. Laboratory results reveal reduced levels of C-reactive protein and IL-2. Which of the following is the most likely underlying cause of this patient's treatment response?
A)Complement inhibition
B)Immune complex clearance
C)Negative selection
D)Peripheral tolerance
E)Sensitization
A)Complement inhibition
B)Immune complex clearance
C)Negative selection
D)Peripheral tolerance
E)Sensitization

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A 24-year-old nurse comes to the office for his annual wellness visit that includes tuberculosis screening. The patient has no chronic medical conditions and does not have recent fever, cough, or other health changes. He receives an intradermal injection of tuberculin on the inner surface of his forearm. Two days later, he has a distinct area of induration 20 mm across at the injection site. Which of the following interactions is essential to the development of this patient's skin reaction?
A)CD14 on epidermal macrophages with bacterial lipopolysaccharide
B)CD16 on natural killer cells with IgG bound to infected cells
C)CD18 on neutrophils with ICAM-1 on endothelial cells
D)CD28 on T lymphocytes with CD80 on epidermal dendritic cells
E)CTLA4 on T lymphocytes with CD80 on epidermal dendritic cells
A)CD14 on epidermal macrophages with bacterial lipopolysaccharide
B)CD16 on natural killer cells with IgG bound to infected cells
C)CD18 on neutrophils with ICAM-1 on endothelial cells
D)CD28 on T lymphocytes with CD80 on epidermal dendritic cells
E)CTLA4 on T lymphocytes with CD80 on epidermal dendritic cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
A 10-month-old boy is brought to the office due to recurrent sinopulmonary infections for the last several months. The infections were caused by encapsulated bacteria, and the patient was also recently hospitalized due to Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia. He was born at full term after an uneventful pregnancy. Family history is significant for a maternal uncle's early childhood death due to severe infection. Genetic testing of the patient reveals missense mutation of the CD40 ligand gene. Interaction between which of the following immune components is most likely impaired in this patient?
A)B cells and complement proteins
B)B cells and foreign antigens
C)Neutrophils and vascular endothelial cells
D)Phagocytes and antigen-bound antibodies
E)T cells and antigen-presenting cells
A)B cells and complement proteins
B)B cells and foreign antigens
C)Neutrophils and vascular endothelial cells
D)Phagocytes and antigen-bound antibodies
E)T cells and antigen-presenting cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
A 2-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department due to 4 days of worsening cough and fevers. This evening, the patient developed increasingly rapid breathing. He has a history of 2 prior episodes of cervical lymphadenitis due to Staphylococcus aureus. Temperature is 39 C (102.2 F). Blood pressure is 100/72 mm Hg, pulse is 130/min, and respirations are 35/min. Prominent intercostal and supraclavicular retractions are present. There are diffuse crackles bilaterally, with decreased breath sounds at the lung bases. Heart sounds are normal. The patient is intubated. Laboratory results are as follows: 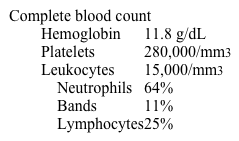 Bronchioalveolar lavage fluid tests positive for Aspergillus fumigatus. Serum immunoglobulin levels are normal. Which of the following is the most likely underlying cause of this patient's presentation?
Bronchioalveolar lavage fluid tests positive for Aspergillus fumigatus. Serum immunoglobulin levels are normal. Which of the following is the most likely underlying cause of this patient's presentation?
A)Decreased macrophage degranulation
B)Disrupted macrophage phagocytosis
C)Dysfunctional neutrophil trafficking
D)Impaired neutrophilic respiratory burst
E)Reduced neutrophilic phagocytosis
 Bronchioalveolar lavage fluid tests positive for Aspergillus fumigatus. Serum immunoglobulin levels are normal. Which of the following is the most likely underlying cause of this patient's presentation?
Bronchioalveolar lavage fluid tests positive for Aspergillus fumigatus. Serum immunoglobulin levels are normal. Which of the following is the most likely underlying cause of this patient's presentation?A)Decreased macrophage degranulation
B)Disrupted macrophage phagocytosis
C)Dysfunctional neutrophil trafficking
D)Impaired neutrophilic respiratory burst
E)Reduced neutrophilic phagocytosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
A 4-year-old kid is brought to the clinic for her yearly checkup. She has no chronic medical issues and has had all previously advised vaccines. Today, the patient will receive multiple immunizations, including a second measles vaccine. Which of the following IgM and IgG trends are likely to develop following initial and subsequent measles vaccinations?
A)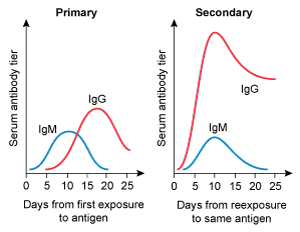
B)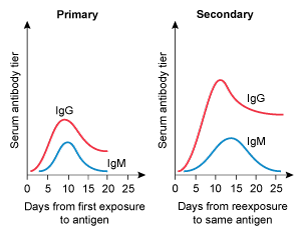
C)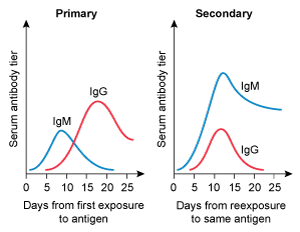
D)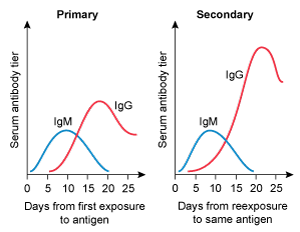
E)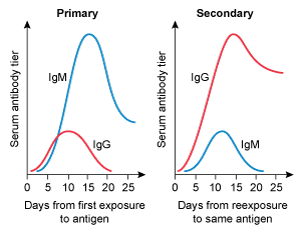
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
An 18-year-old college student is hospitalized due to a high fever and confusion. According to the patient's roommate, the symptoms started about 6 hours ago. The patient was feeling well this morning except for some nausea. She has had several episodes of pneumonia in the past and had bacterial meningitis a year ago, which was treated with ceftriaxone. Temperature is 39.1 C (102.4 F), blood pressure is 104/70 mm Hg, and pulse is 110/min. The patient is lethargic but is able to follow simple commands and give single-word answers with prompting. Physical examination reveals a petechial rash on the trunk and extremities, including the palms and soles. Neck stiffness and photophobia are also noted. Which of the following primary immune system impairments is most likely responsible for this patient's recurrent infections?
A)Defective T-cell maturation
B)Excessive production of IgE antibodies
C)Impaired cellular chemotaxis
D)Inability to form the membrane attack complex
E)Ineffective neutrophil oxidative burst
A)Defective T-cell maturation
B)Excessive production of IgE antibodies
C)Impaired cellular chemotaxis
D)Inability to form the membrane attack complex
E)Ineffective neutrophil oxidative burst

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
A 10-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department by his parents due to increasing lethargy and high fever for the past 12 hours. The boy was well last night but was sluggish this morning. Over the day, his activity level and responsiveness diminished. The patient was treated for Neisseria meningitidis bacteremia 2 years ago. He has received all routine vaccinations and is developing normally. Temperature is 39.6 C (103.3 F). On examination, the patient appears ill and is poorly responsive. He is tachycardic, but heart sounds are otherwise unremarkable. Lungs are clear to auscultation. Numerous purple bruise-like markings and petechiae are noted over his extremities, which have diminished capillary refill. Blood samples are drawn for total complement (CH50) and alternative complement (AH50) measurement. Which of the following sets of results is most likely to be found in this patient? 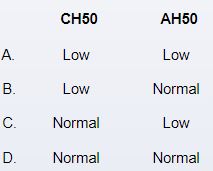
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D

A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
A 64-year-old man visits the clinic after experiencing many weeks of continuous coughing, fever, and weight loss. He smokes a pack of cigarettes every day and consumes 10 to 12 beers on weekends. An infiltration in the left upper lobe is shown by a chest x-ray. Despite receiving broad-spectrum antibiotic therapy for both aspiration and community-acquired pneumonia, the patient's symptoms deteriorate. The Gram stain on sputum does not indicate any microbes. The following picture depicts the results of a lung biopsy: 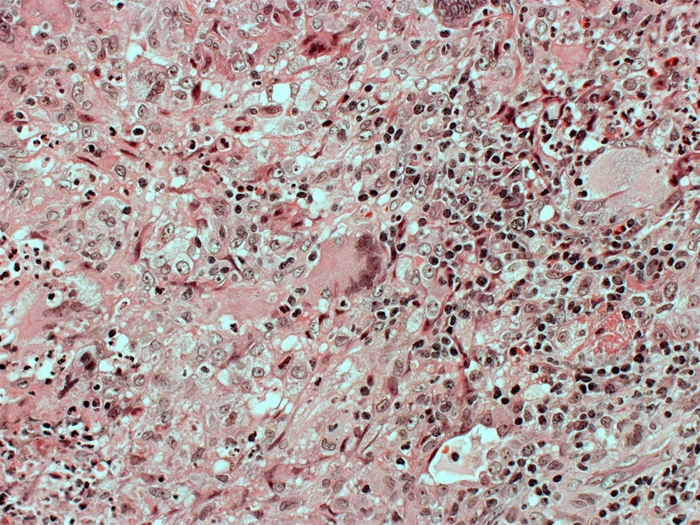 Which of the following substances is most important for driving the development of this patient's observed microscopic lesion?
Which of the following substances is most important for driving the development of this patient's observed microscopic lesion?
A)C3a
B)Fibroblast growth factor
C)Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor
D)IL-4
E)Interferon-alpha
F)Interferon-gamma
 Which of the following substances is most important for driving the development of this patient's observed microscopic lesion?
Which of the following substances is most important for driving the development of this patient's observed microscopic lesion?A)C3a
B)Fibroblast growth factor
C)Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor
D)IL-4
E)Interferon-alpha
F)Interferon-gamma

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
A 28-year-old woman is treated with high-dose prednisone for severe lupus nephritis. Several hours after therapy is initiated, she becomes very agitated and delusional. Blood pressure is 130/70 mm Hg and heart rate is 110/min. A basic metabolic profile, complete blood cell (CBC) count, and urinalysis are obtained. The CBC differential is expected to show an increase in which of the following as a result of this patient's therapy?
A)Basophils
B)Eosinophils
C)Lymphocytes
D)Monocytes
E)Neutrophils
A)Basophils
B)Eosinophils
C)Lymphocytes
D)Monocytes
E)Neutrophils

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
A 35-year-old woman comes to the office due to fever, headache, severe muscle aches, and sore throat for the last 4 days. Physical examination shows mild pharyngeal erythema and nasal congestion. A rapid influenza antigen test is positive. The patient's condition improves over the next several days despite receiving only symptomatic treatment. In response to the influenza virus, infected respiratory epithelial cells begin secreting increased quantities of interferons. The specific interferons secreted by these cells will most likely cause which of the following changes?
A)Decreased apoptosis of infected cells
B)Decreased protein synthesis by infected cells
C)Increased class II MHC expression
D)Increased intracellular killing by macrophages
E)Increased neutrophil recruitment
A)Decreased apoptosis of infected cells
B)Decreased protein synthesis by infected cells
C)Increased class II MHC expression
D)Increased intracellular killing by macrophages
E)Increased neutrophil recruitment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
A 63-year-old man comes to the physician after noticing a reddish tinge to his urine for the last couple of days. During evaluation of his hematuria, an abdominal CT scan reveals a left-sided renal mass. Further workup also shows multiple pulmonary and bone nodules. CT-guided biopsy of a peripherally located lung nodule demonstrates renal cell carcinoma. High-dose interleukin-2 (IL-2) is started, and 4 weeks later there is a significant reduction in his tumor burden. Which of the following mechanisms was most likely responsible for regression of his malignancy?
A)Anti-angiogenic effect of IL-2
B)Direct cytotoxic effect of IL-2 on the tumor cells
C)Enhanced activity of natural killer cells
D)IL-2-induced apoptosis of tumor cells
E)Increased expression of MHC Class 1 on tumor cells
A)Anti-angiogenic effect of IL-2
B)Direct cytotoxic effect of IL-2 on the tumor cells
C)Enhanced activity of natural killer cells
D)IL-2-induced apoptosis of tumor cells
E)Increased expression of MHC Class 1 on tumor cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
A 34-year-old woman comes to the physician for a follow-up visit. She was diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis 3 months ago and started on methotrexate therapy. Despite treatment, she continues to have several hours of morning stiffness daily and frequently awakens at night due to joint pain. Physical examination shows swelling and tenderness in the joints of her hands and wrists. Etanercept is subsequently added to her treatment regimen. This medication is best characterized as which of the following?
A)Cell surface receptor antibody
B)Chimeric monoclonal antibody
C)Humanized monoclonal antibody
D)Small-molecule receptor inhibitor
E)Soluble receptor decoy protein
A)Cell surface receptor antibody
B)Chimeric monoclonal antibody
C)Humanized monoclonal antibody
D)Small-molecule receptor inhibitor
E)Soluble receptor decoy protein

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
A 13-year-old boy has been admitted to the hospital after suffering from fever and fatigue for the past week. The patient had a cadaveric renal transplant for glomerulonephritis, and his immunosuppressive medication regimen was increased a month ago due to early signs of rejection. The temperature is 37.7 degrees Celsius (99.9 F). The heart and lung exams are unremarkable. The liver is slightly enlarged, and the spleen tip can be felt. Adenopathy is present in the bilateral inguinal and axillary regions. A complete blood count reveals that the patient has mild leukopenia. The image below depicts histopathology findings from a biopsy of one of the enlarged lymph nodes.  Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's presentation?
Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's presentation?
A)Aspergillus fumigatus
B)Bartonella henselae
C)Cryptococcus neoformans
D)Epstein-Barr virus
E)Parvovirus B19
 Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's presentation?
Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's presentation?A)Aspergillus fumigatus
B)Bartonella henselae
C)Cryptococcus neoformans
D)Epstein-Barr virus
E)Parvovirus B19

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
A 55-year-old man with end-stage hepatitis C virus infection undergoes orthotopic liver transplantation from a deceased donor. The patient has no perioperative complications and is discharged from the hospital on appropriate immunosuppressant medications. One week after the surgery, he develops nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and bloody diarrhea. Physical examination shows a painful maculopapular rash over his neck, back, and extremities that extends to the palms and soles. Endoscopic evaluation reveals multiple ulcerations of the intestinal mucosa. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's current condition?
A)Graft B cell sensitization against host MHC antigens
B)Graft T cell sensitization against host MHC antigens
C)Host B cell sensitization against graft MHC antigens
D)Host T cell sensitization against graft MHC antigens
E)Preformed antibodies against graft ABO antigens
A)Graft B cell sensitization against host MHC antigens
B)Graft T cell sensitization against host MHC antigens
C)Host B cell sensitization against graft MHC antigens
D)Host T cell sensitization against graft MHC antigens
E)Preformed antibodies against graft ABO antigens

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
A 9-year-old girl is brought to the office due to persistent nasal drainage. Over the past 2 weeks, the patient has had increasing nasal congestion and drainage. The discharge was initially clear but has become dark and foul smelling over the past few days. The patient has a history of multiple skin abscesses that developed when she was an infant, but they typically do not cause discomfort. She has also had atopic dermatitis since infancy. Temperature is 37.1 C (98.8 F). On examination, the patient is interactive and talkative. Thick nasal discharge appears from both nares. Cardiopulmonary examination is normal. There are several diffuse areas of dry, excoriated skin along the trunk and upper extremities. Results of a complete blood count are as follows:  Which of the following patterns of immunoglobulin production is most likely to be seen in this patient?
Which of the following patterns of immunoglobulin production is most likely to be seen in this patient? 
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E
 Which of the following patterns of immunoglobulin production is most likely to be seen in this patient?
Which of the following patterns of immunoglobulin production is most likely to be seen in this patient? 
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
A 6-year-old boy is being evaluated in the office due to a history of recurrent infections and failure to thrive. He has been hospitalized for pneumococcal pneumonia twice and has had 5 episodes of otitis media. The patient also has a history of prolonged diarrhea caused by Giardia intestinalis. Physical examination shows a lack of tonsillar tissue, as well as minimally palpable cervical, axillary, and inguinal lymph nodes. Further evaluation shows that the patient has defective signaling between activated CD4 T cells and B cells. Which of the following laboratory findings are most likely to be found in this patient? 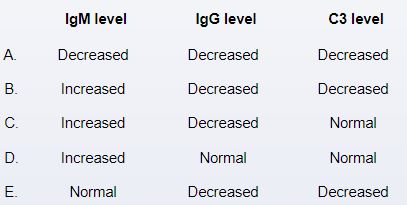
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
A 6-year-old boy is being evaluated in the office due to a history of recurrent infections and failure to thrive. He has been hospitalized for pneumococcal pneumonia twice and has had 5 episodes of otitis media. The patient also has a history of prolonged diarrhea caused by Giardia intestinalis. Physical examination shows a lack of tonsillar tissue, as well as minimally palpable cervical, axillary, and inguinal lymph nodes. Further evaluation shows that the patient has defective signaling between activated CD4 T cells and B cells. Which of the following laboratory findings are most likely to be found in this patient? 
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
A 13-month-old boy is admitted to the hospital due to diarrhea and dehydration. Over the past week, the patient has developed severe, watery diarrhea and has had poor oral intake. Medical history includes multiple episodes of bronchiolitis and, at age 8 months, an intensive care unit admission due to pneumococcal pneumonia requiring a brief period of mechanical intubation and chest tube placement. The parents say that he has been growing poorly over the past 6 months despite feeding well and supplemention with high-calorie formulas. On examination, the patient appears lethargic with sunken eyes and poor skin turgor, as well as moderate tachycardia and tachypnea. As part of the laboratory evaluation, flow cytometry of in vitro-stimulated CD4+ T cells reveals a near absence of CD40 ligand. Which of the following additional findings is most likely associated with this patient's condition?
A)Absent thymic tissue
B)Giant granules within neutrophils
C)Hypoplastic bone marrow
D)Lack of secondary germinal centers
E)Small-volume platelets
A)Absent thymic tissue
B)Giant granules within neutrophils
C)Hypoplastic bone marrow
D)Lack of secondary germinal centers
E)Small-volume platelets

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
A 3-year-old boy experiences recurrent sinusitis and an episode of severe pneumonia. As part of his evaluation, Candida extract is injected intradermally. Forty-eight hours later, he returns to the clinic with a firm nodule measuring 16 mm in diameter where the extract was injected. Which of the following cell types is most likely responsible for the reaction observed in this patient?
A)B lymphocytes
B)Eosinophils
C)Mast cells
D)Neutrophils
E)T lymphocytes
A)B lymphocytes
B)Eosinophils
C)Mast cells
D)Neutrophils
E)T lymphocytes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
A 2-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department due to wheezing and difficulty breathing. The patient had been trick-or-treating with his parents and ate several packs of candy containing peanuts. After he receives an intramuscular epinephrine injection, his symptoms resolve. At a follow up appointment, an allergy specialist places droplets of various allergens on the patient's skin and punctures the epidermis at each site. After 15 minutes, the skin at the site with peanut extract is erythematous with a raised, itchy bump that improves by the time the family leaves the office. Four hours later, the parents notice a hard, red swelling at the puncture site. Which of the following is most likely involved in this secondary reaction?
A)Cell lysis following IgG autoantibody binding
B)Complement activation by immune complexes
C)Epithelial damage by major basic protein
D)IgE-mediated histamine release from mast cells
E)Interferon gamma release from CD4+ T cells
A)Cell lysis following IgG autoantibody binding
B)Complement activation by immune complexes
C)Epithelial damage by major basic protein
D)IgE-mediated histamine release from mast cells
E)Interferon gamma release from CD4+ T cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
An 18-month-old, partially vaccinated boy is brought to the office for a routine well-child examination. His parents have elected a delayed schedule for vaccine administration based on personal preferences. Today, the patient is scheduled to receive the Haemophilus influenzae serotype b (Hib) conjugate vaccine. The parents are given detailed information about the vaccine, but the mother asks, "Why is 'tetanus toxoid conjugate' listed on the package insert?" She adds that her son already received the diphtheria-tetanus-acellular pertussis (DTaP) vaccine. The parents request an explanation for the reason the Hib vaccine contains both the capsular polysaccharide of Hib as well as the conjugated tetanus toxoid. Which of the following best describes the purpose of Hib vaccine conjugation?
A)Decreases adverse vaccine reactions
B)Elicits T cell-dependent immune response
C)Eliminates the need for booster doses
D)Induces immunity against nontypeable H influenzae
E)Induces immunity against the conjugated toxoid
A)Decreases adverse vaccine reactions
B)Elicits T cell-dependent immune response
C)Eliminates the need for booster doses
D)Induces immunity against nontypeable H influenzae
E)Induces immunity against the conjugated toxoid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
A 6-month-old boy is brought to the clinic by his mother and grandmother for a routine well-child visit. The child was born full-term and has no medical problems. He recently learned to sit with support and is starting to eat pureed foods. Vital signs and physical examination are normal. As part of the routine pediatric immunization schedule, the pneumococcal conjugate vaccine is ordered. The patient's grandmother says that she recently received the pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine. Which of the following statements is true regarding the difference between the pneumococcal conjugate and polysaccharide vaccines?
A)The conjugate vaccine causes less local site reactions than the polysaccharide vaccine
B)The conjugate vaccine induces a more robust immune response through B and T cell activation
C)The conjugate vaccine is inactivated while the polysaccharide vaccine is live attenuated
D)The conjugate vaccine protects against meningitis but the polysaccharide vaccine does not
E)The conjugate vaccine protects against more pneumococcal strains than the polysaccharide vaccine
A)The conjugate vaccine causes less local site reactions than the polysaccharide vaccine
B)The conjugate vaccine induces a more robust immune response through B and T cell activation
C)The conjugate vaccine is inactivated while the polysaccharide vaccine is live attenuated
D)The conjugate vaccine protects against meningitis but the polysaccharide vaccine does not
E)The conjugate vaccine protects against more pneumococcal strains than the polysaccharide vaccine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The immune response in a healthy 12-year-old boy is observed after a recurrent bacterial infection. It is characterized by a rapid increase in pathogen-specific immunoglobulin levels. The immunoglobulins bound to the bacteria also attach to phagocytic cells (eg, macrophages, neutrophils) to enhance phagocytosis. Which of the following immunoglobulin regions is most likely involved in interacting with these phagocytic cells?
A)Constant region of the heavy chain
B)Constant region of the light chain
C)Hinge region
D)Variable region of the heavy chain
E)Variable region of the light chain
A)Constant region of the heavy chain
B)Constant region of the light chain
C)Hinge region
D)Variable region of the heavy chain
E)Variable region of the light chain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Preventive disease specialists working in a developing country are investigating vaccination options to limit the spread of poliomyelitis. As part of the study, 2 patients are vaccinated against poliomyelitis. One patient receives an intramuscular inactivated vaccine and the other patient receives a live attenuated oral vaccine. One month after vaccination, the levels of which of the following poliovirus antibodies will differ the most between these 2 patients?
A)Cerebrospinal fluid IgG
B)Duodenal luminal IgA
C)Serum IgA
D)Serum IgG
E)Serum IgM
A)Cerebrospinal fluid IgG
B)Duodenal luminal IgA
C)Serum IgA
D)Serum IgG
E)Serum IgM

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
An 8-year-old male is brought to his pediatrician's office by his mother. The child has had a runny nose, sore throat, cough, and low-grade fever for the past 24 hours. The patient's mother recalls that several of the child's friends have been ill recently with similar symptoms. The mother asks whether the child will need antibiotics for his condition. His pediatrician recommends symptomatic therapy and feels that his illness is most likely of viral etiology. Cytotoxic CD8+ lymphocytes are able to kill virus-infected nasal epithelial cells once sensitized. Cytotoxic CD8+ lymphocyte receptors recognize foreign proteins on the epithelial cell surface. Foreign proteins are presented on the epithelial cell surface by MHC molecules. These MHC molecules comprise which of the following components?
A)MHC class I heavy chain only
B)MHC class I heavy chain and B2-microglobulin
C)MHC class I heavy chain and IgG
D)MHC class II alpha-chain and beta-chain
E)MHC class II alpha-chain only
A)MHC class I heavy chain only
B)MHC class I heavy chain and B2-microglobulin
C)MHC class I heavy chain and IgG
D)MHC class II alpha-chain and beta-chain
E)MHC class II alpha-chain only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



