Deck 9: Microbiology and Virology
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/330
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 9: Microbiology and Virology
1
A 24-year-old woman comes to the office due to 3 weeks of worsening throat pain and difficulty swallowing. She has no chronic medical problems but has had recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis and bacterial folliculitis over the past year. The patient has also had an unintentional weight loss of 4.5-kg (10-lb) over the past 3 months. She is an exchange student from Senegal. Physical examination shows generalized lymphadenopathy and oropharyngeal thrush. Upper endoscopy confirms Candida esophagitis. HIV antigen/antibody immunoassay returns positive. Further testing shows a CD4 count of 180/mm3 but there is no detectable plasma HIV-1 RNA. Which of the following best explains the observed laboratory findings in this patient?
A)False-positive serology from cross-reactive antibodies
B)Homozygous CCR5 deletion
C)Infection with CXCR4 tropic strain
D)Infection with HIV-2
E)Window period of HIV infection
A)False-positive serology from cross-reactive antibodies
B)Homozygous CCR5 deletion
C)Infection with CXCR4 tropic strain
D)Infection with HIV-2
E)Window period of HIV infection
Infection with HIV-2
2
A previously healthy 2-year-old boy is brought to the clinic with fever and mouth pain that began yesterday. He has consumed an adequate amount of fluids but refuses to eat due to the pain. The patient has no medical problems and takes no medications. Physical examination reveals swollen gums and vesicular, inflamed lesions on his hard palate and lips. He has enlarged and tender cervical lymph nodes. Which of the following is most likely responsible for this patient's condition?
A)DNA virus, double-stranded, enveloped
B)DNA virus, double-stranded, non-enveloped
C)DNA virus, single-stranded, non-enveloped
D)RNA virus, double-stranded, positive-sense
E)RNA virus, single-stranded, negative-sense
F)RNA virus, single-stranded, positive-sense
A)DNA virus, double-stranded, enveloped
B)DNA virus, double-stranded, non-enveloped
C)DNA virus, single-stranded, non-enveloped
D)RNA virus, double-stranded, positive-sense
E)RNA virus, single-stranded, negative-sense
F)RNA virus, single-stranded, positive-sense
DNA virus, double-stranded, enveloped
3
A 24-year-old man comes to the physician with painful blisters on the shaft of his penis. The lesions erupted 2 days ago. The patient has had 5 lifetime sexual partners and is currently sexually active with one female partner; he uses condoms inconsistently. Examination shows multiple vesicular lesions on the penis, and Tzanck smear is positive for multinucleated giant cells. HIV testing is negative. The patient has had several similar episodes every year for the past 2 years but had been too embarrassed to seek treatment until now. Which of the following would most likely have prevented recurrence of this patient's condition?
A)Continuous daily valacyclovir
B)Immunoglobulin during the first episode
C)Lamivudine with recurrence of blisters
D)Regular condom use after the first episode
E)Weeklong course of acyclovir during the first episode
A)Continuous daily valacyclovir
B)Immunoglobulin during the first episode
C)Lamivudine with recurrence of blisters
D)Regular condom use after the first episode
E)Weeklong course of acyclovir during the first episode
Continuous daily valacyclovir
4
A 38-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 1-month history of fever and a cough productive of a moderate amount of yellowish sputum. He has had a 6-kg (13-lb) weight loss during this period. He emigrated from the Middle East around 2 years ago. His father died of lung cancer at the age of 54 years. He has smoked one pack of cigarettes daily for 18 years. His only medication is a daily multivitamin. He appears malnourished. Sputum cultures grow acid-fast bacilli that are susceptible to most antimycobacterial drugs in vitro. Isoniazid monotherapy in this patient would most likely result in:
A)Bacteriocidal effect on only extracellular bacilli
B)Decreased transport protein expression on the cell surface
C)Beta-lactamase induction within bacterial cells
D)Rapid mycobacterial elimination from the body
E)Selective survival of bacterial cells secondary to gene mutation
A)Bacteriocidal effect on only extracellular bacilli
B)Decreased transport protein expression on the cell surface
C)Beta-lactamase induction within bacterial cells
D)Rapid mycobacterial elimination from the body
E)Selective survival of bacterial cells secondary to gene mutation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 330 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A 23-year-old man comes to the emergency department with fever, severe headache, and vomiting. He has not felt well for the past 2 weeks due to fatigue, intermittent low-grade fevers, and headaches. The patient is HIV positive and spent several months in prison 3 years ago. Temperature is 38.6 C (101.5 F). Neck stiffness is present on physical examination. A CT scan reveals no intracranial lesions. Cerebrospinal fluid analysis is notable for the following: 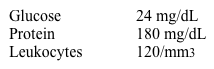 Cerebrospinal fluid cultures grow Mycobacterium tuberculosis with significantly decreased activity of intracellular catalase peroxidase. The isolates would most likely exhibit resistance to which of the following agents?
Cerebrospinal fluid cultures grow Mycobacterium tuberculosis with significantly decreased activity of intracellular catalase peroxidase. The isolates would most likely exhibit resistance to which of the following agents?
A)Ethambutol
B)Isoniazid
C)Pyrazinamide
D)Rifampin
E)Streptomycin
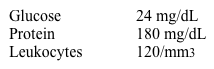 Cerebrospinal fluid cultures grow Mycobacterium tuberculosis with significantly decreased activity of intracellular catalase peroxidase. The isolates would most likely exhibit resistance to which of the following agents?
Cerebrospinal fluid cultures grow Mycobacterium tuberculosis with significantly decreased activity of intracellular catalase peroxidase. The isolates would most likely exhibit resistance to which of the following agents?A)Ethambutol
B)Isoniazid
C)Pyrazinamide
D)Rifampin
E)Streptomycin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 330 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A 2900-g (6.4-lb) male newborn is delivered at term to a 29-year-old primigravid woman. His mother had no routine prenatal care. She reports that the pregnancy was uncomplicated apart from a 2-week episode of a low-grade fever and swollen lymph nodes during her early pregnancy. She has avoided all routine vaccinations because she believes that "natural immunity is better". The newborn is at the 35th percentile for height, 15th percentile for weight, and 90th percentile for head circumference. Fundoscopic examination shows inflammation of the choroid and the retina in both eyes. A CT scan of the head shows diffuse intracranial calcifications and mild ventriculomegaly.Which of the following maternal interventions would have been most effective in preventing this patient's condition?
A)Adequate preconception immunization
B)Avoidance of consumption of undercooked meat
C)Consumption of unpasteurized cow's milk products
D)Strict avoidance of mosquitoes during pregnancy
E)Use of prophylactic penicillin during labor
A)Adequate preconception immunization
B)Avoidance of consumption of undercooked meat
C)Consumption of unpasteurized cow's milk products
D)Strict avoidance of mosquitoes during pregnancy
E)Use of prophylactic penicillin during labor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 330 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A 10-day-old male newborn is brought to the emergency department by his mother because of episodes of weakness and spasms for the past 12 hours. His mother states that he has also had difficulty feeding and opening his mouth. He has not had fever, cough, diarrhea, or vomiting. He was born at 39 weeks' gestation via uncomplicated vaginal delivery at home. Pregnancy was uncomplicated. The mother refused prenatal vaccines out of concern they would cause side effects. She is worried his symptoms may be from some raw honey his older sister maybe inadvertently fed him 5 days ago. He appears irritable. His temperature is 37.1°C (98.8°F). Physical examination shows increased muscle tone throughout, arching of the back, and dorsiflexed feet. In addition to avoid honey feeding to newborn, which of the following is the most effective strategy to prevent this condition?
A)Early postpartum breastfeeding
B)Prophylactic antibiotics
C)Prophylactic immune globulin
D)Vaccination of infants at birth
E)Vaccination of pregnant women
A)Early postpartum breastfeeding
B)Prophylactic antibiotics
C)Prophylactic immune globulin
D)Vaccination of infants at birth
E)Vaccination of pregnant women

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 330 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A 2-month-old boy is brought to the physician by his parents because of a 1-week history of increased fussiness and a rash. Initially, the rash was bright and copper-red but gradually started to fade and peel off. The patient has been feeding poorly and has not gained much weight since birth. He was born at 38 weeks gestation via an uncomplicated vaginal delivery and had an unremarkable neonatal course with no history of birth trauma or excessive bleeding. The mother had inconsistent prenatal care. He cries but calms when his mother picks him up. He is at the 3rd percentile for length and weight. Vital signs are within normal limits. Examination shows diffuse erythematous plaques on the soles and buttocks with desquamation. There is nasal congestion and a white nasal discharge. The liver is palpated 3 cm below the right costal margin. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's illness?
A)Chlamydia infection through an infected cervix at birth
B)HIV infection through breastfeeding
C)Staphylococcus aureus through nosocomial transmission
D)Transplacental transmission of a spirochete
E)Transplacental transmission of a tachyzoite
A)Chlamydia infection through an infected cervix at birth
B)HIV infection through breastfeeding
C)Staphylococcus aureus through nosocomial transmission
D)Transplacental transmission of a spirochete
E)Transplacental transmission of a tachyzoite

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 330 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A 19-year-old man comes to the office with an ulcer on his penis. The patient first noticed the lesion 3 days ago. His temperature is 37.1 C (98.8 F). Physical examination shows an indurated and painless ulcer near the glans penis, with no surrounding erythema and no inguinal lymphadenopathy. The patient is a college student. He has no significant past medical history and takes no medications. He has no known drug allergies. The first-line treatment for this patient has structural similarities with which of the following?
A)D-alanine-D-alanine
B)D-glutamic acid-D-glutamic acid
C)Folic acid
D)L-alanine-D-glutamine
E)N-acetylglucosamine
F)N-acetylmuramic acid
A)D-alanine-D-alanine
B)D-glutamic acid-D-glutamic acid
C)Folic acid
D)L-alanine-D-glutamine
E)N-acetylglucosamine
F)N-acetylmuramic acid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 330 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A 32-year-old man comes to the office due to 2 weeks of fever, malaise, and arthralgia. Temperature is 38.2 C (100.8 F) and pulse is 102/min. Physical examination reveals several enlarged cervical, axillary, and inguinal lymph nodes and a diffuse maculopapular skin rash. Serum aminotransferase levels are elevated. During further testing, the patient's serum is added to a mixture of cardiolipin, cholesterol, and lecithin, which leads to extensive clumping and flocculation. Evaluation for antibodies directed against which of the following is the best next step in management of this patient?
A)Borrelia burgdorferi
B)Fc portion of IgG
C)Histoplasma capsulatum
D)Mitochondrial components
E)Treponema pallidum
A)Borrelia burgdorferi
B)Fc portion of IgG
C)Histoplasma capsulatum
D)Mitochondrial components
E)Treponema pallidum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 330 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A 34-year-old man comes to the office due to a painless penile ulcer, which he first noticed 3 days ago. He had unprotected sexual intercourse with a new partner a few weeks ago. The patient has no significant medical history and takes no medications. Temperature is 37.1 C (98.8 F). Examination reveals a 2-cm nontender ulcer close to the glans penis with a raised, indurated margin and a clean base. There are no surrounding lesions or vesicles. There are several bilateral enlarged inguinal lymph nodes, which are firm, nontender, and rubbery. Physical examination is otherwise unremarkable. Rapid plasma reagin and HIV testing are negative. Infection with which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's symptoms?
A)Chlamydia trachomatis (L serovars)
B)Haemophilus ducreyi
C)Herpes simplex virus
D)Neisseria gonorrhoeae
E)Treponema pallidum
A)Chlamydia trachomatis (L serovars)
B)Haemophilus ducreyi
C)Herpes simplex virus
D)Neisseria gonorrhoeae
E)Treponema pallidum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 330 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A 35-year-old woman comes to the office due to a vulvar lesion. She has also experienced occasional headaches and memory loss recently. The patient has had unprotected sexual intercourse with multiple partners. Cardiovascular examination is notable for a diastolic murmur with a prominent second heart sound. There is a painless indurated nodule on her vulva. Cervical cultures are negative for gonorrhea, but a serum Venereal Disease Research Laboratory (VDRL) test is positive. Chest x-ray reveals calcifications at the level of the ascending aortic arch. Blood cultures are negative. Lumbar puncture shows mild pleocytosis and a positive VDRL result. HIV testing is negative. Which of the following best describes this patient's vulvar lesion?
A)Chancre
B)Condylomata acuminata
C)Condylomata lata
D)Granuloma inguinale
E)Gumma
A)Chancre
B)Condylomata acuminata
C)Condylomata lata
D)Granuloma inguinale
E)Gumma

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 330 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A 1-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department by his mother because of high fever, irritability, and photophobia. He recently underwent ventriculoperitoneal shunt placement for congenital hydrocephalus. On physical examination, his temperature is 38.3° C (101° F), and passive flexion of the neck results in spontaneous flexion of the hips and knees. Blood cultures grow coagulase-negative Staphylococcus. Which of the following is the most important virulence mechanism by which this bacterium causes disease?
A)Intracellular existence
B)Outer polysaccharide capsule
C)Presence of protein A on the cell wall
D)Release of exotoxins
E)Synthesis of an extracellular polysaccharide matrix
A)Intracellular existence
B)Outer polysaccharide capsule
C)Presence of protein A on the cell wall
D)Release of exotoxins
E)Synthesis of an extracellular polysaccharide matrix

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 330 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A 59-year-old woman is brought to the emergency department with fever, skin flushing, and an altered level of consciousness. Her blood pressure is 50/20 mmHg, and her heart rate is 120/min despite receiving IV fluids. If blood cultures are positive for E. coli, which of the following bacterial factors is most directly responsible for this patient's current condition?
A)Capsule
B)Fimbrial antigen
C)Heat-stable exotoxin
D)Lipid A
E)O antigen
A)Capsule
B)Fimbrial antigen
C)Heat-stable exotoxin
D)Lipid A
E)O antigen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 330 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A previously healthy 48-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 2-week history of a nonpruritic rash on his right forearm. The rash began as pustules and progressed to form nodules and 2 other similar papules appeared proximal to the original lesion. He works as a gardener. Physical examination shows a 1-cm, nontender, red nodule on the dorsum of the right hand with 2 smaller papules in linear distribution proximal to it. Which of the following histopathologic findings is most likely present in this patient's skin lesions?
A)Dense inflammatory infiltrate surrounding sulfur granules
B)Granulomas with amastigote parasites inside dermal macrophages
C)Mixed granulomatous and neutrophilic inflammatory reaction
D)Perivascular lymphocytic inflammation and epidermal spongiosis
E)Prominent plasma cell infiltrates and obliterative endarteritis
A)Dense inflammatory infiltrate surrounding sulfur granules
B)Granulomas with amastigote parasites inside dermal macrophages
C)Mixed granulomatous and neutrophilic inflammatory reaction
D)Perivascular lymphocytic inflammation and epidermal spongiosis
E)Prominent plasma cell infiltrates and obliterative endarteritis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 330 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A 38-year-old man comes to the physician because of fever, malaise, productive cough, and left-sided chest pain for 2 weeks. He was diagnosed with HIV infection 1 year ago. He currently stays at a homeless shelter. He has smoked one pack of cigarettes daily for 22 years. He is receiving combined antiretroviral therapy but sometimes misses doses. His temperature is 38.6°C (101.5°F), pulse is 106/min, and blood pressure is 125/85 mm Hg. Pulse oximetry on room air shows an oxygen saturation of 94%. Chest x-ray reveals a right apical lung infiltrate and cavitary lesion. He is placed in respiratory isolation, and appropriate empiric therapy is started. The cavitary lesions seen in this patient most likely formed through which of the following pathogenic mechanisms?
A)Aggregation of activated leukocytes
B)Bacterial toxin-induced cell necrosis
C)Exudation and alveolar hepatization
D)Intraalveolar bacterial overgrowth
E)Obliterative lower airway inflammation
A)Aggregation of activated leukocytes
B)Bacterial toxin-induced cell necrosis
C)Exudation and alveolar hepatization
D)Intraalveolar bacterial overgrowth
E)Obliterative lower airway inflammation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 330 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A 35-year-old woman comes to the emergency department due to an itchy rash that appeared earlier this morning. She recently returned from a family vacation at a resort in Cancun. Two days ago, the patient's husband developed similar symptoms. The patient has no significant past medical history and takes no medications. She has no known allergies. Her temperature is 37.6 C (99.7 F). On examination, there is a diffuse, pruritic, papulopustular rash that is most noticeable on the trunk and extremities. Microbiologic analysis of a pustular fluid sample demonstrates oxidase-positive gram-negative rods that produce pigment on culture medium. Which of the following is the most likely source of this patient's infection?
A)Food
B)Human contact
C)Insects
D)Pets
E)Pool water
F)Soil
A)Food
B)Human contact
C)Insects
D)Pets
E)Pool water
F)Soil

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 330 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A 67-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 6-month history of increasing shortness of breath on exertion, dry cough, and fatigue. He has night sweats and weight loss. Chest x-ray shows pulmonary infiltrates and an area of cavitation in the right upper lobe. Sputum microscopy shows acid-fast bacilli. Which of the following is the most accurate statement concerning this patient's pulmonary infection?
A)First exposure to the bacilli occurred recently
B)Healing of the lung lesion would result in Ghon complex formation
C)It originated from reactivation of an old infection
D)It was facilitated by low levels of protective antibodies
E)Negative tuberculin skin test would signify strong cell-mediated immunity
A)First exposure to the bacilli occurred recently
B)Healing of the lung lesion would result in Ghon complex formation
C)It originated from reactivation of an old infection
D)It was facilitated by low levels of protective antibodies
E)Negative tuberculin skin test would signify strong cell-mediated immunity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 330 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A 13-year-old boy is brought to the physician because of a nonpruritic, painless rash on his face for 5 days. His development is adequate for his age and immunizations are up-to-date. He appears healthy and well-nourished. His temperature is 37.0°C (98.6°F) and pulse is 90/min. Examination shows a nontender rash just inferior to the lower lip. A wound culture is taken, and Gram stain shows gram-positive cocci in chains. Which of the following symptoms would be most likely to develop as a potential complication of this patient's infection?
A)Ascending weakness
B)Facial puffiness and dark urine
C)Fatigue and heart murmur
D)Joint pain and eye redness
E)Unilateral facial drooping
A)Ascending weakness
B)Facial puffiness and dark urine
C)Fatigue and heart murmur
D)Joint pain and eye redness
E)Unilateral facial drooping

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 330 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A 48-year-old man dies in a motor vehicle crash. He had a history of intravenous drug use and had recently been released from prison. The patient's other medical conditions included hepatitis C and hypertension. On autopsy, he is found to have a small, fibrotic focus in the upper portion of the lower lobe of the right lung and a calcified right hilar lymph node. These autopsy findings are most consistent with which of the following?
A)Hematogenous dissemination of Mycobacteria tuberculosis
B)Mycobacterial elimination from the body
C)Poor immunity against mycobacterial infection
D)Primary M tuberculosis infection
E)Secondary M tuberculosis disease
A)Hematogenous dissemination of Mycobacteria tuberculosis
B)Mycobacterial elimination from the body
C)Poor immunity against mycobacterial infection
D)Primary M tuberculosis infection
E)Secondary M tuberculosis disease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 330 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A 28-year-old Marine comes to the veterans' administration outpatient clinic because of a 3-week history of pain on urination. The patient says that the pain has gotten gradually worse and that he has noticed a reddish hue in his urine, especially when he is almost done urinating. He returned from a deployment to Egypt 3 months ago, where he spent 6 months on a mission on the Nile. He has no personal history of serious illness. His father died of metastatic prostate cancer at 82 years of age. He has smoked one pack of cigarettes daily and does not drink alcohol. Vital signs are within normal limits. Physical examination shows no abnormalities. Urine dipstick shows 2+ blood, and urine microscopy shows parasitic eggs with a prominent terminal spine. Which of the following animals is the most likely source of this patient's infection?
A)Bat
B)Dog
C)Fish
D)Pig
E)Sheep
F)Snail
A)Bat
B)Dog
C)Fish
D)Pig
E)Sheep
F)Snail

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 330 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A 7-year-old boy is brought to the physician because of a 3-day history of fever, headache, earache, and sore throat that is worse when swallowing. He has not had a runny nose or cough. His immunizations are up-to-date. He is at the 75th percentile for height and the 50th percentile for weight. His temperature is 38.9°C (102°F), pulse is 136/min, and respirations are 28/min. Examination of the oral cavity reveals a bright red tongue with prominent papillae, a red uvula, and an enlarged right tonsil covered by a whitish membrane. The deep cervical lymph nodes are enlarged and tender. Which of the following complications is most likely to develop in this patient?
A)Aplastic anemia
B)Coronary artery aneurysm
C)Encephalitis
D)Orchitis
E)Rheumatic fever
A)Aplastic anemia
B)Coronary artery aneurysm
C)Encephalitis
D)Orchitis
E)Rheumatic fever

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 330 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A 14-year-old girl is brought to the physician by her father because of fever, chills, abdominal pain, and profuse nonbloody diarrhea. Her symptoms began 1 week ago when she had several days of low-grade fever and constipation. Her father describes continuous fever that has risen slowly to reach a high plateau and is relieved only by antipyretics She returned from Southeast Asia 2 weeks ago, where she spent the summer with her grandparents. Her temperature is 39.3°C (102.8°F). Examination shows diffuse abdominal tenderness and mild hepatosplenomegaly. There is a faint salmon-colored maculopapular rash on her trunk and abdomen. Which of the following is the most likely route of transmission of this patient's infection?
A)Bite from a vector insect
B)Exposure to a carrier animal
C)Ingestion of contaminated food
D)Inhalation of infectious droplets
E)Sexual contact with infected person
A)Bite from a vector insect
B)Exposure to a carrier animal
C)Ingestion of contaminated food
D)Inhalation of infectious droplets
E)Sexual contact with infected person

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 330 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A 48-year-old man comes to the emergency department due to fever. He returned from a vacation in Southeast Asia a week ago and began having symptoms toward the end of his trip. He has also had headaches and abdominal discomfort; he initially had constipation but has had loose stools for the past several days. Temperature is 40 C (104 F), blood pressure is 114/68 mm Hg, and pulse is 62/min. No oropharyngeal lesions, cervical lymphadenopathy, or neck rigidity is present. Lungs are clear on auscultation, and heart sounds are normal. Physical examination reveals a faint, erythematous, macular skin rash over the trunk and abdomen. Blood culture grows non-lactose fermenting gram-negative rods. Which of the following best explains the prolonged and severe disease course from this pathogen compared to the patient's previous bacterial infection?
A)Contact-dependent host cytotoxicity
B)Cross-reacting antibody formation
C)Extensive intra-phagocytic multiplication
D)Potent exotoxin production
E)Villus epithelial cell destruction
A)Contact-dependent host cytotoxicity
B)Cross-reacting antibody formation
C)Extensive intra-phagocytic multiplication
D)Potent exotoxin production
E)Villus epithelial cell destruction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 330 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A previously healthy 24-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 4-day history of fever, headache, myalgias, and abdominal pain. He developed a new rash this morning. He returned from a camping trip in the Appalachian Mountains 5 days ago. He was camping outdoors, drank only filtered water, and used sunscreen. He is sexually active and uses condoms for contraception. He appears ill and fatigued. His temperature is 39.5°C (103.1°F). Physical examination shows conjunctival injection in both eyes without exudate or pus. There is a blanching, macular rash on the palms and soles and petechiae on the wrists and forearms. The patient should be immediately initiated on a medication that targets which of the following?
A)Bacterial DNA unwinding
B)Bacterial folate metabolism
C)Bacterial protein synthesis
D)Fungal ergosterol synthesis
E)Spirochetal cell wall formation
F)Viral reverse transcription
A)Bacterial DNA unwinding
B)Bacterial folate metabolism
C)Bacterial protein synthesis
D)Fungal ergosterol synthesis
E)Spirochetal cell wall formation
F)Viral reverse transcription

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 330 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A 17-year-old boy is hospitalized with recent-onset insomnia, headaches, periodic agitation, and dysphagia. He is a high school student interested in becoming a veterinarian. He owns a snake, fish, and parrot and, about 4 weeks ago, went on a field trip to study bats in a cave. The patient has no known medical problems and is not taking any medications. He does not consume alcohol and has never used illicit drugs. Despite hospitalization and treatment, he develops painful spasms, progressive paralysis, and coma and dies. Which of the following interventions would have most likely prevented this student from developing this illness?
A)Cellular receptor inhibitor drug
B)Inactivated vaccine
C)Interferon therapy
D)Live attenuated vaccine
E)Toxoid vaccine
F)Viral enzyme inhibitor drug
A)Cellular receptor inhibitor drug
B)Inactivated vaccine
C)Interferon therapy
D)Live attenuated vaccine
E)Toxoid vaccine
F)Viral enzyme inhibitor drug

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 330 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A 21-year-old man comes to the emergency department due to shortness of breath, fatigue, myalgias, and debilitating retroorbital headaches for the past several days. The patient is on summer break and came to work at his grandparents' dairy farm 3 weeks ago. He cleans out animal waste from the barn, but he does not handle hay. His past medical history is insignificant. He does not use tobacco or illicit drugs. The patient's temperature is 38.8 C (101.8 F). Bronchial breath sounds are heard in the right lower lung. There are no cardiac murmurs. Abdominal examination is unremarkable. Chest x-ray demonstrates right lower and middle lobe consolidation. Laboratory results are as follows:  An HIV test is negative.Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's symptoms?
An HIV test is negative.Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's symptoms?
A)Borrelia burgdorferi
B)Coxiella burnetii
C)Epstein Barr virus
D)Escherichia coli
E)Salmonella enterica
 An HIV test is negative.Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's symptoms?
An HIV test is negative.Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's symptoms?A)Borrelia burgdorferi
B)Coxiella burnetii
C)Epstein Barr virus
D)Escherichia coli
E)Salmonella enterica

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 330 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A 65-year-old woman presented to the office complaining of painful blisters on the left forehead. Yesterday, she started feeling numbness in her forehead. Physical examination shows vesicles involving the left forehead. This patient could develop blindness due to the involvement of which the following nerves?
A)Abducens
B)Facial
C)Oculomotor
D)Optic
E)Trigeminal
F)Trochlear
A)Abducens
B)Facial
C)Oculomotor
D)Optic
E)Trigeminal
F)Trochlear

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 330 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A 14-year-old girl comes to the physician with dark urine and facial puffiness. About 4 weeks before presentation, she had pustular skin lesions that broke down over a few days to form thick scabs in the lower extremities. Microscopic examination of the urine sediment shows red blood cell casts. The organism responsible for this patient's symptoms would most likely demonstrate which of the following?
A)Bile solubility
B)Catalase positivity
C)Growth in hypertonic saline
D)Optochin sensitivity
E)Pyrrolidonyl arylamidase positivity
A)Bile solubility
B)Catalase positivity
C)Growth in hypertonic saline
D)Optochin sensitivity
E)Pyrrolidonyl arylamidase positivity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 330 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A previously healthy 23-year-old man comes to the office due to abrupt-onset high fever, myalgia, and swelling in his left groin after a recent camping trip in northern California. He appears acutely ill. Physical examination shows tender, left-sided inguinal lymphadenopathy and an enlarged, tender lymph node in the right axilla that is draining bloody necrotic material. Microscopic examination of a lymph node aspirate shows gram-negative coccobacilli with bipolar staining and a safety-pin appearance. This patient's condition is most likely caused by an organism with which of the following reservoirs?
A)Bats
B)Poultry
C)Rodents
D)Sheep
E)Swine
A)Bats
B)Poultry
C)Rodents
D)Sheep
E)Swine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 330 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A microbiologist is studying the structure and function of bacterial cell walls. In an experiment, group A streptococci are treated with chemicals to solubilize the cell wall. Various cell wall-associated proteins are subsequently extracted. Electron microscopic evaluation of a specific protein shows structural homology with mammalian tropomyosin and myosin. This protein acts as a virulence factor for certain species of the organism. Which of the following is the most likely function of this bacterial cell wall-associated protein?
A)Excrete antibiotics
B)Protect from osmotic lysis
C)Provide mechanical cell support
D)Resist phagocytosis
E)Transport nutrients into the cell
A)Excrete antibiotics
B)Protect from osmotic lysis
C)Provide mechanical cell support
D)Resist phagocytosis
E)Transport nutrients into the cell

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 330 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
An 8-year-old boy is brought to the physician because of a 7-day history of a progressively worsening cough. The cough occurs in spells and consists of around 5-10 coughs in succession. After each spell, he takes a deep, noisy breath. He has vomited occasionally following a bout of coughing. He had a runny nose for 1 week before the cough started. His immunization records are unavailable. He lives in an apartment with his father, mother, and 2-week-old sister. The mother was given a Tdap vaccination 11 years ago. The father's vaccination records are unavailable. His temperature is 37.8°C (100.0°F). Examination shows no abnormalities. His leukocyte count is 42,000/mm3. Testing of respiratory secretions shows gram-negative coccobacilli. Which of the following is most likely involved in the pathogenesis of this patient's symptoms?
A)Alveolar influx of polymorphonuclear leukocytes
B)Circulating endotoxin-mediated vasodilation
C)Inflammation and edema of supraglottic tissue
D)Interferon-gamma-induced macrophage activation
E)Loss of ciliated respiratory epithelial cells
A)Alveolar influx of polymorphonuclear leukocytes
B)Circulating endotoxin-mediated vasodilation
C)Inflammation and edema of supraglottic tissue
D)Interferon-gamma-induced macrophage activation
E)Loss of ciliated respiratory epithelial cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 330 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A 34-year-old man, who is a military veteran, comes to the office because of a 2-day history of fever, headache, myalgias, and a lesion on his face. He first noticed a blister on his right cheek, which gradually progressed into a dark sore. He denies recent insect bites, rodent exposure, or animal bites or scratches, but he scratched his face on the ground during a combat exercise. One week ago, he returned from a 1-year deployment in Afghanistan where he worked as an infantry soldier. The patient's medical history is unremarkable. He appears ill and fatigued. His temperature is 38.3°C (101°F). Physical examination shows a 2-cm painless cutaneous ulcer over the right cheek that is surrounded by an edematous halo; the center of the lesion is necrotic. He has multiple abrasions on his face and elbows. There is cervical lymphadenopathy. The toxin causing edema around this patient's ulcer has a mechanism of action most similar to a different toxin produced by which of the following bacteria?
A)Bordetella pertussis
B)Clostridium botulinum
C)Clostridium difficile
D)Shigella dysenteriae
E)Streptococcus pyogenes
A)Bordetella pertussis
B)Clostridium botulinum
C)Clostridium difficile
D)Shigella dysenteriae
E)Streptococcus pyogenes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 330 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A 25-year-old primigravida has a stillbirth at 18 weeks gestation. Her only symptom during pregnancy was pain in both knees and feet, which she attributed to pregnancy-related weight gain and being "on my feet all day" as an elementary school teacher. The pain lasted approximately a week and resolved without medication. The patient was taking prenatal vitamins daily, and her prenatal care was appropriate. Fetal autopsy shows pleural effusion, pulmonary hypoplasia, and ascites. Infection with which of the following is the most likely etiology of the stillbirth?
A)Enveloped, double-stranded DNA virus
B)Enveloped, single-stranded RNA virus
C)Gram-positive coccus in chains
D)Nonenveloped, single-stranded DNA virus
E)Obligate intracellular protozoa
A)Enveloped, double-stranded DNA virus
B)Enveloped, single-stranded RNA virus
C)Gram-positive coccus in chains
D)Nonenveloped, single-stranded DNA virus
E)Obligate intracellular protozoa

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 330 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
A 56-year-old man comes to the emergency department because of a 4-day history of fever and shortness of breath. He has a history of COPD treated with inhaled albuterol. His temperature is 39.0°C (102.2°F), pulse is 95/min, respirations are 20/min, and blood pressure is 130/80 mm Hg. Cardiopulmonary examination shows decreased breath sounds and poor air movement over the left lung. Chest radiograph shows a moderate-sized loculated pleural effusion on the left side. Ultrasonography reveals multiple separate fluid pockets within the pleural space. Chest tube placement produces only a small amount of thick pus. Which of the following is the most likely underlying mechanism for this patient's pleural effusion?
A)Bacterial translocation from alveoli into pleural space
B)Contiguous spread from a mediastinal focus
C)Direct inoculation into the pleural space
D)Hematogenous dissemination of a distant infection
E)Reactivation of a dormant infection
A)Bacterial translocation from alveoli into pleural space
B)Contiguous spread from a mediastinal focus
C)Direct inoculation into the pleural space
D)Hematogenous dissemination of a distant infection
E)Reactivation of a dormant infection

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 330 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A 20-year-old male comes to the physician because of a 1-week-history of a painless ulceration on his penis. The patient is sexually active with multiple partners and does not use barrier protection. He also has a diffuse maculopapular rash involving the trunk, extremities, palms, and soles. An HIV test is negative. Rapid plasma reagin (RPR) and fluorescent treponemal antibody absorption test (FTA-ABS) are positive. Genital examination reveals multiple elevated lesions on the scrotum and perineal region. Histopathologic evaluation of these lesions would most likely reveal which of the following in this patient?
A)Acantholysis with superficial dermal lymphocytic infiltrate
B)Dysplastic spindle cells with viral genome that form vascular channels
C)Intense plasma cell-rich infiltrate with proliferative endarteritis
D)Panniculitis and septal inflammation with multinucleated giant cells
E)Papillomatous epidermal hyperplasia with cytoplasmic vacuolization
A)Acantholysis with superficial dermal lymphocytic infiltrate
B)Dysplastic spindle cells with viral genome that form vascular channels
C)Intense plasma cell-rich infiltrate with proliferative endarteritis
D)Panniculitis and septal inflammation with multinucleated giant cells
E)Papillomatous epidermal hyperplasia with cytoplasmic vacuolization

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 330 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A 65-year-old man comes to his physician because of progressively worsening shortness of breath for the past 2 months. He does not experience shortness of breath at rest. He also occasionally has a dry cough. He has not had fever, chills, or night sweats. The patient has smoked a pack of cigarettes daily for 40 years. His temperature is 37°C (98.6°F), pulse is 86/min, respirations are 22/min, and blood pressure is 133/85 mm Hg. Lung auscultation reveals a prolonged expiratory phase and end-expiratory wheezing. Sputum cultures in specialized media grow round-to-oval, budding yeast, which form germ tubes when incubated at 37 C in serum. Which of the following best explains the presence of the organism in this patient's sputum sample?
A)Colonization of a preexisting lung cavity
B)Contamination by normal oral flora
C)Embolization of infectious microthrombi
D)Lung infection from inhaled microconidia
E)Proliferation of previously latent organism
A)Colonization of a preexisting lung cavity
B)Contamination by normal oral flora
C)Embolization of infectious microthrombi
D)Lung infection from inhaled microconidia
E)Proliferation of previously latent organism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 330 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A 61-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 5-month history of sharp, shooting pain in both legs. Twenty years ago, he had a painless ulcer on his penis that resolved without treatment. He has no history of serious illness. Examination shows small pupils that constrict with accommodation but do not react to light. Sensation to pinprick and light touch is decreased over the distal lower extremities. Patellar reflexes are absent bilaterally. His gait is unsteady and broad-based. This patient is at increased risk for which of the following complications?
A)Atrioventricular block
B)Mitral valve regurgitation
C)Penile squamous cell carcinoma
D)Cerebral artery septic embolism
E)Thoracic aortic aneurysm
A)Atrioventricular block
B)Mitral valve regurgitation
C)Penile squamous cell carcinoma
D)Cerebral artery septic embolism
E)Thoracic aortic aneurysm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 330 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A 45-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 3-week history of diarrhea and a 2.2-kg (5-lb) weight loss. He reports a several weeks of progressive fever, night sweats, and generalized weakness. . He has HIV, gastroesophageal reflux disease, and hypertension. Current medications include chlorthalidone, omeprazole, emtricitabine, tenofovir, and efavirenz. He reports taking efavirenz irregularly. He is employed as a sales manager and regularly flies to South America. Physical examination shows mucosal pallor, generalized lymphadenopathy, and hepatosplenomegaly. CD4+ T-lymphocyte count is 20/mm3. Nucleic acid amplification test of the sample for Mycobacterium tuberculosis is negative. Which of the following pathogens is the most likely cause of this patient's illness?
A)Cryptococcus neoformans
B)Cryptosporidium parvum
C)Legionella pneumophila
D)Mycobacterium avium
E)Mycobacterium marinum
F)Nocardia asteroides
A)Cryptococcus neoformans
B)Cryptosporidium parvum
C)Legionella pneumophila
D)Mycobacterium avium
E)Mycobacterium marinum
F)Nocardia asteroides

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 330 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A 35-year-old man comes to the emergency department with fever, chills, dyspnea, and a productive cough. His symptoms began suddenly 2 days ago. He smokes one pack of cigarettes daily. He is 181 cm (5 ft 11 in) tall and weighs 69 kg (152 lb); BMI is 21 kg/m2. He lives in Illinois and works as a carpenter. His temperature is 38.8°C (101.8°F), pulse is 110/min, respirations are 24/min, and blood pressure is 105/74 mm Hg. Pulse oximetry on room air shows an oxygen saturation of 92%. Leukocyte count is 14,000/mm3 with 80% neutrophils and 7% bands, hemoglobin is 13.6 g/dL, and platelets are 400,000/mm3. Serum levels of which of the following are most likely to be elevated in this patient?
A)B-type natriuretic peptide
B)Cold agglutinins
C)Prealbumin
D)Procalcitonin
E)Transferrin
A)B-type natriuretic peptide
B)Cold agglutinins
C)Prealbumin
D)Procalcitonin
E)Transferrin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 330 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A 31-year-old man is brought to the emergency department after a tonic-clonic seizure. The patient has no known medical conditions. He grew up in a rural part of Guatemala and immigrated to the United States 3 years ago. The patient works as an architect and owns a cat. He has no history of tuberculosis. On examination, the patient is afebrile and has no focal neurologic deficits or meningeal signs. HIV antibody test and interferon-gamma release assay are negative. Chest x-ray is normal. MRI of the head reveals a 1.5-cm cyst within the left sylvian fissure that has minimal enhancement and no associated edema. Which of the following is the most likely means of acquisition of the infection responsible for this patient's findings?
A)Absorption through the skin of the feet
B)Exposure to infected stool
C)Handling of a cat litter box
D)Inhalation of fungal spores
E)Scratch from a cat
F)Sexual transmission
A)Absorption through the skin of the feet
B)Exposure to infected stool
C)Handling of a cat litter box
D)Inhalation of fungal spores
E)Scratch from a cat
F)Sexual transmission

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 330 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
A 56-year-old man comes to the office due to several months of progressive neck swelling. He has also had intermittent epistaxis and headaches. The patient has no chronic medical conditions and takes no medications. He does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs, and he emigrated to the United States from rural China 12 years ago. Physical examination shows several enlarged, firm, and nontender cervical lymph nodes. Nasopharyngeal evaluation reveals a mass arising from the pharyngeal recess. Histopathological examination of the mass shows undifferentiated malignant cells of epithelial origin. Further analysis of these cells is most likely to reveal the presence of nucleic acid sequences from which of the following viruses?
A)Adenovirus
B)Coronavirus
C)Cytomegalovirus
D)Epstein-Barr virus
E)Human herpes virus 8
F)Polyomavirus
A)Adenovirus
B)Coronavirus
C)Cytomegalovirus
D)Epstein-Barr virus
E)Human herpes virus 8
F)Polyomavirus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 330 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
A 35-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a history of malodorous vaginal discharge. She has no pain or pruritus. Menses occur at regular 27-day intervals and last 5 days. Her last menstrual period was 2 weeks ago. She is sexually active with two male partners and uses a diaphragm for contraception. She had a normal Pap smear 3 months ago. She has no history of serious illness and takes no medications. Her temperature is 37.3°C (99°F), pulse is 75/min, and blood pressure is 115/75 mm Hg. Pelvic examination shows malodorous, gray vaginal discharge. The pH of the discharge is 5.0. Application of potassium hydroxide solution to the discharge yields a strong odor. Which of the following is the best treatment option for this patient?
A)Azithromycin
B)Ceftriaxone
C)Clindamycin
D)Fluconazole
E)Penicillin
A)Azithromycin
B)Ceftriaxone
C)Clindamycin
D)Fluconazole
E)Penicillin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 330 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A previously healthy 3-week-old infant is brought to the emergency department 6 hours after the onset of fever and persistent irritability. He had been well until 2 days ago, when he started feeding poorly and sleeping more than usual. He appears lethargic and irritable when roused for examination. His temperature is 39.0°C (102°F). He cries when he is picked up and when his neck is flexed. The remainder of the physical and neurological examinations show no other abnormalities. His serum glucose is 95 mg/mL. His total serum bilirubin is 6.3 mg/dL. CSF culture grows numerous gray colonies on blood agar, with a narrow area of clearing surrounding each colony. Gram staining shows gram-positive cocci in short chains. Which of the following virulence factors is primarily involved in the pathogenesis of this patient's infection?
A)Antigenic variation of membranous proteins
B)Catalyzation of hydrogen peroxide to oxygen and water
C)Increased uptake of extracellular iron
D)Lipopolysaccharide deposition in outer membranes
E)Polysaccharide capsule formation around organism
F)Rapid, flagella-mediated motion
A)Antigenic variation of membranous proteins
B)Catalyzation of hydrogen peroxide to oxygen and water
C)Increased uptake of extracellular iron
D)Lipopolysaccharide deposition in outer membranes
E)Polysaccharide capsule formation around organism
F)Rapid, flagella-mediated motion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 330 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
A 2-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department because of fever and poor feeding for 2 days. He became very fussy the previous evening and cried for most of the night. Examination shows a stiff neck. The pupils are equal and reactive to light. Neck flexion results in flexion of the knee and hip. Muscle strength is decreased in the right upper extremity. Laboratory results are as follows:  While being evaluated, the patient develops apnea and asystole. Despite aggressive resuscitation efforts, the patient dies. Autopsy would most likely reveal which of the following?
While being evaluated, the patient develops apnea and asystole. Despite aggressive resuscitation efforts, the patient dies. Autopsy would most likely reveal which of the following?
A)Adrenal hemorrhage
B)Cardiac tamponade
C)Intracerebral hemorrhage
D)Necrotizing pancreatitis
E)Saddle pulmonary embolus
 While being evaluated, the patient develops apnea and asystole. Despite aggressive resuscitation efforts, the patient dies. Autopsy would most likely reveal which of the following?
While being evaluated, the patient develops apnea and asystole. Despite aggressive resuscitation efforts, the patient dies. Autopsy would most likely reveal which of the following?A)Adrenal hemorrhage
B)Cardiac tamponade
C)Intracerebral hemorrhage
D)Necrotizing pancreatitis
E)Saddle pulmonary embolus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 330 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
A 28-year-old primigravid woman at 31 weeks' gestation comes to the physician because of fever, myalgia, abdominal pain, nausea, and diarrhea for 3 days. Her pregnancy has been uncomplicated. Her only medication is a prenatal vitamin. Her temperature is 39.4°C (102.9°F). Physical examination shows diffuse abdominal pain. Blood cultures incubated at 4°C (39.2°F) grow a gram-positive, catalase-positive organism. Which of the following organisms is most likely responsible for this symptoms?
A)Aspergillus fumigatus
B)Cytomegalovirus
C)Escherichia coli O157:H7
D)Herpes simplex virus
E)Listeria monocytogenes
F)Neisseria meningitidis
G)Streptococcus pneumoniae
H)Toxoplasma gondii
A)Aspergillus fumigatus
B)Cytomegalovirus
C)Escherichia coli O157:H7
D)Herpes simplex virus
E)Listeria monocytogenes
F)Neisseria meningitidis
G)Streptococcus pneumoniae
H)Toxoplasma gondii

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 330 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A 24-year-old man is brought to the physician with fever, malaise, and unilateral facial pain and swelling that began 2 days ago. He has an appendictomy 3 days ago. His temperature is 38.2°C (100.8°F). There is erythema, edema, and tenderness of the right parotid glands. Physical examination shows firm swelling of the preauricular area on the right side extending to the angle of the mandible. Which of the following serum markers is most helpful for confirming the diagnosis?
A)Alkaline phosphatase
B)Amylase
C)Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase
D)Lipase
E)Parathyroid hormone
A)Alkaline phosphatase
B)Amylase
C)Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase
D)Lipase
E)Parathyroid hormone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 330 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A 6-day-old female infant is brought to the emergency department because of poor feeding and irritability for two days. She was born at 39 weeks' gestation, and the pregnancy and delivery were uncomplicated. Her temperature is 39.2°C (102.6°F). She appears lethargic and makes occasional twitching movements in both upper extremities. The anterior fontanelle is soft and full. Empiric cefotaxime and vancomycin therapy is initiated. A lumbar puncture is performed and analysis of the cerebrospinal fluid shows increased protein and decreased glucose. Cerebrospinal fluid culture shows an organism that is resistant to cefotaxime. Which of the following organisms is most likely causing this patient's infection?
A)Haemophilus influenzae
B)Listeria monocytogenes
C)Neisseria meningitidis
D)Streptococcus agalactiae
E)Streptococcus pneumoniae
A)Haemophilus influenzae
B)Listeria monocytogenes
C)Neisseria meningitidis
D)Streptococcus agalactiae
E)Streptococcus pneumoniae

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 330 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A 10-week-old boy is brought to the office for a follow-up visit. As part of his routine immunization schedule, the patient received the first dose of the Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) conjugate vaccine when he was 8 weeks old. However, following vaccine administration, he developed anaphylaxis, requiring epinephrine administration and hospitalization. As a result, the decision was made not to administer additional doses of the Hib vaccine. The patient was born full-term by uncomplicated vaginal delivery and has otherwise been healthy. Physical examination is unremarkable. His older brother has completed the full vaccination course. This patient is at highest risk of which of the following infections compared to his brother?
A)Acute bronchiolitis
B)Bacterial conjunctivitis
C)Meningitis
D)Otitis media
E)Sinusitis
A)Acute bronchiolitis
B)Bacterial conjunctivitis
C)Meningitis
D)Otitis media
E)Sinusitis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 330 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A 10-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department because of high-grade fever and lethargy for 4 days. He has had a severe headache for 3 days and 2 episodes of non-bilious vomiting. He appears ill. His temperature is 40.1°C (104.2°F), pulse is 131/min, and blood pressure is 92/50 mm Hg. Examination shows nuchal rigidity. Kernig and Brudzinski signs are present. A lumbar puncture is performed. Analysis of the cerebrospinal fluid shows a decreased glucose concentration, increased protein concentration, and numerous segmented neutrophils; a Gram stain shows gram-negative cocci in pairs. The parents are concerned about their younger son, who shares a bedroom with the patient. Which of the following is the most appropriate management of this patient's household contacts?
A)Immediate vaccination
B)Observation only
C)Prophylactic penicillin
D)Prophylactic rifampin
E)Prophylactic sulfamethoxazole
A)Immediate vaccination
B)Observation only
C)Prophylactic penicillin
D)Prophylactic rifampin
E)Prophylactic sulfamethoxazole

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 330 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A 5-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department for evaluation of a progressive rash that started 2 days ago. The rash began on the face and progressed to the trunk and extremities. Over the past week, he has had a runny nose, a cough, and red, crusty eyes. He immigrated with his family from Turkey 3 months ago. His father and his older brother have Behçet disease. Immunization records are unavailable. The patient appears irritable and cries during the examination. His temperature is 40.0°C (104°F). Examination shows generalized lymphadenopathy and dry mucous membranes. Skin turgor is decreased. There is a blanching, partially confluent erythematous maculopapular exanthem. Examination of the oral cavity shows two 5-mm aphthous ulcers at the base of the tongue. His hemoglobin concentration is 11.5 g/dL, leukocyte count is 6000/mm3, and platelet count is 215,000/mm3. Deficiency of which of the following is associated with a high rate of complications from this patient's condition?
A)Vitamin A
B)Vitamin B6
C)Vitamin B12
D)Vitamin D
E)Vitamin E
F)Vitamin K
A)Vitamin A
B)Vitamin B6
C)Vitamin B12
D)Vitamin D
E)Vitamin E
F)Vitamin K

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 330 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A 45-year-old man comes to the office with groin pain and swelling. About a month ago, he noticed a sore on his penis but did not seek medical attention because the ulcer was not painful and disappeared within a week. Several days ago, he began to experience painful swelling in his inguinal region, with inflammation of the overlying skin and eventual formation of several draining ulcers. He also has mild fever and malaise that began around the same time as his groin symptoms. The patient is a sailor. His other medical problems include well-controlled hypertension and hyperlipidemia. Cell scrapings from his lesions show cytoplasmic inclusion bodies. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's condition?
A)Chlamydia trachomatis
B)Haemophilus ducreyi
C)Herpes simplex virus
D)Klebsiella granulomatis
E)Treponema pallidum
A)Chlamydia trachomatis
B)Haemophilus ducreyi
C)Herpes simplex virus
D)Klebsiella granulomatis
E)Treponema pallidum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 330 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
A 24-year-old man comes to the physician with painful blisters on the shaft of his penis. The lesions erupted 2 days ago. The patient has had 5 lifetime sexual partners and is currently sexually active with one female partner; he uses condoms inconsistently. Examination shows multiple vesicular lesions on the penis. HIV testing is negative. The patient has had several similar episodes every year for the past 2 years but had been too embarrassed to seek treatment until now. Which of the following is the best diagnostic test for this patient's condition?
A)Biopsy of the lymph node
B)Darkfield microscopy
C)Gram stain of the ulcer swab
D)PCR for viral DNA
E)Potassium hydroxide preparation
A)Biopsy of the lymph node
B)Darkfield microscopy
C)Gram stain of the ulcer swab
D)PCR for viral DNA
E)Potassium hydroxide preparation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 330 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
A 9-month-old girl is brought to the physician by her mother because of a generalized nonpruritic rash for 2 days. The rash began on her trunk and spread to her extremities. Five days ago, she was taken to the emergency department for fever of 40.5°C (104.9°F) and a 1-minute generalized tonic-clonic seizure. The mother says the fever resolved abruptly. The patient was born at term and has no history of serious illness. Her immunizations are up-to-date. Current medications include acetaminophen. Her temperature is 37.2°C (99.0°F) and pulse is 120/min. Examination shows a maculopapular rash that blanches on pressure. Posterior auricular lymphadenopathy is present. Infection with which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's condition?
A)Coxsackievirus A16
B)Herpes simplex virus type 1
C)Human herpesvirus 6
D)Measles virus
E)Parvovirus B19
F)Rubella virus
G)Streptococcus pyogenes
A)Coxsackievirus A16
B)Herpes simplex virus type 1
C)Human herpesvirus 6
D)Measles virus
E)Parvovirus B19
F)Rubella virus
G)Streptococcus pyogenes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 330 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A 30-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a dry cough and chest discomfort for the past 3 days. During this period, the patient has had headaches, muscle aches, joint pain, fever, and chills. Ten days ago, she was hiking with her family in Mississippi. The patient has asthma that is treated with an albuterol inhaler. Her mother has a lung disease treated with methotrexate. The patient has smoked one pack of cigarettes daily for the past 10 years. Her temperature is 38°C (100.4°F). Physical examination shows slight wheezes throughout both lung fields. Chest imaging shows several small calcified nodules in both lungs and a calcified mediastinal lymph node. Urinalysis is positive for a polysaccharide antigen. Tuberculosis skin test shows a <5 mm induration at 48 hours. Which of the following is the most likely cause of the observed findings in this patient?
A)Fungal infection
B)Metastatic cancer
C)Miliary tuberculosis
D)Parathyroid adenoma
E)Silica exposure
A)Fungal infection
B)Metastatic cancer
C)Miliary tuberculosis
D)Parathyroid adenoma
E)Silica exposure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 330 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
A 25-year-old man with multiple injuries sustained in a motorcycle accident develops osteomyelitis while in the hospital. The organism is identified as methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus, and antibiotics are started. Which of the following is the most important measure to reduce the risk of transmission to other patients?
A)Contact precautions
B)Hand hygiene
C)Isolation precautions
D)Masks
E)Restricting visitors
A)Contact precautions
B)Hand hygiene
C)Isolation precautions
D)Masks
E)Restricting visitors

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 330 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A previously healthy 22-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 1-week history of fever, fatigue, myalgia, sore throat, and difficulty swallowing. He works as a tour guide but has been unable to go to work for the last few days because he is easily exhausted. He has no history of serious illness and takes no medications. He appears lethargic. His temperature is 38.7°C (101.7°F), pulse is 72/min, and blood pressure is 116/74 mm Hg. Examination of the neck and oropharynx shows tender cervical lymphadenopathy and erythematous, swollen tonsils with white exudates. Lungs are clear to auscultation. The liver is palpated 3 cm below the right costal margin and the spleen is palpated 2 cm below the left costal margin. His hemoglobin concentration is 13.2 g/dL and his leukocyte count is 16,400/mm3. A blood smear shows atypical lymphocytosis. A heterophile antibody test is positive. Which of the following is most likely to be elicited on further history?
A)Anal sexual intercourse
B)Contact with saliva
C)Exposure to urine
D)Prior blood transfusion
E)Recent tick bite
F)School trip to South Asia
A)Anal sexual intercourse
B)Contact with saliva
C)Exposure to urine
D)Prior blood transfusion
E)Recent tick bite
F)School trip to South Asia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 330 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
A 5-year-old girl is brought to the office by her mother due to 2 weeks of anorexia, nausea, epigastric discomfort, and loose bowel movements. She has had no fever or bloody stools. The patient recently returned from rural Brazil, where she spent the summer with family. She had no gastrointestinal symptoms during the trip but developed intensely pruritic eruptions between the toes of her right foot. The skin rash spontaneously resolved within a few days and was attributed to insect bites from walking barefoot in the fields. The patient has no prior medical conditions, takes no medications, and has received all age-appropriate vaccinations. On physical examination, the abdomen is soft and nontender with normoactive bowel sounds. Stool microscopy reveals smooth, thin-walled eggs. If left untreated, this patient's condition can lead to which of the following complications?
A)Chronic lymphedema
B)Dilated cardiomyopathy
C)Granulomatous endophthalmitis
D)Microcytic anemia
E)Vitamin B12 deficiency
A)Chronic lymphedema
B)Dilated cardiomyopathy
C)Granulomatous endophthalmitis
D)Microcytic anemia
E)Vitamin B12 deficiency

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 330 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
A 35-year-old man comes to the emergency department with fever, chills, dyspnea, and a productive cough. His symptoms began suddenly 2 days ago. The patient has no prior medical conditions and does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs He lives in Illinois and works as a carpenter. His temperature is 38.8°C (101.8°F), pulse is 110/min, respirations are 24/min, and blood pressure is 105/74 mm Hg. Pulse oximetry on room air shows an oxygen saturation of 92%. Examination reveals crackles over the right lower lung base. The remainder of the examination shows no abnormalities. An x-ray of the chest shows a right lower-lobe infiltrate of the lung. The underlying immune response to this patient's infection largely involves T helper (Th1) cells, interferon-gamma, and interleukin-2. Which of the following is the most likely pathogen responsible for this patient's pneumonia?
A)Haemophilus influenzae
B)Legionella pneumophila
C)Pseudomonas aeruginosa
D)Staphylococcus aureus
E)Streptococcus pneumoniae
A)Haemophilus influenzae
B)Legionella pneumophila
C)Pseudomonas aeruginosa
D)Staphylococcus aureus
E)Streptococcus pneumoniae

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 330 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
A previously healthy 25-year-old man who is on active duty in the US Navy comes to the military urgent care clinic with fever, headache, reddening of the eyes, and muscle ache for the past 4 days. He has not had itching or eye discharge. He has been stationed in Hawaii for the past year. He has no travel history and none of his other colleagues have similar complaints. He received the hepatitis A vaccine 2 years ago. He is not in acute distress. His temperature is 38.5°C (101.3°F), pulse is 90/min, respirations are 16/min, and blood pressure is 110/70 mm Hg. Examination of the eyes shows diffusely erythematous conjunctiva bilaterally without an exudate. Bilateral calves are tender to palpation. The remainder of the physical examination is unremarkable. This patient most likely acquired the infection via which of the following?
A)Being in close vicinity of infected bats
B)Bites from infected rodent fleas
C)Exposure to water contaminated with animal urine
D)Hiking in tick-infested wooded areas
E)Hunting and skinning of wild rabbits
A)Being in close vicinity of infected bats
B)Bites from infected rodent fleas
C)Exposure to water contaminated with animal urine
D)Hiking in tick-infested wooded areas
E)Hunting and skinning of wild rabbits

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 330 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
A 28-year-old primigravid woman at 31 weeks' gestation comes to the physician because of fever, myalgia, abdominal pain, nausea, and diarrhea for 3 days. Her pregnancy has been uncomplicated. Her only medication is a prenatal vitamin. Her temperature is 39.4°C (102.9°F). Physical examination shows diffuse abdominal pain. Blood cultures incubated at 4°C (39.2°F) grow a gram-positive, catalase-positive organism. Which of the following is the major virulence factor of the organism responsible for this patient's clinical presentation?
A)Cytotoxin that creates pores in phagosomes
B)Endotoxin-mediated complement and tissue factor activation
C)Exotoxin inhibition of neurotransmitter release
D)Exotoxin-mediated inhibition of elongation factor
A)Cytotoxin that creates pores in phagosomes
B)Endotoxin-mediated complement and tissue factor activation
C)Exotoxin inhibition of neurotransmitter release
D)Exotoxin-mediated inhibition of elongation factor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 330 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
A 73-year-old man is brought to the emergency department because of fever, headaches, and confusion for the past 24 hours. Three years ago, he underwent heart transplantation because of congestive heart failure. His temperature is 38.1°C (100.5°F). He is oriented only to person. Physical examination shows nuchal rigidity. A cerebrospinal fluid culture on blood agar grows colonies of a gram-positive bacillus surrounded by a narrow transparent rim. Which of the following processes is most important for eliminating these bacteria from the body?
A)Cell-mediated immunity
B)Eosinophil action
C)Immunoglobulin secretion
D)Mast cell activation
E)Terminal complement cascade
A)Cell-mediated immunity
B)Eosinophil action
C)Immunoglobulin secretion
D)Mast cell activation
E)Terminal complement cascade

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 330 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
A 2-hour-old girl develops tachypnea and grunting in the newborn nursery. The patient was born via cesarean delivery to a 26-year-old mother, gravida 2 para 2. Respiratory rate is 82/min. The other vital signs are within normal limits. Physical examination shows grunting and subcostal retractions but clear lungs. Blood culture reveals gram-positive rods after 11 hours of incubation. Which of the following pathogens is the most likely cause of this patient's condition?
A)Clostridium tetani
B)Corynebacterium species
C)Escherichia coli
D)Listeria monocytogenes
E)Streptococcus agalactiae
F)Streptococcus pneumoniae
A)Clostridium tetani
B)Corynebacterium species
C)Escherichia coli
D)Listeria monocytogenes
E)Streptococcus agalactiae
F)Streptococcus pneumoniae

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 330 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
A 4-year-old boy is brought to the office due to 3-day history of fever, cough, and a runny nose. The patient emigrated from Syria 2 weeks ago. He has not yet received any routine childhood vaccinations. Physical examination shows an ill-appearing, febrile child. Examination shows conjunctivitis of both eyes. There are multiple, 2-mm-sized, bluish-gray papules with an erythematous rim on the buccal mucosa and the soft palate Over the next several days, which of the following is most likely to develop?
A)Jaundice
B)Maculopapular rash
C)Parotid swelling
D)Paroxysmal cough
E)Upper airway obstruction
F)Vesicular rash
G)Watery diarrhea
A)Jaundice
B)Maculopapular rash
C)Parotid swelling
D)Paroxysmal cough
E)Upper airway obstruction
F)Vesicular rash
G)Watery diarrhea

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 330 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
A 55-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 2-week history of back pain. He has not sustained any recent trauma. He has a history of end-stage renal disease receiving intermittent hemodialysis. He appears well. Temperature is 37.5°C (99.5°F), pulse is 79/min, and blood pressure is 124/78 mm Hg. The patient also has hypertension and type 2 diabetes mellitus and was treated several weeks ago for staphylococcal bacteremia associated with the dialysis catheter. Her temperature is 38 C (100.4 F). On examination, he has tenderness over the upper lumbar vertebrae without overlying skin changes. The straight leg raise test is negative. Which of the following is the best next step in management of this patient?
A)Analgesics and close follow-up
B)CT myelogram
C)Lumbar puncture
D)MRI of the spine
E)Serum protein electrophoresis
A)Analgesics and close follow-up
B)CT myelogram
C)Lumbar puncture
D)MRI of the spine
E)Serum protein electrophoresis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 330 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
A 10-year-old boy is brought to the physician by his mother because of a 2-week history of fever and pain in his right thigh that is causing him to limp. He has no history of recent trauma other than minor scrapes to his knees and elbows while playing outside . His immunizations are up-to-date. The patient appears well. He is at the 40th percentile for height and 45th percentile for weight. His temperature is 38.2°C (100.8°F), pulse is 100/min, respirations are 18/min, and blood pressure is 110/70 mm Hg. Examination shows swelling, tenderness, warmth, and mild erythema over the right upper thigh; range of motion is limited by pain. He has a right-sided antalgic gait. His leukocyte count is 12,300/mm3 and erythrocyte sedimentation rate is 40 mm/h. X-rays of the hips and lower extremities are unremarkable. An MRI of the right lower extremity shows increased T2 and decreased T1 signals over the right femur with periosteal elevation, multiple osteolytic areas in the femoral metaphysis, and bone marrow edema. Which of the following organisms is most likely responsible for this patient's symptoms?
A)Enterococcus faecalis
B)Moraxella catarrhalis
C)Staphylococcus aureus
D)Staphylococcus epidermidis
E)Streptococcus agalactiae
F)Streptococcus pneumoniae
G)Streptococcus pyogenes
A)Enterococcus faecalis
B)Moraxella catarrhalis
C)Staphylococcus aureus
D)Staphylococcus epidermidis
E)Streptococcus agalactiae
F)Streptococcus pneumoniae
G)Streptococcus pyogenes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 330 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
A 28-year-old homeless man presents to the emergency department with pain and discoloration of his left foot. He says that a few days ago, he accidentally stepped on a piece of scrap metal while walking across a parking lot with bare feet. He went to the emergency room and received a dose of tetanus toxoid vaccination for wound prophylaxis. Last night, he felt the sudden onset of pain on the bottom of his left foot and notes that severe pain has spread diffusely to the dorsum of his foot as well. His temperature is 100.8°F (38.2°C), pulse is 110/min, respirations are 18/min, and blood pressure is 108/58 mmHg. Palpation of the skin on the dorsum of his left foot reveals tenderness and crepitus. Which of the following best describes the mechanism of action of the toxin responsible for the necrotic effects seen in this patient?
A)Actin depolymerization
B)Carbohydrate degradation
C)Elongation factor ribosylation
D)Phospholipid splitting
E)Plasminogen activation
F)Presynaptic acetylcholine release inhibition
G)T-cell hyperstimulation
A)Actin depolymerization
B)Carbohydrate degradation
C)Elongation factor ribosylation
D)Phospholipid splitting
E)Plasminogen activation
F)Presynaptic acetylcholine release inhibition
G)T-cell hyperstimulation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 330 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
A 40-year-old man presents to his physician with complaints of a cough and fatigue that have significantly affected his daily routine. He lives alone and denies any sick contacts at his workplace but notes that he was formerly incarcerated and released 3 months ago. Upon further questioning, he states that he has coughed up blood a few times in the past weeks and has been having occasional night sweats. A chest x-ray demonstrates a right apical lung lesion. A tuberculosis diagnosis is made. Which of the following would most likely happen during the first week of infection?
A)Epithelioid transformation of macrophages
B)Interferon secretion by activated T lymphocytes
C)Intracellular bacterial proliferation
D)Mounting response by B lymphocytes
E)Scattered areas of caseous necrosis
A)Epithelioid transformation of macrophages
B)Interferon secretion by activated T lymphocytes
C)Intracellular bacterial proliferation
D)Mounting response by B lymphocytes
E)Scattered areas of caseous necrosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 330 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
A 56-year-old immigrant from Haiti comes to the hospital with a three week history of cough and fever. He has a history of hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and has a 30 pack year smoking history. On physical exam, the upper right lung field is dull to percussion. There are no other significant exam findings. Her temperature is 98.7 °F (37 °C), blood pressure is 142/85 mmHg, pulse is 87/min, respirations are 18/min. Sputum cultures grown on a selective medium demonstrate mycobacteria that appear as parallel chains (serpentine cords) under microscopy. This observed growth pattern in culture medium most strongly correlates with which of the following?
A)Acid-fastness
B)Antibiotic resistance
C)Growth rates
D)Pigmentation
E)Virulence
A)Acid-fastness
B)Antibiotic resistance
C)Growth rates
D)Pigmentation
E)Virulence

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 330 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
A 63-year-old woman comes to the office due to a new-onset cough, night sweats, and hemoptysis since last week. The patient grew up in Bangladesh and immigrated to the United States when she was 35 years old. Her only medical condition is polycystic kidney disease, for which she received a kidney transplant 8 months ago. Her temperature is 98°F (36.7°C), blood pressure is 122/75 mmHg, pulse is 85/min, and respirations are 16/min. On lung auscultation, inspiratory crackles are present. A chest radiograph is ordered and a new cavitary lesion is noted in the apical-posterior segment of her left upper lobe. Bacteria isolated from the lung tissue fail to decolorize with hydrochloric acid and alcohol after staining carbolfuchsin. Which of the following cell wall components is most likely responsible for this staining phenomenon?
A)N-acetylmuramic acid
B)Teichoic acid
C)Lipopolysaccharide
D)Mycolic acid
E)Ergosterol
A)N-acetylmuramic acid
B)Teichoic acid
C)Lipopolysaccharide
D)Mycolic acid
E)Ergosterol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 330 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
A previously healthy 2-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department because of a 2-day history of fever and pain in the left lower extremity. His mother says that he has refused to walk for the past two days and has had a poor appetite. He returned from a weekend camping trip about a month ago. Further medical history reveals that his parents refused to have the vaccination. He is at the 80th percentile for height and 70th percentile for weight. He appears ill. His temperature is 39.3°C (102.7°F), pulse is 115/min, respirations are 19/min, and blood pressure is 95/50 mm Hg. Synovial fluid aspiration shows shows cloudy synovial fluid. Gram stain of the aspirate reveals pleomorphic, gram-negative coccobacilli. Cultures performed on a blood agar plate supplemented with a disk containing hematin and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) grow colonies only near the disk. The organism responsible for this patient's condition most likely produces which of the following virulence factors?
A)Capsule
B)Cytotoxic exotoxin
C)Fimbriae
D)Hemolysins
E)Hyaluronidase
A)Capsule
B)Cytotoxic exotoxin
C)Fimbriae
D)Hemolysins
E)Hyaluronidase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 330 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
An 8-year-old boy is brought to the physician because of a 7-day history of a progressively worsening cough. The cough occurs in spells and consists of around 5-10 coughs in succession. After each spell, he takes a deep, noisy breath. He has vomited occasionally following a bout of coughing. He had a runny nose for 1 week before the cough started. His immunization records are unavailable. He lives in an apartment with his father, mother, and 2-week-old sister. The mother was given a Tdap vaccination 11 years ago. The father's vaccination records are unavailable. His temperature is 37.8°C (100.0°F). Examination shows no abnormalities. His leukocyte count is 42,000/mm3. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's symptoms?
A)Acid-fast bacillus
B)Gram-negative coccobacillus
C)Gram-positive diplococcus
D)Mycoplasma
E)RNA virus
A)Acid-fast bacillus
B)Gram-negative coccobacillus
C)Gram-positive diplococcus
D)Mycoplasma
E)RNA virus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 330 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
A 16-year-old boy is brought to the clinic by his mother for "pink eye." The patient reports that his friend had pink eye about 4 days ago, and he began experiencing some irritation and watery non-purulent discharge in his right eye 2 days prior. Today, he developed similar symptoms in his left eye. Bright lights exacerbate the eye irritation but he denies fever, chills, vision changes, eye pain, or periorbital swelling. His past medical history is unremarkable, and he denies being sexually active. Which of the following is the most likely cause of the outbreak?
A)Adenovirus
B)Coxsackievirus
C)Influenza virus
D)Norovirus
E)Parvovirus
F)Respiratory syncytial virus
A)Adenovirus
B)Coxsackievirus
C)Influenza virus
D)Norovirus
E)Parvovirus
F)Respiratory syncytial virus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 330 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
A 24-year-old woman, gravida 1, para 0, at 33 weeks' gestation, is admitted to the hospital in active labor. She delivers a small male newborn. Apgar scores were 6 and 6 at 1 and 5 minutes, respectively. His mother received no prenatal care. On delivery, the placenta appears enlarged. In addition, the umbilical cord is inflamed with multiple areas of abscess-like foci of necrosis surrounding the umbilical vessels. Which of the following is the most likely cause of these findings?
A)Group B Streptococcus infection
B)Partial hydatidiform mole
C)Placenta accreta
D)Rh(D) incompatibility
E)Spirochete infection
A)Group B Streptococcus infection
B)Partial hydatidiform mole
C)Placenta accreta
D)Rh(D) incompatibility
E)Spirochete infection

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 330 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
A 32-year-old man comes to the physician because of severe burning with urination for the past 3 days. During this period, he has had clear urethral discharge early in the morning. He has no history of serious illness, except for similar symptoms 3 months ago, and urethral swab microscopy showed numerous neutrophils and intracellular gram-negative diplococci. The symptoms resolved after treatment with ceftriaxone and doxycycline but recurred 4 days ago. The patient takes no medications. He is sexually active with one male and one female partner; they use condoms inconsistently. Temperature is 36.8°C (98.0°F), pulse is 75/min, and blood pressure is 135/78 mm Hg. Nucleic acid amplification testing of a clean catch urine specimen is positive for Neisseria gonorrhoeae and negative for Chlamydia trachomatis. Which of the following is the most likely reason for the recurrence of infection in this patient?
A)Absence of memory T cells
B)Decreased antibody production due to malnutrition
C)High variability of microbial antigenic structure
D)Poor antigen recognition due to antigenic mimicry
E)Resistance to antimicrobial agents
A)Absence of memory T cells
B)Decreased antibody production due to malnutrition
C)High variability of microbial antigenic structure
D)Poor antigen recognition due to antigenic mimicry
E)Resistance to antimicrobial agents

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 330 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
A 64-year-old man comes to the emergency department because of a 2-day history of lower back pain, fever, and chills. He has had nausea but no vomiting during this time. He has hypertension, chronic kidney disease, and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Three months ago, he underwent amputation of his left third toe because of a nonhealing ulcer. He has smoked a pack of cigarettes daily for 48 years. Current medications include hydrochlorothiazide, metoprolol, and insulin. His temperature is 39.4°C (102.9°F), pulse is 102/min, respirations are 18/min, and blood pressure is 150/94 mm Hg. Physical examination shows suprapubic and costovertebral angle tenderness. Urinalysis shows 3+ leukocyte esterase and numerous white blood cells. Urine and blood cultures grow non-lactose-fermenting Gram-negative rods. Which of the following pathogens is the most likely culprit?
A)Enterobacter cloacae
B)Enterococcus faecalis
C)Escherichia coli
D)Klebsiella pneumoniae
E)Pseudomonas aeruginosa
F)Staphylococcus saprophyticus
A)Enterobacter cloacae
B)Enterococcus faecalis
C)Escherichia coli
D)Klebsiella pneumoniae
E)Pseudomonas aeruginosa
F)Staphylococcus saprophyticus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 330 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
A 34-year-old woman comes to the emergency department because of right flank pain and vomiting for 5 hours. She has had fever and chills for the past 2 days. She attended a barbecue 3 days ago, where she ate egg salad. She underwent surgery for left ovarian torsion a year ago. Menses occur at regular 28-day intervals and last 5 days. She is sexually active with two male partners and uses condoms inconsistently. Her only medication is an oral contraceptive pill. She is 163 cm (5 ft 4 in) tall and weighs 72.5 kg (160 lb); BMI is 28 kg/m2. She appears uncomfortable. Her temperature is 38.9°C (102°F), pulse is 101/min, and blood pressure is 118/76 mm Hg. The lungs are clear to auscultation. The right lower quadrant and right flank show severe tenderness to palpation. Pelvic examination shows no abnormalities. Laboratory studies show:  Blood and urine cultures are performed, and empiric antibiotics are initiated. Urine cultures grow gram-negative rods that are lactose-fermenting and indole-positive. Which of the following is the most likely organism causing this patient's infection?
Blood and urine cultures are performed, and empiric antibiotics are initiated. Urine cultures grow gram-negative rods that are lactose-fermenting and indole-positive. Which of the following is the most likely organism causing this patient's infection?
A)Enterobacter cloacae
B)Escherichia coli
C)Haemophilus influenzae
D)Proteus mirabilis
E)Pseudomonas aeruginosa
 Blood and urine cultures are performed, and empiric antibiotics are initiated. Urine cultures grow gram-negative rods that are lactose-fermenting and indole-positive. Which of the following is the most likely organism causing this patient's infection?
Blood and urine cultures are performed, and empiric antibiotics are initiated. Urine cultures grow gram-negative rods that are lactose-fermenting and indole-positive. Which of the following is the most likely organism causing this patient's infection?A)Enterobacter cloacae
B)Escherichia coli
C)Haemophilus influenzae
D)Proteus mirabilis
E)Pseudomonas aeruginosa

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 330 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
A 52-year-old man is brought to the emergency department due to worsening right leg pain, fever, and confusion. The patient injured his leg while operating a motorized watercraft on the ocean near Florida 2 days ago. Temperature is 38.9 C (102 F), blood pressure is 90/50 mm Hg, and pulse is 120/min. The patient is lethargic and diaphoretic. Physical examination reveals a small laceration on the dorsum of the right foot with surrounding edema, erythema, and several hemorrhagic bullae. Leukocyte count and serum lactic acid levels are elevated. Intravenous fluids and empiric antibiotics are administered, and surgical debridement of the wound is performed. Blood and wound cultures yield curved gram-negative rods. Which of the following is the greatest risk factor for this patient's infection?
A)Bacterial nasal colonization
B)Condition causing iron overload
C)Exposure to infected rodent urine
D)Lack of booster immunization
E)Recent broad-spectrum antibiotic use
A)Bacterial nasal colonization
B)Condition causing iron overload
C)Exposure to infected rodent urine
D)Lack of booster immunization
E)Recent broad-spectrum antibiotic use

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 330 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
A 43-year-old man comes to the office due to increasing discomfort and pain with sitting for the past several months. He also has had occasional perianal pruritus. Physical examination shows multiple, cauliflower-shaped, verrucous growths measuring 1 to 2 cm on the perianal skin. Histopathologic examination of one of the lesion reveals hyperplastic papillary squamous epithelium with parakeratosis, nuclear irregularity, and "perinuclear halos" of cytoplasmic vacuolization. Which of the following additional studies is most appropriate for this patient at this time?
A)Adhesive paddle test with microscopy
B)Colonoscopy with terminal ileoscopy
C)Darkfield microscopy of the tissue
D)Hepatic venous pressure measurement
E)HIV antigen and antibody testing
A)Adhesive paddle test with microscopy
B)Colonoscopy with terminal ileoscopy
C)Darkfield microscopy of the tissue
D)Hepatic venous pressure measurement
E)HIV antigen and antibody testing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 330 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
A 2800-g (6-lb 3-oz) male newborn is born at 39 weeks' gestation to a 24-year-old woman, gravida 2, para 2, after uncomplicated labor and delivery. The mother did not receive prenatal care. She traveled to Brazil to visit relatives during the first trimester of her pregnancy. She has bipolar disorder treated with lithium. The newborn is at the 50th percentile for height, 25th percentile for weight, and 2nd percentile for head circumference. Neurologic examination shows spasticity of the upper and lower extremities. The wrists are fixed in flexion bilaterally. Deep tendon reflexes are 4+ and symmetric. Ophthalmoscopic examination shows focal pigmentary retinal mottling. Testing for otoacoustic emissions is negative. Which of the following viruses most likely caused this patient's in utero infection?
A)Cytomegalovirus
B)Herpes simplex virus
C)Parvovirus B19
D)Rubella virus
E)Varicella zoster virus
F)Zika virus
A)Cytomegalovirus
B)Herpes simplex virus
C)Parvovirus B19
D)Rubella virus
E)Varicella zoster virus
F)Zika virus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 330 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



