Deck 9: Measures of Effect
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/15
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 9: Measures of Effect
1
The term attributable risk is defined as the ratio of the incidence of a disease among exposed individuals to the incidence among nonexposed individuals.
False
2
The term attributable risk is also known as the rate difference or risk difference.
True
3
The population etiologic fraction is a measure of the proportion of the disease rate in a population attributable to the exposure of interest. This measure of effect is influenced by:
A) the relative risk of the disease in exposed individuals versus unexposed individuals.
B) the prevalence of the disease in the population.
C) the prevalence of the exposure in the population.
D) the relative risk of the disease in exposed individuals versus unexposed individuals and the prevalence of the disease in the population.
E) the relative risk of the disease in exposed individuals versus unexposed individuals and the prevalence of the exposure in the population.
A) the relative risk of the disease in exposed individuals versus unexposed individuals.
B) the prevalence of the disease in the population.
C) the prevalence of the exposure in the population.
D) the relative risk of the disease in exposed individuals versus unexposed individuals and the prevalence of the disease in the population.
E) the relative risk of the disease in exposed individuals versus unexposed individuals and the prevalence of the exposure in the population.
E
4
The population etiologic fraction for a particular disease from Factor X alone is five times greater than that from Factor Y alone. If the relative risk associated with Factor X is 2, and with Factor Y is 20, which of the following statements is true?
A) The risk of developing the disease is greater in those exposed to Factor X only than in those exposed to Factor Y only.
B) Fewer persons are exposed to Factor Y than to Factor X.
C) The proportion of the disease in the population attributable to Factor Y is greater than that attributable to Factor X.
D) More persons are exposed to Factor Y than to Factor X.
E) The risk of developing the disease for persons exposed to Factor Y is five times greater than for persons exposed to Factor X.
A) The risk of developing the disease is greater in those exposed to Factor X only than in those exposed to Factor Y only.
B) Fewer persons are exposed to Factor Y than to Factor X.
C) The proportion of the disease in the population attributable to Factor Y is greater than that attributable to Factor X.
D) More persons are exposed to Factor Y than to Factor X.
E) The risk of developing the disease for persons exposed to Factor Y is five times greater than for persons exposed to Factor X.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The death rate per 100,000 for lung cancer is 7 among nonsmokers and 71 among smokers. The death rate per 100,000 for coronary thrombosis is 422 among nonsmokers and 599 among smokers. The prevalence of smoking in the population is 55%. The relative risk of dying for a smoker compared to a nonsmoker is:
A) 9.1 for lung cancer and 0.30 for coronary thrombosis.
B) 9.1 for lung cancer and 1.4 for coronary thrombosis.
C) 10.1 for lung cancer and 8.4 for coronary thrombosis.
D) 10.1 for lung cancer and 1.4 for coronary thrombosis.
E) 12.4 for lung cancer and 1.7 for coronary thrombosis.
A) 9.1 for lung cancer and 0.30 for coronary thrombosis.
B) 9.1 for lung cancer and 1.4 for coronary thrombosis.
C) 10.1 for lung cancer and 8.4 for coronary thrombosis.
D) 10.1 for lung cancer and 1.4 for coronary thrombosis.
E) 12.4 for lung cancer and 1.7 for coronary thrombosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The death rate per 100,000 for lung cancer is 7 among nonsmokers and 71 among smokers. The death rate per 100,000 for coronary thrombosis is 422 among nonsmokers and 599 among smokers. The prevalence of smoking in the population is 55%. Among smokers, the etiologic fraction of disease due to smoking is:
A) 0.90 for lung cancer and 0.88 for coronary thrombosis.
B) 0.90 for lung cancer and 0.29 for coronary thrombosis.
C) 0.89 for lung cancer and 0.88 for coronary thrombosis.
D) 0.89 for lung cancer and 0.29 for coronary thrombosis.
E) It cannot be determined from the information provided.
A) 0.90 for lung cancer and 0.88 for coronary thrombosis.
B) 0.90 for lung cancer and 0.29 for coronary thrombosis.
C) 0.89 for lung cancer and 0.88 for coronary thrombosis.
D) 0.89 for lung cancer and 0.29 for coronary thrombosis.
E) It cannot be determined from the information provided.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The death rate per 100,000 for lung cancer is 7 among nonsmokers and 71 among smokers. The death rate per 100,000 for coronary thrombosis is 422 among nonsmokers and 599 among smokers. The prevalence of smoking in the population is 55%. The population etiologic fraction of disease due to smoking is:
A) 0.80 for lung cancer and 0.28 for coronary thrombosis.
B) 0.80 for lung cancer and 0.18 for coronary thrombosis.
C) 0.83 for lung cancer and 0.28 for coronary thrombosis.
D) 0.83 for lung cancer and 0.18 for coronary thrombosis.
E) It cannot be determined from the information provided.
A) 0.80 for lung cancer and 0.28 for coronary thrombosis.
B) 0.80 for lung cancer and 0.18 for coronary thrombosis.
C) 0.83 for lung cancer and 0.28 for coronary thrombosis.
D) 0.83 for lung cancer and 0.18 for coronary thrombosis.
E) It cannot be determined from the information provided.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The death rate per 100,000 for lung cancer is 7 among nonsmokers and 71 among smokers. The death rate per 100,000 for coronary thrombosis is 422 among nonsmokers and 599 among smokers. The prevalence of smoking in the population is 55%. On the basis of the relative risk and etiologic fractions associated with smoking for lung cancer and coronary thrombosis, which of the following statements is most likely to be correct?
A) Smoking seems much more likely to be causally related to coronary thrombosis than to lung cancer.
B) Smoking seems much more likely to be causally related to lung cancer than to coronary thrombosis.
C) Smoking seems to be equally causally related to lung cancer and coronary thrombosis.
D) Smoking does not seem to be causally related to either lung cancer or coronary thrombosis.
E) No comparative statement is possible between smoking and lung cancer or coronary thrombosis.
A) Smoking seems much more likely to be causally related to coronary thrombosis than to lung cancer.
B) Smoking seems much more likely to be causally related to lung cancer than to coronary thrombosis.
C) Smoking seems to be equally causally related to lung cancer and coronary thrombosis.
D) Smoking does not seem to be causally related to either lung cancer or coronary thrombosis.
E) No comparative statement is possible between smoking and lung cancer or coronary thrombosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
If it is accepted that an observed association is a causal one, an estimate of the impact that a successful preventive program might have can be derived from:
A) relative risk.
B) higher life expectancy.
C) attributable risk.
D) prevalence rates.
E) All are correct.
A) relative risk.
B) higher life expectancy.
C) attributable risk.
D) prevalence rates.
E) All are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Assuming that the following sample table is for a cohort study, define the risk difference or attributable risk:
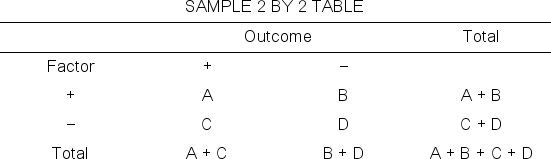
A) (A/A + C) / (B/B + D)
B) (A/A + B) / (C/C + D)
C) (A/A + C) − (B/B + D)
D) (A/A + B) − (C/C + D)
E) None of these is correct.

A) (A/A + C) / (B/B + D)
B) (A/A + B) / (C/C + D)
C) (A/A + C) − (B/B + D)
D) (A/A + B) − (C/C + D)
E) None of these is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
When assessing a positive relationship between alcohol consumption and oral cancer using a case-control study, increasing the sample size of the study will result in which of the following?
A) A lower p value and a smaller 95% confidence interval
B) A greater odds ratio and a higher disease prevalence
C) A lower p value, a smaller 95% confidence interval, and a greater odds ratio
D) A lower p value, a smaller 95% confidence interval, a higher disease prevalence, and a greater odds ratio
E) None of these is correct.
A) A lower p value and a smaller 95% confidence interval
B) A greater odds ratio and a higher disease prevalence
C) A lower p value, a smaller 95% confidence interval, and a greater odds ratio
D) A lower p value, a smaller 95% confidence interval, a higher disease prevalence, and a greater odds ratio
E) None of these is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A causal association between factor and outcome can refer to:
A) statistical independence.
B) secondary association.
C) indirect association.
D) direct association.
E) indirect association and direct association.
A) statistical independence.
B) secondary association.
C) indirect association.
D) direct association.
E) indirect association and direct association.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Calculate the proper measure of association of smoking and lung cancer death. Interpret your results. [Relative risk (RR) = 3.2]

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Calculate the population risk difference. Interpret your results. [IP = 48.6 per 100,000; Ine = 19.1 per 100,000; IP − Ine = 48.6 − 19.1 = 29.5/100,000 per year]

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Calculate the population etiologic fraction for smoking and lung cancer based on these data. Interpret your results. [29.5/48.6 × 100 = 60.7%]

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



