Deck 9: Patterns of Inheritance
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/49
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 9: Patterns of Inheritance
1
In humans,the presence or absence of dimples is a trait controlled by a single gene.What is the genotype of an individual who is heterozygous for dimples?
A) DD
B) Dd
C) dd
D) DI
A) DD
B) Dd
C) dd
D) DI
B
2
Which of these crosses will produce only heterozygous offspring?
A) AA × aa
B) AA × Aa
C) Aa × Aa
D) Aa × aa
A) AA × aa
B) AA × Aa
C) Aa × Aa
D) Aa × aa
A
3
Attached earlobes are recessive to free earlobes.What is the probability of having a child with attached earlobes when an individual with attached earlobes mates with an individual heterozygous for free earlobes?
A) 0%
B) 25%
C) 50%
D) 75%
A) 0%
B) 25%
C) 50%
D) 75%
C
4
An individual who is homozygous ________.
A) expresses the dominant trait
B) carries two different alleles for a gene
C) carries two copies of the same allele for a gene
D) expresses the recessive trait
A) expresses the dominant trait
B) carries two different alleles for a gene
C) carries two copies of the same allele for a gene
D) expresses the recessive trait

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Round seeds (R)are dominant to wrinkled seeds (r),and yellow seeds (Y)are dominant to green seeds (y).What is the expected phenotypic ratio of a cross between an RrYy and an rryy individual?
A) 1:2:1
B) 9:3:3:1
C) 3:1
D) 1:1:1:1
A) 1:2:1
B) 9:3:3:1
C) 3:1
D) 1:1:1:1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A purebred plant that produces yellow seeds is crossed with a purebred plant that produces green seeds.The F₁ plants have yellow seeds.What is the expected phenotypic ratio of seed color of the offspring of an F₁ × F₁ cross?
A) 1:2:1
B) 2:1
C) 3:1
D) 9:3:3:1
A) 1:2:1
B) 2:1
C) 3:1
D) 9:3:3:1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A mating between a purebred purple-flowered pea plant and a purebred white-flowered pea plant would produce a(n)________.
A) purebred variety
B) hybrid
C) P generation
D) F₂ generation
A) purebred variety
B) hybrid
C) P generation
D) F₂ generation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Alleles are described as ________.
A) homologous chromosomes
B) environmental factors that affect gene expression
C) alternate versions of a gene
D) alternate phenotypes
A) homologous chromosomes
B) environmental factors that affect gene expression
C) alternate versions of a gene
D) alternate phenotypes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The best definition of a purebred plant is one that ________.
A) cannot be cross-fertilized
B) self-fertilizes to produce offspring identical to the parent
C) produces sterile offspring when cross-fertilized
D) self-fertilizes to produce hybrid offspring
A) cannot be cross-fertilized
B) self-fertilizes to produce offspring identical to the parent
C) produces sterile offspring when cross-fertilized
D) self-fertilizes to produce hybrid offspring

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The ________ is most commonly found in nature.
A) recessive trait
B) wild-type trait
C) parental type
D) dominant trait
A) recessive trait
B) wild-type trait
C) parental type
D) dominant trait

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
What data or test would you seek to determine whether or not a trait is sex linked?
A) karyotype
B) pedigree
C) DNA sequence
D) blood test
A) karyotype
B) pedigree
C) DNA sequence
D) blood test

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Mendel crossed purebred purple-flowered plants with purebred white-flowered plants,and all of the resulting offspring produced purple flowers.The offspring are all ________,and the allele for purple flowers is ________.
A) heterozygotes... recessive
B) heterozygotes... dominant
C) homozygotes... recessive
D) homozygotes... dominant
A) heterozygotes... recessive
B) heterozygotes... dominant
C) homozygotes... recessive
D) homozygotes... dominant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
According to Mendel's law of segregation,________.
A) two alleles segregate into each gamete
B) more gametes carrying the dominant allele are produced than gametes carrying the recessive allele
C) gametes have one allele copy for each gene
D) gametes are diploid
A) two alleles segregate into each gamete
B) more gametes carrying the dominant allele are produced than gametes carrying the recessive allele
C) gametes have one allele copy for each gene
D) gametes are diploid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A purebred plant that produces yellow seeds is crossed with a purebred plant that produces green seeds.The seeds of all of the offspring are yellow.Why?
A) The yellow allele is recessive to the green allele.
B) All of the offspring are homozygous yellow.
C) The yellow allele is dominant to the green allele.
D) The alleles are codominant.
A) The yellow allele is recessive to the green allele.
B) All of the offspring are homozygous yellow.
C) The yellow allele is dominant to the green allele.
D) The alleles are codominant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
An individual with the genotype AaBb produces four different gametes in equal proportions.This is a demonstration of ________.
A) the chromosomal theory of inheritance
B) Mendel's law of independent assortment
C) linkage
D) Mendel's principle of segregation
A) the chromosomal theory of inheritance
B) Mendel's law of independent assortment
C) linkage
D) Mendel's principle of segregation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A couple has two female children.What is the probability that their next child will be male?
A) 25%
B) 50%
C) 33%
D) 67%
A) 25%
B) 50%
C) 33%
D) 67%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
In humans,free earlobes (E)are dominant to attached earlobes (e)and the presence of freckles (F)is dominant to the absence of freckles (f).If an individual heterozygous for both of these traits were to mate with an individual with attached earlobes and no freckles,what is the probability of having a child with attached earlobes and freckles?
A) 0%
B) 25%
C) 50%
D) 100%
A) 0%
B) 25%
C) 50%
D) 100%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
To determine the phenotype of an individual who expresses a dominant trait,you would cross that individual with an individual who ________.
A) expresses the dominant trait
B) is homozygous recessive for that trait
C) is homozygous dominant for that trait
D) is heterozygous for that trait
A) expresses the dominant trait
B) is homozygous recessive for that trait
C) is homozygous dominant for that trait
D) is heterozygous for that trait

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
What name is given to the specific location of a gene on a chromosome?
A) locus
B) phenotype
C) genotype
D) allele
A) locus
B) phenotype
C) genotype
D) allele

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Attached earlobes are recessive to free earlobes.What genotypic ratio is expected when an individual with attached earlobes mates with an individual heterozygous for free earlobes?
A) 2:1
B) 1:1
C) 1:2:1
D) 3:1
A) 2:1
B) 1:1
C) 1:2:1
D) 3:1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
In humans,the inheritance of ________ is best explained as being polygenic.
A) cystic fibrosis
B) height
C) blood type
D) sickle-cell disease
A) cystic fibrosis
B) height
C) blood type
D) sickle-cell disease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A dihybrid cross produces 30 recombinant offspring out of a total of 1,000 offspring.What is the recombination frequency of the two gene pairs?
A) 6%
B) 3%
C) 30%
D) 1.5%
A) 6%
B) 3%
C) 30%
D) 1.5%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Marfan syndrome is the result of inheriting a single allele.Individuals with Marfan syndrome are tall and long-limbed,and have both cardiovascular and eye defects.Of what type of inheritance is the phenotype of Marfan syndrome an example?
A) codominance
B) homozygous recessive
C) pleiotropy
D) incomplete dominance
A) codominance
B) homozygous recessive
C) pleiotropy
D) incomplete dominance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Red-green color blindness is inherited as a sex-linked recessive trait.The gene is found on the X chromosome.Can a man with normal color vision father a daughter who is red-green color-blind?
A) Yes, if the woman with whom he mates is red-green color-blind.
B) Yes, if the man is heterozygous for red-green color blindness.
C) No, he can't (unless there is a mutation).
D) No, the expression of the trait skips a generation.
A) Yes, if the woman with whom he mates is red-green color-blind.
B) Yes, if the man is heterozygous for red-green color blindness.
C) No, he can't (unless there is a mutation).
D) No, the expression of the trait skips a generation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
________ genes violate Mendel's principle of independent assortment.
A) Codominant
B) Linked
C) Recessive
D) Pleiotropic
A) Codominant
B) Linked
C) Recessive
D) Pleiotropic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
What is the best explanation for a BbCc × bbcc cross producing offspring in a 5:5:1:1 phenotypic ratio?
A) linked genes
B) polygenic inheritance
C) incomplete dominance
D) codominance
A) linked genes
B) polygenic inheritance
C) incomplete dominance
D) codominance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
An individual with (naturally)curly hair and an individual with (naturally)straight hair mate; all of their offspring have (naturally)wavy hair.What is the relationship between the alleles for hair texture?
A) pleiotropy
B) incomplete dominance
C) wavy hair dominant to both straight and curly hair
D) codominance
A) pleiotropy
B) incomplete dominance
C) wavy hair dominant to both straight and curly hair
D) codominance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Achondroplasia is a form of dwarfism caused by a dominant allele.The homozygous dominant genotype causes death,so individuals who have this condition are all heterozygotes.If a person with achondroplasia mates with a person who does not have achondroplasia,what percentage of their children would be expected to have achondroplasia?
A) 0%
B) 50%
C) 75%
D) 100%
A) 0%
B) 50%
C) 75%
D) 100%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Many human traits,such as our performance on intelligence tests or our susceptibility to heart disease,are ________.
A) determined only by our genes
B) influenced by both genes and the environment
C) determined by genes in some people and by the environment in other people
D) not affected by our genes
A) determined only by our genes
B) influenced by both genes and the environment
C) determined by genes in some people and by the environment in other people
D) not affected by our genes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
An individual with the blood group genotype Lᴹᴸᴺ has the phenotype MN.What is the relationship between the Lᴹ and Lᴺ alleles?
A) codominance
B) pleiotropy
C) Lᴺ is dominant
D) incomplete dominance
A) codominance
B) pleiotropy
C) Lᴺ is dominant
D) incomplete dominance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
What is the key to the recognition of codominance?
A) The phenotype of the heterozygote is intermediate between the phenotypes of the homozygotes.
B) The trait exhibits a continuous distribution.
C) The alleles affect more than one trait.
D) The heterozygote expresses the phenotype of both homozygotes.
A) The phenotype of the heterozygote is intermediate between the phenotypes of the homozygotes.
B) The trait exhibits a continuous distribution.
C) The alleles affect more than one trait.
D) The heterozygote expresses the phenotype of both homozygotes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
What is the key to the recognition of incomplete dominance?
A) The phenotype of the heterozygote falls between the phenotypes of the homozygotes.
B) The trait exhibits a continuous distribution.
C) The alleles affect more than one trait.
D) The heterozygote expresses the phenotype of both homozygotes.
A) The phenotype of the heterozygote falls between the phenotypes of the homozygotes.
B) The trait exhibits a continuous distribution.
C) The alleles affect more than one trait.
D) The heterozygote expresses the phenotype of both homozygotes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
What is key to recognition of a trait whose expression is determined by the effects of two or more genes (polygenic inheritance)?
A) A mating between a homozygous and a heterozygous individual produces more than the expected number of offspring expressing the dominant trait.
B) All of the alleles of the gene for that trait are equally expressed.
C) Pleiotropy occurs.
D) The trait varies along a continuum in the population.
A) A mating between a homozygous and a heterozygous individual produces more than the expected number of offspring expressing the dominant trait.
B) All of the alleles of the gene for that trait are equally expressed.
C) Pleiotropy occurs.
D) The trait varies along a continuum in the population.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following techniques is used to collect fetal cells during pregnancy for genetic testing?
A) testcross
B) dihybrid cross
C) amniocentesis
D) pedigree analysis
A) testcross
B) dihybrid cross
C) amniocentesis
D) pedigree analysis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Assume that having three nostrils is inherited as a sex-linked trait on the Y chromosome.A man with three nostrils has a daughter who has a son with a man who has only two nostrils.What is the probability that the three-nostriled man's grandson has three nostrils?
A) 0%
B) 25%
C) 50%
D) 100%
A) 0%
B) 25%
C) 50%
D) 100%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
An individual heterozygous for cystic fibrosis ________.
A) cannot have children with cystic fibrosis
B) is a carrier
C) will have children who are all carriers of cystic fibrosis
D) has cystic fibrosis
A) cannot have children with cystic fibrosis
B) is a carrier
C) will have children who are all carriers of cystic fibrosis
D) has cystic fibrosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
An individual with (naturally)curly hair and an individual with (naturally)straight hair mate; all of their offspring have (naturally)wavy hair.If an individual with wavy hair mates with an individual with straight hair,what is the probability that their child will have curly hair?
A) 0%
B) 25%
C) 50%
D) 75%
A) 0%
B) 25%
C) 50%
D) 75%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
What is the basis of Mendel's laws?
A) the behavior of chromosomes during prophase I of meiosis only
B) the behavior of chromosomes during mitotic anaphase
C) the behavior of chromosomes during prophase I and prophase II of meiosis
D) the behavior of chromosomes during metaphase I and anaphase I of meiosis
A) the behavior of chromosomes during prophase I of meiosis only
B) the behavior of chromosomes during mitotic anaphase
C) the behavior of chromosomes during prophase I and prophase II of meiosis
D) the behavior of chromosomes during metaphase I and anaphase I of meiosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The recombination frequency between gene B and gene C is 11%.The recombination frequency between gene B and gene D is 5%.The recombination frequency between gene C and gene D is 15%.What would be the arrangement of these genes on a linkage map?
A) CDB
B) DBC
C) BCD
D) More information is needed.
A) CDB
B) DBC
C) BCD
D) More information is needed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Linked genes are usually ________.
A) found on the X chromosome
B) found on the Y chromosome
C) codominant
D) located close together on a chromosome
A) found on the X chromosome
B) found on the Y chromosome
C) codominant
D) located close together on a chromosome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Please read the following scenario to answer the following questions.
Widow's peak, a pointed hairline on the forehead, is a genetic trait caused by a dominant allele. It can be traced back through a family's history using pedigree analysis.
The pedigree shown here is of three generations of a family. Notice that some individuals (shown in gray) have a widow's peak (W = dominant allele and w = recessive allele).
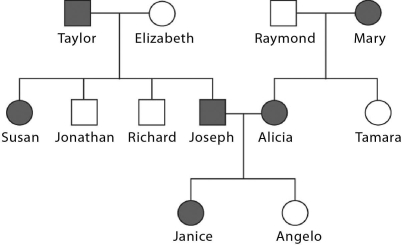
Janice's genotype is ________.
A) Ww
B) WW
C) ww
D) WW or Ww
Widow's peak, a pointed hairline on the forehead, is a genetic trait caused by a dominant allele. It can be traced back through a family's history using pedigree analysis.
The pedigree shown here is of three generations of a family. Notice that some individuals (shown in gray) have a widow's peak (W = dominant allele and w = recessive allele).

Janice's genotype is ________.
A) Ww
B) WW
C) ww
D) WW or Ww

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Please read the following scenario to answer the following question.
The parents of a child with unusual disease symptoms take the child to a doctor for help. The doctor suspects that the condition might have a genetic basis. She recommends that the child be taken to a specialty clinic where physicians and staff members are trained to diagnose genetic diseases and counsel parents. Ultimately, the child is diagnosed with a rare recessively inherited disease. The parents are tested for the gene, and both are found to be heterozygous. The parents want to have another child but are afraid this child will also be affected.
What would genetic counselors say is the probability that the second child will have the disease?
A) 1/2
B) 1/4
C) 1/8
D) 1/16
The parents of a child with unusual disease symptoms take the child to a doctor for help. The doctor suspects that the condition might have a genetic basis. She recommends that the child be taken to a specialty clinic where physicians and staff members are trained to diagnose genetic diseases and counsel parents. Ultimately, the child is diagnosed with a rare recessively inherited disease. The parents are tested for the gene, and both are found to be heterozygous. The parents want to have another child but are afraid this child will also be affected.
What would genetic counselors say is the probability that the second child will have the disease?
A) 1/2
B) 1/4
C) 1/8
D) 1/16

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Please read the following scenario to answer the following questions.
Widow's peak, a pointed hairline on the forehead, is a genetic trait caused by a dominant allele. It can be traced back through a family's history using pedigree analysis.
The pedigree shown here is of three generations of a family. Notice that some individuals (shown in gray) have a widow's peak (W = dominant allele and w = recessive allele).

Mary has the genotype ________.
A) WW
B) ww
C) Ww
D) More information is needed.
Widow's peak, a pointed hairline on the forehead, is a genetic trait caused by a dominant allele. It can be traced back through a family's history using pedigree analysis.
The pedigree shown here is of three generations of a family. Notice that some individuals (shown in gray) have a widow's peak (W = dominant allele and w = recessive allele).

Mary has the genotype ________.
A) WW
B) ww
C) Ww
D) More information is needed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
This hypothetical pedigree for a disease in humans illustrated inheritance that is 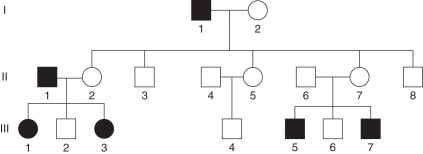
A) autosomal recessive.
B) autosomal dominant.
C) sex-linked dominant.
D) carried on the Y chromosome.

A) autosomal recessive.
B) autosomal dominant.
C) sex-linked dominant.
D) carried on the Y chromosome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Please refer to the following art to answer the following questions.
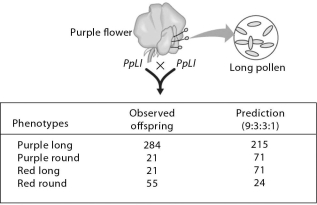
In the accompanying art,you see a table with the actual number of offspring that resulted from a dihybrid cross.The numbers do not show the 9:3:3:1 ratio predicted.One phenotype occurred more than predicted; another occurred less.The reason could be because ________.
A) of errors in mitosis
B) some of the alleles were linked
C) some of the alleles were sex-linked
D) of polygenic inheritance

In the accompanying art,you see a table with the actual number of offspring that resulted from a dihybrid cross.The numbers do not show the 9:3:3:1 ratio predicted.One phenotype occurred more than predicted; another occurred less.The reason could be because ________.
A) of errors in mitosis
B) some of the alleles were linked
C) some of the alleles were sex-linked
D) of polygenic inheritance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Hypophosphatemia (vitamin D-resistant rickets)is inherited as a sex-linked dominant trait.The relevant gene is found on the X chromosome.What is the expected outcome of a cross between a homozygous recessive woman and a man with hypophosphatemia?
A) All of their daughters and none of their sons exhibit hypophosphatemia.
B) Fifty percent of their daughters and fifty percent of their sons exhibit hypophosphatemia.
C) All of their sons and none of their daughters exhibit hypophosphatemia.
D) Twenty-five percent of their offspring exhibit hypophosphatemia.
A) All of their daughters and none of their sons exhibit hypophosphatemia.
B) Fifty percent of their daughters and fifty percent of their sons exhibit hypophosphatemia.
C) All of their sons and none of their daughters exhibit hypophosphatemia.
D) Twenty-five percent of their offspring exhibit hypophosphatemia.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Experience with dog breeding has taught geneticists ________.
A) that, given enough time, any desired trait can be bred into dogs
B) that purebred dogs have offspring with qualities identical to the parents, because all purebred dogs are alike genetically
C) that, while physical traits can be molded through artificial selection, behavioral traits cannot
D) that geographically isolated groups of dogs may be selected for quite different traits, resulting in a different dog breed
A) that, given enough time, any desired trait can be bred into dogs
B) that purebred dogs have offspring with qualities identical to the parents, because all purebred dogs are alike genetically
C) that, while physical traits can be molded through artificial selection, behavioral traits cannot
D) that geographically isolated groups of dogs may be selected for quite different traits, resulting in a different dog breed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Please read the following scenario to answer the following questions.
Widow's peak, a pointed hairline on the forehead, is a genetic trait caused by a dominant allele. It can be traced back through a family's history using pedigree analysis.
The pedigree shown here is of three generations of a family. Notice that some individuals (shown in gray) have a widow's peak (W = dominant allele and w = recessive allele).

This pedigree supports the fact that widow's peak is due to a dominant allele,because if it were due to a recessive allele and both parents show the recessive phenotype,then ________.
A) half of the sons would have a widow's peak
B) all of the offspring would have a widow's peak
C) none of the daughters would have a widow's peak
D) all of the daughters and none of the sons would have a widow's peak
Widow's peak, a pointed hairline on the forehead, is a genetic trait caused by a dominant allele. It can be traced back through a family's history using pedigree analysis.
The pedigree shown here is of three generations of a family. Notice that some individuals (shown in gray) have a widow's peak (W = dominant allele and w = recessive allele).

This pedigree supports the fact that widow's peak is due to a dominant allele,because if it were due to a recessive allele and both parents show the recessive phenotype,then ________.
A) half of the sons would have a widow's peak
B) all of the offspring would have a widow's peak
C) none of the daughters would have a widow's peak
D) all of the daughters and none of the sons would have a widow's peak

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Please refer to the following art to answer the following questions.

Recombinant offspring were produced by the mating shown in the accompanying art.What is the recombination frequency of purple round and red long offspring?
A) 21%
B) 381
C) 21 + 21
D) 11%

Recombinant offspring were produced by the mating shown in the accompanying art.What is the recombination frequency of purple round and red long offspring?
A) 21%
B) 381
C) 21 + 21
D) 11%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



