Deck 13: Characterizing and Classifying Viruses, Viroids, and Prions
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/75
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 13: Characterizing and Classifying Viruses, Viroids, and Prions
1
The genome of influenzavirus is
A) multiple pieces of linear dsDNA.
B) a single circular ssRNA.
C) a single linear dsRNA.
D) a single circular ssDNA.
E) multiple pieces of linear ssRNA.
A) multiple pieces of linear dsDNA.
B) a single circular ssRNA.
C) a single linear dsRNA.
D) a single circular ssDNA.
E) multiple pieces of linear ssRNA.
E
2
Which of the following lists stages of a lytic replication cycle in order, from earliest to latest stages?
I) Synthesis
II) Assembly
III) Attachment
IV) Release
V) Entry
A) III, V, I, II, IV
B) III, II, V, I, IV
C) V, III, II, IV, I
D) I, III, V, II, IV
E) I, II, III, V, IV
I) Synthesis
II) Assembly
III) Attachment
IV) Release
V) Entry
A) III, V, I, II, IV
B) III, II, V, I, IV
C) V, III, II, IV, I
D) I, III, V, II, IV
E) I, II, III, V, IV
A
3
How are fungal viruses transmitted?
A) by insect vectors
B) as a result of abrasion
C) as a result of fusion of cells or hyphae
D) in the air like spores
E) by contact
A) by insect vectors
B) as a result of abrasion
C) as a result of fusion of cells or hyphae
D) in the air like spores
E) by contact
C
4
Which of the following is primarily responsible for the shape of a virion?
A) the type of nucleic acid
B) the number of segments of the viral genome
C) the source of the envelope
D) the capsid
E) the specific host protein the virus targets
A) the type of nucleic acid
B) the number of segments of the viral genome
C) the source of the envelope
D) the capsid
E) the specific host protein the virus targets

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following statements regarding virus taxonomy is true?
A) Viruses are classified on the basis of the taxonomy of their host organisms.
B) Virus classes are well established.
C) Some virus family names are derived from the name of an important member of the family.
D) The species epithet is a latin descriptor of the virion structure.
E) Virus classes are based on the domain of the host organism.
A) Viruses are classified on the basis of the taxonomy of their host organisms.
B) Virus classes are well established.
C) Some virus family names are derived from the name of an important member of the family.
D) The species epithet is a latin descriptor of the virion structure.
E) Virus classes are based on the domain of the host organism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following is associated with the attachment of a bacteriophage to a bacterial cell?
A) random collisions
B) chemical attractions
C) receptor specificity
D) both chemical attractions and receptor specificity
E) random collisions, chemical attractions, and receptor specificity
A) random collisions
B) chemical attractions
C) receptor specificity
D) both chemical attractions and receptor specificity
E) random collisions, chemical attractions, and receptor specificity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A(n) ________ is a virus that infects bacterial cells.
A) virion
B) prion
C) bacteriophage
D) nucleocapsid
E) envelope
A) virion
B) prion
C) bacteriophage
D) nucleocapsid
E) envelope

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following is a characteristic by which viruses are classified?
A) type of nucleic acid
B) type of life cycle
C) number of chromosomes
D) type of host
E) size
A) type of nucleic acid
B) type of life cycle
C) number of chromosomes
D) type of host
E) size

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Host specificity of a virus is due to
A) particular genes that it shares with the infected cell.
B) the presence of an envelope.
C) differences in size between the virus and the host cell.
D) the presence or absence of a cell wall on the host cell.
E) interactions between viral and cellular surface molecules.
A) particular genes that it shares with the infected cell.
B) the presence of an envelope.
C) differences in size between the virus and the host cell.
D) the presence or absence of a cell wall on the host cell.
E) interactions between viral and cellular surface molecules.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The outermost layer of a virion fulfills which of the following functions of the virus?
A) protection
B) recognition
C) replication
D) both protection and recognition
E) both recognition and replication
A) protection
B) recognition
C) replication
D) both protection and recognition
E) both recognition and replication

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A(n) ________ is a bacterial virus which is integrated into the host cell DNA.
A) lytic phage
B) prophage
C) plasmid
D) transposon
E) insertion phage
A) lytic phage
B) prophage
C) plasmid
D) transposon
E) insertion phage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The enzyme lysozyme is critical for which of the stages of a bacteriophage T4 infection cycle?
A) entry
B) assembly
C) entry and release
D) synthesis
E) attachment
A) entry
B) assembly
C) entry and release
D) synthesis
E) attachment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
In what ways do viruses differ from other pathogens?
A) Viruses lack genetic material.
B) Viruses lack cytoplasm and organelles.
C) Viruses have no protein structure.
D) Viruses are composed of protein only.
E) Viruses are composed of both protein and lipid.
A) Viruses lack genetic material.
B) Viruses lack cytoplasm and organelles.
C) Viruses have no protein structure.
D) Viruses are composed of protein only.
E) Viruses are composed of both protein and lipid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following agents is capable of inducing conversion of a prophage to the lytic cycle?
A) UV light
B) X rays
C) presence of +ssRNA
D) both UV light and X rays
E) both UV light and the presence of +ssRNA
A) UV light
B) X rays
C) presence of +ssRNA
D) both UV light and X rays
E) both UV light and the presence of +ssRNA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Replication of most ________ viruses is similar to normal cellular processes.
A) dsDNA
B) ssDNA
C) +ssRNA
D) -ssRNA
E) dsRNA
A) dsDNA
B) ssDNA
C) +ssRNA
D) -ssRNA
E) dsRNA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following events occurs in the lytic cycle of bacteriophage T4 infection but not in the lysogenic cycle?
A) attachment
B) entry
C) digestion of host DNA
D) viral protein synthesis
E) both digestion of host DNA and viral proteins synthesis
A) attachment
B) entry
C) digestion of host DNA
D) viral protein synthesis
E) both digestion of host DNA and viral proteins synthesis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Why is lysogeny advantageous to a bacteriophage?
A) it speeds up the viral infection cycle.
B) the genetic material of the bacteriophage is amplified many times over that seen in a lytic phage.
C) it allows the bacteriophage to infect cells it would not normally infect.
D) it allows the bacteriophage to destroy the host cell's DNA.
E) it enables the bacteriophage to take over the cell.
A) it speeds up the viral infection cycle.
B) the genetic material of the bacteriophage is amplified many times over that seen in a lytic phage.
C) it allows the bacteriophage to infect cells it would not normally infect.
D) it allows the bacteriophage to destroy the host cell's DNA.
E) it enables the bacteriophage to take over the cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following is CORRECT regarding the viral envelope?
A) It contains only viral proteins.
B) It contains only host cell proteins.
C) It is composed of sterols.
D) It is composed of cellular phospholipid membrane, cellular and viral proteins.
E) It is composed of sterols of viral proteins only.
A) It contains only viral proteins.
B) It contains only host cell proteins.
C) It is composed of sterols.
D) It is composed of cellular phospholipid membrane, cellular and viral proteins.
E) It is composed of sterols of viral proteins only.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Attachment of herpesviruses results in ________, a process in which the host cell facilitates viral entry.
A) direct penetration
B) membrane fusion
C) endocytosis
D) exocytosis
E) lysogeny
A) direct penetration
B) membrane fusion
C) endocytosis
D) exocytosis
E) lysogeny

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following is NOT used for the classification of viruses?
A) genus
B) class
C) specific epithet
D) family
E) order
A) genus
B) class
C) specific epithet
D) family
E) order

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Viroids infect
A) bacteria.
B) plants.
C) fungi.
D) plants and animals.
E) all organisms.
A) bacteria.
B) plants.
C) fungi.
D) plants and animals.
E) all organisms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Small circular RNAs called ________ are plant pathogens.
A) plasmids
B) viruses
C) viroids
D) prions
E) phages
A) plasmids
B) viruses
C) viroids
D) prions
E) phages

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following infectious particles do not have protein in their structure?
A) bacteriophages
B) prions
C) animal viruses
D) viroids
E) both prions and viroids
A) bacteriophages
B) prions
C) animal viruses
D) viroids
E) both prions and viroids

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Tumors invade other organs and tissues in a process called
A) neoplasia.
B) uncoating.
C) latency.
D) budding.
E) metastasis.
A) neoplasia.
B) uncoating.
C) latency.
D) budding.
E) metastasis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What is a virion?
A) a virus genome inside a cell
B) an empty capsid
C) a single virus particle outside a cell
D) an extracellular virus genome
E) a virus genome integrated into a host cell genome
A) a virus genome inside a cell
B) an empty capsid
C) a single virus particle outside a cell
D) an extracellular virus genome
E) a virus genome integrated into a host cell genome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Plaque assays are used for
A) evaluating the cancer-causing ability of a virus.
B) determining the density of phage in a culture.
C) the study of prions.
D) cultivating viruses that cannot be grown any other way.
E) counting the number of latent phages in a cell.
A) evaluating the cancer-causing ability of a virus.
B) determining the density of phage in a culture.
C) the study of prions.
D) cultivating viruses that cannot be grown any other way.
E) counting the number of latent phages in a cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following laboratory procedures is used for culturing animal viruses in the laboratory?
A) cell cultures
B) broth cultures
C) embryonated eggs
D) both cell cultures and embryonated eggs
E) synthetic cytoplasm
A) cell cultures
B) broth cultures
C) embryonated eggs
D) both cell cultures and embryonated eggs
E) synthetic cytoplasm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
How are prions different from all other known infectious agents?
A) they cannot reproduce outside a cell.
B) they act as slow viruses.
C) they cause neurological problems.
D) they can be destroyed by incineration.
E) they lack nucleic acid.
A) they cannot reproduce outside a cell.
B) they act as slow viruses.
C) they cause neurological problems.
D) they can be destroyed by incineration.
E) they lack nucleic acid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following virus families has a double-stranded RNA genome?
A) Retroviridae
B) Reoviridae
C) Rhadoviridae
D) Orthomyxoviridae
E) Filoviridae
A) Retroviridae
B) Reoviridae
C) Rhadoviridae
D) Orthomyxoviridae
E) Filoviridae

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following is a feature shared by viruses and living organisms?
A) possession of a genome that directs synthesis of materials necessary for replication
B) presence of cytoplasm
C) metabolic capability
D) responsiveness
E) the ability to increase in size
A) possession of a genome that directs synthesis of materials necessary for replication
B) presence of cytoplasm
C) metabolic capability
D) responsiveness
E) the ability to increase in size

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Disadvantages of continuous cell cultures include
A) they only grow for a limited number of generations.
B) the expense of preparation.
C) they may be significantly different genetically from the original source animal.
D) viruses do not reliably infect them.
E) they are both expensive and have a limited number of division.
A) they only grow for a limited number of generations.
B) the expense of preparation.
C) they may be significantly different genetically from the original source animal.
D) viruses do not reliably infect them.
E) they are both expensive and have a limited number of division.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
How is the HIV provirus different from a lambda-phage prophage?
A) the HIV provirus is integrated permanently into the host cell's DNA.
B) all subsequent generations of HIV-infected cells carry the provirus.
C) all the offspring of a cell infected with a prophage will contain the virus.
D) the HIV provirus is inactive inside the host cell.
E) lambda phage-infected cells produce virus slowly over time.
A) the HIV provirus is integrated permanently into the host cell's DNA.
B) all subsequent generations of HIV-infected cells carry the provirus.
C) all the offspring of a cell infected with a prophage will contain the virus.
D) the HIV provirus is inactive inside the host cell.
E) lambda phage-infected cells produce virus slowly over time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A lipid membrane is present in which of the following?
A) naked viruses
B) enveloped viruses
C) prions
D) viroids
E) both prions and viroids
A) naked viruses
B) enveloped viruses
C) prions
D) viroids
E) both prions and viroids

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following types of animal virus requires RNA-dependent RNA transcriptase to be replicated?
A) +ssRNA viruses
B) ssDNA viruses
C) -ssRNA viruses
D) retroviruses
E) dsDNA viruses
A) +ssRNA viruses
B) ssDNA viruses
C) -ssRNA viruses
D) retroviruses
E) dsDNA viruses

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
A cell is infected with a virus carrying an oncogene sequence in its genome. What process may occur if the oncogene is expressed in the infected cell?
A) lysis
B) neoplasia
C) lysogeny
D) latency
E) both lysis and neoplasia
A) lysis
B) neoplasia
C) lysogeny
D) latency
E) both lysis and neoplasia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following membranes can give rise to a viral envelope?
A) the nuclear membrane
B) the cytoplasmic membrane
C) the endoplasmic reticulum
D) the nuclear and cytoplasmic membranes
E) the nuclear and cytoplasmic membranes and the endoplasmic reticulum
A) the nuclear membrane
B) the cytoplasmic membrane
C) the endoplasmic reticulum
D) the nuclear and cytoplasmic membranes
E) the nuclear and cytoplasmic membranes and the endoplasmic reticulum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Reverse transcriptase is associated with which of the following?
A) dsDNA viruses
B) +ssRNA viruses
C) -ssRNA viruses
D) retroviruses
E) dsRNA viruses
A) dsDNA viruses
B) +ssRNA viruses
C) -ssRNA viruses
D) retroviruses
E) dsRNA viruses

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Naked capsid animal viruses are commonly released from the infected cell by ________, a process the host cell does not survive.
A) budding
B) lysis
C) endocytosis
D) membrane fusion
E) exocytosis
A) budding
B) lysis
C) endocytosis
D) membrane fusion
E) exocytosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The genome of which of the following types of animal virus can act directly as mRNA?
A) retroviruses
B) +ssRNA viruses
C) -ssRNA viruses
D) ssDNA viruses
E) dsRNA viruses
A) retroviruses
B) +ssRNA viruses
C) -ssRNA viruses
D) ssDNA viruses
E) dsRNA viruses

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
One mechanism by which viruses may cause cancer is to interrupt the genetic regulatory sequences of repressor proteins. Which of the following types of viruses is most likely to be involved in causing cancer by this mechanism?
A) +ssRNA viruses
B) dsRNA viruses
C) -ssRNA viruses
D) retroviruses
E) both +ssRNA and -ssRNA viruses
A) +ssRNA viruses
B) dsRNA viruses
C) -ssRNA viruses
D) retroviruses
E) both +ssRNA and -ssRNA viruses

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Viruses with -ssRNA require the activity of (DNA polymerase/reverse transcriptase/RNA-dependent RNA polymerase) for their replication.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Most viruses cannot be seen by light microscopy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
All viruses use the host cell's nucleic acid polymerases for replication.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A ________ is a mass of neoplastic cells.
A) diploid culture
B) metastasis
C) tumor
D) gall
E) plaque
A) diploid culture
B) metastasis
C) tumor
D) gall
E) plaque

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Budding release of virus may result in long lasting or persistent infection.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The genome of all DNA animal viruses is replicated in the nucleus of the cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Viral capsids are composed of subunits called (capsomeres/nucleocapsids/prions).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
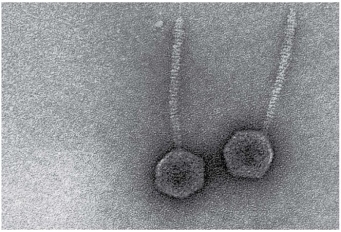
The virions shown in Figure 13.1 have a (complex/helical/polyhedral) capsid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The process known as ________ is a mechanism of release for enveloped viruses.
A) lytic replication
B) persistent infection
C) metastasis
D) latency
E) budding
A) lytic replication
B) persistent infection
C) metastasis
D) latency
E) budding

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The combination of a virus's protein coat and nucleic acid core is called the (capsid/virion/nucleocapsid).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Protozoa are susceptible to viral attack.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Bovine spongiform encephalopathy is an example of a prion disease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Members of a virus family have the same type of nucleic acid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The ________ of a virion determines the type of cell it enters.
A) nucleic acid
B) matrix proteins
C) glycoproteins
D) lipid molecules
E) shape
A) nucleic acid
B) matrix proteins
C) glycoproteins
D) lipid molecules
E) shape

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which of the following infectious particles is most susceptible to damage?
A) naked capsid virus
B) enveloped virus
C) prions
D) bacteriophage
E) both naked capsid viruses and prions
A) naked capsid virus
B) enveloped virus
C) prions
D) bacteriophage
E) both naked capsid viruses and prions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
A viral infection which does not result in the production of new virions is ________ infection(s).
A) a lytic
B) a latent
C) a persistent
D) a lysogenic
E) either latent or lysogenic
A) a lytic
B) a latent
C) a persistent
D) a lysogenic
E) either latent or lysogenic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Continuous cell cultures are developed from (embryonic/haploid/neoplastic) cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Bacteriophage release is a gradual process in which small numbers are released at a time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Viruses cause most human cancers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Fertilized chicken eggs are used to culture some vaccine strains.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Uncontrolled cell division in animals is known as (metastasis/neoplasia/cancer).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Another term for a lysogenic phage is a (temperate/latent/prophage) phage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
A (colony/plaque/prophage) is a clear zone on a bacterial lawn where cells have been killed by the activity of a bacteriophage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The stage of virus infection called (assembly/entry/synthesis) is the stage most dependent on host cell proteins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
A scientist discovers a new virus associated with a cancer. She is able to culture it in the laboratory and begins to analyze it. What features will help her determine the virus' classification? How does this help her understand the virus' mechanism for causing cancer?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Compare and contrast the ways in which animal, plant, and bacterial viruses gain entry into their host cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Seven (orders/families/classes) represent the highest level of taxonomic rank used in classifying viruses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Why is the synthesis of mRNA a central issue for all viruses? How do different types of viruses achieve this goal?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
RNA viruses such as HIV require the activity of reverse (polymerase/transcriptase/transposase) to become proviruses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Genes that play a role in proper cell division but may also play a role in some types of cancer are called (oncogenes/protooncogenes/promoters).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Prions are composed of a single protein called (plaque/BSE/PrP).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
In contrast to most dsDNA animal viruses, the poxviruses replicate solely in the cytoplasm of the host cell. What does this suggest about the virus?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
A "naked" virus lacks (lipid/nucleic acid/protein).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The process during viral infection known as "uncoating" involves the removal of the (capsid/envelope/matrix).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Describe the mechanism by which PrP is infectious.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



