Deck 14: Infection, Infectious Diseases, and Epidemiology
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/76
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 14: Infection, Infectious Diseases, and Epidemiology
1
Which of the following is transmitted by the parenteral route?
A) ringworm
B) warts
C) gonorrhea
D) yellow fever
E) pertussis
A) ringworm
B) warts
C) gonorrhea
D) yellow fever
E) pertussis
D
2
Which of the following statements regarding the demonstration of the etiology of disease is FALSE?
A) The suspect agent must be present in all cases of the disease.
B) The suspect agent must cause the disease under investigation when introduced into a susceptible host organism.
C) The suspect agent must be isolated and cultured in the laboratory.
D) It must be possible to reisolate the suspect agent from the infected experimental host.
E) The suspect agent must be the only potential pathogen present in disease cases.
A) The suspect agent must be present in all cases of the disease.
B) The suspect agent must cause the disease under investigation when introduced into a susceptible host organism.
C) The suspect agent must be isolated and cultured in the laboratory.
D) It must be possible to reisolate the suspect agent from the infected experimental host.
E) The suspect agent must be the only potential pathogen present in disease cases.
E
3
The close contact between newborns and family members allow them to become ________ with microbes that become established as their microbiota. (Choose the most accurate term.)
A) infected
B) parasitized
C) colonized
D) contaminated
E) infiltrated
A) infected
B) parasitized
C) colonized
D) contaminated
E) infiltrated
C
4
Which of the following situations is NOT a way in which a baby acquires normal microbiota?
A) The baby acquires the residential microbiota in the colon after the first meal.
B) Staphylococcus epidermidis is transferred from the hospital staff to the newborn after delivery.
C) microbes cross the placenta during pregnancy.
D) microorganisms grow in the respiratory tract after the baby's first breath.
E) microbes enter the nose and mouth when the baby is in the birth canal.
A) The baby acquires the residential microbiota in the colon after the first meal.
B) Staphylococcus epidermidis is transferred from the hospital staff to the newborn after delivery.
C) microbes cross the placenta during pregnancy.
D) microorganisms grow in the respiratory tract after the baby's first breath.
E) microbes enter the nose and mouth when the baby is in the birth canal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following situations might cause normal microbiota to become opportunistic pathogens?
A) growth of microbes on the surface of intact skin
B) growth of microorganisms on the excreted cellular wastes and dead cells in the large intestine
C) treatment of a cancer patient with radiation
D) growth of Lactobacillus on the surface of teeth
E) presence of Entamoeba in the lumen of the colon
A) growth of microbes on the surface of intact skin
B) growth of microorganisms on the excreted cellular wastes and dead cells in the large intestine
C) treatment of a cancer patient with radiation
D) growth of Lactobacillus on the surface of teeth
E) presence of Entamoeba in the lumen of the colon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following stages of an infectious disease is the most severe?
A) the incubation period
B) the prodromal period
C) the illness period
D) the decline period
E) the convalescence period
A) the incubation period
B) the prodromal period
C) the illness period
D) the decline period
E) the convalescence period

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Among the virulence factors produced by Staphylococcus aureus are hemolysin, coagulase, hyaluronidase, and enterotoxin. Which of these factors contribute to the ability of S. aureus to invade the body?
A) coagulase
B) enterotoxin
C) hemolysin
D) hyaluronidase
E) coagulase and hemolysin
A) coagulase
B) enterotoxin
C) hemolysin
D) hyaluronidase
E) coagulase and hemolysin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following is NOT considered a member of the normal human microbiota?
A) Candida
B) Lactobacillus
C) E. coli
D) Bacteroides
E) Microsporum
A) Candida
B) Lactobacillus
C) E. coli
D) Bacteroides
E) Microsporum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Chagas' disease is transmitted by a bug with mouthparts that penetrate blood vessels. Which type of exposure does this represent?
A) mucous membrane portal
B) parenteral route
C) skin portal
D) contact
E) fomite
A) mucous membrane portal
B) parenteral route
C) skin portal
D) contact
E) fomite

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
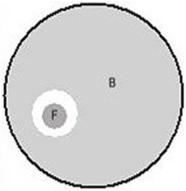 Figure 14.1 represents a Petri dish with a fungus (F), shown in darker gray, growing in the midst of bacterial lawn (B), shown in light gray. The relationship between the fungus and the bacteria would best be described as
Figure 14.1 represents a Petri dish with a fungus (F), shown in darker gray, growing in the midst of bacterial lawn (B), shown in light gray. The relationship between the fungus and the bacteria would best be described asA) synergistic.
B) amensal.
C) commensal.
D) parasitic.
E) None, there is no relationship between the microbes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following is NOT an example of symbiosis?
A) bacteria in the human colon
B) tapeworm in the human intestine
C) tuberculosis in the human lung
D) protozoa in termites
E) microbes crossing the placenta to the fetus
A) bacteria in the human colon
B) tapeworm in the human intestine
C) tuberculosis in the human lung
D) protozoa in termites
E) microbes crossing the placenta to the fetus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Mutualism is a relationship
A) that provides benefits for both members, sometimes to the point that one cannot live without the other.
B) where only one member derives benefit from the other.
C) where one member of the relationship may kill the other.
D) where one member of the relationship benefits without hurting the other.
E) where it is difficult to prove the benefits or disadvantages one member of the relationship may provide for the other.
A) that provides benefits for both members, sometimes to the point that one cannot live without the other.
B) where only one member derives benefit from the other.
C) where one member of the relationship may kill the other.
D) where one member of the relationship benefits without hurting the other.
E) where it is difficult to prove the benefits or disadvantages one member of the relationship may provide for the other.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
In which of the following do the mucous membranes serve as a portal of entry for disease?
A) a pathogen crosses from the mother to the fetus by way of the placenta.
B) A person rubs the eye with contaminated fingers and the pathogen is washed into the nasal cavity by way of tears.
C) A person is bitten by a mosquito that carries the malaria parasite.
D) Fungi digest the outer layer of the skin.
E) A person receives an injection with a contaminated needle.
A) a pathogen crosses from the mother to the fetus by way of the placenta.
B) A person rubs the eye with contaminated fingers and the pathogen is washed into the nasal cavity by way of tears.
C) A person is bitten by a mosquito that carries the malaria parasite.
D) Fungi digest the outer layer of the skin.
E) A person receives an injection with a contaminated needle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following is a symptom of disease?
A) temperature
B) swelling
C) diarrhea
D) fatigue
E) rash
A) temperature
B) swelling
C) diarrhea
D) fatigue
E) rash

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Diseases that are induced by modern medical procedures are referred to as ________ infections.
A) iatrogenic
B) exogenous
C) opportunistic
D) endogenous
E) subacute
A) iatrogenic
B) exogenous
C) opportunistic
D) endogenous
E) subacute

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A toxin common to all Gram-negative bacteria is
A) neurotoxin.
B) coagulase.
C) lipid A.
D) hemolysin.
E) collagenase.
A) neurotoxin.
B) coagulase.
C) lipid A.
D) hemolysin.
E) collagenase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following is a sign of disease?
A) headache
B) dizziness
C) fever
D) nausea
E) cramps
A) headache
B) dizziness
C) fever
D) nausea
E) cramps

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following is considered a mechanical vector transmission?
A) cockroach transmission of Shigella
B) mosquito transmission of Plasmodium
C) flea transmission of Yersinia
D) tsetse fly transmission of Trypanosoma
E) louse transmission of Rickettsia
A) cockroach transmission of Shigella
B) mosquito transmission of Plasmodium
C) flea transmission of Yersinia
D) tsetse fly transmission of Trypanosoma
E) louse transmission of Rickettsia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Symptoms are
A) subjective characteristics of a disease that only the patient can feel.
B) objective manifestations of a disease that can be measured.
C) objective manifestations of a disease that can be observed by others.
D) characteristics of a disease, such as sweating.
E) laboratory tests used to diagnose a disease.
A) subjective characteristics of a disease that only the patient can feel.
B) objective manifestations of a disease that can be measured.
C) objective manifestations of a disease that can be observed by others.
D) characteristics of a disease, such as sweating.
E) laboratory tests used to diagnose a disease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The bacterium Staphylococcus aureus is commonly found in the nasal cavity of healthy people. If inhaled into the lungs, however, it may cause pneumonia. Staphylococcus aureus is best described as
A) a parasite.
B) resident microbiota.
C) a mutualist symbiotic partner.
D) transient microbiota.
E) both resident microbiota and opportunistic pathogen.
A) a parasite.
B) resident microbiota.
C) a mutualist symbiotic partner.
D) transient microbiota.
E) both resident microbiota and opportunistic pathogen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A pathogen is best described as
A) a microorganism that remains with the person throughout life.
B) any microorganism that causes disease.
C) an organism that remains in the body for a short time.
D) a microorganism that may cause a disease under certain circumstances.
E) a source of microbial contamination.
A) a microorganism that remains with the person throughout life.
B) any microorganism that causes disease.
C) an organism that remains in the body for a short time.
D) a microorganism that may cause a disease under certain circumstances.
E) a source of microbial contamination.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Infectious diseases can be classified on the basis of
A) severity and duration of the disease.
B) means of transmission.
C) organs or organ systems affected by the disease.
D) type of microbe that causes the disease.
E) disease severity and duration, organ system affected or type of microbe.
A) severity and duration of the disease.
B) means of transmission.
C) organs or organ systems affected by the disease.
D) type of microbe that causes the disease.
E) disease severity and duration, organ system affected or type of microbe.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The person known to history as "Typhoid Mary" never had typhoid fever but was identified by public health officials as a source of Salmonella enterica Typhi. Which of the following is the most accurate description of her in this scenario?
A) contact carrier
B) human carrier
C) reservoir
D) both a human carrier and a reservoir
E) a reservoir but not a carrier
A) contact carrier
B) human carrier
C) reservoir
D) both a human carrier and a reservoir
E) a reservoir but not a carrier

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Aerosols may be involved in ________ transmission of pathogens.
A) droplet
B) direct
C) vector
D) fecal-oral
E) waterborne
A) droplet
B) direct
C) vector
D) fecal-oral
E) waterborne

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A strain of Neisseria gonorrhea has a mutation which has caused it to lose the ability to produce fimbriae and become less virulent as a consequence. What function has this pathogen lost?
A) the ability to adhere to cells of the body
B) the ability to move from one location in the body to another
C) the ability to produce an endotoxin
D) the ability to establish a latent infection
E) the ability to prevent phagocytes killing it
A) the ability to adhere to cells of the body
B) the ability to move from one location in the body to another
C) the ability to produce an endotoxin
D) the ability to establish a latent infection
E) the ability to prevent phagocytes killing it

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following virulence factors directly contributes to severe inflammation?
A) coagulase
B) lipid A
C) hyaluronidase
D) kinase
E) collagenase
A) coagulase
B) lipid A
C) hyaluronidase
D) kinase
E) collagenase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A person is exposed to rotten wood with fungal growth and develops blastomycosis. No one taking care of him/her becomes ill. Blastomycosis is an example of a ________ disease.
A) contagious
B) subacute
C) chronic
D) noncommunicable
E) latent
A) contagious
B) subacute
C) chronic
D) noncommunicable
E) latent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A new influenza strain appears and is spreading rapidly. What measures might be taken by public health agencies to stop the spread?
A) Facilitate access to vaccines.
B) Identify and treat people who are infected.
C) Educate members of the public about ways to protect themselves.
D) Educate the public, promote vaccination, and treat those who are infected.
E) Shut down public transportation.
A) Facilitate access to vaccines.
B) Identify and treat people who are infected.
C) Educate members of the public about ways to protect themselves.
D) Educate the public, promote vaccination, and treat those who are infected.
E) Shut down public transportation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following is the CORRECT sequence of a disease process?
A) convalescence, incubation, prodromal period, illness, decline
B) prodromal period, convalescence, incubation, illness, decline
C) incubation, convalescence, prodromal period, illness, decline
D) incubation, prodromal period, illness, decline, convalescence
E) illness, convalescence, incubation, prodromal period, decline
A) convalescence, incubation, prodromal period, illness, decline
B) prodromal period, convalescence, incubation, illness, decline
C) incubation, convalescence, prodromal period, illness, decline
D) incubation, prodromal period, illness, decline, convalescence
E) illness, convalescence, incubation, prodromal period, decline

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Organisms that are resident microbiota are best described as
A) microorganisms that remain with the person throughout life.
B) any microorganisms that cause disease.
C) organisms that are present in or on the body for a short time without causing harm.
D) microorganisms that may cause a disease under certain circumstances.
E) microorganisms that never cause disease.
A) microorganisms that remain with the person throughout life.
B) any microorganisms that cause disease.
C) organisms that are present in or on the body for a short time without causing harm.
D) microorganisms that may cause a disease under certain circumstances.
E) microorganisms that never cause disease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
People who wash their hands frequently during cold season typically have fewer colds than those who do not. This observation suggests cold viruses can be transmitted by
A) fomites.
B) mechanical vectors.
C) biological vectors.
D) direct contact.
E) both direct contact and fomites.
A) fomites.
B) mechanical vectors.
C) biological vectors.
D) direct contact.
E) both direct contact and fomites.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The bacterium that causes tuberculosis can be expelled from the lungs by a cough and remain viable in the air for an hour or more. If a person inhales the bacteria from the air, what type of transmission has occurred?
A) indirect contact
B) airborne
C) waterborne
D) foodborne
E) bodily fluid
A) indirect contact
B) airborne
C) waterborne
D) foodborne
E) bodily fluid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The incidence of tuberculosis in the year 2000 in the United States was 12.43/100,000 cases. This means
A) 12.43 of every 100,000 people in the United States had tuberculosis in the year 2000.
B) 12.43 of every 100,000 people died of tuberculosis in the United States in the year 2000.
C) there were 12.43 new cases of tuberculosis for every 100,000 people in the United States in the year 2000.
D) there were 12.43 tubercle bacilli per 100,000 microbes in the United States in the year 2000.
E) 12.43 of every 100,000 cases of tuberculosis were treated in the United States in the year 2000.
A) 12.43 of every 100,000 people in the United States had tuberculosis in the year 2000.
B) 12.43 of every 100,000 people died of tuberculosis in the United States in the year 2000.
C) there were 12.43 new cases of tuberculosis for every 100,000 people in the United States in the year 2000.
D) there were 12.43 tubercle bacilli per 100,000 microbes in the United States in the year 2000.
E) 12.43 of every 100,000 cases of tuberculosis were treated in the United States in the year 2000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Over 470,000 cases of cholera were reported in Haiti in the two years following the 2010 earthquake. Which of the following was the most likely mode of transmission?
A) mosquitoes
B) aerosols
C) contact
D) contaminated water
E) contaminated milk
A) mosquitoes
B) aerosols
C) contact
D) contaminated water
E) contaminated milk

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Microbes known as transient microbiota are
A) microorganisms that remain with the person throughout life.
B) microorganisms that may cause a disease under certain circumstances.
C) organisms that remain in the body for a short time.
D) unsuccessful microbial invaders because of the presence of preexisting microbes.
E) sources of microbial contamination.
A) microorganisms that remain with the person throughout life.
B) microorganisms that may cause a disease under certain circumstances.
C) organisms that remain in the body for a short time.
D) unsuccessful microbial invaders because of the presence of preexisting microbes.
E) sources of microbial contamination.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Treatment with high doses of antibiotics may lead to which type of healthcare-associated infection (HAI)?
A) subclinical disease
B) exogenous infection
C) latent infection
D) superinfection
E) zoonotic
A) subclinical disease
B) exogenous infection
C) latent infection
D) superinfection
E) zoonotic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
In early spring 2009, the CDC reported several dozen cases of novel H1N1 influenza ("swine flu") in the United States. By the summer, the number of confirmed cases was reported as over 40,000. The pattern of novel H1N1 cases in the United States represents a(n) ________ disease.
A) epidemic
B) endemic
C) sporadic
D) pandemic
E) opportunistic
A) epidemic
B) endemic
C) sporadic
D) pandemic
E) opportunistic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Koch's postulates were used to demonstrate the relationship between
A) HIV and AIDS.
B) Mycobacterium leprae and leprosy.
C) liver parasites and liver cancer.
D) Haemophilus influenzae and meningitis.
E) Haemophilus influenzae and the flu.
A) HIV and AIDS.
B) Mycobacterium leprae and leprosy.
C) liver parasites and liver cancer.
D) Haemophilus influenzae and meningitis.
E) Haemophilus influenzae and the flu.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Fomites are
A) insects that transmit pathogens from an infected host to a noninfected host.
B) inanimate objects involved in the indirect contact transmission of pathogens.
C) fecal material from infected hosts.
D) animal sources for human pathogens.
E) silent carriers of infectious diseases.
A) insects that transmit pathogens from an infected host to a noninfected host.
B) inanimate objects involved in the indirect contact transmission of pathogens.
C) fecal material from infected hosts.
D) animal sources for human pathogens.
E) silent carriers of infectious diseases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following diseases may be reduced by improved public sanitation measures?
A) malaria
B) HIV
C) cholera
D) chickenpox
E) rabies
A) malaria
B) HIV
C) cholera
D) chickenpox
E) rabies

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A syndrome is a group of symptoms and signs that collectively characterize a particular disease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
All infections result in disease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
An axenic environment is one
A) in which microorganisms remain with the person throughout life.
B) that is free of microbes.
C) that is a source of contamination.
D) in which microorganisms remain present only for a short time.
E) contaminated by microbial toxins.
A) in which microorganisms remain with the person throughout life.
B) that is free of microbes.
C) that is a source of contamination.
D) in which microorganisms remain present only for a short time.
E) contaminated by microbial toxins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Toxins that affect the lining of the digestive tract are (endotoxins/enterotoxins/exotoxins).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The (incubation/morbidity/prodromal) period is the time between infection and the occurrence of the first symptoms or signs of the disease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Normal microbiota may cause disease if conditions change in the body.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The (intestines/nasal cavities/lungs) are normally axenic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A reservoir is
A) a source of microbial contamination.
B) an environment that is free of microbes.
C) any microorganism that causes disease.
D) a condition in which organisms remain in the body for a short time.
E) a source of microbes for laboratory testing.
A) a source of microbial contamination.
B) an environment that is free of microbes.
C) any microorganism that causes disease.
D) a condition in which organisms remain in the body for a short time.
E) a source of microbes for laboratory testing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Biofilms provide an alternative means for bacteria to attach to surfaces within the body.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The degree to which a microbe is able to cause disease is known as its (morbidity/virulence/toxicity).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Microbial contamination always results in infection.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Commensalism is best described as a(n)
A) unsuccessful microbial invasion due to the presence of preexisting microbes.
B) relationship between two organisms where only one member benefits and the other is unharmed.
C) relationship between two organisms where both members benefit.
D) relationship in which a microorganism causes disease.
E) source of contamination.
A) unsuccessful microbial invasion due to the presence of preexisting microbes.
B) relationship between two organisms where only one member benefits and the other is unharmed.
C) relationship between two organisms where both members benefit.
D) relationship in which a microorganism causes disease.
E) source of contamination.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The condition known as microbial antagonism may be defined as
A) microorganisms that remain with a person throughout life.
B) a relationship between two organisms where one member harms the other.
C) a relationship between two organisms where only one member benefits.
D) an unsuccessful microbial invasion due to the presence of preexisting microbes.
E) a relationship between two organisms where both members benefit.
A) microorganisms that remain with a person throughout life.
B) a relationship between two organisms where one member harms the other.
C) a relationship between two organisms where only one member benefits.
D) an unsuccessful microbial invasion due to the presence of preexisting microbes.
E) a relationship between two organisms where both members benefit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
In commensalism, one member of the relationship harms the other.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Influenza is an example of a chronic disease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
All diseases go through the stages known as incubation period, prodromal period, and illness.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The condition called parasitism is characterized as a(n)
A) relationship between two organisms where only one member benefits and the other is unharmed.
B) relationship between two organisms where both members benefit.
C) nonsymbiotic relationship.
D) unsuccessful microbial invasion due to the presence of preexisting microbes.
E) relationship between two organisms where one member harms the other.
A) relationship between two organisms where only one member benefits and the other is unharmed.
B) relationship between two organisms where both members benefit.
C) nonsymbiotic relationship.
D) unsuccessful microbial invasion due to the presence of preexisting microbes.
E) relationship between two organisms where one member harms the other.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
People in the asymptomatic incubation stage of a disease may be a reservoir of the agent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Koch's postulates can be applied to every infectious disease to identify its causative pathogen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Bacterial capsules are (antiphagocytic/cytotoxic/exotoxic) virulence factors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Researchers have proposed that the herpes virus responsible for the childhood illness roseola may cause a type of T cell leukemia. Ninety percent of the population has been infected by the virus by two years of age, but the T cell leukemia is relatively rare. The virus can be cultured in the laboratory in tissue culture, but not in mature organisms. Discuss the obstacles to applying Koch's postulates to the etiology of this disease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The bacterium that causes cholera is capable of living independently in freshwater. As a consequence, cholera epidemics primarily involve (animal/nonliving/zoonotic) reservoirs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Persons with asymptomatic infections may be (contaminants/reservoirs/zoonoses) of disease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The study of the cause of disease is known as (epidemiology/etiology/pathology).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Compare and contrast analytical, descriptive and experimental epidemiology.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Compare and contrast endotoxins and exotoxins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Pathogens in droplets of body fluids are spread by (contact/indirect/vehicle) transmission.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
A patient has an upper GI endoscopic procedure and later develops a severe (endogenous/iatrogenic/secondary) infection with the Gram-negative pathogen known as CRE.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Staphylococcus bacteria are commonly present in the human nasal cavity but rarely cause disease of the upper respiratory system. This situation is an example of (commensalism/mutualism/parasitism).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
A (chronic/latent/subclinical) infection is one in which the microbe is actively reproducing but not causing symptoms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Virions attach to a target host cell by means of (capsules/capsids/ligands).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
In 2012, a new kind of fungal meningitis (infection of the nervous system) was discovered. Disease occurred among patients who had received steroid injections in the spine. Discuss whether these were healthcare-associated infections (HAIs): defend your answer. Discuss the route of transmission and what measures public health agencies could take to reduce disease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Describe three types of reservoirs of infectious disease in humans. Give an example disease for each type of reservoir.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
In early 2014, West African countries began diagnosing and reporting cases of Ebola for the first time in their history. This is an example of a(n) (endemic/epidemic/sporadic) disease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Lipid A is a(n) (cytotoxin/endotoxin/exotoxin) that stimulates the body to release chemicals that cause fever, inflammation, diarrhea, hemorrhaging, shock, and blood coagulation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Nausea is an example of a (sign/symptom/syndrome) of disease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



