Deck 15: Innate Immunity
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/75
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 15: Innate Immunity
1
Antimicrobial peptides called ________ are secreted in sweat and damage bacteria and fungi.
A) antibodies
B) dermcidins
C) TLRs
D) complement factors
E) cytokines
A) antibodies
B) dermcidins
C) TLRs
D) complement factors
E) cytokines
B
2
The complement cascade and its by-products contribute to
A) attracting phagocytes to sites of infection.
B) triggering inflammation.
C) triggering release of interferons.
D) triggering inflammation and release of interferons.
E) both triggering inflammation and attracting phagocytes to sites of infection.
A) attracting phagocytes to sites of infection.
B) triggering inflammation.
C) triggering release of interferons.
D) triggering inflammation and release of interferons.
E) both triggering inflammation and attracting phagocytes to sites of infection.
E
3
The process of phagocytosis involve all of the following EXCEPT
A) chemotaxis.
B) secretion of cytotoxins.
C) adhesion.
D) elimination.
E) vesicle fusion.
A) chemotaxis.
B) secretion of cytotoxins.
C) adhesion.
D) elimination.
E) vesicle fusion.
B
4
Cells of the second line of defense called ________ recognize and kill virus-infected cells.
A) basophils
B) eosinophils
C) macrophages
D) NK cells
E) dendritic cells
A) basophils
B) eosinophils
C) macrophages
D) NK cells
E) dendritic cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Response to specific pathogens that can improve with subsequent exposure is
A) the first line of defense.
B) the second line of defense.
C) the third line of defense.
D) microbial antagonism.
E) innate immunity.
A) the first line of defense.
B) the second line of defense.
C) the third line of defense.
D) microbial antagonism.
E) innate immunity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Protection from infection known as species resistance is a result of
A) the lack of suitable environment in the body.
B) the absence of receptors required for microbial attachment.
C) the presence of phagocytes in the tissues.
D) the salty, acidic condition of normal skin.
E) both the absence of necessary receptors and lack of suitable environment in the body.
A) the lack of suitable environment in the body.
B) the absence of receptors required for microbial attachment.
C) the presence of phagocytes in the tissues.
D) the salty, acidic condition of normal skin.
E) both the absence of necessary receptors and lack of suitable environment in the body.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following statements about eosinophil function is CORRECT?
A) They produce defensins.
B) They secrete toxins onto virally infected cells.
C) They are involved in the removal of neoplastic cells.
D) They attach to the surface of parasitic helminths and produce toxins that kill the parasite.
E) They identify and spare normal cells.
A) They produce defensins.
B) They secrete toxins onto virally infected cells.
C) They are involved in the removal of neoplastic cells.
D) They attach to the surface of parasitic helminths and produce toxins that kill the parasite.
E) They identify and spare normal cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following cells is a component of the body's first line defense?
A) monocyte
B) goblet cell
C) NK cell
D) neutrophil
E) microglial cells
A) monocyte
B) goblet cell
C) NK cell
D) neutrophil
E) microglial cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following contributes to protecting the eyes from microbial invasion?
A) tears contain lysozyme and salt.
B) a mucus layer traps and removes microbes.
C) tears mechanically flush particles from the eyes.
D) tears contain lysozyme and salt and mechanically flush particles from the eyes.
E) tears and mucus combine to trap microbes and remove them.
A) tears contain lysozyme and salt.
B) a mucus layer traps and removes microbes.
C) tears mechanically flush particles from the eyes.
D) tears contain lysozyme and salt and mechanically flush particles from the eyes.
E) tears and mucus combine to trap microbes and remove them.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following is the best definition of "microbial antagonism"?
A) the presence of pathogens on the surface of the skin, which will invade the body through abrasions
B) the presence of normal microbiota that protect the body by competing with pathogens in a variety of ways to prevent pathogens from invading the body
C) the presence of normal microbiota that can become pathogens under certain conditions
D) the ability of microbiota to mutate into pathogens
E) the presence of resident bacteria on the surface of the body and in cavities that connect to the surface
A) the presence of pathogens on the surface of the skin, which will invade the body through abrasions
B) the presence of normal microbiota that protect the body by competing with pathogens in a variety of ways to prevent pathogens from invading the body
C) the presence of normal microbiota that can become pathogens under certain conditions
D) the ability of microbiota to mutate into pathogens
E) the presence of resident bacteria on the surface of the body and in cavities that connect to the surface

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following leukocytes are called "agranulocytes" because of the absence of granules in their cytoplasm revealed by basic or acidic dyes?
A) eosinophils
B) basophils
C) lymphocytes
D) neutrophils
E) both basophils and eosinophils
A) eosinophils
B) basophils
C) lymphocytes
D) neutrophils
E) both basophils and eosinophils

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following areas of the body have mucous membranes?
A) mouth
B) nasal cavity
C) urinary system
D) mouth and nasal cavity
E) mouth, nasal cavity, and urinary system
A) mouth
B) nasal cavity
C) urinary system
D) mouth and nasal cavity
E) mouth, nasal cavity, and urinary system

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Mannose sugar occurs on the surface of some bacteria and fungi and can trigger the
A) release of cytotoxins by NK cells.
B) release of histamines by basophils.
C) classical pathway of complement activation.
D) lectin pathway of complement activation.
E) release of NETs by neutrophils.
A) release of cytotoxins by NK cells.
B) release of histamines by basophils.
C) classical pathway of complement activation.
D) lectin pathway of complement activation.
E) release of NETs by neutrophils.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The second line of defense against invading microbes includes
A) the skin.
B) mucous membranes.
C) antibodies.
D) phagocytic white blood cells.
E) microbiota.
A) the skin.
B) mucous membranes.
C) antibodies.
D) phagocytic white blood cells.
E) microbiota.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following statements regarding the surface of the skin is false?
A) It has sebum as a coating.
B) It has normal microbiota.
C) It has goblet cells.
D) It is salty.
E) It is acidic.
A) It has sebum as a coating.
B) It has normal microbiota.
C) It has goblet cells.
D) It is salty.
E) It is acidic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
What antibacterial chemical is present in tear fluid?
A) antibodies
B) complement
C) defensins
D) lysozyme
E) interferon
A) antibodies
B) complement
C) defensins
D) lysozyme
E) interferon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following are phagocytic cells descended from monocytes?
A) alveolar macrophages
B) dendritic cells
C) microglial cells
D) alveolar macrophages and dendritic cells
E) alveolar macrophages and microglial cells
A) alveolar macrophages
B) dendritic cells
C) microglial cells
D) alveolar macrophages and dendritic cells
E) alveolar macrophages and microglial cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Mucous membranes are quite thin and fragile. How can such delicate tissue provide defense against microbial invaders?
A) the mucus secreted by the mucous membrane physically traps microbes.
B) the mucus contains a variety of antimicrobial chemicals and molecules.
C) both the mucus and the outer layer of cells are shed frequently.
D) the mucus is a physical trap that contains a variety of antimicrobial chemicals.
E) the mucus physically traps microbes, contains a variety of antimicrobial chemicals, and is shed constantly, along with the outermost layer of cells.
A) the mucus secreted by the mucous membrane physically traps microbes.
B) the mucus contains a variety of antimicrobial chemicals and molecules.
C) both the mucus and the outer layer of cells are shed frequently.
D) the mucus is a physical trap that contains a variety of antimicrobial chemicals.
E) the mucus physically traps microbes, contains a variety of antimicrobial chemicals, and is shed constantly, along with the outermost layer of cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The first and second lines of defense against microbial invasion are part of
A) innate immunity.
B) adaptive immunity.
C) species resistance.
D) microbial antagonism.
E) both species resistance and adaptive immunity.
A) innate immunity.
B) adaptive immunity.
C) species resistance.
D) microbial antagonism.
E) both species resistance and adaptive immunity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following cells increase in number during an infection with parasitic worms?
A) basophils
B) macrophages
C) neutrophils
D) eosinophils
E) lymphocytes
A) basophils
B) macrophages
C) neutrophils
D) eosinophils
E) lymphocytes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Alpha and beta interferons
A) help protect virus-infected cells from the effects of the pathogen.
B) protect the cells that secrete them from being invaded by a virus.
C) are produced by infected fibroblasts and macrophages.
D) produce active antiviral proteins (AVPs) that coat the surface of healthy cells and prevent the attachment of pathogenic viruses.
E) produce no adverse effects in the body.
A) help protect virus-infected cells from the effects of the pathogen.
B) protect the cells that secrete them from being invaded by a virus.
C) are produced by infected fibroblasts and macrophages.
D) produce active antiviral proteins (AVPs) that coat the surface of healthy cells and prevent the attachment of pathogenic viruses.
E) produce no adverse effects in the body.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Fever is beneficial during viral infection because the higher temperature
A) inactivates interferons.
B) increases vasodilation, contributing to inflammation.
C) increases sweating and consequently the barrier effect.
D) prevents viral infection of fibroblasts.
E) increases the effectiveness of interferons.
A) inactivates interferons.
B) increases vasodilation, contributing to inflammation.
C) increases sweating and consequently the barrier effect.
D) prevents viral infection of fibroblasts.
E) increases the effectiveness of interferons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following are among the activities of neutrophils?
A) formation of neutrophil extracellular traps
B) release of histamines
C) enzyme production that leads to the formation of nitric oxide
D) formation of neutrophil extracellular traps and release of histamines
E) formation of neutrophil extracellular traps and production of nitric oxide
A) formation of neutrophil extracellular traps
B) release of histamines
C) enzyme production that leads to the formation of nitric oxide
D) formation of neutrophil extracellular traps and release of histamines
E) formation of neutrophil extracellular traps and production of nitric oxide

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following acts as a chemotactic factor?
A) C5a
B) interferon β
C) leukotriene
D) MAC
E) factor P
A) C5a
B) interferon β
C) leukotriene
D) MAC
E) factor P

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following statements is true of eosinophils?
A) They are in intact skin, sebum, tears, etc.
B) They produce the coating of a pathogen by complement.
C) They secrete toxins onto the surface of helminth parasites.
D) They decline during allergic reaction.
E) They release prostaglandins and leukotrienes in response to microbes.
A) They are in intact skin, sebum, tears, etc.
B) They produce the coating of a pathogen by complement.
C) They secrete toxins onto the surface of helminth parasites.
D) They decline during allergic reaction.
E) They release prostaglandins and leukotrienes in response to microbes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The phenomenon known as chemotaxis is defined as
A) the squeezing of cells through the lining of capillaries.
B) the release of prostaglandins and leukotrienes in response to microbes.
C) the movement of a cell toward or away from a chemical stimulus.
D) the coating of a pathogen by complement.
E) an increase in allergies and helminth infection.
A) the squeezing of cells through the lining of capillaries.
B) the release of prostaglandins and leukotrienes in response to microbes.
C) the movement of a cell toward or away from a chemical stimulus.
D) the coating of a pathogen by complement.
E) an increase in allergies and helminth infection.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
How does aspirin act to decrease the symptoms of inflammation?
A) it acts as an antiprostaglandin.
B) it is an antitoxoid for most microbial toxins.
C) it prevents complement activation.
D) it interferes with the action of interferons.
E) it blocks the release of histamine.
A) it acts as an antiprostaglandin.
B) it is an antitoxoid for most microbial toxins.
C) it prevents complement activation.
D) it interferes with the action of interferons.
E) it blocks the release of histamine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following substances contributes to the edema associated with inflammation?
A) leukotrienes
B) histamine
C) interferon
D) defensin
E) both leukotrienes and histamine
A) leukotrienes
B) histamine
C) interferon
D) defensin
E) both leukotrienes and histamine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The components of the second line of defense against microbes may be characterized as
A) responders to invasion.
B) passive barriers.
C) mechanisms to strengthen the first line of defense.
D) detecting the unique features of specific pathogens.
E) both passive barriers and detecting specific pathogen features.
A) responders to invasion.
B) passive barriers.
C) mechanisms to strengthen the first line of defense.
D) detecting the unique features of specific pathogens.
E) both passive barriers and detecting specific pathogen features.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Opsonization is
A) the coating of a pathogen by complement to facilitate phagocytosis.
B) the sticking of monocytes to the wall of the blood vessels at the site of infection.
C) damage resulting in cell lysis.
D) nonspecific leukocyte secretion of toxins onto the surface of virally infected cells.
E) phagocyte receptors detecting PAMPs.
A) the coating of a pathogen by complement to facilitate phagocytosis.
B) the sticking of monocytes to the wall of the blood vessels at the site of infection.
C) damage resulting in cell lysis.
D) nonspecific leukocyte secretion of toxins onto the surface of virally infected cells.
E) phagocyte receptors detecting PAMPs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A type of lymphocyte called a(n) ________ detects cells with abnormal surface proteins and kills them.
A) eosinophil
B) NK cell
C) neutrophil
D) basophil
E) mast cell
A) eosinophil
B) NK cell
C) neutrophil
D) basophil
E) mast cell

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following is an iron-binding protein produced by pathogens to access the body's store of iron?
A) gastroferritin
B) hemolysin
C) ferritin
D) transferrin
E) siderophores
A) gastroferritin
B) hemolysin
C) ferritin
D) transferrin
E) siderophores

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The alternative pathway of complement cascade activation begins with ________ binding to the surface of a microbe.
A) C1
B) factor B
C) C3b
D) C5a
E) C5b
A) C1
B) factor B
C) C3b
D) C5a
E) C5b

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following is NOT an example of a walled-off site of infection that contains a fluid made of dead and dying tissue cells, leukocytes, and pathogens?
A) a boil
B) an abscess
C) a pimple
D) a pustule
E) a tumor
A) a boil
B) an abscess
C) a pimple
D) a pustule
E) a tumor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which cell becomes a macrophage when leaving the bloodstream?
A) monocyte
B) lymphocyte
C) basophil
D) eosinophil
E) neutrophil
A) monocyte
B) lymphocyte
C) basophil
D) eosinophil
E) neutrophil

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following statements regarding phagocyte recognition of pathogens is true?
A) TLRs in the phagocyte cytoplasmic membrane bind surface structures of microbes.
B) TLRs on the surface of microbes trigger the accumulation of opsonins.
C) Lectins on the surface of microbes are bound by chemokine receptors.
D) NOD proteins on the surface of microbes are detected by TLRs.
E) MACs on the surface of microbes are detected by NOD proteins.
A) TLRs in the phagocyte cytoplasmic membrane bind surface structures of microbes.
B) TLRs on the surface of microbes trigger the accumulation of opsonins.
C) Lectins on the surface of microbes are bound by chemokine receptors.
D) NOD proteins on the surface of microbes are detected by TLRs.
E) MACs on the surface of microbes are detected by NOD proteins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following proteins are part of the first line of defense against microbial invasion?
A) dermcidins
B) TLRs
C) NOD proteins
D) C3 and C5
E) interferons
A) dermcidins
B) TLRs
C) NOD proteins
D) C3 and C5
E) interferons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following are macrophage functions?
A) phagocytosis of pathogens and debris
B) release of alpha interferon
C) production of NETs
D) phagocytosis of pathogens and production of NETs
E) phagocytosis of pathogens and secretion of alpha interferons and leukotrienes
A) phagocytosis of pathogens and debris
B) release of alpha interferon
C) production of NETs
D) phagocytosis of pathogens and production of NETs
E) phagocytosis of pathogens and secretion of alpha interferons and leukotrienes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Proteins on the surface of phagocytes called ________ aid in the detection of pathogen molecules.
A) lectins
B) TLRs
C) NOD proteins
D) lectins and C3 protein
E) both TLRs and NOD proteins
A) lectins
B) TLRs
C) NOD proteins
D) lectins and C3 protein
E) both TLRs and NOD proteins

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
What are NOD proteins?
A) cytoplasmic receptors of microbial molecules
B) cellular signals triggering inflammation
C) receptors of microbial molecules in phagocyte cell membranes
D) activators of complement
E) chemotactic factors
A) cytoplasmic receptors of microbial molecules
B) cellular signals triggering inflammation
C) receptors of microbial molecules in phagocyte cell membranes
D) activators of complement
E) chemotactic factors

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Innate immunity is not effective against fungus infections.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
First line of defense may be described as
A) the release of prostaglandins and leukotrienes in response to microbes.
B) intact skin, mucous membranes, sebum, tears, and so forth.
C) damage resulting in cell lysis.
D) the coating of a pathogen by complement.
E) nonspecific leukocytes that secrete toxins onto the surface of virally infected cells.
A) the release of prostaglandins and leukotrienes in response to microbes.
B) intact skin, mucous membranes, sebum, tears, and so forth.
C) damage resulting in cell lysis.
D) the coating of a pathogen by complement.
E) nonspecific leukocytes that secrete toxins onto the surface of virally infected cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The resident microbiota have no role in defense against pathogen invasion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Acute inflammation is normally beneficial.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The growth of some microbes is inhibited by elevated body temperature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Neutrophils can kill bacteria by nonphagocytic mechanisms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The absence of necessary receptors is the basis of the defense against microbial invasion known as (natural/innate/species) resistance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Interferons alpha and beta are effective against viruses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Some toll-like receptors (TLRs) are found on the surface of host cells and recognize specific microbial molecules.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Inflammation is an important part of the body's first line of defense, and it involves migration of phagocytes to the area.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Sweat glands produce (lysozyme/dermcidin/acid), which destroys the cell wall of bacteria by cleaving the bonds between the sugar subunits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Sebum contains ________ which contributes to creating an inhospitable environment on the surface of the body.
A) lysozyme
B) collagens
C) acids
D) salts
E) bile
A) lysozyme
B) collagens
C) acids
D) salts
E) bile

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Sweat can cause damage to bacteria because it contains salt and lysozyme.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The phenomenon known as species resistance is a highly specific defense against infectious agents.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The (epithelial/goblet/mucous) cells in the tracheal mucous membrane produce mucus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The oily substance that lowers the pH of the skin's surface to about pH 5 and is inhibitory to many bacteria is (sebum/sweat/serum).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
TLRs are
A) phagocyte receptors that detect PAMPs.
B) the coatings of pathogens by complement.
C) molecules that damage cells, resulting in cell lysis.
D) present in intact skin, sebum, tears, etc.
E) nonspecific leukocytes that secrete toxins onto the surface of virally infected cells.
A) phagocyte receptors that detect PAMPs.
B) the coatings of pathogens by complement.
C) molecules that damage cells, resulting in cell lysis.
D) present in intact skin, sebum, tears, etc.
E) nonspecific leukocytes that secrete toxins onto the surface of virally infected cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The leukocytes called natural killer lymphocytes
A) release prostaglandins and leukotrienes in response to microbes.
B) increase in allergies and helminth infection.
C) respond to the coating of a pathogen by complement.
D) are nonspecific leukocytes that secrete toxins onto the surface of virus-infected cells.
E) are specialists in killing bacteria.
A) release prostaglandins and leukotrienes in response to microbes.
B) increase in allergies and helminth infection.
C) respond to the coating of a pathogen by complement.
D) are nonspecific leukocytes that secrete toxins onto the surface of virus-infected cells.
E) are specialists in killing bacteria.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Microbial molecules detected by phagocytes are called
A) TLRs.
B) NODs.
C) PAMPs.
D) leukotrienes.
E) prostaglandins.
A) TLRs.
B) NODs.
C) PAMPs.
D) leukotrienes.
E) prostaglandins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
White blood cells known as (basophils/lymphocytes/neutrophils) are the main cells involved in the third line of defense.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Intracellular PAMPs are detected by (C1/NOD/TLR) proteins. (Be sure to use capital letters in your answer.)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Eosinophils respond to (complement/lipopolysaccharide/histamines) and kill bacteria in a nonphagocytic process.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Macrophages release (bradykinin/histamine/prostaglandin) in response to microbes and thereby contribute to acute inflammation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Proteins produced by the innate immune response to fight virus infection are (complement/interferons/opsonins).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Intact skin layers are part of the body's (first/second/third) line of defense against pathogens.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
What is phagocytosis? What does it involve?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The normal microbiota interact with potential pathogens in a variety of ways to protect the body, creating a situation known as microbial (antagonism/competition/resistance).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Neutrophils use their own (DNA/RNA/TLR) in the formation of NETs to trap bacteria.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Describe the events of the acute inflammatory response and their effect on a site of infection. Include the cells and chemicals involved.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
In a process called (cytokinesis/hematopoiesis/hematocrit), blood stem cells located in the bone marrow produce the three types of formed elements found in the blood.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Describe at least three physical mechanisms that are part of the first line of defense.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Some pathogens produce toxins which function as (histamines/prostaglandins/pyrogens) to cause fever.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
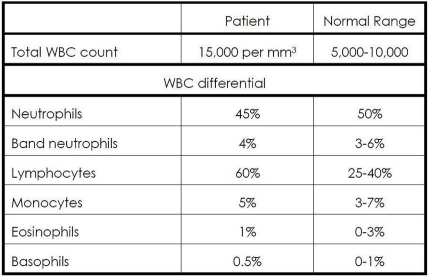
Examine the WBC count and differential data in Table 15.1. What type of disease is indicated by this set of data?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Nonphagocytic (eosinophils/monocytes/NK cells) are a type of lymphocyte which produce toxins to kill abnormal cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
What are macrophages, and what are their functions?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



