Deck 21: Microbial Cardiovascular and Systemic Diseases
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/71
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 21: Microbial Cardiovascular and Systemic Diseases
1
Blood returning from circulation through the body first enters the
A) left ventricle.
B) right atrium.
C) right ventricle.
D) pulmonary vein.
E) left atrium.
A) left ventricle.
B) right atrium.
C) right ventricle.
D) pulmonary vein.
E) left atrium.
B
2
Infection of the lymphatic vessels is known as
A) disseminated intravascular coagulation.
B) bacteremia.
C) lymphangitis.
D) petechiae.
E) recurrent fever.
A) disseminated intravascular coagulation.
B) bacteremia.
C) lymphangitis.
D) petechiae.
E) recurrent fever.
C
3
Which of the following vessels carries blood from the heart to the rest of the body?
A) the aorta
B) the superior vena cava
C) the inferior vena cava
D) the pulmonary arteries
E) capillaries
A) the aorta
B) the superior vena cava
C) the inferior vena cava
D) the pulmonary arteries
E) capillaries
A
4
A person is brought to the emergency room with constant high fever, extensive edema, low blood pressure, and petechiae. From which of the following may the person be suffering?
A) septicemia
B) plague
C) Lyme disease
D) brucellosis
E) infectious mononucleosis
A) septicemia
B) plague
C) Lyme disease
D) brucellosis
E) infectious mononucleosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The chief diagnostic sign of brucellosis is
A) petechiae.
B) jaundice.
C) "bull's eye" rash.
D) fever which recurs at 24 hour intervals.
E) fever which cycles every 72 hours.
A) petechiae.
B) jaundice.
C) "bull's eye" rash.
D) fever which recurs at 24 hour intervals.
E) fever which cycles every 72 hours.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following is characteristic of Yersinia pestis infections?
A) petechiae
B) a "bull's-eye" rash
C) jaundice
D) arthritis
E) buboes
A) petechiae
B) a "bull's-eye" rash
C) jaundice
D) arthritis
E) buboes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
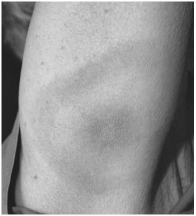 The appearance of this rash is characteristic of infections with which of the following?
The appearance of this rash is characteristic of infections with which of the following?A) Francisella tularensis
B) dengue virus
C) Borrelia burgdorferi
D) Epstein-Barr virus
E) Yersinia pestis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The chambers and valves of the heart are lined by the
A) pericardium.
B) myocardium.
C) endocardium.
D) erythrocytes.
E) vena cava.
A) pericardium.
B) myocardium.
C) endocardium.
D) erythrocytes.
E) vena cava.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Toxic shock syndrome (TSS) is associated with
A) Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
B) Staphylococcus aureus.
C) Streptococcus pyogenes.
D) Neisseria meningitidis.
E) both Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes.
A) Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
B) Staphylococcus aureus.
C) Streptococcus pyogenes.
D) Neisseria meningitidis.
E) both Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Unprotected contact with the bodily fluids of an infected animal may result in
A) African sleeping sickness.
B) brucellosis.
C) blackwater fever.
D) Lyme disease.
E) toxoplasmosis.
A) African sleeping sickness.
B) brucellosis.
C) blackwater fever.
D) Lyme disease.
E) toxoplasmosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Primary infection with Epstein-Barr virus is known as
A) infectious mononucleosis.
B) Burkitt's lymphoma.
C) Hodgkin's lymphoma.
D) chronic fatigue syndrome.
E) oral hairy leukoplakia.
A) infectious mononucleosis.
B) Burkitt's lymphoma.
C) Hodgkin's lymphoma.
D) chronic fatigue syndrome.
E) oral hairy leukoplakia.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A few days of fever with vomiting followed by high fever, jaundice, and "black vomit" are characteristic of
A) malaria.
B) dengue fever.
C) Chagas' disease.
D) yellow fever.
E) schistosomiasis.
A) malaria.
B) dengue fever.
C) Chagas' disease.
D) yellow fever.
E) schistosomiasis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following is/are a reservoir for Francisella tularensis?
A) rabbits
B) ticks
C) humans
D) rabbits and ticks
E) humans, rabbits and ticks
A) rabbits
B) ticks
C) humans
D) rabbits and ticks
E) humans, rabbits and ticks

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The normal habitat of ________ is rodents, but humans bitten by fleas carrying the pathogen have fever, severely inflamed lymph nodes, and headache. Later, areas of black, necrotic tissue may develop.
A) Clostridium perfringens
B) Yersinia pestis
C) Francisella tularensis
D) Borrelia burgdorferi
E) Toxoplasma gondii
A) Clostridium perfringens
B) Yersinia pestis
C) Francisella tularensis
D) Borrelia burgdorferi
E) Toxoplasma gondii

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A blood sample from a patient is examined on a microscope. Bacterial cells are detected in the sample. The patient has
A) bacteremia.
B) lymphangitis.
C) toxemia.
D) lipidemia.
E) viremia.
A) bacteremia.
B) lymphangitis.
C) toxemia.
D) lipidemia.
E) viremia.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) is a complication resulting from the
A) release of cytotoxins.
B) triggering of the complement system.
C) attachment of bacterial cells to the endocardium.
D) release of heme from damaged RBCs.
E) release of lipid A from dying Gram-negative bacteria.
A) release of cytotoxins.
B) triggering of the complement system.
C) attachment of bacterial cells to the endocardium.
D) release of heme from damaged RBCs.
E) release of lipid A from dying Gram-negative bacteria.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Vegetations are associated with which of the following disease processes?
A) septicemia
B) endocarditis
C) tularemia
D) plague
E) toxoplasmosis
A) septicemia
B) endocarditis
C) tularemia
D) plague
E) toxoplasmosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
How does Borrelia burgdorferi evade the body's defenses?
A) It has a polysaccharide capsule.
B) It has manganese-containing enzymes.
C) It is capable of antigenic variation.
D) It has a polysaccharide capsule and antiphagocytic proteins.
E) It is capable of antigenic variation and has manganese-containing enzymes.
A) It has a polysaccharide capsule.
B) It has manganese-containing enzymes.
C) It is capable of antigenic variation.
D) It has a polysaccharide capsule and antiphagocytic proteins.
E) It is capable of antigenic variation and has manganese-containing enzymes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Epstein-Barr virus infections are typically asymptomatic in ________ because of incomplete development of adaptive immunity.
A) the elderly
B) AIDS patients
C) adolescents
D) adults
E) young children
A) the elderly
B) AIDS patients
C) adolescents
D) adults
E) young children

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Fever, difficulty breathing, extreme fatigue, and elevated heart rate are characteristic of
A) Bang's disease.
B) ehrlichiosis.
C) infectious mononucleosis.
D) plague.
E) endocarditis.
A) Bang's disease.
B) ehrlichiosis.
C) infectious mononucleosis.
D) plague.
E) endocarditis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A young man living in the Southeastern U.S. is an avid outdoorsman and has a history of tick bites. Blood tests show that he has leukopenia.. He may have contracted
A) brucellosis.
B) tularemia.
C) Lyme disease.
D) ehrlichiosis.
E) Chagas' disease.
A) brucellosis.
B) tularemia.
C) Lyme disease.
D) ehrlichiosis.
E) Chagas' disease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following is the infective form of Trypanosoma cruzi?
A) epimastigotes
B) trypomastigotes
C) pseudocysts
D) amastigotes
E) miricidia
A) epimastigotes
B) trypomastigotes
C) pseudocysts
D) amastigotes
E) miricidia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following statements concerning Toxoplasma infection is CORRECT?
A) It is a rare infection.
B) It is transmitted by biting insects.
C) It is typically contracted by eating undercooked meat.
D) Freshwater snails are intermediate hosts.
E) In most individuals, the infection results in lasting damage to the heart.
A) It is a rare infection.
B) It is transmitted by biting insects.
C) It is typically contracted by eating undercooked meat.
D) Freshwater snails are intermediate hosts.
E) In most individuals, the infection results in lasting damage to the heart.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following is/are transmitted by Aedes mosquitoes?
A) dengue fever
B) yellow fever
C) malaria
D) both dengue fever and yellow fever
E) dengue fever, yellow fever, and malaria
A) dengue fever
B) yellow fever
C) malaria
D) both dengue fever and yellow fever
E) dengue fever, yellow fever, and malaria

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following diseases is a major problem for AIDS patients?
A) Chagas' disease
B) toxoplasmosis
C) hemorrhagic fevers
D) Lyme disease
E) brucellosis
A) Chagas' disease
B) toxoplasmosis
C) hemorrhagic fevers
D) Lyme disease
E) brucellosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following diseases is currently vaccine-preventable in humans?
A) schistosomiasis
B) malaria
C) Lyme disease
D) plague
E) yellow fever
A) schistosomiasis
B) malaria
C) Lyme disease
D) plague
E) yellow fever

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The normal hosts for Ebola viruses are probably
A) birds.
B) cats.
C) rodents.
D) bats.
E) humans.
A) birds.
B) cats.
C) rodents.
D) bats.
E) humans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Plasmodium species reproduce sexually in
A) birds.
B) Aedes mosquitoes.
C) Ixodes ticks.
D) humans.
E) Anopheles mosquitoes.
A) birds.
B) Aedes mosquitoes.
C) Ixodes ticks.
D) humans.
E) Anopheles mosquitoes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Dengue hemorrhagic fever is the result of
A) an immediate immune reaction to the initial infection with dengue virus.
B) an antibody-antigen complex reaction.
C) a hyperimmune response to reinfection with dengue virus.
D) an autoimmune disease.
E) the chronic carrier state associated with dengue virus infection.
A) an immediate immune reaction to the initial infection with dengue virus.
B) an antibody-antigen complex reaction.
C) a hyperimmune response to reinfection with dengue virus.
D) an autoimmune disease.
E) the chronic carrier state associated with dengue virus infection.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Another name for brucellosis is ________ fever.
A) blackwater
B) yellow
C) snail
D) rabbit
E) undulant
A) blackwater
B) yellow
C) snail
D) rabbit
E) undulant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Plasmodium falciparum produces proteins that cause ________ in addition to the anemia due to erythrocyte destruction.
A) DIC
B) toxemia
C) black vomit
D) capillary damage
E) damage to the heart muscle
A) DIC
B) toxemia
C) black vomit
D) capillary damage
E) damage to the heart muscle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A large number of people in an African village become ill a couple of weeks after sharing a feast of stew made from the meat of jungle animals. They initially have fever, headache and fatigue, and develop petechiae. Most then experience bloody diarrhea and vomiting, and a few days later begin bleeding from the mouth and eyes. What is the most likely preliminary diagnosis?
A) dengue hemorrhagic fever
B) ebola hemorrhagic fever
C) yellow fever
D) malaria
E) African trypanosomiasis
A) dengue hemorrhagic fever
B) ebola hemorrhagic fever
C) yellow fever
D) malaria
E) African trypanosomiasis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Schizogony is an important aspect of which of the following pathogens?
A) Yersinia pestis
B) Plasmodium species
C) Toxoplasma gondii
D) Trypanosoma cruzi
E) Schistosoma mansoni
A) Yersinia pestis
B) Plasmodium species
C) Toxoplasma gondii
D) Trypanosoma cruzi
E) Schistosoma mansoni

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Infection with Schistosoma species is acquired by
A) mosquito bite.
B) tick bite.
C) eating undercooked meat.
D) eating undercooked fish.
E) wading or swimming in fresh water.
A) mosquito bite.
B) tick bite.
C) eating undercooked meat.
D) eating undercooked fish.
E) wading or swimming in fresh water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
A young woman develops a fever after a recent trip to a Caribbean island. She also experiences severe headache and pain "in the bones." After a few days, she also develops a rash. Which of the following did she most likely contract?
A) yellow fever virus
B) dengue virus
C) malaria
D) Toxoplasma
E) Chagas' disease
A) yellow fever virus
B) dengue virus
C) malaria
D) Toxoplasma
E) Chagas' disease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Cycles of fever, chills, anemia and headache along with passage of dark colored urine are the symptoms of infection with
A) yellow fever virus.
B) P. vivax.
C) P. ovale.
D) P. falciparum.
E) dengue virus.
A) yellow fever virus.
B) P. vivax.
C) P. ovale.
D) P. falciparum.
E) dengue virus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Depletion of clotting proteins from the serum leads to the uncontrollable hemorrhaging seen in ________ infections.
A) yellow fever virus
B) malaria
C) dengue virus
D) Ebola virus
E) Epstein-Barr virus
A) yellow fever virus
B) malaria
C) dengue virus
D) Ebola virus
E) Epstein-Barr virus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
An indication of infection with Human herpesvirus 4 is
A) "swimmer's itch."
B) "bull's eye" rash.
C) a bubo.
D) high fever and sore throat.
E) an ulcerating sore.
A) "swimmer's itch."
B) "bull's eye" rash.
C) a bubo.
D) high fever and sore throat.
E) an ulcerating sore.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Lyme disease becomes chronic because
A) Borrelia changes its surface antigens frequently.
B) Borrelia can lie dormant in liver cells.
C) the bacterium resists phagocytosis.
D) Borrelia is an intracellular parasite of erythrocytes.
E) the bacterium resists phagocytosis and "hides" erythrocytes.
A) Borrelia changes its surface antigens frequently.
B) Borrelia can lie dormant in liver cells.
C) the bacterium resists phagocytosis.
D) Borrelia is an intracellular parasite of erythrocytes.
E) the bacterium resists phagocytosis and "hides" erythrocytes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following is known to be teratogenic?
A) Epstein-Barr virus
B) cytomegalovirus
C) Plasmodium
D) Borrelia
E) dengue virus
A) Epstein-Barr virus
B) cytomegalovirus
C) Plasmodium
D) Borrelia
E) dengue virus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Lipid A can cause septic shock.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Epstein-Barr virus causes the cells it infects to become immortal because it suppresses (apoptosis/cytolysis/oncogenesis).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
One of the factors leading to the initial characterization of Lyme disease in 1975 was the greater-than-expected incidence of (arthritis/osteomyelitis/mononucleosis) among children.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
It is the (larvae/nymph/adult) stage of the tick genus Ixodes that most often transmits Lyme disease to humans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Anaplasma primarily infects (erythrocytes/monocytes/neutrophils).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Small doses of antimicrobial drugs are effective in treatment of the late stages of Borrelia infection because the microbe is extremely susceptible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Human herpesvirus 4 is better known as cytomegalovirus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
When bacteria in the bloodstream invade the bones, this leads to a painful condition called (endocarditis/osteomyelitis/lymphangitis).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The terms "bacteremia" and "septicemia" are synonymous.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Blood returns to the heart from the lungs through the pulmonary (arteries/veins/valves).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Cytomegalovirus infection of the retina is now treated with (interferon/fomivirsen/ganciclovir), the first antisense RNA drug.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
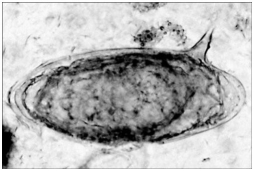 A person reports to a clinic complaining of fever and abdominal pain. The abdomen is swollen, and blood tests indicate kidney damage. A stool sample is examined under a microscope and found to contain the egg shown in the figure. The indications are consistent with infection with
A person reports to a clinic complaining of fever and abdominal pain. The abdomen is swollen, and blood tests indicate kidney damage. A stool sample is examined under a microscope and found to contain the egg shown in the figure. The indications are consistent with infection withA) Plasmodium falciparum.
B) Anaplasma phagocytophilium.
C) Schistosoma mansoni.
D) Toxoplasma gondii.
E) Trypanosoma cruzi.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The release of bacterial toxins into the blood leads to (bacteremia/septicemia/toxemia).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
People with genes for a form of hemoglobin known as hemoglobin C are at risk of fatal malaria disease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Both bubonic and pneumonic plague cause the formation of buboes and tissue necrosis of the extremities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Cytomegalovirus may be latent for years and reactivate when immunosuppression occurs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The zoonosis known as (ehrlichiosis/plague/tularemia) is transmitted to humans by fleas.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The three developmental stages of Ehrlichia are the elementary body, the initial body, and the morula.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Lymph is produced in the lymph nodes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Patients with occult septicemia are asymptomatic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The Ebola and Marburg viruses are the sole members of the (Flaviviridae/Filoviridae/Herpesviridae) family, named for their unusual filamentous form. (Be sure to use proper form.)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The intermediate host for Schistosoma mansoni is a (mosquito/tick/snail).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Explain the difference between bacteremia and septicemia, and describe some of the factors that can lead to septicemia.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The final stage of Chagas' disease is typically fatal because the parasite infects cells of the (blood/heart/liver).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Compare and contrast bubonic and pneumonic plague.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Compare and contrast dengue hemorrhagic fever and Ebola hemorrhagic fever. Discuss both the pathogens and the pathology.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Plasmodium (gametocytes/merozoites/sporozoites) reproduce by schizogony in humans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Yellow fever is named for the (anemia/jaundice/vomiting) it typically causes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
How does the age of the infected individual play a role in the development of Epstein-Barr virus (HHV-4) infections such as infectious mononucleosis?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
True bugs in the genus (Aedes/Ixodes/Triatoma) transmit Chagas' disease. (Be sure to use proper nomenclature form.)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
List and describe the three stages of malaria, paying attention to the various forms of the protozoan parasite present in each stage of the disease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



