Deck 22: Microbial Diseases of the Respiratory System
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/70
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 22: Microbial Diseases of the Respiratory System
1
Group A streptococci produce ________ which breaks down blood clots, allowing the bacteria to spread.
A) M proteins
B) a hyaluronic acid capsule
C) C5a peptidase
D) streptokinase
E) pyrogenic toxins
A) M proteins
B) a hyaluronic acid capsule
C) C5a peptidase
D) streptokinase
E) pyrogenic toxins
D
2
Which of the following is an opportunistic pathogen commonly present in the nasal cavity as a member of the microbiota?
A) Staphylococcus aureus
B) Bordetella pertussis
C) Legionella pneumophilia
D) Pneumocystis jiroveci
E) Veillonella species
A) Staphylococcus aureus
B) Bordetella pertussis
C) Legionella pneumophilia
D) Pneumocystis jiroveci
E) Veillonella species
A
3
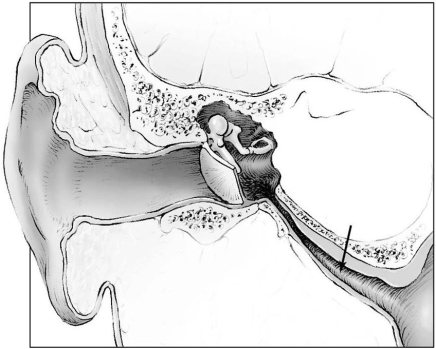 The structure indicated by the arrow connects the middle ear to what part of the respiratory system?
The structure indicated by the arrow connects the middle ear to what part of the respiratory system?A) nasal cavity
B) larynx
C) pharynx
D) sinuses
E) trachea
C
4
Which of the following Streptococcus pyogenes virulence factors kills leukocytes and erythrocytes?
A) streptolysins
B) pyrogenic toxins
C) streptokinases
D) the hyaluronic acid capsule
E) C5a peptidase
A) streptolysins
B) pyrogenic toxins
C) streptokinases
D) the hyaluronic acid capsule
E) C5a peptidase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The microbe which causes primary atypical pneumonia is
A) Bordetella pertussis.
B) MERS.
C) Chlamydophila pneumoniae.
D) Mycoplasma pneumoniae.
E) SARS.
A) Bordetella pertussis.
B) MERS.
C) Chlamydophila pneumoniae.
D) Mycoplasma pneumoniae.
E) SARS.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following statements is TRUE concerning diphtheria?
A) No effective vaccine is available to prevent infection.
B) A diffuse rash is the major sign of diphtheria.
C) The signs and symptoms of the disease are directly caused by a bacterial toxin.
D) The pseudomembrane is easily removed by surgery.
E) A microscopic exam of bacterial samples is sufficient for conclusive diagnosis.
A) No effective vaccine is available to prevent infection.
B) A diffuse rash is the major sign of diphtheria.
C) The signs and symptoms of the disease are directly caused by a bacterial toxin.
D) The pseudomembrane is easily removed by surgery.
E) A microscopic exam of bacterial samples is sufficient for conclusive diagnosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Ornithosis, a disease of birds that can be transmitted to humans, is caused by
A) Yersinia pestis.
B) Klebsiella pneumoniae.
C) Chlamydophila psittaci.
D) Mycoplasma pneumoniae.
E) Chlamydophila pneumoniae.
A) Yersinia pestis.
B) Klebsiella pneumoniae.
C) Chlamydophila psittaci.
D) Mycoplasma pneumoniae.
E) Chlamydophila pneumoniae.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
What is the primary determinant of virulence in Streptococcus pneumoniae?
A) the presence of a particular Lancefield antigen
B) the production of pneumolysin
C) the presence of a polysaccharide capsule
D) the ability to lyse red blood cells
E) strain-specific teichoic acids in its cell wall
A) the presence of a particular Lancefield antigen
B) the production of pneumolysin
C) the presence of a polysaccharide capsule
D) the ability to lyse red blood cells
E) strain-specific teichoic acids in its cell wall

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Bordetella pertussis produces
A) dermonecrotic toxin.
B) adenylate cyclase toxin.
C) pyrogenic toxin.
D) dermonecrotic and adenylate cyclase toxins.
E) dermonecrotic, adenylate cyclase, and pyrogenic toxins.
A) dermonecrotic toxin.
B) adenylate cyclase toxin.
C) pyrogenic toxin.
D) dermonecrotic and adenylate cyclase toxins.
E) dermonecrotic, adenylate cyclase, and pyrogenic toxins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following statements is TRUE regarding the common cold?
A) Only coronaviruses cause the common cold.
B) The viruses can infect both the upper and lower respiratory tracts.
C) Cold viruses reproduce most effectively at 37°C.
D) Cold viruses are frequently spread by contaminated fomites.
E) The immune system cannot develop an effective response to cold viruses.
A) Only coronaviruses cause the common cold.
B) The viruses can infect both the upper and lower respiratory tracts.
C) Cold viruses reproduce most effectively at 37°C.
D) Cold viruses are frequently spread by contaminated fomites.
E) The immune system cannot develop an effective response to cold viruses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The designation "group A," used to help classify Streptococcus pyogenes, refers to this bacterium's
A) Lancefield antigen.
B) hemolysis pattern.
C) M protein.
D) type of streptokinase produced.
E) disease associations.
A) Lancefield antigen.
B) hemolysis pattern.
C) M protein.
D) type of streptokinase produced.
E) disease associations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Neutrophils are inhibited from gathering at the site of infection by Mycobacterium tuberculosis by what virulence factor of the pathogen?
A) mycolic acid
B) cord factor
C) kinase
D) the capsule
E) hemolysin
A) mycolic acid
B) cord factor
C) kinase
D) the capsule
E) hemolysin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Inflammation of the pharynx with pus-filled abscesses and swollen tonsils is known as
A) diphtheria.
B) otitis media.
C) croup.
D) RSV.
E) streptococcal pharyngitis ("strep throat").
A) diphtheria.
B) otitis media.
C) croup.
D) RSV.
E) streptococcal pharyngitis ("strep throat").

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Pathogenic streptococci of the upper respiratory tract (such as Streptococcus pyogenes) are distinguished from non-pathogenic streptococci by
A) alpha hemolytic activity.
B) beta hemolytic activity.
C) no hemolytic activity.
D) the absence of a capsule.
E) the presence of a lysogenic phage.
A) alpha hemolytic activity.
B) beta hemolytic activity.
C) no hemolytic activity.
D) the absence of a capsule.
E) the presence of a lysogenic phage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The majority of cases of pneumonia are caused by
A) Mycoplasma pneumoniae.
B) Klebsiella pneumoniae.
C) Haemophilus influenzae.
D) Streptococcus pneumoniae.
E) Chlamydophila pneumoniae.
A) Mycoplasma pneumoniae.
B) Klebsiella pneumoniae.
C) Haemophilus influenzae.
D) Streptococcus pneumoniae.
E) Chlamydophila pneumoniae.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following statements is TRUE regarding tuberculosis?
A) It occurs only in the lungs.
B) Several hundred cells are required for infection.
C) It remains viable in dried aerosol droplets for up to eight months.
D) Only virulent strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis produce mycolic acid.
E) The immune system is not affected by the infection.
A) It occurs only in the lungs.
B) Several hundred cells are required for infection.
C) It remains viable in dried aerosol droplets for up to eight months.
D) Only virulent strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis produce mycolic acid.
E) The immune system is not affected by the infection.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A pneumonia caused by Gram-positive diplococci is known as
A) primary atypical pneumonia.
B) pleurisy.
C) pneumocystic pneumonia.
D) pneumonic plague.
E) pneumococcal pneumonia.
A) primary atypical pneumonia.
B) pleurisy.
C) pneumocystic pneumonia.
D) pneumonic plague.
E) pneumococcal pneumonia.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Diphtheria toxin kills cells by interfering with which of the following processes?
A) complement function
B) nucleic acid synthesis
C) cytoplasmic membrane function
D) protein synthesis
E) adenylate cyclase activity
A) complement function
B) nucleic acid synthesis
C) cytoplasmic membrane function
D) protein synthesis
E) adenylate cyclase activity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following is part of the upper respiratory system?
A) larynx
B) trachea
C) bronchi
D) pharynx
E) alveoli
A) larynx
B) trachea
C) bronchi
D) pharynx
E) alveoli

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis called MDR are resistant to
A) levofloxacin.
B) isoniazid.
C) rifampin.
D) isoniazid and rifampin.
E) levofloxacin, isoniazid and rifampin.
A) levofloxacin.
B) isoniazid.
C) rifampin.
D) isoniazid and rifampin.
E) levofloxacin, isoniazid and rifampin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following factors is primarily responsible for the ability of Mycobacterium tuberculosis to survive long periods of time in dried droplets of respiratory aerosols?
A) production of cord factor
B) pyrogenic toxin
C) formation of tubercles
D) the presence of LPS in the outer membrane
E) the presence of mycolic acid in the cell wall
A) production of cord factor
B) pyrogenic toxin
C) formation of tubercles
D) the presence of LPS in the outer membrane
E) the presence of mycolic acid in the cell wall

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Even though mycoplasmas pass through filters that normally trap bacteria, they are known to be bacteria, not viruses, because they
A) contain both DNA and RNA.
B) synthesize peptidoglycan.
C) divide by binary fission.
D) contain both DNA and RNA and divide by binary fission.
E) synthesize peptidoglycan and divide by snapping division.
A) contain both DNA and RNA.
B) synthesize peptidoglycan.
C) divide by binary fission.
D) contain both DNA and RNA and divide by binary fission.
E) synthesize peptidoglycan and divide by snapping division.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following diseases is almost diagnostic for AIDS?
A) blastomycosis
B) coccidioidomycosis
C) Pneumocystis pneumonia
D) histoplasmosis
E) Hantavirus pulmonary syndrome
A) blastomycosis
B) coccidioidomycosis
C) Pneumocystis pneumonia
D) histoplasmosis
E) Hantavirus pulmonary syndrome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Inhalation anthrax is frequently fatal even with antibiotic therapy because
A) Bacillus anthracis is resistant to a wide range of antibiotics.
B) it is transmitted as endospores.
C) the anthrax toxin triggers necrosis and severe edema of the lungs.
D) the bacteria are enclosed within a biofilm that antibiotics cannot penetrate.
E) the dying cells release lipid A, triggering a severe inflammatory response.
A) Bacillus anthracis is resistant to a wide range of antibiotics.
B) it is transmitted as endospores.
C) the anthrax toxin triggers necrosis and severe edema of the lungs.
D) the bacteria are enclosed within a biofilm that antibiotics cannot penetrate.
E) the dying cells release lipid A, triggering a severe inflammatory response.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What distinguishes influenza from the common cold?
A) Fever
B) Pharyngitis
C) Cough
D) Malaise
E) Nasal congestion
A) Fever
B) Pharyngitis
C) Cough
D) Malaise
E) Nasal congestion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Why are nearly all AIDS patients at risk of developing Pneumocystis pneumonia?
A) Pneumocystis jiroveci is becoming a wide-spread contaminant in health care environments.
B) Pneumocystis jiroveci is commonly found in a wide variety of soils.
C) The pathogen is easily transmitted from infected persons to others.
D) Pneumocystis jiroveci is a common member of the respiratory microbiome in humans and opportunistic pathogen.
E) Pneumocystis jiroveci is zoonotic in a wide range of vertebrates and exposure is unavoidable.
A) Pneumocystis jiroveci is becoming a wide-spread contaminant in health care environments.
B) Pneumocystis jiroveci is commonly found in a wide variety of soils.
C) The pathogen is easily transmitted from infected persons to others.
D) Pneumocystis jiroveci is a common member of the respiratory microbiome in humans and opportunistic pathogen.
E) Pneumocystis jiroveci is zoonotic in a wide range of vertebrates and exposure is unavoidable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A young man who works on a ranch and lives in the log bunkhouse experiences sudden fever with muscle aches. A few days later he begins to cough and have difficulty breathing, and goes to an urgent care clinic. His blood pressure is low. A blood sample reveals a low platelet count. A Gram stain of a sputum sample shows only a few small bacteria present. Which of the following is the most likely infecting agent?
A) Bacillus anthracis
B) Hantavirus
C) Histoplasma capsulatum
D) influenza
E) Mycoplasma pneumonia
A) Bacillus anthracis
B) Hantavirus
C) Histoplasma capsulatum
D) influenza
E) Mycoplasma pneumonia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The DTaP vaccine protects against which of the following respiratory diseases?
A) pneumonia
B) pertussis
C) anthrax
D) the common cold
E) tuberculosis
A) pneumonia
B) pertussis
C) anthrax
D) the common cold
E) tuberculosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Blastomycosis results from
A) inhalation of spherules.
B) inhalation of respiratory droplets.
C) inhalation of fungal spores.
D) contact with fomites.
E) contact with infected sputum.
A) inhalation of spherules.
B) inhalation of respiratory droplets.
C) inhalation of fungal spores.
D) contact with fomites.
E) contact with infected sputum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following is a common cause of otitis media?
A) Chlamydophila pneumoniae
B) Mycobacterium tuberculosis
C) Blastomyces dermatitidis
D) Streptococcus pneumoniae
E) Pneumocystis jiroveci
A) Chlamydophila pneumoniae
B) Mycobacterium tuberculosis
C) Blastomyces dermatitidis
D) Streptococcus pneumoniae
E) Pneumocystis jiroveci

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A recently retired man appears at his doctor's office complaining of difficulty breathing, body aches and fatigue. He is also running a high fever and has a dry cough. He reports having just returned from a trip to the Middle East where he visited several historical sites. Test results are negative for a rapid test for influenza A. No bacteria are visible in a microscopic exam of his sputum. Which of the following is a likely explanation?
A) inhalation anthrax
B) pertussis
C) valley fever
D) coronavirus respiratory syndrome
E) primary atypical pneumonia
A) inhalation anthrax
B) pertussis
C) valley fever
D) coronavirus respiratory syndrome
E) primary atypical pneumonia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Exposure to large accumulations of bird dropping may result in which of the following mycoses?
A) Pneumocystis pneumonia
B) blastomycosis
C) coccidioidomycosis
D) histoplasmosis
E) valley fever
A) Pneumocystis pneumonia
B) blastomycosis
C) coccidioidomycosis
D) histoplasmosis
E) valley fever

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following statements is TRUE regarding infection with Mycoplasma pneumoniae?
A) It is extremely difficult to treat.
B) The causative agent attaches to ciliated cells in the respiratory tract.
C) The causative agent is a fast-growing Gram-positive bacillus.
D) It causes disease which is usually severe enough to require hospitalization.
E) It is diagnosed by the appearance of typical "fried-egg" colonies on agar.
A) It is extremely difficult to treat.
B) The causative agent attaches to ciliated cells in the respiratory tract.
C) The causative agent is a fast-growing Gram-positive bacillus.
D) It causes disease which is usually severe enough to require hospitalization.
E) It is diagnosed by the appearance of typical "fried-egg" colonies on agar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A woman who breeds parrots develops a fever and cough, and begins to have difficulty breathing. Small Gram-negative bacteria are detected inside cells of a sputum sample. Which of the following diseases is she likely to have contracted?
A) histoplasmosis
B) influenza
C) primary atypical pneumonia
D) ornithosis
E) inhalation anthrax
A) histoplasmosis
B) influenza
C) primary atypical pneumonia
D) ornithosis
E) inhalation anthrax

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Dust storms in arid regions of the Southwestern U.S. may lead to outbreaks of
A) blastomycosis.
B) histoplasmosis.
C) Pneumocystis pneumonia.
D) Hantavirus pulmonary syndrome.
E) coccidioidomycosis.
A) blastomycosis.
B) histoplasmosis.
C) Pneumocystis pneumonia.
D) Hantavirus pulmonary syndrome.
E) coccidioidomycosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A nursing student develops a positive reaction to the tuberculin skin test. A history reveals possible exposure to patients with tuberculosis. A sputum sample is acid-fast negative. When asked for vaccination records, the student reports that childhood vaccination records were lost when the family emigrated from a Southeast Asian country. What is the best explanation for the test results?
A) The student has been infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
B) The student has been exposed to Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
C) The student is not infected.
D) The student has been exposed to Mycobacterium tuberculosis or was vaccinated with BCG vaccine.
E) No conclusion is possible with the information provided.
A) The student has been infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
B) The student has been exposed to Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
C) The student is not infected.
D) The student has been exposed to Mycobacterium tuberculosis or was vaccinated with BCG vaccine.
E) No conclusion is possible with the information provided.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A new vaccine for the upcoming flu season is developed from an influenza isolate designated A/Shanghai/2/2013(H7N9). This nomenclature means the isolate is
A) a type A with antigens HA 7 and NA 9 isolated in Shanghai in February 2013.
B) a type A with 7 HA antigens and 9 NA antigens isolated in Shanghai in February 2013.
C) the second type A strain with HA 7 and NA 9 antigens isolated in Shanghai in 2013.
D) a type B strain with antigens HA 7 and NA 9, first isolated in February 2013.
E) a hybrid of 2 type As combining 7 HA and 9 NA antigens, created in February 2013.
A) a type A with antigens HA 7 and NA 9 isolated in Shanghai in February 2013.
B) a type A with 7 HA antigens and 9 NA antigens isolated in Shanghai in February 2013.
C) the second type A strain with HA 7 and NA 9 antigens isolated in Shanghai in 2013.
D) a type B strain with antigens HA 7 and NA 9, first isolated in February 2013.
E) a hybrid of 2 type As combining 7 HA and 9 NA antigens, created in February 2013.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Legionella pneumophila is an opportunistic pathogen that
A) is part of the microbiome of the lower respiratory system.
B) is part of the microbiota of the nasal cavity which occasionally invades the lungs.
C) survives in the environment as an intracellular parasite of a protozoan.
D) is capable of forming endospores.
E) is a disease of birds transmissible to humans.
A) is part of the microbiome of the lower respiratory system.
B) is part of the microbiota of the nasal cavity which occasionally invades the lungs.
C) survives in the environment as an intracellular parasite of a protozoan.
D) is capable of forming endospores.
E) is a disease of birds transmissible to humans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The disease known as "Croup" is often a result of infection with which of the following?
A) hantavirus
B) influenzavirus
C) Bordetella pertussis
D) Mycoplasma pneumoniae
E) respiratory syncytial virus
A) hantavirus
B) influenzavirus
C) Bordetella pertussis
D) Mycoplasma pneumoniae
E) respiratory syncytial virus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Limiting exposure to rodents and their waste is an important means of preventing
A) coccidioidomycosis.
B) Hantavirus pulmonary syndrome.
C) histoplasmosis.
D) bronchiolitis.
E) inhalational anthrax.
A) coccidioidomycosis.
B) Hantavirus pulmonary syndrome.
C) histoplasmosis.
D) bronchiolitis.
E) inhalational anthrax.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Pleurisy is the accumulation of pus in the lungs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Hantavirus pulmonary syndrome can be transmitted from person-to-person and from rodents to humans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The "common cold" is so common because there of the large number of viruses that cause it.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Recent outbreaks of multidrug-resistant HAP are primarily caused by members of the genus (Bordetella/ Klebsiella/Mycobacteria), Gram-negative opportunists.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Some of the signs of scarlet fever (scarlatina) are due to the production of (pertussis/pneumolysin/pyrogenic) toxin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Klebsiella pneumoniae is a leading cause of HAP infections.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Otitis media is more common in adults than children because of differences in the anatomy of the head.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A key diagnostic sign of diphtheria is the presence of the (pseudomembrane/pharyngitis/rash/tubercle).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
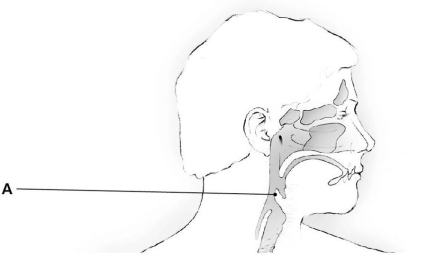
The structure indicated by the letter "A" is the (pharynx/larynx/epiglottis).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The smallest free-living microbes are (mycobacteria/mycoplasmas/Chlamydophila).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Exposure to soil with decaying plant material may result in pus-filled lesions characteristic of (coccidioidomycosis/blastomycosis/histoplasmosis).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Elongation factor, a protein required for eukaryotic (transcription/translation/expression), is the cellular target of the toxin produced by Corynebacterium diphtheriae.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Pneumocystis jiroveci infects only immunocompromised patients.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Otitis media is a bacterial infection of the (ear/pharynx/sinuses).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Macrophages effectively phagocytize and kill Mycobacterium tuberculosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Haemophilus influenzae is a common cause of sinus infections.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Staphylococcus aureus is part of the upper respiratory microbiome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
A type of pneumonia in which the alveoli and bronchioles become filled with pus is (emphysema/empyema/pleurisy).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The attachment protein for almost all rhinoviruses is (BCG/ICAM-1/IgA). (Be sure your answer is in uppercase letters.)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Cold viruses are prevented from infecting most areas of the body because these areas are either too warm or too acidic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
When Mycobacterium tuberculosis spreads to sites such as the bone marrow and spleen it results in (disseminated/secondary/reactivated) tuberculosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Describe the pathogenesis of tuberculosis, paying special attention to the characteristics of Mycobacterium tuberculosis that make it so pathogenic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis designated as (BCG/MDR/XDR) strains are resistant in vitro to three or more antitubercular drugs in addition to isoniazid and rifampin. (Be sure to use uppercase letters in your answer.)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
A major change in the surface glycoproteins of influenza A, which occurs every 10 years on average, is called (antigenic/genetic/protein) shift.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Why is immunity to the common cold so difficult to develop, either naturally or through vaccines?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The mycoplasmas have been successively classified as viruses, Gram-negative bacteria, and Gram-positive bacteria largely due to the lack of cell (membranes/walls/RNA) in their structure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Explain the necessity of producing a new vaccine for each year's flu season.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Compare and contrast pneumococcal and mycoplasmal pneumonia.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Inflammation of the trachea and bronchi, commonly called (croup/pertussis/pneumonia), is frequently caused by paramyxoviruses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Numerous bacteria can cause pneumoniae in the elderly or immunocompromised. The most common ones were covered in the section "Bacterial Diseases of the Lower Respiratory System." Devise a set of laboratory tests that could be used to distinguish between these bacteria in a clinical laboratory. Have as your goal the minimum number of tests necessary. (Hints: Try to make a dichotomous key to start. You may also need to recall material from previous chapters.)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



