Deck 3: Demand
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/116
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 3: Demand
1
Which of the following best describes the demand schedule?
A) the quantity of a good that is demanded at a specific price
B) the amount that is being demanded at every possible price
C) the time at which something is purchased
D) the decrease in willingness to purchase a good as quantity increases
A) the quantity of a good that is demanded at a specific price
B) the amount that is being demanded at every possible price
C) the time at which something is purchased
D) the decrease in willingness to purchase a good as quantity increases
B
2
A table that indicates the quantity of a good that would be demanded in a given period at various prices is known as a:
A) demand schedule.
B) demand graph.
C) utility table.
D) marginal utility table.
A) demand schedule.
B) demand graph.
C) utility table.
D) marginal utility table.
A
3
Use Table: Demand Schedules for Three Cookie Buyers. If these three buyers are the only cookie consumers in the market, how many cookies will the market demand at a price of $1?
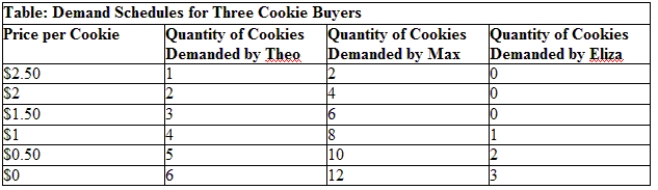
A) four
B) 13
C) eight
D) one

A) four
B) 13
C) eight
D) one
B
4
Use Table: Demand Schedules for Three Cookie Buyers. If these are the only cookie consumers in the market, how will total cookie consumption change if the price falls from $1 to $0.50?
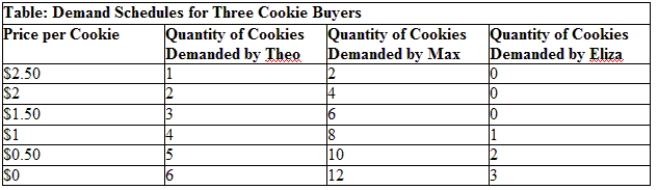
A) The quantity of cookies demanded will increase from four to five.
B) The quantity of cookies demanded will increase from 13 to 17.
C) The quantity of cookies demanded will decrease from 10 to eight.
D) The quantity of cookies demanded will increase from 12 to 15.

A) The quantity of cookies demanded will increase from four to five.
B) The quantity of cookies demanded will increase from 13 to 17.
C) The quantity of cookies demanded will decrease from 10 to eight.
D) The quantity of cookies demanded will increase from 12 to 15.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Use Table: Demand Schedule for Pairs of Leather Boots. What is the most that Brian would be willing to pay for his first pair of leather boots?
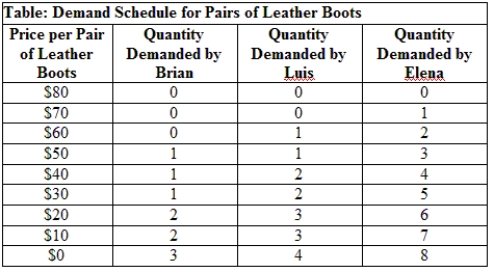
A) $20
B) $30
C) $50
D) $80

A) $20
B) $30
C) $50
D) $80

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Use Table: Demand Schedule for Pairs of Leather Boots. What is the highest price that can be charged to make all three potential buyers willing to buy boots?
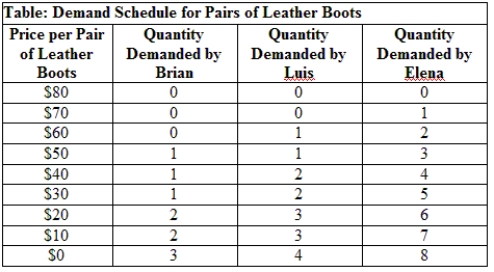
A) $70
B) $60
C) $50
D) $80

A) $70
B) $60
C) $50
D) $80

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Use Table: Demand Schedules for Three Cookie Buyers. If these are the only cookie consumers in the market, how many cookies will the market demand at a price of $2?
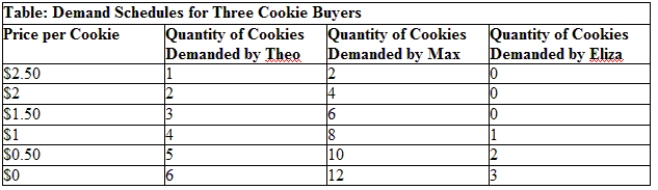
A) six
B) 13
C) two
D) four

A) six
B) 13
C) two
D) four

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Use Table: Individual Demand Schedules for Pairs of Socks. What is the market demand if the price of a pair of socks is $7?
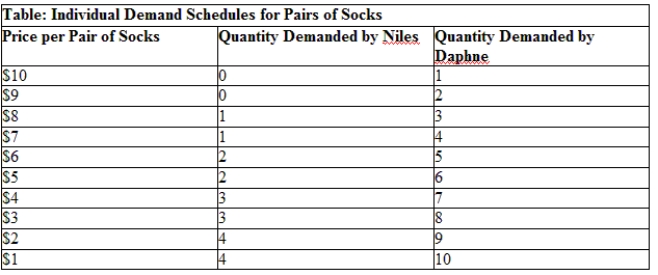
A) one
B) four
C) seven
D) five

A) one
B) four
C) seven
D) five

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Use Table: Individual Demand Schedules for Pairs of Socks. What is the increase in the market demand if the price of a pair of socks falls from $7 to $6?
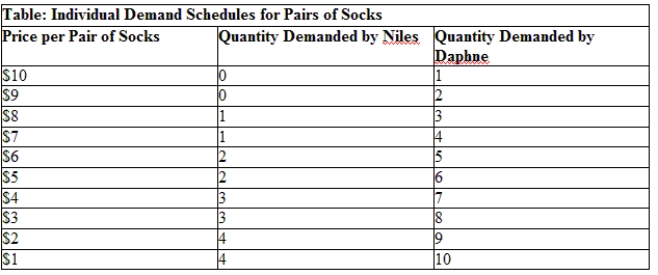
A) five
B) seven
C) two
D) one

A) five
B) seven
C) two
D) one

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Use Table: Individual Demand Schedules for Pairs of Socks. What is the increase in the market demand if the price of a pair of socks falls from $4 to $3?
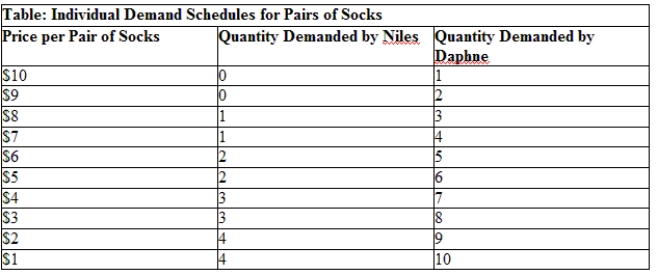
A) 10
B) 11
C) two
D) one

A) 10
B) 11
C) two
D) one

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Quintin enjoys chili dogs. He is willing to pay $5 for his first chili dog, $4 for his second, $2 for his third, and zero for his fourth chili dog. Quintin's willingness to pay decreases with more chili dogs due to:
A) increasing opportunity cost.
B) increasing returns to scale.
C) diminishing marginal product of labor.
D) diminishing marginal utility.
A) increasing opportunity cost.
B) increasing returns to scale.
C) diminishing marginal product of labor.
D) diminishing marginal utility.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following concepts best describes why a consumer's willingness to pay for a good decreases as the quantity consumed increases?
A) diminishing marginal utility
B) increasing additional cost
C) constant marginal benefit
D) decreasing additional cost
A) diminishing marginal utility
B) increasing additional cost
C) constant marginal benefit
D) decreasing additional cost

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The price that a consumer is willing to pay for each unit of a good is based on the:
A) value of marginal utility for that quantity.
B) utility of that quantity.
C) average utility of that quantity.
D) total satisfaction that a person feels from consuming that quantity.
A) value of marginal utility for that quantity.
B) utility of that quantity.
C) average utility of that quantity.
D) total satisfaction that a person feels from consuming that quantity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
If a person wants to find the marginal utility that is gained from consuming four tacos instead of three tacos, the correct way to calculate it would be to measure the:
A) average of the utility from consuming three tacos and four tacos.
B) difference between the utility from consuming four tacos and the utility from consuming three tacos.
C) total utility from consuming three tacos.
D) total utility from consuming four tacos.
A) average of the utility from consuming three tacos and four tacos.
B) difference between the utility from consuming four tacos and the utility from consuming three tacos.
C) total utility from consuming three tacos.
D) total utility from consuming four tacos.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
_____ is the satisfaction or happiness that individuals feel from consuming goods and services.
A) Utility
B) Marginal utility
C) Demand curve
D) Demand schedule
A) Utility
B) Marginal utility
C) Demand curve
D) Demand schedule

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The satisfaction or happiness received from consuming one more unit of a good is the:
A) demand schedule.
B) marginal utility.
C) quantity demanded.
D) maximum willingness to pay.
A) demand schedule.
B) marginal utility.
C) quantity demanded.
D) maximum willingness to pay.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The first cookie that you eat is delicious, and a second cookie is also delicious but not as good as the first cookie. This statement best describes the idea of:
A) diminishing marginal utility.
B) increasing marginal utility.
C) utility.
D) constant marginal utility.
A) diminishing marginal utility.
B) increasing marginal utility.
C) utility.
D) constant marginal utility.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
What does the word "marginal" mean in the phrase "diminishing marginal utility"?
A) one more
B) average
C) all
D) constant
A) one more
B) average
C) all
D) constant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Use Table: Demand Schedule for Pairs of Leather Boots. What is the dollar value of Elena's marginal utility of a third pair of boots?
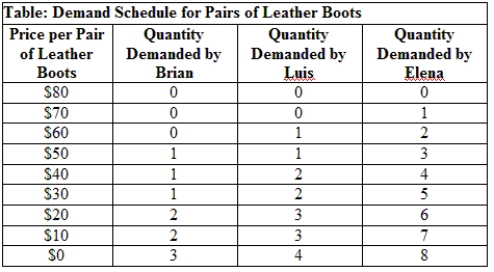
A) zero
B) $80
C) $70
D) $50

A) zero
B) $80
C) $70
D) $50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Use Table: Individual Demand Schedules for Pairs of Socks. What is the value of Daphne's marginal utility from the fourth pair of socks?
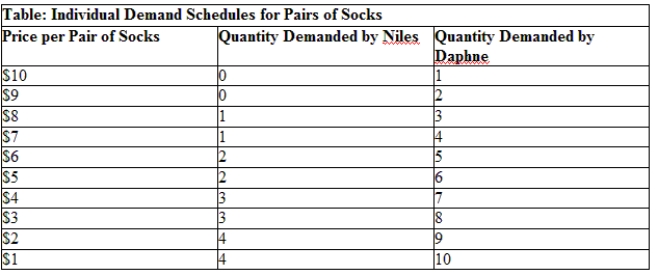
A) $7
B) $4
C) $34
D) $8.50

A) $7
B) $4
C) $34
D) $8.50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Use Table: Individual Demand Schedules for Pairs of Socks. What is the value of Niles's marginal utility from the third pair of socks?
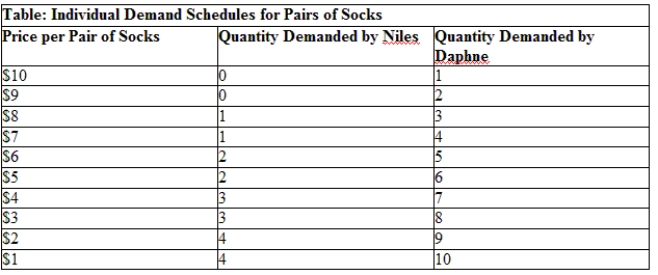
A) $7
B) $4
C) $11
D) $1

A) $7
B) $4
C) $11
D) $1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
What does the demand curve illustrate?
A) an inverse relationship between consumer income and the quantity of a good demanded
B) a direct relationship between the price of a good and the price of a substitute good
C) an inverse relationship between the price of a good and the quantity demanded
D) a direct relationship between the price of a good and the quantity supplied
A) an inverse relationship between consumer income and the quantity of a good demanded
B) a direct relationship between the price of a good and the price of a substitute good
C) an inverse relationship between the price of a good and the quantity demanded
D) a direct relationship between the price of a good and the quantity supplied

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following is a curve that illustrates the relationship between the price of a good and the quantity that people are willing to buy at each price?
A) the supply curve
B) the demand curve
C) diminishing marginal benefit
D) utility
A) the supply curve
B) the demand curve
C) diminishing marginal benefit
D) utility

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
What is measured on the vertical axis of a demand graph?
A) price
B) quantity
C) utility
D) satisfaction
A) price
B) quantity
C) utility
D) satisfaction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What is measured on the horizontal axis of a demand graph?
A) price
B) quantity
C) utility
D) satisfaction
A) price
B) quantity
C) utility
D) satisfaction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
When other influences remain unchanged, consumers will demand more of a good or service at lower prices than at higher prices. This statement reflects:
A) increasing marginal utility.
B) utility.
C) demand shifters.
D) the law of demand.
A) increasing marginal utility.
B) utility.
C) demand shifters.
D) the law of demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The downward slope of the demand curve results from:
A) increasing opportunity cost.
B) diminishing marginal utility.
C) increasing marginal product of labor.
D) increasing marginal utility.
A) increasing opportunity cost.
B) diminishing marginal utility.
C) increasing marginal product of labor.
D) increasing marginal utility.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A graph of the demand for cookies would be smoothest for which of the following groups?
A) nations
B) cities
C) households
D) individuals
A) nations
B) cities
C) households
D) individuals

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Holding all other factors constant, when the price of running shoes falls, the:
A) demand curve for running shoes will shift to the right.
B) demand curve for running shoes will shift to the left.
C) quantity of running shoes demanded will increase.
D) quantity of running shoes demanded will decrease.
A) demand curve for running shoes will shift to the right.
B) demand curve for running shoes will shift to the left.
C) quantity of running shoes demanded will increase.
D) quantity of running shoes demanded will decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Holding all other factors constant, when the price of running shoes rises, the:
A) demand curve for running shoes will shift to the right.
B) demand curve for running shoes will shift to the left.
C) quantity of running shoes demanded will increase.
D) quantity of running shoes demanded will decrease.
A) demand curve for running shoes will shift to the right.
B) demand curve for running shoes will shift to the left.
C) quantity of running shoes demanded will increase.
D) quantity of running shoes demanded will decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
When the price of ice cream cones is $2 per cone, Valentina buys three cones in a month. Which of the following describes an increase in Valentina's monthly demand for ice cream cones?
A) When the price of ice cream cones is $1, she will buy four cones per month.
B) When the price of ice cream cones is $2, she will buy two cones per month.
C) When the price of ice cream cones is $3, she will buy two cones per month.
D) When the price of ice cream cones is $2, she will buy four cones per month.
A) When the price of ice cream cones is $1, she will buy four cones per month.
B) When the price of ice cream cones is $2, she will buy two cones per month.
C) When the price of ice cream cones is $3, she will buy two cones per month.
D) When the price of ice cream cones is $2, she will buy four cones per month.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
When the price of ice cream cones is $2 per cone, Valentina buys three cones in a month. Which of the following describes a decrease in Valentina's monthly demand for ice cream cones?
A) When the price of ice cream cones is $1, she will buy four cones per month.
B) When the price of ice cream cones is $2, she will buy two cones per month.
C) When the price of ice cream cones is $3, she will buy two cones per month.
D) When the price of ice cream cones is $2, she will buy four cones per month.
A) When the price of ice cream cones is $1, she will buy four cones per month.
B) When the price of ice cream cones is $2, she will buy two cones per month.
C) When the price of ice cream cones is $3, she will buy two cones per month.
D) When the price of ice cream cones is $2, she will buy four cones per month.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
When the price of ice cream cones is $2 per cone, Celine buys three cones in a month. Which of the following describes a downward movement along Celine's monthly demand for ice cream cones?
A) When the price of ice cream cones is $1, she will buy four cones per month.
B) When the price of ice cream cones is $2, she will buy two cones per month.
C) When the price of ice cream cones is $3, she will buy two cones per month.
D) When the price of ice cream cones is $2, she will buy four cones per month.
A) When the price of ice cream cones is $1, she will buy four cones per month.
B) When the price of ice cream cones is $2, she will buy two cones per month.
C) When the price of ice cream cones is $3, she will buy two cones per month.
D) When the price of ice cream cones is $2, she will buy four cones per month.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
When the price of ice cream cones is $2 per cone, Celine buys three cones in a month. Which of the following describes an upward movement along Celine's monthly demand for ice cream cones?
A) When the price of ice cream cones is $1, she will buy four cones per month.
B) When the price of ice cream cones is $2, she will buy two cones per month.
C) When the price of ice cream cones is $3, she will buy two cones per month.
D) When the price of ice cream cones is $2, she will buy four cones per month.
A) When the price of ice cream cones is $1, she will buy four cones per month.
B) When the price of ice cream cones is $2, she will buy two cones per month.
C) When the price of ice cream cones is $3, she will buy two cones per month.
D) When the price of ice cream cones is $2, she will buy four cones per month.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The smoothest demand curve for good X is produced when there are _____ demanders and when good X can be purchased:
A) many; in small fractions of a full unit.
B) few; only in full units.
C) many; only in full units.
D) few; in small fractions of a full unit.
A) many; in small fractions of a full unit.
B) few; only in full units.
C) many; only in full units.
D) few; in small fractions of a full unit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A change in demand is:
A) a shift of the entire demand curve.
B) a movement to the left along the demand curve.
C) a movement to the right along the demand curve.
D) caused by a change in the price of a good.
A) a shift of the entire demand curve.
B) a movement to the left along the demand curve.
C) a movement to the right along the demand curve.
D) caused by a change in the price of a good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
An increase in demand will be caused by:
A) an increase in the price of a good.
B) a decrease in the price of a good.
C) a decrease in utility.
D) a change in something other than price.
A) an increase in the price of a good.
B) a decrease in the price of a good.
C) a decrease in utility.
D) a change in something other than price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A movement to the right along a demand curve is caused by:
A) an increase in the price of a good.
B) a decrease in the price of a good.
C) a decrease in utility.
D) a change in something other than price.
A) an increase in the price of a good.
B) a decrease in the price of a good.
C) a decrease in utility.
D) a change in something other than price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
If something changes that makes people more willing to buy a good at every possible price, this represents:
A) an increase in quantity demanded.
B) a decrease in quantity demanded.
C) an increase in demand.
D) a decrease in demand.
A) an increase in quantity demanded.
B) a decrease in quantity demanded.
C) an increase in demand.
D) a decrease in demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
If something changes that makes people less willing to buy a good at every possible price, this represents:
A) an increase in quantity demanded.
B) a decrease in quantity demanded.
C) an increase in demand.
D) a decrease in demand.
A) an increase in quantity demanded.
B) a decrease in quantity demanded.
C) an increase in demand.
D) a decrease in demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Uchenna expects a hurricane to hit his region next week and wants to buy more gasoline today. All else equal, how would this be reflected in a graph of his demand for gasoline?
A) a movement to the left along a demand curve
B) a movement to the right along a demand curve
C) an increase in demand
D) a decrease in demand
A) a movement to the left along a demand curve
B) a movement to the right along a demand curve
C) an increase in demand
D) a decrease in demand

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Pam expects that the price of swimming suits will increase soon. All else equal, how would this be reflected in a graph of her demand for swimming suits?
A) a movement to the left along a demand curve
B) a movement to the right along a demand curve
C) an increase in demand
D) a decrease in demand
A) a movement to the left along a demand curve
B) a movement to the right along a demand curve
C) an increase in demand
D) a decrease in demand

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
If tacos are a normal good and all else is equal, when average consumer income rises, the demand curve for tacos will:
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) remain unchanged.
D) see a movement downward along the curve.
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) remain unchanged.
D) see a movement downward along the curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
If gasoline is a normal good and all else is qual, when average consumer income falls, the demand curve for gasoline will:
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) remain unchanged.
D) see a movement downward along the curve.
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) remain unchanged.
D) see a movement downward along the curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
If gasoline is a normal good and all else is equal, when average consumer income falls, the demand curve for gasoline will:
A) shift to the right.
B) shift to the left.
C) see a movement upward to the left along the curve.
D) see a movement downward to the right along the curve.
A) shift to the right.
B) shift to the left.
C) see a movement upward to the left along the curve.
D) see a movement downward to the right along the curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
All else equal, the demand for _____ good will decrease when income increases.
A) an inferior
B) a normal
C) a complementary
D) a substitute
A) an inferior
B) a normal
C) a complementary
D) a substitute

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
All else equal, the demand for _____ good will increase when income increases.
A) an inferior
B) a normal
C) a complementary
D) a substitute
A) an inferior
B) a normal
C) a complementary
D) a substitute

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
All else equal, the demand for _____ good will decrease when income increases.
A) an inferior
B) a normal
C) a complementary
D) a substitute
A) an inferior
B) a normal
C) a complementary
D) a substitute

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
All else equal, when the demand for a good decreases in response to a decrease in the price of another good, these goods must be _____ goods.
A) inferior
B) normal
C) complementary
D) substitute
A) inferior
B) normal
C) complementary
D) substitute

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
All else equal, when the demand for a good increases in response to a decrease in the price of another good, these goods must be _____ goods.
A) inferior
B) normal
C) complementary
D) substitute
A) inferior
B) normal
C) complementary
D) substitute

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
If second-hand mattresses are an inferior good, when average consumer income falls, the demand curve for second-hand mattresses will _____, all else equal.
A) remain unchanged
B) decrease
C) increase
D) see a movement upward along the curve
A) remain unchanged
B) decrease
C) increase
D) see a movement upward along the curve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
If bologna is an inferior good, when average consumer income rises, the demand curve for bologna will _____, all else equal.
A) see a movement upward along the curve
B) remain unchanged
C) decrease
D) increase
A) see a movement upward along the curve
B) remain unchanged
C) decrease
D) increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Suppose that persuasive advertising has caused people to increase their demand for orange juice. This increase in demand can best be attributed to a change in _____, all else equal.
A) income
B) the price of a substitute good
C) the price of the good
D) tastes
A) income
B) the price of a substitute good
C) the price of the good
D) tastes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Extensive medical research has concluded that using tobacco is harmful to your health. As a result, fewer Americans use tobacco today than they did 40 years ago. Economists would say that this change in _____ decreased the demand for tobacco, all else equal.
A) tastes
B) incomes
C) the price of a complementary product
D) the price of a substitute product
A) tastes
B) incomes
C) the price of a complementary product
D) the price of a substitute product

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
All else held constant, when consumers have a stronger taste for a product, the demand curve:
A) shifts to the left.
B) shifts to the right.
C) decreases.
D) remains constant.
A) shifts to the left.
B) shifts to the right.
C) decreases.
D) remains constant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
All else held constant, when consumers exhibit a weakened desire to purchase a product, the demand curve:
A) shifts to the left.
B) shifts to the right.
C) increases.
D) remains constant.
A) shifts to the left.
B) shifts to the right.
C) increases.
D) remains constant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A storm has disrupted gasoline production, and consumers expect that the price of gasoline will increase in the next few days. Today the demand curve for gasoline will:
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) remain unchanged.
D) see a movement downward along the curve.
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) remain unchanged.
D) see a movement downward along the curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Joanne has come to expect that horse feed prices increase every May. All else equal, how will this affect how Joanne buys horse feed in April?
A) Her demand in April increases.
B) Her quantity demanded in April decreases.
C) Her demand in April isn't affected.
D) Her demand in April decreases.
A) Her demand in April increases.
B) Her quantity demanded in April decreases.
C) Her demand in April isn't affected.
D) Her demand in April decreases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Jia expects that her income is going to go down in the future. All else equal, how will this impact her demand for beets, an inferior good, today?
A) Her demand today decreases.
B) Her quantity demanded today increases.
C) Her demand today isn't affected.
D) Her demand today increases.
A) Her demand today decreases.
B) Her quantity demanded today increases.
C) Her demand today isn't affected.
D) Her demand today increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Jaeyoung believes that the price of coffee will increase soon. All else equal, how will this affect his demand for coffee today?
A) His demand for coffee today decreases.
B) His demand for coffee today isn't affected.
C) His quantity demanded of coffee increases.
D) His demand for coffee today increases.
A) His demand for coffee today decreases.
B) His demand for coffee today isn't affected.
C) His quantity demanded of coffee increases.
D) His demand for coffee today increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Manuella learns that she is going to lose her job in six months. In response, her demand for lattes decreases. What shifter of demand does this statement describe?
A) number of buyers
B) tastes
C) expectations
D) price of related goods
A) number of buyers
B) tastes
C) expectations
D) price of related goods

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
When the price of chips increases, Hector's demand for soda decreases. What kinds of goods does Hector consider chips and soda?
A) complements
B) substitutes
C) inferior goods
D) normal goods
A) complements
B) substitutes
C) inferior goods
D) normal goods

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Netta considers apples and oranges complements. All else equal, what will happen to Netta's demand for oranges when the price of apples increases?
A) The demand for oranges will shift to the right.
B) The quantity demanded of oranges will increase.
C) The demand for oranges will shift to the left.
D) The demand for oranges will not be affected.
A) The demand for oranges will shift to the right.
B) The quantity demanded of oranges will increase.
C) The demand for oranges will shift to the left.
D) The demand for oranges will not be affected.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
In response to an increase in income, Stella buys fewer jars of pickles. Based on this statement, we can infer that Stella:
A) considers pickles complements to other goods.
B) has an irrational demand for pickles.
C) considers pickles inferior goods.
D) considers pickles normal goods.
A) considers pickles complements to other goods.
B) has an irrational demand for pickles.
C) considers pickles inferior goods.
D) considers pickles normal goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Consumers are worried that the economy will soon slip into a recession and incomes will fall. Assuming that gasoline is a normal good, today the demand curve for gasoline will _____, all else equal.
A) increase
B) decrease
C) remain unchanged
D) see a movement downward along the curve
A) increase
B) decrease
C) remain unchanged
D) see a movement downward along the curve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Suppose that bicycles and bicycle helmets are complementary goods. All else equal, if the price of bicycles increases, there will be:
A) a downward movement along the bicycle demand curve.
B) a decrease in the demand curve for helmets.
C) a decrease in the demand curve for bicycles.
D) an upward movement along the helmet demand curve.
A) a downward movement along the bicycle demand curve.
B) a decrease in the demand curve for helmets.
C) a decrease in the demand curve for bicycles.
D) an upward movement along the helmet demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Suppose that bicycles and skateboards are substitute goods. All else equal, if the price of bicycles decreases, there will be:
A) an upward movement upward along the bicycle demand curve.
B) an increase in the demand curve for bicycles.
C) a decrease in the demand curve for skateboards.
D) a downward movement along the skateboard demand curve.
A) an upward movement upward along the bicycle demand curve.
B) an increase in the demand curve for bicycles.
C) a decrease in the demand curve for skateboards.
D) a downward movement along the skateboard demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Consumers consider that good A and good B are substitutable in consumption. When the price of good A decreases, there is an expectation that there is _____ in quantity of good A demanded and _____ in the demand for good
A) an increase; an increase
B) an increase; a decrease
C) a decrease; an increase
D) a decrease; a decrease
A) an increase; an increase
B) an increase; a decrease
C) a decrease; an increase
D) a decrease; a decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Consumers consider that good A and good B are substitutable in consumption. When the price of good A increases, there is an expectation that there is _____ in quantity of good A demanded and _____ in the demand for good
A) an increase; an increase
B) an increase; a decrease
C) a decrease; an increase
D) a decrease; a decrease
A) an increase; an increase
B) an increase; a decrease
C) a decrease; an increase
D) a decrease; a decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Consumers consider that good A and good B are complements in consumption. When the price of good A decreases, there is an expectation that there is _____ in the quantity of good A demanded and ______ in the demand for good
A) an increase; an increase
B) an increase; a decrease
C) a decrease; an increase
D) a decrease; a decrease
A) an increase; an increase
B) an increase; a decrease
C) a decrease; an increase
D) a decrease; a decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Consumers consider that good A and good B are complements in consumption. When the price of good A increases, there is an expectation that there is _____ in quantity of good A demanded and _____ in the demand for good
A) an increase; an increase
B) an increase; a decrease
C) a decrease; an increase
D) a decrease; a decrease
A) an increase; an increase
B) an increase; a decrease
C) a decrease; an increase
D) a decrease; a decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Suppose that the demand for product Z increases when the price of product W falls. Economists would say that products Z and W are _____ goods.
A) complementary
B) unrelated
C) normal
D) substitute
A) complementary
B) unrelated
C) normal
D) substitute

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
If lamps and light bulbs are complements, then when the price of lamps increases, the quantity demanded of lamps _____, and the demand for light bulbs _____.
A) decreases; increases
B) decreases; decreases
C) increases; increases
D) increases; decreases
A) decreases; increases
B) decreases; decreases
C) increases; increases
D) increases; decreases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
If eggs and waffles are complements, then when the price of eggs decreases, the quantity demanded of eggs _____, and the demand for waffles _____.
A) decreases; decreases
B) decreases; increases
C) increases; increases
D) increases; decreases
A) decreases; decreases
B) decreases; increases
C) increases; increases
D) increases; decreases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
If chips and pretzels are substitutes, then when the price of chips decreases, the quantity demanded of chips _____, and the demand for pretzels _____.
A) decreases; decreases
B) decreases; increases
C) increases; increases
D) increases; decreases
A) decreases; decreases
B) decreases; increases
C) increases; increases
D) increases; decreases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
If eggs and sausage are substitutes, then when the price of eggs increases, the quantity demanded of eggs _____, and the demand for sausage _____.
A) decreases; decreases
B) decreases; increases
C) increases; increases
D) increases; decreases
A) decreases; decreases
B) decreases; increases
C) increases; increases
D) increases; decreases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Suppose that the demand for product Z increases when the price of product W rises. Economists would say that products Z and W are _____ goods.
A) complementary
B) unrelated
C) normal
D) substitute
A) complementary
B) unrelated
C) normal
D) substitute

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Suppose that the demand for product Z decreases when the price of product W falls. Economists would say that products Z and W are _____ goods.
A) complementary
B) unrelated
C) normal
D) substitute
A) complementary
B) unrelated
C) normal
D) substitute

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Suppose that the demand for product Z decreases when the price of product W rises. Economists would say that products Z and W are _____ goods.
A) complementary
B) unrelated
C) normal
D) substitute
A) complementary
B) unrelated
C) normal
D) substitute

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
All else equal, when income increases, this is reflected in a graph of the demand for an inferior good as:
A) a movement to the left along a demand curve.
B) a movement to the right along a demand curve.
C) an increase in demand.
D) a decrease in demand.
A) a movement to the left along a demand curve.
B) a movement to the right along a demand curve.
C) an increase in demand.
D) a decrease in demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



