Deck 30: Inflation Expectations and Stabilization Policies
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/100
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 30: Inflation Expectations and Stabilization Policies
1
According to the simple Phillips curve, in the short run, if inflation rises, then:
A) the Federal Reserve will increase the money supply.
B) unemployment will drop.
C) unemployment will rise.
D) the economy will stop growing.
A) the Federal Reserve will increase the money supply.
B) unemployment will drop.
C) unemployment will rise.
D) the economy will stop growing.
B
2
The graph below shows the relationship between the rate of inflation and the rate of unemployment. Inflation tends to be higher when the unemployment rate is lower. Which model is it? 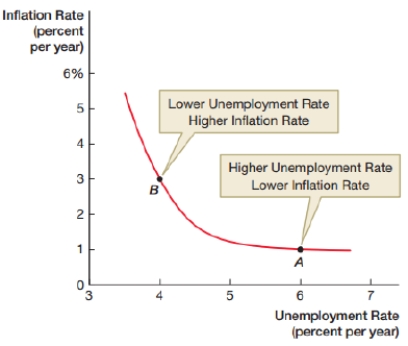
A) the unemployment rate model
B) the Keynesian model
C) the simplified Phillips model
D) the classical model

A) the unemployment rate model
B) the Keynesian model
C) the simplified Phillips model
D) the classical model
C
3
According to the simple Phillips curve, in the short run, if unemployment decreases, then:
A) inflation rises.
B) inflation drops.
C) interest rates rise.
D) interest rates drop.
A) inflation rises.
B) inflation drops.
C) interest rates rise.
D) interest rates drop.
A
4
The graphs below show the simplified Phillips curves in the United States, between 1960 and 2016. The data in Panel B for the period between 1970 and 2016 shows:
A) there is a tradeoff between inflation and unemployment.
B) inflation and unemployment are positively correlated.
C) inflation and unemployment are negatively correlated.
D) no apparent relationship between inflation and unemployment.
A) there is a tradeoff between inflation and unemployment.
B) inflation and unemployment are positively correlated.
C) inflation and unemployment are negatively correlated.
D) no apparent relationship between inflation and unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The slope of the short-run simple Phillips curve is:
A) vertical.
B) positive.
C) horizontal.
D) negative.
A) vertical.
B) positive.
C) horizontal.
D) negative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
According to the simple Phillips curve, when unemployment is _____, then inflation is:
A) high; high.
B) high; low.
C) low; low.
D) low; unpredictable.
A) high; high.
B) high; low.
C) low; low.
D) low; unpredictable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
During a recession, an economy typically would be operating in what portion of its simple Phillips curve?
A) upper portion with high inflation and low unemployment
B) upper portion with low inflation and high unemployment
C) lower portion with high inflation and low unemployment
D) lower portion with low inflation and high unemployment
A) upper portion with high inflation and low unemployment
B) upper portion with low inflation and high unemployment
C) lower portion with high inflation and low unemployment
D) lower portion with low inflation and high unemployment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
During a period of rapidly rising prices, an economy typically would be operating in what portion of its simple Phillips curve?
A) upper portion with high inflation and low unemployment
B) upper portion with low inflation and high unemployment
C) lower portion with high inflation and low unemployment
D) lower portion with low inflation and high unemployment
A) upper portion with high inflation and low unemployment
B) upper portion with low inflation and high unemployment
C) lower portion with high inflation and low unemployment
D) lower portion with low inflation and high unemployment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Wages are most likely to rise during an economic _____ and are most likely to fall during an economic:
A) recession; boom.
B) boom; recession.
C) trough; expansion.
D) expansion; boom.
A) recession; boom.
B) boom; recession.
C) trough; expansion.
D) expansion; boom.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A mistaken assumption about the simple Phillips curve is to assume that it:
A) represents a permanent trade-off between inflation and unemployment.
B) applies more to the short run than the long run.
C) shows a relationship between inflation and unemployment.
D) has a negative slope.
A) represents a permanent trade-off between inflation and unemployment.
B) applies more to the short run than the long run.
C) shows a relationship between inflation and unemployment.
D) has a negative slope.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Evidence over time indicates that the relationship depicted in the simple Phillips curve holds true only if policymakers:
A) aggressively pursue countercyclical solutions to inflation and unemployment problems.
B) do nothing to take advantage of the positive relationship on the graph.
C) do nothing to take advantage of the negative relationship on the graph.
D) realize that output cannot stabilize at the natural rate of unemployment.
A) aggressively pursue countercyclical solutions to inflation and unemployment problems.
B) do nothing to take advantage of the positive relationship on the graph.
C) do nothing to take advantage of the negative relationship on the graph.
D) realize that output cannot stabilize at the natural rate of unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The examination of inflation and unemployment data from the United States from 1960 through 2016 indicates that the simple Phillips curve:
A) applied over the entire time period.
B) was inconsistent with data over the entire time period.
C) was inconsistent with data early in the time period but did apply later in the time period.
D) was consistent with data early in the time period but did not apply later in the time period.
A) applied over the entire time period.
B) was inconsistent with data over the entire time period.
C) was inconsistent with data early in the time period but did apply later in the time period.
D) was consistent with data early in the time period but did not apply later in the time period.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The United States economy behaved according to the simple Phillips curve from _____ and did not follow that pattern from:
A) 1970 to 2016; 1960 to 1969.
B) 1930 to 1945; 1960 to 1969.
C) 1960 to 1969; 1970 to 2016.
D) 1970-2016; 1930 to 1945.
A) 1970 to 2016; 1960 to 1969.
B) 1930 to 1945; 1960 to 1969.
C) 1960 to 1969; 1970 to 2016.
D) 1970-2016; 1930 to 1945.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
What movement would occur on an economy's simple Phillips curve when the economy's aggregate demand curve shifts to the left? There would be a movement to a _____ point on the curve with:
A) lower; higher unemployment and lower inflation.
B) higher; higher unemployment and lower inflation.
C) lower; lower unemployment and higher inflation.
D) higher; lower unemployment and higher inflation.
A) lower; higher unemployment and lower inflation.
B) higher; higher unemployment and lower inflation.
C) lower; lower unemployment and higher inflation.
D) higher; lower unemployment and higher inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
What movement would occur on an economy's simple Phillips curve when the economy's aggregate demand curve shifts to the right? There would be a movement to a _____ point on the curve with:
A) lower; higher unemployment and lower inflation.
B) higher; higher unemployment and lower inflation.
C) lower; lower unemployment and higher inflation.
D) higher; lower unemployment and higher inflation.
A) lower; higher unemployment and lower inflation.
B) higher; higher unemployment and lower inflation.
C) lower; lower unemployment and higher inflation.
D) higher; lower unemployment and higher inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The simple Phillips curve is consistent with the changes in equilibrium in the aggregate supply and aggregate demand model that occur when the _____ curve shifts.
A) aggregate demand
B) long-run aggregate supply
C) short-run aggregate supply
D) product market demand
A) aggregate demand
B) long-run aggregate supply
C) short-run aggregate supply
D) product market demand

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
In the late 1960s, Milton Friedman and Edmund Phelps identified a major flaw in how economists were looking at the Phillips curve data. Economists were:
A) ignoring the role that is played by employment expectations.
B) giving too much weight to employment expectations.
C) ignoring the role that is played by inflation expectations.
D) giving too much weight to inflation expectations.
A) ignoring the role that is played by employment expectations.
B) giving too much weight to employment expectations.
C) ignoring the role that is played by inflation expectations.
D) giving too much weight to inflation expectations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The term "inflation expectations" refers to the:
A) amount of inflation that is expected by an appointed panel of research economists.
B) amount of inflation that is expected by businesses and consumers.
C) target level of inflation that is set by the Federal Reserve.
D) target level of inflation that is set by fiscal policymakers.
A) amount of inflation that is expected by an appointed panel of research economists.
B) amount of inflation that is expected by businesses and consumers.
C) target level of inflation that is set by the Federal Reserve.
D) target level of inflation that is set by fiscal policymakers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
. In the self-correction mechanism, due to an increase in aggregate demand, the economy moves from point a to point b. The short-run aggregate supply eventually shifts _____ and the economy shifts to the _____. 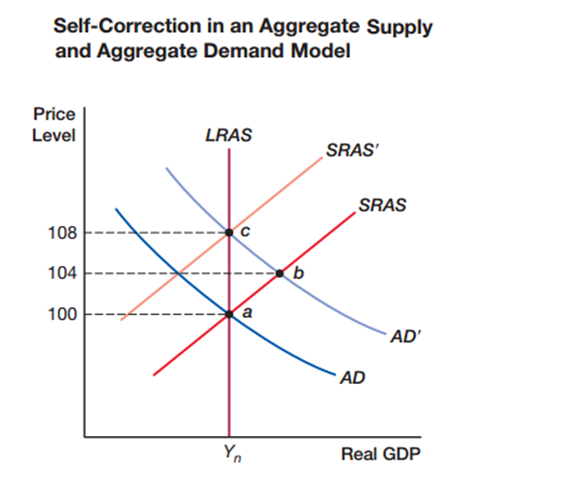
A) left; maximum rate at point c
B) left; natural rate at point c
C) right; natural rate at point c
D) right; maximum rate at point c

A) left; maximum rate at point c
B) left; natural rate at point c
C) right; natural rate at point c
D) right; maximum rate at point c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
In the self-correction and the long-run Phillips curve, at point b actual inflation (4%) is above expected inflation (0%). Then inflation expectations will start to rise, and the Phillips curve will shift upward, moving the economy to point c. According to the natural rate hypothesis, there is _____ between inflation and unemployment, and thus the long-run Phillips curve is _____. 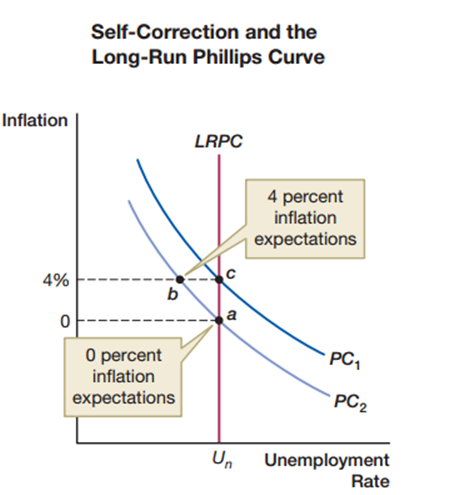
A) no permanent trade off; a vertical line
B) permanent trade off; a vertical line
C) no permanent trade off; undetermined
D) permanent trade off; undetermined

A) no permanent trade off; a vertical line
B) permanent trade off; a vertical line
C) no permanent trade off; undetermined
D) permanent trade off; undetermined

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
When businesses and workers start to expect higher inflation:
A) prices and wages tend to fall.
B) output tends to rise.
C) the economy moves into recession.
D) prices and wages tend to rise.
A) prices and wages tend to fall.
B) output tends to rise.
C) the economy moves into recession.
D) prices and wages tend to rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The natural rate theory is based on the hypothesis that:
A) unemployment will be maintained at the natural rate regardless of the actual inflation rate.
B) unemployment will be maintained at the natural rate regardless of the expected inflation rate.
C) when inflation expectations adjust, the unemployment rate will return to the natural rate.
D) when the unemployment rate adjusts, inflation will return to its natural rate.
A) unemployment will be maintained at the natural rate regardless of the actual inflation rate.
B) unemployment will be maintained at the natural rate regardless of the expected inflation rate.
C) when inflation expectations adjust, the unemployment rate will return to the natural rate.
D) when the unemployment rate adjusts, inflation will return to its natural rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
In the short run, higher than expected inflation puts _____ pressure on real wages and real rents, which leads businesses to _____ hiring.
A) downward; increase
B) upward; increase
C) downward; reduce
D) upward; reduce
A) downward; increase
B) upward; increase
C) downward; reduce
D) upward; reduce

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Rising wages and business expenses tend to cause _____ inflation expectations, which shifts the:
A) higher; aggregate demand curve to the right.
B) higher; short-run aggregate supply curve to the left.
C) lower; aggregate demand curve to the left.
D) lower; short-run aggregate supply curve to the right.
A) higher; aggregate demand curve to the right.
B) higher; short-run aggregate supply curve to the left.
C) lower; aggregate demand curve to the left.
D) lower; short-run aggregate supply curve to the right.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The short-run aggregate supply curve will shift to the left when:
A) Phillips curve expectations rise.
B) Phillips curve expectations fall.
C) inflation expectations rise.
D) inflation expectations fall.
A) Phillips curve expectations rise.
B) Phillips curve expectations fall.
C) inflation expectations rise.
D) inflation expectations fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following is NOT a typical cause for the Phillips curve to shift?
A) changing inflation expectations
B) an economy's self-correcting mechanism
C) a shifting short-run aggregate supply
D) a changing unemployment rate
A) changing inflation expectations
B) an economy's self-correcting mechanism
C) a shifting short-run aggregate supply
D) a changing unemployment rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The theory that when inflation expectations adjust to actual inflation, the rate of unemployment returns to the natural rate is known as the:
A) Phillips curve theory.
B) natural rate hypothesis.
C) rational expectations hypothesis.
D) internal-correcting theory.
A) Phillips curve theory.
B) natural rate hypothesis.
C) rational expectations hypothesis.
D) internal-correcting theory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
According to the natural rate hypothesis, there is:
A) a permanent trade-off between inflation and unemployment.
B) no permanent trade-off between inflation and unemployment.
C) a permanent trade-off between expectations and the Phillips curve.
D) no permanent trade-off between expectations and the Phillips curve.
A) a permanent trade-off between inflation and unemployment.
B) no permanent trade-off between inflation and unemployment.
C) a permanent trade-off between expectations and the Phillips curve.
D) no permanent trade-off between expectations and the Phillips curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
If the natural rate hypothesis is accepted, then the Phillips curve would:
A) have a positive slope.
B) have a negative slope.
C) be a horizontal line.
D) be a vertical line.
A) have a positive slope.
B) have a negative slope.
C) be a horizontal line.
D) be a vertical line.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following is NOT consistent with the natural rate hypothesis?
A) Actual inflation = Expected inflation
B) Actual inflation > Expected inflation
C) Actual inflation > Expected inflation
D) Actual inflation < Expected inflation
A) Actual inflation = Expected inflation
B) Actual inflation > Expected inflation
C) Actual inflation > Expected inflation
D) Actual inflation < Expected inflation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
What lowers unemployment?
A) inflation regardless of expectations
B) higher than expected inflation
C) lower than expected inflation
D) escalating inflation rates
A) inflation regardless of expectations
B) higher than expected inflation
C) lower than expected inflation
D) escalating inflation rates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A major flaw in the development of the simple Phillips curve is that it fails to account for the fact that:
A) the unemployment rate can change.
B) the price level can change.
C) expectations can change.
D) policies can change.
A) the unemployment rate can change.
B) the price level can change.
C) expectations can change.
D) policies can change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The negative relationship between inflation and unemployment occurs when:
A) unemployment expectations are stable.
B) inflation is rising.
C) inflation expectations are stable.
D) countercyclical policy is being used.
A) unemployment expectations are stable.
B) inflation is rising.
C) inflation expectations are stable.
D) countercyclical policy is being used.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
When inflation expectations are stable, the Phillips curve:
A) is a vertical line.
B) shows a negative relationship between inflation and unemployment.
C) is a horizontal line.
D) shows a positive relationship between inflation and unemployment.
A) is a vertical line.
B) shows a negative relationship between inflation and unemployment.
C) is a horizontal line.
D) shows a positive relationship between inflation and unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The simple Phillips curve relies on the assumption that the business cycle is caused by _____ shocks:
A) demand
B) short-run supply
C) long-run supply
D) inflation rate
A) demand
B) short-run supply
C) long-run supply
D) inflation rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A negative relationship between inflation and unemployment would NOT be shown by:
A) an increase in aggregate demand.
B) a movement downward on a simple Phillips curve.
C) a decrease in aggregate demand.
D) a decrease in short-run aggregate supply.
A) an increase in aggregate demand.
B) a movement downward on a simple Phillips curve.
C) a decrease in aggregate demand.
D) a decrease in short-run aggregate supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following situations would NOT be consistent with the relationship in the simple Phillips curve?
A) a decrease in aggregate demand
B) a decrease in short-run aggregate supply
C) a negative relationship between inflation and unemployment
D) steady inflation expectations
A) a decrease in aggregate demand
B) a decrease in short-run aggregate supply
C) a negative relationship between inflation and unemployment
D) steady inflation expectations

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The simple Phillips curve relationship requires a stable:
A) money supply.
B) unemployment rate.
C) inflation rate.
D) natural rate of unemployment.
A) money supply.
B) unemployment rate.
C) inflation rate.
D) natural rate of unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following is NOT a reason that the Great Recession of 2007 to 2009 seemed consistent with the simple Phillips curve?
A) A reduction in inflation stemmed from reduction in aggregate demand.
B) Inflation expectations were stable.
C) The rise in unemployment was predictable.
D) The natural rate of unemployment was fairly stable.
A) A reduction in inflation stemmed from reduction in aggregate demand.
B) Inflation expectations were stable.
C) The rise in unemployment was predictable.
D) The natural rate of unemployment was fairly stable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The simple Phillips curve model was _____ with what occurred during the Great Recession because:
A) consistent; the self-correcting mechanism was allowed to work.
B) consistent; the main flaws in the model did not apply to the situation.
C) inconsistent; the self-correcting mechanism was not allowed to work.
D) inconsistent; the main flaws in the model applied to the situation.
A) consistent; the self-correcting mechanism was allowed to work.
B) consistent; the main flaws in the model did not apply to the situation.
C) inconsistent; the self-correcting mechanism was not allowed to work.
D) inconsistent; the main flaws in the model applied to the situation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The simple Phillips curve model continues to perform well in many countries where three conditions are present. Which of the following is NOT one of the three conditions?
A) relatively few supply shocks
B) a stable natural rate of unemployment
C) relatively few demand shocks
D) stable inflation expectations
A) relatively few supply shocks
B) a stable natural rate of unemployment
C) relatively few demand shocks
D) stable inflation expectations

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Jane assumes that tomorrow's weather will be like today's weather. Jane's expectation of the weather is consistent with _____ expectations.
A) adaptive
B) rational
C) neutral
D) consistency
A) adaptive
B) rational
C) neutral
D) consistency

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Expecting the future to be like the recent past is an approach to forming expectations that economists call _____ expectations.
A) neutral
B) rational
C) adaptive
D) consistency
A) neutral
B) rational
C) adaptive
D) consistency

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Jonah earned a C in ECON 101, and so he expects to earn a C in ECON 102. Jonah's prediction is consistent with _____ expectations.
A) neutral
B) adaptive
C) consistency
D) rational
A) neutral
B) adaptive
C) consistency
D) rational

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Marcela earned a C in ECON 101. She predicts that she will earn a B in ECON 102 next semester because she will be taking fewer credit hours and she will have a new tutor. Marcela's prediction is consistent with _____ expectations.
A) neutral
B) adaptive
C) consistency
D) rational
A) neutral
B) adaptive
C) consistency
D) rational

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which of the following is NOT consistent with the rational expectations hypothesis?
A) Individuals use past information in forecasting future values.
B) Individuals use current information in forecasting future values.
C) Expectations incorporate an individual's understanding about how the economy operates.
D) Expectations are based on an assumption that the near future will simply repeat or continue the current situation.
A) Individuals use past information in forecasting future values.
B) Individuals use current information in forecasting future values.
C) Expectations incorporate an individual's understanding about how the economy operates.
D) Expectations are based on an assumption that the near future will simply repeat or continue the current situation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The view that people use all available information, including their past experiences, in forming their expectations and that these expectations impact their behavior is known as the _____ view.
A) adaptive expectations
B) learning curve
C) natural expectations
D) rational expectations
A) adaptive expectations
B) learning curve
C) natural expectations
D) rational expectations

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
If people form expectations in accordance with the rational expectations hypothesis and they correctly anticipate policy actions, then the policies will:
A) not impact output in either the short run or the long run.
B) impact output in both the short run and the long run.
C) impact output in the short run but have no effect in the long run.
D) impact output in the long run but have no effect in the short run.
A) not impact output in either the short run or the long run.
B) impact output in both the short run and the long run.
C) impact output in the short run but have no effect in the long run.
D) impact output in the long run but have no effect in the short run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which of the following statements is consistent with the adaptive expectations view?
A) Knowledge is power.
B) Surprises happen.
C) The past repeats itself in the future.
D) Whatever will be, will be.
A) Knowledge is power.
B) Surprises happen.
C) The past repeats itself in the future.
D) Whatever will be, will be.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Manu has received a 2% raise each year for the past 10 years. The company where he works has just experienced its most profitable year during that time, and Manu has had his most productive year yet and was the most productive worker in his section. Which of the following expectations of next year's salary would be consistent with Manu basing his expectations on rational expectations?
A) Manu expects a 4% raise.
B) Manu expects no raise.
C) Manu has no idea of what raise he expects.
D) Manu expects a 2% raise.
A) Manu expects a 4% raise.
B) Manu expects no raise.
C) Manu has no idea of what raise he expects.
D) Manu expects a 2% raise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Policymakers want to collect 10% more in sales tax revenue next year, and so they raise the sales tax rate by 10% from 5% to 5.5%. Which of the following assessments would be consistent with adaptive expectations? Next year sales tax revenue will:
A) increase by 10%.
B) increase by more than 10%.
C) change by some amount that is less than a 10% increase.
D) rise by a small amount and then escalate rapidly.
A) increase by 10%.
B) increase by more than 10%.
C) change by some amount that is less than a 10% increase.
D) rise by a small amount and then escalate rapidly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Policymakers want to collect 10% more in sales tax revenue next year, and so they raise the sales tax rate by 10% from 5% to 5.5%. Which of the following assessments would be consistent with rational expectations? Next year, sales tax revenue will:
A) increase by 10%.
B) increase by more than 10%.
C) change by some amount that is less than a 10% increase.
D) rise by a small amount and then escalate rapidly.
A) increase by 10%.
B) increase by more than 10%.
C) change by some amount that is less than a 10% increase.
D) rise by a small amount and then escalate rapidly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
In 1997, the British government suddenly announced that the central bank, the Bank of England, would become independent. Evidence shows that the public immediately began to expect lower inflation. This behavior in forming expectations is consistent with _____ expectations.
A) adaptive
B) rational
C) reality-based
D) information-based
A) adaptive
B) rational
C) reality-based
D) information-based

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
An important lesson from the Lucas critique that policymakers need to heed is that policy will have its desired impact when policymakers:
A) the Lucas critique.
B) why the Lucas critique is not correct.
C) adaptive expectations.
D) the simple Phillips curve.
A) the Lucas critique.
B) why the Lucas critique is not correct.
C) adaptive expectations.
D) the simple Phillips curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which of the following statements is consistent with the Lucas critique?
A) A penny saved is a penny earned.
B) Honesty is the best policy.
C) Correlation is not causation.
D) History repeats itself.
A) A penny saved is a penny earned.
B) Honesty is the best policy.
C) Correlation is not causation.
D) History repeats itself.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The view that past correlations may not apply in the future because policy changes may impact expectations and behavior is consistent with:
A) adaptive expectations.
B) evolutionary adjustment mechanisms.
C) the Lucas critique.
D) the relative adjustment critique.
A) adaptive expectations.
B) evolutionary adjustment mechanisms.
C) the Lucas critique.
D) the relative adjustment critique.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The Lucas critique noted that:
A) policies are neutral and have no impact.
B) the impact of policy is intensified if the policy is expected.
C) expectations have no impact on the effectiveness of policy.
D) statistical correlations that held in the past may not hold if new policy is adopted.
A) policies are neutral and have no impact.
B) the impact of policy is intensified if the policy is expected.
C) expectations have no impact on the effectiveness of policy.
D) statistical correlations that held in the past may not hold if new policy is adopted.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
How does the Lucas critique relate to analysis using the simple Phillips curve? The Lucas critique:
A) supports analysis using the simple Phillips curve.
B) explains why the relationship depicted in the simple Phillips curve may not hold.
C) supports movement along a simple Phillips curve but only when policy changes cause the movement.
D) indicates that there are no conditions when the simple Phillips curve is accurate.
A) supports analysis using the simple Phillips curve.
B) explains why the relationship depicted in the simple Phillips curve may not hold.
C) supports movement along a simple Phillips curve but only when policy changes cause the movement.
D) indicates that there are no conditions when the simple Phillips curve is accurate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
How is the unexpected inflation rate measured on the expectations-augmented Phillips curve?
A) expected inflation rate minus inflation rate
B) inflation rate minus expected inflation rate
C) expected inflation rate plus actual inflation rate
D) inflation rate divided by expected inflation rate
A) expected inflation rate minus inflation rate
B) inflation rate minus expected inflation rate
C) expected inflation rate plus actual inflation rate
D) inflation rate divided by expected inflation rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The graph below shows an expectations-augmented Phillips curve. If inflation is higher than expected, then unemployment is below the natural rate. If inflation is lower than expected, then unemployment is higher than the natural rate. For example, if inflation is expected to be 5% but actual inflation is 2%, then: 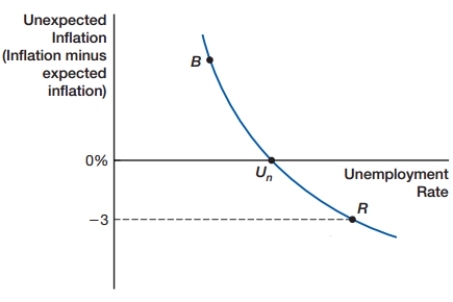
A) inflation will be at 3%.
B) the economy will be at the point Un.
C) the economy will be at the point
D) the economy will be at the point R.

A) inflation will be at 3%.
B) the economy will be at the point Un.
C) the economy will be at the point
D) the economy will be at the point R.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
How can the natural rate of unemployment be identified on the expectations-augmented Phillips curve? It is the unemployment rate associated with _____ unexpected inflation.
A) 5%
B) 2%
C) zero
D) -2%
A) 5%
B) 2%
C) zero
D) -2%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
What happens on the expectations-augmented Phillips curve graph when higher inflation is expected?
A) The curve shifts upward.
B) The curve remains stationary.
C) Unexpected inflation rises.
D) The actual inflation rate drops.
A) The curve shifts upward.
B) The curve remains stationary.
C) Unexpected inflation rises.
D) The actual inflation rate drops.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
When will the economy be at a point on the expectations-augmented Phillips curve that has a high unemployment rate?
A) Inflation is lower than expected.
B) Inflation is higher than expected.
C) Inflation expectations have risen.
D) Inflation is at the target level.
A) Inflation is lower than expected.
B) Inflation is higher than expected.
C) Inflation expectations have risen.
D) Inflation is at the target level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
When will the economy be at a point on the expectations-augmented Phillips curve that has an unemployment rate below the natural rate?
A) Inflation is lower than expected.
B) Inflation is higher than expected.
C) Inflation expectations have fallen significantly.
D) Inflation is at the target level.
A) Inflation is lower than expected.
B) Inflation is higher than expected.
C) Inflation expectations have fallen significantly.
D) Inflation is at the target level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
According to the expectations-augmented Phillips curve, when unexpected inflation is negative, unemployment will be:
A) lower than the natural rate.
B) at the natural rate.
C) higher than the natural rate.
D) unpredictable.
A) lower than the natural rate.
B) at the natural rate.
C) higher than the natural rate.
D) unpredictable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
According to the expectations-augmented Phillips curve, when unexpected inflation is positive, unemployment will be:
A) lower than the natural rate.
B) at the natural rate.
C) higher than the natural rate.
D) unpredictable.
A) lower than the natural rate.
B) at the natural rate.
C) higher than the natural rate.
D) unpredictable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
When an economy is in recession, the unexpected inflation rate will be:
A) positive.
B) zero.
C) negative.
D) the natural rate.
A) positive.
B) zero.
C) negative.
D) the natural rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
A credible policy is defined as a policy that:
A) have the high expected inflation rate.
B) move into a recession.
C) have an increase in output.
D) have expected unemployment that is higher than actual unemployment.
A) have the high expected inflation rate.
B) move into a recession.
C) have an increase in output.
D) have expected unemployment that is higher than actual unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
If people believe that the central bank will achieve its target rate of inflation, then unemployment is likely to move to:
A) a level that is higher than desired.
B) the natural rate.
C) a level that is lower than desired.
D) the credible rate of unemployment.
A) a level that is higher than desired.
B) the natural rate.
C) a level that is lower than desired.
D) the credible rate of unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
When the central bank has credible policy, the economy is likely to be:
A) at the natural rate because unexpected inflation equals zero.
B) expanding because the credibility of the policy makes the public optimistic.
C) stable because inflation is lower than expected.
D) expanding because inflation is lower than expected.
A) at the natural rate because unexpected inflation equals zero.
B) expanding because the credibility of the policy makes the public optimistic.
C) stable because inflation is lower than expected.
D) expanding because inflation is lower than expected.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Which of the following is NOT likely to happen if the public expects an inflation rate of 8% when the actual rate is 4%?
A) Nominal interest rates will be higher than 8%.
B) Workers will want annual raises of at least 8%.
C) Firms will lay off workers.
D) Borrowers will gain from the difference in inflation rates.
A) Nominal interest rates will be higher than 8%.
B) Workers will want annual raises of at least 8%.
C) Firms will lay off workers.
D) Borrowers will gain from the difference in inflation rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Why will business firms lay off workers if the actual inflation rate ends up being lower than was expected?
A) Firms will not trust employees who made mistakes in anticipating inflation, so they will be fired.
B) The prices of the firm's products will be higher than expected, which creates imbalance.
C) The firm's investments will become burdensome as interest rates drop.
D) Firms will have a hard time paying high wages that were negotiated on expectations of higher prices.
A) Firms will not trust employees who made mistakes in anticipating inflation, so they will be fired.
B) The prices of the firm's products will be higher than expected, which creates imbalance.
C) The firm's investments will become burdensome as interest rates drop.
D) Firms will have a hard time paying high wages that were negotiated on expectations of higher prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
When central bank policies are credible, then unexpected inflation tends to be:
A) near zero.
B) high.
C) rising.
D) unpredictable.
A) near zero.
B) high.
C) rising.
D) unpredictable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
(Figure: Demand Shock 0) When the economy moves from A to B, as shown in the graph on the left, how will inflation and the unemployment rate be affected, as shown in the graph on the right?
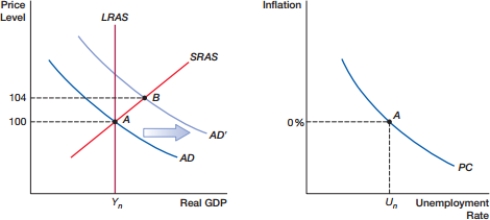
A) There will be movement on the curve, so that inflation increases and unemployment decreases.
B) There will be movement on the curve, so that inflation decreases and unemployment increases.
C) The curve will shift left, so that both unemployment and inflation decrease.
D) The curve will shift right, so that both unemployment and inflation increase.

A) There will be movement on the curve, so that inflation increases and unemployment decreases.
B) There will be movement on the curve, so that inflation decreases and unemployment increases.
C) The curve will shift left, so that both unemployment and inflation decrease.
D) The curve will shift right, so that both unemployment and inflation increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
(Figure: Demand Shock I) The movement shown in the figure will only reduce the unemployment rate if:
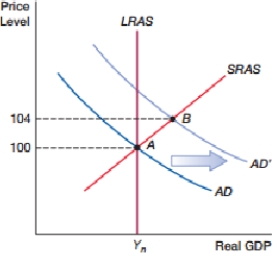
A) actual inflation is equal to expected inflation.
B) actual inflation is lower than expected inflation.
C) actual inflation is higher than expected inflation.
D) there are no expectations concerning inflation.

A) actual inflation is equal to expected inflation.
B) actual inflation is lower than expected inflation.
C) actual inflation is higher than expected inflation.
D) there are no expectations concerning inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
(Figure: Demand Shock A) When the economy moves from A to B, as shown in the graph on the left, how will inflation and the unemployment rate be affected, as shown in the graph on the right?
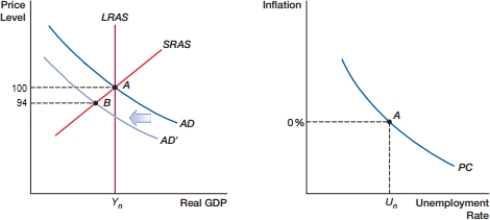
A) There will be movement on the curve, so that inflation increases and unemployment decreases.
B) There will be movement on the curve, so that inflation decreases and unemployment increases.
C) The curve will shift left, so that both unemployment and inflation decrease.
D) The curve will shift right, so that both unemployment and inflation increase.

A) There will be movement on the curve, so that inflation increases and unemployment decreases.
B) There will be movement on the curve, so that inflation decreases and unemployment increases.
C) The curve will shift left, so that both unemployment and inflation decrease.
D) The curve will shift right, so that both unemployment and inflation increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
(Figure: Demand Shock Alpha) The movement shown in the figure will only increase the unemployment rate if:
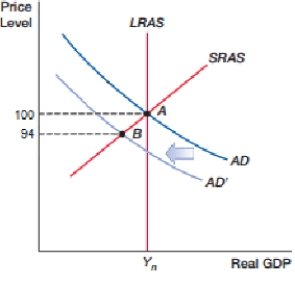
A) actual inflation is equal to expected inflation.
B) actual inflation is lower than expected inflation.
C) actual inflation is higher than expected inflation.
D) there are no expectations concerning inflation.

A) actual inflation is equal to expected inflation.
B) actual inflation is lower than expected inflation.
C) actual inflation is higher than expected inflation.
D) there are no expectations concerning inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
(Figure: Expectations 0) In the figure, what is the cause of the movement from point a to b?
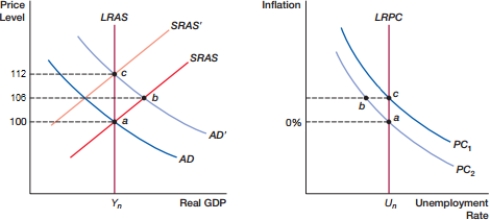
A) positive demand shock
B) negative demand shock
C) self-correcting mechanism
D) inflation expectations

A) positive demand shock
B) negative demand shock
C) self-correcting mechanism
D) inflation expectations

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
(Figure: Expectations 0) In the figure, what is the cause of the movement from point b to c?
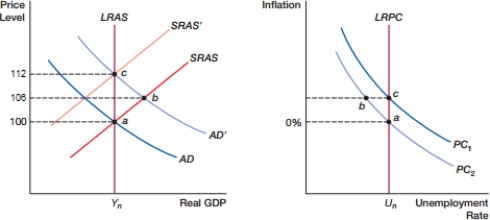
A) positive demand shock
B) negative demand shock
C) self-correcting mechanism
D) inflation expectations

A) positive demand shock
B) negative demand shock
C) self-correcting mechanism
D) inflation expectations

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
(Figure: Expectations 0) In the figure, what is the inflation rate at point c?
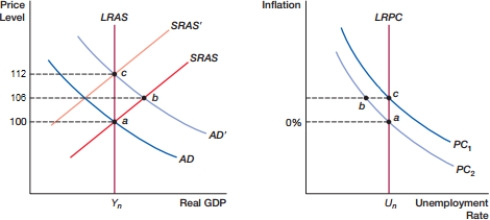
A) 0%
B) 3%
C) 6%
D) 12%

A) 0%
B) 3%
C) 6%
D) 12%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



