Deck 27: Monetary Policy and Interest Rates
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/108
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 27: Monetary Policy and Interest Rates
1
Changes in the money supply and interest rates that are initiated by the central bank with a goal of stabilizing the economy are referred to as:
A) stabilization initiatives.
B) fiscal policy.
C) currency policy.
D) monetary policy.
A) stabilization initiatives.
B) fiscal policy.
C) currency policy.
D) monetary policy.
D
2
Which of the following is an example of monetary policy?
A) A bank raises the interest rate on loans to compensate for losses on bad loans.
B) Old currency is pulled out of circulation and replaced with new currency due to inflated old currency.
C) The Federal Reserve reduces the money supply in an effort to reduce inflation.
D) The legislature increases government spending to reduce unemployment.
A) A bank raises the interest rate on loans to compensate for losses on bad loans.
B) Old currency is pulled out of circulation and replaced with new currency due to inflated old currency.
C) The Federal Reserve reduces the money supply in an effort to reduce inflation.
D) The legislature increases government spending to reduce unemployment.
C
3
What two goals are the dual mandate of the U.S. Federal Reserve System?
A) Maximize employment, and keep price level stable.
B) Maintain money value, and reduce national deficit.
C) Keep the price level stable, and maintain foreign exchange value.
D) Keep unemployment low, and keep national deficit low.
A) Maximize employment, and keep price level stable.
B) Maintain money value, and reduce national deficit.
C) Keep the price level stable, and maintain foreign exchange value.
D) Keep unemployment low, and keep national deficit low.
A
4
The Federal Reserve's mandate to achieve maximum employment means that the Fed is trying to achieve:
A) zero unemployment.
B) the natural rate of unemployment.
C) the lowest possible rate of unemployment.
D) an unemployment rate that is no higher than 6.5%.
A) zero unemployment.
B) the natural rate of unemployment.
C) the lowest possible rate of unemployment.
D) an unemployment rate that is no higher than 6.5%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The Federal Reserve's mandate to achieve stable prices means that the Fed's policies try to achieve:
A) zero inflation.
B) an inflation rate in the range of -1% to 1%.
C) an inflation rate of about 2%.
D) unchanging wages, interest rates, and prices.
A) zero inflation.
B) an inflation rate in the range of -1% to 1%.
C) an inflation rate of about 2%.
D) unchanging wages, interest rates, and prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following inflation rates do policymakers view as consistent with the Federal Reserve's mandate to achieve stable prices?
A) 2%
B) 0%
C) -2%
D) 5%
A) 2%
B) 0%
C) -2%
D) 5%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In the United States, the natural rate of unemployment is approximately:
A) 0%.
B) 5%.
C) 2%.
D) 8%.
A) 0%.
B) 5%.
C) 2%.
D) 8%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following does the Federal Reserve consider to be the best option for an inflation goal for the US?
A) 0%
B) -1%
C) 2%
D) 4%
A) 0%
B) -1%
C) 2%
D) 4%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Changes in a nation's money supply affect _____ in the short run but affect _____ in the long run.
A) both price level and output level; only output level
B) both price level and output level; only price level
C) only output level; both price level and output level
D) only price level; both price level and output level
A) both price level and output level; only output level
B) both price level and output level; only price level
C) only output level; both price level and output level
D) only price level; both price level and output level

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following is NOT an outcome of higher interest rates?
A) Fewer investment opportunities appear profitable to businesses.
B) Households cannot afford to borrow as much toward a home purchase.
C) Savers face higher buying costs in the loanable funds markets.
D) It is more expensive for business firms to borrow money.
A) Fewer investment opportunities appear profitable to businesses.
B) Households cannot afford to borrow as much toward a home purchase.
C) Savers face higher buying costs in the loanable funds markets.
D) It is more expensive for business firms to borrow money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
When interest rates are high due to a reduction in saving, business firms are likely to:
A) increase investments in capital due to high interest rate returns.
B) reduce investments in capital due to high borrowing costs.
C) expand operations due to the high return on savings.
D) contract operations due to low return on savings.
A) increase investments in capital due to high interest rate returns.
B) reduce investments in capital due to high borrowing costs.
C) expand operations due to the high return on savings.
D) contract operations due to low return on savings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
According to economists, short-term interest rates apply to loans and savings _____, and long-term interest rates apply to loans and savings:
A) when product markets are not at equilibrium; when product markets are at equilibrium.
B) when all market adjustments have occurred; when markets have not yet completed all adjustments.
C) for less than one year; for more than one year.
D) when credit markets are at equilibrium; when credit markets have not yet adjusted to equilibriums.
A) when product markets are not at equilibrium; when product markets are at equilibrium.
B) when all market adjustments have occurred; when markets have not yet completed all adjustments.
C) for less than one year; for more than one year.
D) when credit markets are at equilibrium; when credit markets have not yet adjusted to equilibriums.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The Federal Reserve has more impact on interest rates:
A) in the long run than in the short run.
B) when banks have a lot of excess reserve than when banks have zero excess reserve.
C) when they are falling than when they are rising.
D) in the short run than in the long run.
A) in the long run than in the short run.
B) when banks have a lot of excess reserve than when banks have zero excess reserve.
C) when they are falling than when they are rising.
D) in the short run than in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The interest rate that a bank pays to borrow another bank's excess reserves is called the:
A) discount rate.
B) federal funds rate.
C) savings account rate rate.
D) monetary loan rate.
A) discount rate.
B) federal funds rate.
C) savings account rate rate.
D) monetary loan rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The _____ rate is the interest rate that banks pay to borrow from the Federal Reserve, and the _____ rate is the interest rate that banks pay to borrow another bank's excess reserves.
A) discount; federal funds
B) federal funds; discount
C) open market; federal funds
D) discount; open market
A) discount; federal funds
B) federal funds; discount
C) open market; federal funds
D) discount; open market

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
When the Federal Reserve sets an interest rate goal, it typically focuses on having the _____ rate reach that goal.
A) open market
B) quantitative easing
C) money market
D) federal funds
A) open market
B) quantitative easing
C) money market
D) federal funds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Demand for which of the following is NOT increased by low interest rates?
A) automobiles
B) capital investments
C) hamburgers
D) homes
A) automobiles
B) capital investments
C) hamburgers
D) homes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
In the market for money, the _____ is the cost of holding money.
A) average price level for goods and services
B) GDP deflator
C) foreign exchange rate
D) interest rate
A) average price level for goods and services
B) GDP deflator
C) foreign exchange rate
D) interest rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
(Figure: Money Supply and Demand) The money demand curve (MD) is downward sloping, reflecting the opportunity cost of holding liquid forms of money such as cash. The money supply curve (MS) is determined by _____. Point (P) is the _____.
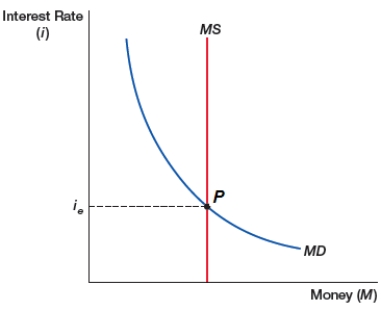
A) the Federal Reserve; maximum interest rate
B) the Mortgage Banks; maximum interest rate
C) the Federal Reserve; equilibrium interest rate
D) the Mortgage Banks; equilibrium interest rate

A) the Federal Reserve; maximum interest rate
B) the Mortgage Banks; maximum interest rate
C) the Federal Reserve; equilibrium interest rate
D) the Mortgage Banks; equilibrium interest rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
(Figure: Decrease in Money Supply) The figure shows a decrease in the money supply through open market sales. Which of these is INCORRECT concerning this figure?
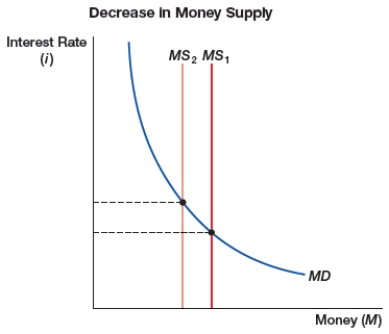
A) the money supply line shifts to the left.
B) the monetary base decreases.
C) the equilibrium interest rate decreases.
D) there is tighter money in the market.

A) the money supply line shifts to the left.
B) the monetary base decreases.
C) the equilibrium interest rate decreases.
D) there is tighter money in the market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
In the market for money, the _____ rate is the price because it:
A) interest; is the opportunity cost of holding money.
B) interest; varies in response to monetary policy.
C) foreign exchange; impacts net exports.
D) foreign exchange; affects the desirability of holding cash balances.
A) interest; is the opportunity cost of holding money.
B) interest; varies in response to monetary policy.
C) foreign exchange; impacts net exports.
D) foreign exchange; affects the desirability of holding cash balances.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The money demand curve has:
A) a downward slope.
B) an upward slope.
C) a vertical slope.
D) a horizontal slope.
A) a downward slope.
B) an upward slope.
C) a vertical slope.
D) a horizontal slope.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The money supply curve has:
A) a downward slope.
B) an upward slope.
C) a vertical slope.
D) a horizontal slope.
A) a downward slope.
B) an upward slope.
C) a vertical slope.
D) a horizontal slope.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Most people evaluate current monetary policy by looking at:
A) the price level.
B) interest rates.
C) shifts in the money demand curve.
D) movements along the money supply curve.
A) the price level.
B) interest rates.
C) shifts in the money demand curve.
D) movements along the money supply curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
In the short run, a decrease in the money supply will have which of the following impacts on the market for money?
A) Interest rates will fall.
B) Interest rates will rise.
C) The demand for money will increase.
D) The demand for money will decrease.
A) Interest rates will fall.
B) Interest rates will rise.
C) The demand for money will increase.
D) The demand for money will decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In the short run, an increase in the money supply will have which of the following impacts on the market for money?
A) Interest rates will fall.
B) Interest rates will rise.
C) The demand for money will increase.
D) The demand for money will decrease.
A) Interest rates will fall.
B) Interest rates will rise.
C) The demand for money will increase.
D) The demand for money will decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
An increase in the money supply is referred to as _____ money policy.
A) easy
B) tight
C) generous
D) rigid
A) easy
B) tight
C) generous
D) rigid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A decrease in the money supply is referred to as _____ money policy.
A) easy
B) tight
C) generous
D) rigid
A) easy
B) tight
C) generous
D) rigid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The Federal Reserve is able to achieve its dual mandate because monetary policy affects:
A) short-run aggregate supply.
B) aggregate demand.
C) long-run aggregate supply.
D) government spending.
A) short-run aggregate supply.
B) aggregate demand.
C) long-run aggregate supply.
D) government spending.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following is NOT a reason that monetary policy impacts aggregate demand?
A) the exchange rate and net export effect
B) the excess cash balance effect
C) the budget deficit effect
D) the interest rate effect
A) the exchange rate and net export effect
B) the excess cash balance effect
C) the budget deficit effect
D) the interest rate effect

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
An example of the asset price effect occurs when the increase in the money supply leads to:
A) increases in the prices of goods and services.
B) increases in the purchasing power of each unit of currency.
C) a decrease in the value of savings accounts.
D) an increase in the prices of shares of stocks.
A) increases in the prices of goods and services.
B) increases in the purchasing power of each unit of currency.
C) a decrease in the value of savings accounts.
D) an increase in the prices of shares of stocks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A decrease in the money supply tends to _____ the foreign exchange value of the dollar, which causes net exports to:
A) increase; decrease.
B) increase; increase.
C) decrease; decrease.
D) decrease; increase.
A) increase; decrease.
B) increase; increase.
C) decrease; decrease.
D) decrease; increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
An increase in the money supply tends to _____ the foreign exchange value of the dollar, which will cause net exports to:
A) increase; decrease.
B) increase; increase.
C) decrease; decrease.
D) decrease; increase.
A) increase; decrease.
B) increase; increase.
C) decrease; decrease.
D) decrease; increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Econia decreases its money supply. What is likely to happen to the value of Econia's currency in foreign exchange markets and to the level of Econia's net exports?
A) Currency appreciates, and net exports increase.
B) Currency appreciates, and net exports decrease.
C) Currency depreciates, and net exports increase.
D) Currency depreciates, and net exports decrease.
A) Currency appreciates, and net exports increase.
B) Currency appreciates, and net exports decrease.
C) Currency depreciates, and net exports increase.
D) Currency depreciates, and net exports decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Econia increases its money supply. What is likely to happen to the value of Econia's currency in foreign exchange markets and to the level of Econia's net exports?
A) Currency appreciates, and net exports increase.
B) Currency appreciates, and net exports decrease.
C) Currency depreciates, and net exports increase.
D) Currency depreciates, and net exports decrease.
A) Currency appreciates, and net exports increase.
B) Currency appreciates, and net exports decrease.
C) Currency depreciates, and net exports increase.
D) Currency depreciates, and net exports decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following is a good example of the net export or open economy effect of monetary policy?
A) An expansionary monetary policy causes net exports to rise, which helps to decrease unemployment.
B) An expansionary monetary policy causes net exports to fall, which helps to decrease inflationary pressures.
C) A contractionary monetary policy causes net exports to rise, which helps to decrease inflationary pressures.
D) A contractionary monetary policy causes net exports to fall, which helps to reduce unemployment.
A) An expansionary monetary policy causes net exports to rise, which helps to decrease unemployment.
B) An expansionary monetary policy causes net exports to fall, which helps to decrease inflationary pressures.
C) A contractionary monetary policy causes net exports to rise, which helps to decrease inflationary pressures.
D) A contractionary monetary policy causes net exports to fall, which helps to reduce unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
An increase in the money supply will cause interest rates to _____, which causes _____ to:
A) increase; government spending; fall.
B) increase; consumer and investment spending; fall.
C) decrease; government spending; rise.
D) decrease; consumer and investment spending; rise.
A) increase; government spending; fall.
B) increase; consumer and investment spending; fall.
C) decrease; government spending; rise.
D) decrease; consumer and investment spending; rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
During the early 2000s, the Federal Reserve had _____ monetary policy that contributed to _____ home sales and home prices.
A) a tight; falling
B) a tight; rising
C) an easy; falling
D) an easy; rising
A) a tight; falling
B) a tight; rising
C) an easy; falling
D) an easy; rising

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
When the Federal Reserve reduces the money supply, aggregate ____ will _____, causing short-run output to:
A) demand; fall; fall.
B) demand; rise; rise.
C) supply; fall; fall.
D) supply; rise; rise.
A) demand; fall; fall.
B) demand; rise; rise.
C) supply; fall; fall.
D) supply; rise; rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
When the Federal Reserve increases the money supply, aggregate ____ will _____, causing short-run output to:
A) demand; fall; fall.
B) demand; rise; rise.
C) supply; fall; fall.
D) supply; rise; rise.
A) demand; fall; fall.
B) demand; rise; rise.
C) supply; fall; fall.
D) supply; rise; rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
If the Federal Reserve wants to cause a recession to end, it will choose ______ monetary policy to cause _____ to:
A) an expansionary; aggregate demand; rise.
B) an expansionary; short-run aggregate supply; rise.
C) a contractionary; aggregate demand; fall.
D) a contractionary; short-run aggregate supply; rise.
A) an expansionary; aggregate demand; rise.
B) an expansionary; short-run aggregate supply; rise.
C) a contractionary; aggregate demand; fall.
D) a contractionary; short-run aggregate supply; rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
(Figure: Changing Money Supply) What do graphs 'A' and 'B' represent for an economy?
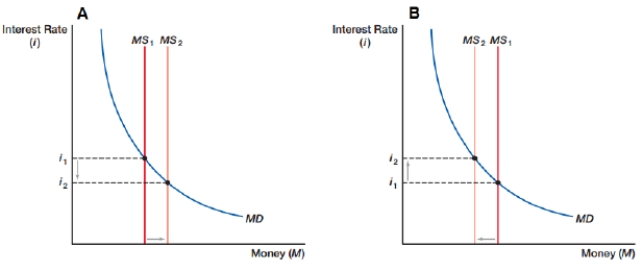
A) "A" represents an expansionary monetary policy; "B" represents a contractionary monetary policy
B) "A" represents a contractionary monetary policy; "B" represents an expansionary monetary policy
C) "A" represents an economy moving out of an inflationary boom; "B" represents an economy moving out of a recession
D) "A" represents a decrease in money demand; "B" represents an increase in money demand

A) "A" represents an expansionary monetary policy; "B" represents a contractionary monetary policy
B) "A" represents a contractionary monetary policy; "B" represents an expansionary monetary policy
C) "A" represents an economy moving out of an inflationary boom; "B" represents an economy moving out of a recession
D) "A" represents a decrease in money demand; "B" represents an increase in money demand

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
In the short run, after a decrease in the money supply, employment _____, and the price level:
A) rises; rises.
B) rises; falls.
C) falls; rises.
D) falls; falls.
A) rises; rises.
B) rises; falls.
C) falls; rises.
D) falls; falls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
(Figure: Changing Demand) What do graphs "A" and "B" represent for an economy?
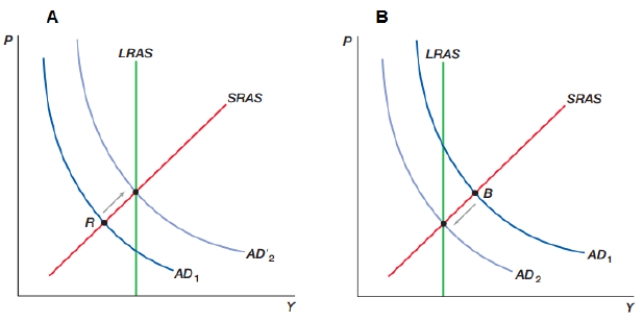
A) "A" represents an expansionary monetary policy; "B" represents a contractionary monetary policy
B) "A" represents a contractionary monetary policy; "B" represents an expansionary monetary policy
C) "A" represents an economy moving out of an inflationary boom; "B" represents an economy moving out of a recession
D) "A" represents a decrease in money supply; "B" represents an increase in money supply

A) "A" represents an expansionary monetary policy; "B" represents a contractionary monetary policy
B) "A" represents a contractionary monetary policy; "B" represents an expansionary monetary policy
C) "A" represents an economy moving out of an inflationary boom; "B" represents an economy moving out of a recession
D) "A" represents a decrease in money supply; "B" represents an increase in money supply

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
(Figure: Business Cycle 0) The figure shows effective monetary policy over the business cycle. What does point 1 represent?
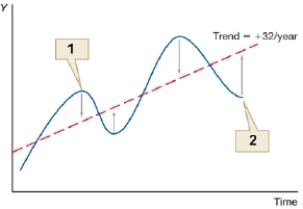
A) expansionary policy during recession
B) contractionary policy during inflationary boom
C) contractionary policy during recession
D) expansionary policy during inflationary boom

A) expansionary policy during recession
B) contractionary policy during inflationary boom
C) contractionary policy during recession
D) expansionary policy during inflationary boom

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
(Figure: Business Cycle 0) The figure shows effective monetary policy over the business cycle. What does point 2 represent?
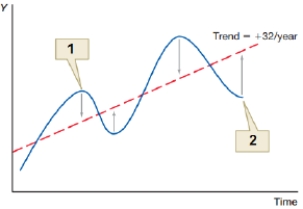
A) expansionary policy during recession
B) contractionary policy during inflationary boom
C) contractionary policy during recession
D) expansionary policy during inflationary boom

A) expansionary policy during recession
B) contractionary policy during inflationary boom
C) contractionary policy during recession
D) expansionary policy during inflationary boom

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
In the short run, after an increase in the money supply, employment _____, and the price level:
A) rises; rises.
B) rises; falls.
C) falls; rises.
D) falls; falls.
A) rises; rises.
B) rises; falls.
C) falls; rises.
D) falls; falls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
What type of monetary policy is typically used to counter a recession?
A) expansionary
B) contractionary
C) supply-based
D) demand-based
A) expansionary
B) contractionary
C) supply-based
D) demand-based

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The goal of monetary policymakers with regard to the business cycle is to:
A) accentuate the positive aspects of each stage of the business cycle.
B) focus on the long-run growth of the economy.
C) eliminate the swings in the business cycle.
D) increase reliance on the business cycle.
A) accentuate the positive aspects of each stage of the business cycle.
B) focus on the long-run growth of the economy.
C) eliminate the swings in the business cycle.
D) increase reliance on the business cycle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which of the following monetary policies was used in Japan in 2013 to address the deflation of the previous twenty years?
A) disinflationary
B) deflationary
C) expansionary
D) contractionary
A) disinflationary
B) deflationary
C) expansionary
D) contractionary

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
An expansionary monetary policy affects a country's foreign exchange rate by making the country's currency:
A) appreciate.
B) depreciate.
C) lose purchasing power due to deflation.
D) gain purchasing power due to deflation.
A) appreciate.
B) depreciate.
C) lose purchasing power due to deflation.
D) gain purchasing power due to deflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A lower exchange rate has which of the following impacts on a country's net exports and aggregate demand?
A) Both net exports and aggregate demand rise.
B) Net exports rise, and aggregate demand falls.
C) Both net exports and aggregate demand fall.
D) Net exports fall, and aggregate demand rises.
A) Both net exports and aggregate demand rise.
B) Net exports rise, and aggregate demand falls.
C) Both net exports and aggregate demand fall.
D) Net exports fall, and aggregate demand rises.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The Keynesian approach to policy focuses on using policy tools to manipulate _____ to create full employment in the economy.
A) long-run aggregate supply
B) short-run aggregate supply
C) aggregate demand
D) velocity
A) long-run aggregate supply
B) short-run aggregate supply
C) aggregate demand
D) velocity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
To stabilize an economy, the Keynesian policy approach tends to favor using _____ over:
A) fiscal policy; monetary policy.
B) monetary policy; fiscal policy.
C) aggregate supply; interest rates.
D) interest rates; aggregate supply.
A) fiscal policy; monetary policy.
B) monetary policy; fiscal policy.
C) aggregate supply; interest rates.
D) interest rates; aggregate supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
As a result of the Great Depression, economists were more concerned about _____ than _____ for decades.
A) unemployment; inflation
B) fiscal policy; monetary policy
C) inflation; unemployment
D) monetary policy; fiscal policy
A) unemployment; inflation
B) fiscal policy; monetary policy
C) inflation; unemployment
D) monetary policy; fiscal policy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which of the following economists developed a theory during the Great Depression that dominated macroeconomic policy approaches for the next fifty years?
A) Milton Friedman
B) Ben Bernanke
C) John Maynard Keynes
D) Adam Smith
A) Milton Friedman
B) Ben Bernanke
C) John Maynard Keynes
D) Adam Smith

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Monetarists recommend that the money supply should grow at a:
A) rate that changes as the economy moves from stage to stage in the business cycle.
B) steady rate that is higher than output's growth rate to stimulate growth.
C) rate that varies in direct proportion to unemployment to offset it.
D) slow, steady rate that is based on the long-run real GDP growth rate.
A) rate that changes as the economy moves from stage to stage in the business cycle.
B) steady rate that is higher than output's growth rate to stimulate growth.
C) rate that varies in direct proportion to unemployment to offset it.
D) slow, steady rate that is based on the long-run real GDP growth rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Monetarists believe that _____ policy is more effective than _____ policy.
A) monetary; fiscal
B) fiscal; monetary
C) expansionary; contractionary
D) contractionary; expansionary
A) monetary; fiscal
B) fiscal; monetary
C) expansionary; contractionary
D) contractionary; expansionary

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
In their analysis, monetarists rely heavily on:
A) the aggregate supply and aggregate demand model.
B) business cycle fluctuations.
C) the effects of changing interest rates
D) the equation of exchange.
A) the aggregate supply and aggregate demand model.
B) business cycle fluctuations.
C) the effects of changing interest rates
D) the equation of exchange.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The economist who is the best-known monetarist is:
A) John Maynard Keynes.
B) Ben Bernanke.
C) Milton Friedman.
D) Jerome Powell.
A) John Maynard Keynes.
B) Ben Bernanke.
C) Milton Friedman.
D) Jerome Powell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The monetarists assume that velocity is _____ and that changes in the money supply lead to _____ changes in nominal GDP.
A) fairly stable; proportionate
B) fairly stable; escalating
C) variable; proportionate
D) variable; escalating
A) fairly stable; proportionate
B) fairly stable; escalating
C) variable; proportionate
D) variable; escalating

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The school of thought in economics that focuses on the role that the money supply plays in determining nominal GDP and inflation is called:
A) Keynesianism.
B) monetarism.
C) fiscalism.
D) money marketism.
A) Keynesianism.
B) monetarism.
C) fiscalism.
D) money marketism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The new Keynesian perspective focuses on targeting:
A) short-term interest rates.
B) long-term interest rates.
C) money supply growth.
D) government spending.
A) short-term interest rates.
B) long-term interest rates.
C) money supply growth.
D) government spending.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
New Keynesians believe that the Federal Reserve should target ____ rather than:
A) the money supply; interest rates.
B) interest rates; the money supply.
C) money supply; taxes.
D) taxes; interest rates.
A) the money supply; interest rates.
B) interest rates; the money supply.
C) money supply; taxes.
D) taxes; interest rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
New Keynesians do NOT believe that:
A) monetary policy should use interest rate targets.
B) when interest rates are near zero, fiscal policy is more effective than monetary policy.
C) central banks should target the money supply instead of interest rates.
D) monetary policy typically is the most effective tool for stabilizing an economy.
A) monetary policy should use interest rate targets.
B) when interest rates are near zero, fiscal policy is more effective than monetary policy.
C) central banks should target the money supply instead of interest rates.
D) monetary policy typically is the most effective tool for stabilizing an economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
An economy is in a liquidity trap when:
A) an increase in the money supply has created excess cash balances.
B) people are being tricked into selling financial assets to get cash.
C) the savings rate is rising rapidly.
D) interest rates are near zero.
A) an increase in the money supply has created excess cash balances.
B) people are being tricked into selling financial assets to get cash.
C) the savings rate is rising rapidly.
D) interest rates are near zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
When conducting monetary policy, the U.S. Federal Reserve now uses the tools of monetary policy to target the level of which of the following variables?
A) foreign exchange rate
B) money supply
C) federal funds rate
D) velocity of money
A) foreign exchange rate
B) money supply
C) federal funds rate
D) velocity of money

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
(Figure: Interest Rate Targeting) The figure shows interest rate targeting. Initially, the fed funds interest rate equilibrium (E) is the targeted interest rate (iT). If money demand increases, the Federal Reserve _____ to maintain the interest rate target.
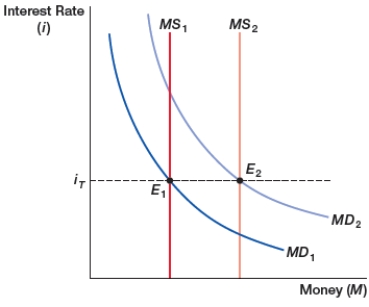
A) decreases the interest rate
B) increases the interest rate
C) decreases the money supply
D) increases the money supply

A) decreases the interest rate
B) increases the interest rate
C) decreases the money supply
D) increases the money supply

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The target interest rate for monetary policy in the United States is decided by:
A) the board of governors of the U.S. Federal Reserve.
B) the members of the Federal Open Market Committee.
C) the U.S. Congress.
D) the U.S. president.
A) the board of governors of the U.S. Federal Reserve.
B) the members of the Federal Open Market Committee.
C) the U.S. Congress.
D) the U.S. president.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
If the Federal Reserve wishes to maintain an unchanging target interest rate and the demand for money is rising, then the Fed will:
A) raise the inflation rate.
B) reduce the demand for money.
C) increase the supply of money.
D) decrease the supply of money.
A) raise the inflation rate.
B) reduce the demand for money.
C) increase the supply of money.
D) decrease the supply of money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
If the Federal Reserve wishes to maintain an unchanging target interest rate and the demand for money is falling, then the Fed will:
A) raise the inflation rate.
B) reduce the demand for money.
C) increase the supply of money.
D) decrease the supply of money.
A) raise the inflation rate.
B) reduce the demand for money.
C) increase the supply of money.
D) decrease the supply of money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
When an economy has too much inflation, then the Federal Reserve will _____ the target interest rate in order to _____ aggregate demand.
A) increase; reduce
B) increase; increase
C) reduce; reduce
D) reduce; increase
A) increase; reduce
B) increase; increase
C) reduce; reduce
D) reduce; increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
When an economy has too much unemployment, then the Federal Reserve will _____ the target interest rate in order to _____ aggregate demand.
A) increase; reduce
B) increase; increase
C) reduce; reduce
D) reduce; increase
A) increase; reduce
B) increase; increase
C) reduce; reduce
D) reduce; increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
When the Federal Reserve engages in expansionary monetary policy, which of the following will NOT be a result?
A) The money supply increases.
B) Aggregate demand rises.
C) The Fed makes open market purchases.
D) The federal funds rate target is raised.
A) The money supply increases.
B) Aggregate demand rises.
C) The Fed makes open market purchases.
D) The federal funds rate target is raised.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
When the Federal Reserve engages in contractionary monetary policy, which of the following will NOT be a result?
A) The money supply decreases.
B) Aggregate demand falls.
C) The Fed makes open market purchases.
D) The federal funds rate target is raised.
A) The money supply decreases.
B) Aggregate demand falls.
C) The Fed makes open market purchases.
D) The federal funds rate target is raised.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
If an expansionary monetary policy raises expectations for inflation, then interest rates:
A) may not fall as normally expected but may rise due to the Fisher effect.
B) may not rise as normally expected but may fall due to the Fisher effect.
C) will rise but will rise even more than normally expected due to the Fisher effect.
D) will fall but will fall even more than normally expected due to the Fisher effect.
A) may not fall as normally expected but may rise due to the Fisher effect.
B) may not rise as normally expected but may fall due to the Fisher effect.
C) will rise but will rise even more than normally expected due to the Fisher effect.
D) will fall but will fall even more than normally expected due to the Fisher effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
An increase in interest rates can be caused by a _____ money policy or _____ in expected inflation.
A) tight; a decrease
B) tight; an increase
C) loose; an increase
D) loose; a decrease
A) tight; a decrease
B) tight; an increase
C) loose; an increase
D) loose; a decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Low interest rates could exist due to either a _____ money supply or _____ inflationary expectations.
A) larger; high
B) larger; low
C) tight; high
D) tight; low
A) larger; high
B) larger; low
C) tight; high
D) tight; low

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
High interest rates could exist due to either a _____ money supply or _____ inflationary expectations.
A) larger; high
B) larger; low
C) tight; high
D) tight; low
A) larger; high
B) larger; low
C) tight; high
D) tight; low

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Which of the following is an example of the Fisher effect?
A) Expansionary monetary policy reduces inflation by 3%, and interest rates rise 3%.
B) Inflationary expectations rise from 2% to 6%, which causes interest rates to rise from 5% to 9%.
C) Contractionary monetary policy reduces inflation by 2%, and interest rates rise by 3%.
D) Inflationary expectations fall from 4% to 2%, which causes interest rates to rise from 6% to 8%.
A) Expansionary monetary policy reduces inflation by 3%, and interest rates rise 3%.
B) Inflationary expectations rise from 2% to 6%, which causes interest rates to rise from 5% to 9%.
C) Contractionary monetary policy reduces inflation by 2%, and interest rates rise by 3%.
D) Inflationary expectations fall from 4% to 2%, which causes interest rates to rise from 6% to 8%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



