Deck 26: Aggregate Supply and Aggregate Demand
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/116
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 26: Aggregate Supply and Aggregate Demand
1
The aggregate supply and aggregate demand model below provides insights into the causes of the Great Depression of the 1930s. Indicate points 1 and 2 and whether price level increases or decreases when aggregate demand changes from AD1 to AD2. 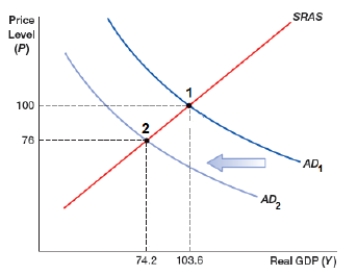
A) Point 1 is the booming of 1920s, point 2 is the depression of 1930s; price level decreases
B) Point 1 is the booming of 1920s, point 2 is the depression of 1930s; price level increases
C) Point 1 is the depression of 1930s, point 2 is the booming of 1920s; price level decreases
D) Point 1 is the depression of 1930s, point 2 is the booming of 1920s; price level increases

A) Point 1 is the booming of 1920s, point 2 is the depression of 1930s; price level decreases
B) Point 1 is the booming of 1920s, point 2 is the depression of 1930s; price level increases
C) Point 1 is the depression of 1930s, point 2 is the booming of 1920s; price level decreases
D) Point 1 is the depression of 1930s, point 2 is the booming of 1920s; price level increases
A
2
The graph of the aggregate supply and aggregate demand model measures _____ on the horizontal axis and _____ on the vertical axis.
A) net exports; interest rate
B) average price level; net exports
C) interest rate; total quantity of goods and services
D) total quantity of goods and services; average price level
A) net exports; interest rate
B) average price level; net exports
C) interest rate; total quantity of goods and services
D) total quantity of goods and services; average price level
D
3
A sudden and large shift in an aggregate demand curve is known as:
A) a demand shock.
B) a demand trigger reaction.
C) an immediate demand adjustment.
D) a demand bolt.
A) a demand shock.
B) a demand trigger reaction.
C) an immediate demand adjustment.
D) a demand bolt.
A
4
Aggregate demand is the:
A) total demand for a good or service across all possible buyers.
B) total amount of goods that would be purchased in an economy at the current price level.
C) total amount of goods and services that would be purchased in an economy at each given average price level.
D) global demand for all goods and services.
A) total demand for a good or service across all possible buyers.
B) total amount of goods that would be purchased in an economy at the current price level.
C) total amount of goods and services that would be purchased in an economy at each given average price level.
D) global demand for all goods and services.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
When aggregate demand declines, an economy will experience _____ in the average price level and _____ in the amount of goods and services purchased.
A) a decrease; an increase
B) a decrease; a decrease
C) an increase; an increase
D) an increase; a decrease
A) a decrease; an increase
B) a decrease; a decrease
C) an increase; an increase
D) an increase; a decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
If Econia's aggregate demand falls, the price level will _____, and the output level will:
A) increase; increase.
B) increase; decrease.
C) decrease; increase.
D) decrease; decrease.
A) increase; increase.
B) increase; decrease.
C) decrease; increase.
D) decrease; decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
(Figure: ASAD0) In the figure, in the 1930s the economy moved from point 1 to 2. What does point 2 suggest?
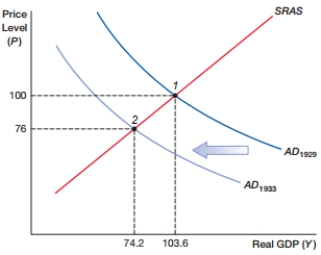
A) economic growth
B) inflation
C) a recession
D) disinflation

A) economic growth
B) inflation
C) a recession
D) disinflation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
(Figure: ASAD0) In the figure, the price level went from 100 to 76. This suggests the economy was experiencing a(n):
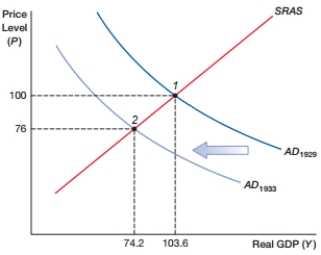
A) inflationary recession
B) inflationary expansion
C) deflationary recession
D) deflationary expansion

A) inflationary recession
B) inflationary expansion
C) deflationary recession
D) deflationary expansion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The slope of the long-run aggregate supply curve is:
A) upward sloping.
B) downward sloping.
C) vertical.
D) horizontal.
A) upward sloping.
B) downward sloping.
C) vertical.
D) horizontal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
(Figure: Natural Rate) What does the figure represent?
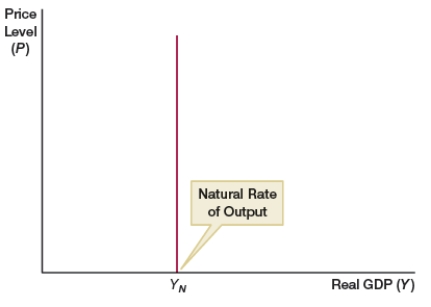
A) long-run aggregate demand curve
B) short-run aggregate demand curve
C) long-run aggregate supply curve
D) short-run aggregate supply curve

A) long-run aggregate demand curve
B) short-run aggregate demand curve
C) long-run aggregate supply curve
D) short-run aggregate supply curve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
In the long run, total national output:
A) is not impacted by the price level.
B) has a positive relationship with the price level.
C) has a negative relationship with the price level.
D) varies widely at a fixed, given price level.
A) is not impacted by the price level.
B) has a positive relationship with the price level.
C) has a negative relationship with the price level.
D) varies widely at a fixed, given price level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Why does the amount of national output remain steady in the long run even though the price level may change?
A) The price level has no impact on the amount of goods and services that are demanded.
B) The price level does not impact the stock of productive resources or technology.
C) Price-level changes are evidence of moving equilibriums and changing outputs.
D) When output varies, the price level must vary.
A) The price level has no impact on the amount of goods and services that are demanded.
B) The price level does not impact the stock of productive resources or technology.
C) Price-level changes are evidence of moving equilibriums and changing outputs.
D) When output varies, the price level must vary.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
What determines national output on the long-run aggregate supply curve?
A) the natural rate of output
B) the price level
C) aggregate demand
D) government policy
A) the natural rate of output
B) the price level
C) aggregate demand
D) government policy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
How is economic growth shown on a graph of a long-run aggregate supply (LRAS) curve?
A) Output moves to a higher point on the LRAS curve.
B) Output moves to a lower point on the LRAS curve.
C) The LRAS curve shifts up.
D) The LRAS curve shifts to the right.
A) Output moves to a higher point on the LRAS curve.
B) Output moves to a lower point on the LRAS curve.
C) The LRAS curve shifts up.
D) The LRAS curve shifts to the right.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following would NOT shift a nation's long-run aggregate supply curve?
A) Technology in the nation changes.
B) The level of human capital in the nation changes.
C) The level of investment in physical capital changes.
D) The nation's average price level changes.
A) Technology in the nation changes.
B) The level of human capital in the nation changes.
C) The level of investment in physical capital changes.
D) The nation's average price level changes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A nation's natural rate of output is the output level that occurs when:
A) there is no government policy interference.
B) the unemployment rate is zero.
C) the economy is at full employment.
D) only cyclical unemployment is present.
A) there is no government policy interference.
B) the unemployment rate is zero.
C) the economy is at full employment.
D) only cyclical unemployment is present.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following does NOT describe the natural rate of output?
A) It occurs when the economy is at full employment.
B) It is the output that exists when all wages and prices have adjusted.
C) It is the output level that is associated with the long-run aggregate supply curve.
D) It always occurs when no government policy impacts the economy.
A) It occurs when the economy is at full employment.
B) It is the output that exists when all wages and prices have adjusted.
C) It is the output level that is associated with the long-run aggregate supply curve.
D) It always occurs when no government policy impacts the economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
(Figure: LRAS0) In the figure, the economy is showing:
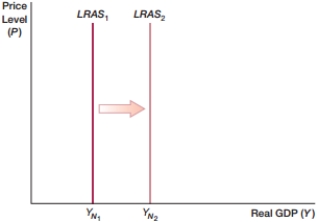
A) a recession.
B) inflation.
C) economic growth.
D) disinflation.

A) a recession.
B) inflation.
C) economic growth.
D) disinflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
(Figure: LRAS0) In the figure, what would NOT be a cause of the LRAS curve shifting rightward?
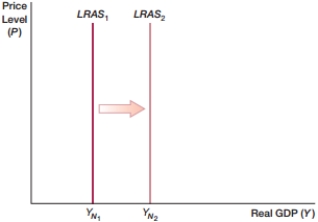
A) innovations and new technology
B) investments in physical capital
C) improvements in human capital
D) higher tax rates

A) innovations and new technology
B) investments in physical capital
C) improvements in human capital
D) higher tax rates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
When business cycles are analyzed, what part of the aggregate demand and aggregate supply model is assumed to be unchanging?
A) price level
B) aggregate demand curve
C) short-run aggregate supply curve
D) long-run aggregate supply curve
A) price level
B) aggregate demand curve
C) short-run aggregate supply curve
D) long-run aggregate supply curve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
What is the difference between the short-run aggregate supply curve and the long-run aggregate supply curve?
A) Output varies with the price level in the short run but is constant in the long run.
B) Output varies in the opposite direction of the price level in the short run but is constant in the long run.
C) Output does not have enough time to vary in the short run but varies with the price level in the long run.
D) Output does not have enough time to vary in the short run but has a negative relationship with the price level in the long run.
A) Output varies with the price level in the short run but is constant in the long run.
B) Output varies in the opposite direction of the price level in the short run but is constant in the long run.
C) Output does not have enough time to vary in the short run but varies with the price level in the long run.
D) Output does not have enough time to vary in the short run but has a negative relationship with the price level in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
(Figure: Curve) What does the figure represent?
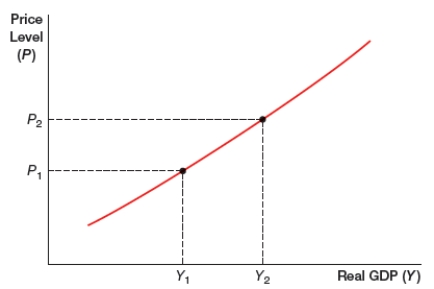
A) long-run aggregate demand curve
B) short-run aggregate demand curve
C) long-run aggregate supply curve
D) short-run aggregate supply curve

A) long-run aggregate demand curve
B) short-run aggregate demand curve
C) long-run aggregate supply curve
D) short-run aggregate supply curve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following is NOT a reason that the short-run aggregate supply curve has a positive slope?
A) sticky wages
B) money neutrality
C) sticky prices
D) the money illusion
A) sticky wages
B) money neutrality
C) sticky prices
D) the money illusion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
In the short run, when the average price level rises due to a shift in AD, total output:
A) varies unpredictably.
B) remains constant.
C) falls.
D) rises.
A) varies unpredictably.
B) remains constant.
C) falls.
D) rises.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
In the short run, what type of relationship exists between the average price level and the output level in an economy?
A) positive
B) negative
C) unchanging price regardless of output level
D) it depends on whether the price level change is caused by a supply shift or a demand shift
A) positive
B) negative
C) unchanging price regardless of output level
D) it depends on whether the price level change is caused by a supply shift or a demand shift

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A study of the frequency of price changes for commonly purchased items found that ____ products tend to change price frequently and that _____ product prices change less frequently.
A) laundromat; processed food
B) processed food; commodity
C) commodity; catalog
D) catalog; laundromat
A) laundromat; processed food
B) processed food; commodity
C) commodity; catalog
D) catalog; laundromat

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
What change occurs in the aggregate supply and aggregate demand model when the cost of doing business rises due to higher input costs?
A) The aggregate demand curve shifts right, and aggregate supply remains stable.
B) Aggregate demand remains stable, and short-run aggregate supply shifts left.
C) Aggregate demand remains stable, and short-run aggregate supply shifts right.
D) Aggregate demand remains stable, and both short-run aggregate supply and long-run aggregate supply shift right.
A) The aggregate demand curve shifts right, and aggregate supply remains stable.
B) Aggregate demand remains stable, and short-run aggregate supply shifts left.
C) Aggregate demand remains stable, and short-run aggregate supply shifts right.
D) Aggregate demand remains stable, and both short-run aggregate supply and long-run aggregate supply shift right.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
(Figure: Decrease in Short-Run Aggregate Supply) The figure shows a shift of a short-run aggregate supply curve to the left due to one or more of the following sources, EXCEPT:
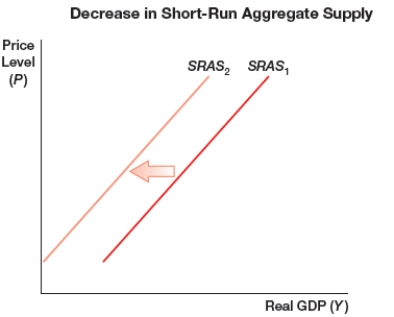
A) decreases in wages.
B) increase in rents.
C) increases in price of raw materials.
D) decrease in productivity.

A) decreases in wages.
B) increase in rents.
C) increases in price of raw materials.
D) decrease in productivity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
(Figure: Increase in Short-Run Aggregate Supply) The figure shows a shift of a short-run aggregate supply curve to the right due to one or more of the following sources, EXCEPT:
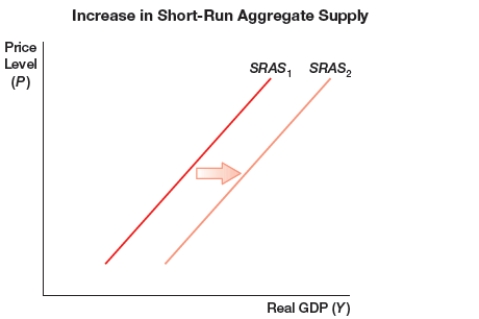
A) decreases in wages.
B) decrease in rents.
C) increase in price of raw materials.
D) increase in productivity.

A) decreases in wages.
B) decrease in rents.
C) increase in price of raw materials.
D) increase in productivity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following would NOT shift a country's short-run aggregate supply curve to the right?
A) lower nominal wages
B) higher productivity
C) lower input costs
D) higher inflation
A) lower nominal wages
B) higher productivity
C) lower input costs
D) higher inflation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
After an advance in technology that improves productivity, a country's short-run aggregate supply curve will:
A) shift to the right.
B) shift to the left.
C) rotate to a steeper slope.
D) rotate to a more horizontal slope.
A) shift to the right.
B) shift to the left.
C) rotate to a steeper slope.
D) rotate to a more horizontal slope.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
(Figure: SRAS0) In the figure, what will NOT cause the shift from SRAS1 to SRAS2?
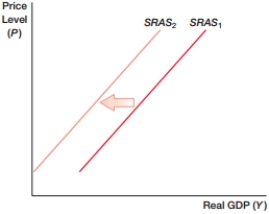
A) lower wages
B) higher raw material costs
C) lower productivity levels
D) All of the above could cause the shift.

A) lower wages
B) higher raw material costs
C) lower productivity levels
D) All of the above could cause the shift.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
(Figure: SRAS0) In the figure, what will NOT cause the shift from SRAS1 to SRAS2?
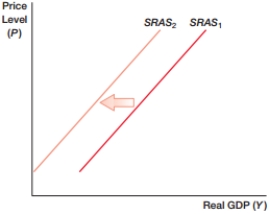
A) higher wages
B) higher raw material costs
C) improved productivity levels
D) All of the above could cause the shift.

A) higher wages
B) higher raw material costs
C) improved productivity levels
D) All of the above could cause the shift.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
(Figure: SRAS0) In the figure, what will cause the shift from SRAS1 to SRAS2?
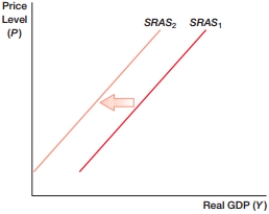
A) higher oil prices
B) lower wages
C) lower levels of government spending
D) increased personal income tax rates

A) higher oil prices
B) lower wages
C) lower levels of government spending
D) increased personal income tax rates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
(Figure: SRAS0) In the figure, what will cause the shift from SRAS1 to SRAS2?
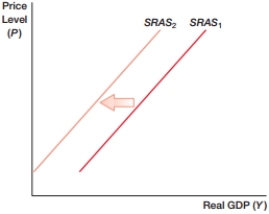
A) higher wages
B) improved productivity levels
C) lower levels of government spending
D) increased personal income tax rates

A) higher wages
B) improved productivity levels
C) lower levels of government spending
D) increased personal income tax rates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
(Figure: SRASA) In the figure, what will cause the shift from SRAS1 to SRAS2?
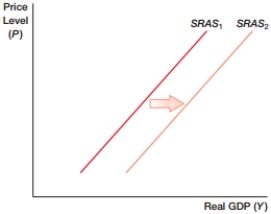
A) higher oil prices
B) lower wages
C) lower levels of government spending
D) increased personal income tax rates

A) higher oil prices
B) lower wages
C) lower levels of government spending
D) increased personal income tax rates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
(Figure: SRASA) In the figure, what will NOT cause the shift from SRAS1 to SRAS2?
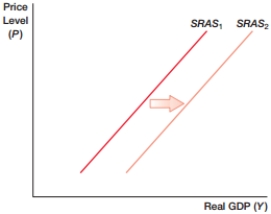
A) higher wages
B) lower raw material costs
C) improved productivity levels
D) All of the above could cause the shift.

A) higher wages
B) lower raw material costs
C) improved productivity levels
D) All of the above could cause the shift.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
(Figure: SRASA) In the figure, what will NOT cause the shift from SRAS1 to SRAS2?
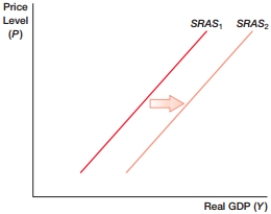
A) lower wages
B) lower raw material costs
C) lower productivity levels
D) All of the above could cause the shift.

A) lower wages
B) lower raw material costs
C) lower productivity levels
D) All of the above could cause the shift.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The Martinez household has $40,000 in savings to cover some upcoming expenses. As the average price level rises, their savings allow the Martinez family to make fewer purchases. Economists refer to this impact on the value of financial assets as the _____ effect.
A) real value
B) price level
C) money illusion
D) wealth
A) real value
B) price level
C) money illusion
D) wealth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
(Figure: Curve 0) What does the figure represent?
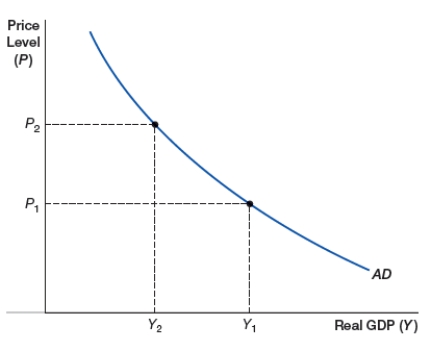
A) aggregate demand curve
B) demand curve
C) aggregate supply curve
D) supply curve

A) aggregate demand curve
B) demand curve
C) aggregate supply curve
D) supply curve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
In the context of aggregate demand, the interest rate effect means that an increase in the average price level will lead to _____ in interest rates and _____ in investment spending.
A) an increase; a decrease
B) an increase; an increase
C) a decrease; a decrease
D) a decrease; an increase
A) an increase; a decrease
B) an increase; an increase
C) a decrease; a decrease
D) a decrease; an increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
In the context of aggregate demand, the interest rate effect means that a decrease in the average price level will lead to _____ in interest rates and _____ in investment spending.
A) an increase; a decrease
B) an increase; an increase
C) a decrease; a decrease
D) a decrease; an increase
A) an increase; a decrease
B) an increase; an increase
C) a decrease; a decrease
D) a decrease; an increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which of the following is a difference between aggregate demand and the demand for a single product when price changes?
A) The wealth effect applies to demand for a single product but cannot affect aggregate demand because it includes all products.
B) The wealth effect applies to aggregate demand but not to demand for a single product because the purchasing power of money has no impact on individual product purchases.
C) The substitution effect applies to demand for a single product but cannot affect aggregate demand because aggregate demand includes all products.
D) The substitution effect applies to aggregate demand but not to demand for a single product because there is nothing to substitute when there is just one type of product.
A) The wealth effect applies to demand for a single product but cannot affect aggregate demand because it includes all products.
B) The wealth effect applies to aggregate demand but not to demand for a single product because the purchasing power of money has no impact on individual product purchases.
C) The substitution effect applies to demand for a single product but cannot affect aggregate demand because aggregate demand includes all products.
D) The substitution effect applies to aggregate demand but not to demand for a single product because there is nothing to substitute when there is just one type of product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
According to the net exports effect, along a given AD curve the average price level is _____ related to net exports.
A) inversely
B) directly
C) unpredictably
D) not
A) inversely
B) directly
C) unpredictably
D) not

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which of the following is NOT a reason for the negative slope of the aggregate demand curve?
A) net export effect
B) interest rate effect
C) expectations effect
D) wealth effect
A) net export effect
B) interest rate effect
C) expectations effect
D) wealth effect

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
A shift in an aggregate demand curve occurs when something causes:
A) the price level to change regardless of the spending level.
B) production to change at a given price level.
C) spending to change at a given price level.
D) spending to change in a direct relationship with the price level.
A) the price level to change regardless of the spending level.
B) production to change at a given price level.
C) spending to change at a given price level.
D) spending to change in a direct relationship with the price level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
(Figure: Decrease in Aggregate Demand) The figure shows a shift of aggregate demand curve to the left due to one or more of the following sources, EXCEPT:
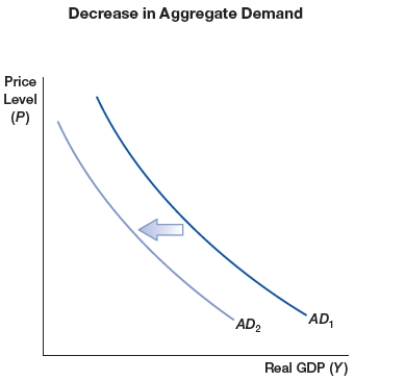
A) increase in taxes
B) decrease in money supply
C) decrease in government spending
D) optimistic expectations

A) increase in taxes
B) decrease in money supply
C) decrease in government spending
D) optimistic expectations

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
(Figure: Increase in Aggregate Demand) The figure shows a shift of aggregate demand curve to the right due to one or more of the following sources, EXCEPT:
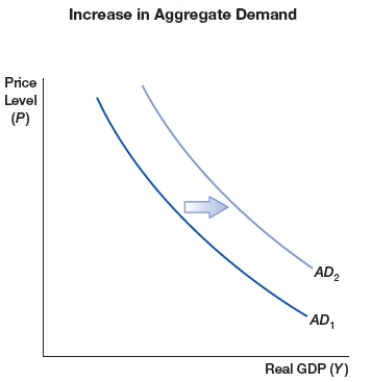
A) financial distress and uncertainty global stagnation
B) increase in money supply
C) increase in government spending
D) decrease in taxes

A) financial distress and uncertainty global stagnation
B) increase in money supply
C) increase in government spending
D) decrease in taxes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The aggregate demand curve has a slope that is:
A) horizontal.
B) vertical.
C) positive.
D) negative.
A) horizontal.
B) vertical.
C) positive.
D) negative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which of the following is NOT a reason for the negative relationship between the average price level and the total amount of goods that are purchased in an economy?
A) wealth effect
B) government purchase effect
C) net export effect
D) interest rate effect
A) wealth effect
B) government purchase effect
C) net export effect
D) interest rate effect

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which of the following would NOT cause the aggregate demand curve to shift?
A) Financial distress and uncertainty change.
B) Monetary policy changes.
C) Fiscal policy changes.
D) The average price level changes.
A) Financial distress and uncertainty change.
B) Monetary policy changes.
C) Fiscal policy changes.
D) The average price level changes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which of the following would NOT cause the aggregate demand curve to shift?
A) Expectations change.
B) Input costs change.
C) Financial distress and uncertainty change.
D) Monetary policy changes.
A) Expectations change.
B) Input costs change.
C) Financial distress and uncertainty change.
D) Monetary policy changes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which of the following would cause a nation's aggregate demand curve to shift to the right?
A) Reductions are made in government spending.
B) Global economic conditions deteriorate.
C) Higher levels of financial distress and uncertainty occur.
D) The money supply increases.
A) Reductions are made in government spending.
B) Global economic conditions deteriorate.
C) Higher levels of financial distress and uncertainty occur.
D) The money supply increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which of the following would cause aggregate demand to increase in a country's economy?
A) Pessimism and uncertainty about jobs and future income increase.
B) Taxes increase.
C) Real interest rates increase.
D) The value of the country's currency depreciates.
A) Pessimism and uncertainty about jobs and future income increase.
B) Taxes increase.
C) Real interest rates increase.
D) The value of the country's currency depreciates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which of the following would cause aggregate demand to decrease in a country's economy?
A) The sense of future income decreases.
B) Improvements are observed in the economic conditions in other countries.
C) Tax decreases are passed.
D) The value of the country's currency depreciates.
A) The sense of future income decreases.
B) Improvements are observed in the economic conditions in other countries.
C) Tax decreases are passed.
D) The value of the country's currency depreciates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which of the following would NOT cause the aggregate demand curve to shift?
A) Fiscal policy changes.
B) Global economic conditions change.
C) Input prices change.
D) Expectations change.
A) Fiscal policy changes.
B) Global economic conditions change.
C) Input prices change.
D) Expectations change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which of the following did NOT contribute to the falling aggregate demand that triggered the Great Depression in the United States?
A) Interest rates fell due to expansionary monetary policy.
B) Taxes were increased.
C) Consumers and businesses were pessimistic after the 1929 stock market crash.
D) Thousands of banks failed, causing many to lose their life's savings.
A) Interest rates fell due to expansionary monetary policy.
B) Taxes were increased.
C) Consumers and businesses were pessimistic after the 1929 stock market crash.
D) Thousands of banks failed, causing many to lose their life's savings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
When the average price level of a country rises, which of the following would NOT cause a drop in the total amount of the country's goods and services that would be purchased?
A) The money that people hold will have less purchasing power than it had before the price level changed.
B) A higher price level causes interest rates to rise, which causes purchases to fall for the kinds of items that typically are bought on credit.
C) When the price level rises in country A but not in country B, citizens of country B will be less likely to import products from country A, leading to a reduction in country A's net exports.
D) The higher price level leads to higher wages, which raise the costs of production for firms.
A) The money that people hold will have less purchasing power than it had before the price level changed.
B) A higher price level causes interest rates to rise, which causes purchases to fall for the kinds of items that typically are bought on credit.
C) When the price level rises in country A but not in country B, citizens of country B will be less likely to import products from country A, leading to a reduction in country A's net exports.
D) The higher price level leads to higher wages, which raise the costs of production for firms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Why was the 2007 to 2009 recession in the United States not classified as a depression?
A) Although unemployment was high, output also was high, so the event did not meet the criteria for a depression.
B) Prices were falling in 2007 to 2009, but inflation must be present for the classification of depression.
C) From 2007 to 2009, the number of jobs rose even though the unemployment rate rose.
D) The decrease in output and increase in unemployment were not severe enough to warrant the classification.
A) Although unemployment was high, output also was high, so the event did not meet the criteria for a depression.
B) Prices were falling in 2007 to 2009, but inflation must be present for the classification of depression.
C) From 2007 to 2009, the number of jobs rose even though the unemployment rate rose.
D) The decrease in output and increase in unemployment were not severe enough to warrant the classification.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
In the United States, both the Great Depression of the 1930s and the Great Recession of 2007 to 2009 were triggered by a:
A) fall in aggregate demand.
B) fall in short-run aggregate supply.
C) rise in the average price level.
D) rise in long-run aggregate supply but not short-run aggregate supply.
A) fall in aggregate demand.
B) fall in short-run aggregate supply.
C) rise in the average price level.
D) rise in long-run aggregate supply but not short-run aggregate supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Which of the following would cause a recession?
A) The long-run aggregate supply curve shifts rightward.
B) The aggregate demand curve shifts rightward.
C) The short-run aggregate supply curve shifts leftward.
D) The price level increases.
A) The long-run aggregate supply curve shifts rightward.
B) The aggregate demand curve shifts rightward.
C) The short-run aggregate supply curve shifts leftward.
D) The price level increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
(Figure: Decline in Aggregate Demand) The figure shows a decline in aggregate demand. A possible effect of this would be:
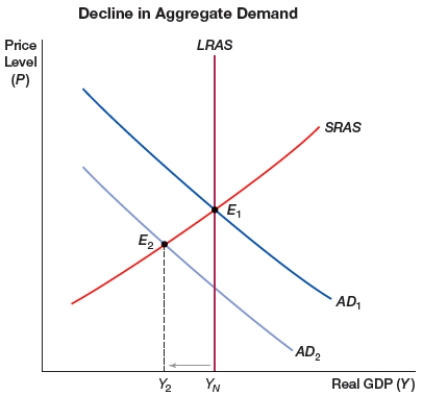
A) an increase in long-run aggregate supply
B) an inflation
C) a recession
D) an increase in price level

A) an increase in long-run aggregate supply
B) an inflation
C) a recession
D) an increase in price level

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
(Figure: Decline in Aggregate Supply) The figure shows a decline in aggregate supply. A possible effect of this would be:
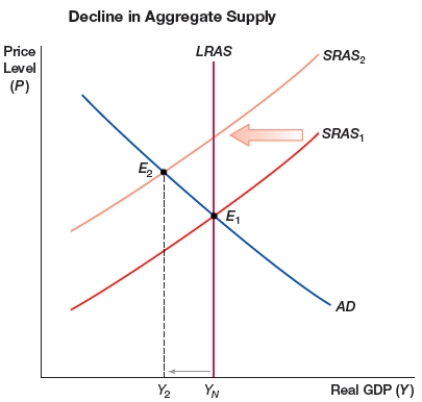
A) a recession
B) an increase in real GDP
C) a boom
D) a decrease in price level

A) a recession
B) an increase in real GDP
C) a boom
D) a decrease in price level

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Which of the following would cause a recession?
A) The aggregate demand curve shifts leftward.
B) The short-run aggregate supply curve shifts rightward.
C) The aggregate demand curve shifts rightward.
D) The long-run aggregate supply curve shifts leftward.
A) The aggregate demand curve shifts leftward.
B) The short-run aggregate supply curve shifts rightward.
C) The aggregate demand curve shifts rightward.
D) The long-run aggregate supply curve shifts leftward.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
What happens in an economy when aggregate demand decreases?
A) The price level rises, output rises, and an expansion occurs.
B) The price level rises, output falls, and a recession occurs.
C) The price level falls, output rises, and an expansion occurs.
D) The price level falls, output falls, and a recession occurs.
A) The price level rises, output rises, and an expansion occurs.
B) The price level rises, output falls, and a recession occurs.
C) The price level falls, output rises, and an expansion occurs.
D) The price level falls, output falls, and a recession occurs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
What happens in an economy when short-run aggregate supply decreases?
A) The price level rises, output rises, and an expansion occurs.
B) The price level rises, output falls, and a recession occurs.
C) The price level falls, output rises, and an expansion occurs.
D) The price level falls, output falls, and a recession occurs.
A) The price level rises, output rises, and an expansion occurs.
B) The price level rises, output falls, and a recession occurs.
C) The price level falls, output rises, and an expansion occurs.
D) The price level falls, output falls, and a recession occurs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
On the aggregate demand/aggregate supply graph, an economy operates at the intersection of:
A) AD and LRAS.
B) SRAD and SRAS.
C) SRAD and LRAS.
D) AD and SRAS.
A) AD and LRAS.
B) SRAD and SRAS.
C) SRAD and LRAS.
D) AD and SRAS.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
If a country's aggregate demand falls, output _____, and the price level:
A) rises; rises.
B) rises; falls.
C) falls; rises.
D) falls; falls.
A) rises; rises.
B) rises; falls.
C) falls; rises.
D) falls; falls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
If a country's short-run aggregate supply falls, output _____, and the price level:
A) rises: rises.
B) rises; falls.
C) falls; rises.
D) falls; falls.
A) rises: rises.
B) rises; falls.
C) falls; rises.
D) falls; falls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
If a country's aggregate demand rises, output _____, and the price level:
A) rises; rises.
B) rises; falls.
C) falls; rises.
D) falls; falls.
A) rises; rises.
B) rises; falls.
C) falls; rises.
D) falls; falls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
If a country's short-run aggregate supply increases, output _____, and the price level:
A) rises; rises.
B) rises; falls.
C) falls; rises.
D) falls; falls.
A) rises; rises.
B) rises; falls.
C) falls; rises.
D) falls; falls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Which of the following would cause inflation?
A) The short-run aggregate supply curve shifts rightward.
B) The long-run aggregate supply curve shifts rightward.
C) The aggregate demand curve shifts rightward.
D) The aggregate demand curve shifts leftward.
A) The short-run aggregate supply curve shifts rightward.
B) The long-run aggregate supply curve shifts rightward.
C) The aggregate demand curve shifts rightward.
D) The aggregate demand curve shifts leftward.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Which of the following would cause inflation?
A) The short-run aggregate supply curve shifts leftward.
B) The long-run aggregate supply curve shifts rightward.
C) The aggregate demand curve shifts leftward.
D) The short-run aggregate supply curve shifts rightward.
A) The short-run aggregate supply curve shifts leftward.
B) The long-run aggregate supply curve shifts rightward.
C) The aggregate demand curve shifts leftward.
D) The short-run aggregate supply curve shifts rightward.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
According to the aggregate supply and aggregate demand model, inflation is caused when the short-run aggregate supply _____ or the aggregate demand:
A) decreases; decreases.
B) decreases; increases.
C) increases; decreases.
D) increases; increases.
A) decreases; decreases.
B) decreases; increases.
C) increases; decreases.
D) increases; increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Cost-push inflation is caused by:
A) an increase in aggregate demand.
B) an increase in short-run aggregate supply.
C) a decrease in aggregate demand.
D) a decrease in short-run aggregate supply.
A) an increase in aggregate demand.
B) an increase in short-run aggregate supply.
C) a decrease in aggregate demand.
D) a decrease in short-run aggregate supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Demand-pull inflation is caused by:
A) an increase in aggregate demand.
B) an increase in short-run aggregate supply.
C) a decrease in aggregate demand.
D) a decrease in short-run aggregate supply.
A) an increase in aggregate demand.
B) an increase in short-run aggregate supply.
C) a decrease in aggregate demand.
D) a decrease in short-run aggregate supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Which of the following is something that could cause cost-push inflation?
A) An epidemic increases the need for medical care, pushing up the price level.
B) A reduction in consumer spending due to consumer pessimism reduces demand.
C) A reduction in regulation causes a surge in business activity.
D) An increase in the price of oil raises the transportation and energy expenses of producers.
A) An epidemic increases the need for medical care, pushing up the price level.
B) A reduction in consumer spending due to consumer pessimism reduces demand.
C) A reduction in regulation causes a surge in business activity.
D) An increase in the price of oil raises the transportation and energy expenses of producers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
After an increase in consumer confidence leads to a rise in consumer purchases, there is:
A) an increase in unemployment.
B) an increase in the money supply.
C) cost-push inflation.
D) demand-pull inflation.
A) an increase in unemployment.
B) an increase in the money supply.
C) cost-push inflation.
D) demand-pull inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Which of the following are associated with cost-push inflation?
A) Aggregate demand increases.
B) Aggregate demand decreases.
C) Long-run aggregate supply increases.
D) Short-run aggregate supply decreases.
A) Aggregate demand increases.
B) Aggregate demand decreases.
C) Long-run aggregate supply increases.
D) Short-run aggregate supply decreases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Which of the following might cause demand-pull inflation?
A) Higher demand for exports.
B) The price of labor increases.
C) Government purchases decrease.
D) Wage rates decrease.
A) Higher demand for exports.
B) The price of labor increases.
C) Government purchases decrease.
D) Wage rates decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



