Deck 25: Money and the Price Level in the Long Run
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/105
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 25: Money and the Price Level in the Long Run
1
The view that inflation is caused by excessive growth in the money supply is known as the _____ school of economic thought.
A) inflationary
B) Keynesian
C) monetarist
D) reserve
A) inflationary
B) Keynesian
C) monetarist
D) reserve
C
2
The monetarist school of thought is also referred to as the _____ theory of money.
A) quantity
B) money
C) open market
D) fractional reserve
A) quantity
B) money
C) open market
D) fractional reserve
A
3
The theory that a given change in the money supply leads to a proportional change in the price level in the long run is known as the:
A) equation of money theory.
B) quantity theory of money.
C) M1 theory.
D) money supply theory.
A) equation of money theory.
B) quantity theory of money.
C) M1 theory.
D) money supply theory.
B
4
Markus believes that in the long run, the average price level will increase at a rate that is consistent with the rate of increase in the money supply. Economists would say that Markus believes in the:
A) equation theory of money.
B) proportional monetary price theory.
C) money supply theory.
D) quantity theory of money.
A) equation theory of money.
B) proportional monetary price theory.
C) money supply theory.
D) quantity theory of money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
What is the time frame of focus in the quantity theory of money?
A) short run
B) less than one year
C) long run
D) more than one year
A) short run
B) less than one year
C) long run
D) more than one year

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
According to the quantity theory of money, increases in the money supply lead to _____, which can cause:
A) increased production; higher productivity.
B) excess cash balances; increased spending.
C) excess cash balances; increased production.
D) increased production; excess cash balances.
A) increased production; higher productivity.
B) excess cash balances; increased spending.
C) excess cash balances; increased production.
D) increased production; excess cash balances.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
According to the quantity theory of money, what is the three-stage chain of events that occurs after an increase in the money supply?
A) increased saving, investment in capital, higher productivity
B) increase spending, higher prices, increased saving
C) higher prices, excess cash balances, higher productivity
D) excess cash balances, increased spending, higher prices
A) increased saving, investment in capital, higher productivity
B) increase spending, higher prices, increased saving
C) higher prices, excess cash balances, higher productivity
D) excess cash balances, increased spending, higher prices

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
According to the quantity theory of money, in the long run, changes in the money supply affect:
A) the purchasing power of money.
B) output.
C) employment.
D) the money illusion.
A) the purchasing power of money.
B) output.
C) employment.
D) the money illusion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
According to the quantity theory of money, in the long run, changes in the money supply affect ____ GDP but not _____ GDP.
A) nominal; per capita
B) per capita; nominal
C) real; nominal
D) nominal; real
A) nominal; per capita
B) per capita; nominal
C) real; nominal
D) nominal; real

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
When considering money supply and money demand, the price of money is measured:
A) through the value set by central bankers.
B) through the average wage rate.
C) by its purchasing power.
D) by its productivity.
A) through the value set by central bankers.
B) through the average wage rate.
C) by its purchasing power.
D) by its productivity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
An increase in the price level will cause _____ in the value of money.
A) an increase
B) a decrease
C) a rotation
D) a reversal
A) an increase
B) a decrease
C) a rotation
D) a reversal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A higher value of money is associated with a _____ average price level for goods and services.
A) higher
B) lower
C) reversing
D) revolving
A) higher
B) lower
C) reversing
D) revolving

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A lower value of money is associated with a _____ average price level for goods and services.
A) higher
B) lower
C) reversing
D) revolving
A) higher
B) lower
C) reversing
D) revolving

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The value of money is calculated as:
A) M1 × Price level.
B) Price level / Money supply.
C) 1 / Price level.
D) Interest rate / Price level.
A) M1 × Price level.
B) Price level / Money supply.
C) 1 / Price level.
D) Interest rate / Price level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
In the long-run money supply and money demand model, the slope of the money demand curve is _____, and the slope of the money supply curve is:
A) upward sloping; downward sloping.
B) downward sloping; upward sloping.
C) vertical; upward sloping.
D) downward sloping; vertical.
A) upward sloping; downward sloping.
B) downward sloping; upward sloping.
C) vertical; upward sloping.
D) downward sloping; vertical.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
According to the quantity theory of money, central banks _____ the real value of the public's total money balances.
A) determine any change in
B) sometimes by chance change
C) cannot change
D) choose whether to change
A) determine any change in
B) sometimes by chance change
C) cannot change
D) choose whether to change

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The graph shows the long-run money supply and money demand model. Increases in the money supply result in a proportional _____ in the value of money and a(n) _____ in the price level. 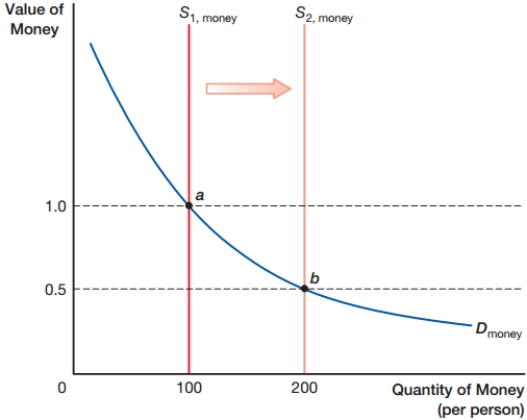
A) increase; increase
B) decline; increase
C) decline; decline
D) increase; decline

A) increase; increase
B) decline; increase
C) decline; decline
D) increase; decline

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The graph shows the long-run money supply and money demand model. The value of money is estimated as: 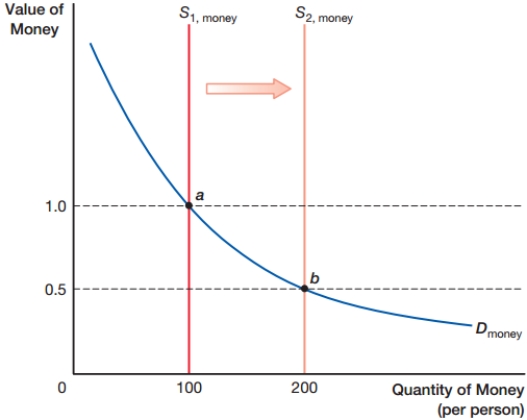
A) 1 - price level
B) 1 + price level
C) price level
D) 1 ÷ price level

A) 1 - price level
B) 1 + price level
C) price level
D) 1 ÷ price level

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following is a correct description of the money supply and money demand model?
A) The demand curve has a negative slope, and the supply curve is vertical.
B) The demand curve has a negative slope, and the supply curve is horizontal.
C) The demand curve is horizontal, and the supply curve has an upward slope.
D) The demand curve is vertical, and the supply curve has an upward slope.
A) The demand curve has a negative slope, and the supply curve is vertical.
B) The demand curve has a negative slope, and the supply curve is horizontal.
C) The demand curve is horizontal, and the supply curve has an upward slope.
D) The demand curve is vertical, and the supply curve has an upward slope.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
In 2010, the average price level in Macroland is 130, and in 2015, the price level rises to 162. During the same time period, Inga's salary rises from $70,000 to $85,000. Over this time period, the purchasing power of Inga's income:
A) fell by 3.2%.
B) rose by 21.4%.
C) fell by 9.4%.
D) rose by 24.6%.
A) fell by 3.2%.
B) rose by 21.4%.
C) fell by 9.4%.
D) rose by 24.6%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The real value of money is:
A) its foreign exchange rate.
B) its purchasing power.
C) set by the government that creates the money.
D) determined by the material out of which the money is made.
A) its foreign exchange rate.
B) its purchasing power.
C) set by the government that creates the money.
D) determined by the material out of which the money is made.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Monetary neutrality means that money:
A) has no impact on real variables such as national output.
B) is not used to gain advantages or support particular participants in wars.
C) supply cannot be increased or decreased but will remain constant.
D) the price level is not an indicator of the strength and health of an economy.
A) has no impact on real variables such as national output.
B) is not used to gain advantages or support particular participants in wars.
C) supply cannot be increased or decreased but will remain constant.
D) the price level is not an indicator of the strength and health of an economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Nelson's father tells him, "Regardless of how much money you have, you cannot buy more goods unless there are more goods available for purchase." This advice is consistent with what economic concept?
A) money demand
B) the Fisher effect
C) the neutrality of money
D) the gold standard
A) money demand
B) the Fisher effect
C) the neutrality of money
D) the gold standard

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Extremely rapid increases in the average price level are known as:
A) the money illusion.
B) megaflation.
C) deflation.
D) hyperinflation.
A) the money illusion.
B) megaflation.
C) deflation.
D) hyperinflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which statement is NOT consistent with monetary neutrality?
A) It is most applicable to long-run situations.
B) The amount of money has no effect on the economy.
C) Changes in the money supply will change the price level.
D) Output is not affected by the money supply in the long run.
A) It is most applicable to long-run situations.
B) The amount of money has no effect on the economy.
C) Changes in the money supply will change the price level.
D) Output is not affected by the money supply in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The situation of extremely rapid increases in the average price level of a country is called:
A) mega-inflation.
B) deflation.
C) hyperinflation.
D) acceleration
A) mega-inflation.
B) deflation.
C) hyperinflation.
D) acceleration

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
According to the classical dichotomy, real variables are determined by _____, and nominal variables are determined by:
A) resources and technology; monetary policy.
B) monetary policy; resources and technology.
C) supply and demand; production.
D) production; supply and demand.
A) resources and technology; monetary policy.
B) monetary policy; resources and technology.
C) supply and demand; production.
D) production; supply and demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Why did Germany experience hyperinflation after World War I?
A) The supply of output was extremely limited due to capital destroyed during the war.
B) After the war, consumers spent heavily due to demand that had been building during the war.
C) The flood of foreign aid increased spending in the country.
D) To pay off war debts, the government increased the money supply.
A) The supply of output was extremely limited due to capital destroyed during the war.
B) After the war, consumers spent heavily due to demand that had been building during the war.
C) The flood of foreign aid increased spending in the country.
D) To pay off war debts, the government increased the money supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The classical dichotomy divides macroeconomics into the study of _____ and:
A) real variables; nominal variables.
B) employment issues; price issues.
C) money supply; money demand.
D) production issues; spending issues.
A) real variables; nominal variables.
B) employment issues; price issues.
C) money supply; money demand.
D) production issues; spending issues.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Monetary policy affects _____ but does NOT affect:
A) nominal variables; short-run business cycles.
B) real GDP in the long-run; short-run business cycles.
C) real GDP in the long-run; nominal variables.
D) short-run business cycles; real GDP in the long-run.
A) nominal variables; short-run business cycles.
B) real GDP in the long-run; short-run business cycles.
C) real GDP in the long-run; nominal variables.
D) short-run business cycles; real GDP in the long-run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which is NOT true of the classical dichotomy?
A) Monetary policy affects nominal variables.
B) Monetary policy impacts short-run business cycles.
C) Monetary policy has no impact on long-run real GDP.
D) Monetary policy affects output but not prices.
A) Monetary policy affects nominal variables.
B) Monetary policy impacts short-run business cycles.
C) Monetary policy has no impact on long-run real GDP.
D) Monetary policy affects output but not prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The Venn diagram shows real variables versus nominal variables, where both nominal and real variables play roles in the business cycle. All the following are examples of real variables, EXCEPT: 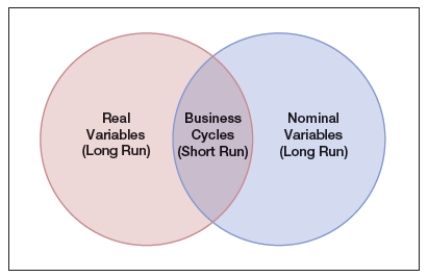
A) inflation.
B) innovation and new technology.
C) investments in physical capital.
D) improvements in human capital.

A) inflation.
B) innovation and new technology.
C) investments in physical capital.
D) improvements in human capital.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The Venn diagram shows real variables versus nominal variables, where both nominal and real variables play roles in the business cycle. All the following are examples of nominal variables, EXCEPT: 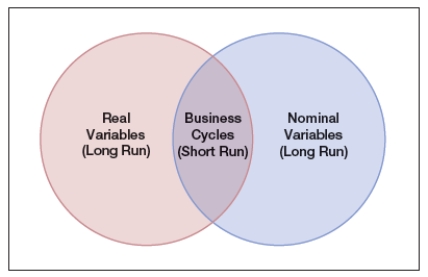
A) inflation.
B) deflation
C) innovation
D) GDP

A) inflation.
B) deflation
C) innovation
D) GDP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
(Table 1: Econia's Consumer Price Index and Salary Data, 2008 and 2018) Table 1 provides data on Econia's Consumer Price Index (CPI) and average salaries for two years. A newspaper headline states "Well-being of Econia's workers doubles over decade." Was this headline correct?
A) Yes; average salary doubled.
B) Yes; average salary rose twice as fast as the price level.
C) No; salaries adjusted for the price level did not double.
D) No; real salaries rose twice as fast as prices.
A) Yes; average salary doubled.
B) Yes; average salary rose twice as fast as the price level.
C) No; salaries adjusted for the price level did not double.
D) No; real salaries rose twice as fast as prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
(Table 1: Econia's Consumer Price Index and Salary Data, 2008 and 2018) Table 1 provides data on Econia's Consumer Price Index (CPI) and average salaries for two years. Junko says that Econia's workers are twice as prosperous as they were before, but Marko disagrees. Who is suffering from the money illusion and why?
A) Junko is suffering from the money illusion because she is considering only nominal values and not real values.
B) Junko is suffering from the money illusion because she should focus only on the CPI and not on salaries to make the determination.
C) Marko is suffering from the money illusion because he is focused only on the CPI and not on salaries.
D) Marko is suffering from the money illusion because he is considering real values rather than nominal values.
A) Junko is suffering from the money illusion because she is considering only nominal values and not real values.
B) Junko is suffering from the money illusion because she should focus only on the CPI and not on salaries to make the determination.
C) Marko is suffering from the money illusion because he is focused only on the CPI and not on salaries.
D) Marko is suffering from the money illusion because he is considering real values rather than nominal values.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
(Table 2: Income and Consumer Price Index Data for Four Cities, 2008 and 2018) Table 2 provides income and Consumer Price Index (CPI) data for four cities for two years. Citizens of which city would be suffering from the money illusion if they claimed that they were better-off financially in 2018?
A) city A
B) city B
C) city C
D) city D
A) city A
B) city B
C) city C
D) city D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
People who are subject to the money illusion focus on:
A) output rather than price variables.
B) price rather than output variables.
C) nominal rather than real variables.
D) real rather than nominal variables.
A) output rather than price variables.
B) price rather than output variables.
C) nominal rather than real variables.
D) real rather than nominal variables.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The table shows how the salary of an individual will increase after 40 years and how price level will increase for the same period. What will be the real income x for the individual in 2060?
A) $90,000
B) $60,000
C) $540,000
D) $150,000
A) $90,000
B) $60,000
C) $540,000
D) $150,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
(Table 3: Average Hourly Wages in Four Companies, 2017 and 2018) Table 3 provides the average hourly wage paid by each of four companies for two years. The inflation rate during 2018 was 3%. Workers at which company are suffering from the money illusion if they think that they are better off financially in 2018 than they were in 2017?
A) company A
B) company B
C) company C
D) company D
A) company A
B) company B
C) company C
D) company D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
What is currency reform?
A) the adoption of a new currency by a country
B) a change in the denominations of currency that are available in a country
C) a change in the money supply in a country
D) the switch from using currency to having a cashless money system
A) the adoption of a new currency by a country
B) a change in the denominations of currency that are available in a country
C) a change in the money supply in a country
D) the switch from using currency to having a cashless money system

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
When a country replaces its currency with another currency, the country is employing:
A) exchange rate reform.
B) currency adoption transfer.
C) monetary adoption.
D) currency reform.
A) exchange rate reform.
B) currency adoption transfer.
C) monetary adoption.
D) currency reform.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
In most cases, the main reason that a country engages in currency reform is to:
A) gain greater control over the money supply.
B) eliminate the money illusion.
C) replace a currency that has been devalued by years of high inflation.
D) increase the interest rate after years of low returns.
A) gain greater control over the money supply.
B) eliminate the money illusion.
C) replace a currency that has been devalued by years of high inflation.
D) increase the interest rate after years of low returns.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
In 2002, what major currency reform occurred in the world?
A) China adopted the yen as its currency.
B) Many European countries adopted the euro as currency.
C) All European countries adopted the euro as currency.
D) China adopted the rupiah as its new currency.
A) China adopted the yen as its currency.
B) Many European countries adopted the euro as currency.
C) All European countries adopted the euro as currency.
D) China adopted the rupiah as its new currency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The velocity of money is:
A) the speed at which people save money.
B) the speed at which prices rise and cause a need for more money.
C) the average number of times that a unit of money is spent on final goods and services in a year.
D) the speed at which the central bank increases the money supply during a year.
A) the speed at which people save money.
B) the speed at which prices rise and cause a need for more money.
C) the average number of times that a unit of money is spent on final goods and services in a year.
D) the speed at which the central bank increases the money supply during a year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
What two formulas both represent the equation of exchange?
A) M × V = GDPnominal; P × Yreal GDP = Pillusion × Ynominal
B) M × V = GDPnominal; M × V = P × Yreal GDP
C) P × Yreal GDP = Pillusion × Ynominal; M × V = P × Yreal GDP
D) M × V = P × Yreal GDP; GDPnominal = Pillusion × Ynominal
A) M × V = GDPnominal; P × Yreal GDP = Pillusion × Ynominal
B) M × V = GDPnominal; M × V = P × Yreal GDP
C) P × Yreal GDP = Pillusion × Ynominal; M × V = P × Yreal GDP
D) M × V = P × Yreal GDP; GDPnominal = Pillusion × Ynominal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The equation of exchange shows the relationship between:
A) prices, output, the money supply, and illusion.
B) money neutrality, output, and velocity.
C) the money supply, velocity, and nominal GDP.
D) the money supply and money demand.
A) prices, output, the money supply, and illusion.
B) money neutrality, output, and velocity.
C) the money supply, velocity, and nominal GDP.
D) the money supply and money demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The equation of exchange indicates that if velocity is steady, then a rising money supply will cause:
A) per capita GDP to rise.
B) real GDP to fall.
C) nominal GDP to fall.
D) nominal GDP to rise.
A) per capita GDP to rise.
B) real GDP to fall.
C) nominal GDP to fall.
D) nominal GDP to rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The equation of exchange indicates that if velocity is steady, then a decreasing money supply will cause:
A) per capita GDP to fall.
B) real GDP to rise.
C) nominal GDP to fall.
D) nominal GDP to rise.
A) per capita GDP to fall.
B) real GDP to rise.
C) nominal GDP to fall.
D) nominal GDP to rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The formula to compute the velocity of money is:
A) (P × Yreal GDP) / M.
B) real GDP / M.
C) M × Yreal GDP / P.
D) P / M × Yreal GDP.
A) (P × Yreal GDP) / M.
B) real GDP / M.
C) M × Yreal GDP / P.
D) P / M × Yreal GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The velocity of money is estimated by:
A) multiplying the money supply by the price level.
B) dividing the money supply by nominal GDP.
C) multiplying the money supply by real GDP and then dividing the product by the price level.
D) dividing nominal GDP by the money supply.
A) multiplying the money supply by the price level.
B) dividing the money supply by nominal GDP.
C) multiplying the money supply by real GDP and then dividing the product by the price level.
D) dividing nominal GDP by the money supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
If velocity is relatively stable, then changes in the money supply:
A) relate negatively to changes in real GDP.
B) cause negatively related changes in nominal GDP.
C) relate positively to changes in nominal GDP.
D) cause positively related changes in illusion neutrality.
A) relate negatively to changes in real GDP.
B) cause negatively related changes in nominal GDP.
C) relate positively to changes in nominal GDP.
D) cause positively related changes in illusion neutrality.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The average number of times that a unit of currency is spent on final goods and services in a year is called the:
A) variation in the interest rate.
B) price level in the economy.
C) velocity of money.
D) value of the annual output.
A) variation in the interest rate.
B) price level in the economy.
C) velocity of money.
D) value of the annual output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The equation of exchange emphasizes the connection between changes in:
A) taxes and changes in inflation and/or output.
B) government purchases and changes in inflation and/or output.
C) interest rates and changes in a nation's inflation and/or unemployment.
D) the money supply and changes in inflation and/or output.
A) taxes and changes in inflation and/or output.
B) government purchases and changes in inflation and/or output.
C) interest rates and changes in a nation's inflation and/or unemployment.
D) the money supply and changes in inflation and/or output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which of the following reflects the basic concept of the equation of exchange?
A) MV = PY
B) Change in equilibrium real GDP = Change in autonomous spending × 1/(1 - MPC)
C) Potential change in M1 = Change in excess reserves × (1/r)
D) Unemployment rate = Number of unemployed / Number in labor force
A) MV = PY
B) Change in equilibrium real GDP = Change in autonomous spending × 1/(1 - MPC)
C) Potential change in M1 = Change in excess reserves × (1/r)
D) Unemployment rate = Number of unemployed / Number in labor force

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
According to U.S. data for the past sixty years, money supply growth is:
A) positively related to growth in velocity.
B) negatively related to growth in velocity.
C) positively related to growth in nominal GDP.
D) negatively related to growth in nominal GDP.
A) positively related to growth in velocity.
B) negatively related to growth in velocity.
C) positively related to growth in nominal GDP.
D) negatively related to growth in nominal GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The equation of exchange indicates that if a decrease in the money supply does not impact velocity or real GDP, then it must:
A) cause currency reform to accelerate.
B) cause currency reform to decelerate.
C) lead to a decrease in the price level.
D) lead to an increase in the price level.
A) cause currency reform to accelerate.
B) cause currency reform to decelerate.
C) lead to a decrease in the price level.
D) lead to an increase in the price level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Over the past year, Macroland's economy experienced several changes. Money supply grew by 3%, velocity grew by 1%, real GDP grew by 2%, and employment grew by 1.5%. According to the equation of exchange, what inflation rate would be expected in Macroland for this time period?
A) 2%
B) 2.5%
C) 0%
D) 6%
A) 2%
B) 2.5%
C) 0%
D) 6%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Over the past year, Macroland's economy experienced several changes. Money supply grew by 3%, velocity grew by 1%, real GDP grew by 2%, and employment grew by 1.5%. According to the equation of exchange, what growth rate in nominal GDP would be expected in Macroland for this time period?
A) 2%
B) 4%
C) 0%
D) 6%
A) 2%
B) 4%
C) 0%
D) 6%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Over the past year, Macroland's economy experienced several changes. Money supply grew by 2.5%, velocity grew by 0.5%, real GDP grew by 2%, and employment grew by 1%. According to the equation of exchange, what inflation rate would be expected in Macroland for this time period?
A) 0.%
B) 1.5%
C) 1%
D) 3%
A) 0.%
B) 1.5%
C) 1%
D) 3%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Over the past year, Macroland's economy experienced several changes. Money supply grew by 2.5%, velocity grew by 0.5%, real GDP grew by 2%, and employment grew by 1%. According to the equation of exchange, what growth rate in nominal GDP would be expected in Macroland for this time period?
A) 0%
B) 1.5%
C) 1%
D) 3%
A) 0%
B) 1.5%
C) 1%
D) 3%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The quantity theory of money seems to be most consistent when growth in the money supply is _____ and the time period is _____.
A) small; long
B) small; short
C) large; long
D) large; short
A) small; long
B) small; short
C) large; long
D) large; short

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Evidence from many countries during the last half of the twentieth century shows a _____ relationship between money supply growth and:
A) positive; inflation.
B) negative; inflation.
C) positive; GDP growth.
D) negative; GDP growth.
A) positive; inflation.
B) negative; inflation.
C) positive; GDP growth.
D) negative; GDP growth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The time period known as the great inflation shows that the relationship between money supply growth and inflation seems to be _____ in countries with _____ inflation.
A) stronger; higher
B) stronger; lower
C) weaker; more variable
D) more inconsistent; stronger
A) stronger; higher
B) stronger; lower
C) weaker; more variable
D) more inconsistent; stronger

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Country data from the time period known as the great inflation indicate that when a country has high rates of growth in output, then changes in the money supply have:
A) a stronger impact on inflation.
B) less impact on inflation.
C) less impact on velocity.
D) more impact on velocity.
A) a stronger impact on inflation.
B) less impact on inflation.
C) less impact on velocity.
D) more impact on velocity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The Fisher equation is:
A) Nominal GDP growth rate = Real GDP growth rate + inflation rate.
B) MV = PY.
C) V = Nominal GDP / M.
D) Real interest rate = Nominal interest rate - inflation rate.
A) Nominal GDP growth rate = Real GDP growth rate + inflation rate.
B) MV = PY.
C) V = Nominal GDP / M.
D) Real interest rate = Nominal interest rate - inflation rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
What insight about negative interest rates is clear from the Fisher equation?
A) Negative real interest rates are most likely to occur when the inflation rate is low.
B) Negative nominal interest rates are most likely to occur when the inflation rate is low.
C) Negative real interest rates are more likely to occur than negative nominal interest rates.
D) Negative nominal interest rates are more likely to occur than negative real interest rates.
A) Negative real interest rates are most likely to occur when the inflation rate is low.
B) Negative nominal interest rates are most likely to occur when the inflation rate is low.
C) Negative real interest rates are more likely to occur than negative nominal interest rates.
D) Negative nominal interest rates are more likely to occur than negative real interest rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The following data are for Macroland during 2010. The nominal GDP was $13.8 billion, the inflation rate was 3%, the nominal interest rate was 5.5%, and the nominal GDP growth rate was 1.5%. What was Macroland's real interest rate during 2010?
A) 8.5%
B) 2.5%
C) 4%
D) 4.5%
A) 8.5%
B) 2.5%
C) 4%
D) 4.5%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The following data are for Econia during 2010. The nominal GDP was $440 billion, the inflation rate was 2%, the nominal interest rate was 6.5%, and the nominal GDP growth rate was 3%. What was Econia's real interest rate during 2010?
A) 3.5%
B) 1%
C) 8.5%
D) 4.5%
A) 3.5%
B) 1%
C) 8.5%
D) 4.5%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Currently, Econia's nominal interest rate is 5%. Its inflation rate is forecast to rise from 2% to 3% next year. According to the Fisher effect, if Econia's inflation rate rises as predicted, then its nominal interest rate will be _____, and its real interest rate will be:
A) 6%; 3%.
B) 6%; 2%.
C) 4%; 1%.
D) 4%; 7%.
A) 6%; 3%.
B) 6%; 2%.
C) 4%; 1%.
D) 4%; 7%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The Fisher effect is the idea that a change in:
A) the real interest rate leads to an equal size change in the inflation rate.
B) the nominal interest rate leads to an equal size change in the real interest rate.
C) expected inflation leads to an equal size change in nominal interest rates.
D) expected inflation leads to an equal size change in the real GDP growth rate.
A) the real interest rate leads to an equal size change in the inflation rate.
B) the nominal interest rate leads to an equal size change in the real interest rate.
C) expected inflation leads to an equal size change in nominal interest rates.
D) expected inflation leads to an equal size change in the real GDP growth rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Why is the expected inflation rate rather than the current inflation rate typically used in analysis of the Fisher effect?
A) The Fisher effect is an estimate, so an estimated inflation rate is more appropriate than an actual inflation rate.
B) The expected inflation rate is what impacts the current real interest rate because the current inflation rate impacts that past.
C) The Fisher effect deals with the future and does not explain the present situation.
D) Interest rates impact borrowing and saving, which are activities that have connections to the future.
A) The Fisher effect is an estimate, so an estimated inflation rate is more appropriate than an actual inflation rate.
B) The expected inflation rate is what impacts the current real interest rate because the current inflation rate impacts that past.
C) The Fisher effect deals with the future and does not explain the present situation.
D) Interest rates impact borrowing and saving, which are activities that have connections to the future.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Carlos borrowed $100 for a year at 5% interest. At the end of the year, he repaid the loan with a payment of $105. The inflation rate that year was 4%. The real rate of interest on his loan was:
A) 9%.
B) 5%.
C) 4%.
D) 1%.
A) 9%.
B) 5%.
C) 4%.
D) 1%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
A negative real interest rate exists when the:
A) rate of growth in the money supply is lower than the inflation rate.
B) rate of growth in the money supply is greater than the inflation rate.
C) inflation rate is higher than the nominal interest rate.
D) inflation rate is lower than the nominal interest rate.
A) rate of growth in the money supply is lower than the inflation rate.
B) rate of growth in the money supply is greater than the inflation rate.
C) inflation rate is higher than the nominal interest rate.
D) inflation rate is lower than the nominal interest rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Assume that interest rates have been 7% and the inflation rate has been 3% for the past three years. Changes in the Federal Reserve's policies are causing the expected inflation rate to increase to 4.5%. If the Fisher effect holds, the nominal rate will _____, and the real interest rate will:
A) rise to 8.5%; remain 4%.
B) remain at 7%; drop to 2.5%.
C) fall to 5.5%; drop to 3%.
D) rise to 8.5%; remain 3%.
A) rise to 8.5%; remain 4%.
B) remain at 7%; drop to 2.5%.
C) fall to 5.5%; drop to 3%.
D) rise to 8.5%; remain 3%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The statement "Real interest rate = Nominal interest rate - Inflation" is known as the:
A) monetarist relationship.
B) equation of exchange.
C) Fisher equation.
D) classical dichotomy.
A) monetarist relationship.
B) equation of exchange.
C) Fisher equation.
D) classical dichotomy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The inflation rate is 3% and stable. If a bank wants to earn a real interest rate of 4%, what interest rate will Hua Xing need to pay on the car loan that she is requesting?
A) -1%
B) 1%
C) 7%
D) 12%
A) -1%
B) 1%
C) 7%
D) 12%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Econia's banks have been charging an interest rate of 6.5% on loans while the inflation rate is 2.5%. The inflation rate is expected to drop to -1%. According to the Fisher effect, the banks' interest rate on new loans is likely to:
A) rise to 8%.
B) drop to 5.5%.
C) rise to 7.5%.
D) drop to 3%.
A) rise to 8%.
B) drop to 5.5%.
C) rise to 7.5%.
D) drop to 3%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
In most countries, the nominal interest rate is _____ than the real interest rate because inflation is:
A) higher; positive.
B) higher; negative.
C) lower; positive.
D) lower; negative.
A) higher; positive.
B) higher; negative.
C) lower; positive.
D) lower; negative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The real interest rate will be higher than the nominal interest rate when:
A) inflation is positive.
B) inflation is negative.
C) the money illusion confuses thinking.
D) the Fisher effect is applied to make real adjustments.
A) inflation is positive.
B) inflation is negative.
C) the money illusion confuses thinking.
D) the Fisher effect is applied to make real adjustments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Mario thinks that nominal interest rates will increase or decrease by the same amount that the expected inflation rate increases or decreases. Economists would say that Mario believes in:
A) the money illusion.
B) interest reform.
C) the Fisher effect.
D) the classical dichotomy.
A) the money illusion.
B) interest reform.
C) the Fisher effect.
D) the classical dichotomy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



