Deck 28: Postindustrial Society and the End of the Cold War Order, 1960s-1989
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/65
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 28: Postindustrial Society and the End of the Cold War Order, 1960s-1989
1
How did medical technology and research change contraception, conception, and childbirth in the 1970s?
Answer would ideally include the following. Family size and sexual behavior became less tied to the challenges of agricultural productivity. Public demand for reliable, inexpensive birth control led to the development of newer and more effective methods of contraception, including the birth-control pill. Conception and childbirth were also changed by developments in medical technology: by 1970, most women gave birth in hospitals rather than at home. New techniques made abortions safer and more a matter for medical professionals. The development of in vitro fertilization, a process in which a woman's egg is fertilized with sperm outside the body, gave infertile couples the hope of having children.
2
How did the development of multinational corporations change the global economy?
Answer would ideally include the following. Multinationals established significant manufacturing and managerial centers in countries other than their home base. Increasingly, companies, especially in the United States, Europe, and Japan, did a significant portion of their business abroad. Multinationals often set up shop where labor costs were lowest, often in formerly colonized states. Multinationals provided jobs in developing areas, but also sent profits to stockholders who usually lived elsewhere. Multinationals often lacked interest in the well-being of localities and nations where they operated, leading some to conclude that they represented a new form of imperialism.
3
What was the nature of youth culture in this era, and what was the generation gap?
Answer would ideally include the following. In the late nineteenth century, teenagers had become full-fledged members of the workforce, with a great degree of financial and social independence. By the 1970s, most teens were students and were financially dependent on their parents, and they sometimes continued to be so into their twenties. These young people were the focus of extensive merchandising campaigns-particularly inspired by rock music-which often encouraged rebellion against parents and other authority figures. During the time that teenagers were financially bound to a family, they were often bound emotionally to a commercial youth culture that challenged family authority. The idea of a generation gap refers to the growing sense that there was a distinctive youth culture that could not be properly understood from the outside.
4
In what ways was the study of anthropology, and the work of Claude Lévi-Strauss in particular, influenced by the ways in which Western societies were ordered and run?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Compare the ways in which religion and religious practices changed in Europe and in the United States during the 1960s and 1970s.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
What were some of the policies enacted by Lyndon B. Johnson that prompted the Black novelist Ralph Ellison to call him "the greatest American president for the poor and the Negroes"?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In what ways could protests by European students in the 1960s be characterized as an expression of individualism, and how did they show this in their lifestyles and attire?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
What is stagflation, and what role did the Middle East play in its development in the West during the 1970s?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
What was the main approach to foreign policy followed by Ronald Reagan?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
What was the Solidarity movement?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Consider how technology affected the development of the postindustrial economy. What specific technologies were most influential, and how did they change life for workers?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Describe the groups who were most active in protests beginning in the 1960s. To what extent might the prosperity of society have contributed to their anger?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Explain how the idea of the cold war as a struggle between Western democracies and international communism for world domination was weakened by events of the 1970s.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Describe how Margaret Thatcher reshaped the West's political and economic ideas in the 1980s. What impact did her policies have on Europe? What were the consequences of her economic and political policies?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Ronald Reagan was U.S. president from 1981 until 1989. During this time, he addressed economic crises as well as foreign policy concerns surrounding the Soviet Union and the cold war. Explain how President Reagan approached the economic crisis in the United States during this time and what influenced his economic policies. Then describe Reagan's approach to foreign policy, particularly when it came to the cold war and relations with the Soviet Union.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following was a technological advancement of the 1960s?
A) Mass printing of newspapers
B) Instantaneous radio and television news
C) Communication via mail
D) Three-dimensional movies
A) Mass printing of newspapers
B) Instantaneous radio and television news
C) Communication via mail
D) Three-dimensional movies

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
What did one philosopher mean when, in the last third of the twentieth century, she proclaimed that people had become cyborgs?
A) Technology had advanced so greatly that transplants, artificial limbs, contact lenses, and other intrusive medical innovations had become a regular part of life.
B) People had become so fascinated with outer space that they were more interested in space technology than they were in their own lives.
C) People had become so reliant on machines that they were no longer self-sufficient; instead, they needed machines to sustain ordinary life processes.
D) Modern culture was so alienating that people in society functioned more like machines than sentient beings.
A) Technology had advanced so greatly that transplants, artificial limbs, contact lenses, and other intrusive medical innovations had become a regular part of life.
B) People had become so fascinated with outer space that they were more interested in space technology than they were in their own lives.
C) People had become so reliant on machines that they were no longer self-sufficient; instead, they needed machines to sustain ordinary life processes.
D) Modern culture was so alienating that people in society functioned more like machines than sentient beings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Why did European governments in the postwar era fund both radio and television broadcasting with tax dollars?
A) To secure broadcasting space for government programming aimed at instilling democratic values and inuring the populace to Communist propaganda
B) To elevate the quality of programming and avoid what they perceived as the substandard fare offered by American commercial TV
C) As part of their attempt to stabilize the ever-weakening social order
D) As part of a broader effort to stay several steps ahead of the Soviet Union's eastern-bloc countries in providing a desirable quality of life for their citizenry
A) To secure broadcasting space for government programming aimed at instilling democratic values and inuring the populace to Communist propaganda
B) To elevate the quality of programming and avoid what they perceived as the substandard fare offered by American commercial TV
C) As part of their attempt to stabilize the ever-weakening social order
D) As part of a broader effort to stay several steps ahead of the Soviet Union's eastern-bloc countries in providing a desirable quality of life for their citizenry

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
What was the climactic moment of the "space race" between the United States and the Soviet Union?
A) When U.S. astronauts Neil Armstrong and Edwin "Buzz" Aldrin walked on the moon's surface before a worldwide television audience in July 1969
B) When the Soviet Union launched the satellite Sputnik into orbit in 1957
C) When Soviet cosmonaut Valentina Tereshkova became the first woman in space in 1963
D) When the American space crew of the Apollo 13 mission lost an oxygen tank in space and returned to earth in a "lifeboat" module in April 1970
A) When U.S. astronauts Neil Armstrong and Edwin "Buzz" Aldrin walked on the moon's surface before a worldwide television audience in July 1969
B) When the Soviet Union launched the satellite Sputnik into orbit in 1957
C) When Soviet cosmonaut Valentina Tereshkova became the first woman in space in 1963
D) When the American space crew of the Apollo 13 mission lost an oxygen tank in space and returned to earth in a "lifeboat" module in April 1970

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The 1968 film 2001: A Space Odyssey not only reflected the enormous popular interest in space but also showed that science fiction was increasingly
A) forgoing intricate or intellectual plots in favor of creating astounding special effects to dazzle the viewer.
B) replacing other television and film genres, such as Westerns and sitcoms.
C) concerned with explaining the dry, technical aspects of the space race in a way that would be easy for the audience to understand.
D) addressing issues about life and humanity that were formerly the domain of church leaders.
A) forgoing intricate or intellectual plots in favor of creating astounding special effects to dazzle the viewer.
B) replacing other television and film genres, such as Westerns and sitcoms.
C) concerned with explaining the dry, technical aspects of the space race in a way that would be easy for the audience to understand.
D) addressing issues about life and humanity that were formerly the domain of church leaders.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Intelsat I, the first commercial communications satellite, was launched in 1965 and was an example of
A) U.S.-Soviet technological cooperation, and thus it was a first step toward détente.
B) international collaboration in communications technology, with the United States as the predominant player.
C) poor planning and the often misguided beginnings of the U.S. commercial space program.
D) the impressive imaging technology developed by the European Space Research Organization in its drive to catch up with the United States and the Soviet Union.
A) U.S.-Soviet technological cooperation, and thus it was a first step toward détente.
B) international collaboration in communications technology, with the United States as the predominant player.
C) poor planning and the often misguided beginnings of the U.S. commercial space program.
D) the impressive imaging technology developed by the European Space Research Organization in its drive to catch up with the United States and the Soviet Union.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
In 1952, scientists Francis Crick and James Watson made which of the following discoveries?
A) The Salk vaccine against polio, leading to the first mass immunization program against the dreaded virus
B) Penicillin, which helped to launch the boom in the use of antibiotics to treat everything from syphilis to streptococcal infections
C) The configuration of DNA, thus vastly expanding our knowledge of biological inheritance
D) The fire-retardant properties of asbestos, thus leading to an explosion in the material's use by the construction industry, much to the dismay of health experts later
A) The Salk vaccine against polio, leading to the first mass immunization program against the dreaded virus
B) Penicillin, which helped to launch the boom in the use of antibiotics to treat everything from syphilis to streptococcal infections
C) The configuration of DNA, thus vastly expanding our knowledge of biological inheritance
D) The fire-retardant properties of asbestos, thus leading to an explosion in the material's use by the construction industry, much to the dismay of health experts later

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What medical advance of the 1960s that was first marketed in the United States revolutionized sexual behavior in the industrialized West?
A) In vitro fertilization
B) The birth-control pill
C) The herpes vaccine
D) The latex condom
A) In vitro fertilization
B) The birth-control pill
C) The herpes vaccine
D) The latex condom

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
In 1978, Louise Brown, the first "test-tube baby," was born in Britain after being conceived through what complex process?
A) Surrogacy
B) Womb transplantation
C) Cloning
D) In vitro fertilization
A) Surrogacy
B) Womb transplantation
C) Cloning
D) In vitro fertilization

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
New multinational corporations opened factories and employed workers in impoverished areas of the world beginning in the 1960s, but they brought little wealth to such countries. Why?
A) The corporations paid their workers low wages, and company profits mostly went to the shareholders, who usually lived in wealthier countries.
B) Too few jobs were created to make much difference in these countries' economies.
C) Multinational corporations demanded tax breaks that negated the economic benefits for the countries to which they moved their operations.
D) Continuing unrest and government instability kept workers from putting their earnings back into the local economy.
A) The corporations paid their workers low wages, and company profits mostly went to the shareholders, who usually lived in wealthier countries.
B) Too few jobs were created to make much difference in these countries' economies.
C) Multinational corporations demanded tax breaks that negated the economic benefits for the countries to which they moved their operations.
D) Continuing unrest and government instability kept workers from putting their earnings back into the local economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The Airbus project was an example of the
A) marketplace advantages of U.S. multinational corporations in the global sphere.
B) cooperation among government, business, and science and among members of the Common Market.
C) ability of the Soviet bloc to build viable consumer goods that could compete in the global marketplace.
D) ability of French corporations to compete with conglomerates and multinationals.
A) marketplace advantages of U.S. multinational corporations in the global sphere.
B) cooperation among government, business, and science and among members of the Common Market.
C) ability of the Soviet bloc to build viable consumer goods that could compete in the global marketplace.
D) ability of French corporations to compete with conglomerates and multinationals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
How did the new working class in postindustrial society undermine old socioeconomic distinctions?
A) Virtually everyone went to college, so no one could claim superiority on the basis of a better education.
B) Men and women now entered all professions equally, so the idea that certain jobs were "men's work" or "women's work" disappeared.
C) Wealthy people could now take technological jobs for the simple enjoyment of solving complex problems without losing status.
D) Those who performed service work or managerial functions were not necessarily better paid than blue-collar workers.
A) Virtually everyone went to college, so no one could claim superiority on the basis of a better education.
B) Men and women now entered all professions equally, so the idea that certain jobs were "men's work" or "women's work" disappeared.
C) Wealthy people could now take technological jobs for the simple enjoyment of solving complex problems without losing status.
D) Those who performed service work or managerial functions were not necessarily better paid than blue-collar workers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following is an example of how postindustrial life in the Soviet bloc differed from life in the West?
A) The percentage of farmers remained higher in the Soviet bloc than in western Europe, despite changes and the consolidation of farming.
B) Fewer women worked in the Soviet bloc than in western Europe, where 80 to 95 percent of women worked full time.
C) Women earned the same wages as men in the Soviet bloc, whereas there continued to be a gap between men's and women's wages in the West.
D) The line between professional and industrial occupations became more blurred in the Soviet bloc than in western Europe.
A) The percentage of farmers remained higher in the Soviet bloc than in western Europe, despite changes and the consolidation of farming.
B) Fewer women worked in the Soviet bloc than in western Europe, where 80 to 95 percent of women worked full time.
C) Women earned the same wages as men in the Soviet bloc, whereas there continued to be a gap between men's and women's wages in the West.
D) The line between professional and industrial occupations became more blurred in the Soviet bloc than in western Europe.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Why did Soviet-bloc nations often have great difficulty applying their achievements in science to commercial applications?
A) The Soviets continued to be suspicious of their satellite states' intentions and insisted on burdensome monitoring of their research and development efforts.
B) The process of gaining bureaucratic approval for innovations was inefficient, and findings often became obsolete before they could be applied to technology.
C) The slow but steady brain drain to the West continued with the flight of hundreds of researchers and scientists.
D) The Soviet bloc's emphasis on heavy industry offered ambitious scientists few incentives to produce for domestic consumption.
A) The Soviets continued to be suspicious of their satellite states' intentions and insisted on burdensome monitoring of their research and development efforts.
B) The process of gaining bureaucratic approval for innovations was inefficient, and findings often became obsolete before they could be applied to technology.
C) The slow but steady brain drain to the West continued with the flight of hundreds of researchers and scientists.
D) The Soviet bloc's emphasis on heavy industry offered ambitious scientists few incentives to produce for domestic consumption.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Historians have observed that, whereas early modern families focused their efforts on independent subsistence production and the teaching of craft skills to younger generations, postindustrial families
A) increased production-even in relative terms-because more family members worked outside the home.
B) squandered their resources and neglected their young.
C) served a predominantly psychological purpose, with parents providing emotional support to children who gained their intellectual skills in school.
D) saw a drop in their standard of living-in relative terms-because the hectic demands of postindustrial life had negative health effects, resulting in a decrease in production.
A) increased production-even in relative terms-because more family members worked outside the home.
B) squandered their resources and neglected their young.
C) served a predominantly psychological purpose, with parents providing emotional support to children who gained their intellectual skills in school.
D) saw a drop in their standard of living-in relative terms-because the hectic demands of postindustrial life had negative health effects, resulting in a decrease in production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
What prompted the Western media to announce the arrival of a "sexual revolution"?
A) Betty Friedan's founding of the National Organization for Women (NOW) in 1966
B) Greater openness about sexuality in postindustrial society, especially within youth culture
C) The creation of the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission, which worked to fight job discrimination based on gender or sexual orientation
D) The enormous decline in the marriage rate in western Europe, which fell nearly 30 percent in the decades after the baby boom
A) Betty Friedan's founding of the National Organization for Women (NOW) in 1966
B) Greater openness about sexuality in postindustrial society, especially within youth culture
C) The creation of the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission, which worked to fight job discrimination based on gender or sexual orientation
D) The enormous decline in the marriage rate in western Europe, which fell nearly 30 percent in the decades after the baby boom

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
What new style in the visual arts featured images from everyday life and employed the glossy techniques and products of mass advertising?
A) New realism
B) Situationism
C) Pop art
D) Abstract expressionism
A) New realism
B) Situationism
C) Pop art
D) Abstract expressionism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following was one of the most famous postwar practitioners of pop art?
A) Claes Oldenburg
B) John Cage
C) Sigmar Polke
D) Andy Warhol
A) Claes Oldenburg
B) John Cage
C) Sigmar Polke
D) Andy Warhol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Musical innovations in the 1960s and 1970s included
A) a focus on minimalism, adding sounds made by striking ordinary objects, and the use of repetition, sustained notes, and silence.
B) a return to the idea of musical romanticism and the rediscovery of the great romantic composers, such as Beethoven.
C) an emphasis on lush orchestration, with many layers of instrumentation filling as much "sound space" as possible.
D) an elimination of all nonvocal sounds because they were thought to be unnatural.
A) a focus on minimalism, adding sounds made by striking ordinary objects, and the use of repetition, sustained notes, and silence.
B) a return to the idea of musical romanticism and the rediscovery of the great romantic composers, such as Beethoven.
C) an emphasis on lush orchestration, with many layers of instrumentation filling as much "sound space" as possible.
D) an elimination of all nonvocal sounds because they were thought to be unnatural.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Why did the study of anthropology become attractive to many university students during the postindustrial era?
A) It was a new subject, and many students thought they could make real breakthroughs in the field.
B) By the 1960s, it had lost its scientific, quantitative emphasis, which made it less difficult to master.
C) It offered the chance to study cultures that were relatively untouched by modernization and industrialization.
D) It was one of the few social sciences in which women intellectuals were welcomed and given the leeway to make impressive contributions.
A) It was a new subject, and many students thought they could make real breakthroughs in the field.
B) By the 1960s, it had lost its scientific, quantitative emphasis, which made it less difficult to master.
C) It offered the chance to study cultures that were relatively untouched by modernization and industrialization.
D) It was one of the few social sciences in which women intellectuals were welcomed and given the leeway to make impressive contributions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following was one of the major changes in religious life in western Europe?
A) A tremendous increase in religious observance, as shown by the numbers of people who regularly attended church
B) A dramatic drop in the levels of anti-Semitism as a result of guilt over the Holocaust
C) A strengthening of the Catholic church's influence over European governments
D) A rise in the number of non-Christian and non-Jewish places of worship, such as mosques, Buddhist temples, and other shrines
A) A tremendous increase in religious observance, as shown by the numbers of people who regularly attended church
B) A dramatic drop in the levels of anti-Semitism as a result of guilt over the Holocaust
C) A strengthening of the Catholic church's influence over European governments
D) A rise in the number of non-Christian and non-Jewish places of worship, such as mosques, Buddhist temples, and other shrines

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The West German foreign minister Willy Brandt's anti-cold war policy of opening up trade with Communist East Germany in the late 1960s was known as what?
A) Ostpolitik
B) Détente
C) Glasnost
D) Rapprochement
A) Ostpolitik
B) Détente
C) Glasnost
D) Rapprochement

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following measures did French president Charles de Gaulle undertake in an effort to assert French independence in a world increasingly dominated by superpower rivalry?
A) He attempted to recolonize parts of Africa that had gained independence from Europe in order to expand France's global influence.
B) He cut off trade with the United States and started parallel institutions to allow France to become financially independent.
C) He cooled France's relations with West Germany in response to that country's agreement to station U.S. antiballistic missiles on German soil.
D) He withdrew French forces from NATO and increased the nation's investment in nuclear development.
A) He attempted to recolonize parts of Africa that had gained independence from Europe in order to expand France's global influence.
B) He cut off trade with the United States and started parallel institutions to allow France to become financially independent.
C) He cooled France's relations with West Germany in response to that country's agreement to station U.S. antiballistic missiles on German soil.
D) He withdrew French forces from NATO and increased the nation's investment in nuclear development.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following was a system through which government-banned literature was secretly published and distributed in the Soviet Union?
A) Détente
B) Samizdat
C) Glasnost
D) Perestroika
A) Détente
B) Samizdat
C) Glasnost
D) Perestroika

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which U.S. president successfully shepherded the 1964 Civil Rights Act through the U.S. Congress, legislation that forbade job discrimination based on race, color, religion, or sex and outlawed segregation in public accommodations?
A) Harry Truman
B) John F. Kennedy
C) Richard M. Nixon
D) Lyndon B. Johnson
A) Harry Truman
B) John F. Kennedy
C) Richard M. Nixon
D) Lyndon B. Johnson

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
According to this map, which of the following countries most likely supported the communist takeover of Vietnam?
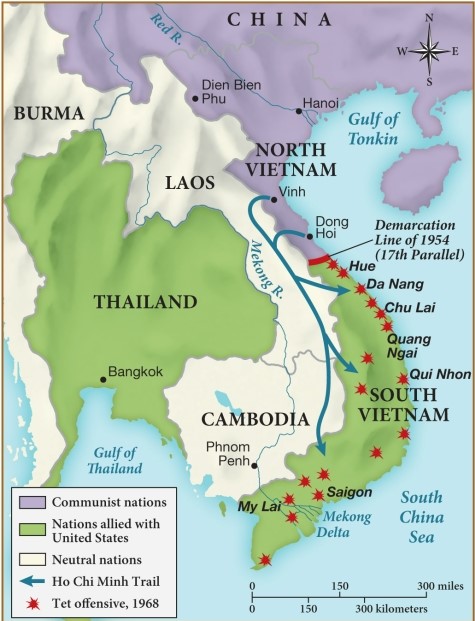
A) Thailand
B) China
C) Cambodia
D) Burma

A) Thailand
B) China
C) Cambodia
D) Burma

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The Black Panthers compared their struggle in the United States to
A) slaves fighting for liberty in the U.S. Civil War.
B) Communists overthrowing the tsar in the Russian revolution.
C) sans-culottes throwing off their oppressors in the French Revolution.
D) the struggles of formerly colonized peoples for independence.
A) slaves fighting for liberty in the U.S. Civil War.
B) Communists overthrowing the tsar in the Russian revolution.
C) sans-culottes throwing off their oppressors in the French Revolution.
D) the struggles of formerly colonized peoples for independence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
What does the acronym NOW stand for?
A) The National Organization for Women, founded in 1966 in the United States
B) The National Organization of Workers, founded in 1962 in Great Britain
C) The National Organization for Welders, founded in 1967 in Poland
D) The National Organization of Winemakers, founded in 1965 in France
A) The National Organization for Women, founded in 1966 in the United States
B) The National Organization of Workers, founded in 1962 in Great Britain
C) The National Organization for Welders, founded in 1967 in Poland
D) The National Organization of Winemakers, founded in 1965 in France

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The 1968 student protests in France attracted workers as well as students, as both were demanding
A) an increase in the national minimum wage.
B) an end to gender and racial discrimination in official hiring policies.
C) a greater voice in official decision making, whether on campus or in the factory.
D) the end of France's involvement in the Common Market.
A) an increase in the national minimum wage.
B) an end to gender and racial discrimination in official hiring policies.
C) a greater voice in official decision making, whether on campus or in the factory.
D) the end of France's involvement in the Common Market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
According to this map, who mobilized to Czechoslovakia in 1968 during the Prague Spring?
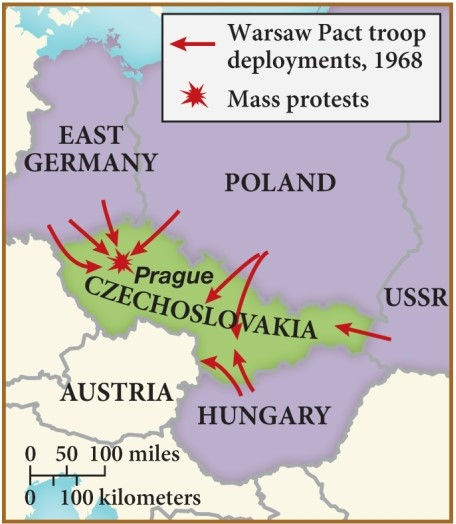
A) The United States military
B) Those countries who were party to the Treaty of Versailles
C) Members of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization
D) Nations that were part of the Warsaw Pact

A) The United States military
B) Those countries who were party to the Treaty of Versailles
C) Members of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization
D) Nations that were part of the Warsaw Pact

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
What was distinctive about the 1968 revolt in Czechoslovakia, also known as the Prague Spring?
A) It was almost entirely a protest about women's rights in the Soviet bloc, but it gained international support in the wake of the Soviets' draconian response.
B) It was the only uprising that was successful in achieving meaningful and lasting reform within the Soviet bloc.
C) It began within the Czechoslovak Communist Party as an attempt at reform based on the idea of "socialism with a human face."
D) Although it was a student-led movement, the participation of housewives and mid-level bureaucrats kept the momentum going.
A) It was almost entirely a protest about women's rights in the Soviet bloc, but it gained international support in the wake of the Soviets' draconian response.
B) It was the only uprising that was successful in achieving meaningful and lasting reform within the Soviet bloc.
C) It began within the Czechoslovak Communist Party as an attempt at reform based on the idea of "socialism with a human face."
D) Although it was a student-led movement, the participation of housewives and mid-level bureaucrats kept the momentum going.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
What was the Brezhnev Doctrine, which the Soviets announced in November 1968?
A) An opening of trade and diplomatic ties with the West, designed to be a complement to Willy Brandt's Ostpolitik
B) A secret buildup of Soviet nuclear arms in response to American military actions in Vietnam and West Germany
C) A reform movement in the Soviet bloc that allowed basic freedom of speech and several other freedoms in all of the Soviet satellites
D) A policy that stated that all Soviet-bloc reform movements would face swift repression
A) An opening of trade and diplomatic ties with the West, designed to be a complement to Willy Brandt's Ostpolitik
B) A secret buildup of Soviet nuclear arms in response to American military actions in Vietnam and West Germany
C) A reform movement in the Soviet bloc that allowed basic freedom of speech and several other freedoms in all of the Soviet satellites
D) A policy that stated that all Soviet-bloc reform movements would face swift repression

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
What was the title of Aleksandr Solzhenitsyn's book that detailed life in Soviet forced-labor camps and brought about his expulsion from the USSR?
A) The Book of Laughter and Forgetting
B) The Gulag Archipelago
C) The Unbearable Lightness of Being
D) Divided Heaven
A) The Book of Laughter and Forgetting
B) The Gulag Archipelago
C) The Unbearable Lightness of Being
D) Divided Heaven

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Richard Nixon won election as president of the United States in 1968 partly because of what campaign promise?
A) That he would bring peace to Vietnam
B) That he would support political protesters in the United States
C) That he would introduce an equal rights amendment to the U.S. Constitution
D) That he would clean up government, especially the financing of political campaigns
A) That he would bring peace to Vietnam
B) That he would support political protesters in the United States
C) That he would introduce an equal rights amendment to the U.S. Constitution
D) That he would clean up government, especially the financing of political campaigns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
U.S. president Richard M. Nixon's 1972 visit to what country helped to speed up the process of détente between the United States and the Soviet Union?
A) Vietnam
B) The Soviet Union
C) Cuba
D) China
A) Vietnam
B) The Soviet Union
C) Cuba
D) China

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
What was the consequence of the negotiations that produced SALT I?
A) A cap on the number of antimissile systems the U.S.- and Soviet-led blocs could have
B) A closer alliance between the United States and China
C) The first global trade arrangements that led to freer trade
D) The limitation of "superpower" interventions in Latin America
A) A cap on the number of antimissile systems the U.S.- and Soviet-led blocs could have
B) A closer alliance between the United States and China
C) The first global trade arrangements that led to freer trade
D) The limitation of "superpower" interventions in Latin America

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
In the 1975 Helsinki accords, Western countries agreed to officially recognize Soviet territorial acquisitions in World War II in exchange for which of the following?
A) An end to the Soviet Union's support of Communists fighting in Africa
B) Greater cultural and scientific exchange between the West and eastern-bloc countries
C) The Soviet Union's participation in arms reduction
D) The Soviet bloc's guarantee of basic human rights
A) An end to the Soviet Union's support of Communists fighting in Africa
B) Greater cultural and scientific exchange between the West and eastern-bloc countries
C) The Soviet Union's participation in arms reduction
D) The Soviet bloc's guarantee of basic human rights

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Why did the Arab nations of the Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) impose an oil embargo on the United States and its allies in the 1970s?
A) They were frustrated that Western nations were turning to nuclear energy instead of maintaining their reliance on Middle Eastern oil.
B) They were attempting to gain support from the USSR, which the Middle East judged to be in a position of power in the early 1970s.
C) They were angry that the United States had offered support to Israel in its conflicts with Egypt, Syria, and Jordan during the 1960s and 1970s.
D) They wanted to punish the United States for refusing to trade fairly with non-Western nations.
A) They were frustrated that Western nations were turning to nuclear energy instead of maintaining their reliance on Middle Eastern oil.
B) They were attempting to gain support from the USSR, which the Middle East judged to be in a position of power in the early 1970s.
C) They were angry that the United States had offered support to Israel in its conflicts with Egypt, Syria, and Jordan during the 1960s and 1970s.
D) They wanted to punish the United States for refusing to trade fairly with non-Western nations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The combination of economic conditions-rising prices, rising interest rates, and high unemployment-that hit the oil-dependent Western nations as a result of the OPEC oil embargo became known as what?
A) Stagflation
B) Trickle-down economics
C) Hyperinflation
D) Depression
A) Stagflation
B) Trickle-down economics
C) Hyperinflation
D) Depression

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The wave of terrorism that hit Europe and the Middle East in the 1970s
A) was mainly the result of Soviet funding of guerrilla movements in Europe's former colonies.
B) emerged after the CIA began funneling money and weapons to anti-Communist movements in eastern Europe and central Asia.
C) began in the West, as young people in Europe responded to the suppression of activism and poor economic conditions with kidnappings, bank robberies, bombings, and assassinations.
D) was condoned by Western governments, and often supported by U.S. intelligence forces, because it was mainly directed at leftists and Communist leaders.
A) was mainly the result of Soviet funding of guerrilla movements in Europe's former colonies.
B) emerged after the CIA began funneling money and weapons to anti-Communist movements in eastern Europe and central Asia.
C) began in the West, as young people in Europe responded to the suppression of activism and poor economic conditions with kidnappings, bank robberies, bombings, and assassinations.
D) was condoned by Western governments, and often supported by U.S. intelligence forces, because it was mainly directed at leftists and Communist leaders.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
In what country did British troops fire on nationalists and civil rights demonstrators in a 1972 event known as "Bloody Sunday"?
A) The Falkland Islands
B) Northern Ireland
C) England
D) Scotland
A) The Falkland Islands
B) Northern Ireland
C) England
D) Scotland

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The two maps reproduced here collectively exemplify the emergence of what in 1970s Europe?
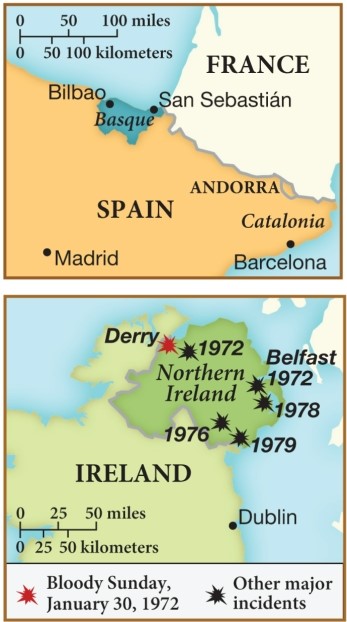
A) Nationalist movements
B) Cold war tensions
C) Religious dissention
D) Neoliberalism

A) Nationalist movements
B) Cold war tensions
C) Religious dissention
D) Neoliberalism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which Western leader, in power between 1979 and 1990, did more than anyone else to reshape the West's political and economic ideas by demolishing the welfare state and supporting business leaders?
A) Helmut Kohl
B) Mikhail Gorbachev
C) Margaret Thatcher
D) Ronald Reagan
A) Helmut Kohl
B) Mikhail Gorbachev
C) Margaret Thatcher
D) Ronald Reagan

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Margaret Thatcher's economic policies, which were based on monetarist, or supply-side, economic theory, came to be known as
A) neosocialism.
B) compassionate conservatism.
C) neoliberalism.
D) libertarianism.
A) neosocialism.
B) compassionate conservatism.
C) neoliberalism.
D) libertarianism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
As neoliberalism took hold in the 1980s and 1990s and European governments began cutting the welfare state, which country maintained a full array of social programs?
A) France
B) Sweden
C) West Germany
D) Ireland
A) France
B) Sweden
C) West Germany
D) Ireland

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Mikhail Gorbachev's program of economic "restructuring," intended to increase productivity and gradually introduce market-based incentives, was called
A) glasnost.
B) Solidarity.
C) the Brezhnev Doctrine.
D) perestroika.
A) glasnost.
B) Solidarity.
C) the Brezhnev Doctrine.
D) perestroika.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
What Polish labor movement led by Lech Walesa and Anna Walentynowicz, workers at the shipyards of Gdańsk, Poland, helped bring down Soviet communism?
A) The Polish United Workers' Party
B) Solidarity
C) The Unity Movement
D) The Federation of Shipyard Workers
A) The Polish United Workers' Party
B) Solidarity
C) The Unity Movement
D) The Federation of Shipyard Workers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Which event symbolized for the world the fall of Soviet Communism in 1989?
A) The first free elections in the Soviet Union since 1917
B) The resignation of the Communist leadership in Czechoslovakia and the elevation of Czech playwright Václav Havel to the presidency
C) When East and West German citizens tore down the Berlin Wall with sledgehammers in November 1989
D) The execution of Romanian dictator Nicolae Ceauşescu on Christmas Day
A) The first free elections in the Soviet Union since 1917
B) The resignation of the Communist leadership in Czechoslovakia and the elevation of Czech playwright Václav Havel to the presidency
C) When East and West German citizens tore down the Berlin Wall with sledgehammers in November 1989
D) The execution of Romanian dictator Nicolae Ceauşescu on Christmas Day

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Which of the following nations experienced the greatest concentration of popular demonstrations against communism from 1989 through 1990?
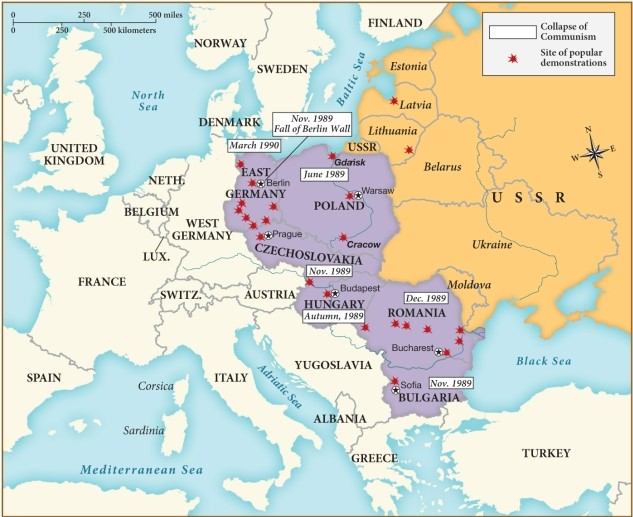
A) East Germany
B) Poland
C) Hungary
D) Lithuania

A) East Germany
B) Poland
C) Hungary
D) Lithuania

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Which of the following nations was the first to become free from communism?
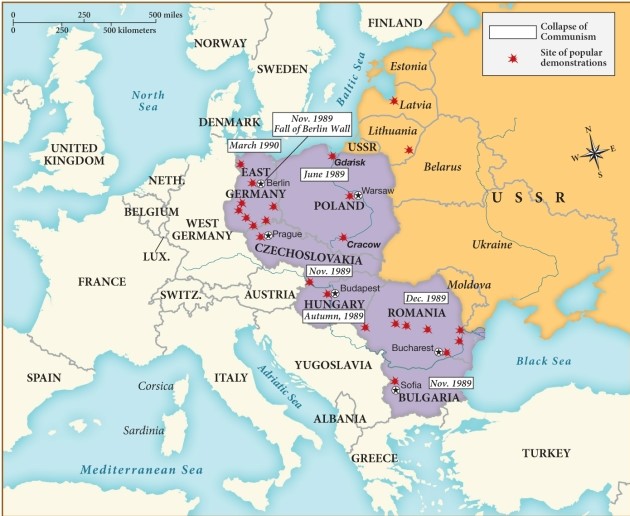
A) East Germany
B) Poland
C) Bulgaria
D) Hungary

A) East Germany
B) Poland
C) Bulgaria
D) Hungary

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



