Deck 24: Environmental and Industrial Microbiology
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/88
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 24: Environmental and Industrial Microbiology
1
What is the correct order in Ecological Hierarchy from most exclusive to most inclusive?
1) Individual organism
2) Biosphere
3) Ecosystem
4) Community
5) Population
A) 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
B) 2, 4, 1, 3, 5
C) 1, 5, 4, 3, 2
D) 2, 3, 4, 5, 1
1) Individual organism
2) Biosphere
3) Ecosystem
4) Community
5) Population
A) 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
B) 2, 4, 1, 3, 5
C) 1, 5, 4, 3, 2
D) 2, 3, 4, 5, 1
C
2
Characteristics of populations include _________________. (Select all that apply)
A) Being composed of individuals of the same species living in a specified area
B) A specific growth rate
C) Interspecific competition
D) predation
A) Being composed of individuals of the same species living in a specified area
B) A specific growth rate
C) Interspecific competition
D) predation
A,B
3
Communities differ from populations in all of the following ways EXCEPT ________.
A) Communities are composed of multiple different populations
B) Communities participate in nutrient cycling which does not occur at the population level
C) Symbiotic relationships occur at the community level
D) Predation is a component of communities and not populations
A) Communities are composed of multiple different populations
B) Communities participate in nutrient cycling which does not occur at the population level
C) Symbiotic relationships occur at the community level
D) Predation is a component of communities and not populations
B
4
Ecosystem interactions include _____________________. (Select all that apply)
A) Communities and the abiotic properties of their geographic area
B) Energy acquisition
C) Nutrient cycling
D) Biome features
A) Communities and the abiotic properties of their geographic area
B) Energy acquisition
C) Nutrient cycling
D) Biome features

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A bacterial cell in a community is also a member of what other ecological level(s)?
A) The community only
B) A population and a community only
C) The community and biosphere only
D) All levels, from individual to biosphere
A) The community only
B) A population and a community only
C) The community and biosphere only
D) All levels, from individual to biosphere

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Examine the image below and determine its level in the ecological hierarchy.
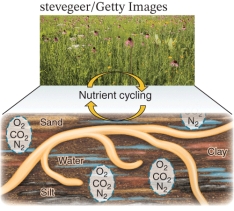
A) Population
B) Community
C) Ecosystem
D) Biosphere

A) Population
B) Community
C) Ecosystem
D) Biosphere

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Earth's ecosystems are divided into _______________. (Select all that apply)
A) Aquatic
B) Atmospheric
C) Terrestrial
D) Subterranean
A) Aquatic
B) Atmospheric
C) Terrestrial
D) Subterranean

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The microbial species composition of a community is best determined by __________.
A) Sampling areas of the region with a swab and culturing the samples
B) Examining DNA samples from the region using metagenomics analysis
C) Sequencing 16S rRNA specimens collected in the community
D) Performing Western blot analysis on community samples
A) Sampling areas of the region with a swab and culturing the samples
B) Examining DNA samples from the region using metagenomics analysis
C) Sequencing 16S rRNA specimens collected in the community
D) Performing Western blot analysis on community samples

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following descriptions is NOT true of atmospheric communities?
A) there are 104 to 106 bacteria/m3
B) numbers of airborne bacteria may increase more than 75% in the heat and humidity of the summer because of rapid reproduction
C) most airborne microbes come from soil, dust, and leaf surfaces
D) in cities dog feces contribute to airborne microbiota
A) there are 104 to 106 bacteria/m3
B) numbers of airborne bacteria may increase more than 75% in the heat and humidity of the summer because of rapid reproduction
C) most airborne microbes come from soil, dust, and leaf surfaces
D) in cities dog feces contribute to airborne microbiota

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which air samples show a higher proportion of pathogens that may be directly transmitted between people?
A) sample from agricultural region
B) sample from forest
C) sample from coastal region
D) indoor sample
A) sample from agricultural region
B) sample from forest
C) sample from coastal region
D) indoor sample

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
In terrestrial microbial communities, 1 gram of surface soil may contain more than ____ microbes.
A) 1 million
B) 10 million
C) 1 billion
D) 10 billion
A) 1 million
B) 10 million
C) 1 billion
D) 10 billion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Bacterial species composition in soil communities is highly variable within short periods of time because of changes in _____________. (Select all that apply)
A) soil moisture
B) soil pH
C) ambient temperature
D) oxygen levels
A) soil moisture
B) soil pH
C) ambient temperature
D) oxygen levels

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Variability in aquatic ecosystems results from all of the following EXCEPT ________________.
A) Light intensity
B) Nutrient availability
C) Water temperature
D) Water depth
A) Light intensity
B) Nutrient availability
C) Water temperature
D) Water depth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Marine bacteriophages infecting bacteria in the community actually enhance microbial growth due to _____. (Select all that apply)
A) Reducing interspecific competition
B) Increasing the rate of glucose production by cyanobacteria
C) Viral priming, boosting nutrient availability
D) Enhancing the rate of oxygen production by cyanobacteria
A) Reducing interspecific competition
B) Increasing the rate of glucose production by cyanobacteria
C) Viral priming, boosting nutrient availability
D) Enhancing the rate of oxygen production by cyanobacteria

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
___________ contribute more than 40% of Earth's primary productivity.
A) Bacteriophages
B) Nitrogen-fixing bacteria
C) Marine cyanobacteria
D) Aquatic fungi
A) Bacteriophages
B) Nitrogen-fixing bacteria
C) Marine cyanobacteria
D) Aquatic fungi

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Key features of the hydrologic cycle include _______________. (Select all that apply)
A) Water phase changes from solid to liquid to gas and back
B) Limiting microbial redistribution within the environment
C) Cloud formation, nucleation and precipitation
D) Sequestering water in deep aquifers to prevent sea level from rising
A) Water phase changes from solid to liquid to gas and back
B) Limiting microbial redistribution within the environment
C) Cloud formation, nucleation and precipitation
D) Sequestering water in deep aquifers to prevent sea level from rising

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Eutrophication involves all of the following EXCEPT ____________.
A) Rapid growth of algae and cyanobacteria
B) Depletion of dissolve oxygen that leads to fish kills
C) Excessive algal growth in surface waters that reduces available nitrogen
D) Excess nutrients triggering an algal bloom
A) Rapid growth of algae and cyanobacteria
B) Depletion of dissolve oxygen that leads to fish kills
C) Excessive algal growth in surface waters that reduces available nitrogen
D) Excess nutrients triggering an algal bloom

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
All of the following are steps in the formation of a biofilm EXCEPT ____________.
A) colonizing bacteria attach to surfaces coated with organic material using their fimbriae and capsules
B) As the colonizing bacteria secrete proteins and oligosaccharides or release DNA fragments, a sticky extracellular matrix forms
C) A new wave of microorganisms, enriched in bacteriophages, arrives and attaches to the matrix
D) Some microbes in mature biofilms break free and float
A) colonizing bacteria attach to surfaces coated with organic material using their fimbriae and capsules
B) As the colonizing bacteria secrete proteins and oligosaccharides or release DNA fragments, a sticky extracellular matrix forms
C) A new wave of microorganisms, enriched in bacteriophages, arrives and attaches to the matrix
D) Some microbes in mature biofilms break free and float

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
How does quorum sensing benefit microbial members of a biofilm? (Select all that apply)
A) This chemical intercellular communication helps regulate gene expression as cell density in the biofilm changes
B) Chemicals can be sent throughout the colony to help individual cells adapt to changing nutrient levels
C) Signals are sent to help community members avoid toxins
D) Intercellular messages help the microbial community evade immune attack and defend against competing microorganisms
A) This chemical intercellular communication helps regulate gene expression as cell density in the biofilm changes
B) Chemicals can be sent throughout the colony to help individual cells adapt to changing nutrient levels
C) Signals are sent to help community members avoid toxins
D) Intercellular messages help the microbial community evade immune attack and defend against competing microorganisms

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Quorum sensing communication works ________
A) Only between members of the same species in the biofilm
B) Only between bacterial species within the biofilm
C) Between all members of the biofilm
D) Between the members of any other biofilm
A) Only between members of the same species in the biofilm
B) Only between bacterial species within the biofilm
C) Between all members of the biofilm
D) Between the members of any other biofilm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
On which of the following surfaces will biofilms tend NOT to form?
A) Teeth and contact lenses
B) Replacement joints
C) Catheters and artificial heart valves
D) Peptide 1018-treated surfaces
A) Teeth and contact lenses
B) Replacement joints
C) Catheters and artificial heart valves
D) Peptide 1018-treated surfaces

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
What problems do biofilms cause to health care professionals? (Select all that apply)
A) Biofilm microbes are 2x more resistant to antibiotic therapy than non-communal microbes
B) Biofilm members are able to modify their antibiotic sensitivity
C) Biofilm microbes may be responsible for up to 25% of all chronic infections
D) Many drugs that could be effective against the microbes are unable to penetrate the extracellular matrix to reach the pathogens
A) Biofilm microbes are 2x more resistant to antibiotic therapy than non-communal microbes
B) Biofilm members are able to modify their antibiotic sensitivity
C) Biofilm microbes may be responsible for up to 25% of all chronic infections
D) Many drugs that could be effective against the microbes are unable to penetrate the extracellular matrix to reach the pathogens

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
How would Peptide 1018 reduce the number of serious infections caused by biofilm formation on indwelling medical devices? (Select all that apply)
A) It disables (p)ppGpp or guanosine pentaphosphate, a critical chemical signal for biofilm structure
B) Pretreatment of indwelling devices like catheters and stents with Peptide 1018 would dramatically reduce biofilm formation
C) Use of lower concentrations of Peptide 1018 as a pretreatment would eliminate biofilm formation
D) It inactivates (p)ppApp or adenosine pentaphosphate, which is essential for quorum sensing in a biofilm
A) It disables (p)ppGpp or guanosine pentaphosphate, a critical chemical signal for biofilm structure
B) Pretreatment of indwelling devices like catheters and stents with Peptide 1018 would dramatically reduce biofilm formation
C) Use of lower concentrations of Peptide 1018 as a pretreatment would eliminate biofilm formation
D) It inactivates (p)ppApp or adenosine pentaphosphate, which is essential for quorum sensing in a biofilm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Biogeochemical cycles can be described as __________________.
A) Circulation of chemical elements exclusively through the biotic portions of the biosphere
B) Recycling of essential elements directly between living organisms
C) Use of biochemical reactions in microbes to change unusable forms of elements from the physical environment into chemical forms that can be metabolized by other living organisms
D) Circulation of chemical elements exclusively through the abiotic portions of the biosphere
A) Circulation of chemical elements exclusively through the biotic portions of the biosphere
B) Recycling of essential elements directly between living organisms
C) Use of biochemical reactions in microbes to change unusable forms of elements from the physical environment into chemical forms that can be metabolized by other living organisms
D) Circulation of chemical elements exclusively through the abiotic portions of the biosphere

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
In the nitrogen cycle, nitrogen compounds can undergo ______ chemical reactions.
A) 2
B) 3
C) 4
D) 6
A) 2
B) 3
C) 4
D) 6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following statements concerning the Nitrogen Cycle is FALSE?
A) It is an atmospheric cycle.
B) In nitrogen fixation, unusable nitrogen gas is oxidized to the usable ammonium ion (NH4+)
C) Nitrogenase is the enzyme responsible for nitrogen fixation.
D) In ammonification, NH4+ is produced during the breakdown of amino acids by soil microbes during the decomposition of organic matter.
A) It is an atmospheric cycle.
B) In nitrogen fixation, unusable nitrogen gas is oxidized to the usable ammonium ion (NH4+)
C) Nitrogenase is the enzyme responsible for nitrogen fixation.
D) In ammonification, NH4+ is produced during the breakdown of amino acids by soil microbes during the decomposition of organic matter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Stages of the nitrogen cycle in which an abiotic phase converts to a biotic phase occur when ______. (Select all that apply)
A) NO3- is absorbed into plants through their roots and used to make amino acids
B) Herbivores consume plant material
C) N2 gas is fixed into NH4+ in the roots of a soybean plant
D) Denitrifying soil bacteria reduce NO3- to N2
A) NO3- is absorbed into plants through their roots and used to make amino acids
B) Herbivores consume plant material
C) N2 gas is fixed into NH4+ in the roots of a soybean plant
D) Denitrifying soil bacteria reduce NO3- to N2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
___________ is a microbe that participates in nitrogen fixation. (Select all that apply)
A) Anabaena
B) Rhizobium
C) Pseudomonas
D) Nitrobacter
A) Anabaena
B) Rhizobium
C) Pseudomonas
D) Nitrobacter

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
___________ is a microbial action that results in nitrogen conversion through reduction. (Select all that apply)
A) Nitrogen fixation
B) Nitrification
C) Denitrification
D) Ammonification
A) Nitrogen fixation
B) Nitrification
C) Denitrification
D) Ammonification

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
In ___________ , soil microbes generate NO2- and NO3- which are easily taken up by plant roots.
A) Nitrogen fixation
B) Nitrification
C) Denitrification
D) Ammonification
A) Nitrogen fixation
B) Nitrification
C) Denitrification
D) Ammonification

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The carbon cycle involves ___________. (Select all that apply)
A) The reciprocal processes of photosynthesis and cellular respiration
B) Movement of CO2 through Earth's limestone deposits
C) Absorption of CO2 from the atmosphere as fossil fuels are burned
D) The process of ammonification
A) The reciprocal processes of photosynthesis and cellular respiration
B) Movement of CO2 through Earth's limestone deposits
C) Absorption of CO2 from the atmosphere as fossil fuels are burned
D) The process of ammonification

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Carbon dioxide gas is released into the atmosphere when ___________. (Select all that apply)
A) Microorganisms perform fermentation
B) Microorganisms carry out aerobic respiration
C) Limestone deposits are compacted
D) Microorganisms perform photosynthesis
A) Microorganisms perform fermentation
B) Microorganisms carry out aerobic respiration
C) Limestone deposits are compacted
D) Microorganisms perform photosynthesis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Greenhouse gases ________. (Select all that apply)
A) Include CO2, N2O, and CH4
B) Absorb and reflect heat back to Earth's surface
C) Have increased global mean temperature by 1o C
D) Have reduced air pollution
A) Include CO2, N2O, and CH4
B) Absorb and reflect heat back to Earth's surface
C) Have increased global mean temperature by 1o C
D) Have reduced air pollution

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Ruminants like cows rely on bacteria in their stomachs to break down the cellulose in the plants they eat. This has ___________. (Select all that apply)
A) Released large amounts of methane gas into the atmosphere due to cow flatulence and belching
B) Greatly exacerbated the problem of global warming because CH4 is almost 20X better at trapping atmospheric heat than CO2
C) Resulted in lowered global oxygen levels due to the bacterial respiration
D) Resulted in lowered global CO2 levels due to bacterial respiration
A) Released large amounts of methane gas into the atmosphere due to cow flatulence and belching
B) Greatly exacerbated the problem of global warming because CH4 is almost 20X better at trapping atmospheric heat than CO2
C) Resulted in lowered global oxygen levels due to the bacterial respiration
D) Resulted in lowered global CO2 levels due to bacterial respiration

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Unlike the nitrogen and carbon cycles, the phosphorous cycle is a sedimentary cycle because the principle reservoirs are in __________.
A) rock and soil
B) soil and water
C) rock and sand
D) limestone and water
A) rock and soil
B) soil and water
C) rock and sand
D) limestone and water

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The two pathways in the phosphorous cycle involve _______. (Select all that apply)
A) Slow cycling between abiotic and biotic forms as part of organic molecules
B) Rapid cycling between soluble and insoluble abiotic forms trapped in rock and released by acie-secreting microbes
C) Rapid cycling between abiotic and biotic forms as part of organic molecules
D) Slow cycling between soluble and insoluble abiotic forms trapped in rock and released by acid-secreting microbes
A) Slow cycling between abiotic and biotic forms as part of organic molecules
B) Rapid cycling between soluble and insoluble abiotic forms trapped in rock and released by acie-secreting microbes
C) Rapid cycling between abiotic and biotic forms as part of organic molecules
D) Slow cycling between soluble and insoluble abiotic forms trapped in rock and released by acid-secreting microbes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Phosphorous cycles rapidly through the food web as _______. (Select all that apply)
A) Microbes like Bacillus, Pseudomonas, and Rhizobium convert phosphorous into soluble compounds
B) Plants take up the soluble compounds and pass them on to herbivores
C) Decomposition of dead organisms return phosphorous to the soil and water
D) Acid secretion by mycorrhizae elevates soil pH, improving solubility of phosphorous compounds
A) Microbes like Bacillus, Pseudomonas, and Rhizobium convert phosphorous into soluble compounds
B) Plants take up the soluble compounds and pass them on to herbivores
C) Decomposition of dead organisms return phosphorous to the soil and water
D) Acid secretion by mycorrhizae elevates soil pH, improving solubility of phosphorous compounds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The phosphorous cycle is essential for providing usable phosphorous to organisms who need it to make ___________. (Select all that apply)
A) ATP
B) Carbohydrates
C) Nucleic acids
D) Phospholipids
A) ATP
B) Carbohydrates
C) Nucleic acids
D) Phospholipids

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The red waters of the Tinto River have a pH of 1.5-3.1 ____________. (Select all that apply)
A) As a result of the sulfur- and iron-metabolizing bacterial community composed of Leptospirullum, Acidithiobacillus, Ferroplasma, and Thermoplasma
B) And sulfide-rich sediments similar to equatorial subsurface areas on Mars
C) Which result in the geochemical conditions that produce Jarosite, a rare mineral also discovered on Mars
D) Just like the microbe-rich rivers on Mars
A) As a result of the sulfur- and iron-metabolizing bacterial community composed of Leptospirullum, Acidithiobacillus, Ferroplasma, and Thermoplasma
B) And sulfide-rich sediments similar to equatorial subsurface areas on Mars
C) Which result in the geochemical conditions that produce Jarosite, a rare mineral also discovered on Mars
D) Just like the microbe-rich rivers on Mars

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The ________ biogeochemical cycle relies on redox reactions to interconvert compounds. (Select all that apply)
A) Hydrologic
B) Nitrogen
C) Phosphorous
D) Sulfur
A) Hydrologic
B) Nitrogen
C) Phosphorous
D) Sulfur

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Bioremediation __________. (Select all that apply)
A) Intentionally introduces specific microorganisms to degrade and/or consumer pollutants
B) Uses naturally-occurring microorganisms to degrade and/or consume pollutants
C) Introduces man-made chemicals into a habitat to inhibit the growth of microorganisms
D) Permits habitat decontamination
A) Intentionally introduces specific microorganisms to degrade and/or consumer pollutants
B) Uses naturally-occurring microorganisms to degrade and/or consume pollutants
C) Introduces man-made chemicals into a habitat to inhibit the growth of microorganisms
D) Permits habitat decontamination

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Heavy metals from mining pollution and aromatic hydrocarbons from petroleum product spills can be bioremediated using ________.
A) Dechloromonas aromatic
B) Geobacter spp.
C) Nitrobacter hamburgensis
D) Pseudomonas putida
A) Dechloromonas aromatic
B) Geobacter spp.
C) Nitrobacter hamburgensis
D) Pseudomonas putida

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Excess ammonium, nitrates, and nitrites from fertilizer can be removed from the soil using ________.
A) Dechloromonas aromatic
B) Geobacter spp.
C) Nitrobacter hamburgensis
D) Pseudomonas putida
A) Dechloromonas aromatic
B) Geobacter spp.
C) Nitrobacter hamburgensis
D) Pseudomonas putida

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
What A habitat accidentally contaminated by the release of radioactive waste can be bioremediated by ________.
A) Dechloromonas aromatic
B) Deinococcus radiodurans
C) Phanerochaete chrysosporium
D) Pleurotus ostreatus
A) Dechloromonas aromatic
B) Deinococcus radiodurans
C) Phanerochaete chrysosporium
D) Pleurotus ostreatus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The fungus _____ can bioremediate habitats contaminated with dioxins, cyanides, or carbon tetrachloride.
A) Dechloromonas aromatic
B) Deinococcus radiodurans
C) Phanerochaete chrysosporium
D) Pleurotus ostreatus
A) Dechloromonas aromatic
B) Deinococcus radiodurans
C) Phanerochaete chrysosporium
D) Pleurotus ostreatus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Bioremediation of the Cuyahoga River ________. (Select all that apply)
A) Was required to overcome the damage resulting from agricultural run-off and industrial dumping
B) Was enhanced by the passage of the Ohio Clean Water Act (OCWA) in 1992 which made it illegal to dump pollutants into the river
C) Was facilitated by the activity of bacterial species such as Bacillus, Burkholderia and Pseudomonas
D) Has seen the gradual return of many fish species as water quality improved
A) Was required to overcome the damage resulting from agricultural run-off and industrial dumping
B) Was enhanced by the passage of the Ohio Clean Water Act (OCWA) in 1992 which made it illegal to dump pollutants into the river
C) Was facilitated by the activity of bacterial species such as Bacillus, Burkholderia and Pseudomonas
D) Has seen the gradual return of many fish species as water quality improved

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Biostimulation ___________. (Select all that apply)
A) Involves modification of environmental conditions so naturally-occurring microorganisms increase their metabolic reactions to speed pollutant degradation
B) Involves changing habitat pH, temperature, and nutrient availability
C) Requires the introduction of GMOs into the contaminated habitat
D) Uses microorganisms to generate commercially valuable proteins
A) Involves modification of environmental conditions so naturally-occurring microorganisms increase their metabolic reactions to speed pollutant degradation
B) Involves changing habitat pH, temperature, and nutrient availability
C) Requires the introduction of GMOs into the contaminated habitat
D) Uses microorganisms to generate commercially valuable proteins

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
___________ is an example of successful bioremediation of a contaminated habitat. (Select all that apply)
A) The Cuyahoga River in Cleveland, Ohio
B) The Gulf of Mexico following the Deepwater Horizon oil spill in 2010
C) The Tinto River in Spain
D) Grand Lake St. Mary's
A) The Cuyahoga River in Cleveland, Ohio
B) The Gulf of Mexico following the Deepwater Horizon oil spill in 2010
C) The Tinto River in Spain
D) Grand Lake St. Mary's

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Bioaugmentation displays all of the following characteristics EXCEPT _________.
A) The addition of specifically selected microbes chosen because they metabolize a specific pollutant
B) Using microbes that are genetically modified
C) Selectively speeding up the degradation of industrial versus naturally-occurring pollutants
D) Using naturally-occurring microorganisms
A) The addition of specifically selected microbes chosen because they metabolize a specific pollutant
B) Using microbes that are genetically modified
C) Selectively speeding up the degradation of industrial versus naturally-occurring pollutants
D) Using naturally-occurring microorganisms

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
All of the following are problems associated with treating sewage and wastewater EXCEPT _________.
A) Microbes must be added to the waste in order to process it
B) The high amounts of nitrogen and phosphorous promote habitat enrichment, leading to algal blooms
C) The BOD of microbes that digest the waste is so high that normal oxygen levels are inadequate to support aquatic life
D) The removal of high levels of nitrogen and phosphorous from the organic matter
A) Microbes must be added to the waste in order to process it
B) The high amounts of nitrogen and phosphorous promote habitat enrichment, leading to algal blooms
C) The BOD of microbes that digest the waste is so high that normal oxygen levels are inadequate to support aquatic life
D) The removal of high levels of nitrogen and phosphorous from the organic matter

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The cleanest surface water is disinfected with chlorine or UV light as the excess nitrogen and phosphorous are removed in the _________ phase of sewage remediation.
A) Primary
B) Secondary
C) Tertiary
D) Sterilization
A) Primary
B) Secondary
C) Tertiary
D) Sterilization

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Raw sewage is pumped into a holding tank, the refuse and oils skimmed from the surface, and particulate matters settle to the bottom of the tank in the _________ phase of sewage remediation.
A) Primary
B) Secondary
C) Tertiary
D) Sterilization
A) Primary
B) Secondary
C) Tertiary
D) Sterilization

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Wastewater is transferred to an aeration chamber so oxidation by microbes can remove 75% of the BOD in the _________ phase of sewage remediation.
A) Primary
B) Secondary
C) Tertiary
D) Sterilization
A) Primary
B) Secondary
C) Tertiary
D) Sterilization

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
What happens to the sludge produced during the first two phases of sewage processing? (Select all that apply)
A) It is used as agricultural fertilizer since it contains high levels of NPK and organic material
B) It is converted into biofuels because of its high CO2 levels
C) It can be converted into biogases such as methane
D) It can be heat-treated and used to make construction materials
A) It is used as agricultural fertilizer since it contains high levels of NPK and organic material
B) It is converted into biofuels because of its high CO2 levels
C) It can be converted into biogases such as methane
D) It can be heat-treated and used to make construction materials

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which of the following statements about municipal water supply treatment for safe human consumption is FALSE?
A) Surface water picks up many pathogenic and nonpathogenic microbes from rain water contamination
B) Animal feces are a source of many microbes contaminating reservoirs
C) Indicator microbes are usually fecal coliforms like E. coli that live in the colons of animals and suggest that more dangerous microbial contaminants could be present
D) The presence of indicator organisms confirms the presence of pathogenic contaminants
A) Surface water picks up many pathogenic and nonpathogenic microbes from rain water contamination
B) Animal feces are a source of many microbes contaminating reservoirs
C) Indicator microbes are usually fecal coliforms like E. coli that live in the colons of animals and suggest that more dangerous microbial contaminants could be present
D) The presence of indicator organisms confirms the presence of pathogenic contaminants

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
All of the following are major steps in treating freshwater to make it potable EXCEPT ________.
A) Reservoirs are used as large holding areas that allow particulates to settle to the bottom
B) Water is treated with magnesium sulfate to reduce the growth of photosynthetic microbes
C) Water is eventually pumped into special tanks that filter it with rocks or sand to remove the majority of microorganisms
D) The final step pumps water into holding tanks for disinfecting chlorination or light treatments
A) Reservoirs are used as large holding areas that allow particulates to settle to the bottom
B) Water is treated with magnesium sulfate to reduce the growth of photosynthetic microbes
C) Water is eventually pumped into special tanks that filter it with rocks or sand to remove the majority of microorganisms
D) The final step pumps water into holding tanks for disinfecting chlorination or light treatments

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which of the following characteristics describe a fecal coliform? (Select all that apply)
A) Lactose-fermenter
B) Gram positive
C) Gas-generators
D) Base-secretors
A) Lactose-fermenter
B) Gram positive
C) Gas-generators
D) Base-secretors

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Microorganisms are used to produce many valuable products commonly used in modern society such as _______. (Select all that apply)
A) Food preservatives like acetic acid
B) Toxins for pesticide use in agriculture
C) Enzymes to create faded blue jean finishes
D) Vitamin supplements
A) Food preservatives like acetic acid
B) Toxins for pesticide use in agriculture
C) Enzymes to create faded blue jean finishes
D) Vitamin supplements

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
_______ is used to make antibiotics for treating bacterial infections.
A) Streptomyces
B) Cunninghamella
C) Rhizopus
D) GMO E. coli
A) Streptomyces
B) Cunninghamella
C) Rhizopus
D) GMO E. coli

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
_______ is used to make steroids used in producing birth control products. (Select all that apply)
A) Streptomyces
B) Cunninghamella
C) Rhizopus
D) GMO E. coli
A) Streptomyces
B) Cunninghamella
C) Rhizopus
D) GMO E. coli

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
_______ is used to make Humalog, a recombinant human insulin used to control blood glucose levels.
A) Streptomyces
B) Cunninghamella
C) Rhizopus
D) GMO E. coli
A) Streptomyces
B) Cunninghamella
C) Rhizopus
D) GMO E. coli

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Industrial fermentation utilizes a bioreactor to _______ . (Select all that apply)
A) maximize microbial growth and product generation
B) control variables such as temperature, pH, oxygen concentration, and nutrient levels
C) cultivate a starter culture community of microbes
D) vent gases generated during fermentation
A) maximize microbial growth and product generation
B) control variables such as temperature, pH, oxygen concentration, and nutrient levels
C) cultivate a starter culture community of microbes
D) vent gases generated during fermentation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
______ is used to make a toxin that stops larval development, acting as a pesticide.
A) Clostridium spp.
B) Aspergillus
C) Bacillus (Bti)
D) Chlamydomonas
A) Clostridium spp.
B) Aspergillus
C) Bacillus (Bti)
D) Chlamydomonas

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
______ is used to make the solvent acetone.
A) Clostridium spp.
B) Bradyrhizobium
C) Bacillus (Bti)
D) Chlamydomonas
A) Clostridium spp.
B) Bradyrhizobium
C) Bacillus (Bti)
D) Chlamydomonas

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
______ is used to make fertilizers by promoting nitrogen fixation.
A) Clostridium spp.
B) Bradyrhizobium
C) Bacillus (Bti)
D) Chlamydomonas
A) Clostridium spp.
B) Bradyrhizobium
C) Bacillus (Bti)
D) Chlamydomonas

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Which of the following food products is mismatched with the microbe responsible for giving it a distinctive flavor?
A) Sauerkraut, poi, kimchi, and kombucha get their tangy flavor from Lactobacillus brevis
B) Summer sausages and salamis get their savory flavor from Leuconostoc mesenteroides
C) Buttermilk, kefir, and sour cream are made using Lactococcus lactis
D) Yogurt production involves Lactobacillus bulgaricus
A) Sauerkraut, poi, kimchi, and kombucha get their tangy flavor from Lactobacillus brevis
B) Summer sausages and salamis get their savory flavor from Leuconostoc mesenteroides
C) Buttermilk, kefir, and sour cream are made using Lactococcus lactis
D) Yogurt production involves Lactobacillus bulgaricus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Yogurt production utilizes microbial fermentation of milk to lower the pH and promote the tangy flavor and creamy texture. Put the steps for this process in the correct order.
1) Excess fat is skimmed off raw milk and protein content is raised with milk products,
2) Milk is cooled to 50o C and inoculated with L. bulgaricus and L. thermophiles
3) Fermentation generates formic and lactic acids that drop pH to 4.3 and coagulates milk proteins
4) Contents are pasteurized and homogenized
5) Additional flavorings may be added before dispensing yogurt into containers and sealing them
A) 4, 2, 3, 1. 5
B) 1, 4, 2, 3, 5
C) 1, 3, 4, 2, 5
D) 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
1) Excess fat is skimmed off raw milk and protein content is raised with milk products,
2) Milk is cooled to 50o C and inoculated with L. bulgaricus and L. thermophiles
3) Fermentation generates formic and lactic acids that drop pH to 4.3 and coagulates milk proteins
4) Contents are pasteurized and homogenized
5) Additional flavorings may be added before dispensing yogurt into containers and sealing them
A) 4, 2, 3, 1. 5
B) 1, 4, 2, 3, 5
C) 1, 3, 4, 2, 5
D) 1, 2, 3, 4, 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Which of the following terms and descriptions are mismatched?
A) curds/coagulated milk proteins such as casein
B) whey/milk fluid containing proteins and other nutrients
C) unripened cheese/Brie
D) secondary cultured cheeses/Swiss
A) curds/coagulated milk proteins such as casein
B) whey/milk fluid containing proteins and other nutrients
C) unripened cheese/Brie
D) secondary cultured cheeses/Swiss

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Why is the maximum alcohol content of wine typically around 12%?
A) Because at this point, the alcohol poisons the yeast and the fermentation process that produces the alcohol stops
B) Because the yeast runs out of a carbohydrate source to ferment
C) Because the accumulation of alcohol lowers the temperature enough that fermentation cannot proceed
D) Because the pH is raised during fermentation which denatures the enzymes needed to continue the process
A) Because at this point, the alcohol poisons the yeast and the fermentation process that produces the alcohol stops
B) Because the yeast runs out of a carbohydrate source to ferment
C) Because the accumulation of alcohol lowers the temperature enough that fermentation cannot proceed
D) Because the pH is raised during fermentation which denatures the enzymes needed to continue the process

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Which of the following statements describes the term "malting" in the process of making beer?
A) The grain is crushed to expose more starch as substrate to the digestive enzymes
B) The crushed grain is treated with hot water to increase enzyme activity
C) The liquid is separated from the grain mash and mixed with hops to add flavor
D) The grain is germinated to release alpha-amylase which digests starch to glucose
A) The grain is crushed to expose more starch as substrate to the digestive enzymes
B) The crushed grain is treated with hot water to increase enzyme activity
C) The liquid is separated from the grain mash and mixed with hops to add flavor
D) The grain is germinated to release alpha-amylase which digests starch to glucose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Why did the attempt to make bacon beer in the case study fail?
A) Anaerobic conditions were not produced so fermentation never occurred.
B) The strain of yeast used did not perform fermentation in the homemade anaerobic chamber.
C) Fermentation requires a carbohydrate source such as glucose, which is not found in bacon.
D) In order for yeast to ferment the lipids in the bacon, the temperature should have been significantly elevated.
A) Anaerobic conditions were not produced so fermentation never occurred.
B) The strain of yeast used did not perform fermentation in the homemade anaerobic chamber.
C) Fermentation requires a carbohydrate source such as glucose, which is not found in bacon.
D) In order for yeast to ferment the lipids in the bacon, the temperature should have been significantly elevated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Rapid onset of gastroenteritis symptoms following food ingestion typically suggests _________. (Select all that apply)
A) Infection, as it would require a large population of contaminating microbes which would take time to produce
B) Intoxication, as toxins secreted into the food by contaminating microbes are immediately available to bind host GI receptors and initiate symptoms
C) Contamination of the food with a pathogen such as Staphylococcus aureus, a notorious toxin-secretor
D) The importance of meticulous hygiene during food preparation as intoxication can still occur if toxin-secreting pathogens are killed by cooking
A) Infection, as it would require a large population of contaminating microbes which would take time to produce
B) Intoxication, as toxins secreted into the food by contaminating microbes are immediately available to bind host GI receptors and initiate symptoms
C) Contamination of the food with a pathogen such as Staphylococcus aureus, a notorious toxin-secretor
D) The importance of meticulous hygiene during food preparation as intoxication can still occur if toxin-secreting pathogens are killed by cooking

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The seven principles of the HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point) system do not include ___________.
A) Identification points of where food safety could be compromised
B) The establishment of clear critical limits for cooking temperature and time, food color, texture, and general appearance
C) Inspection of food items prior to entrance into manufacturing operations
D) Establishment of corrective actions in advance so products inadvertently made under unsafe conditions do not enter the market
A) Identification points of where food safety could be compromised
B) The establishment of clear critical limits for cooking temperature and time, food color, texture, and general appearance
C) Inspection of food items prior to entrance into manufacturing operations
D) Establishment of corrective actions in advance so products inadvertently made under unsafe conditions do not enter the market

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point) system originated as a collaboration between ___________.
A) NASA and US Army Laboratories and Pillsbury to develop a protocol to provide safe food on manned space missions
B) the USDA, FDA, and Pillsbury to develop a protocol to provide safe food on manned space missions
C) the USDA, FDA, and US Army Laboratories to develop a protocol to provide safe food for deployed military personnel
D) the USDA, FDA, and Pillsbury to develop a protocol to provide safe processed foods to the US public
A) NASA and US Army Laboratories and Pillsbury to develop a protocol to provide safe food on manned space missions
B) the USDA, FDA, and Pillsbury to develop a protocol to provide safe food on manned space missions
C) the USDA, FDA, and US Army Laboratories to develop a protocol to provide safe food for deployed military personnel
D) the USDA, FDA, and Pillsbury to develop a protocol to provide safe processed foods to the US public

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Spices and nuts are often preserved by adding ___________.
A) Citric and propionic acids
B) Sulfur dioxide
C) Alkylating agents
D) Nitrates
A) Citric and propionic acids
B) Sulfur dioxide
C) Alkylating agents
D) Nitrates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Processed meats like bacon are often preserved by adding ___________.
A) Citric and propionic acids
B) Sulfur dioxide
C) Alkylating agents
D) Nitrates
A) Citric and propionic acids
B) Sulfur dioxide
C) Alkylating agents
D) Nitrates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Juices, soft drinks, cereals, and pastries are often preserved by adding ___________.
A) Citric and propionic acids
B) Sulfur dioxide
C) Alkylating agents
D) Nitrates
A) Citric and propionic acids
B) Sulfur dioxide
C) Alkylating agents
D) Nitrates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
________ is often used to decontaminate fruit juice before it undergoes fermentation to make wine.
A) Citric and propionic acids
B) Sulfur dioxide
C) Alkylating agents
D) Nitrates
A) Citric and propionic acids
B) Sulfur dioxide
C) Alkylating agents
D) Nitrates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Which of the following physical methods of microbial control is gaining popularity and public acceptance because of its effectiveness?
A) Chemical desiccation and dehydration
B) Ionizing radiation to damage microbial DNA
C) High pressure treatments of 90,000 psi
D) Freeze-drying
A) Chemical desiccation and dehydration
B) Ionizing radiation to damage microbial DNA
C) High pressure treatments of 90,000 psi
D) Freeze-drying

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Which of the following statements about pasteurization is FALSE?
A) It is a process of heating liquid foods to kill vegetative microbes that lead to spoilage.
B) It increases the length of time that products are safe to consume
C) It uses an inverse ratio so the higher the pasteurization temperature, the shorter the time needed for heating
D) It destroys all of the pathogens in the treated food product
A) It is a process of heating liquid foods to kill vegetative microbes that lead to spoilage.
B) It increases the length of time that products are safe to consume
C) It uses an inverse ratio so the higher the pasteurization temperature, the shorter the time needed for heating
D) It destroys all of the pathogens in the treated food product

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



