Deck 8: The Geography of Agriculture and Food: Shaping the Land, Feeding the World
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/248
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 8: The Geography of Agriculture and Food: Shaping the Land, Feeding the World
1
The principal occupation of humanity since the origin of our species has been:
A) Trade
B) food acquisition
C) development
D) Migration
A) Trade
B) food acquisition
C) development
D) Migration
B
2
Most people throughout history have interacted with the environment for the purpose of:
A) finding and cultivating food
B) the building of human dwellings
C) the building of office space
D) the preservation of park space
A) finding and cultivating food
B) the building of human dwellings
C) the building of office space
D) the preservation of park space
A
3
Which of the following is NOT an agricultural practice?
A) herding livestock
B) growing fiber for clothing
C) mining
D) cultivation of crops
A) herding livestock
B) growing fiber for clothing
C) mining
D) cultivation of crops
C
4
What is the primary factor determining the type of agriculture possible in any particular place?
A) culture
B) invasive species
C) topography
D) climate
A) culture
B) invasive species
C) topography
D) climate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Regional agricultural patterns tend to reflect:
A) regional climate patterns
B) dominant cultural traits
C) state policies
D) topography
A) regional climate patterns
B) dominant cultural traits
C) state policies
D) topography

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which term refers to the practices of farming and livestock raising that require low levels of labor and capital relative to the amount of land under production?
A) subsistence agriculture
B) industrial agriculture
C) extensive agriculture
D) intensive agriculture
A) subsistence agriculture
B) industrial agriculture
C) extensive agriculture
D) intensive agriculture

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which type of agriculture uses high levels of labor and capital relative to the size of the land holding?
A) subsistence agriculture
B) industrial agriculture
C) extensive agriculture
D) intensive agriculture
A) subsistence agriculture
B) industrial agriculture
C) extensive agriculture
D) intensive agriculture

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which is NOT commonly associated with intensive agriculture?
A) swidden practices
B) use of chemical pesticides and herbicides
C) irrigation
D) genetic engineering
A) swidden practices
B) use of chemical pesticides and herbicides
C) irrigation
D) genetic engineering

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Another term for slash-and-burn clearing is:
A) paddy rice farming
B) intertillage
C) swidden cultivation
D) intercropping
A) paddy rice farming
B) intertillage
C) swidden cultivation
D) intercropping

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The first step in swidden cultivation is:
A) the application of fertilizer to the land
B) the harvesting of crops
C) the clearing of the land
D) the planting of seeds
A) the application of fertilizer to the land
B) the harvesting of crops
C) the clearing of the land
D) the planting of seeds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11

-Which type of agricultural activity is represented in the photo?
A) peasant grain farming
B) nomadic herding
C) paddy rice farming
D) swidden agriculture

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12

-Which is NOT a characteristic of the agricultural activity shown in the photo?
A) high levels of water use
B) high amounts of human labor
C) very high land productivity
D) three crop harvests per year

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13

-The photo was MOST likely taken somewhere in:
A) Africa
B) East Asia
C) Scandinavia
D) Australia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Shifting cultivation involves what kind of agricultural practice?
A) animal husbandry
B) intensive agriculture
C) green revolution
D) land rotation
A) animal husbandry
B) intensive agriculture
C) green revolution
D) land rotation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which agricultural activity is NOT characteristic of shifting cultivation?
A) growing several different types of crops in one field
B) slash-and-burn techniques
C) subsistence agriculture
D) raising of large amounts of livestock
A) growing several different types of crops in one field
B) slash-and-burn techniques
C) subsistence agriculture
D) raising of large amounts of livestock

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which statement about most shifting cultivators is NOT true?
A) Their traditional methods have endured for millennia and reveal a deep knowledge of the environment.
B) They can return more calories of food per energy unit spent in food production than can contemporary mechanized agriculture.
C) Their unsustainable type of agriculture tends to be ecologically damaging.
D) In poor countries with large populations of landless peasants, shifting cultivators are often encroaching on the forests.
A) Their traditional methods have endured for millennia and reveal a deep knowledge of the environment.
B) They can return more calories of food per energy unit spent in food production than can contemporary mechanized agriculture.
C) Their unsustainable type of agriculture tends to be ecologically damaging.
D) In poor countries with large populations of landless peasants, shifting cultivators are often encroaching on the forests.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Shifting cultivation can cause severe environmental damage primarily when:
A) population exceeds environmental capacity through population increases
B) it upsets the local ecology through increased use of fertilizers
C) overgrazing by draft animals increases soil erosion
D) climate change alters precipitation, resulting in erosion and depletion of soil nutrients
A) population exceeds environmental capacity through population increases
B) it upsets the local ecology through increased use of fertilizers
C) overgrazing by draft animals increases soil erosion
D) climate change alters precipitation, resulting in erosion and depletion of soil nutrients

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which is NOT an advantage of intercropping?
A) Smaller plants are protected by larger ones.
B) The risk of crop loss from disease or pests is reduced.
C) It provides farmers with a varied diet.
D) It lowers the amount of taxes farmers must pay to their municipality.
A) Smaller plants are protected by larger ones.
B) The risk of crop loss from disease or pests is reduced.
C) It provides farmers with a varied diet.
D) It lowers the amount of taxes farmers must pay to their municipality.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
In swidden cultivation, fertilizers:
A) come mostly from animal dung
B) are provided through the clearing of land with fire
C) come from genetically modified seeds
D) tend to be chemicals
A) come mostly from animal dung
B) are provided through the clearing of land with fire
C) come from genetically modified seeds
D) tend to be chemicals

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which is NOT an advantage of swidden agriculture?
A) In many cases, it is ecologically sustainable.
B) Some swidden systems actually increase biodiversity.
C) It permits increasing yields on the same patch of land with each passing year.
D) In many areas, swidden cultivation has left most of the forest intact over centuries of continuous use.
A) In many cases, it is ecologically sustainable.
B) Some swidden systems actually increase biodiversity.
C) It permits increasing yields on the same patch of land with each passing year.
D) In many areas, swidden cultivation has left most of the forest intact over centuries of continuous use.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Subsistence agriculture means agriculture produced for:
A) the family
B) a farmers' cooperative
C) tax revenue
D) the people of nearby cities
A) the family
B) a farmers' cooperative
C) tax revenue
D) the people of nearby cities

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A flooded rice field is known as a:
A) paddy
B) swidden
C) cadastral pattern
D) rice ranch
A) paddy
B) swidden
C) cadastral pattern
D) rice ranch

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which characteristic is NOT true of subsistence paddy rice farming?
A) Paddy rice farming requires large amounts of water and fertilizer.
B) Paddy rice farming traditionally requires enormous amounts of human labor but yields little food per unit area of land.
C) Paddy rice farms are often only 3 acres in size but are adequate to support a family.
D) Paddy rice farmers often plant and harvest the same parcel of land twice each year.
A) Paddy rice farming requires large amounts of water and fertilizer.
B) Paddy rice farming traditionally requires enormous amounts of human labor but yields little food per unit area of land.
C) Paddy rice farms are often only 3 acres in size but are adequate to support a family.
D) Paddy rice farmers often plant and harvest the same parcel of land twice each year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which statement is NOT true of paddy rice farming in more developed countries today?
A) It produces high output.
B) It requires a large amount of water.
C) It produces rice primarily for rural markets.
D) It often takes place on terraced hillsides.
A) It produces high output.
B) It requires a large amount of water.
C) It produces rice primarily for rural markets.
D) It often takes place on terraced hillsides.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which is NOT true of peasant farming?
A) It benefits from modern fertilizers and technologies.
B) It is usually a form of folk culture.
C) Peasant farmers not only raise crops but also raise animals.
D) The dominant grains raised by peasant farmers include wheat and barley.
A) It benefits from modern fertilizers and technologies.
B) It is usually a form of folk culture.
C) Peasant farmers not only raise crops but also raise animals.
D) The dominant grains raised by peasant farmers include wheat and barley.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In various parts of the world, peasant farmers practice a diverse form of agriculture that:
A) is based on modern agricultural technologies to raise bread grains, root crops, and livestock
B) also represents strong folk cultures
C) is a wholly subsistence economy
D) has no access to irrigation or to commercial markets
A) is based on modern agricultural technologies to raise bread grains, root crops, and livestock
B) also represents strong folk cultures
C) is a wholly subsistence economy
D) has no access to irrigation or to commercial markets

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
All of the following are accurate descriptions of plantations EXCEPT:
A) They tend to be located near the seacoast.
B) They usually grow one crop.
C) They originated in Italian colonies.
D) Their workers usually live right on the plantation.
A) They tend to be located near the seacoast.
B) They usually grow one crop.
C) They originated in Italian colonies.
D) Their workers usually live right on the plantation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Most of the crops produced by plantations are:
A) consumed on the plantation
B) exported to other countries
C) sold within the country in which they are harvested
D) used to produce biofuels
A) consumed on the plantation
B) exported to other countries
C) sold within the country in which they are harvested
D) used to produce biofuels

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The form of agriculture known for hostilities between workers and managers is:
A) swidden agriculture
B) market gardening
C) livestock ranching
D) plantation agriculture
A) swidden agriculture
B) market gardening
C) livestock ranching
D) plantation agriculture

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Most plantations are owned and controlled by:
A) subsistence farmers
B) local monarchs
C) multinational corporations
D) farmers' cooperatives
A) subsistence farmers
B) local monarchs
C) multinational corporations
D) farmers' cooperatives

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Profits from and ownership of plantations is concentrated in:
A) the hands of the laborers in a form of communal sharing
B) the European and U.S. governments, which have provided development capital
C) a few multinational corporations, such as Dole and Chiquita
D) the upper tier of management, which runs the plantations
A) the hands of the laborers in a form of communal sharing
B) the European and U.S. governments, which have provided development capital
C) a few multinational corporations, such as Dole and Chiquita
D) the upper tier of management, which runs the plantations

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
All of the following are distinguishing traits of plantations EXCEPT:
A) They are geared to the large-scale production of a single crop.
B) They are typically owned by corporations or governments.
C) They are usually located in the interior of tropical or subtropical regions.
D) There is often a rigid social segregation between labor and management.
A) They are geared to the large-scale production of a single crop.
B) They are typically owned by corporations or governments.
C) They are usually located in the interior of tropical or subtropical regions.
D) There is often a rigid social segregation between labor and management.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
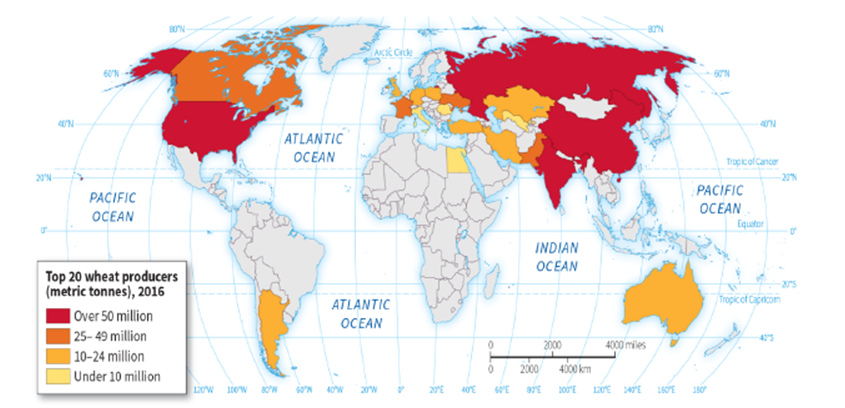
-According to the map, wheat is produced in all of the following states EXCEPT:
A) South Africa
B) Egypt
C) Russia
D) Canada

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34

-According to the map, which has the lowest production of sugarcane?
A) Australia
B) India
C) Argentina
D) Italy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which form of cultivation is LEAST likely to be owned and operated by large-scale agribusiness?
A) dairying
B) grain farming
C) market gardening
D) plantation agriculture
A) dairying
B) grain farming
C) market gardening
D) plantation agriculture

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Plantations emphasize _____ crops at the expense of _____ crops.
A) export/grain
B) commercial/subsistence
C) mono/intertillage
D) commercial/extensive
A) export/grain
B) commercial/subsistence
C) mono/intertillage
D) commercial/extensive

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which is NOT a characteristic of plantation agriculture?
A) capital-intensive
B) large-scale
C) extensive use of manual labor
D) a variety of crops
A) capital-intensive
B) large-scale
C) extensive use of manual labor
D) a variety of crops

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which statement is NOT true of market gardening?
A) It is also known as truck farming.
B) It raises no livestock.
C) Many market gardeners take part in cooperative marketing arrangements.
D) It is only found in the United States.
A) It is also known as truck farming.
B) It raises no livestock.
C) Many market gardeners take part in cooperative marketing arrangements.
D) It is only found in the United States.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
In which type of agriculture do we often see farmers' marketing cooperatives?
A) livestock fattening
B) nomadic herding
C) swidden agriculture
D) market gardening
A) livestock fattening
B) nomadic herding
C) swidden agriculture
D) market gardening

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Truck farms:
A) raise livestock
B) are mostly located in developing countries
C) are found around the Mediterranean
D) grow a wide variety of produce
A) raise livestock
B) are mostly located in developing countries
C) are found around the Mediterranean
D) grow a wide variety of produce

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which is NOT characteristic of market gardening?
A) use of migratory seasonal farm labor
B) cooperative marketing arrangements
C) locations in developed countries
D) extensive raising of livestock
A) use of migratory seasonal farm labor
B) cooperative marketing arrangements
C) locations in developed countries
D) extensive raising of livestock

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
A local market owns farmland on which vegetables are grown and trucked daily to the refrigerated warehouses and stores. This is an example of what type of gardening?
A) extensive
B) after-market
C) subsistence
D) market
A) extensive
B) after-market
C) subsistence
D) market

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
In the United States, market gardens are found:
A) clustered around the Great Lakes
B) only in California and Florida
C) along the East Coast from New England to Virginia
D) in California eastward through the Gulf and Atlantic coast states
A) clustered around the Great Lakes
B) only in California and Florida
C) along the East Coast from New England to Virginia
D) in California eastward through the Gulf and Atlantic coast states

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which statement about livestock fattening is NOT true?
A) Slaughterhouses are often located near feedlots.
B) It is often dependent on migrant labor.
C) It is common in the northeastern United States.
D) It is common in the U.S. Corn Belt.
A) Slaughterhouses are often located near feedlots.
B) It is often dependent on migrant labor.
C) It is common in the northeastern United States.
D) It is common in the U.S. Corn Belt.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which of these crops is NOT associated with livestock fattening?
A) potatoes
B) oats
C) corn
D) rice
A) potatoes
B) oats
C) corn
D) rice

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The Cargill and ConAgra companies control much of the supply in which industry?
A) oil
B) beef
C) sheep
D) wheat
A) oil
B) beef
C) sheep
D) wheat

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Much of the control of the livestock-fattening-and-slaughtering industry is concentrated in:
A) Europe
B) a very few companies that dominate the grain market, feedlots, and slaughterhouses
C) Canada, due to the advantage of the NAFTA agreement
D) island nations
A) Europe
B) a very few companies that dominate the grain market, feedlots, and slaughterhouses
C) Canada, due to the advantage of the NAFTA agreement
D) island nations

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
In which type of agriculture do farmers primarily grow rice, wheat, or corn for commercial markets?
A) grain ranching
B) swidden agriculture
C) grain farming
D) market gardening
A) grain ranching
B) swidden agriculture
C) grain farming
D) market gardening

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which is NOT a major wheat-producing region?
A) the Argentine pampas
B) the steppes of Ukraine and Russia
C) Australia
D) Brazil
A) the Argentine pampas
B) the steppes of Ukraine and Russia
C) Australia
D) Brazil

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The world's leading wheat and corn exporter is:
A) Brazil
B) Mexico
C) China
D) the United States
A) Brazil
B) Mexico
C) China
D) the United States

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which is NOT among the political entities responsible for 85 percent of all global wheat exports?
A) China
B) Australia
C) Argentina
D) European Union
A) China
B) Australia
C) Argentina
D) European Union

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
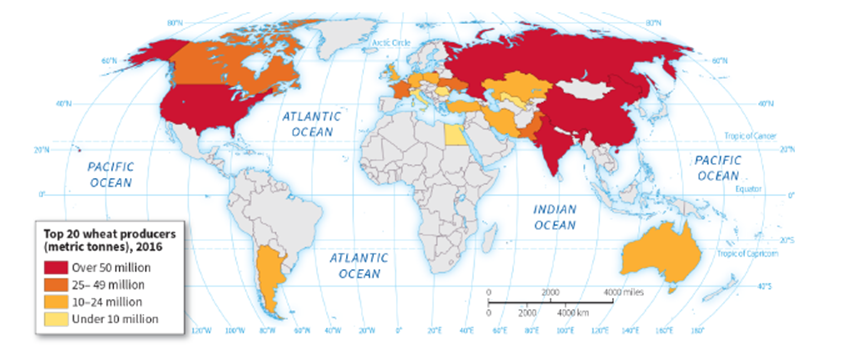
-According to the map, wheat is NOT produced in any of the following countries EXCEPT:
A) South Africa
B) Argentina
C) Mexico
D) Greenland

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53

-According to the map, which region produces the LEAST amount of wheat?
A) the United States
B) China
C) Australia
D) Italy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
What technology helps guide 60-foot-wide tractors that harvest wheat?
A) lasers
B) satellites
C) radios
D) GPS
A) lasers
B) satellites
C) radios
D) GPS

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Large-scale grain farming is made possible by all of the following EXCEPT:
A) chemical fertilizers and pesticides
B) large machinery
C) improved seed varieties
D) swidden cultivation
A) chemical fertilizers and pesticides
B) large machinery
C) improved seed varieties
D) swidden cultivation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The primary environmental factor that determines the types of cereal grains cultivated in any given area is:
A) topography
B) proximity to livestock
C) climate
D) access to water
A) topography
B) proximity to livestock
C) climate
D) access to water

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The dependence of grain-growing regions upon climate creates:
A) belts
B) plantations
C) ergonomic areas
D) aquaculture
A) belts
B) plantations
C) ergonomic areas
D) aquaculture

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Dairy products vary from region to region in North America depending on:
A) the particular breed of cows
B) the areal extent of the dairy farm
C) whether hay is produced as winter feed
D) how close the farms are to their markets
A) the particular breed of cows
B) the areal extent of the dairy farm
C) whether hay is produced as winter feed
D) how close the farms are to their markets

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which dairy product is MOST likely to be produced by cattle closest to large urban centers?
A) butter
B) cheese
C) eggs
D) milk
A) butter
B) cheese
C) eggs
D) milk

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which of the following is the most durable agricultural product, and could be produced farthest from the central city? :
A) wheat
B) milk
C) eggs
D) spinach
A) wheat
B) milk
C) eggs
D) spinach

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Dairy belts located far from from urban centers usually produce:
A) milk
B) cheese or butter
C) eggs
D) organic produce
A) milk
B) cheese or butter
C) eggs
D) organic produce

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which is NOT true of dairying today?
A) It is the one form of agriculture not affected by globalization.
B) It is increasingly using a feedlot system.
C) It often relies on hired laborers.
D) Dairy farms are increasingly becoming large-scale agribusinesses.
A) It is the one form of agriculture not affected by globalization.
B) It is increasingly using a feedlot system.
C) It often relies on hired laborers.
D) Dairy farms are increasingly becoming large-scale agribusinesses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Nomadic herders north of the tree line in Eurasia tend to raise:
A) pigs
B) moose
C) reindeer
D) cows
A) pigs
B) moose
C) reindeer
D) cows

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The common characteristic of all nomadic herding is:
A) swidden agriculture
B) mobility
C) the reliance on migrant labor
D) the need to herd animals from horseback
A) swidden agriculture
B) mobility
C) the reliance on migrant labor
D) the need to herd animals from horseback

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
In nomadic herding societies, wealth is usually determined by:
A) the accumulation of land
B) the amount of personal property owned
C) the number of employees a herder has
D) the number of heads of livestock owned by the herder
A) the accumulation of land
B) the amount of personal property owned
C) the number of employees a herder has
D) the number of heads of livestock owned by the herder

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Nomadic livestock herding is:
A) based on herding animals such as sheep, cattle, goats, and camels, often in arid areas unsuitable for cultivation
B) based on romantic and religious adherence to traditional folkways, rather than a response to environmental conditions
C) a growing response to providing extensive, low-technology food in arid regions and is, therefore, encouraged by governments such as China, Kazakhstan, and Mongolia
D) practiced throughout at least 30 percent of the world's land area by millions of people
A) based on herding animals such as sheep, cattle, goats, and camels, often in arid areas unsuitable for cultivation
B) based on romantic and religious adherence to traditional folkways, rather than a response to environmental conditions
C) a growing response to providing extensive, low-technology food in arid regions and is, therefore, encouraged by governments such as China, Kazakhstan, and Mongolia
D) practiced throughout at least 30 percent of the world's land area by millions of people

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which people herd on camels?
A) Mongolians
B) Bedouins
C) Kazakhs
D) the Rendille
A) Mongolians
B) Bedouins
C) Kazakhs
D) the Rendille

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The need for mobility for people engaged in transhumance requires that individual possessions be:
A) left behind
B) large
C) colorful
D) portable
A) left behind
B) large
C) colorful
D) portable

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which does NOT practice sedentary cultivation?
A) livestock ranching
B) nomadic herding
C) paddy rice farming
D) plantation agriculture
A) livestock ranching
B) nomadic herding
C) paddy rice farming
D) plantation agriculture

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Which two animals are the primary products of livestock ranching?
A) chickens and turkeys
B) deer and pigs
C) cattle and sheep
D) oxen and llamas
A) chickens and turkeys
B) deer and pigs
C) cattle and sheep
D) oxen and llamas

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Which country is one of the largest centers of wool production?
A) the United States
B) Brazil
C) Italy
D) New Zealand
A) the United States
B) Brazil
C) Italy
D) New Zealand

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
In Dar es Salaam, 90 percent of the leafy green vegetables consumed in cities come from:
A) swidden agriculture
B) market gardening
C) plantations
D) urban agriculture
A) swidden agriculture
B) market gardening
C) plantations
D) urban agriculture

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Urban agriculture:
A) produces 90 percent or more of the vegetables consumed in Chinese cities
B) refers to the portion of agricultural production intended for processing in cities
C) is important as a community empowerment tool, but produces little actual food
D) is found almost exclusively in China and Africa
A) produces 90 percent or more of the vegetables consumed in Chinese cities
B) refers to the portion of agricultural production intended for processing in cities
C) is important as a community empowerment tool, but produces little actual food
D) is found almost exclusively in China and Africa

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Which is a distinguishing feature of livestock ranching?
A) the commercial raising of livestock on a large landholding
B) raising feed crops, such as soybeans and corn
C) used in the commercial production of cattle and subsistence production of sheep
D) emphasizes bringing meat products to local markets
A) the commercial raising of livestock on a large landholding
B) raising feed crops, such as soybeans and corn
C) used in the commercial production of cattle and subsistence production of sheep
D) emphasizes bringing meat products to local markets

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
All of the following are true of nomadic herders and livestock ranchers EXCEPT:
A) They specialize in animal husbandry.
B) They raise only sheep and cattle.
C) They typically do not raise crops.
D) Nomadic herders are mobile, while livestock ranchers are sedentary.
A) They specialize in animal husbandry.
B) They raise only sheep and cattle.
C) They typically do not raise crops.
D) Nomadic herders are mobile, while livestock ranchers are sedentary.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Most vegetables sold in the cities of China come from:
A) subsistence plots
B) agribusiness communes
C) suitcase farms
D) urban farms
A) subsistence plots
B) agribusiness communes
C) suitcase farms
D) urban farms

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Which statement is NOT true of aquaculture?
A) It is expected to decline in the coming decades due to decreased demand for seafood.
B) It tends to be prevalent along tropical coasts.
C) Large-scale aquaculture is replacing small-scale aquaculture.
D) Asia and the Pacific regions produce 90 percent of the world's total aquaculture harvest.
A) It is expected to decline in the coming decades due to decreased demand for seafood.
B) It tends to be prevalent along tropical coasts.
C) Large-scale aquaculture is replacing small-scale aquaculture.
D) Asia and the Pacific regions produce 90 percent of the world's total aquaculture harvest.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Aquaculture produces about two-thirds of all fish and seafood consumed worldwide and is growing in importance because:
A) urban residents find the aquaculture landscape attractive
B) it focuses on high-value crops such as shrimp and pearls
C) the technology is simple and familiar, having remained unchanged for thousands of years
D) there is a growing demand for seafood and a decline in wild fish stocks
A) urban residents find the aquaculture landscape attractive
B) it focuses on high-value crops such as shrimp and pearls
C) the technology is simple and familiar, having remained unchanged for thousands of years
D) there is a growing demand for seafood and a decline in wild fish stocks

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The principal food products obtained by hunting-and-gathering groups include all of the following EXCEPT:
A) game
B) fish
C) soybeans
D) medicinal and edible wild plants
A) game
B) fish
C) soybeans
D) medicinal and edible wild plants

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Aquaculture production is found mostly in:
A) highly developed nations
B) coastal areas
C) nations that rank high on the environmental sustainability index (ESI)
D) continental interiors
A) highly developed nations
B) coastal areas
C) nations that rank high on the environmental sustainability index (ESI)
D) continental interiors

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



