Deck 1: Human Geography: A Cultural Approach
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/192
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 1: Human Geography: A Cultural Approach
1
The core focus of human geography is:
A) identifying places on a map
B) understanding regional similarities
C) describing cultural practices
D) relationships between people and spaces
A) identifying places on a map
B) understanding regional similarities
C) describing cultural practices
D) relationships between people and spaces
D
2
Geographic information systems and remote sensing are examples of:
A) spatial modeling
B) visualization tools
C) theoretical perspectives
D) humanistic geography
A) spatial modeling
B) visualization tools
C) theoretical perspectives
D) humanistic geography
B
3
The word culture describes:
A) a means of communicating beliefs, practices, and values
B) the interactions between humans and their environments
C) the methods used to navigate between different places
D) traditional practices of indigenous peoples around the world
A) a means of communicating beliefs, practices, and values
B) the interactions between humans and their environments
C) the methods used to navigate between different places
D) traditional practices of indigenous peoples around the world
A
4
Clothing, religious rituals, and food are examples of:
A) environmental determinism
B) cultural practices
C) globalization
D) spatial patterns
A) environmental determinism
B) cultural practices
C) globalization
D) spatial patterns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Understanding the political, economic, and cultural effects of the distribution of Catholicism around the world is a way to examine:
A) spatial modeling
B) ecological systems
C) cultural landscapes
D) spatial patterns
A) spatial modeling
B) ecological systems
C) cultural landscapes
D) spatial patterns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which is NOT a part of culture?
A) genetics
B) ideology
C) technology
D) livelihood
A) genetics
B) ideology
C) technology
D) livelihood

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Understanding how human cultures interact with their environment reflects a(n):
A) spatial perspective
B) physical environment
C) ecological perspective
D) environmental determinism
A) spatial perspective
B) physical environment
C) ecological perspective
D) environmental determinism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Culture is:
A) instinctive behavior
B) inherited, individual behavior
C) genetically derived group behavior
D) learned, collective behavior
A) instinctive behavior
B) inherited, individual behavior
C) genetically derived group behavior
D) learned, collective behavior

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which would NOT be studied by human geographers?
A) religion
B) language
C) government
D) anatomy
A) religion
B) language
C) government
D) anatomy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which would NOT be studied by physical geographers?
A) climate
B) terrain
C) government
D) vegetation
A) climate
B) terrain
C) government
D) vegetation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which is NOT an accurate definition of culture?
A) the complete population of a given county, state, or country
B) a dynamic mix of symbols, beliefs, speech, and practices; a distinctive group identity
C) the local, customary way of doing things (a "way of life")
D) a total way of life held in common by a people, including technology and government
A) the complete population of a given county, state, or country
B) a dynamic mix of symbols, beliefs, speech, and practices; a distinctive group identity
C) the local, customary way of doing things (a "way of life")
D) a total way of life held in common by a people, including technology and government

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The social activities and interactions, ranging from religious rituals to food and clothing preferences, that collectively distinguish group identity are called:
A) cultural traits
B) cultural exhibits
C) cultural practices
D) cultural taboos
A) cultural traits
B) cultural exhibits
C) cultural practices
D) cultural taboos

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A cultural approach to human geography would study all of the following EXCEPT:
A) the ways in which culture is expressed and symbolized on the built landscape
B) the ways in which language, religion, economy, and government vary or remain constant from place to place
C) how people function spatially and identify with place and region
D) how culture remains primarily a divisive force in a multicultural society
A) the ways in which culture is expressed and symbolized on the built landscape
B) the ways in which language, religion, economy, and government vary or remain constant from place to place
C) how people function spatially and identify with place and region
D) how culture remains primarily a divisive force in a multicultural society

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
In order to investigate the spatial pattern of wheat production in the world, a geographer would investigate:
1) climate and soil characteristics
2) available technology
3) cultural preferences
4) food taboos
5) government policies
A) 1 only
B) 1 and 2
C) 3, 4, and 5
D) 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5
1) climate and soil characteristics
2) available technology
3) cultural preferences
4) food taboos
5) government policies
A) 1 only
B) 1 and 2
C) 3, 4, and 5
D) 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
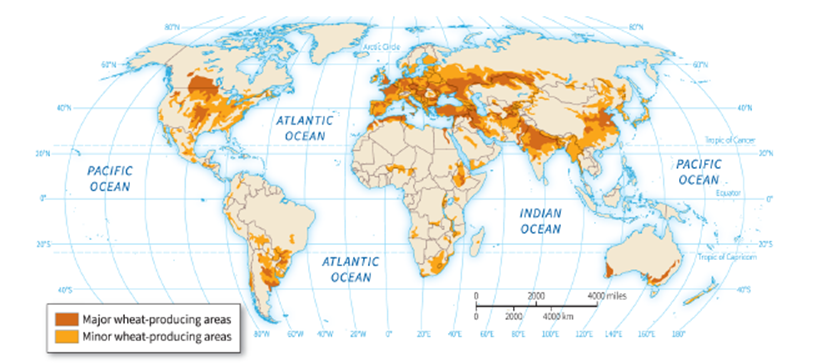
-Based on the figure, which statement is NOT true?
A) All continents, except Antarctica, contain both major and minor wheat-producing areas.
B) In Africa, the only major wheat-producing area is found in Egypt.
C) More of western Australia is used for producing wheat than eastern Australia.
D) Wheat production in South America is found solely in the southern portion of the continent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16

-According to the figure, which African country is NOT home to a minor wheat-producing area?
A) Morocco
B) Botswana
C) South Africa
D) Tunisia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following is an example of folk culture?
A) punk rockers in Japan
B) California sushi rolls
C) cowboys in the American West
D) Somali refugees in Kenya
A) punk rockers in Japan
B) California sushi rolls
C) cowboys in the American West
D) Somali refugees in Kenya

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The hippies of the 1960s formed a distinct segment of American society that set itself up in opposition to what it perceived as the problems of the dominant culture. Hippies can be said to have composed a distinctive:
A) subculture
B) culture
C) enclave
D) nonmaterial culture
A) subculture
B) culture
C) enclave
D) nonmaterial culture

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which would NOT be considered a subculture?
A) NASCAR
B) punks
C) Catholics
D) Hip-hop
A) NASCAR
B) punks
C) Catholics
D) Hip-hop

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Folk cultures and indigenous cultures have what characteristic in common?
A) They are ingrained in the national identity of their host country.
B) They are associated with geographically isolated areas.
C) Practitioners are ingrained into mainstream society.
D) Their cultures are not reliant upon local materials.
A) They are ingrained in the national identity of their host country.
B) They are associated with geographically isolated areas.
C) Practitioners are ingrained into mainstream society.
D) Their cultures are not reliant upon local materials.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Airports that have museum exhibits specific to the history of the city or state in which they are located are attempting to overcome:
A) placelessness
B) popular culture
C) folk culture
D) nonmaterial culture
A) placelessness
B) popular culture
C) folk culture
D) nonmaterial culture

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The wide range of beliefs, values, myths, and symbolic meanings of a culture form its:
A) nonmaterial culture
B) material culture
C) subculture
D) diaspora culture
A) nonmaterial culture
B) material culture
C) subculture
D) diaspora culture

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which is NOT an element of nonmaterial culture?
A) myths
B) values
C) beliefs
D) buildings
A) myths
B) values
C) beliefs
D) buildings

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which is an example of nonmaterial culture?
A) house types
B) eating utensils
C) clothing
D) myths
A) house types
B) eating utensils
C) clothing
D) myths

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
In the nineteenth and early twentieth centuries in the United States, which was seen as a symbol of the American national character?
A) the railroad worker
B) the cowboy
C) the shopkeeper
D) the farmer
A) the railroad worker
B) the cowboy
C) the shopkeeper
D) the farmer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which concept suggests that a country's population possesses a set of recognizable characteristics or traits that characterize the "core" traits of that country?
A) urban culture
B) national culture
C) national character
D) folk culture
A) urban culture
B) national culture
C) national character
D) folk culture

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A folk culture is NOT likely to be:
A) conservative
B) homogeneous
C) steeped in tradition
D) culturally diverse
A) conservative
B) homogeneous
C) steeped in tradition
D) culturally diverse

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A(n) _____ culture is one composed of self-identified tribal peoples whose social, cultural, and economic conditions distinguish them from the national society of the country in which they live.
A) folk
B) indigenous
C) rural
D) national
A) folk
B) indigenous
C) rural
D) national

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Indigenous peoples are often the descendants of the people who lived in a state or territory prior to:
A) the Renaissance
B) colonization
C) the twentieth century
D) the rise of slavery
A) the Renaissance
B) colonization
C) the twentieth century
D) the rise of slavery

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which statement is NOT true of indigenous cultures?
A) They are the result of colonial efforts.
B) They are now minorities in their homelands.
C) They may share some of the material and nonmaterial characteristics that define folk cultures.
D) They typically provide the foundation for a national culture.
A) They are the result of colonial efforts.
B) They are now minorities in their homelands.
C) They may share some of the material and nonmaterial characteristics that define folk cultures.
D) They typically provide the foundation for a national culture.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which statement is NOT true of popular culture?
A) The term was coined by the urban elite.
B) It focuses on specific, individual choices.
C) Its material culture tends to be mass-produced.
D) It was made possible by the invention of long-distance communication technologies.
A) The term was coined by the urban elite.
B) It focuses on specific, individual choices.
C) Its material culture tends to be mass-produced.
D) It was made possible by the invention of long-distance communication technologies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The presence of _____ in a downtown area may contribute to a sense of placelessness.
A) Walmart and McDonald's
B) a local hardware store
C) public parks
D) children
A) Walmart and McDonald's
B) a local hardware store
C) public parks
D) children

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33

-Which concept developed by Edward Relph is illustrated in this photo?
A) local consumption culture
B) leisure landscape
C) vernacular culture region
D) Placelessness

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The overall phenomenon responsible for the landscape shown in this photo is:
A) the influence of a continental or worldwide popular culture
B) the tendency for diasporic landscapes to be located in easily accessible areas
C) the lower mobility of people in an era of globalization
D) the presence of thriving folk cultures in large swaths of the United States and Canada
A) the influence of a continental or worldwide popular culture
B) the tendency for diasporic landscapes to be located in easily accessible areas
C) the lower mobility of people in an era of globalization
D) the presence of thriving folk cultures in large swaths of the United States and Canada

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
In popular culture, authority tends to be:
A) religious
B) dispersed
C) secular
D) conservative
A) religious
B) dispersed
C) secular
D) conservative

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A geographer who uses an imaginary situation or abstraction in an attempt to isolate causes is building a:
A) model
B) space vs. place distinction
C) map
D) cartogram
A) model
B) space vs. place distinction
C) map
D) cartogram

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A study that analyzes how sea level rise will impact small islands in the Pacific Ocean is looking at how a global process impacts regional places. This is an example of looking at:
A) spatial modeling
B) different spatial scales
C) environmental determinism
D) abstract space
A) spatial modeling
B) different spatial scales
C) environmental determinism
D) abstract space

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
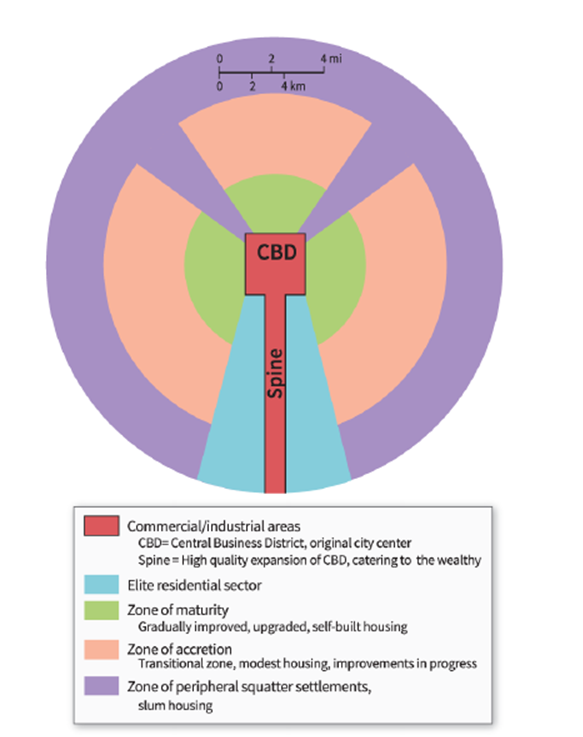
-According to this model, the elite residential sector lies:
A) in the periphery of the city
B) at the core of the city
C) along the spine leading to/from the central business district
D) in the zone of accretion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39

-According to this model, housing for the poorest people is MOST likely to be found in Sector:
A) zone of maturity
B) elite residential sector
C) zone of accretion
D) zone of peripheral squatter settlements

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40

-According to the model shown here, middle-class housing is MOST likely to be found in Sector:
A) commercial/ industrial areas
B) elite residential sector
C) zone of peripheral squatter settlements
D) zone of accretion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41

-According to the model shown here, the transitional area between the mature zone and the periphery is found in Sector:
A) spine
B) elite residential sector
C) zone of peripheral squatter settlements
D) zone of accretion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which perspective on human geography tends to generalize diversity in an effort to reveal processes creating spatial patterns?
A) power and ideology
B) topophilia
C) model building
D) sense of place
A) power and ideology
B) topophilia
C) model building
D) sense of place

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Understanding how people make meaning from experiences in places is a goal of:
A) spatial modeling
B) topophilia
C) the humanistic perspective
D) regionalism
A) spatial modeling
B) topophilia
C) the humanistic perspective
D) regionalism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A geographer seeking to understand why people are reserved and quiet at memorials would be examining:
A) power and ideology
B) topophilia
C) model building
D) sense of place
A) power and ideology
B) topophilia
C) model building
D) sense of place

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
A community protest against a proposal to build a highway nearby is trying to assert:
A) the meaning and value that people derive from place
B) a new spatial model to justify their opposition
C) the highway will only work at the state scale
D) that democratic processes are not appropriate at the local scale
A) the meaning and value that people derive from place
B) a new spatial model to justify their opposition
C) the highway will only work at the state scale
D) that democratic processes are not appropriate at the local scale

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
A geographer asking questions about why laws against loitering on sidewalks are only enforced on some people and not others is asking questions from a:
A) humanistic perspective
B) social theoretical perspective
C) regional perspective
D) spatial modeling perspective
A) humanistic perspective
B) social theoretical perspective
C) regional perspective
D) spatial modeling perspective

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Human geographers with a social theoretical perspective ask questions about:
A) power and ideology
B) topophilia
C) model building
D) sense of place
A) power and ideology
B) topophilia
C) model building
D) sense of place

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Human geographers who want to understand how power influences people of different races, genders, or class will commonly use methods such as:
A) literary texts and works of art
B) spatial models
C) interviews and surveys
D) cartography
A) literary texts and works of art
B) spatial models
C) interviews and surveys
D) cartography

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Latitude and longitude coordinates were invented to help people:
A) navigate across oceans
B) find a precise position on earth
C) locate the prime meridian
D) find the north and south poles
A) navigate across oceans
B) find a precise position on earth
C) locate the prime meridian
D) find the north and south poles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The location of the prime meridian through Greenwich, England, represents:
A) 0° latitude
B) 0° longitude
C) 180° longitude
D) 180° latitude
A) 0° latitude
B) 0° longitude
C) 180° longitude
D) 180° latitude

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
How many satellites are necessary for a GPS receiver to be precisely located in time and space?
A) 12
B) 4
C) 1
D) 5
A) 12
B) 4
C) 1
D) 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which of the following is an example of absolute location?
A) 40.7128°N, 74.0060°W
B) South of Portland
C) 97477-5218
D) Near the St. Louis Arch
A) 40.7128°N, 74.0060°W
B) South of Portland
C) 97477-5218
D) Near the St. Louis Arch

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
When Google Maps is telling us which way to turn to find a destination, it is converting absolute location into:
A) a sense of place
B) geographic information systems
C) relative location
D) global positioning system
A) a sense of place
B) geographic information systems
C) relative location
D) global positioning system

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Most of the images of urban areas on Google Maps are from:
A) satellite images
B) global positioning systems
C) aerial photographs
D) geographic information systems
A) satellite images
B) global positioning systems
C) aerial photographs
D) geographic information systems

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which of the following types of data would be analyzed with a geographic information system?
A) voter demographics
B) sales figures at a store
C) road networks
D) household budgets
A) voter demographics
B) sales figures at a store
C) road networks
D) household budgets

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The study of human geography is organized around these five geographical concepts or themes:
A) region, mobility, globalization, nature-culture, and cultural landscape
B) climates, soils, globalization, cultural landscape, and region
C) mobility, region, globalization, diplomacy, and cultural landscape
D) mobility, immigration, globalization, nature-culture, and cultural landscape
A) region, mobility, globalization, nature-culture, and cultural landscape
B) climates, soils, globalization, cultural landscape, and region
C) mobility, region, globalization, diplomacy, and cultural landscape
D) mobility, immigration, globalization, nature-culture, and cultural landscape

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which is NOT a type of region recognized by human geographers?
A) vernacular region
B) continental region
C) formal region
D) functional region
A) vernacular region
B) continental region
C) formal region
D) functional region

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
A region inhabited by people who have one or more traits in common is a:
A) vernacular region
B) continental region
C) formal region
D) functional region
A) vernacular region
B) continental region
C) formal region
D) functional region

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which represents a functional region?
A) a region that grows pistachios
B) a region in which Welsh is spoken
C) a region showing the readership of a particular magazine
D) a region in which the descendants of American slaves live
A) a region that grows pistachios
B) a region in which Welsh is spoken
C) a region showing the readership of a particular magazine
D) a region in which the descendants of American slaves live

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The number of formal regions recognized by geographers is:
A) zero
B) approximately 500
C) approximately 20,000
D) infinite
A) zero
B) approximately 500
C) approximately 20,000
D) infinite

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Within a formal region, the cultural traits tend to be strongest:
A) at the core
B) in the periphery
C) on the outskirts
D) in the border zone
A) at the core
B) in the periphery
C) on the outskirts
D) in the border zone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Because cultures overlap and mix, formal region boundaries are often:
A) sharp
B) clearly delineated
C) geometric
D) fuzzy
A) sharp
B) clearly delineated
C) geometric
D) fuzzy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Which is NOT a formal region?
A) a corn-growing county in Iowa
B) a distribution network of the Washington Post
C) a Chinese community in California's San Gabriel Valley
D) the part of Russia called Siberia
A) a corn-growing county in Iowa
B) a distribution network of the Washington Post
C) a Chinese community in California's San Gabriel Valley
D) the part of Russia called Siberia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Formal regions typically exhibit:
A) a core-periphery pattern
B) well-defined boundaries
C) functional nodes
D) a set of culture traits with identical spatial patterns
A) a core-periphery pattern
B) well-defined boundaries
C) functional nodes
D) a set of culture traits with identical spatial patterns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The hallmark of a formal region is cultural:
A) diversity
B) stratification
C) harmony
D) homogeneity
A) diversity
B) stratification
C) harmony
D) homogeneity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The Amish people live mostly in Lancaster County, Pennsylvania, and the surrounding areas. The people of this religious group are known for their simple lifestyles and their rejection of modern conveniences. A map showing the distribution of Amish in Pennsylvania would help to define a(n):
A) vernacular region
B) urban region
C) formal region
D) functional region
A) vernacular region
B) urban region
C) formal region
D) functional region

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which is NOT an example of a functional region?
A) religion
B) county
C) city
D) precinct
A) religion
B) county
C) city
D) precinct

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Which type of region is organized to operate politically, socially, or economically as one unit?
A) vernacular region
B) continental region
C) formal region
D) functional region
A) vernacular region
B) continental region
C) formal region
D) functional region

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
State capitals and city halls are both examples of:
A) edges
B) nodes
C) peripheral architecture
D) border zones
A) edges
B) nodes
C) peripheral architecture
D) border zones

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
A region that is perceived to exist by its inhabitants is a:
A) formal region
B) functional region
C) vernacular region
D) cultural region
A) formal region
B) functional region
C) vernacular region
D) cultural region

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Each state within the United States, and each province within Canada, can be considered a:
A) vernacular region
B) continental region
C) state region
D) functional region
A) vernacular region
B) continental region
C) state region
D) functional region

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Which statement is NOT true of functional regions?
A) Their borders may or may not be clearly defined.
B) Their interpretation varies widely.
C) They generally do not coincide spatially with formal culture regions.
D) They are concrete rather than abstract entities.
A) Their borders may or may not be clearly defined.
B) Their interpretation varies widely.
C) They generally do not coincide spatially with formal culture regions.
D) They are concrete rather than abstract entities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The pattern of church attendance and the distribution area of a first-run film are:
A) formal regions
B) functional regions
C) relocation regions
D) vernacular regions
A) formal regions
B) functional regions
C) relocation regions
D) vernacular regions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The "Midwest" and the "South" of the United States are best described as:
A) vernacular regions
B) urban regions
C) formal regions
D) functional regions
A) vernacular regions
B) urban regions
C) formal regions
D) functional regions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75

-A city's downtown area, as pictured here for Denver, is often the _____ of a functional region.
A) edge
B) node
C) model
D) ecosystem

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
At a basic level, the vernacular region grows out of:
A) people's sense of belonging to and identification with a specific region
B) cultural homogeneity
C) the nodes of a functional region
D) functional organization
A) people's sense of belonging to and identification with a specific region
B) cultural homogeneity
C) the nodes of a functional region
D) functional organization

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
A culture region that is perceived to exist by its inhabitants is a:
A) vernacular region
B) continental region
C) formal region
D) functional region
A) vernacular region
B) continental region
C) formal region
D) functional region

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
In a large city with multiple neighborhoods at different elevations, one part of the city is located at a higher altitude, and the people living in that neighborhood call it The Hills. The Hills is an example of a:
A) vernacular region
B) continental region
C) formal region
D) functional region
A) vernacular region
B) continental region
C) formal region
D) functional region

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The spread of people, ideas, or things from one location to other locations where these items are not initially found is:
A) diffusion
B) interaction
C) ecology
D) teleology
A) diffusion
B) interaction
C) ecology
D) teleology

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The migration of Europeans into the Western Hemisphere included those people introducing Christianity into the Americas, thereby illustrating the process of this type of diffusion.
A) stimulus
B) hierarchical
C) contagious
D) relocation
A) stimulus
B) hierarchical
C) contagious
D) relocation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



