Deck 11: Music and Speech Perception
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/50
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 11: Music and Speech Perception
1
_______ is the psychological aspect of a sound, related mainly to perceived frequency.
A) Chroma
B) Sound
C) Tone
D) Octave
E) Pitch
A) Chroma
B) Sound
C) Tone
D) Octave
E) Pitch
Pitch
2
An octave is the
A) amplitude of a piece of music.
B) interval between two sound frequencies having a ratio of 2:1.
C) frequency range of a particular piece of music.
D) musical distance between two chords.
E) absolute frequency difference between two notes in the same interval.
A) amplitude of a piece of music.
B) interval between two sound frequencies having a ratio of 2:1.
C) frequency range of a particular piece of music.
D) musical distance between two chords.
E) absolute frequency difference between two notes in the same interval.
interval between two sound frequencies having a ratio of 2:1.
3
_______ is a sound quality whereby a sound is heard to be of higher or lower pitch.
A) Tone height
B) Octave
C) Tone chroma
D) Musical pitch
E) Missing fundamental
A) Tone height
B) Octave
C) Tone chroma
D) Musical pitch
E) Missing fundamental
Tone height
4
If the frequency of a sound is doubled, what happens to the tone height and tone chroma of the sound?
A) The tone height increases and the tone chroma increases.
B) The tone height increases and the tone chroma decreases.
C) The tone height increases but the tone chroma stays the same.
D) The tone height decreases and the tone chroma stays the same.
E) The tone height decreases and the tone chroma decreases.
A) The tone height increases and the tone chroma increases.
B) The tone height increases and the tone chroma decreases.
C) The tone height increases but the tone chroma stays the same.
D) The tone height decreases and the tone chroma stays the same.
E) The tone height decreases and the tone chroma decreases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which sound frequency would have the most similar tone chroma to a 220-Hz tone?
A) 200 Hz
B) 320 Hz
C) 400 Hz
D) 440 Hz
E) 500 Hz
A) 200 Hz
B) 320 Hz
C) 400 Hz
D) 440 Hz
E) 500 Hz

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
_______ is a sound quality shared by tones that have the same octave interval.
A) Tone height
B) Chord
C) Tone chroma
D) Musical pitch
E) Missing fundamental
A) Tone height
B) Chord
C) Tone chroma
D) Musical pitch
E) Missing fundamental

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Refer to the figure.
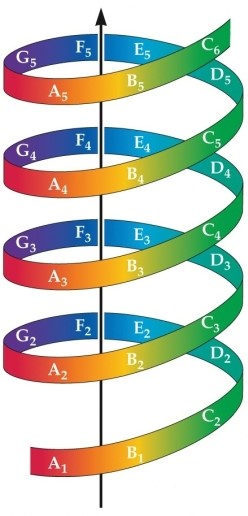 The vertical arrow refers to the
The vertical arrow refers to the
A) tone chroma.
B) musical scale.
C) frequency range.
D) tone height.
E) timbre.
 The vertical arrow refers to the
The vertical arrow refers to theA) tone chroma.
B) musical scale.
C) frequency range.
D) tone height.
E) timbre.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Refer to the figure.
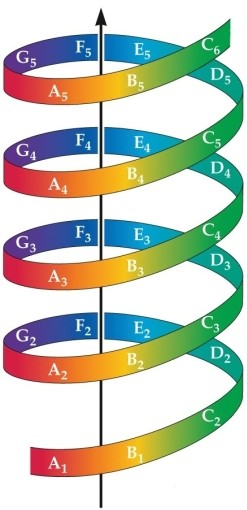 The colors of the ribbon refer to the
The colors of the ribbon refer to the
A) tone chroma.
B) musical scale.
C) frequency range.
D) tone height.
E) timbre.
 The colors of the ribbon refer to the
The colors of the ribbon refer to theA) tone chroma.
B) musical scale.
C) frequency range.
D) tone height.
E) timbre.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A _______ is a combination of three or more musical notes with different pitches played simultaneously.
A) melody
B) tempo
C) chord
D) sonata
E) tone
A) melody
B) tempo
C) chord
D) sonata
E) tone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
What is the effect of culture on the perception of music?
A) People who are from cultures without music cannot perceive tone chroma.
B) People who are from cultures without music cannot perceive tone height.
C) People from all cultures hear musical notes in the same way.
D) People tend to hear musical notes in ways that are dependent on their genetic heritage.
E) People tend to hear musical notes in ways that correspond to their culture.
A) People who are from cultures without music cannot perceive tone chroma.
B) People who are from cultures without music cannot perceive tone height.
C) People from all cultures hear musical notes in the same way.
D) People tend to hear musical notes in ways that are dependent on their genetic heritage.
E) People tend to hear musical notes in ways that correspond to their culture.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Suppose a new culture is discovered that has nine notes per octave in their musical scale, as opposed to the seven notes per octave in traditional Western music. What might we predict about their hearing of pitches?
A) They will perceive a wider range of pitches that qualify for a given note.
B) They will perceive a narrower range of pitches that qualify for a given note.
C) They will perceive the same range of pitches that qualify for a given note.
D) After a few moments listening to music in the seven-note Western scale, their hearing of pitches will switch over to the Western scale.
E) They will have difficulty hearing the difference between consonant and dissonant chords.
A) They will perceive a wider range of pitches that qualify for a given note.
B) They will perceive a narrower range of pitches that qualify for a given note.
C) They will perceive the same range of pitches that qualify for a given note.
D) After a few moments listening to music in the seven-note Western scale, their hearing of pitches will switch over to the Western scale.
E) They will have difficulty hearing the difference between consonant and dissonant chords.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The rare ability whereby some people are able to very accurately name or produce notes without comparison to other notes is called _______ pitch.
A) direct
B) natural
C) absolute
D) relative
E) super
A) direct
B) natural
C) absolute
D) relative
E) super

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A person who can tune a guitar or piano by ear alone, without using an electronic tuning device, has _______ pitch.
A) direct
B) absolute
C) natural
D) super
E) relative
A) direct
B) absolute
C) natural
D) super
E) relative

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A melody is defined by the _______, rather than by an exact sequence of sound frequencies.
A) tempo
B) chords
C) increasing frequency pattern
D) pattern of rises and falls in pitch
E) tone height
A) tempo
B) chords
C) increasing frequency pattern
D) pattern of rises and falls in pitch
E) tone height

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
If you transform a sequence of notes by raising all of their frequencies by exactly 100 Hz, which aspect would not change?
A) Melody
B) Tone height
C) Tone chroma
D) Pitch
E) Musical scale
A) Melody
B) Tone height
C) Tone chroma
D) Pitch
E) Musical scale

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
_______ is the perceived speed of the presentation of sounds.
A) Melody
B) Pitch
C) Tempo
D) Musical scale
E) Octave
A) Melody
B) Pitch
C) Tempo
D) Musical scale
E) Octave

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Refer to the figure.
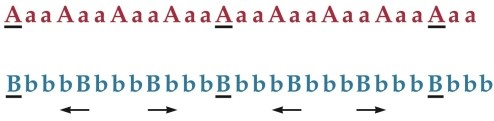 According to the figure, when two rhythms are played together
According to the figure, when two rhythms are played together
A) one rhythm tends to dominate, and the nondominant rhythm is perceptually adjusted to correspond to the dominant rhythm.
B) one rhythm tends to dominate, and the dominant rhythm is perceptually adjusted to correspond to the nondominant rhythm.
C) neither rhythm dominates.
D) the rhythm with the higher frequency dominates.
E) the rhythm with the richer tone chroma dominates.
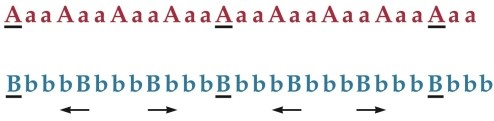 According to the figure, when two rhythms are played together
According to the figure, when two rhythms are played togetherA) one rhythm tends to dominate, and the nondominant rhythm is perceptually adjusted to correspond to the dominant rhythm.
B) one rhythm tends to dominate, and the dominant rhythm is perceptually adjusted to correspond to the nondominant rhythm.
C) neither rhythm dominates.
D) the rhythm with the higher frequency dominates.
E) the rhythm with the richer tone chroma dominates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
_______ is a deviation from a regular rhythm.
A) Phonation
B) Articulation
C) Modulation
D) Syncopation
E) Coarticulation
A) Phonation
B) Articulation
C) Modulation
D) Syncopation
E) Coarticulation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Jazz musicians often "swing" the timing of when they play notes in a song such that there is a systematic deviation from the regular rhythm. This is an example of
A) syncopation.
B) articulation.
C) modulation.
D) phonation.
E) coarticulation.
A) syncopation.
B) articulation.
C) modulation.
D) phonation.
E) coarticulation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Refer to the figure.
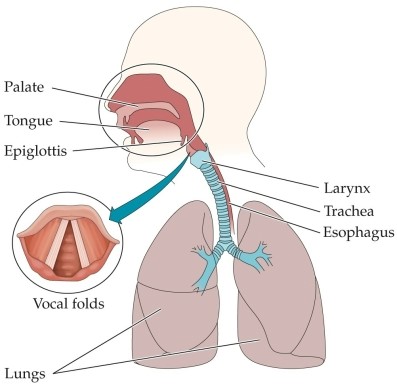 In the figure, phonation occurs in the
In the figure, phonation occurs in the
A) oral tract.
B) larynx.
C) vocal folds.
D) lungs.
E) esophagus.
 In the figure, phonation occurs in the
In the figure, phonation occurs in theA) oral tract.
B) larynx.
C) vocal folds.
D) lungs.
E) esophagus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which part of speed production would be most affected if the vocal folds are anesthetized to be immobile?
A) Respiration
B) Phonation
C) Articulation
D) Enunciation
E) Syncopation
A) Respiration
B) Phonation
C) Articulation
D) Enunciation
E) Syncopation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
_______ is the process through which the vocal folds are made to vibrate when air pushes out of the lungs.
A) Articulation
B) Phonation
C) Enunciation
D) Syncopation
E) Respiration
A) Articulation
B) Phonation
C) Enunciation
D) Syncopation
E) Respiration

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The _______ is the airway above the larynx that is used for the production of speech and includes the oral and nasal tracts.
A) throat
B) esophagus
C) trachea
D) epiglottis
E) vocal tract
A) throat
B) esophagus
C) trachea
D) epiglottis
E) vocal tract

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
To initiate speech sound, the _______ pushes air out of the lungs, through the trachea, and up to the larynx.
A) diaphragm
B) tongue
C) palate
D) oral tract
E) esophagus
A) diaphragm
B) tongue
C) palate
D) oral tract
E) esophagus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Snoring happens during sleep because air is pushed out from the lungs and the _______ is/are engaged, thus making noise.
A) diaphragm
B) esophagus
C) soft palate
D) vocal folds
E) oral tract
A) diaphragm
B) esophagus
C) soft palate
D) vocal folds
E) oral tract

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The three basic components of the production of speech are respiration, phonation, and
A) resonation.
B) tempo perception.
C) articulation.
D) rhythm keeping.
E) melody.
A) resonation.
B) tempo perception.
C) articulation.
D) rhythm keeping.
E) melody.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
_______ is the act or manner of producing speech sound using the vocal tract.
A) Articulation
B) Phonation
C) Enunciation
D) Resonation
E) Voicing
A) Articulation
B) Phonation
C) Enunciation
D) Resonation
E) Voicing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Each consonant we produce can be classified according to three articulatory dimensions: place of articulation, manner of articulation, and
A) coarticulation.
B) phonation.
C) resonation of sound.
D) voicing.
E) formants.
A) coarticulation.
B) phonation.
C) resonation of sound.
D) voicing.
E) formants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Refer to the graph.
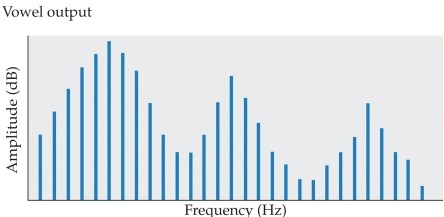 In this graph, the peaks are referred to as
In this graph, the peaks are referred to as
A) troughs.
B) formants.
C) sine waves.
D) positive values.
E) maxima.
 In this graph, the peaks are referred to as
In this graph, the peaks are referred to asA) troughs.
B) formants.
C) sine waves.
D) positive values.
E) maxima.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A(n) _______ is a pattern for sound analysis that provides a three-dimensional display, plotting time on the horizontal axis, frequency on the vertical axis, and intensity in color or gray scale?
A) vocalization plot
B) sine wave
C) encephalogram
D) cartogram
E) spectrogram
A) vocalization plot
B) sine wave
C) encephalogram
D) cartogram
E) spectrogram

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Refer to the figure.
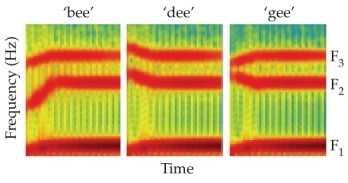 This figure shows _______ of sounds.
This figure shows _______ of sounds.
A) graphs
B) frequencies
C) articulations
D) spectrograms
E) vocalization plots
 This figure shows _______ of sounds.
This figure shows _______ of sounds.A) graphs
B) frequencies
C) articulations
D) spectrograms
E) vocalization plots

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The phenomenon in speech whereby attributes of successive speech units overlap in articulatory or acoustic patterns is known as
A) articulation.
B) coarticulation.
C) voicing.
D) obstruction.
E) resonance.
A) articulation.
B) coarticulation.
C) voicing.
D) obstruction.
E) resonance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Understanding human speech is a challenge for computers because the same phoneme might be pronounced differently depending on the phonemes coming before or after it. This is called
A) voicing.
B) resonance.
C) obstruction.
D) articulation.
E) coarticulation.
A) voicing.
B) resonance.
C) obstruction.
D) articulation.
E) coarticulation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
In categorical perception, listeners
A) discriminate sounds that are labeled differently.
B) discriminate the intensity of sounds.
C) articulate various sounds.
D) choose the correct sound.
E) recognize melodies.
A) discriminate sounds that are labeled differently.
B) discriminate the intensity of sounds.
C) articulate various sounds.
D) choose the correct sound.
E) recognize melodies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The theory stating that the processes used to produce speech are run in reverse to understand speech is called the _______ theory.
A) special speech
B) speech-specific
C) motor
D) speech perception
E) melodic inference
A) special speech
B) speech-specific
C) motor
D) speech perception
E) melodic inference

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
_______ is the phenomenon whereby a person repeats the sound "gah" while the sound "bah" comes from a speaker and the observer hears the sound "dah"?
A) The phonemic restoration effect
B) The McGurk effect
C) The speech continuity effect
D) The cone of confusion
E) Noncategorical perception
A) The phonemic restoration effect
B) The McGurk effect
C) The speech continuity effect
D) The cone of confusion
E) Noncategorical perception

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Refer to the figure.
 This figure demonstrates the concept of
This figure demonstrates the concept of
A) transformation.
B) blending.
C) articulation.
D) contrast.
E) categorical perception.
 This figure demonstrates the concept of
This figure demonstrates the concept ofA) transformation.
B) blending.
C) articulation.
D) contrast.
E) categorical perception.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Amazing evidence supporting the idea of "learning to listen" comes from
A) dogs.
B) newborns.
C) the elderly.
D) stroke patients.
E) monkeys.
A) dogs.
B) newborns.
C) the elderly.
D) stroke patients.
E) monkeys.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
If someone listens to a series of phonemes that smoothly and continuously morphs between "bah" and "dah" in four steps, she most likely hears
A) sounds in the middle as a combination of "bah" and "dah."
B) all of the sounds as "bah."
C) all of the sounds as "dah."
D) the sounds in the middle as either "bah" or "dah."
E) the sounds in the middle as "lah."
A) sounds in the middle as a combination of "bah" and "dah."
B) all of the sounds as "bah."
C) all of the sounds as "dah."
D) the sounds in the middle as either "bah" or "dah."
E) the sounds in the middle as "lah."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Native listeners learn to
A) pronounce all possible sounds in all languages.
B) pronounce vowels first.
C) listen attentively to foreign languages.
D) filter out irrelevant acoustic information.
E) pronounce consonants first.
A) pronounce all possible sounds in all languages.
B) pronounce vowels first.
C) listen attentively to foreign languages.
D) filter out irrelevant acoustic information.
E) pronounce consonants first.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Suppose a baby grows up in a home with its parents and grandparents. The parents speak one language and the grandparents speak another, so the baby hears both languages in the home. What will most likely happen to the baby's ability to perceive and produce phonemes from the two languages at about one year old?
A) The baby will be able to perceive and produce phonemes from the parents' language but not the grandparents' language.
B) The baby will be able to perceive and produce phonemes from the grandparents' language but not the parents' language.
C) The baby will be able to perceive and produce phonemes from both languages.
D) The baby will not be able to perceive and produce phonemes from either language.
E) The baby will be able to perceive and produce phonemes from every language in the world, including languages not heard in the home.
A) The baby will be able to perceive and produce phonemes from the parents' language but not the grandparents' language.
B) The baby will be able to perceive and produce phonemes from the grandparents' language but not the parents' language.
C) The baby will be able to perceive and produce phonemes from both languages.
D) The baby will not be able to perceive and produce phonemes from either language.
E) The baby will be able to perceive and produce phonemes from every language in the world, including languages not heard in the home.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
After listening to manufactured sentence streams such as tupirogolabudapikutilado-golabutupirotiladodapiku for just two minutes, infants
A) stopped responding to words in their native language.
B) learned how to articulate new sounds.
C) can repeat the phrase perfectly.
D) listen more intently to words from the stream than to novel words.
E) listen more intently to novel words than words from the stream.
A) stopped responding to words in their native language.
B) learned how to articulate new sounds.
C) can repeat the phrase perfectly.
D) listen more intently to words from the stream than to novel words.
E) listen more intently to novel words than words from the stream.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The development of _______ has made it possible for us to learn about how speech is processed in the brain.
A) spectrograms
B) frequency graphs
C) imaging techniques
D) speech indicators
E) Fourier analysis
A) spectrograms
B) frequency graphs
C) imaging techniques
D) speech indicators
E) Fourier analysis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
If you image the brain of somebody who was listening to speech, what lobe of the brain is the most active?
A) Frontal
B) Temporal
C) Parietal
D) Medial
E) Occipital
A) Frontal
B) Temporal
C) Parietal
D) Medial
E) Occipital

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
What are chords, and what makes some chords sound "better" than others?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
What is syncopation and what does it have to do with rhythm?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
How do children learn to recognize speech sounds?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
What are some influences of culture on music perception?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Describe the processes of respiration, phonation, and articulation in speech production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
What is the concept of categorical perception, how is it measured, and what does it have to do with speech perception?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



