Deck 4: Quantitative Models of Art Therapy Research
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/22
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 4: Quantitative Models of Art Therapy Research
1
Identify the independent and dependent variables in this hypothesis: Clients who participate in a solution-focused art therapy program are more likely to stop abusing drugs than clients who participate in an art activities program.
A) Art activity is the dependent variable; solution-focused art therapy program is the independent variable.
B) Solution-focused art therapy program is the dependent variable; cessation of drug abuse is the independent variable.
C) Cessation of drug abuse is the dependent variable; solution-focused art therapy program is the independent variable.
D) Cessation of drug abuse is the independent variable; solution-focused art therapy and art activity are dependent variables.
A) Art activity is the dependent variable; solution-focused art therapy program is the independent variable.
B) Solution-focused art therapy program is the dependent variable; cessation of drug abuse is the independent variable.
C) Cessation of drug abuse is the dependent variable; solution-focused art therapy program is the independent variable.
D) Cessation of drug abuse is the independent variable; solution-focused art therapy and art activity are dependent variables.
C
2
Define the conditions of random sampling.
A) Participants are sorted randomly and placed in either an experimental group or a control group.
B) Participants are selected without knowing what the experimental variable is in the study.
C) Participants are selected to represent the general population and are randomly placed in either the experimental or control group.
D) Participants are selected to represent the population being studied and have an equal chance of being placed in the experimental as in the control group.
A) Participants are sorted randomly and placed in either an experimental group or a control group.
B) Participants are selected without knowing what the experimental variable is in the study.
C) Participants are selected to represent the general population and are randomly placed in either the experimental or control group.
D) Participants are selected to represent the population being studied and have an equal chance of being placed in the experimental as in the control group.
D
3
Match the following four research questions with their most effective designs (A-D).
-Do adolescents who participate in an art therapy program at "X" Alternative High School have a smaller chance of dropping out of school as compared to the drop-out rates of adolescents in the district public high school?
A)
B)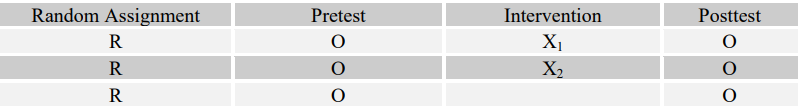
C)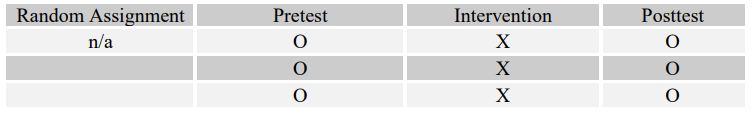
D)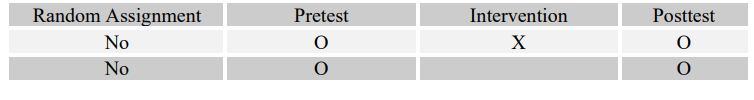
-Do adolescents who participate in an art therapy program at "X" Alternative High School have a smaller chance of dropping out of school as compared to the drop-out rates of adolescents in the district public high school?
A)

B)

C)

D)

D
quasi-experimental compares two (not randomly assigned) groups and studies the effects of treatment on only one of the groups.
quasi-experimental compares two (not randomly assigned) groups and studies the effects of treatment on only one of the groups.
4
Match the following four research questions with their most effective designs (A-D).
-Do at-risk adolescents who participate in an art therapy program have a greater chance of staying in school than at-risk adolescents who do not?
A)
B)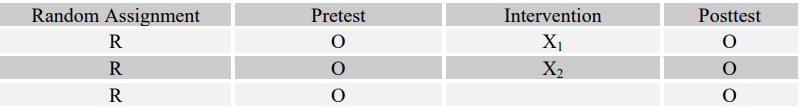
C)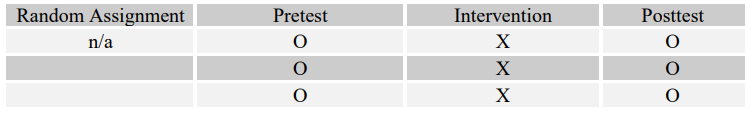
D)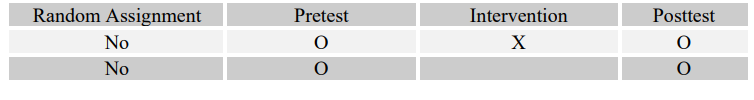
-Do at-risk adolescents who participate in an art therapy program have a greater chance of staying in school than at-risk adolescents who do not?
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Match the following four research questions with their most effective designs (A-D).
-What are the measurable effects of art therapy for each adolescent's risk of dropping out of "X" Alternative High School over the course of a semester?
A)
B)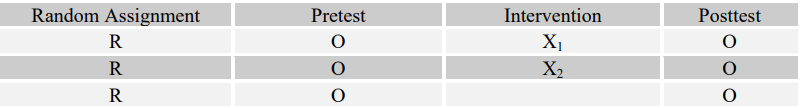
C)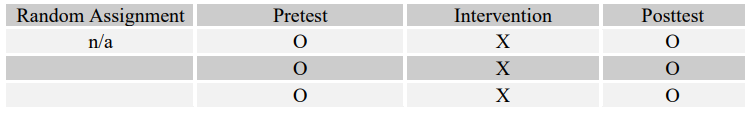
D)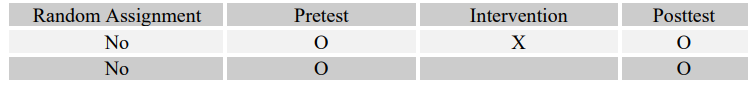
-What are the measurable effects of art therapy for each adolescent's risk of dropping out of "X" Alternative High School over the course of a semester?
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Match the following four research questions with their most effective designs (A-D).
-Which kind of program is more effective in helping at-risk adolescents stay in school: art therapy, art education, or no arts program at all?
A)
B)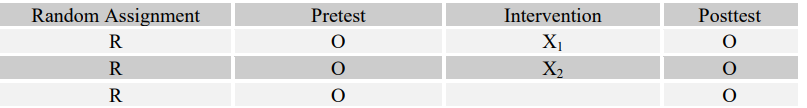
C)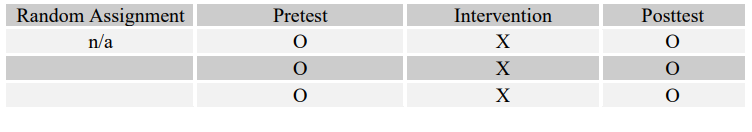
D)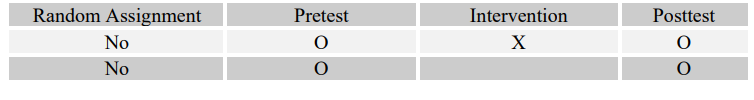
-Which kind of program is more effective in helping at-risk adolescents stay in school: art therapy, art education, or no arts program at all?
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In the following examples, which type of statistics should you use, descriptive or inferential?
-The number of sessions that produce the greatest effect on reducing symptoms in a client group
A) descriptive
B) inferential
-The number of sessions that produce the greatest effect on reducing symptoms in a client group
A) descriptive
B) inferential

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
In the following examples, which type of statistics should you use, descriptive or inferential?
-The probability that what happened to a client group was not due to chance
A) descriptive
B) inferential
-The probability that what happened to a client group was not due to chance
A) descriptive
B) inferential

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
In the following examples, which type of statistics should you use, descriptive or inferential?
-The likelihood that the same effect could happen again even when another art therapist facilitates the session
A) descriptive
B) inferential
-The likelihood that the same effect could happen again even when another art therapist facilitates the session
A) descriptive
B) inferential

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
In the following examples, which type of statistics should you use, descriptive or inferential?
-The degree of change between one session and the next when the same test or measurement is used
A) descriptive
B) inferential
-The degree of change between one session and the next when the same test or measurement is used
A) descriptive
B) inferential

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
In the following examples, which type of statistics should you use, descriptive or inferential?
-The intensity of the effect when compared over time
A) descriptive
B) inferential
-The intensity of the effect when compared over time
A) descriptive
B) inferential

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
In the following examples, which type of statistics should you use, descriptive or inferential?
-The comparison of more than one variable in both the control and experimental groups
A) descriptive
B) inferential
-The comparison of more than one variable in both the control and experimental groups
A) descriptive
B) inferential

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
An art therapist observes that Mr. Miller is less agitated on days when art therapy is scheduled and more agitated on days when no art therapy is scheduled. She reviews the nursing charts and finds that her observation is confirmed by daily physiological and behavioral assessments recorded by the staff. Is she conducting a valid form of research?
A) Yes, because she has a record of repeated measurements over time that shows a confirming pattern, which she can further test to rule out rival hypotheses.
B) No, because she does not have a control, and without a larger sample she cannot predict that art therapy is causing Mr. Miller's change in behavior.
C) Yes, because clinical observations are more valid than experimental designs in showing the effects of art therapy.
D) No, because she doesn't know how other clients are responding to art therapy and they may be more or less agitated than Mr. Miller.
A) Yes, because she has a record of repeated measurements over time that shows a confirming pattern, which she can further test to rule out rival hypotheses.
B) No, because she does not have a control, and without a larger sample she cannot predict that art therapy is causing Mr. Miller's change in behavior.
C) Yes, because clinical observations are more valid than experimental designs in showing the effects of art therapy.
D) No, because she doesn't know how other clients are responding to art therapy and they may be more or less agitated than Mr. Miller.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
An art therapist collects data from six weekly art therapy sessions conducted at more than one site to show that art therapy reduces the symptoms of depression in clients who have lost a spouse. How could the design be modified to improve external validity?
A) Use more than one test or measurement.
B) Use a protocol or treatment manual to minimize variations in treatment at each site.
C) Use a standard test or measurement rather than a self-report.
D) Eliminate the scores of participants who did not complete the entire 6 weeks of art therapy.
A) Use more than one test or measurement.
B) Use a protocol or treatment manual to minimize variations in treatment at each site.
C) Use a standard test or measurement rather than a self-report.
D) Eliminate the scores of participants who did not complete the entire 6 weeks of art therapy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
An art therapist conducts correlational research by reviewing data on the drawing preferences of people who are in early stage Alzheimer's disease. Which of the following is a positive correlation that her study could identify?
A) There are more patients in early stage Alzheimer's disease who draw images of labyrinths than any other kind of spontaneous image.
B) Fewer patients in early stage Alzheimer's disease draw images of labyrinths after art therapy treatment than before art therapy treatment.
C) More patients in early stage Alzheimer's disease draw images of labyrinths than patients in later stages of Alzheimer's.
D) There was no relation between the preference for drawing labyrinths and the number of patients in early stage Alzheimer's disease.
A) There are more patients in early stage Alzheimer's disease who draw images of labyrinths than any other kind of spontaneous image.
B) Fewer patients in early stage Alzheimer's disease draw images of labyrinths after art therapy treatment than before art therapy treatment.
C) More patients in early stage Alzheimer's disease draw images of labyrinths than patients in later stages of Alzheimer's.
D) There was no relation between the preference for drawing labyrinths and the number of patients in early stage Alzheimer's disease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Shelly wants to know how many of her peers use computers in art therapy. She posts
A) Yes, because 95% is a large enough percentage to show significance.
B) Yes, survey research is important for disseminating information and predicting trends in the field.
C) No, because the results are biased toward art therapists under 30 who are more likely to use computers for a variety of purposes including surveys.
D) No, because a survey cannot adequately address the therapeutic benefits or liabilities of using computers in therapy.
A) Yes, because 95% is a large enough percentage to show significance.
B) Yes, survey research is important for disseminating information and predicting trends in the field.
C) No, because the results are biased toward art therapists under 30 who are more likely to use computers for a variety of purposes including surveys.
D) No, because a survey cannot adequately address the therapeutic benefits or liabilities of using computers in therapy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Formulate a hypothesis for the following question: What are the therapeutic effects of storyboard drawing with adolescents diagnosed with attention deficit disorder?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Apply your research question to the protocol template found in the text.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Design an experiment to test the following observation (or substitute a problem of your own): Art therapy seems to be an effective for helping children adjust to a new foster home placement. Modify your experiment to make it a single-subject design, a quasi-experiment, and a correlational study.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Design an experiment for a creative problem you can solve in your art studio (e.g. what colors are most effective for expressing a childhood memory?). Then adapt its basic features to apply it to an art therapy problem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Create an artwork that shows a cause-and-effect relationship between two variables (e.g. compositional elements, media interactions, design principles). Then create an artwork that shows a correlational or linear relationship between two variables.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Select a published research study that interests you and create an artwork that best illustrates its findings. Write a reflection on the artwork and how it relates to the study and its strengths or limitations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



