Deck 2: Internal and External Validity
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/30
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 2: Internal and External Validity
1
Joe is interested in examining how the availability of recycling bins influences people's recycling behavior. Specifically, he went around his office building, noting where all the recycling bins and trash cans were. Then, before trash day, he weighed the amount of recyclable material that was in each trash can, as well as the distance that those trash cans were from recycling bins. This type of investigation best reflects what general type of research design?
A) experimental design
B) quasi-experiment design
C) nonexperimental design
D) randomized control design
A) experimental design
B) quasi-experiment design
C) nonexperimental design
D) randomized control design
C
2
Experimental and nonexperimental designs both have their own limitations. Specifically, experimental designs are often preferred because (all things being equal) they have especially good _____(a)________. Alternatively, while nonexperimental designs usually have low _______(a)______, they often offer higher levels of _______(b)________.
A) external validity; internal validity
B) internal validity; external validity
C) generalizability; replicability
D) laboratory studies; field studies
A) external validity; internal validity
B) internal validity; external validity
C) generalizability; replicability
D) laboratory studies; field studies
B
3
In a laboratory experiment, Bill and Jason find that when children are induced to perceive their parents as having eyes in the back of their heads (i.e., that the parents are always "watching them"), the children are less likely to do drugs in the future. In a follow-up study, children who do drugs reported less agreement with the statement "my parents seem to have eyes in the back of their head." In this example, the relationship between drug use and parental monitoring is most likely:
A) noncausal covariation
B) spurious correlation
C) bidirectional causation
D) unidirectional causation
A) noncausal covariation
B) spurious correlation
C) bidirectional causation
D) unidirectional causation
D
4
In a (fictional) series of quasi-experimental studies, low self-esteem was found to be correlated with preference for contact sports (e.g., hockey). However, researchers subsequently discovered that the relationship between self-esteem and contact sports was stronger for men than it was for women. In this example, gender best reflects what type of variable?
A) moderator variable
B) mediator variable
C) spurious third variable
D) unidirectional causal variable
A) moderator variable
B) mediator variable
C) spurious third variable
D) unidirectional causal variable

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
In a (fictional) series of quasi-experimental studies, low self-esteem was found to be correlated with preference for contact sports (e.g., hockey). However, researchers subsequently discovered that the relationship between self-esteem and contact sports was only present in people who had had their wisdom teeth removed when they were young. In this example, wisdom teeth best reflects what type of variable?
A) moderator variable
B) mediator variable
C) extraneous third variable
D) unidirectional causal variable
A) moderator variable
B) mediator variable
C) extraneous third variable
D) unidirectional causal variable

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A variable (C) that affects the strength of a relationship between two other variables (A and
A) mediator; moderator
B) extraneous variable; causal variable
C) independent variable; dependent variable
D) moderator; mediator
A) mediator; moderator
B) extraneous variable; causal variable
C) independent variable; dependent variable
D) moderator; mediator

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In a study, the temperature of an interview room was slowly raised to 100° F, and participants were given the opportunity to determine the difficulty of a task for someone they had interacted with previously. In this example, temperature functions as a(n) __________, while task difficulty score functions as a(n) __________.
A) dependent variable; independent variable
B) criterion variable; predictor variable
C) independent variable; dependent variable
D) predictor variable; independent variable
A) dependent variable; independent variable
B) criterion variable; predictor variable
C) independent variable; dependent variable
D) predictor variable; independent variable

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Whether the findings of a study can be appropriately extrapolated to people outside of the research sample is an issue of _____________.
A) internal validity
B) external validity
C) control vs. experimental treatments
D) maturation effects
A) internal validity
B) external validity
C) control vs. experimental treatments
D) maturation effects

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Liana is writing a grant proposal for her next study, wherein she wants to investigate the conditions under which a numerical minority in a group context can alter the visual perception of majority group members. Specifically, the treatments involved groups of seven people who were shown the color blue on a screen and asked to report what color they saw. In condition A, one person (a confederate) claims to see green; in condition B, two confederates claim to see green; in condition C, three people claim to see green; and condition D functioned as a control group, with no confederates. Liana finds that the size of a numerical minority influences the effect it has on the majority. This research best reflects what type of research?
A) applied research
B) field research
C) basic research
D) quasi-experimental research
A) applied research
B) field research
C) basic research
D) quasi-experimental research

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
An example of ____(a)______ research would be: investigating whether spending time in nature makes people act in a more environmentally friendly way. An example of _____(b)_____ research would be: investigating whether people view the environment differently when their family is primed versus when their non-familial group membership is primed.
A) field; quasi-experimental
B) basic; applied
C) applied; basic
D) experimental; field
A) field; quasi-experimental
B) basic; applied
C) applied; basic
D) experimental; field

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Over the course of a year-long 2 (depression: depressed, control) by 2 (therapy: video game therapy, none) experiment, the stock market crashed! Baseline measurements showed people who were initially depressed (mean = 7.5) were significantly more depressed than non-depressed participants (mean = 3.5). By the end of the study, the researchers concluded that video game therapy was not an effective treatment for depression because there were no differences between therapy (mean = 6.0) and control (mean = 6.0) conditions. Based on this example, what other potential factors are likely to have influenced these results? (circle all that apply)
A) history
B) testing
C) instrumentation
D) regression toward the mean
E) none of the above
A) history
B) testing
C) instrumentation
D) regression toward the mean
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
All things being equal, compared to cross-sectional studies, longitudinal studies are more vulnerable to what threats to internal validity? (circle all that apply)
A) maturation
B) testing
C) regression toward the mean
D) selection
E) none of the above
A) maturation
B) testing
C) regression toward the mean
D) selection
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
In a longitudinal study with random assignment to treatment groups, approximately 10 percent of the sample dropped out of the study early. Those who dropped out were similar to those who did not, and the percentage of dropped participants was roughly equal across conditions. In this example, the issue of participants leaving represents what potential problem(s)?
A) mortality
B) systematic error
C) selection
D) parts A & C
E) all of the above
F) none of the above
A) mortality
B) systematic error
C) selection
D) parts A & C
E) all of the above
F) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The idea that researchers themselves can sometimes unintentionally influence results simply by having preconceived expectations about the study, or by giving subtle cues to participants, is a variant of what threat to internal validity?
A) selection
B) instrumentation
C) testing
D) history
A) selection
B) instrumentation
C) testing
D) history

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Failing to reject the null hypothesis when in reality there was an effect present represents:
A) Type I error
B) Type II error
C) sampling error
D) random error
A) Type I error
B) Type II error
C) sampling error
D) random error

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Random assignment increases __________, random selection increases ___________.
A) internal validity; external validity
B) external validity; internal validity
C) generalizability; replicability
D) random error; systematic error
A) internal validity; external validity
B) external validity; internal validity
C) generalizability; replicability
D) random error; systematic error

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
When thinking about external validity, it is important to consider the extent to which the __________ in a study is/are generalizable. (choose all that apply)
A) operationalizations
B) experimental context
C) participant sample
D) experimental effects
A) operationalizations
B) experimental context
C) participant sample
D) experimental effects

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
In a true experiment on anxiety and electric shock, 15 people drop out of the experimental group while one person drops out of the control group. This differential drop out rate reflects what potential problem(s) for the study? (circle all that apply)
A) sampling error
B) selection
C) mortality
D) low generalizability
E) none of the above
A) sampling error
B) selection
C) mortality
D) low generalizability
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
You are conducting an experiment with group membership as your IV and attitudes toward Barack Obama as your DV, and you hypothesize that people in Group 1 will rate Obama higher than people in Group 2. In terms of the inferential statistical tests you would use to test your hypothesis, briefly explain the four possible outcomes that you could have regarding the correspondence between treatment effect and reality. In other words, use the variables above to describe the outcomes in each cell of the 2x2 matrix of treatment (effect/no effect) by reality (effect/no effect) (be sure to label error types when appropriate).
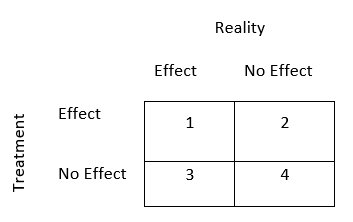
a. You find that Group 1 rates Obama higher than Group 2, when in fact there was that effect present. This would be a correct conclusion, and the probability in which we will make this conclusion (given the presence of treatment and "real" effects) reflects the statistical power of the study.
b. You find that Group 1 rates Obama higher than Group 2, but in fact there was no difference between groups in reality. This represents Type 1 error.
c. You find that there was no difference in Obama's ratings between Groups 1 and 2 when in fact there was a difference present. This represents Type 2 error.
d. You find that there was no difference in Obama's ratings between Groups 1 and 2 when in fact there was no difference between groups. This would be a correct conclusion.

a. You find that Group 1 rates Obama higher than Group 2, when in fact there was that effect present. This would be a correct conclusion, and the probability in which we will make this conclusion (given the presence of treatment and "real" effects) reflects the statistical power of the study.
b. You find that Group 1 rates Obama higher than Group 2, but in fact there was no difference between groups in reality. This represents Type 1 error.
c. You find that there was no difference in Obama's ratings between Groups 1 and 2 when in fact there was a difference present. This represents Type 2 error.
d. You find that there was no difference in Obama's ratings between Groups 1 and 2 when in fact there was no difference between groups. This would be a correct conclusion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Briefly describe and compare internal and external validity. In your answer, be sure to include for each type: (a) a definition, (b) the critical issue it addresses, and (c) whether it is higher or lower in experimental versus nonexperimental (field) research.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Compare random selection and random assignment. In your response, be sure to define each term and an explanation for how they differ.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Hermione and Luna conducted a study on the effects of marijuana on academic performance, and the effect of school on marijuana usage. They recruited 50 people from a well-known group of potheads at school, and 50 people from a well-known group of abstainers. At the beginning of the 2014 school year, they administered three measurements of key variables: (a) marijuana use - "how often do you smoke marijuana?"; (b) grade point average - "what were your grades for the previous semester"; and (c) relationship with their teachers - "in general, how good is your relationship with your teachers?" At the end of the school year, the researchers reassessed the three key variables: (a) marijuana use - "how often did you use marijuana in the past year?"; (b) GPA - "what are your grades for the current semester?"; and (c) relationship with teachers - obtained teachers' ratings of their relationships with the students in the study. By the end of the school year, 25 percent of potheads had dropped out of school (and thus out of the study), while none of the abstainers dropped out. Overall, the researchers found that people who use marijuana had significantly poorer GPAs and relationships with their teachers compared to non-users. However, the also found that marijuana users decreased their usage by the end of the school year, whereas a significant percentage of abstainers started using marijuana by the end of the school year. Thus, they concluded that marijuana negatively impacts people's scholastic achievements, and that school helps habitual users stop using marijuana but simultaneously causes people who never used marijuana to start using. Obviously, this study has many problems, particularly with its internal validity. Please describe how four of the eight threats to internal validity may have influenced the results of this study, and offer solutions for how to deal with these internal validity threats. In your answer, be sure to (a) describe each threat, (b) identify how each threat is present in the study, (c) explain how the threat would specifically impact the results of the study, and (d) offer one suggestion for how to solve or prevent each threat.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What are some of the advantages and disadvantages of field research and laboratory research?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
What are a couple key differences between random assignment and random selection?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What kinds of research decisions need to be made in order to achieve internal validity? External validity?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
What is the role of inferential statistics in research design and hypothesis testing?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
You are conducting an experiment with group membership as your IV and attitudes toward Barack Obama as your DV, and you hypothesize that people in Group 1 will rate Obama higher than people in Group 2. In terms of the inferential statistical tests you would use to test your hypothesis, briefly explain the four possible outcomes that you could have regarding the correspondence between treatment effect and reality. In other words, use the variables above to describe the outcomes in each cell of the 2x2 matrix of treatment (effect/no effect) by reality (effect/no effect). (Be sure to label error types when appropriate).
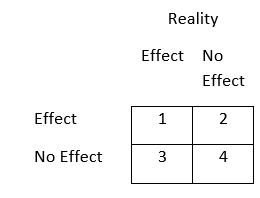
a. You find that Group 1 rates Obama higher than Group 2, when in fact there was that effect present. This would be a correct conclusion, and the probability in which we will make this conclusion (given the presence of treatment and "real" effects) reflects the statistical power of the study.
b. 2. You find that Group 1 rates Obama higher than Group 2, but in fact there was no difference between groups in reality. This represents Type 1 error.
c. 3. You find that there was no difference in Obama's ratings between Groups 1 and 2 when in fact there was a difference present. This represents Type 2 error.
d. You find that there was no difference in Obama's ratings between Groups 1 and 2 when in fact there was no difference between groups. This would be a correct conclusion.

a. You find that Group 1 rates Obama higher than Group 2, when in fact there was that effect present. This would be a correct conclusion, and the probability in which we will make this conclusion (given the presence of treatment and "real" effects) reflects the statistical power of the study.
b. 2. You find that Group 1 rates Obama higher than Group 2, but in fact there was no difference between groups in reality. This represents Type 1 error.
c. 3. You find that there was no difference in Obama's ratings between Groups 1 and 2 when in fact there was a difference present. This represents Type 2 error.
d. You find that there was no difference in Obama's ratings between Groups 1 and 2 when in fact there was no difference between groups. This would be a correct conclusion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Briefly describe and compare internal and external validity. In your answer, be sure to include for each type: (a) a definition, (b) the critical issue it addresses, and (c) whether it is higher or lower in experimental versus nonexperimental (field) research.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Compare random selection and random assignment. In your response, be sure to define each term and an explanation for how they differ.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Hermione and Luna conducted a study on the effects of marijuana on academic performance, and the effect of school on marijuana usage. They recruited 50 people from a well-known group of potheads at school, and 50 people from a well-known group of abstainers. At the beginning of the 2014 school year, they administered three measurements of key variables: (a) marijuana use - "how often do you smoke marijuana?"; (b) grade point average - "what were your grades for the previous semester"; and (c) relationship with their teachers - "in general, how good is your relationship with your teachers?" At the end of the school year, the researchers reassessed the three key variables: (a) marijuana use - "how often did you use marijuana in the past year?"; (b) GPA - "what are your grades for the current semester?"; and (c) relationship with teachers - obtained teachers' ratings of their relationships with the students in the study. By the end of the school year, 25 percent of potheads had dropped out of school (and thus out of the study), while none of the abstainers dropped out. Overall, the researchers found that people who use marijuana had significantly poorer GPAs and relationships with their teachers compared to non-users. However, they also found that marijuana users decreased their usage by the end of the school year, whereas a significant percentage of abstainers started using marijuana by the end of the school year. Thus, they concluded that marijuana negatively impacts people's scholastic achievements, and that school helps habitual users stop using marijuana but simultaneously causes people who never used marijuana to start using. Obviously, this study has many problems, particularly with its internal validity. Please describe how four of the eight threats to internal validity may have influenced the results of this study, and offer solutions for how to deal with these internal validity threats. In your answer, be sure to (a) describe each threat, (b) identify how each threat is present in the study, (c) explain how the threat would specifically impact the results of the study, and (d) offer one suggestion for how to solve or prevent each threat.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



