Deck 8: Chi-Square and Nonparametric Tests
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/22
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 8: Chi-Square and Nonparametric Tests
1
The chi-square test of independence can be used when:
A) Groups being compared are independent
B) The same people are measured multiple times
C) A t-test cannot be used because assumptions have been violated
D) All of the above
A) Groups being compared are independent
B) The same people are measured multiple times
C) A t-test cannot be used because assumptions have been violated
D) All of the above
A
2
The chi-square test is used to test the null hypothesis that:
A) The medians of groups being compared are equal
B) Two categorical variables are independent (not related)
C) The expected cell sizes are zero
D) The odds ratio is zero
A) The medians of groups being compared are equal
B) Two categorical variables are independent (not related)
C) The expected cell sizes are zero
D) The odds ratio is zero
B
3
A chi-square test is not appropriate if:
A) The distribution of scores is not normal
B) The observed frequency in any cell is 0
C) The expected frequency in any cell is 0
D) There are more than five levels of one of the variables
A) The distribution of scores is not normal
B) The observed frequency in any cell is 0
C) The expected frequency in any cell is 0
D) There are more than five levels of one of the variables
C
4
For a cell in a crosstab table, the row total is 10, the column total is 20, and the overall sample size is 40. What is the expected frequency for that cell?
A) 2
B) 5
C) 20
D) It depends on how many cells there are.
A) 2
B) 5
C) 20
D) It depends on how many cells there are.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Assume a chi-square is computed as follows: χ2 = 1.25 + 1.25 + 2.25 + 2.25 + .50 + .50 = 8.0. What is the dimensionality of the contingency table?
A) 2 % 2
B) 2 % 3
C) 3 % 3
D) It cannot be determined.
A) 2 % 2
B) 2 % 3
C) 3 % 3
D) It cannot be determined.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
In a 4 % 3 contingency table, how many degrees of freedom would there be for a chi-square test?
A) 3
B) 4
C) 6
D) 12
A) 3
B) 4
C) 6
D) 12

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A 3 % 3 contingency table has two cells for which the expected frequency is 4. What test should be used?
A) Pearson's chi-square test
B) Chi-square goodness of fit test
C) Chi-square test with Yates correction
D) Fisher's exact test
A) Pearson's chi-square test
B) Chi-square goodness of fit test
C) Chi-square test with Yates correction
D) Fisher's exact test

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
In a 2 % 2 contingency table, the magnitude of effects could be communicated by any of the following except:
A) Likelihood ratio
B) OR
C) Phi coefficient
D) RR
A) Likelihood ratio
B) OR
C) Phi coefficient
D) RR

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
In a power analysis, the chi-square analog to eta-squared as an effect size index is:
A) Cramér's V
B) Likelihood ratio
C) Phi coefficient
D) Yates continuity factor
A) Cramér's V
B) Likelihood ratio
C) Phi coefficient
D) Yates continuity factor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
In a 2 % 2 contingency table, which of the following is true?
A) Effect sizes for differences in proportions near .50 are larger than those near .10
B) Effect sizes for differences in proportions near .10 are larger than those near .50
C) Effect sizes for differences in proportions near .50 are the same as those near .10
D) Effect sizes for differences in proportions near .50 and near .10 would depend on how much power is needed
A) Effect sizes for differences in proportions near .50 are larger than those near .10
B) Effect sizes for differences in proportions near .10 are larger than those near .50
C) Effect sizes for differences in proportions near .50 are the same as those near .10
D) Effect sizes for differences in proportions near .50 and near .10 would depend on how much power is needed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following is not a rank test?
A) Chi-square test
B) Kruskal-Wallis test
C) Mann-Whitney U test
D) Wilcoxon test
A) Chi-square test
B) Kruskal-Wallis test
C) Mann-Whitney U test
D) Wilcoxon test

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
In the following situation, which test should be used? Independent variable = pretest vs. posttest measurement; dependent variable = stress measured on a 7-point scale
A) Friedman test
B) Mann-Whitney U test
C) McNemar test
D) Wilcoxon test
A) Friedman test
B) Mann-Whitney U test
C) McNemar test
D) Wilcoxon test

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
In the following situation, which test should be used? Independent variable = educational status (high school diploma vs. Bachelor's degree vs. graduate degree); dependent variable = frequency of insomnia (1= never, 2 = 1-5 times/year; 3 = 6-10 times/year; 4 = 11-25 times/year; 5 = 25-49 times/year; 6 = 50+ times/year)
A) Chi-square test
B) Kruskal-Wallis test
C) Cochran's Q
D) McNemar test
A) Chi-square test
B) Kruskal-Wallis test
C) Cochran's Q
D) McNemar test

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
In the following situation, which test should be used? Independent variable = group status (experimental vs. control); dependent variable = re-hospitalization status within 6 months post-surgery (yes vs. no)
A) Chi-square test
B) Kruskal-Wallis test
C) Cochran's Q
D) McNemar test
A) Chi-square test
B) Kruskal-Wallis test
C) Cochran's Q
D) McNemar test

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
In the following situation, which test should be used? Independent variable = first-born child vs. second born child; dependent variable = mother's decision to breastfeed (yes vs. no)
A) Chi-square test
B) Kruskal-Wallis test
C) Cochran's Q
D) McNemar test
A) Chi-square test
B) Kruskal-Wallis test
C) Cochran's Q
D) McNemar test

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following is the nonparametric analog of an RM-ANOVA?
A) McNemar test
B) Friedman test
C) Cochran's Q test
D) Wilcoxon test
A) McNemar test
B) Friedman test
C) Cochran's Q test
D) Wilcoxon test

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
For which of the following tests might the Dunn procedure be appropriate?
A) Mann Whitney U test
B) McNemar test
C) Wilcoxon test
D) Kruskal-Wallis test
A) Mann Whitney U test
B) McNemar test
C) Wilcoxon test
D) Kruskal-Wallis test

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A Dunn procedure has been performed for a 4-group comparison and a Bonferroni correction is applied. What should the value of alpha be to keep the risk of a Type I error to .05?
A) .05 ÷ 2 = .025
B) 05 ÷ 3 = .017
C) 05 ÷ 4 = .0125
D) 05 ÷ 6 = .008
A) .05 ÷ 2 = .025
B) 05 ÷ 3 = .017
C) 05 ÷ 4 = .0125
D) 05 ÷ 6 = .008

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Questions pertain to the following table (Table 8), which presents fictitious results regarding selected risk factors for perineal dermatitis among elderly residents of a nursing home.
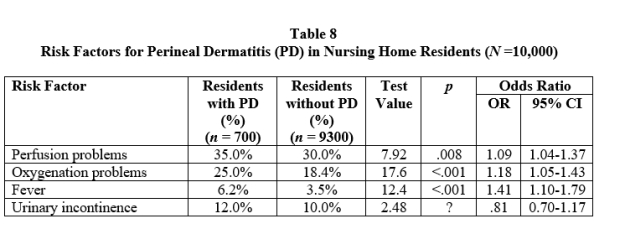
-Refer to Table 8. The p value for the risk factor "urinary incontinence" is missing from the table. Which of the following is the most likely p value?
A) <.001
B) .02
C) .04
D) .11

-Refer to Table 8. The p value for the risk factor "urinary incontinence" is missing from the table. Which of the following is the most likely p value?
A) <.001
B) .02
C) .04
D) .11

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Questions pertain to the following table (Table 8), which presents fictitious results regarding selected risk factors for perineal dermatitis among elderly residents of a nursing home.

-Refer to Table 8. Which test statistic was likely used in these analyses-that is, which statistic should be in the heading for the column "Test Value"?
A) t
B) U
C) χ2
D) It cannot be determined-there are several possibilities.

-Refer to Table 8. Which test statistic was likely used in these analyses-that is, which statistic should be in the heading for the column "Test Value"?
A) t
B) U
C) χ2
D) It cannot be determined-there are several possibilities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Questions pertain to the following table (Table 8), which presents fictitious results regarding selected risk factors for perineal dermatitis among elderly residents of a nursing home.

-Refer to Table 8. What were the degrees of freedom in these analyses?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4

-Refer to Table 8. What were the degrees of freedom in these analyses?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Questions pertain to the following table (Table 8), which presents fictitious results regarding selected risk factors for perineal dermatitis among elderly residents of a nursing home.

-Refer to Table 8. Which of the four risk factors had the strongest relationship with perineal dermatitis?
A) Perfusion problems
B) Oxygenation problems
C) Fever
D) Urinary incontinence

-Refer to Table 8. Which of the four risk factors had the strongest relationship with perineal dermatitis?
A) Perfusion problems
B) Oxygenation problems
C) Fever
D) Urinary incontinence

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



