Deck 9: The Keynesian Model: Extensions to China and Beyond
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/9
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 9: The Keynesian Model: Extensions to China and Beyond
1
Go the Federal Reserve Economic Database (FRED) and graph government consumption as a share of GDP in China.
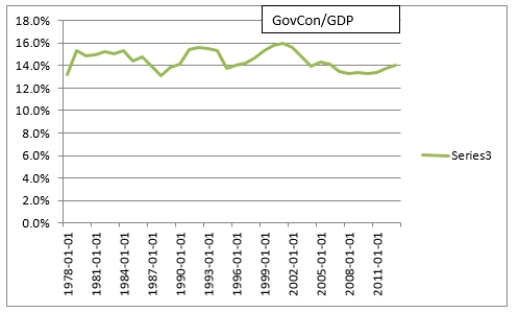 And by way of comparison for the United States:
And by way of comparison for the United States:
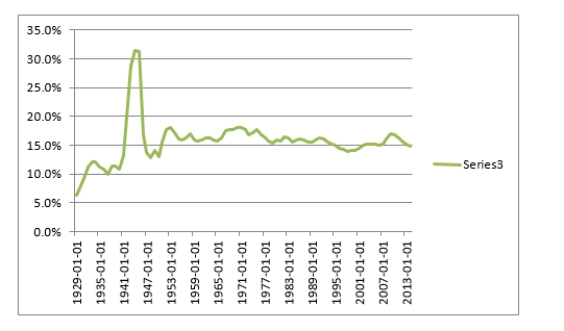
 And by way of comparison for the United States:
And by way of comparison for the United States:

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 9 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
2
Suppose that China's economy in Graph 9.8 is located right between the two chopsticks in the shaded area. Using Graph 9.4, show what natural economic forces will tend to build up and move the economy in one direction or the other?
For any given interest rate, Y is too small relative to the LM and too large relative to IS or we are above the LM and above the IS this is equivalent to Quadrant 2. At that point there is an excess supply of money plus inventory accumulatiom Interest rates will fall and assuming the IS curve has a stronger pull than the LM, output will fall too. We will move closer to the IS curve's base. Keep in mind, however, that our chopstick economy has no equilibrium in a Keynesian sense.
3
Explain why "crowding out" in China has a very different meaning compared to the notion in the United States. Be specific about where crowding out is occurring-on the production side or the uses side, and which sectors (C, I, G or NX) are crowding out which other sectors.
In the US we think of increased govt. demand (use) crowding out investment demand (use) and consumption (use). In China, government encouraged investment and exports crowd out consumption. When SOE's produce consumer goods this tends to crowd out private production ( a production rather than uses form of crowding out ).
4
Explain why flexible prices (or itsabsence) is a linchpin (a critical assumption) in the Keynesian framework. Now explain the analogous role that the "great economic shock absorber" plays.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 9 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Explain why it would be important for any emerging economy (including China) to clarify, in a legal sense, the ownership of domestically owned assets before opening its assets markets to international capital mobility. In this context, explain the advantages and disadvantages of an emerging economy delaying the opening up of its financial markets to international investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 9 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Explain what warning signs are and are not contained in China's appreciating exchange rate in recent years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 9 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
If in fact, China's comes to rely less on exports and less on investment as a source of demand in the coming years, how will fiscal policy need to be different from its current situation?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 9 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Discuss: In the coming years, China's labor force will come to show increasing inflexibility and this will present new challenges for fiscal policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 9 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
In Macro Finance Insight 9.2, what assumption must we be making in the background regarding the fixity or flexibility of the exchange rate? How would Macro Finance Insight 9.2 be altered if we changed that assumption?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 9 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



