Deck 11: Two-Sample T-Test: Related Samples Design
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/52
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 11: Two-Sample T-Test: Related Samples Design
1
A repeated measures study involves
A) two sets of scores from the same subjects.
B) two sets of scores from two different samples.
C) replicating a study to see if similar results are obtained.
D) participants doing the same task repeatedly.
A) two sets of scores from the same subjects.
B) two sets of scores from two different samples.
C) replicating a study to see if similar results are obtained.
D) participants doing the same task repeatedly.
A
2
A repeated measures study is
A) also called a within-subjects design.
B) also called a between-subjects design.
C) a type of related samples design.
D) both "a" and "c" are correct.
A) also called a within-subjects design.
B) also called a between-subjects design.
C) a type of related samples design.
D) both "a" and "c" are correct.
D
3
The standard deviation for a two-sample, repeated measures t test is called the
A) standard error of the mean.
B) standard error of the mean difference.
C) standard error of the difference between means.
D) standard error of the deviation of means.
A) standard error of the mean.
B) standard error of the mean difference.
C) standard error of the difference between means.
D) standard error of the deviation of means.
B
4
The symbol for the standard error value for a repeated measures t test is
A) s
B) sM
C)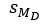
D) sM₁-M₂
A) s
B) sM
C)
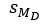
D) sM₁-M₂

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
If the sum of the difference scores in a repeated measures t test is 68 and n = 16, what is the mean difference value?
A) 4.25
B) 4.53
C) 17
D) 23
A) 4.25
B) 4.53
C) 17
D) 23

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Given difference values of 21, -6, 17, -10, and 13, what is MD?
A) 35
B) 7
C) 8.75
D) 15.63
A) 35
B) 7
C) 8.75
D) 15.63

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following will give you MD
A) ∑D
B) ∑D²
C) ∑D/n
D) ∑D²/n
A) ∑D
B) ∑D²
C) ∑D/n
D) ∑D²/n

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
In a repeated measures t test, difference values are determined by
A) subtracting post-test scores from pre-test scores.
B) subtracting pre-test scores from post-test scores.
C) squaring the post-test scores.
D) squaring the pre-test scores.
A) subtracting post-test scores from pre-test scores.
B) subtracting pre-test scores from post-test scores.
C) squaring the post-test scores.
D) squaring the pre-test scores.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following is the working formula for the repeated measures t test?
A)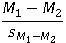
B)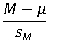
C)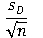
D)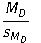
A)
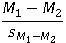
B)
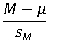
C)
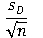
D)
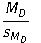

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which is the correct df for a related samples t test?
A) n - 1
B) n₁ + n₂ - 2
C) n₁ - n₂ + 2
D) n + 1
A) n - 1
B) n₁ + n₂ - 2
C) n₁ - n₂ + 2
D) n + 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A repeated measures t test was conducted using a sample size of n = 28. What is the df?
A) 26
B) 27
C) 54
D) 30
A) 26
B) 27
C) 54
D) 30

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
If df = 34 for a repeated measures t test, how many subjects participated in the study?
A) 17
B) 16
C) 35
D) 36
A) 17
B) 16
C) 35
D) 36

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
For a repeated measures t test, the null hypothesis attributes
A) mean differences between pre- and post-test scores to random sampling error.
B) any differences between the means for group 1 and group 2 to random sampling error.
C) mean differences between pre- and post-test scores to the effects of an independent variable.
D) any differences between the means for group 1 and group 2 to the effects of an independent variable.
A) mean differences between pre- and post-test scores to random sampling error.
B) any differences between the means for group 1 and group 2 to random sampling error.
C) mean differences between pre- and post-test scores to the effects of an independent variable.
D) any differences between the means for group 1 and group 2 to the effects of an independent variable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
For a repeated measures t test, the alternative hypothesis attributes
A) mean differences between pre- and post-test scores to random sampling error.
B) any differences between the means for group 1 and group 2 to random sampling error.
C) mean differences between pre- and post-test scores to the effects of an independent variable.
D) any differences between the means for group 1 and group 2 to the effects of an independent variable.
A) mean differences between pre- and post-test scores to random sampling error.
B) any differences between the means for group 1 and group 2 to random sampling error.
C) mean differences between pre- and post-test scores to the effects of an independent variable.
D) any differences between the means for group 1 and group 2 to the effects of an independent variable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following is the correct notation for the nondirectional alternative hypothesis of a repeated measures t test?
A) H₁: μD ≠ 0
B) H₁: μD > 0
C) H₁: μD < 0
D) either "b" or "c" above
A) H₁: μD ≠ 0
B) H₁: μD > 0
C) H₁: μD < 0
D) either "b" or "c" above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following is the correct notation for the null hypothesis of a repeated measures t test for which the alternative hypothesis is nondirectional?
A) H₀: μ₁ = μ₂
B) H₀: μD = 0
C) H₀: μ₁ - μ₂ = 0
D) H₀: either "a" or "c" above
A) H₀: μ₁ = μ₂
B) H₀: μD = 0
C) H₀: μ₁ - μ₂ = 0
D) H₀: either "a" or "c" above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following is a directional alternative hypothesis for a repeated measures t test?
A) H₁: μ₁ ≥ μ₂
B) H₁: μ₁ > <μ₂
C) H₁: μD ≤ 0
D) H₁: μD < 0
A) H₁: μ₁ ≥ μ₂
B) H₁: μ₁ > <μ₂
C) H₁: μD ≤ 0
D) H₁: μD < 0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following is a directional null hypothesis for a repeated measures t test?
A) H₀: μD < 0
B) H₀: μD ≥ 0
C) H₀: μ₁ > μ₂
D) H₀: μ₁ ≤ μ₂
A) H₀: μD < 0
B) H₀: μD ≥ 0
C) H₀: μ₁ > μ₂
D) H₀: μ₁ ≤ μ₂

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Given an alpha level of .01 and n = 22, what would tcrit be for a nondirectional repeated measures t test?
A) -2.518
B) +2.518
C) ±2.831
D) either "a" or "b" above
A) -2.518
B) +2.518
C) ±2.831
D) either "a" or "b" above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Given an alpha level of .05 and n = 18, what would tcrit be for a nondirectional repeated measures test?
A) ±1.746
B) ±2.120
C) ±1.740
D) ±2.110
A) ±1.746
B) ±2.120
C) ±1.740
D) ±2.110

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following is one of the procedures involved in conducting a repeated measures t test?
A) Each set of scores will be squared.
B) The pre-test scores are subtracted from the post-test scores.
C) Each set of scores will be added; the total of each will then be divided by n to arrive at a mean for each group.
D) The mean difference value is determined by dividing ∑D² by n.
A) Each set of scores will be squared.
B) The pre-test scores are subtracted from the post-test scores.
C) Each set of scores will be added; the total of each will then be divided by n to arrive at a mean for each group.
D) The mean difference value is determined by dividing ∑D² by n.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following terms is eliminated from the original formula for the related samples t test?
A) μD
B) MD
C)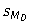
D)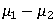
A) μD
B) MD
C)
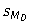
D)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Given: ∑D = 32, n = 8, and sD = 5, what is Cohen's d?
A) 4
B) .8
C) 6.4
D) .4
A) 4
B) .8
C) 6.4
D) .4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Given ∑D = 64, n = 9, and sD = 8, what is ?
A) 8
B) 7.11
C) 2.67
D) .88
A) 8
B) 7.11
C) 2.67
D) .88

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Given ∑D = 224, n = 16, and sD = 11, what is tobt?
A) 14
B) 1.45
C) 5.09
D) 16
A) 14
B) 1.45
C) 5.09
D) 16

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Given SSD = 408, MD = 8, and n = 9, what is ?
A) 2.38
B) 51
C) 45.33
D) 2.67
A) 2.38
B) 51
C) 45.33
D) 2.67

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which is the correct Cohen d formula for a repeated measures t test?
A)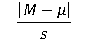
B)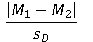
C)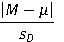
D)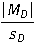
A)
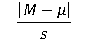
B)
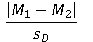
C)
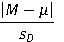
D)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the assumptions below does not apply to a repeated measures t test?
A) independent and random sampling
B) normal distribution of the dependent variable
C) measurement of the dependent variable on interval or ratio scales
D) homogeneity of variance
A) independent and random sampling
B) normal distribution of the dependent variable
C) measurement of the dependent variable on interval or ratio scales
D) homogeneity of variance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following is NOT one of the advantages of a repeated measures t test?
A) the measurement of developmental changes
B) fewer subjects
C) order effects
D) less variability
A) the measurement of developmental changes
B) fewer subjects
C) order effects
D) less variability

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
One of the disadvantages of the repeated measures design is
A) order effects.
B) the greater number of subjects required.
C) more sampling error.
D) greater variability due to individual differences.
A) order effects.
B) the greater number of subjects required.
C) more sampling error.
D) greater variability due to individual differences.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
If you wanted to measure developmental changes over time, which t test(s) would be most suitable?
A) one-sample t test
B) two-sample t test, independent samples design
C) two-sample t test, repeated measures design
D) either "b" or "c" above
A) one-sample t test
B) two-sample t test, independent samples design
C) two-sample t test, repeated measures design
D) either "b" or "c" above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which type of study uses the same subjects on more than one occasion?
A) z-test
B) t test, independent samples design
C) t test, repeated measures design
D) one-sample t test
A) z-test
B) t test, independent samples design
C) t test, repeated measures design
D) one-sample t test

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Problems that could arise related to the order in which the independent variable was presented include all of the following, except
A) boredom.
B) lingering effects of a medication.
C) improved performance due to practice.
D) counterbalancing.
A) boredom.
B) lingering effects of a medication.
C) improved performance due to practice.
D) counterbalancing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
To control for some of the problems associated with order effects in a repeated measures t test, you could
A) shorten the length of time between conditions.
B) use counterbalancing.
C) allow subjects to take a nap between treatment conditions.
D) use different subjects for the second condition.
A) shorten the length of time between conditions.
B) use counterbalancing.
C) allow subjects to take a nap between treatment conditions.
D) use different subjects for the second condition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
If a researcher exposes half of the subjects in an experiment to condition A and then B, and the other half of the subjects to condition B first and then A, what procedure has been used?
A) counterbalancing
B) order effects
C) switchback
D) reversal
A) counterbalancing
B) order effects
C) switchback
D) reversal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
In a repeated measures t test,
A) one group of subjects is exposed to one treatment condition.
B) different subjects are exposed to different treatments.
C) more than one dependent variable is being measured.
D) the same subjects are measured before and after a treatment intervention.
A) one group of subjects is exposed to one treatment condition.
B) different subjects are exposed to different treatments.
C) more than one dependent variable is being measured.
D) the same subjects are measured before and after a treatment intervention.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
One study involved one group with n = 16 and M = 48 and another group with n = 18 and M = 62. Which of the following statistical tests would be appropriate for the analysis?
A) one-sample t test
B) two-sample t test, independent samples design
C) two-sample t test, repeated measures design
D) either "b" or "c" above
A) one-sample t test
B) two-sample t test, independent samples design
C) two-sample t test, repeated measures design
D) either "b" or "c" above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The emergence of self-recognition is sometimes studied using the red dot test in which a red dot is placed on a child's forehead or nose. The child is then placed in front of a mirror. If the child touches his or her nose rather than pointing at the mirror or looking behind it for someone, then self-recognition is inferred. A developmental psychologist conducts the red dot test by using a sample of 15 one-month-old babies. She tests them again at 18 months of age. What type of test was employed?
A) z-test
B) one-sample t test
C) independent samples t test
D) repeated measures t test
A) z-test
B) one-sample t test
C) independent samples t test
D) repeated measures t test

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The emergence of self-recognition is sometimes studied using the red dot test in which a red dot is placed on a child's forehead or nose. The child is then placed in front of a mirror. If the child touches his or her nose rather than pointing at the mirror or looking behind it for someone, then self-recognition is inferred. A developmental psychologist conducts the red dot test by using a sample of 15 one-month-old babies and another sample of 18 month-old babies. What type of test was employed?
A) z-test
B) one-sample t test
C) independent samples t test
D) repeated measures t test
A) z-test
B) one-sample t test
C) independent samples t test
D) repeated measures t test

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A researcher studying the psychological effects of color measures the blood pressure of a sample of 16 subjects while sitting in an all blue room. She then moves them to an all yellow room and takes their blood pressure again. What type of test was employed?
A) z-test
B) one-sample t test
C) independent samples t test
D) repeated measures t test
A) z-test
B) one-sample t test
C) independent samples t test
D) repeated measures t test

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
What is a repeated measures study?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
What is the sampling distribution called for a t test with a repeated measures design?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
What is the standard deviation called for a t test with a repeated measures design?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
What are the assumptions for a two-sample t test, repeated measures design?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
What are the advantages of using a repeated measures t test rather than an independent samples t test?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
What are the disadvantages of using a repeated measures t test?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
What is meant by counterbalancing?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
For the items below, indicate what type of t test is called for: a one-sample t test, an independent samples t test, or a repeated measures t test.
a. Motivation scores are measured for a sample of students before and after Spring Break.
b. University freshmen in the state of Minnesota have a mean score of 65 on a math test. A teacher has developed a new technique for teaching math and a sample of high school graduates completes the program over the summer. Before beginning their university studies, they are administered the math test to see if students who completed the program score higher than the state average.
c. The average number of times that females contribute to class discussions over the course of a semester is compared to the average number of times that males contribute.
d. The national average on a measure of Need for Achievement is 50. An Olympic coach believes that athletes training for the Olympics would score higher on this trait and so she administers the test to her trainees to compare.
e. A psychologist used the smile/frown technique to study the facial feedback hypothesis which proposes that feedback from the skeletal muscles in our face influences our emotional experience. The psychologist asked one group to rate the funniness of a packet of cartoons while holding a pencil between their teeth without touching their lips (as if to smile). Another group rated the same packet of cartoons while holding the pencil between their lips without touching their teeth (as if to frown).
f. An optimism test is given to military personnel upon their enlistment and then again at the end of their military service.
a. Motivation scores are measured for a sample of students before and after Spring Break.
b. University freshmen in the state of Minnesota have a mean score of 65 on a math test. A teacher has developed a new technique for teaching math and a sample of high school graduates completes the program over the summer. Before beginning their university studies, they are administered the math test to see if students who completed the program score higher than the state average.
c. The average number of times that females contribute to class discussions over the course of a semester is compared to the average number of times that males contribute.
d. The national average on a measure of Need for Achievement is 50. An Olympic coach believes that athletes training for the Olympics would score higher on this trait and so she administers the test to her trainees to compare.
e. A psychologist used the smile/frown technique to study the facial feedback hypothesis which proposes that feedback from the skeletal muscles in our face influences our emotional experience. The psychologist asked one group to rate the funniness of a packet of cartoons while holding a pencil between their teeth without touching their lips (as if to smile). Another group rated the same packet of cartoons while holding the pencil between their lips without touching their teeth (as if to frown).
f. An optimism test is given to military personnel upon their enlistment and then again at the end of their military service.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
For the summary values that follow for a repeated measures t test, calculate: 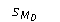 ∑D = -21, ∑D² = 171, n = 6
∑D = -21, ∑D² = 171, n = 6
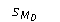 ∑D = -21, ∑D² = 171, n = 6
∑D = -21, ∑D² = 171, n = 6
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Given the summary values that follow for a repeated measures t test, calculate tobt: ∑D = 31, ∑D² = 331, n = 10.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
For the scores that follow, conduct a two-tailed, repeated measures test using α = .05.



Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Professors who teach introductory psychology courses often hear students say that psychology is just "common sense." To test this assumption, Professor Empiricism administers a Fact or Fiction Survey at the beginning of the semester and then again at the end of the semester. She believes that after students are exposed to research-based evidence, students will score higher on the end-of-semester survey. Pre- and post-scores for a sample of her students are listed below:
 a. Test the professor's hypothesis using a one-tailed, repeated measures t test with α = .05.
a. Test the professor's hypothesis using a one-tailed, repeated measures t test with α = .05.
b. Calculate Cohen's d effect size and interpret the result.
 a. Test the professor's hypothesis using a one-tailed, repeated measures t test with α = .05.
a. Test the professor's hypothesis using a one-tailed, repeated measures t test with α = .05.b. Calculate Cohen's d effect size and interpret the result.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



