Deck 11: Some Slopes Are Bigger Than Others: Calculating and Interpreting Beta Coefficients
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/35
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 11: Some Slopes Are Bigger Than Others: Calculating and Interpreting Beta Coefficients
1
Which set of independent variables would you have to standardize in order to compare their effects?
A) marital status (married or not married), age
B) income in dollars, wealth in dollars
C) education in years, age in years
D) all of these need to be standardized
A) marital status (married or not married), age
B) income in dollars, wealth in dollars
C) education in years, age in years
D) all of these need to be standardized
D
2
What statistic do we use in order to standardize slopes?
A) the standard deviation
B) the standard error of the mean
C) the standard coefficient
D) the standard error of the slope
A) the standard deviation
B) the standard error of the mean
C) the standard coefficient
D) the standard error of the slope
A
3
Another name for a standardized regression coefficient is:
A) an alpha
B) a beta
C) a theta
D) a sigma
A) an alpha
B) a beta
C) a theta
D) a sigma
B
4
Imagine we run a regression using the following independent variables: sex, race (white or non-white), years of education, and age. All of their unstandardized slopes are exactly the same value. Which one likely has the highest standardized slope?
A) sex
B) race
C) years of education
D) age
A) sex
B) race
C) years of education
D) age

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
We have a regression with two independent variables: A and B. The slope for Variable A is .25, and the slope for Variable B is 1.00. The standard deviation for Variable A is 2, and the standard deviation for Variable B is .5. Which of the following is true?
A) Variable A has a larger effect than Variable B.
B) Variable B has a larger effect than Variable A.
C) Neither variable has a larger effect than the other variable.
D) Without the standard deviation for the dependent variable, you can't assess the truth of the other choices.
A) Variable A has a larger effect than Variable B.
B) Variable B has a larger effect than Variable A.
C) Neither variable has a larger effect than the other variable.
D) Without the standard deviation for the dependent variable, you can't assess the truth of the other choices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
We have a regression with two independent variables: A and B. The slope for Variable A is .20, and the slope for Variable B is 2.00. The standard deviation for Variable A is .20, and the standard deviation for Variable B is 2.00. Which of the following is true?
A) Variable B has the same effect as Variable A.
B) Variable B has twice the effect as Variable A.
C) Variable B has ten times the effect of Variable A.
D) Variable B has one hundred times the effect of Variable A.
A) Variable B has the same effect as Variable A.
B) Variable B has twice the effect as Variable A.
C) Variable B has ten times the effect of Variable A.
D) Variable B has one hundred times the effect of Variable A.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Here are some statistics and some regression results using GSS2008 data:
Standard Deviations:
Number of times respondent goes to a bar per month: 3.77
Education of respondent in years: 3.04
Age of respondent: 16.85
#TIMES TO BAR PER MONTH: 1.51 +.12 (EDUC) - .04 (AGE)
Both slopes are statistically significant.
Which of the following statements is most accurate?
A) Age has almost twice the effect that education has.
B) Education has almost three times the effect that age has.
C) Age and education have roughly the same effect.
D) Education's effect is .16 larger than age's effect.
Standard Deviations:
Number of times respondent goes to a bar per month: 3.77
Education of respondent in years: 3.04
Age of respondent: 16.85
#TIMES TO BAR PER MONTH: 1.51 +.12 (EDUC) - .04 (AGE)
Both slopes are statistically significant.
Which of the following statements is most accurate?
A) Age has almost twice the effect that education has.
B) Education has almost three times the effect that age has.
C) Age and education have roughly the same effect.
D) Education's effect is .16 larger than age's effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Here are some statistics and regression results using GSS2008 data:
Standard Deviations:
Score on a four-point racism index: 1.11
Education of respondent in years: 2.86
Race of respondent (White=0, Black=1): .37
Regression Equation:
SCORE ON RACISM INDEX = 3.12 -.09 (EDUC) - .48 (RACE)
Both slopes are statistically significant.
Which of the following statements is most accurate?
A) Education has a larger effect than race does.
B) Race has a somewhat larger effect than education does.
C) Race has a much larger effect than education does.
D) The two variables have nearly the same effect.
Standard Deviations:
Score on a four-point racism index: 1.11
Education of respondent in years: 2.86
Race of respondent (White=0, Black=1): .37
Regression Equation:
SCORE ON RACISM INDEX = 3.12 -.09 (EDUC) - .48 (RACE)
Both slopes are statistically significant.
Which of the following statements is most accurate?
A) Education has a larger effect than race does.
B) Race has a somewhat larger effect than education does.
C) Race has a much larger effect than education does.
D) The two variables have nearly the same effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Here are some statistics and some regression results using GSS2006 data:
Standard Deviations:
Score on a nine-point religiosity index: 2.46
Sex of respondent (Female=0, Male=1): .50
Age of respondent: 17.12
Regression Equation:
SCORE ON RELIGIOSITY INDEX = 4.65 -.93 (SEX) +.03 (AGE)
Both slopes are statistically significant.
Which of the following statements is most accurate?
A) Sex has a slightly larger effect than age does.
B) Sex has a much larger effect than age does.
C) Age has a slightly larger effect than sex does.
D) Age has a much larger effect than sex does.
Standard Deviations:
Score on a nine-point religiosity index: 2.46
Sex of respondent (Female=0, Male=1): .50
Age of respondent: 17.12
Regression Equation:
SCORE ON RELIGIOSITY INDEX = 4.65 -.93 (SEX) +.03 (AGE)
Both slopes are statistically significant.
Which of the following statements is most accurate?
A) Sex has a slightly larger effect than age does.
B) Sex has a much larger effect than age does.
C) Age has a slightly larger effect than sex does.
D) Age has a much larger effect than sex does.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Here are some statistics and some regression results using GSS2006 data:
Standard Deviations:
Hours per week respondent uses internet: 10.24
Education of respondent in years: 2.94
Age of respondent: 17.05
Live in Big City? (No=0, Yes=1): .30
Regression Equation:
INTERNETHRS = .02 +.73 (EDUC) - .10 (AGE) + 1.95 (LIVEINCITY)
All slopes are statistically significant.
From biggest to smallest effect, which is the correct listing of the variables?
A) city, education, age
B) age, city, education
C) city, age, education
D) education, age, city
Standard Deviations:
Hours per week respondent uses internet: 10.24
Education of respondent in years: 2.94
Age of respondent: 17.05
Live in Big City? (No=0, Yes=1): .30
Regression Equation:
INTERNETHRS = .02 +.73 (EDUC) - .10 (AGE) + 1.95 (LIVEINCITY)
All slopes are statistically significant.
From biggest to smallest effect, which is the correct listing of the variables?
A) city, education, age
B) age, city, education
C) city, age, education
D) education, age, city

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
When you use z-scores in a regression model, what will the outcome be?
A) SPSS will not run the model.
B) The betas will be twice the unstandardized slopes.
C) The betas will be exactly the same as the unstandardized slopes.
D) The betas will be half the unstandardized slopes.
A) SPSS will not run the model.
B) The betas will be twice the unstandardized slopes.
C) The betas will be exactly the same as the unstandardized slopes.
D) The betas will be half the unstandardized slopes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
If you have two independent variables and a dependent variable, and all three have standard deviations of 1, what will happen?
A) the independent variables will have equal betas
B) the betas will be half as small as the unstandardized slopes
C) the betas will be the same as the unstandardized slopes
D) the betas will be twice as large as the unstandardized slopes
A) the independent variables will have equal betas
B) the betas will be half as small as the unstandardized slopes
C) the betas will be the same as the unstandardized slopes
D) the betas will be twice as large as the unstandardized slopes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
In the "religion and homosexuality attitudes" example, which aspect of religiosity had the largest effect?
A) attendance at religious services
B) belief in the Bible as the literal word of God
C) having had a born-again experience
D) they all had the same beta, and thus the same level of effect
A) attendance at religious services
B) belief in the Bible as the literal word of God
C) having had a born-again experience
D) they all had the same beta, and thus the same level of effect

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
According to the textbook, in what way is educational achievement patterned in a gendered way?
A) Men's educational achievement is much more affected by their fathers' educational achievement than their mothers' educational achievement.
B) Women's educational achievement is much more affected by their mothers' educational achievement than their fathers' educational achievement.
C) Men's educational achievement is not affected by their mothers' educational achievement.
D) Women's educational achievement is not affected by their fathers' educational achievement.
A) Men's educational achievement is much more affected by their fathers' educational achievement than their mothers' educational achievement.
B) Women's educational achievement is much more affected by their mothers' educational achievement than their fathers' educational achievement.
C) Men's educational achievement is not affected by their mothers' educational achievement.
D) Women's educational achievement is not affected by their fathers' educational achievement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
What, according to the textbook, was the surprising finding in the "gender and happiness" example?
A) that women are happier than men are
B) that women's primary determinant of happiness was job satisfaction
C) that men's primary determinant of happiness was marital satisfaction
D) that marital satisfaction had no effect on men's or women's happiness
A) that women are happier than men are
B) that women's primary determinant of happiness was job satisfaction
C) that men's primary determinant of happiness was marital satisfaction
D) that marital satisfaction had no effect on men's or women's happiness

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
In Welch and Payne's research on school punishment, what was the unit of analysis?
A) the individual student
B) the individual teacher
C) the school
D) the state
A) the individual student
B) the individual teacher
C) the school
D) the state

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Welch and Payne's regression analyses are testing the ___________ hypothesis.
A) punitive schools
B) racial threat
C) state-sanctioned discipline
D) everyday racism
A) punitive schools
B) racial threat
C) state-sanctioned discipline
D) everyday racism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
According to Welch and Payne's regression results, which type of school would have the most punitive disciplinary response?
A) a school with a high percentage black students, a high percentage free/reduced lunch, and a very involved principal
B) a school with a low percentage black students, a low percentage free/reduced lunch, and a very involved principal
C) a school with a high percentage black students, a high percentage free/reduced lunch, and a very uninvolved principal
D) a school with a high percentage black students, a low percentage free/reduced lunch, and a very uninvolved principal
A) a school with a high percentage black students, a high percentage free/reduced lunch, and a very involved principal
B) a school with a low percentage black students, a low percentage free/reduced lunch, and a very involved principal
C) a school with a high percentage black students, a high percentage free/reduced lunch, and a very uninvolved principal
D) a school with a high percentage black students, a low percentage free/reduced lunch, and a very uninvolved principal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Welch and Payne find that the primary determinant of punishment policies in schools is:
A) the percentage of students who are black
B) the percentage of students who get a free lunch
C) the level of involvement of the principal
D) all had equal betas
A) the percentage of students who are black
B) the percentage of students who get a free lunch
C) the level of involvement of the principal
D) all had equal betas

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
According to Barkan, most research finds that:
A) women are more likely to favor legal abortion
B) men are more likely to favor legal abortion
C) women and men are equally likely to favor legal abortion
D) older women are more likely to favor legal abortion than younger women
A) women are more likely to favor legal abortion
B) men are more likely to favor legal abortion
C) women and men are equally likely to favor legal abortion
D) older women are more likely to favor legal abortion than younger women

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
In Barkan's full model, which variable has the largest effect on attitude toward legal abortion?
A) political conservatism
B) number of children
C) religious affiliation
D) religiosity
A) political conservatism
B) number of children
C) religious affiliation
D) religiosity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
In his article on abortion attitudes, Barkan provides evidence for:
A) the intervening role of religiosity
B) the suppressing role of religiosity
C) the additive role of religiosity
D) the relative role of religiosity
A) the intervening role of religiosity
B) the suppressing role of religiosity
C) the additive role of religiosity
D) the relative role of religiosity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Once Barkan controls for religiosity, the effect of gender on abortion attitudes:
A) goes away completely
B) goes down, but remains statistically significant
C) becomes statistically significant, with women supporting legal abortion more than men
D) becomes statistically significant, with men supporting legal abortion more than women
A) goes away completely
B) goes down, but remains statistically significant
C) becomes statistically significant, with women supporting legal abortion more than men
D) becomes statistically significant, with men supporting legal abortion more than women

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
In SPSS, which button in the regression box do you push to get the betas?
A) "Betas"
B) "Standardize"
C) "Weighting"
D) There is no button, as SPSS gives the betas as part of the regular regression output.
A) "Betas"
B) "Standardize"
C) "Weighting"
D) There is no button, as SPSS gives the betas as part of the regular regression output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
According to the textbook, if you have both the unstandardized and the standardized coefficients, which should you present in a professional table?
A) the unstandardized coefficients
B) the standardized coefficients
C) both the unstandardized coefficients and the standardized coefficients
D) it depends on whether your presentation is oral or written
A) the unstandardized coefficients
B) the standardized coefficients
C) both the unstandardized coefficients and the standardized coefficients
D) it depends on whether your presentation is oral or written

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Someone argues: "The variables age and education are both measured in years. Because they're in the same units: years, I don't need to standardized the slopes in order to compare them." Explain why this is an incorrect statement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Here is some SPSS output using GSS2008 data:
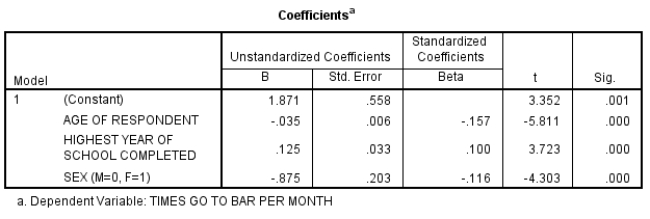 Someone looks at this output and says: "age has the smallest effect." Correct this person.
Someone looks at this output and says: "age has the smallest effect." Correct this person.
 Someone looks at this output and says: "age has the smallest effect." Correct this person.
Someone looks at this output and says: "age has the smallest effect." Correct this person.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Here is some SPSS output using GSS2008 data:
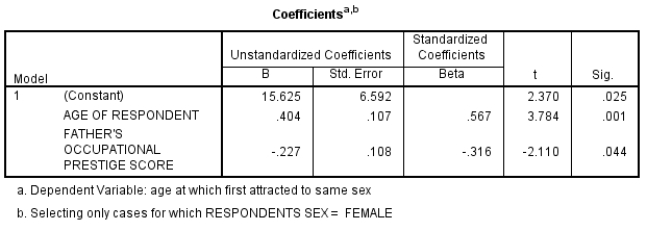 Describe these findings, paying particular attention to the relative size of the effects.
Describe these findings, paying particular attention to the relative size of the effects.
 Describe these findings, paying particular attention to the relative size of the effects.
Describe these findings, paying particular attention to the relative size of the effects.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Here is some SPSS output using GSS2008 data:
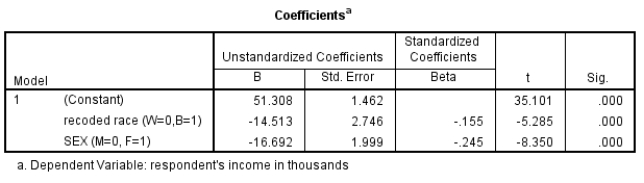 Among the unstandardized slopes, the slope for sex is only 15% larger than the slope for race. Among the standardized slopes, the slope for sex is 58% larger than the slope for race. Given what you know about American demographics, explain what you think happened.
Among the unstandardized slopes, the slope for sex is only 15% larger than the slope for race. Among the standardized slopes, the slope for sex is 58% larger than the slope for race. Given what you know about American demographics, explain what you think happened.
 Among the unstandardized slopes, the slope for sex is only 15% larger than the slope for race. Among the standardized slopes, the slope for sex is 58% larger than the slope for race. Given what you know about American demographics, explain what you think happened.
Among the unstandardized slopes, the slope for sex is only 15% larger than the slope for race. Among the standardized slopes, the slope for sex is 58% larger than the slope for race. Given what you know about American demographics, explain what you think happened.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Here are some totally bogus hypothetical regression results from a hypothetical law firm:
Dependent Variable: Lawyer's Salary in $1,000s
 Focusing on the strangeness of the standardized slopes, explain how you know these results simply cannot be correct.
Focusing on the strangeness of the standardized slopes, explain how you know these results simply cannot be correct.
Dependent Variable: Lawyer's Salary in $1,000s
 Focusing on the strangeness of the standardized slopes, explain how you know these results simply cannot be correct.
Focusing on the strangeness of the standardized slopes, explain how you know these results simply cannot be correct.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Using GSS2006 data, we get the following regression equation:
 Standardize these slopes and interpret the overall story.
Standardize these slopes and interpret the overall story.
 Standardize these slopes and interpret the overall story.
Standardize these slopes and interpret the overall story.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Here are statistics and a regression equation using GSS2006 data:
Standard deviations:
Age when respondent was first married: 6.13
Respondent's years of education: 3.22
Sex of respondent (female=0, male=1): .50
AGE WHEN FIRST MARRIED: 19.15 + .23 (EDUC) + 2.72 (SEX)
Standardize the slopes and interpret your results:
Standard deviations:
Age when respondent was first married: 6.13
Respondent's years of education: 3.22
Sex of respondent (female=0, male=1): .50
AGE WHEN FIRST MARRIED: 19.15 + .23 (EDUC) + 2.72 (SEX)
Standardize the slopes and interpret your results:

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Is a respondent's attendance at religious services affected equally by his/her mother's and father's attendance at religious services? Here are some statistics and regression results using GSS2008 data:
Standard Deviations:
Respondent's times attending religious services per month: 2.41
Respondent's mother's times attending religious services per month: 3.48
Respondent's father's times attending religious services per month: 3.06
RELRESPONDENT = 1.24 + .07 (RELMOTHER) + .15 (RELFATHER)
Standardize these slopes and address the original question.
Standard Deviations:
Respondent's times attending religious services per month: 2.41
Respondent's mother's times attending religious services per month: 3.48
Respondent's father's times attending religious services per month: 3.06
RELRESPONDENT = 1.24 + .07 (RELMOTHER) + .15 (RELFATHER)
Standardize these slopes and address the original question.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Here are statistics and regression equations for men and women. They use 2008GSS data and the dependent variable is an index of abortion attitudes where 0 = no support for abortion, up to 7 = full support for abortion.
 Regression Equation for Men:
Regression Equation for Men:
ABORTION INDEX SCORE = 5.30 - .34 (RELATT) - 1.25 (BIBLE)
Regression Equation for Women:
ABORTION INDEX SCORE = 5.32 - .29 (RELATT) - 1.88 (BIBLE)
Standardize all four slopes, present your results, and interpret the differences.
 Regression Equation for Men:
Regression Equation for Men:ABORTION INDEX SCORE = 5.30 - .34 (RELATT) - 1.25 (BIBLE)
Regression Equation for Women:
ABORTION INDEX SCORE = 5.32 - .29 (RELATT) - 1.88 (BIBLE)
Standardize all four slopes, present your results, and interpret the differences.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Explain why when you run a regression using the z-score version of the variables, the unstandardized and standardized effects are the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



