Deck 10: Above and Beyond: The Logic of Controlling and The Power of Nested Regression Models
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/35
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 10: Above and Beyond: The Logic of Controlling and The Power of Nested Regression Models
1
Which of the following is not the same as the others?
A) "controlling for…"
B) "holding constant…"
C) "keeping constant…"
D) "regressing onto…"
A) "controlling for…"
B) "holding constant…"
C) "keeping constant…"
D) "regressing onto…"
D
Explanation:The first three terms are used throughout chapter, last term has nothing to do with nested models.
Explanation:The first three terms are used throughout chapter, last term has nothing to do with nested models.
2
In Model 1, Independent Variable A has a statistically significant effect. In Model 2, we add Independent Variable B, which has a statistically significant effect, and the effect of Independent Variable A moves closer to zero and loses its statistical significance. What might we have here?
A) an intervening relationship
B) a dependent relationship
C) an independent relationship
D) a controlling relationship
A) an intervening relationship
B) a dependent relationship
C) an independent relationship
D) a controlling relationship
A
3
What symbol is used to signify "this independent variable is not in this model, but it will be introduced in a subsequent model?
A) ---
B) ***
C) >>>
D) :::
A) ---
B) ***
C) >>>
D) :::
A
4
When you have a first regression model, then a second regression model with an additional independent variable, then a third regression model with yet another additional independent variable, we call these a set of:
A) concurrent models
B) nested models
C) incremental models
D) subsequent models
A) concurrent models
B) nested models
C) incremental models
D) subsequent models

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The smallest number of regression models you need to have nested modeling is:
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
We run a regression model using GSS2006 data and find out that the older one is, the higher he/she scores on an index of religiosity (where 0=not religious up to 9=very religious). Then, we hypothesize that, because women outlive men, and because women are typically more religious than men are, part of this age effect is actually due to sex. We run a second model in which we add a variable for sex:
Which of the following is the most appropriate interpretation of what is going on here?
A) Sex clearly has a larger effect than age, so our hypothesis is supported.
B) The value of R-Squared rises, so our hypothesis is supported.
C) The effect of age does not change, so our hypothesis is not supported.
D) The constant increases, so our hypothesis is not supported.
Which of the following is the most appropriate interpretation of what is going on here?
A) Sex clearly has a larger effect than age, so our hypothesis is supported.
B) The value of R-Squared rises, so our hypothesis is supported.
C) The effect of age does not change, so our hypothesis is not supported.
D) The constant increases, so our hypothesis is not supported.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Here are two models made using GSS2006 data. The dependent variable is hours of television watched per day:
Which of the following pairs of people watches the same hours of television?
A) a retired 50-year-old and a retired 80-year-old
B) two 80 year-olds: one who is working, one who is retired
C) two 50-year-olds: one who is working, one who is retired
D) a 20-year-old working person and an 86-year-old retired person
Which of the following pairs of people watches the same hours of television?
A) a retired 50-year-old and a retired 80-year-old
B) two 80 year-olds: one who is working, one who is retired
C) two 50-year-olds: one who is working, one who is retired
D) a 20-year-old working person and an 86-year-old retired person

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
We hypothetically observe that the higher one's education, the happier one is. We hypothesize that this is actually because of income: people with higher education tend to make higher incomes, and it is these higher incomes, not education, that causes the higher happiness. Here are hypothetical models (using a dependent variable where 0=not at all happy, up to 10=very happy):
To support the hypothesis, what is the most likely number that would go in the place of the "???" in Model 2?
A) .03
B) .20**
C) .35***
D) .50***
To support the hypothesis, what is the most likely number that would go in the place of the "???" in Model 2?
A) .03
B) .20**
C) .35***
D) .50***

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
In the "Attitudes toward Inequality" example in the textbook, which group's difference from whites is most robust?
A) blacks
B) others
C) both blacks and others have similarly robust effects
D) neither blacks nor others differ from whites
A) blacks
B) others
C) both blacks and others have similarly robust effects
D) neither blacks nor others differ from whites

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
In the "Attitudes toward Inequality" example in the textbook, what happens to the effect of political party once income is controlled for?
A) it loses its statistical significance
B) it goes down by a lot, but maintains its statistical significance
C) it goes down by a little
D) it goes up
A) it loses its statistical significance
B) it goes down by a lot, but maintains its statistical significance
C) it goes down by a little
D) it goes up

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
In Model 1, Independent Variable A does not have a statistically significant effect. In Model 2, we add Independent Variable B, which has a statistically significant effect, and the effect of Independent Variable A gets larger and is now statistically significant. Independent Variable B is called:
A) an intervening variable
B) a controlling variable
C) a suppressor variable
D) a detracting variable
A) an intervening variable
B) a controlling variable
C) a suppressor variable
D) a detracting variable

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The "BMI, Internet Use, and Age" example in the textbook offered an example of a(n) _______________ relationship.
A) intervening
B) suppressor
C) robust
D) dependent
A) intervening
B) suppressor
C) robust
D) dependent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
What statistical test do we use to see if a second regression model is better than the first regression model?
A) the chi-square test
B) the t-test
C) the improvement test
D) the F-test
A) the chi-square test
B) the t-test
C) the improvement test
D) the F-test

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Someone hypothetically comes to you with some regression results that are confusing him:
He is confused by what happens to the effect of education between Model 1 and Model 2: the value of the slope is the same, but it is no longer statistically significant.
What is the most likely explanation for this?
A) It is not that education has an effect, but that people with more education are more likely to use a computer at work.
B) The value for R-squared stayed the same, so having two independent variables is no better than having one independent variable.
C) The constant in Model 2 decreased by a value greater than the slope for education.
D) The sample size has decreased.
He is confused by what happens to the effect of education between Model 1 and Model 2: the value of the slope is the same, but it is no longer statistically significant.
What is the most likely explanation for this?
A) It is not that education has an effect, but that people with more education are more likely to use a computer at work.
B) The value for R-squared stayed the same, so having two independent variables is no better than having one independent variable.
C) The constant in Model 2 decreased by a value greater than the slope for education.
D) The sample size has decreased.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Ainsworth-Darnell and Downey use which dataset for their study of student grades?
A) The National Longitudinal Study of Adolescent to Adult Health
B) The General Social Survey
C) The National Educational Longitudinal Study
D) The International Study of Student Performance
A) The National Longitudinal Study of Adolescent to Adult Health
B) The General Social Survey
C) The National Educational Longitudinal Study
D) The International Study of Student Performance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The explanation that Ainsworth-Darnell and Downey refute with their statistical analysis of racial differences in grades is called:
A) the culture of poverty
B) oppositional culture
C) racial differential association
D) culturally biased testing
A) the culture of poverty
B) oppositional culture
C) racial differential association
D) culturally biased testing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
In the Ainsworth-Darnell and Downey research on racial differences in grades, which of the following nested stories is not present?
A) where the original independent variable's effect stays the same
B) where the original independent variable's effect decreases, but remains statistically significant
C) where the original independent variable's effect goes away completely
D) where the original independent variable's effect comes back
A) where the original independent variable's effect stays the same
B) where the original independent variable's effect decreases, but remains statistically significant
C) where the original independent variable's effect goes away completely
D) where the original independent variable's effect comes back

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
With regard to the expectation that black students have more negative attitudes toward school than white students, Ainsworth-Darnell and Downey provide findings that _________ this expectation.
A) fully support
B) provide some support for
C) refute
D) don't address
A) fully support
B) provide some support for
C) refute
D) don't address

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Regarding the interconnections between race and social class in the Ainsworth-Darnell and Downey article about grades, which of the following statements best captures their overall findings:
A) Race and social class are not at all interconnected.
B) Social class fully accounts for racial differences.
C) Race fully accounts for social class differences.
D) Social class partially accounts for racial differences.
A) Race and social class are not at all interconnected.
B) Social class fully accounts for racial differences.
C) Race fully accounts for social class differences.
D) Social class partially accounts for racial differences.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
What was Callanan's dependent variable?
A) exposure to television news
B) exposure to crime dramas on television
C) risk of crime
D) fear of crime
A) exposure to television news
B) exposure to crime dramas on television
C) risk of crime
D) fear of crime

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
What media does Callanan NOT use to explain variation on her dependent variable?
A) local TV news
B) national TV news
C) TV crime dramas
D) crime reality TV
A) local TV news
B) national TV news
C) TV crime dramas
D) crime reality TV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
According to Callanan, which group has a larger and more robust difference with whites?
A) Blacks
B) Hispanics
C) Asians
D) American Indians
A) Blacks
B) Hispanics
C) Asians
D) American Indians

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Once Callanan controls for perceived risk of crime, the effect of crime victimhood on fear of crime:
A) loses its statistical significance
B) goes down, but does not lose its statistical significance
C) stays the same
D) goes up
A) loses its statistical significance
B) goes down, but does not lose its statistical significance
C) stays the same
D) goes up

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
To add a second independent variable and have SPSS run a set of nested models, which button do you NOT use?
A) the "Statistics" button
B) the "Next" button
C) the "Selection Variable" button
D) all of these buttons are used
A) the "Statistics" button
B) the "Next" button
C) the "Selection Variable" button
D) all of these buttons are used

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
You are creating a table of regression results, and one of your independent variables is sex. Which of the following would be the worst way to list this variable in your results?
A) Sex
B) Male
C) F=0, M=1
D) Female=0, Male=1
A) Sex
B) Male
C) F=0, M=1
D) Female=0, Male=1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Interpret the following set of models (they use GSS2008 data):
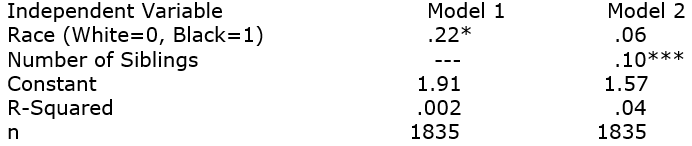
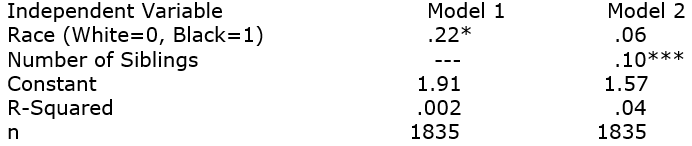

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Here is a box of SPSS output that uses GSS2008 data. The dependent variable is an index of abortion attitudes where 0=pro-life and 7=pro-choice.
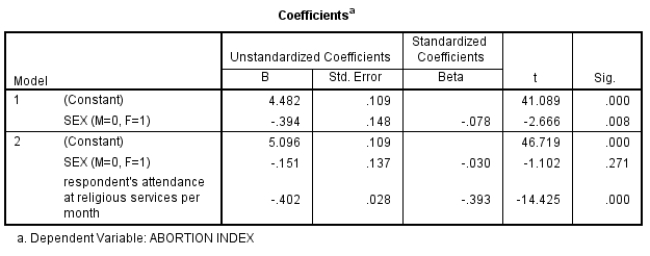 Tell the overall story the models are trying to tell as a set.
Tell the overall story the models are trying to tell as a set.
 Tell the overall story the models are trying to tell as a set.
Tell the overall story the models are trying to tell as a set.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Using one of the income examples from Chapter 10, explain why nested modeling is an important aspect of regression analysis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
We run a regression model using GSS2006 data. The dependent variable is an index of support for science (where 0=no support for science, up to 9=full support for science).
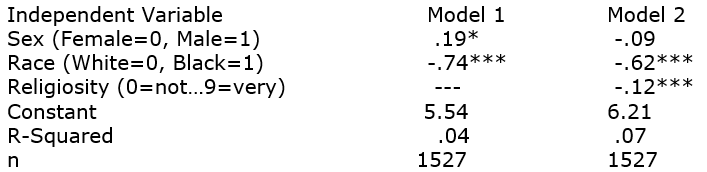 Explain what these models tell us.
Explain what these models tell us.
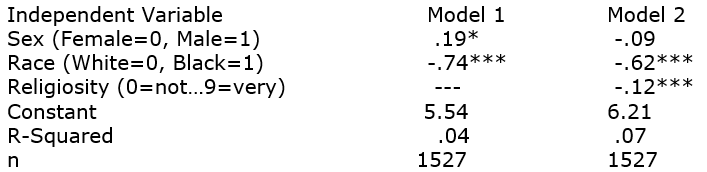 Explain what these models tell us.
Explain what these models tell us.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Use the following models (which use GSS2008 data) to address the following questions: 1. Do gay people go to bars more often than heterosexuals? 2. Do married people go to bars less often than non-married people? 3. If gay people go to bars more often, is this because they are less likely to be married?
Dependent Variable: Number of Times Respondent Goes to Bar Per Month

Dependent Variable: Number of Times Respondent Goes to Bar Per Month


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Researcher A hypothesizes that the prestige of someone's occupation is determined by income: the higher the income, the more prestige. Researcher B hypothesizes that, while income may play a role, education also plays a role: the higher the education, the more the prestige.
Here are results from a set of models using GSS2008 data (the dependent variable - occupational prestige score - is measured from a low of 17 to a high of 86). Address the researchers' hypotheses by interpreting this output.
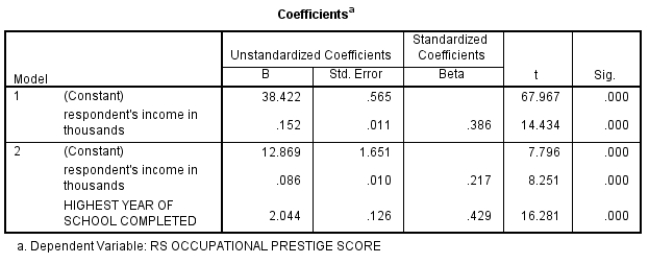
Here are results from a set of models using GSS2008 data (the dependent variable - occupational prestige score - is measured from a low of 17 to a high of 86). Address the researchers' hypotheses by interpreting this output.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
In the GSS2008, they asked people how many times in the past year they had been to a public library. Interpret the following models, explaining how we can consider income a suppressor variable in the relationship between education and library visits.
Dependent Variable: Number of Times Visited Library
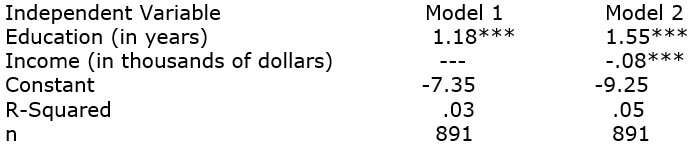
Dependent Variable: Number of Times Visited Library
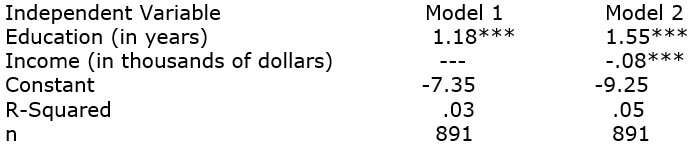

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Below is a box of SPSS output, using GSS2008 data. The dependent variable is an index of racial prejudice against blacks, ranging from 0 (not prejudiced) to 4 (very prejudiced).
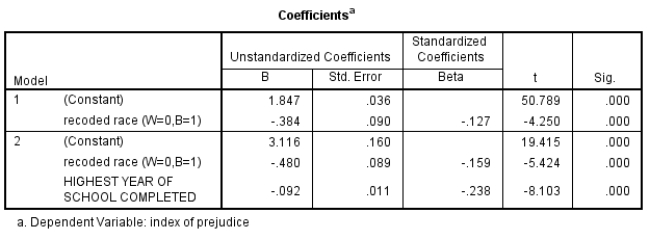 What is the story within this set of models? As you tell the story, be sure to talk about how education is a suppressor variable.
What is the story within this set of models? As you tell the story, be sure to talk about how education is a suppressor variable.
 What is the story within this set of models? As you tell the story, be sure to talk about how education is a suppressor variable.
What is the story within this set of models? As you tell the story, be sure to talk about how education is a suppressor variable.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Here is a box of SPSS output that uses GSS2008 data:
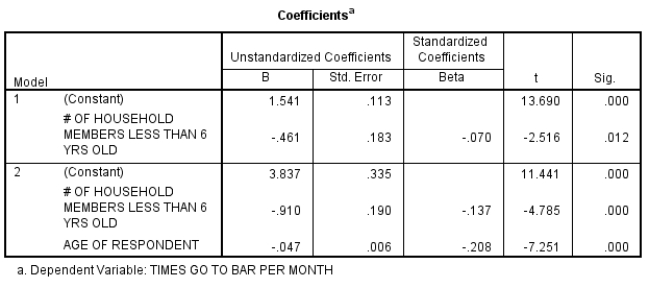 Explain how the age variable can be considered a suppressor variable. By explaining the likely relationships among the variables, describe why age acts as a suppressor variable in this situation.
Explain how the age variable can be considered a suppressor variable. By explaining the likely relationships among the variables, describe why age acts as a suppressor variable in this situation.
 Explain how the age variable can be considered a suppressor variable. By explaining the likely relationships among the variables, describe why age acts as a suppressor variable in this situation.
Explain how the age variable can be considered a suppressor variable. By explaining the likely relationships among the variables, describe why age acts as a suppressor variable in this situation.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Using the "Education, Nativity, and Attitudes towards Immigration" example from the textbook, explain what a suppressor variable is.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



