Deck 8: Learning
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/147
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 8: Learning
1
The acquisition of knowledge, skills, attitudes, or understanding brought about by experience is called
A) learning.
B) adaptation.
C) memory enhancement.
D) habituation.
A) learning.
B) adaptation.
C) memory enhancement.
D) habituation.
A
2
A stimulus is
A) something that is relatively long lasting.
B) any sensory event that an individual can detect.
C) anything that begins the process of learning.
D) any mental or physical activity that moves an individual to action.
A) something that is relatively long lasting.
B) any sensory event that an individual can detect.
C) anything that begins the process of learning.
D) any mental or physical activity that moves an individual to action.
B
3
For the first few nights after you purchased a clock, you had trouble sleeping because the ticking of the second hand disturbed you. Now you do not notice the sound of the second hand at all. This is an example of
A) sensory adaptation.
B) classical conditioning.
C) habituation.
D) muscle exhaustion.
A) sensory adaptation.
B) classical conditioning.
C) habituation.
D) muscle exhaustion.
C
4
Which of the following best demonstrates sensory adaptation?
A) A week after moving into an apartment near railroad tracks, you no longer notice when a train passes.
B) After attending a loud rock concert, your hearing is temporarily impaired.
C) Unless they think about it, long-time workers at a bakery do not notice the aroma of bread baking in the oven.
D) A clerk in a bookstore no longer looks up when the bell rings each time a customer comes in.
A) A week after moving into an apartment near railroad tracks, you no longer notice when a train passes.
B) After attending a loud rock concert, your hearing is temporarily impaired.
C) Unless they think about it, long-time workers at a bakery do not notice the aroma of bread baking in the oven.
D) A clerk in a bookstore no longer looks up when the bell rings each time a customer comes in.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Sensory adaptation is not considered true learning because in sensory adaptation
A) a stimulus is noticed but simply ignored.
B) stimuli that are important for survival can be overlooked.
C) only stimuli that are spread apart are ignored.
D) the ability to detect stimuli is not present.
A) a stimulus is noticed but simply ignored.
B) stimuli that are important for survival can be overlooked.
C) only stimuli that are spread apart are ignored.
D) the ability to detect stimuli is not present.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following is most like the opposite of habituation?
A) Sensitization
B) Dishabituation
C) Sensory adaptation
D) Learning
A) Sensitization
B) Dishabituation
C) Sensory adaptation
D) Learning

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
This morning, a very loud clap of thunder right outside your window startled you. For the rest of the day, any kind of loud sound-a car backfiring, a dropped dish-causes you to jump out of your chair. This is an example of
A) sensory adaptation.
B) habituation.
C) associative learning.
D) sensitization.
A) sensory adaptation.
B) habituation.
C) associative learning.
D) sensitization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which statement about non-associative and associative learning is true?
A) Non-associative learning involves forming a relationship between multiple events, while associative learning involves exposure to a single event.
B) Non-associative learning requires the subject to be able to detect a stimulus, while associative learning does not.
C) Non-associative learning does not involve any particular relationship among stimuli, while associative learning involves learning a relationship among multiple stimuli.
D) Non-associative learning is fairly temporary, while associative learning results in a relatively long-lasting change in behavior.
A) Non-associative learning involves forming a relationship between multiple events, while associative learning involves exposure to a single event.
B) Non-associative learning requires the subject to be able to detect a stimulus, while associative learning does not.
C) Non-associative learning does not involve any particular relationship among stimuli, while associative learning involves learning a relationship among multiple stimuli.
D) Non-associative learning is fairly temporary, while associative learning results in a relatively long-lasting change in behavior.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following is an example of non-associative learning?
A) Operant conditioning
B) Classical conditioning
C) Sensory adaptation
D) Sensitization
A) Operant conditioning
B) Classical conditioning
C) Sensory adaptation
D) Sensitization

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
While studying the digestive process of dogs, _______ was the first person to describe learning as acquired through classical conditioning.
A) John Watson
B) Ivan Pavlov
C) B. F. Skinner
D) Albert Bandura
A) John Watson
B) Ivan Pavlov
C) B. F. Skinner
D) Albert Bandura

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Your cat comes running as soon as she hears you open a can of food. In this example, the _______ is the conditioned stimulus.
A) can of food
B) sound of the can being opened
C) presence of you in the kitchen
D) running cat
A) can of food
B) sound of the can being opened
C) presence of you in the kitchen
D) running cat

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Your sister attempts to condition her dog to salivate at the sound of a bell. She gives the dog a biscuit and a second later rings the bell. She does this several times, but no conditioning seems to occur. Why isn't this conditioning working?
A) There should be at least a five-second interval between the biscuit and the bell.
B) The bell was probably not loud enough for the dog to notice it.
C) The bell should have been rung before the dog ate the biscuit.
D) The conditioned response and unconditioned stimulus must be simultaneous.
A) There should be at least a five-second interval between the biscuit and the bell.
B) The bell was probably not loud enough for the dog to notice it.
C) The bell should have been rung before the dog ate the biscuit.
D) The conditioned response and unconditioned stimulus must be simultaneous.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A toddler's fear at the sight of a dog is
A) a conditioned response.
B) an unconditioned response.
C) a conditioned stimulus.
D) an unconditioned stimulus.
A) a conditioned response.
B) an unconditioned response.
C) a conditioned stimulus.
D) an unconditioned stimulus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Suppose you have been conditioned to blink your eyes each time an experimenter sounds a buzzer. Art some point, the experimenter says the word "buzz" before sounding the buzzer. Eventually, you will learn to blink your eyes when the experimenter simply says the word "buzz"-even if the buzzer is not sounded. This is an example of
A) habituation.
B) extinction.
C) stimulus generalization.
D) second-order conditioning.
A) habituation.
B) extinction.
C) stimulus generalization.
D) second-order conditioning.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Ever since Ryan was bitten by a gray cat, he cries when he sees any gray cat. One day, he sees a gray squirrel scamper across his front yard and he begins crying. Ryan's behavior illustrates
A) stimulus generalization.
B) extinction.
C) stimulus discrimination.
D) second-order conditioning.
A) stimulus generalization.
B) extinction.
C) stimulus discrimination.
D) second-order conditioning.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Use the following to answer questions
Refer to the figure below.
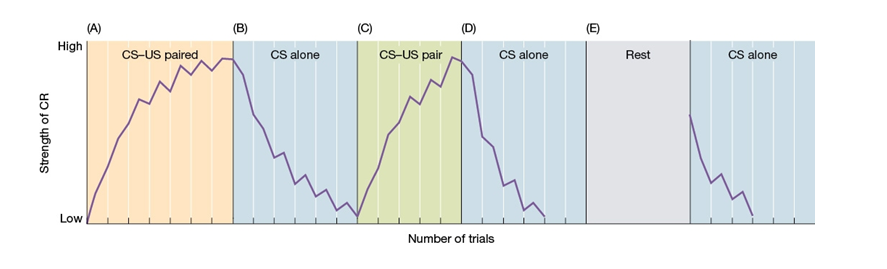
-Section A of the chart best illustrates
A) second-order conditioning.
B) spontaneous recovery.
C) acquisition.
D) recall.
Refer to the figure below.

-Section A of the chart best illustrates
A) second-order conditioning.
B) spontaneous recovery.
C) acquisition.
D) recall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Use the following to answer questions
Refer to the figure below.

-Section B of the chart best illustrates
A) stimulus generalization.
B) extinction.
C) stimulus discrimination.
D) recall.
Refer to the figure below.

-Section B of the chart best illustrates
A) stimulus generalization.
B) extinction.
C) stimulus discrimination.
D) recall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
As a child, Adrienne received a burn from a campfire and subsequently developed a fear of open flames. As she got older, the fear gradually faded until Adrienne had all but forgotten it. In her late teens, Adrienne was invited to a party at a neighbor's house. As she walked into the backyard, she noticed flames roaring up from a fire pit, and she felt fearful. Her behavior is an example of
A) stimulus discrimination.
B) acquisition.
C) recall.
D) spontaneous recovery.
A) stimulus discrimination.
B) acquisition.
C) recall.
D) spontaneous recovery.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
To stop coyotes from attacking and devouring his sheep, a rancher kills one of the flock, laces its body with chemicals that produce nausea, and leaves the sheep out for the coyotes to find and eat. In this case, the rancher is applying the research of
A) John Garcia.
B) Ivan Pavlov.
C) Konrad Lorenz.
D) Robert Rescorla.
A) John Garcia.
B) Ivan Pavlov.
C) Konrad Lorenz.
D) Robert Rescorla.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Regarding conditioned taste aversion, which of the following best describes the relationship between a CS and a US?
A) The delay between the CS and the US can be as long as one hour.
B) The US and the CS must be paired dozens of times for taste aversion to occur.
C) The CS must immediately precede the US or the conditioning will not take place.
D) The CS will lead to considerable stimulus generalization because the US will be similar to many different stimuli.
A) The delay between the CS and the US can be as long as one hour.
B) The US and the CS must be paired dozens of times for taste aversion to occur.
C) The CS must immediately precede the US or the conditioning will not take place.
D) The CS will lead to considerable stimulus generalization because the US will be similar to many different stimuli.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The tendency of baby birds to recognize, bond with, and follow the first moving object they see is called
A) habituation.
B) acquisition.
C) stimulus generation.
D) imprinting.
A) habituation.
B) acquisition.
C) stimulus generation.
D) imprinting.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The observation that animals tend to readily form associations between certain stimuli and responses, such as taste and nausea, due to the survival value of the learning is called
A) spontaneous recovery.
B) sensory adaptation.
C) biological constraints on learning.
D) stimulus generalization.
A) spontaneous recovery.
B) sensory adaptation.
C) biological constraints on learning.
D) stimulus generalization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The acquisition of a phobia is an example of
A) non-associative learning.
B) fear conditioning.
C) conditioned taste aversion.
D) shaping.
A) non-associative learning.
B) fear conditioning.
C) conditioned taste aversion.
D) shaping.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
An animal's fearful reaction to a previously neutral stimulus can be unlearned by repeatedly presenting the _______ without the _______.
A) UR; US
B) US; CS
C) CR; CS
D) CS; US
A) UR; US
B) US; CS
C) CR; CS
D) CS; US

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What would be Thorndike's response to the question: "What is the best way to predict the likelihood that an organism will repeatedly engage in a specific behavior?"
A) An organism's behavior will generally mimic that of its closest genetic ancestor.
B) If a behavior helps the organism find a mate, the organism will engage in the behavior.
C) An organism will imitate the behavior it sees other organisms engaging in.
D) If a behavior provides pleasure, the organism will engage in the behavior.
A) An organism's behavior will generally mimic that of its closest genetic ancestor.
B) If a behavior helps the organism find a mate, the organism will engage in the behavior.
C) An organism will imitate the behavior it sees other organisms engaging in.
D) If a behavior provides pleasure, the organism will engage in the behavior.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Thorndike believed that most learning occurred by
A) trial and error.
B) insight.
C) observation.
D) personal development.
A) trial and error.
B) insight.
C) observation.
D) personal development.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A researcher is keenly interested in recording observable behavior in her test subjects, but she has no interest in studying what goes on inside the subjects' brains to make them behave as they do. This researcher is apparently a proponent of the
A) sensory adaptation theory.
B) cognitive perspective.
C) black box perspective.
D) social learning theory.
A) sensory adaptation theory.
B) cognitive perspective.
C) black box perspective.
D) social learning theory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
For a behaviorist, the goal of psychology is to
A) pay close attention to what one is experiencing at any given moment.
B) understand the practical function of internal mental processes.
C) help troubled individuals restore their mental health.
D) determine how various experiences result in different behaviors.
A) pay close attention to what one is experiencing at any given moment.
B) understand the practical function of internal mental processes.
C) help troubled individuals restore their mental health.
D) determine how various experiences result in different behaviors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
According to _______ theory, behavior is influenced by its consequences.
A) classical conditioning
B) observational learning
C) operant conditioning
D) cognitive learning
A) classical conditioning
B) observational learning
C) operant conditioning
D) cognitive learning

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following best distinguishes operant conditioning from classical conditioning?
A) Operant conditioning focuses mainly on internal mental processes; classical conditioning focuses mainly on behavior.
B) In operant conditioning, a behavior elicits a stimulus; in classical conditioning, a stimulus elicits a behavior.
C) Operant conditioning involves involuntary responses; classical conditioning involves voluntary behavior.
D) In operant conditioning, responses depend on the autonomic nervous system; in classical conditioning, responses depend on the skeletal muscles.
A) Operant conditioning focuses mainly on internal mental processes; classical conditioning focuses mainly on behavior.
B) In operant conditioning, a behavior elicits a stimulus; in classical conditioning, a stimulus elicits a behavior.
C) Operant conditioning involves involuntary responses; classical conditioning involves voluntary behavior.
D) In operant conditioning, responses depend on the autonomic nervous system; in classical conditioning, responses depend on the skeletal muscles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following researchers is most closely associated with operant learning?
A) John Garcia
B) Ivan Pavlov
C) Albert Bandura
D) B. F. Skinner
A) John Garcia
B) Ivan Pavlov
C) Albert Bandura
D) B. F. Skinner

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A reinforcer is a consequence that _______ a behavior.
A) extinguishes
B) weakens
C) reverses
D) strengthens
A) extinguishes
B) weakens
C) reverses
D) strengthens

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
When your friends visit, you want your dog to sit quietly rather than jumping on them as she does now. How would you accomplish this?
A) First, reward the dog with treats when she obeys your "Down!" command. Then reward her only when she is standing near your friends but not jumping on them. Finally, reward her only when she is sitting quietly.
B) Extinguish the bad behavior by closing the dog in a bathroom when she jumps on your friends.
C) Teach the dog to associate the sound of the doorbell with the acquisition of food so she will be distracted and not bother your friends.
D) Withhold food for several hours after the dog jumps on someone.
A) First, reward the dog with treats when she obeys your "Down!" command. Then reward her only when she is standing near your friends but not jumping on them. Finally, reward her only when she is sitting quietly.
B) Extinguish the bad behavior by closing the dog in a bathroom when she jumps on your friends.
C) Teach the dog to associate the sound of the doorbell with the acquisition of food so she will be distracted and not bother your friends.
D) Withhold food for several hours after the dog jumps on someone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following individuals is displaying superstition?
A) Every time Jorge hears a certain tune, he thinks of the night he proposed to his wife. Today he heard a similar tune, which also made him think of the night of his proposal.
B) The last time Rose hit a homerun, she patted her batting helmet just before taking her swing; now she pats her batting helmet every time she enters the batting box.
C) Ian was conditioned to laugh at the sight of a clown, but over time his response weakened. He no longer laughs when he sees clowns.
D) After being bitten by a brown dog, Allison is afraid of all brown dogs.
A) Every time Jorge hears a certain tune, he thinks of the night he proposed to his wife. Today he heard a similar tune, which also made him think of the night of his proposal.
B) The last time Rose hit a homerun, she patted her batting helmet just before taking her swing; now she pats her batting helmet every time she enters the batting box.
C) Ian was conditioned to laugh at the sight of a clown, but over time his response weakened. He no longer laughs when he sees clowns.
D) After being bitten by a brown dog, Allison is afraid of all brown dogs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Suppose you are afraid of snakes. You become highly agitated even if you see a picture of a snake, but your fear disappears when you look away. In this case, your avoidance of snakes is being
A) extinguished.
B) cured.
C) positively reinforced.
D) negatively reinforced.
A) extinguished.
B) cured.
C) positively reinforced.
D) negatively reinforced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which is an example of positive punishment?
A) A student loses a "good behavior" token for not following directions.
B) Two siblings squabble over a toy, so their father takes the toy away from both children.
C) A student is caught texting in class and the professor reprimands him in front of his classmates.
D) A teenager is grounded for a week for being rude to her mother.
A) A student loses a "good behavior" token for not following directions.
B) Two siblings squabble over a toy, so their father takes the toy away from both children.
C) A student is caught texting in class and the professor reprimands him in front of his classmates.
D) A teenager is grounded for a week for being rude to her mother.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Why does punishment tend to be an ineffective way to change a child's behavior?
A) Fear of punishment causes the child to forget the behavior that is being punished.
B) Punishment causes the child to become resentful, leading to disobedient behavior.
C) Punishment interferes with the child's ability to learn what good behaviors are.
D) The learning generated by punishment is non-associative and therefore not long-lasting.
A) Fear of punishment causes the child to forget the behavior that is being punished.
B) Punishment causes the child to become resentful, leading to disobedient behavior.
C) Punishment interferes with the child's ability to learn what good behaviors are.
D) The learning generated by punishment is non-associative and therefore not long-lasting.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A response a subject has learned to make in order to avoid an aversive stimulus is called
A) active avoidance.
B) extinction.
C) sensory adaptation.
D) dishabituation.
A) active avoidance.
B) extinction.
C) sensory adaptation.
D) dishabituation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Dana is very shy and awkward in social situations. Consequently, she tends not to go to parties or attend other social gatherings. Dana is engaging in
A) active avoidance.
B) escape conditioning.
C) passive avoidance.
D) shaping.
A) active avoidance.
B) escape conditioning.
C) passive avoidance.
D) shaping.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following is the simplest partial reinforcement schedule?
A) Variable interval
B) Fixed interval
C) Variable ratio
D) Fixed ratio
A) Variable interval
B) Fixed interval
C) Variable ratio
D) Fixed ratio

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Whenever a rat pushes a red button, it is rewarded with a piece of food. This is an example of a(n) _______ reinforcement schedule.
A) intermittent
B) partial
C) ratio
D) continuous
A) intermittent
B) partial
C) ratio
D) continuous

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Todd's parents promise him a reward of his choice if his GPA is above 3.0 for three consecutive semesters. A _______ reinforcement schedule is being used by Todd's parents.
A) variable ratio
B) fixed ratio
C) fixed interval
D) continuous
A) variable ratio
B) fixed ratio
C) fixed interval
D) continuous

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
You work three hours a day Monday through Friday and receive a paycheck every Friday afternoon. You are being paid on a _______ reinforcement schedule.
A) fixed interval
B) fixed ratio
C) variable interval
D) variable ratio
A) fixed interval
B) fixed ratio
C) variable interval
D) variable ratio

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which of the following reinforcement schedules should be used if a parent's goal is to elicit consistent, long-lasting behavior from a child?
A) Variable ratio
B) Variable interval
C) Fixed ratio
D) Fixed interval
A) Variable ratio
B) Variable interval
C) Fixed ratio
D) Fixed interval

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Midori cleaned her room without being asked. Using a primary reinforcer to encourage Midori to do more chores, Midori's mother might
A) increase her allowance.
B) go on Facebook and tell her friends what Midori did.
C) offer her praise at dinnertime in front of the whole family.
D) let her stay up late that night to watch a favorite movie.
A) increase her allowance.
B) go on Facebook and tell her friends what Midori did.
C) offer her praise at dinnertime in front of the whole family.
D) let her stay up late that night to watch a favorite movie.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
A _______ is a primary reinforcer, whereas a _______ is a secondary reinforcer.
A) lollipop; diploma
B) glass of water; sandwich
C) paycheck; hug
D) report card; hamburger
A) lollipop; diploma
B) glass of water; sandwich
C) paycheck; hug
D) report card; hamburger

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A group of parents are discussing whether music videos featuring scantily clad women are encouraging teenagers to become sexually active. Which of the following processes is being considered by the parents as the reason that music videos influence sexual activity in teens?
A) Observational learning
B) Operant conditioning
C) Classical conditioning
D) Insight
A) Observational learning
B) Operant conditioning
C) Classical conditioning
D) Insight

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which of the following researchers is most closely associated with the idea of a cognitive map?
A) John Garcia
B) B. F. Skinner
C) Ivan Pavlov
D) Edward Tolman
A) John Garcia
B) B. F. Skinner
C) Ivan Pavlov
D) Edward Tolman

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Two groups of subjects are asked to work their way through a maze. Group 1 is allowed to view the maze from 15 feet above before beginning; Group 2 is given a practice run through the maze before beginning. Predict the performance of the groups.
A) Group 1 will be just as capable of working their way through the maze as Group 2.
B) Group 1 will be less capable of working their way through the maze as Group 2.
C) Forming a mental representation of the layout of the maze will likely confuse most people in Group 1 because people tend to learn best by doing, not thinking.
D) The ability to form accurate mental representations of the layout of the maze will be difficult for most people in Group 1, so they will likely perform very badly on this task.
A) Group 1 will be just as capable of working their way through the maze as Group 2.
B) Group 1 will be less capable of working their way through the maze as Group 2.
C) Forming a mental representation of the layout of the maze will likely confuse most people in Group 1 because people tend to learn best by doing, not thinking.
D) The ability to form accurate mental representations of the layout of the maze will be difficult for most people in Group 1, so they will likely perform very badly on this task.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The _______ appears to be especially important in the formation of cognitive maps.
A) cerebellum
B) hippocampus
C) brain stem
D) amygdala
A) cerebellum
B) hippocampus
C) brain stem
D) amygdala

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Regarding the concept of latent learning, John Watson is most likely to have
A) been opposed to studying latent learning because he believed that all learning is innate.
B) supported the study of latent learning because he rejected the idea that rewards or punishments impact behavior.
C) been opposed to studying latent learning because he focused only on observable behaviors.
D) supported the study of latent learning because it dovetailed nicely with his theory of the tabula rasa.
A) been opposed to studying latent learning because he believed that all learning is innate.
B) supported the study of latent learning because he rejected the idea that rewards or punishments impact behavior.
C) been opposed to studying latent learning because he focused only on observable behaviors.
D) supported the study of latent learning because it dovetailed nicely with his theory of the tabula rasa.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Behaviorists were particularly skeptical of Edward Tolman's research because it seemed to indicate that learning could take place even in the absence of
A) habituation.
B) reinforcement.
C) modeling.
D) imitation.
A) habituation.
B) reinforcement.
C) modeling.
D) imitation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
_______ learning is hidden until it becomes useful.
A) Innate
B) Observational
C) Insight
D) Latent
A) Innate
B) Observational
C) Insight
D) Latent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
To learn anything through observation, the learner must
A) ask questions about the task to do it correctly.
B) pay attention to the model.
C) be able to multitask.
D) be rewarded for a specific behavior.
A) ask questions about the task to do it correctly.
B) pay attention to the model.
C) be able to multitask.
D) be rewarded for a specific behavior.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Observational learning requires the presence of which of the following elements?
A) Above-average intelligence
B) A reinforcement schedule
C) Imitation
D) The threat of punishment
A) Above-average intelligence
B) A reinforcement schedule
C) Imitation
D) The threat of punishment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which of the following best demonstrates observational learning?
A) Holly hears a weather report calling for snow, so she begins to plan a trip to a local ski slope.
B) After looking carefully at the kitchen drainpipes, Joe understands how to reassemble them.
C) Natasha figures out that if she does not give her boss a hard time, he is a lot nicer to be around.
D) Ben watched a skateboarder do a trick many times and now Ben can perform the trick, himself.
A) Holly hears a weather report calling for snow, so she begins to plan a trip to a local ski slope.
B) After looking carefully at the kitchen drainpipes, Joe understands how to reassemble them.
C) Natasha figures out that if she does not give her boss a hard time, he is a lot nicer to be around.
D) Ben watched a skateboarder do a trick many times and now Ben can perform the trick, himself.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The best-known example of observational learning in birds is
A) flying.
B) singing.
C) foraging.
D) nesting.
A) flying.
B) singing.
C) foraging.
D) nesting.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Young children playing tag in the park are engaged in
A) social learning.
B) latent learning.
C) non-associative learning.
D) habituation.
A) social learning.
B) latent learning.
C) non-associative learning.
D) habituation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which researcher is most closely associated with the Bobo doll studies?
A) Wolfgang Köhler
B) Edward Tolman
C) B.F. Skinner
D) Albert Bandura
A) Wolfgang Köhler
B) Edward Tolman
C) B.F. Skinner
D) Albert Bandura

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Bethany grows up in a home where her mother is unloving toward Bethany's father. She hears her mother insult her father, and she notices that her father rarely protests being treated this way. Based on the work of Bandura, what might we predict about Bethany's future relationships?
A) She will treat men well, because she knows how much her father was hurt by her mother.
B) She may treat men with disrespect, as she is apt to repeat her mother's behavior.
C) She is likely to spend her life alone because her parents taught her that relationships are unhappy.
D) She is unlikely to remember how her mother treated her father and will be unaffected by it.
A) She will treat men well, because she knows how much her father was hurt by her mother.
B) She may treat men with disrespect, as she is apt to repeat her mother's behavior.
C) She is likely to spend her life alone because her parents taught her that relationships are unhappy.
D) She is unlikely to remember how her mother treated her father and will be unaffected by it.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Your sister watches a video about how to rewire a lamp, then tries to rewire one, herself. Her lamp still doesn't work. She goes back over the steps and finds that she did not connect one of the socket wires. Which of Bandura's criteria for observational learning failed?
A) Attention
B) Memory
C) Referencing
D) Motivation
A) Attention
B) Memory
C) Referencing
D) Motivation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which of the following is the best example of social referencing?
A) Rachel is not hurt when she takes a tumble on the playground, but when she sees her mother looking alarmed she begins to cry as though she were badly injured.
B) Will gets sick soon after eating a big bowl of chili and declares that he will never eat chili again.
C) Three-year-old Jeannie gets a shot from her doctor. Later in the day she sees a picture of a woman in a white coat and pushes it away.
D) Audra learns that when she eats all of her dinner, her parents let her have dessert.
A) Rachel is not hurt when she takes a tumble on the playground, but when she sees her mother looking alarmed she begins to cry as though she were badly injured.
B) Will gets sick soon after eating a big bowl of chili and declares that he will never eat chili again.
C) Three-year-old Jeannie gets a shot from her doctor. Later in the day she sees a picture of a woman in a white coat and pushes it away.
D) Audra learns that when she eats all of her dinner, her parents let her have dessert.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Which of the following is best known for studying the phenomenon of insight in animals?
A) Wolfgang Köhler
B) Edward Tolman
C) Ivan Pavlov
D) Albert Bandura
A) Wolfgang Köhler
B) Edward Tolman
C) Ivan Pavlov
D) Albert Bandura

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
You accidentally break off the pull tab when attempting to open a can of soup. You are about to reach for another can when it occurs to you that you can use a regular can opener. You have just demonstrated
A) acquisition.
B) shaping.
C) the law of effect.
D) insight.
A) acquisition.
B) shaping.
C) the law of effect.
D) insight.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
"Eureka moments" are most closely associated with
A) learned helplessness.
B) insight.
C) classical conditioning.
D) cognitive restructuring.
A) learned helplessness.
B) insight.
C) classical conditioning.
D) cognitive restructuring.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Researchers have suggested that insight occurs
A) only in humans.
B) in both humans and animals.
C) even in one-celled organisms.
D) in animals that can imitate humans.
A) only in humans.
B) in both humans and animals.
C) even in one-celled organisms.
D) in animals that can imitate humans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The works of Skinner and Bandura are related in that both acknowledge the importance of
A) stimulus generalization.
B) reinforcement.
C) sensory adaptation.
D) cognitive maps.
A) stimulus generalization.
B) reinforcement.
C) sensory adaptation.
D) cognitive maps.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Robyn's mother shows her how to cut hearts from construction paper. No matter how hard Robyn tries, she cannot cut the paper correctly. Bandura would say that Robyn's attempts failed because she was not
A) paying close enough attention.
B) able to remember how to cut the hearts.
C) able to reproduce the behavior.
D) sufficiently motivated to cut the hearts.
A) paying close enough attention.
B) able to remember how to cut the hearts.
C) able to reproduce the behavior.
D) sufficiently motivated to cut the hearts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The sudden return of a response that had formerly been habituated is called _______.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Learning to make a reflex response to a stimulus when it is repeatedly paired with the original, naturally occurring stimulus is called _______.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The gradual appearance of the CR in response to the CS alone is called _______.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
When you learned that red lights mean "stop" and green lights mean "go," you were being trained to use a classical conditioning concept called stimulus _______.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The perspective that psychologists should study externally visible behavior rather than make inferences about internal processes is called _______.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The process of _______ involves gradually training an organism to perform a specific behavior by reinforcing responses that are increasingly closer to the desired response.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Nate believes that if he bounces the basketball exactly three times before trying a free-throw shot, he will be more likely to make the shot. B.F. Skinner would characterize Nate's belief as _______.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
A stimulus presented to a person or animal that decreases the probability of a particular response is known as _______ punishment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Generally, responses trained by _______ schedules are slower to extinguish than behaviors trained by _______ schedules.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
A(n) _______ map is an internal representation of the layout of an area.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Learning that occurs without being immediately apparent and often without reinforcement is called _______ learning.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Learning that occurs when one animal imitates the behavior of another animal is called _______ learning.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



