Deck 15: Non-Parametric Tests
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/58
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 15: Non-Parametric Tests
1
non-parametric and parametric tests make different assumptions about data
True
2
Non-parametric tests assume that the data are on a nominal scale
False
3
Nonparametric tests are still inferential tests.
True
4
All measurement scales can be manipulated with mathematical operations like addition and division

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Statistics can be manipulated for the author's benefit, so sometimes we must be careful how must we trust them.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Nonparametric tests do not necessarily test differences between means .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
skewed data is measured on a scale where 0 indicates very little to skew.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The Mann-Whitney U-test is the nonparametric equivalent of a dependent samples t-test.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The null hypothesis for a Mann-Whitney U-test states that the distributions of ranked data for both groups are different.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The Mann-Whitney U test is a nonparametric method that compares means between two groups

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
When conducting a Mann-Whitney U-test, if your calculated U-value is smaller than that of the critical value, than the test is considered statistically significant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The degrees of freedom in a Wilcoxon Signed-Rank is based on the number of matched pairs as opposed to the number of individual data points.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The Wilcoxon Signed-Rank test produces a t value. If the observed t -value is greater than the critical value, then the results are deemed to be statistically significant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The Wilcoxon signed-rank test should be used in place of its parametric equivalent when the data is non-normal or on an ordinal scale

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
One method of dealing with skewed data is to use its rank order instead of actual values.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
There are three types of skewed data: positive, negative, and one-dimensional

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
If the data are skewed, one should try use a parametric test instead of resorting to nonparametric tests.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Nonparametric tests do not produce a significance level. Instead, they generate effect sizes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Ranked data is best described to be on an ordinal scale.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Generally speaking, if a nonparametric test is used on rank data, the dataset is on a ___________ scale.
A) ratio.
B) nominal.
C) interval.
D) ordinal.
A) ratio.
B) nominal.
C) interval.
D) ordinal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Why is it the case that skewed data poses a problem for parametric tests?
A) There mean is larger than the median.
B) The assumption of normality is violated.
C) The data does not represent the population.
D) The assumption of independence is violated.
A) There mean is larger than the median.
B) The assumption of normality is violated.
C) The data does not represent the population.
D) The assumption of independence is violated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following is not an assumption of parametric tests?
A) Observations are independent
B) The data are either on an interval or ratio scale
C) Central limit theorem holds
D) The data are skewed positive.
A) Observations are independent
B) The data are either on an interval or ratio scale
C) Central limit theorem holds
D) The data are skewed positive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following characteristics would lead you to choose a non-parametric test over a parametric test?
A) Skewed data
B) Having data that is not normally distributed
C) Data that are ranked
D) All of the above
A) Skewed data
B) Having data that is not normally distributed
C) Data that are ranked
D) All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Why might a spearman correlation be appropriate for a given dataset?
A) The data are on a ratio scale
B) The sample size is too large
C) The sample is skewed with a small sample size
D) The data are on a nominal scale
A) The data are on a ratio scale
B) The sample size is too large
C) The sample is skewed with a small sample size
D) The data are on a nominal scale

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The Perception of Competitiveness Scale (PCS) developed by Carter and Weissbrod (2011) is a likert scale. If you assume that the scale is ordinal and are examining its relation to age or some other ranked data, you should…
A) use a Spearman correlation
B) use a Mann Whitney U test
C) use a Wilcoxon Signed-Rank test
D) use a Pearson correlation
A) use a Spearman correlation
B) use a Mann Whitney U test
C) use a Wilcoxon Signed-Rank test
D) use a Pearson correlation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In a spearman correlation, how do you determine the strength of the correlation coefficient?
A) Negative correlations are weaker than positive correlations
B) Correlations are weaker as they approach 0.
C) The strength of the correlation depends on the sample size. Smaller samples tend to be stronger
D) Correlations become stronger as they approach 0.
A) Negative correlations are weaker than positive correlations
B) Correlations are weaker as they approach 0.
C) The strength of the correlation depends on the sample size. Smaller samples tend to be stronger
D) Correlations become stronger as they approach 0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The Mann-Whitney U test makes assumptions about which of the following?
A) The data are quantitative
B) The data are normally distributed and generalize to the population
C) Observations are independent
D) Equal variances in both groups
A) The data are quantitative
B) The data are normally distributed and generalize to the population
C) Observations are independent
D) Equal variances in both groups

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
In which of the following situations should a Wilcoxon signed-rank test be used?
A) When matched data is normally distributed and ranked
B) When observations are non-independent and the data are skewed
C) When you wanted to use an independent samples t-test but the data ends up being heavily skewed.
D) When the sample size is very large and on a ratio scale.
A) When matched data is normally distributed and ranked
B) When observations are non-independent and the data are skewed
C) When you wanted to use an independent samples t-test but the data ends up being heavily skewed.
D) When the sample size is very large and on a ratio scale.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Why is it a problem if data are skewed when considering parametric tests?
A) The assumption of independence is violated
B) The data is qualitative
C) The assumption of normality is violated.
D) There is no method to calculate estimates of population parameters
A) The assumption of independence is violated
B) The data is qualitative
C) The assumption of normality is violated.
D) There is no method to calculate estimates of population parameters

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
After conducting a Mann-Whitney U test, how do you determine statistical significance?
A) If the U-statistic is smaller than the critical value, the result is non-significant.
B) If your calculated U-value is smaller the critical value, than the result is statistically significant.
C) If the U-value is smaller than median rank, the result is statistically significant
D) If the U-value is greater than the median rank, the result is statistically significant.
A) If the U-statistic is smaller than the critical value, the result is non-significant.
B) If your calculated U-value is smaller the critical value, than the result is statistically significant.
C) If the U-value is smaller than median rank, the result is statistically significant
D) If the U-value is greater than the median rank, the result is statistically significant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
How is a Mann-Whitney U test and a Wilcoxon Signed-Rank test different?
A) the Mann Whitney U test is used on matched data and the Wilcoxon Signed-Rank test is not.
B) The Mann-Whitney U test is a parametric procedure, and the Wilcoxon Signed-Rank test is a nonparametric procedure.
C) The Mann-Whitney U test is used on 3 or more groups, and the Wilcoxon Signed-Rank test is used to test for relationships
D) The Mann-Whitney U test is used for two independent groups and the Wilcoxon Signed-Rank test is used for paired or matched data.
A) the Mann Whitney U test is used on matched data and the Wilcoxon Signed-Rank test is not.
B) The Mann-Whitney U test is a parametric procedure, and the Wilcoxon Signed-Rank test is a nonparametric procedure.
C) The Mann-Whitney U test is used on 3 or more groups, and the Wilcoxon Signed-Rank test is used to test for relationships
D) The Mann-Whitney U test is used for two independent groups and the Wilcoxon Signed-Rank test is used for paired or matched data.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
If you have 12 pairs of participants what is your critical value for a two-tailed Wilcoxon Signed-rank test at = .01?
A) 7
B) 3
C) 5
D) 9
A) 7
B) 3
C) 5
D) 9

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A researcher has 16 matched pairs for a Wilcoxon Signed-Rank test. For this two-tailed Wilcoxon Signed-Rank test to be significant at = .05, the test statistic must be…
A) greater than 30
B) less than 30
C) greater than 25
D) less than 25
A) greater than 30
B) less than 30
C) greater than 25
D) less than 25

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A researcher has two independent groups with ranked data with 20 participants in each group. When using a Mann-Whitney U test (assume assuming α = 0.05), the researcher has data that is statistically significant if…
A) the U statistic is less than 127
B) the U statistic is greater than 127
C) the U statistic is less than 113
D) The U statistic is greater than 113
A) the U statistic is less than 127
B) the U statistic is greater than 127
C) the U statistic is less than 113
D) The U statistic is greater than 113

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Consider the following dataset on standardized test scores: 134, 145, 142, 145, 146, 152, 155, 155, 159. There are _______ ties and the score 152 is in the _____ rank.
A) 2; 6
B) 3; 6
C) 2; 5.5
D) 3; 5.5
A) 2; 6
B) 3; 6
C) 2; 5.5
D) 3; 5.5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A researcher conducted a correlational study. He studied the relationship between individuals' perceptions of their own bodies on a rating scale (higher scores meant most positive self-perception) and their perception of the college (higher scores meant more positive perception of the college). He found a spearman correlation of -.68 and the result is statistically significant. What does this mean?
A) Body image and college ratings are positively correlated: those who have better self-perception of their body had worse perceptions of the college.
B) Body image and college ratings are positively correlated: those who have better self-perception of their body had better perceptions of the college
C) Body image and college ratings are negatively correlated: as self-perception of one's body got higher, perception of the college got lower.
D) Body image and college ratings are negatively correlated: as self-perception of one's body got higher, perception of the college got higher.
A) Body image and college ratings are positively correlated: those who have better self-perception of their body had worse perceptions of the college.
B) Body image and college ratings are positively correlated: those who have better self-perception of their body had better perceptions of the college
C) Body image and college ratings are negatively correlated: as self-perception of one's body got higher, perception of the college got lower.
D) Body image and college ratings are negatively correlated: as self-perception of one's body got higher, perception of the college got higher.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Consider the following data: 6, 8, 10, 10, 10, 11, 12, 15, 18, 18, 19, 20, 24, 25. The data in rank 4 is ___ and rank 11 is ____.
A) 10; 19
B) 12; 19
C) 10; 20
D) 12; 20
A) 10; 19
B) 12; 19
C) 10; 20
D) 12; 20

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
If you have quantitative data that is skewed, which of the following can be used to "unskew" it?
A) rank the data
B) use the mode
C) use the median
D) convert it to a ratio or interval scale.
A) rank the data
B) use the mode
C) use the median
D) convert it to a ratio or interval scale.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
If using a two-tailed spearman correlation with 10 pairs and an alpha level of .05, what is the critical value?
A) .745
B) .700
C) .564
D) .648
A) .745
B) .700
C) .564
D) .648

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A statistical method to measure hidden or latent variables from observed data is…
A) spearman correlation
B) factor analysis
C) eugenics
D) Wilcoxon sign-ranked test
A) spearman correlation
B) factor analysis
C) eugenics
D) Wilcoxon sign-ranked test

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Supporters of eugenics would likely agree that…
A) intelligence is developed via environmental influences
B) intelligence is inherited
C) intelligence cannot be measured objectively
D) None of the above.
A) intelligence is developed via environmental influences
B) intelligence is inherited
C) intelligence cannot be measured objectively
D) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
With regards to skewed distributions, which best describes them?
A) There are two types of skewed distribution, and if a dataset is heavily skewed enough, parametric tests are not suitable for it.
B) There are two types of skewed distributions, and skewed data can be on interval, ratio, or ordinal scales
C) Skewed data are ranked or qualitative, making it unsuitable for parametric analyses
D) Skewed data do not pose issues for parametric tests, but are not suitable for nonparametric tests.
A) There are two types of skewed distribution, and if a dataset is heavily skewed enough, parametric tests are not suitable for it.
B) There are two types of skewed distributions, and skewed data can be on interval, ratio, or ordinal scales
C) Skewed data are ranked or qualitative, making it unsuitable for parametric analyses
D) Skewed data do not pose issues for parametric tests, but are not suitable for nonparametric tests.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
When using nonparametric analyses, you are generally dealing with __________ instead of ___________ and __________.
A) rank; means; standard deviations
B) rank; medians; interquartile range
C) means; rank; range
D) rank; means; sample size
A) rank; means; standard deviations
B) rank; medians; interquartile range
C) means; rank; range
D) rank; means; sample size

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Data on an ordinal scale are generally analyzed by…
A) nonparametric analyses
B) parametric analyses
C) either parametric or nonparametric analyses
D) there is insufficient information about the data.
A) nonparametric analyses
B) parametric analyses
C) either parametric or nonparametric analyses
D) there is insufficient information about the data.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The data below that records the number of inches of snowfall in different parts of the country
 Rank the data.
Rank the data.
 Rank the data.
Rank the data.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The data below that records the number of inches of snowfall in different parts of the country
 What is the 7th rank?
What is the 7th rank?
 What is the 7th rank?
What is the 7th rank?
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The data below that records the number of inches of snowfall in different parts of the country
 Are there any ties? If so, at which rank?
Are there any ties? If so, at which rank?
 Are there any ties? If so, at which rank?
Are there any ties? If so, at which rank?
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A researcher hypothesizes that individuals' interest in politics is related to the amount of television they watch. He asks participants to rate on a scale from 1 (not interested at all) to 10 (extremely interested) the extent to which they are interested in politics, and also asks for the amount of television they watch. Below are the data
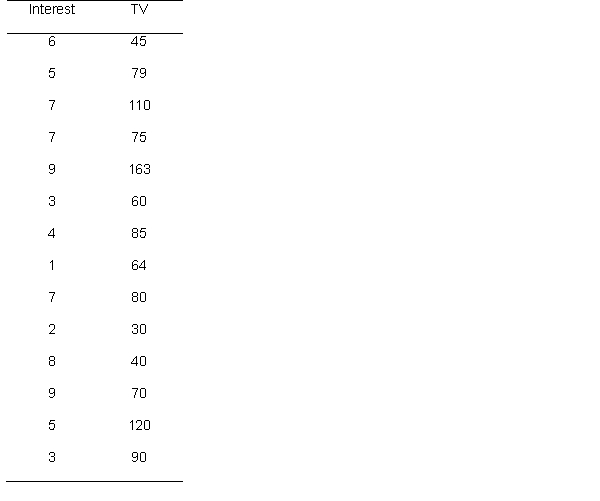 If calculating a spearman correlation, what is the null hypothesis?
If calculating a spearman correlation, what is the null hypothesis?
 If calculating a spearman correlation, what is the null hypothesis?
If calculating a spearman correlation, what is the null hypothesis?
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A researcher hypothesizes that individuals' interest in politics is related to the amount of television they watch. He asks participants to rate on a scale from 1 (not interested at all) to 10 (extremely interested) the extent to which they are interested in politics, and also asks for the amount of television they watch. Below are the data
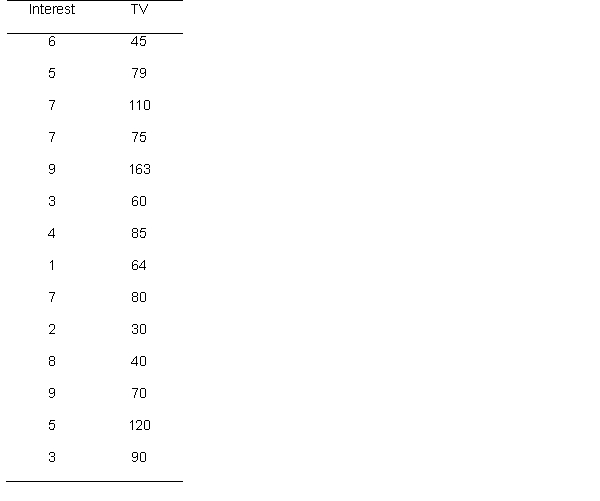 What is the critical value, assuming a two-tailed test and alpha of .05?
What is the critical value, assuming a two-tailed test and alpha of .05?
 What is the critical value, assuming a two-tailed test and alpha of .05?
What is the critical value, assuming a two-tailed test and alpha of .05?
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A researcher hypothesizes that individuals' interest in politics is related to the amount of television they watch. He asks participants to rate on a scale from 1 (not interested at all) to 10 (extremely interested) the extent to which they are interested in politics, and also asks for the amount of television they watch. Below are the data
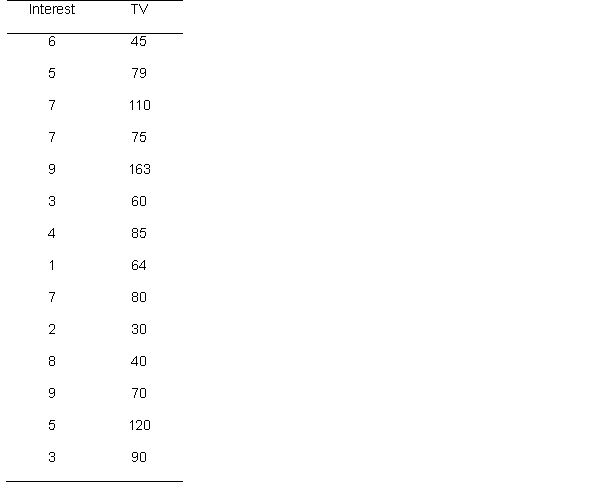 What is the observed correlation?
What is the observed correlation?
 What is the observed correlation?
What is the observed correlation?
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A researcher hypothesizes that individuals' interest in politics is related to the amount of television they watch. He asks participants to rate on a scale from 1 (not interested at all) to 10 (extremely interested) the extent to which they are interested in politics, and also asks for the amount of television they watch. Below are the data
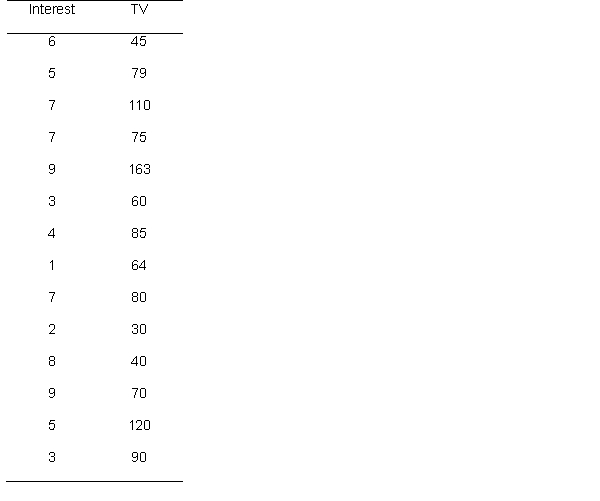 What is the conclusion?
What is the conclusion?
 What is the conclusion?
What is the conclusion?
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Do men and women differ in the way they rate the cuteness of babies? In a study, a team of researchers examined whether gender differences existed in ratings for infants. The data below show average ratings by male and female participants for infant pictures. The team used a Mann-Whitney U test to compare the two groups. Higher scores indicate that the participant thought the image represented a cuter baby.
 What is the critical value, if you assume alpha = .05 and a two-tailed test?
What is the critical value, if you assume alpha = .05 and a two-tailed test?
 What is the critical value, if you assume alpha = .05 and a two-tailed test?
What is the critical value, if you assume alpha = .05 and a two-tailed test?
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Do men and women differ in the way they rate the cuteness of babies? In a study, a team of researchers examined whether gender differences existed in ratings for infants. The data below show average ratings by male and female participants for infant pictures. The team used a Mann-Whitney U test to compare the two groups. Higher scores indicate that the participant thought the image represented a cuter baby.
 Calculate the Mann-Whitney U-test U-value and determine the smaller of the two values.
Calculate the Mann-Whitney U-test U-value and determine the smaller of the two values.
 Calculate the Mann-Whitney U-test U-value and determine the smaller of the two values.
Calculate the Mann-Whitney U-test U-value and determine the smaller of the two values.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Do men and women differ in the way they rate the cuteness of babies? In a study, a team of researchers examined whether gender differences existed in ratings for infants. The data below show average ratings by male and female participants for infant pictures. The team used a Mann-Whitney U test to compare the two groups. Higher scores indicate that the participant thought the image represented a cuter baby.
 Is the difference significant if the test were two-tailed?
Is the difference significant if the test were two-tailed?
 Is the difference significant if the test were two-tailed?
Is the difference significant if the test were two-tailed?
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
In 2017, Nintendo (a Japanese video game company) released a new console called the Nintendo Switch. Nintendo was interested to see how existing customers with their previous generation console (i.e., the Wii U) rate the new product. Below are data of individuals who rated the first console and now rated the Nintendo Switch. Nintendo decided that given the small sample and ranked data, they would use a Wilcoxon Ranked-Sign test.
What is the critical value for this test, assuming two tails and = .05?
What is the critical value for this test, assuming two tails and = .05?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
In 2017, Nintendo (a Japanese video game company) released a new console called the Nintendo Switch. Nintendo was interested to see how existing customers with their previous generation console (i.e., the Wii U) rate the new product. Below are data of individuals who rated the first console and now rated the Nintendo Switch. Nintendo decided that given the small sample and ranked data, they would use a Wilcoxon Ranked-Sign test.
 What is the test statistic after calculating the Wilcoxon Signed Rank test?
What is the test statistic after calculating the Wilcoxon Signed Rank test?
 What is the test statistic after calculating the Wilcoxon Signed Rank test?
What is the test statistic after calculating the Wilcoxon Signed Rank test?
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
In 2017, Nintendo (a Japanese video game company) released a new console called the Nintendo Switch. Nintendo was interested to see how existing customers with their previous generation console (i.e., the Wii U) rate the new product. Below are data of individuals who rated the first console and now rated the Nintendo Switch. Nintendo decided that given the small sample and ranked data, they would use a Wilcoxon Ranked-Sign test.
 What is the conclusion?
What is the conclusion?
 What is the conclusion?
What is the conclusion?
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Explain why non-parametric tests are important. Be sure to discuss when they are used, and any important controversies that might influence their use.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



