Deck 14: Energy Conversion: Mitochondria and Chloroplasts
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/49
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 14: Energy Conversion: Mitochondria and Chloroplasts
1
In the following schematic drawing of the inner and outer mitochondrial membranes, in what region (A to D) would you expect to find more ATP synthase dimers? 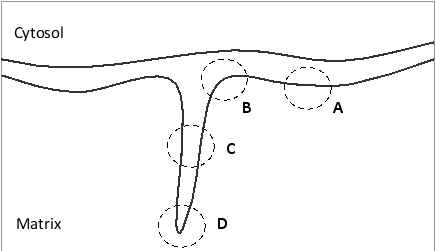

D
2
Consider the remarkable structure of the F1Fo ATP synthase shown in the following schematic drawing. Answer the following question(s) based on the structure.
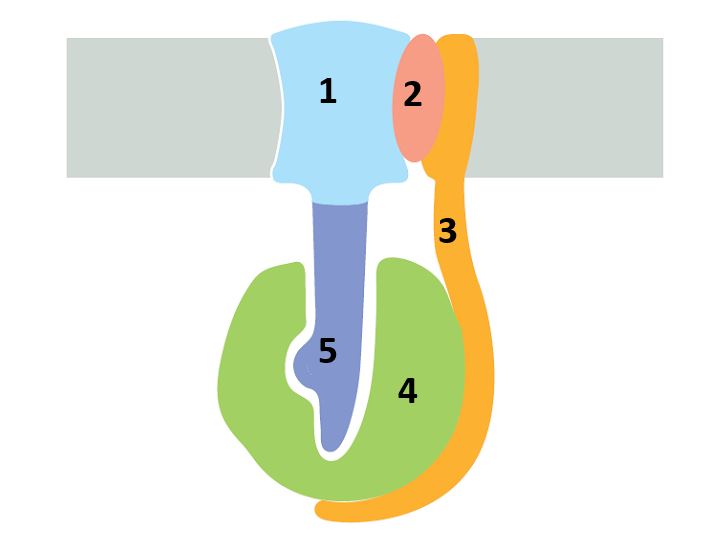
-In Escherichia coli, the c ring of ATP synthase is composed of 12 c subunits. For one fully productive revolution of this ring, how many protons are transported across the membrane for each molecule of ATP produced? Write down your answer as a number, rounded to the nearest integer, e.g. 17.

-In Escherichia coli, the c ring of ATP synthase is composed of 12 c subunits. For one fully productive revolution of this ring, how many protons are transported across the membrane for each molecule of ATP produced? Write down your answer as a number, rounded to the nearest integer, e.g. 17.
4
3
In actively respiring mitochondria, where in the following schematic drawing of the inner and outer mitochondrial membranes would you expect to find the lowest local pH? 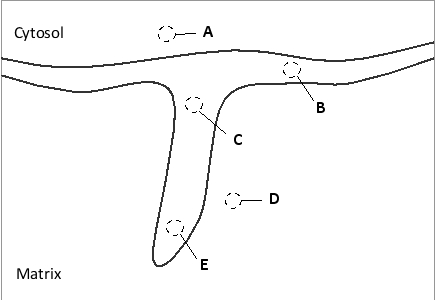

E
4
Consider the remarkable structure of the F1Fo ATP synthase shown in the following schematic drawing. Answer the following question(s) based on the structure.

-In the schematic drawing of the structure of ATP synthase shown above, indicate whether each of the numbered components of the machine (from 1 to 5, respectively) is rotary (R) or stationary (S). Your answer would be a five-letter string composed of letters R and S only, e.g. RRSRS.

-In the schematic drawing of the structure of ATP synthase shown above, indicate whether each of the numbered components of the machine (from 1 to 5, respectively) is rotary (R) or stationary (S). Your answer would be a five-letter string composed of letters R and S only, e.g. RRSRS.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Consider the remarkable structure of the F1Fo ATP synthase shown in the following schematic drawing. Answer the following question(s) based on the structure.

-As seen from the F? head in the matrix, the rotation of the c ring is counterclockwise in the ATP-synthesis mode of the motor and clockwise in the ATP-hydrolysis mode of the motor. As shown in the above drawing, the "a subunit" (labeled 2) is part of the stator embedded in the membrane, and it forms the entry and exit sites for the protons that are bound by the rotating c ring. How do you think the two half-channels of the a subunit are arranged as seen from the c ring? Write down A or B from the following schematic diagram as your answer.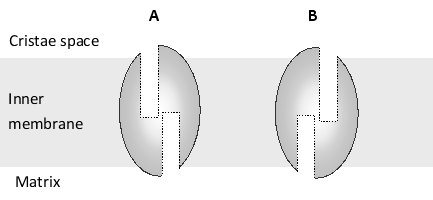

-As seen from the F? head in the matrix, the rotation of the c ring is counterclockwise in the ATP-synthesis mode of the motor and clockwise in the ATP-hydrolysis mode of the motor. As shown in the above drawing, the "a subunit" (labeled 2) is part of the stator embedded in the membrane, and it forms the entry and exit sites for the protons that are bound by the rotating c ring. How do you think the two half-channels of the a subunit are arranged as seen from the c ring? Write down A or B from the following schematic diagram as your answer.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The synthetic toxin 2,4-dinitrophenol can uncouple ATP synthesis from mitochondrial respiration by decreasing the permeability of the inner membrane to protons. What would be the effect of dinitrophenol treatment on the amount of ATP produced by mitochondria and on the rate of ATP transport across the inner membrane, respectively?
A) Positive; positive
B) Positive; negative
C) Negative; positive
D) Negative; negative
A) Positive; positive
B) Positive; negative
C) Negative; positive
D) Negative; negative

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
For mitochondria that are active in respiration, indicate whether the movement of each of the following molecules into (I) or out of (O) the matrix is thermodynamically favorable. Your answer would be a four-letter string composed of letters I and O only, e.g. IOOI.
( ) O2
( ) H+
( ) ADP
( ) CO2
( ) O2
( ) H+
( ) ADP
( ) CO2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
In addition to their respiratory function, mitochondria have other important roles in cellular metabolism. Which of the following processes is NOT carried out mainly by mitochondria?
A) Biosynthesis of cardiolipin
B) Biosynthesis of fatty acids
C) Catabolism of amino acids
D) Biosynthesis of heme
E) Biosynthesis of iron-sulfur clusters
A) Biosynthesis of cardiolipin
B) Biosynthesis of fatty acids
C) Catabolism of amino acids
D) Biosynthesis of heme
E) Biosynthesis of iron-sulfur clusters

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Consider the remarkable structure of the F1Fo ATP synthase shown in the following schematic drawing. Answer the following question(s) based on the structure.

With about 7000 c-ring revolutions per minute, on average how many moles of these pumps should be working at each moment in an entire human body to make about 50 kilograms of ATP per day? The molecular weight of ATP is about 500.
A) About 300 millimoles
B) About 3 millimoles
C) About 30 micromoles
D) About 0.3 micromoles

With about 7000 c-ring revolutions per minute, on average how many moles of these pumps should be working at each moment in an entire human body to make about 50 kilograms of ATP per day? The molecular weight of ATP is about 500.
A) About 300 millimoles
B) About 3 millimoles
C) About 30 micromoles
D) About 0.3 micromoles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The free-energy change for ATP hydrolysis to ADP inside the cell is about -50 kJ/mole. The complete cellular oxidation of glucose to carbon dioxide and water has a free-energy change of about -3000 kJ/mole. What is the efficiency of the cellular metabolism in harvesting this amount of free energy in the form of ATP synthesis?
A) About 10%
B) About 20%
C) About 30%
D) About 50%
E) About 70%
A) About 10%
B) About 20%
C) About 30%
D) About 50%
E) About 70%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Indicate true (T) and false (F) statements below regarding mitochondria. Your answer would be a four-letter string composed of letters T and F only, e.g. TFTT.
( ) Mitochondria are small round organelles that are often associated with actin filaments of the cytoskeleton.
( ) In sperm cells, mitochondria are seen wrapping tightly around the nucleus.
( ) Mitochondria are large enough to be seen with modern light microscopy, and can occupy as much as 20% of cytoplasmic volume.
( ) The outer mitochondrial membrane is freely permeable to ions and small molecules.
( ) Mitochondria are small round organelles that are often associated with actin filaments of the cytoskeleton.
( ) In sperm cells, mitochondria are seen wrapping tightly around the nucleus.
( ) Mitochondria are large enough to be seen with modern light microscopy, and can occupy as much as 20% of cytoplasmic volume.
( ) The outer mitochondrial membrane is freely permeable to ions and small molecules.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Indicate whether each of the following descriptions better matches the outer mitochondrial membrane (O), the intermembrane space (S), the crista membrane portion of the inner mitochondrial membrane (I), or the matrix (M). Your answer would be a four-letter string composed of letters O, S, I, and M only, e.g. OMIM.
( ) It is where NADH is produced.
( ) It is composed of 75% protein by weight.
( ) It is where the respiratory chain is located.
( ) It has the same electrochemical potential for H? as the cytoplasm.
( ) It is where NADH is produced.
( ) It is composed of 75% protein by weight.
( ) It is where the respiratory chain is located.
( ) It has the same electrochemical potential for H? as the cytoplasm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The free-energy change of ATP hydrolysis to ADP inside the cell is about -50 kJ/mole. The standard free-energy change for the same reaction is about -30 kJ/mole. This necessitates that [ATP] inside the cell be …
A) higher than that under standard conditions.
B) greater than [ADP].
C) greater than [ADP] × [Pᵢ]
D) greater than [ADP] × [Pᵢ] × Kₑq
E) greater than [ADP] × [Pᵢ] / Kₑq
A) higher than that under standard conditions.
B) greater than [ADP].
C) greater than [ADP] × [Pᵢ]
D) greater than [ADP] × [Pᵢ] × Kₑq
E) greater than [ADP] × [Pᵢ] / Kₑq

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A facultative anaerobic bacterium can survive both aerobic and anaerobic conditions. Under both conditions, the cell maintains a proton-motive force across the plasma membrane that drives many cellular processes including nutrient import. Under aerobic conditions, the proton-motive force is produced by a respiratory chain. What is the mode of action of the plasma membrane ATP synthase in this bacterium under aerobic conditions: ATP-hydrolysis mode (H) or ATP-synthesis mode (S)? Write down H or S as your answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Indicate whether each of the following descriptions better applies to cytochrome c oxidase complex (O), cytochrome c reductase complex (R), or NADH dehydrogenase complex (N). Your answer would be a four-letter string composed of letters O, R, and N only, e.g. RONN.
( ) It is the largest of the three respiratory complexes.
( ) It accounts for the majority of O? uptake in most cells.
( ) It employs the Q cycle to increase proton pumping.
( ) It contains separate modules for electron transport and proton pumping.
( ) It is the largest of the three respiratory complexes.
( ) It accounts for the majority of O? uptake in most cells.
( ) It employs the Q cycle to increase proton pumping.
( ) It contains separate modules for electron transport and proton pumping.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
ATP synthase molecules in mitochondria form dimers that are localized mostly to sharp cristae ridges. What should happen if subunits of the synthase that are required for dimerization are mutated in yeast?
A) Oxygen consumption would drop
B) Cristae ridges would disappear
C) Cell growth would slow down
D) Monomeric ATP synthases would distribute randomly over the inner membrane
E) All of the above
A) Oxygen consumption would drop
B) Cristae ridges would disappear
C) Cell growth would slow down
D) Monomeric ATP synthases would distribute randomly over the inner membrane
E) All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A hypothetical electron-transport chain contains an electron donor (1), an electron carrier (2), and an electron acceptor (3). Which of these molecules has the highest redox potential? Write down 1, 2, or 3 as your answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
You have isolated mitochondria from a liver tissue sample, suspended them in a hypotonic buffer that causes them to swell and burst their outer membrane, and then added sucrose to a final concentration of about 25%. You then layer the suspension on a density gradient, ultracentrifuge, collect the different fractions, and analyze their protein content. Which of the following proteins would you expect to be highly enriched in the lower density and higher density fractions, respectively?
A) Cytochrome oxidase; porin
B) Cytochrome oxidase; ATP synthase
C) ATP synthase; cytochrome oxidase
D) Porin; ATP synthase
A) Cytochrome oxidase; porin
B) Cytochrome oxidase; ATP synthase
C) ATP synthase; cytochrome oxidase
D) Porin; ATP synthase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following molecules can serve as the terminal electron acceptor in bacterial electron-transport chains?
A) Oxygen
B) Sulfate
C) Fumarate
D) Nitrite
E) All of the above
A) Oxygen
B) Sulfate
C) Fumarate
D) Nitrite
E) All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Sort the following molecules to reflect the order in which they carry electrons in the respiratory chain. Your answer would be a seven-letter string composed of letters A to G only, e.g. GFADCBE.
(A) NADH dehydrogenase complex
(B) Cytochrome c oxidase complex
(C) Cytochrome c reductase complex
(D) Cytochrome c
(E) Ubiquinone
(F) NADH
(G) H?O
(A) NADH dehydrogenase complex
(B) Cytochrome c oxidase complex
(C) Cytochrome c reductase complex
(D) Cytochrome c
(E) Ubiquinone
(F) NADH
(G) H?O

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Indicate whether each of the following descriptions better applies to photosystem I (1) or photosystem II (2). Your answer would be a four-digit number composed of digits 1 and 2 only, e.g. 2212.
( ) It reduces plastoquinone.
( ) It uses a manganese cluster to oxidize water.
( ) It is confined to unstacked thylakoids.
( ) It contains the special pair P???.
( ) It reduces plastoquinone.
( ) It uses a manganese cluster to oxidize water.
( ) It is confined to unstacked thylakoids.
( ) It contains the special pair P???.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Indicate which letter (A to D) in the schematic drawings below of a mitochondrion and a chloroplast corresponds to each of the following features. Your answer would be a four-letter string composed of letters A to D only, e.g. BDCA. Each letter should be used once.
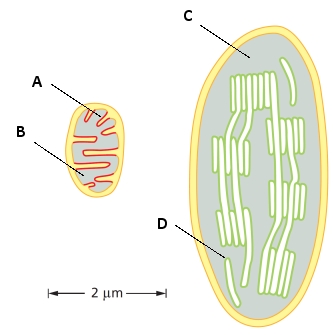
( ) Crista
( ) Stroma
( ) Matrix
( ) Thylakoid

( ) Crista
( ) Stroma
( ) Matrix
( ) Thylakoid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following probably occurred first on Earth?
A) H₂O photosynthesis
B) H₂S photosynthesis
C) O₂ respiration
D) Eukaryotic photosynthesis
A) H₂O photosynthesis
B) H₂S photosynthesis
C) O₂ respiration
D) Eukaryotic photosynthesis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Photosynthesis provides the strongest known electron donor as well as the strongest known electron acceptor in all biology. What do you think the donor and the acceptor are, respectively?
A) Excited P₇₀₀; excited P₆₈₀
B) Excited P₇₀₀; ionized P₆₈₀
C) Ionized P₇₀₀; excited P₆₈₀
D) Ionized P₇₀₀; ionized P₆₈₀
A) Excited P₇₀₀; excited P₆₈₀
B) Excited P₇₀₀; ionized P₆₈₀
C) Ionized P₇₀₀; excited P₆₈₀
D) Ionized P₇₀₀; ionized P₆₈₀

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following is true regarding light-harvesting complexes in plant chloroplasts?
A) They contain chlorophyll and other pigments.
B) They are found in both photosystem I and photosystem II.
C) They can protect the cell by preventing the generation of reactive oxygen species.
D) They cannot carry out charge separation.
E) All of the above.
A) They contain chlorophyll and other pigments.
B) They are found in both photosystem I and photosystem II.
C) They can protect the cell by preventing the generation of reactive oxygen species.
D) They cannot carry out charge separation.
E) All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The water-splitting step in photosynthesis …
A) occurs on the stromal side of the thylakoid membrane.
B) is catalyzed by an iron-sulfur cluster.
C) consumes H⁺ and therefore contributes to the proton gradient across the thylakoid membrane.
D) generates all the O₂ in the Earth's atmosphere.
E) All of the above.
A) occurs on the stromal side of the thylakoid membrane.
B) is catalyzed by an iron-sulfur cluster.
C) consumes H⁺ and therefore contributes to the proton gradient across the thylakoid membrane.
D) generates all the O₂ in the Earth's atmosphere.
E) All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The electrons used in carbon fixation by chloroplasts ultimately come from …
A) Atmospheric oxygen
B) Atmospheric carbon dioxide
C) Water
D) Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
A) Atmospheric oxygen
B) Atmospheric carbon dioxide
C) Water
D) Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
What is the main reason why atmospheric oxygen levels did not rise immediately after the mass production of the gas by photosynthetic bacteria?
A) Because oxygen was rapidly consumed by aerobic microorganisms.
B) Because oxygen was dissolved in water.
C) Because large amounts of ferrous ions reduced the oxygen molecules.
D) Because oxygen was rapidly recycled by early photosynthetic bacteria.
A) Because oxygen was rapidly consumed by aerobic microorganisms.
B) Because oxygen was dissolved in water.
C) Because large amounts of ferrous ions reduced the oxygen molecules.
D) Because oxygen was rapidly recycled by early photosynthetic bacteria.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Indicate true (T) and false (F) statements below regarding the evolution of photosynthesis and oxidative phosphorylation. Your answer would be a five-letter string composed of letters T and F only, e.g. TTFTF.
( ) Chloroplasts are thought to descend from ancient purple sulfur bacteria.
( ) Mitochondria are thought to descend from ancient ?-proteobacteria.
( ) The first photosynthetic cyanobacteria evolved before the first aerobic proteobacteria.
( ) All photosynthetic and aerobic bacteria are thought to have evolved from a common ancestor capable of fermentation and membrane electron transport.
( ) Chloroplasts are thought to descend from ancient purple sulfur bacteria.
( ) Mitochondria are thought to descend from ancient ?-proteobacteria.
( ) The first photosynthetic cyanobacteria evolved before the first aerobic proteobacteria.
( ) All photosynthetic and aerobic bacteria are thought to have evolved from a common ancestor capable of fermentation and membrane electron transport.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The cytochrome b₆-f complex that transfers electrons between the two photosystems in photosynthesis is structurally and functionally similar to which of the complexes in the mitochondrial electron-transport chain?
A) NADH dehydrogenase
B) Succinate dehydrogenase
C) Cytochrome c reductase
D) Cytochrome c oxidase
E) ATP synthase
A) NADH dehydrogenase
B) Succinate dehydrogenase
C) Cytochrome c reductase
D) Cytochrome c oxidase
E) ATP synthase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Two haploid budding yeast cells are allowed to mate. One of them carries a mutation in its mitochondrial DNA that makes the yeast cell resistant to an antifungal drug. If the resulting diploid zygote is allowed to propagate (in the absence of the drug), how do you predict that the fraction of drug-resistant cells will change over time in the population? Choose the best curve (A to F) from the following graph. Note that the "population" is only composed of one cell at the beginning of the experiment. The curves are smoothened to cancel stochastic fluctuations that happen at such low population sizes. 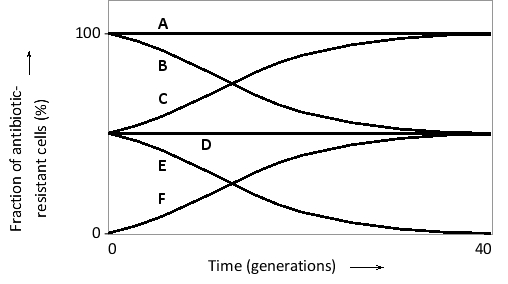


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
When the special pair in a photosystem is excited by a quantum of light, charge separation can occur. Where does this take place? What is the charge of the ionized chlorophyll?
A) In the antenna complex; positive
B) In the antenna complex; negative
C) In the reaction center; positive
D) In the reaction center; negative
A) In the antenna complex; positive
B) In the antenna complex; negative
C) In the reaction center; positive
D) In the reaction center; negative

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Indicate true (T) and false (F) statements below regarding carbon fixation in plant cells. Your answer would be a five-letter string composed of letters T and F only, e.g. TTFTF.
( ) Carbon fixation in photosynthetic cells eventually generates glucose, the major form of sugar that is transported to other plant tissues.
( ) Plant cells can generate fat droplets in their chloroplasts using glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate.
( ) ATP generated in the light cycle is the major source of ATP used by the plant cell to power all of its biochemical reactions.
( ) Plant cells can generate starch granules in their chloroplasts using glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate.
( ) Pyruvate is generated in the chloroplast by the glycolytic pathway.
( ) Carbon fixation in photosynthetic cells eventually generates glucose, the major form of sugar that is transported to other plant tissues.
( ) Plant cells can generate fat droplets in their chloroplasts using glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate.
( ) ATP generated in the light cycle is the major source of ATP used by the plant cell to power all of its biochemical reactions.
( ) Plant cells can generate starch granules in their chloroplasts using glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate.
( ) Pyruvate is generated in the chloroplast by the glycolytic pathway.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
In the following simplified diagram of the Calvin cycle, which step (A to E) is catalyzed by the abundant enzyme Rubisco? 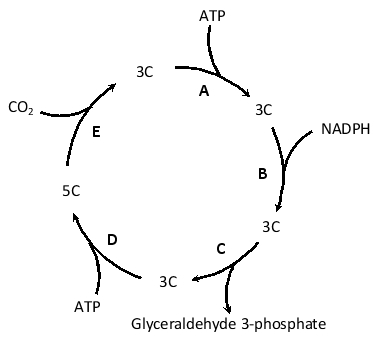


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Indicate whether each of the following descriptions better applies to the light (L) or dark (D) reactions in plant chloroplasts. Your answer would be a five-letter string composed of letters L and D only, e.g. DDDLD.
( ) It produces the sugar glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate.
( ) It involves the electron-transfer chain embedded in the thylakoid membrane.
( ) It involves O2 production.
( ) It involves fixation of CO2.
( ) It generates ATP.
( ) It produces the sugar glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate.
( ) It involves the electron-transfer chain embedded in the thylakoid membrane.
( ) It involves O2 production.
( ) It involves fixation of CO2.
( ) It generates ATP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Order the following metabolic innovations to reflect the most likely order in which they evolved during biological evolution. Your answer would be a four-letter string composed of letters A to D only, e.g. BDCA.
(A) Using light energy to generate reducing power
(B) Splitting of water molecules (an electron source)
(C) Fermentation of organic material
(D) Reduction of molecular oxygen (a terminal electron acceptor)
(A) Using light energy to generate reducing power
(B) Splitting of water molecules (an electron source)
(C) Fermentation of organic material
(D) Reduction of molecular oxygen (a terminal electron acceptor)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Indicate whether each of the following statements better describes ATP production in chloroplasts (C) or in mitochondria (M). Your answer would be a four-letter string composed of letters C and M only, e.g. MCMM.
( ) The electrochemical gradient that drives ATP production is dominated by the electrical component.
( ) It involves a significant pH difference across the membrane.
( ) The ATP synthase molecules form dimers.
( ) The ATP synthase molecules are distributed randomly in flat membrane regions.
( ) The electrochemical gradient that drives ATP production is dominated by the electrical component.
( ) It involves a significant pH difference across the membrane.
( ) The ATP synthase molecules form dimers.
( ) The ATP synthase molecules are distributed randomly in flat membrane regions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Sort the following molecules to reflect the order in which they transfer electrons in noncyclic photophosphorylation in plants. Your answer would be an eight-letter string composed of letters A to H only, e.g. FCDEHGBA.
(A) Ferredoxin-NADP? reductase
(B) Plastoquinone
(C) Ferredoxin
(D) Cytochrome b?-f complex
(E) H?O
(F) Plastocyanin
(G) Photosystem I
(H) Photosystem II
(A) Ferredoxin-NADP? reductase
(B) Plastoquinone
(C) Ferredoxin
(D) Cytochrome b?-f complex
(E) H?O
(F) Plastocyanin
(G) Photosystem I
(H) Photosystem II

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following does NOT occur in the normal process of light-driven production of ATP and NADPH in plant chloroplasts?
A) The cytochrome b₆-f complex pumps protons from the stroma into the thylakoid lumen.
B) The oxygen-evolving enzyme generates protons in the thylakoid lumen.
C) The ferredoxin-NADP⁺ reductase generates protons in the thylakoid lumen.
D) The ATP synthase transports protons from the thylakoid lumen to the stroma.
A) The cytochrome b₆-f complex pumps protons from the stroma into the thylakoid lumen.
B) The oxygen-evolving enzyme generates protons in the thylakoid lumen.
C) The ferredoxin-NADP⁺ reductase generates protons in the thylakoid lumen.
D) The ATP synthase transports protons from the thylakoid lumen to the stroma.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Some photosynthetic bacteria have only one type of photosystem in their plasma membrane. Which of the following is likely to be true regarding such bacteria?
A) They absorb purple light only.
B) Their photosystem is unrelated to those in cyanobacteria and plants.
C) They do not use water as the electron donor.
D) They lack ATP synthase.
E) All of the above.
A) They absorb purple light only.
B) Their photosystem is unrelated to those in cyanobacteria and plants.
C) They do not use water as the electron donor.
D) They lack ATP synthase.
E) All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Consider two organisms, one with a much larger mitochondrial genome than the other. Which one is expected to show more deviations from the universal genetic code: the one with the larger mitochondrial genome (L) or the one with a smaller genome (S)? Write down L or S as your answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
In mammals, mitochondria are inherited …
A) in a non-Mendelian fashion.
B) maternally.
C) cytoplasmically.
D) uniparentally.
E) All of the above
A) in a non-Mendelian fashion.
B) maternally.
C) cytoplasmically.
D) uniparentally.
E) All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Indicate whether each of the following descriptions better applies to chloroplasts (C) or mitochondria (M). Your answer would be a five-letter string composed of letters C and M only, e.g. MMMMC.
( ) Extensive editing occurs on their RNAs.
( ) They utilize dynamin-like GTPases to divide from the outside.
( ) The organization of gene clusters in their genome is strikingly similar to cyanobacteria.
( ) They typically have larger genomes.
( ) They have a more ancient endosymbiotic relationship with their host.
( ) Extensive editing occurs on their RNAs.
( ) They utilize dynamin-like GTPases to divide from the outside.
( ) The organization of gene clusters in their genome is strikingly similar to cyanobacteria.
( ) They typically have larger genomes.
( ) They have a more ancient endosymbiotic relationship with their host.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which of the following is NOT correct regarding the fusion and fission of mitochondria?
A) They both require dynamin-related GTPases.
B) Fission normally proceeds in a single step in which both outer and inner membranes are severed.
C) They both proceed in a single step in which both outer and inner membranes are fused or severed.
D) They both require GTP hydrolysis for force generation.
A) They both require dynamin-related GTPases.
B) Fission normally proceeds in a single step in which both outer and inner membranes are severed.
C) They both proceed in a single step in which both outer and inner membranes are fused or severed.
D) They both require GTP hydrolysis for force generation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which of the following is NOT universally encoded by the mitochondrial DNA?
A) Small ribosomal RNA
B) Large ribosomal RNA
C) A cytochrome oxidase subunit
D) Transfer RNA
A) Small ribosomal RNA
B) Large ribosomal RNA
C) A cytochrome oxidase subunit
D) Transfer RNA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Who has a different mitochondrial DNA in a family?
A) The son
B) The father
C) The mother
D) The daughter
E) The maternal grandmother
A) The son
B) The father
C) The mother
D) The daughter
E) The maternal grandmother

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Indicate whether each of the following descriptions better applies to the genome of mitochondria (M) or nuclei (N) in vertebrates. Your answer would be a four-letter string composed of letters M and N only, e.g. MNMN.
( ) It has a higher percentage of noncoding DNA.
( ) It has a stricter codon usage.
( ) Its genes are present at higher copy numbers per cell.
( ) Its evolutionary clock ticks much faster.
( ) It has a higher percentage of noncoding DNA.
( ) It has a stricter codon usage.
( ) Its genes are present at higher copy numbers per cell.
( ) Its evolutionary clock ticks much faster.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Mitotic segregation of organelles can lead to so-called homoplasmy, when all organelles in each cell carry the same genome. In contrast, heteroplasmy describes the presence of organelles within the same cell that are different with respect to their genomic sequences. Would you expect a defect in the mitochondrial fusion machinery to favor homoplasmy (M) or heteroplasmy (T)? Write down M or T as your answer.
Answers
Answers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Indicate true (T) and false (F) statements below regarding the genetic systems of mitochondria and chloroplasts. Your answer would be a four-letter string composed of letters T and F only, e.g. TFTT.
( ) Most proteins in these organelles are encoded by the organelle's genome.
( ) Mammalian mtDNA can make up less than 1% of the total cellular DNA.
( ) In some highly specialized animal cells, mtDNA can comprise as much as 99% of the cellular DNA.
( ) The genetic systems of these organelles are most similar to extremophilic archaea.
( ) Most proteins in these organelles are encoded by the organelle's genome.
( ) Mammalian mtDNA can make up less than 1% of the total cellular DNA.
( ) In some highly specialized animal cells, mtDNA can comprise as much as 99% of the cellular DNA.
( ) The genetic systems of these organelles are most similar to extremophilic archaea.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



