Deck 9: Chemistry
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/19
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 9: Chemistry
1
The following equation describes Henry's Law: S = kPgₐs
According to this Law,an increase in the partial pressure of the gas indicates that the mass of the dissolved gas
A) decreases.
B) increases.
C) remains constant.
D) none of the above
According to this Law,an increase in the partial pressure of the gas indicates that the mass of the dissolved gas
A) decreases.
B) increases.
C) remains constant.
D) none of the above
increases.
2
A solution of pure water is placed on the left side of a chamber.A solution of 10 mol/L glucose in water is placed on the right side of the chamber.A semi-permeable membrane that only permits water to pass is placed between the two chambers.After five minutes there has been a net movement of water to the right chamber.Which of the following best explains why?
A) The water moves because it is attracted to the negatively charged glucose molecules.
B) The water moves to absorb the free glucose molecules.
C) The water moves to evenly distribute the pressure of the glucose molecules.
D) The water moves to reduce the difference in the concentration of the two solutions.
A) The water moves because it is attracted to the negatively charged glucose molecules.
B) The water moves to absorb the free glucose molecules.
C) The water moves to evenly distribute the pressure of the glucose molecules.
D) The water moves to reduce the difference in the concentration of the two solutions.
The water moves to reduce the difference in the concentration of the two solutions.
3
What is the significance of the following reaction? H₂CO₃ ⇌ H⁺ + HCO₃⁻
A) It is the fastest known physiological enzymatic reaction.
B) It is the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation.
C) It is the Michaelis-Menten reaction.
D) It is part of the pH buffering system in the blood.
A) It is the fastest known physiological enzymatic reaction.
B) It is the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation.
C) It is the Michaelis-Menten reaction.
D) It is part of the pH buffering system in the blood.
It is part of the pH buffering system in the blood.
4
Which of the following statements about osmolality is true?
A) In the laboratory, osmolality is routinely calculated from the concentrations of the major osmotically active solutes.
B) Osmolality is measured as the number of moles of particles per liter of solution.
C) Osmolality is the number of moles of particles per kilogram of solvent.
D) All of the above
A) In the laboratory, osmolality is routinely calculated from the concentrations of the major osmotically active solutes.
B) Osmolality is measured as the number of moles of particles per liter of solution.
C) Osmolality is the number of moles of particles per kilogram of solvent.
D) All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Serum vitamin B₁₂ is highly unstable when exposed to light and can tolerate only a single absorbance reading before breaking down.Therefore,it is not possible to generate a standard curve for B₁₂.When the concentration of B₁₂ must be ascertained in a patient specimen,how should the technician go about doing so?
A) Calculate the concentration of B₁₂ directly from its absorbance in the solution using Beer's Law.
B) Determine the Km and Vmₐₓ of B₁₂ and apply those values to Ohm's Law to calculate the concentration of B₁₂.
C) Generate a standard curve using a more stable vitamin of similar chemical structure.
D) Measure transmittance of B₁₂ and create a standard curve using transmittance against concentration.
A) Calculate the concentration of B₁₂ directly from its absorbance in the solution using Beer's Law.
B) Determine the Km and Vmₐₓ of B₁₂ and apply those values to Ohm's Law to calculate the concentration of B₁₂.
C) Generate a standard curve using a more stable vitamin of similar chemical structure.
D) Measure transmittance of B₁₂ and create a standard curve using transmittance against concentration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The following graph illustrates the typical phases of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction. 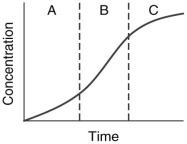
In which phase or phases has the substrate supply diminished so much that product formation slows down?
A) Phase A
B) Phase B
C) Phase C
D) Phases A and C

In which phase or phases has the substrate supply diminished so much that product formation slows down?
A) Phase A
B) Phase B
C) Phase C
D) Phases A and C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Why does the initial rate of an enzymatic reaction eventually plateau at a maximal velocity even though the concentration of the substrate continues to be increased?
A) Enzymes are denatured following action on a substrate.
B) High concentrations of substrate inhibit movement of the substrate to available enzymes.
C) The enzyme available in the solution has been consumed.
D) The enzyme is saturated and unable to bind substrate at a higher rate.
A) Enzymes are denatured following action on a substrate.
B) High concentrations of substrate inhibit movement of the substrate to available enzymes.
C) The enzyme available in the solution has been consumed.
D) The enzyme is saturated and unable to bind substrate at a higher rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following explains the difference between acidosis and alkalosis?
A) Acidosis is a condition in which an increase in acid impairs the enzymatic reaction, and alkalosis is a condition in which an increase in acid makes an enzymatic reaction more efficient.
B) Acidosis is a condition in which the presence of an acid catalyzes an enzymatic reaction, and alkalosis is a condition in which the presence of a base catalyzes an enzymatic reaction.
C) Acidosis is a condition in which the rate of an enzymatic reaction is decreased, and alkalosis is a condition in which the rate of an enzymatic reaction is increased.
D) Acidosis is a condition in which too much acid is present, and alkalosis is a condition in which too little acid is present.
A) Acidosis is a condition in which an increase in acid impairs the enzymatic reaction, and alkalosis is a condition in which an increase in acid makes an enzymatic reaction more efficient.
B) Acidosis is a condition in which the presence of an acid catalyzes an enzymatic reaction, and alkalosis is a condition in which the presence of a base catalyzes an enzymatic reaction.
C) Acidosis is a condition in which the rate of an enzymatic reaction is decreased, and alkalosis is a condition in which the rate of an enzymatic reaction is increased.
D) Acidosis is a condition in which too much acid is present, and alkalosis is a condition in which too little acid is present.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The computerization of modern laboratories has made linear transformations almost obsolete.However,linear transformations remain a critical part of any laboratory training program.Why is it important to understand linear transformations,particularly Lineweaver-Burk plots?
A) They are commonly found in older literature.
B) They are still commonly used even in the presence of computerized functions.
C) They display data in a uniquely effective way.
D) All of the above
A) They are commonly found in older literature.
B) They are still commonly used even in the presence of computerized functions.
C) They display data in a uniquely effective way.
D) All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following is NOT a factor on which absorbance depends?
A) The concentration of the absorbing chemical substance
B) The inherent ability of the chromophore to absorb light
C) The length of the path the light takes when passing through the solution
D) The refractive nature of the ambient air surrounding the solution
A) The concentration of the absorbing chemical substance
B) The inherent ability of the chromophore to absorb light
C) The length of the path the light takes when passing through the solution
D) The refractive nature of the ambient air surrounding the solution

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
What impact would an increase in the concentration of HCO₃⁻ and decrease in the concentration of unquantified anions have on the value of the anion gap?
A) It would decrease.
B) It would increase.
C) It would remain constant.
D) None of the above
A) It would decrease.
B) It would increase.
C) It would remain constant.
D) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Why is it more practical to measure the concentration of CO₂ than that of H₂CO₃ when analyzing the blood buffering system?
A) H₂CO₃ emits toxic fumes which makes it dangerous to work with regularly in the laboratory.
B) In the blood, H₂CO₃ is bound to a carrier molecule that obscures its detection.
C) The concentration of H₂CO₃ in the blood is negligibly small.
D) Both A and C are correct.
A) H₂CO₃ emits toxic fumes which makes it dangerous to work with regularly in the laboratory.
B) In the blood, H₂CO₃ is bound to a carrier molecule that obscures its detection.
C) The concentration of H₂CO₃ in the blood is negligibly small.
D) Both A and C are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A laboratory technician measures the transmittance of light through a solution containing an unknown concentration of glucose.She determines that 75% of the light passing through the sample was transmitted.Which of the following equations defines the absorbance of the solution?
A) A = -log0.25
B) A = -log0.75
C) A = log2.5
D) A = log75.0
A) A = -log0.25
B) A = -log0.75
C) A = log2.5
D) A = log75.0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The Beer-Lambert Law (also called "Beer's Law")defines the relationship between absorbance and what three other factors?
A) Concentration, molar absorptivity, and path length
B) Concentration, photon number, and wavelength
C) Molar absorptivity, path length, and photon number
D) Path length, photon number, and wavelength
A) Concentration, molar absorptivity, and path length
B) Concentration, photon number, and wavelength
C) Molar absorptivity, path length, and photon number
D) Path length, photon number, and wavelength

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Why is the kinetic assay considered a more reliable measure of reaction rate than either the end-point assay or two-point assay?
A) The kinetic assay compares the results of many different samples.
B) The kinetic assay measures both the absorbance and kinetic energy of the sample.
C) The kinetic assay measures the motion of the substrate molecules.
D) The kinetic assay provides confirmation of the linear relationship between product amount and time.
A) The kinetic assay compares the results of many different samples.
B) The kinetic assay measures both the absorbance and kinetic energy of the sample.
C) The kinetic assay measures the motion of the substrate molecules.
D) The kinetic assay provides confirmation of the linear relationship between product amount and time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
You are asked to calculate the creatinine clearance rate for a patient and are presented with the following data:
What other information do you need to calculate the creatinine clearance for this patient?
A) The total volume of the patient
B) The total volume of the patient's plasma
C) The total volume of the plasma sample
D) The total volume of the urine sample
What other information do you need to calculate the creatinine clearance for this patient?
A) The total volume of the patient
B) The total volume of the patient's plasma
C) The total volume of the plasma sample
D) The total volume of the urine sample

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The Henderson-Hasselbalch equation is written as follows: 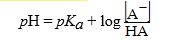
For what practical purpose is this equation used in the laboratory setting?
A) Calculating the optimum pH at which an enzymatic reaction occurs
B) Comparing the strength of an acid against a base
C) Determining the pH of a physiological reaction
D) Preparing a buffer at a specific pH
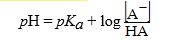
For what practical purpose is this equation used in the laboratory setting?
A) Calculating the optimum pH at which an enzymatic reaction occurs
B) Comparing the strength of an acid against a base
C) Determining the pH of a physiological reaction
D) Preparing a buffer at a specific pH

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The Friedewald equation is used to calculate the concentration of LDL cholesterol in a sample.In cases of suspected lipid disorders,the Friedewald equation should not be used.Which of the following explains why?
A) In lipid disorders, the measure of total cholesterol frequently is less than the measure of HDL, resulting in a negative LDL value.
B) LDL values obtained from the Friedewald equation do not include the concentration of solid, crystalline LDL.
C) The calculation does not take into account interfering concentrations of gaseous CO₂.
D) The Friedewald equation assumes that nearly all the circulating TG is in VLDLs.
A) In lipid disorders, the measure of total cholesterol frequently is less than the measure of HDL, resulting in a negative LDL value.
B) LDL values obtained from the Friedewald equation do not include the concentration of solid, crystalline LDL.
C) The calculation does not take into account interfering concentrations of gaseous CO₂.
D) The Friedewald equation assumes that nearly all the circulating TG is in VLDLs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following best explains the fact that patient specimens are typically assayed at saturating substrate concentrations so that v is at Vmₐₓ?
A) To ensure that only the concentration of enzyme in the specimen affects the measured rate
B) To fit the data onto the standard curve generated by "y = mx + b"
C) To more closely mimic the enzymatic reaction as it occurs in vivo where enzymes generally only function at Vmₐₓ
D) To prevent inactive enzyme molecules from being mistakenly counted as substrate.
A) To ensure that only the concentration of enzyme in the specimen affects the measured rate
B) To fit the data onto the standard curve generated by "y = mx + b"
C) To more closely mimic the enzymatic reaction as it occurs in vivo where enzymes generally only function at Vmₐₓ
D) To prevent inactive enzyme molecules from being mistakenly counted as substrate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



