Deck 9: Varieties of Dictatorship
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/52
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 9: Varieties of Dictatorship
1
The textbook distinguishes between the types of dictatorships based on:
A) size of the country
B) title of the leader
C) identity of their support coalitions
D) type of election
A) size of the country
B) title of the leader
C) identity of their support coalitions
D) type of election
C
2
The three basic types of authoritarian regime outlined in the textbook include all of the following EXCEPT:
A) monarchies.
B) oligarchies.
C) military.
D) civilian.
A) monarchies.
B) oligarchies.
C) military.
D) civilian.
B
3
Those dictators that hold elections and tolerate some degree of pluralism yet violate democratic standards are called:
A) electoral authoritarian.
B) democratic pluralism.
C) liberal democracy.
D) pluralist dictatorship.
A) electoral authoritarian.
B) democratic pluralism.
C) liberal democracy.
D) pluralist dictatorship.
A
4
Dictatorships that rely on their family and kin network to come to power and stay in power are called:
A) monarchies.
B) military dictatorships.
C) dominant-party dictatorships.
D) personalistic dictatorships.
A) monarchies.
B) military dictatorships.
C) dominant-party dictatorships.
D) personalistic dictatorships.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
In the country of Qatar, the successor to the king is selected by the ruling family by consensus based on their own best interests. Based on this information, Qatar can be labeled a:
A) monarchy.
B) military dictatorship.
C) dominant-party dictatorship.
D) personalistic dictatorship.
A) monarchy.
B) military dictatorship.
C) dominant-party dictatorship.
D) personalistic dictatorship.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A dictatorship ruled by a "junta" is a:
A) monarchy.
B) military dictatorship.
C) dominant-party dictatorship.
D) personalistic dictatorship.
A) monarchy.
B) military dictatorship.
C) dominant-party dictatorship.
D) personalistic dictatorship.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Military dictatorships often claim the "guardians of the national interest:"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Military dictatorships rule in an altruistic manner and are unburdened by economic interests:

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The unstable nature of the regime in Guinea demonstrates:
A) that personalistic dictatorships are prone to being overthrown via popular revolution.
B) that military dictatorships are prone to military coups.
C) that dominant-party dictatorships are prone to external invasion.
D) that monarchies make efforts to slowly liberalize institutions.
A) that personalistic dictatorships are prone to being overthrown via popular revolution.
B) that military dictatorships are prone to military coups.
C) that dominant-party dictatorships are prone to external invasion.
D) that monarchies make efforts to slowly liberalize institutions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Dictatorships that rely on the support of a "junta" of leaders of the armed forces to remain in power are called:
A) monarchies.
B) military dictatorships.
C) dominant-party dictatorships.
D) personalistic dictatorships.
A) monarchies.
B) military dictatorships.
C) dominant-party dictatorships.
D) personalistic dictatorships.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Dictatorships that do not rely on either the support of the military or a ruling family or kin network are called:
A) monarchies.
B) military dictatorships.
C) civilian dictatorships.
A) monarchies.
B) military dictatorships.
C) civilian dictatorships.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
When we see a dictator removed from power, we are likely to see the dictator replaced by a dictator of a similar type:

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The most common form of dictatorship from 1946 to 2008 has always been:
A) monarchies.
B) military dictatorships.
C) civilian dictatorships.
A) monarchies.
B) military dictatorships.
C) civilian dictatorships.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The Communist Party in the former Soviet Union is an excellent example of this type of regime:
A) democracy.
B) monarchy.
C) military dictatorship.
D) personalistic dictatorship.
E) dominant-party dictatorship.
A) democracy.
B) monarchy.
C) military dictatorship.
D) personalistic dictatorship.
E) dominant-party dictatorship.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Dominant-party dictatorships rely on the following to stay in power:
A) controlling the military.
B) tying monetary and nonmonetary benefits to membership in the party.
C) restricting the ability off opposition parties to effectively compete .
D) only B and C.
E) all of these.
A) controlling the military.
B) tying monetary and nonmonetary benefits to membership in the party.
C) restricting the ability off opposition parties to effectively compete .
D) only B and C.
E) all of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Dominant-party and personalistic dictatorships are both subcategories of the following type of dictatorship:
A) monarchies.
B) military dictatorships.
C) civilian dictatorships.
A) monarchies.
B) military dictatorships.
C) civilian dictatorships.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The military in personalistic dictatorships is often deliberately kept weak so as to not act as a power base for a potential rival:

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Personalistic dictatorships are often characterized by which of the following?
A) strong parties, strong militaries, and weak leaders
B) free press, competitive elections, and multipartism
C) weak press, strong secret police, and arbitrary uses of force
A) strong parties, strong militaries, and weak leaders
B) free press, competitive elections, and multipartism
C) weak press, strong secret police, and arbitrary uses of force

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Personalistic dictators rely on ______ to maintain the loyalty of their support coalition and the citizenry more generally.
A) cult of personality
B) strong parties
C) free media
D) supportive military
A) cult of personality
B) strong parties
C) free media
D) supportive military

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
All of the following dictators are examples of personalist dictators EXCEPT:
A) Alberto Fujimori (Peru).
B) Kim Jong-il (North Korea).
C) Saparmurat Niyazov (Turkmenistan).
D) Muammar al-Qaddafi (Libya).
A) Alberto Fujimori (Peru).
B) Kim Jong-il (North Korea).
C) Saparmurat Niyazov (Turkmenistan).
D) Muammar al-Qaddafi (Libya).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The difference between hegemonic electoral authoritarian regimes and competitive authoritarian regimes is that:
A) the former is where the major party wins only half the time and the latter is where the major party wins the vast majority of the time.
B) the former is where the opposition parties win substantial minorities and the latter is where opposition parties often win in presidential elections.
C) the former is where the leader's party wins with overwhelming majorities and the latter is where the opposition parties win substantial minorities in elections.
D) none of these.
A) the former is where the major party wins only half the time and the latter is where the major party wins the vast majority of the time.
B) the former is where the opposition parties win substantial minorities and the latter is where opposition parties often win in presidential elections.
C) the former is where the leader's party wins with overwhelming majorities and the latter is where the opposition parties win substantial minorities in elections.
D) none of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The dictatorship type that will be in office the shortest time is expected to be:
A) military dictatorships.
B) personalistic dictatorships.
C) dominant-party dictatorships.
A) military dictatorships.
B) personalistic dictatorships.
C) dominant-party dictatorships.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The dictatorship type that is most likely to be followed by competitive elections is:
A) military dictatorships.
B) personalistic dictatorships.
C) dominant-party dictatorships.
A) military dictatorships.
B) personalistic dictatorships.
C) dominant-party dictatorships.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
What is the basic assumption behind the selectorate theory?
A) That dictators care more about staying in power than democratic leaders do.
B) That dictators use elections to discourage internal rivals from attempting coups.
C) That all political leaders are motivated by the desire to gain and maintain office.
D) All of these are important assumptions of the selectorate theory.
A) That dictators care more about staying in power than democratic leaders do.
B) That dictators use elections to discourage internal rivals from attempting coups.
C) That all political leaders are motivated by the desire to gain and maintain office.
D) All of these are important assumptions of the selectorate theory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
According to BDM2S2, what is the selectorate?
A) These are all of the people who could elect the leader.
B) These are all of the people who do elect the leader.
C) These are all of the people who could select the leader.
D) These are all of the people who do select the leader.
E) none of these.
A) These are all of the people who could elect the leader.
B) These are all of the people who do elect the leader.
C) These are all of the people who could select the leader.
D) These are all of the people who do select the leader.
E) none of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
According to BDM2S2, what is the winning coalition?
A) The party that wins.
B) The government coalition that wins.
C) The group of people who keep the leader in power.
D) The group of people who can select the leader.
E) The group of people who actually selected the leader.
A) The party that wins.
B) The government coalition that wins.
C) The group of people who keep the leader in power.
D) The group of people who can select the leader.
E) The group of people who actually selected the leader.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
To stay in power, leaders must keep members of their winning coalitions happy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
If members of a winning coalition get "paid" with things like money, special legal protections, or special business advantages, then this is an example of the government providing:
A) public goods.
B) private goods.
A) public goods.
B) private goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
If members of a winning coalition get "paid" with things like national security, rule of law, primary and secondary education, then this is an example of the government providing:
A) public goods.
B) private goods.
A) public goods.
B) private goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A key part of the selectorate theory is that the actions of the leader (e.g., setting the tax rate) can affect the level of economic growth for the entire country.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
When will leaders have an incentive to provide public goods?
A) When S is small.
B) When S is large.
C) When W is small.
D) When W is large.
A) When S is small.
B) When S is large.
C) When W is small.
D) When W is large.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
BDM2S2 argue that a leader's decision to provide (mostly) public versus (mostly) private goods is based on how civic-minded they are.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
According to the selectorate theory, when are the members of the winning coalition likely to have the highest loyalty to their leader?
A) When W/S is large.
B) When W/S is small.
C) When W/S is average size.
D) It doesn't matter whether W/S is large, average, or small; they are always loyal.
A) When W/S is large.
B) When W/S is small.
C) When W/S is average size.
D) It doesn't matter whether W/S is large, average, or small; they are always loyal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
If you were the leader, what type of institutions would you want to set up (assuming that you wanted to stay in power)?
A) Institutions that would generate a small W and a small W/S.
B) Institutions that would generate a small W and a large W/S.
C) Institutions that would generate a large W and a large W/S.
D) Institutions that would generate a large W and a small W/S.
A) Institutions that would generate a small W and a small W/S.
B) Institutions that would generate a small W and a large W/S.
C) Institutions that would generate a large W and a large W/S.
D) Institutions that would generate a large W and a small W/S.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
If you were a member of the winning coalition, what type of institutions would you want to set up (assuming that you wanted to receive as many goods as possible)?
A) Institutions that would generate a small W and a small W/S.
B) Institutions that would generate a small W and a large W/S.
C) Institutions that would generate a large W and a large W/S.
D) Institutions that would generate a large W and a small W/S.
A) Institutions that would generate a small W and a small W/S.
B) Institutions that would generate a small W and a large W/S.
C) Institutions that would generate a large W and a large W/S.
D) Institutions that would generate a large W and a small W/S.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
If you were a member of the selectorate but not the winning coalition, what type of institutions would you want to set up (assuming that you wanted to receive as many goods as possible)?
A) Institutions that would generate a small W and a small W/S.
B) Institutions that would generate a small W and a large W/S.
C) Institutions that would generate a large W and a large W/S.
D) Institutions that would generate a large W and a small W/S.
A) Institutions that would generate a small W and a small W/S.
B) Institutions that would generate a small W and a large W/S.
C) Institutions that would generate a large W and a large W/S.
D) Institutions that would generate a large W and a small W/S.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Loyalty toward the incumbent leader declines as the winning coalition grows relative to the selectorate (that is, as W/S gets larger).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Who was Leopold II?
A) The King of Belgium from 1865 to 1909, who had a large winning coalition. He was known as a progressive leader who worked hard to provide public goods.
B) The ruler of the Congo Free State from 1885 to 1908. He had a small winning coalition and was known as a monstrously cruel and greedy leader.
C) "Leopold II" is the name of a hypothetical leader of a small S, large W/S regime.
D) Both (A) and (B) are true.
A) The King of Belgium from 1865 to 1909, who had a large winning coalition. He was known as a progressive leader who worked hard to provide public goods.
B) The ruler of the Congo Free State from 1885 to 1908. He had a small winning coalition and was known as a monstrously cruel and greedy leader.
C) "Leopold II" is the name of a hypothetical leader of a small S, large W/S regime.
D) Both (A) and (B) are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
In the United States of America, who belongs to the selectorate?
A) Everyone who lives in the United States.
B) Everyone who lives in the United States legally.
C) Everyone who is eligible to vote in presidential and congressional elections.
D) Everyone who actually does vote in presidential and congressional elections.
A) Everyone who lives in the United States.
B) Everyone who lives in the United States legally.
C) Everyone who is eligible to vote in presidential and congressional elections.
D) Everyone who actually does vote in presidential and congressional elections.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
According to a BBC article, President Robert Mugabe of Zimbabwe had opposition leaders arrested after police broke up a banned political rally on March 11, 2007 ( http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/africa/6457329.stm). The opposition leader Morgan Tsvangirai appeared in court two days later with "a badly bruised face and stitches in a head wound." The U.S. government, among others, was considering sanctions in response to Mugabe's actions. According to the British Foreign Office minister, Lord David Triesman, "Zimbabwe's government had committed 'actions . . . bordering on crimes against humanity.' Lord Triesman pointed to the government's suppression of Mr. Tsvangirai's Movement for Democratic Change and the eviction of hundreds of thousands of people from urban areas in 2005." The article also notes, "More than 80% of Zimbabweans are living in poverty, with chronic unemployment and inflation running at more than 1,700%-the highest in the world." Which of the following systems would provide incentives for the type of behavior described in this article?
A) Large W, large S
B) Small W, small S
C) Small W, large S
D) Large W, small S
A) Large W, large S
B) Small W, small S
C) Small W, large S
D) Large W, small S

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
One way to describe the relationship between corruption and kleptocracy is to say that kleptocracy is corruption on a large scale-for example, when corruption is actually organized by a country's political leaders with the goal of their personal enrichment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
What set of institutions makes kleptocracy most likely?
A) a large W/S and a small W
B) a small W/S and a small W
C) a large W/S and a large W
A) a large W/S and a small W
B) a small W/S and a small W
C) a large W/S and a large W

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
According to some recent expert surveys, the experts estimate that North Korea has a winning coalition of 73 people! (This is down from several hundred a few decades ago.) This means that the W/S ratio is very, very small compared with almost any other country. Based on the selectorate theory, what kind of government performance should we expect to see in North Korea?
A) We should expect a high level of public goods provision and a high rate of economic growth.
B) We should expect a low-to-medium level of public goods provision and a medium rate of economic growth.
C) We should expect a low level of public goods provision and a low rate of economic growth.
A) We should expect a high level of public goods provision and a high rate of economic growth.
B) We should expect a low-to-medium level of public goods provision and a medium rate of economic growth.
C) We should expect a low level of public goods provision and a low rate of economic growth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
We are able to use the concepts of W (the winning coalition) and S (the selectorate) from the selectorate theory to make useful distinctions among regime types such as democracies, monarchies, military juntas, and so on. However, the authors of the selectorate theory themselves only consider the institutions in each country that determine W and S, rather than talking about countries in terms of being democracies or dictatorships (or different types of dictatorships).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Once we apply the selectorate theory to our usual typology of regime types (democracies as well as various types of dictatorships), it provides us with a potential story both for why democracies produce a relatively high level of material well-being and for why some dictatorships perform better than others.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
According to the selectorate theory, when are we likely to see the best economic performance?
A) When W is big.
B) When W is small.
C) When W/S is big and W is big.
D) When W/S is small and W is big.
A) When W is big.
B) When W is small.
C) When W/S is big and W is big.
D) When W/S is small and W is big.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Let's say we want to apply the insights from the selectorate theory to analyze some question we have about democracies and dictatorships. In the language of the selectorate theory, the key factor that distinguishes democracies from dictatorships is the size of the winning coalition. If we further want to distinguish among dictatorships, we would examine the countries with small winning coalitions and look at variation over the size of the selectorate (so we would be comparing W/S).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Consider Figure 1, below, and answer the following questions.
Figure 1
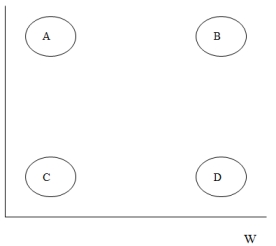
-Looking at Figure 1, where would you place most modern democracies?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) none of these
Figure 1

-Looking at Figure 1, where would you place most modern democracies?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Consider Figure 1, below, and answer the following questions.
Figure 1

-Looking at Figure 1, where would you place military dictatorships (juntas)?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) none of these
Figure 1

-Looking at Figure 1, where would you place military dictatorships (juntas)?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Table l: Effect of W and W/S on Health Care
Dependent variable: Government spending on health care as share of GDP.
GDP = gross domestic product.
-Consider the results from Model 1 in Table 1, above. Does an increase in the Winning coalition significantly increase, decrease, or have no effect on the government spending on health care (measured as the share of GDP)?
A) It significantly increases spending on health care.
B) It significantly decreases spending on health care.
C) It has no effect on health care spending.
Dependent variable: Government spending on health care as share of GDP.
GDP = gross domestic product.
-Consider the results from Model 1 in Table 1, above. Does an increase in the Winning coalition significantly increase, decrease, or have no effect on the government spending on health care (measured as the share of GDP)?
A) It significantly increases spending on health care.
B) It significantly decreases spending on health care.
C) It has no effect on health care spending.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Table l: Effect of W and W/S on Health Care
Dependent variable: Government spending on health care as share of GDP.
GDP = gross domestic product.
-Consider the results from Model 2 in Table 1, above. Does an increase in W/S significantly increase, decrease, or have no effect on the government spending on health care (measured as the share of GDP)?
A) It significantly increases spending on health care.
B) It significantly decreases spending on health care.
C) It has no effect on health care spending.
Dependent variable: Government spending on health care as share of GDP.
GDP = gross domestic product.
-Consider the results from Model 2 in Table 1, above. Does an increase in W/S significantly increase, decrease, or have no effect on the government spending on health care (measured as the share of GDP)?
A) It significantly increases spending on health care.
B) It significantly decreases spending on health care.
C) It has no effect on health care spending.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
According to the selectorate theory put forth by Bueno de Mesquita, Morrow, Siverson, and Smith, what are the two attributes of a polity that create incentives for leaders to produce economic growth and other desirable policy outcomes? Explain the mechanism by which these institutional features create such incentives and summarize the empirical evidence presented in class that is consistent with this theory. What, if anything does this theory say about the relationship between policy performance and democracy? What does it say about the relationship between policy performance and autocracy?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



