Deck 30: IS-MP Analysis: Interest Rates and Output
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/123
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 30: IS-MP Analysis: Interest Rates and Output
1
You spend $45 on a haircut, $30 on a couple of T-shirts, and $17 on lunch at a restaurant. In which component of aggregate expenditure are these expenditures included?
A)consumption
B)planned investment
C)government expenditure
D)exports
A)consumption
B)planned investment
C)government expenditure
D)exports
A
2
You spend $400 on new books for your courses this semester. In which component of aggregate expenditure is this expenditure included?
A)government expenditure
B)exports
C)consumption
D)planned investment
A)government expenditure
B)exports
C)consumption
D)planned investment
C
3
Consumption is the:
A)goods and services that are not produced for the market.
B)expenditure on capital goods by businesses.
C)expenditure by households on goods and services.
D)expenditure by foreigners on goods exported from the United States.
A)goods and services that are not produced for the market.
B)expenditure on capital goods by businesses.
C)expenditure by households on goods and services.
D)expenditure by foreigners on goods exported from the United States.
C
4
If the local cookie factory purchases a new energy efficient industrial oven, this expenditure is:
A)consumption.
B)planned investment.
C)government expenditure.
D)exports.
A)consumption.
B)planned investment.
C)government expenditure.
D)exports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
You are driving to see your grandparents when you get caught in traffic caused by construction on the interstate. The construction is an example of:
A)planned investment.
B)exports.
C)consumption.
D)government expenditure.
A)planned investment.
B)exports.
C)consumption.
D)government expenditure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Planned investment is the:
A)expenditure on goods and services by consumers.
B)use of electricity and water by factories.
C)expenditure on capital goods by businesses.
D)planned purchases of stocks and bonds by consumers.
A)expenditure on goods and services by consumers.
B)use of electricity and water by factories.
C)expenditure on capital goods by businesses.
D)planned purchases of stocks and bonds by consumers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following is an example of government expenditure?
(i) military spending
(ii) interstate highway construction
(iii) construction of a new factory
A)(i), (ii), and (iii)
B)(i) and (ii)
C)(ii) and (iii)
D)(iii) only
(i) military spending
(ii) interstate highway construction
(iii) construction of a new factory
A)(i), (ii), and (iii)
B)(i) and (ii)
C)(ii) and (iii)
D)(iii) only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The equation for aggregate expenditure in an open economy is:
A)Y - C - I.
B)C - I - G - NX.
C)C + I +
D)C + I + G + (X - M).
A)Y - C - I.
B)C - I - G - NX.
C)C + I +
D)C + I + G + (X - M).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
In a closed economy, the equation for aggregate expenditure is:
A)Y - C - I.
B)C - I - G - NX.
C)C + I +
D)C + I + G + (X - M).
A)Y - C - I.
B)C - I - G - NX.
C)C + I +
D)C + I + G + (X - M).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
At macroeconomic equilibrium in an open economy:
A)Y = C + I + G + (X - M).
B)Y > AE.
C)Y = C - I - G - NX.
D)Y < AE.
A)Y = C + I + G + (X - M).
B)Y > AE.
C)Y = C - I - G - NX.
D)Y < AE.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Consumption is $151 billion, government expenditure is $70.2 billion, investment is $65.8 billion, and net exports amount to -$21 billion. What is aggregate expenditure in this economy?
A)$308 billion
B)$287 billion
C)$266 billion
D)$151 billion
A)$308 billion
B)$287 billion
C)$266 billion
D)$151 billion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Consumption is $1.2 trillion, government expenditure is $0.75 trillion, investment is $0.8 trillion, and net exports amount to $0.4 trillion. What is aggregate expenditure in this economy?
A)$2.35 trillion
B)$1.55 trillion
C)$2.75 trillion
D)$3.15 trillion
A)$2.35 trillion
B)$1.55 trillion
C)$2.75 trillion
D)$3.15 trillion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Refer to the table shown here. What is the level of aggregate expenditure in the economy?
A)-$0.6 trillion
B)$11.76 trillion
C)$13.91 trillion
D)$11.16 trillion
A)-$0.6 trillion
B)$11.76 trillion
C)$13.91 trillion
D)$11.16 trillion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Refer to the table shown here. What is the level of aggregate expenditure in the economy?
A)$136 billion
B)$327.2 billion
C)$323 billion
D)$318.8 billion
A)$136 billion
B)$327.2 billion
C)$323 billion
D)$318.8 billion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Refer to the table shown here. What is the level of aggregate expenditure in the economy?
A)$409 billion
B)$337 billion
C)$373 billion
D)$179 billion
A)$409 billion
B)$337 billion
C)$373 billion
D)$179 billion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
If Y > AE:
A)there will be a build-up of inventories in the economy.
B)the stock of inventories will fall in the economy.
C)managers will respond by ramping up production.
D)the economy has surpassed potential GDP.
A)there will be a build-up of inventories in the economy.
B)the stock of inventories will fall in the economy.
C)managers will respond by ramping up production.
D)the economy has surpassed potential GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
If Y > AE:
A)the economy is producing more than potential GDP.
B)the stock of inventories will fall in the economy.
C)managers will respond by ramping up production.
D)managers will respond by lowering production.
A)the economy is producing more than potential GDP.
B)the stock of inventories will fall in the economy.
C)managers will respond by ramping up production.
D)managers will respond by lowering production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
If Y < AE:
A)there will be a build-up of inventories in the economy.
B)the stock of inventories will fall in the economy.
C)managers will respond by lowering production.
D)the economy must be producing less than potential GDP.
A)there will be a build-up of inventories in the economy.
B)the stock of inventories will fall in the economy.
C)managers will respond by lowering production.
D)the economy must be producing less than potential GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
If Y < AE:
A)planned investment will decrease in the economy.
B)prices must be falling in the economy.
C)managers will respond by ramping up production.
D)managers will respond by lowering production.
A)planned investment will decrease in the economy.
B)prices must be falling in the economy.
C)managers will respond by ramping up production.
D)managers will respond by lowering production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
If actual GDP is less than potential GDP:
A)businesses are producing at maximum capacity.
B)the economy is unable to increase production any further.
C)aggregate expenditure must be less than output.
D)unemployment will rise in the economy.
A)businesses are producing at maximum capacity.
B)the economy is unable to increase production any further.
C)aggregate expenditure must be less than output.
D)unemployment will rise in the economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
If actual GDP is greater than potential GDP:
A)businesses can easily increase supply.
B)the economy can experience inflation.
C)businesses are not producing at maximum capacity.
D)unemployment must be higher than the natural rate of unemployment.
A)businesses can easily increase supply.
B)the economy can experience inflation.
C)businesses are not producing at maximum capacity.
D)unemployment must be higher than the natural rate of unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
If potential GDP is $19.04 trillion and actual GDP is $20.07 trillion, the output gap is:
A)1.03%.
B)5.13%.
C)5.41%.
D)-1.03%.
A)1.03%.
B)5.13%.
C)5.41%.
D)-1.03%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
If potential GDP is $7.04 trillion and actual GDP is $6.93 trillion, the output gap is:
A)2.1%.
B)1.56%.
C)-0.11%.
D)-1.56%.
A)2.1%.
B)1.56%.
C)-0.11%.
D)-1.56%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
If potential GDP is $990 billion and actual GDP is $990 billion, the output gap is:
A)zero.
B)positive.
C)negative.
D)increasing over time.
A)zero.
B)positive.
C)negative.
D)increasing over time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The output gap is negative when:
A)potential GDP exceeds actual GDP.
B)aggregate expenditure is greater than planned output.
C)the IS curve and the MP curve meet.
D)there is a positive spending shock.
A)potential GDP exceeds actual GDP.
B)aggregate expenditure is greater than planned output.
C)the IS curve and the MP curve meet.
D)there is a positive spending shock.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The output gap is zero when:
A)planned investment equals actual investment.
B)the economy is experiencing macroeconomic equilibrium.
C)monetary and fiscal policy are in agreement.
D)potential GDP meets actual GDP.
A)planned investment equals actual investment.
B)the economy is experiencing macroeconomic equilibrium.
C)monetary and fiscal policy are in agreement.
D)potential GDP meets actual GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The output gap is positive when:
A)monetary policy actions exceed fiscal policy actions.
B)actual GDP surpasses potential GDP.
C)actual GDP is lower than potential GDP.
D)potential GDP meets actual GDP.
A)monetary policy actions exceed fiscal policy actions.
B)actual GDP surpasses potential GDP.
C)actual GDP is lower than potential GDP.
D)potential GDP meets actual GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The IS curve is constructed by:
A)plotting savings at each real interest rate.
B)adding consumption and savings at each real interest rate.
C)adding up the level of aggregate expenditure at each real interest rate.
D)adding up consumption and investment and plotting these two expenditure levels to income.
A)plotting savings at each real interest rate.
B)adding consumption and savings at each real interest rate.
C)adding up the level of aggregate expenditure at each real interest rate.
D)adding up consumption and investment and plotting these two expenditure levels to income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
If potential GDP is $26.5 trillion and actual GDP is $27.49 trillion, the output gap is:
A)3.74%.
B)3.98%.
C)-3.98%.
D)-3.74%.
A)3.74%.
B)3.98%.
C)-3.98%.
D)-3.74%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Suppose that with a real interest rate of 3%, no output gap exists in the economy. If the real interest rate is above 3%, the economic forecast predicts:
A)a positive output gap.
B)an inflationary output gap.
C)a negative output gap.
D)increased investment by managers.
A)a positive output gap.
B)an inflationary output gap.
C)a negative output gap.
D)increased investment by managers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Suppose that with a real interest rate of 3%, no output gap exists in the economy. If the real interest rate is below 3%, the economic forecast predicts:
A)a recessionary output gap.
B)deflation in the economy.
C)a positive output gap.
D)decreased sales forecasts.
A)a recessionary output gap.
B)deflation in the economy.
C)a positive output gap.
D)decreased sales forecasts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
How do interest rates affect consumption in the economy?
A)Lower interest rates encourage consumers to save more money, and thus consumption rises.
B)Lower real interest rates imply a lower opportunity cost of consumption, and thus consumption rises.
C)Higher interest rates encourage consumers to increase financed purchases, and this encourages consumption.
D)Higher interest rates make it more expensive for firms to take loans, and so consumption falls.
A)Lower interest rates encourage consumers to save more money, and thus consumption rises.
B)Lower real interest rates imply a lower opportunity cost of consumption, and thus consumption rises.
C)Higher interest rates encourage consumers to increase financed purchases, and this encourages consumption.
D)Higher interest rates make it more expensive for firms to take loans, and so consumption falls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
How do interest rates affect consumption in the economy?
A)Lower interest rates encourage consumers to save more money, and thus consumption rises.
B)Lower real interest rates raise the opportunity cost of consumption, and thus consumption falls.
C)Higher interest rates discourage consumers from making financed purchases, and this lowers consumption.
D)Higher interest rates make it more expensive for firms to take loans, and so consumption falls.
A)Lower interest rates encourage consumers to save more money, and thus consumption rises.
B)Lower real interest rates raise the opportunity cost of consumption, and thus consumption falls.
C)Higher interest rates discourage consumers from making financed purchases, and this lowers consumption.
D)Higher interest rates make it more expensive for firms to take loans, and so consumption falls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
How do interest rates affect investment in the economy?
A)Lower interest rates lower the cost of borrowing for firms, and so investment rises.
B)Lower interest rates lower the after-tax profit for firms, and thus investment falls.
C)Higher interest rates lower the cost of borrowing for firms, and so firms save more in banks.
D)Higher interest rates increase government expenditure and thus raise investment.
A)Lower interest rates lower the cost of borrowing for firms, and so investment rises.
B)Lower interest rates lower the after-tax profit for firms, and thus investment falls.
C)Higher interest rates lower the cost of borrowing for firms, and so firms save more in banks.
D)Higher interest rates increase government expenditure and thus raise investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
How do interest rates affect government purchases in the economy?
A)Higher interest rates cause the government to increase government expenditure.
B)Higher interest rates increase the government's debt repayments, and so the government has to spend more money to match the debt.
C)Lower interest rates reduce the government's debt repayments, and this frees up money for government expenditure.
D)Lower interest rates cause the government to lower government expenditure.
A)Higher interest rates cause the government to increase government expenditure.
B)Higher interest rates increase the government's debt repayments, and so the government has to spend more money to match the debt.
C)Lower interest rates reduce the government's debt repayments, and this frees up money for government expenditure.
D)Lower interest rates cause the government to lower government expenditure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Lower interest rates cause the U.S. dollar to:
A)depreciate.
B)appreciate.
C)remain unchanged.
D)gain value.
A)depreciate.
B)appreciate.
C)remain unchanged.
D)gain value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Higher interest rates cause the U.S. dollar to:
A)depreciate.
B)appreciate.
C)remain unchanged.
D)gain value.
A)depreciate.
B)appreciate.
C)remain unchanged.
D)gain value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
What is the relationship between lower interest rates and aggregate expenditure?
A)Lower interest rates raise consumption and investment but lower government purchases and net exports, and thus they have an indeterminate effect on aggregate expenditure.
B)Lower interest rates boost aggregate expenditure.
C)Aggregate expenditure is not affected by changes in real interest rates.
D)Lower interest rates cause aggregate expenditure to fall.
A)Lower interest rates raise consumption and investment but lower government purchases and net exports, and thus they have an indeterminate effect on aggregate expenditure.
B)Lower interest rates boost aggregate expenditure.
C)Aggregate expenditure is not affected by changes in real interest rates.
D)Lower interest rates cause aggregate expenditure to fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
What is the relationship between higher interest rates and aggregate expenditure?
A)Higher interest rates lower consumption and investment but raise government expenditures and net exports, and thus they have an indeterminate effect on aggregate expenditure.
B)Higher interest rates boost aggregate expenditure.
C)Aggregate expenditures are determined independently from changes in real interest rates.
D)Higher interest rates cause aggregate expenditure to fall.
A)Higher interest rates lower consumption and investment but raise government expenditures and net exports, and thus they have an indeterminate effect on aggregate expenditure.
B)Higher interest rates boost aggregate expenditure.
C)Aggregate expenditures are determined independently from changes in real interest rates.
D)Higher interest rates cause aggregate expenditure to fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The lower the opportunity cost of consumption, the:
A)lower the investment in the economy.
B)lower the consumption.
C)higher the aggregate expenditures.
D)more to the left the economy is along the IS curve.
A)lower the investment in the economy.
B)lower the consumption.
C)higher the aggregate expenditures.
D)more to the left the economy is along the IS curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The higher the opportunity cost of consumption, the:
A)higher the investment in the economy.
B)higher the consumption.
C)lower the aggregate expenditures.
D)more to the right the economy is along the IS curve.
A)higher the investment in the economy.
B)higher the consumption.
C)lower the aggregate expenditures.
D)more to the right the economy is along the IS curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The IS curve performs the function of illustrating the relationship between:
A)lower interest rates and higher real GDP and thus more positive output gaps.
B)higher interest rates and higher real GDP and thus more negative output gaps.
C)lower prices in the economy and higher real GDP.
D)lower incomes and lower aggregate expenditures in the economy.
A)lower interest rates and higher real GDP and thus more positive output gaps.
B)higher interest rates and higher real GDP and thus more negative output gaps.
C)lower prices in the economy and higher real GDP.
D)lower incomes and lower aggregate expenditures in the economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which of the figures correctly represents the shape of the IS curve?
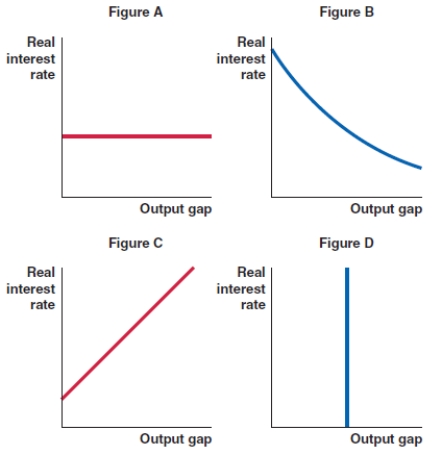
A)Figure A
B)Figure B
C)Figure C
D)Figure D

A)Figure A
B)Figure B
C)Figure C
D)Figure D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A fall in the real interest rate causes:
A)a right shift of the IS curve.
B)movement up and to the left along the same IS curve.
C)movement down and to the right along the same IS curve.
D)a left shift of the IS curve.
A)a right shift of the IS curve.
B)movement up and to the left along the same IS curve.
C)movement down and to the right along the same IS curve.
D)a left shift of the IS curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
A rise in the real interest rate causes:
A)a right shift of the IS curve.
B)movement up and to the left along the same IS curve.
C)movement down and to the right along the same IS curve.
D)a left shift of the IS curve.
A)a right shift of the IS curve.
B)movement up and to the left along the same IS curve.
C)movement down and to the right along the same IS curve.
D)a left shift of the IS curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which of the following causes shifts in the IS curve?
A)The real interest rate decreases.
B)Financial shocks occur.
C)The real interest rate increases.
D)Spending shocks occur.
A)The real interest rate decreases.
B)Financial shocks occur.
C)The real interest rate increases.
D)Spending shocks occur.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The Kenyan government constructs a new intercity highway. As a result:
A)there is a movement down and to the right along the IS curve.
B)there is a movement up and to the left along the IS curve.
C)the IS curve shifts to the right.
D)the IS curve shifts to the left.
A)there is a movement down and to the right along the IS curve.
B)there is a movement up and to the left along the IS curve.
C)the IS curve shifts to the right.
D)the IS curve shifts to the left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The Ugandan shilling depreciates. How does this affect the IS curve in Uganda?
A)Any change in the value of the Ugandan shilling will cause a movement along the IS curve in Uganda.
B)The depreciation of the Ugandan shilling decreases net exports, and this negative spending shock shifts the IS curve to the left.
C)The depreciation of the Ugandan shilling increases net exports, and this positive spending shock shifts the IS curve to the right.
D)Changes in the value of the Ugandan shilling affect only the IS curves of Uganda's trading partners and not the IS curve for Uganda.
A)Any change in the value of the Ugandan shilling will cause a movement along the IS curve in Uganda.
B)The depreciation of the Ugandan shilling decreases net exports, and this negative spending shock shifts the IS curve to the left.
C)The depreciation of the Ugandan shilling increases net exports, and this positive spending shock shifts the IS curve to the right.
D)Changes in the value of the Ugandan shilling affect only the IS curves of Uganda's trading partners and not the IS curve for Uganda.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The Dow Jones Industrial Average rose more than 1,080 points on December 26, 2018. How does a change like this impact the IS curve?
A)The increase in perceived wealth will lead to an increase in taxes, which will cause a left shift of the IS curve.
B)The increase in the real interest rate lowers consumption, which causes a movement down and to the right along the same IS curve.
C)The increase in perceived wealth lowers consumption, which shifts the IS curve to the left.
D)The increase in perceived wealth boosts consumption, which shifts the IS curve to the right.
A)The increase in perceived wealth will lead to an increase in taxes, which will cause a left shift of the IS curve.
B)The increase in the real interest rate lowers consumption, which causes a movement down and to the right along the same IS curve.
C)The increase in perceived wealth lowers consumption, which shifts the IS curve to the left.
D)The increase in perceived wealth boosts consumption, which shifts the IS curve to the right.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
From March 2018 to September 2019, Turkey's consumer confidence index fell from 99.1 to 94.2. How would such a change impact the IS curve in Turkey?
A)Decreased consumer confidence about the future lowers current consumption, causing the IS curve to shift left.
B)The increase in the consumer confidence index means consumers expect income to rise, and this increased consumer spending leads to a right shift in the IS curve.
C)The IS curve is not affected by changes in consumer confidence.
D)The decreased consumer confidence today implies a higher consumer confidence for the future, and this increases consumption and shifts the IS curve to the left.
A)Decreased consumer confidence about the future lowers current consumption, causing the IS curve to shift left.
B)The increase in the consumer confidence index means consumers expect income to rise, and this increased consumer spending leads to a right shift in the IS curve.
C)The IS curve is not affected by changes in consumer confidence.
D)The decreased consumer confidence today implies a higher consumer confidence for the future, and this increases consumption and shifts the IS curve to the left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
From September 2017 to April 2018, South Africa's consumer confidence index rose from 98.8 to 103.2. How would such a change have impacted the IS curve in South Africa?
A)Decreased consumer confidence about the future lowers current consumption, which would cause the IS curve to shift left.
B)The increase in the consumer confidence index means consumers expect income to rise, and this increase in consumer spending would lead to a right shift in the IS curve.
C)The IS curve is not affected by changes in consumer confidence.
D)The decreased consumer confidence today would imply a higher consumer confidence for the future, and this would increase consumption and shift the IS curve to the left.
A)Decreased consumer confidence about the future lowers current consumption, which would cause the IS curve to shift left.
B)The increase in the consumer confidence index means consumers expect income to rise, and this increase in consumer spending would lead to a right shift in the IS curve.
C)The IS curve is not affected by changes in consumer confidence.
D)The decreased consumer confidence today would imply a higher consumer confidence for the future, and this would increase consumption and shift the IS curve to the left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
If the U.S. government lowers personal income tax rates:
A)government expenditure rises, and this leads to a right shift of the IS curve.
B)government expenditure falls, and this leads to a left shift of the IS curve.
C)disposable income increases, and this leads to an increase in consumption and a right shift of the IS curve.
D)investment decreases, and this leads to a left shift in the IS curve.
A)government expenditure rises, and this leads to a right shift of the IS curve.
B)government expenditure falls, and this leads to a left shift of the IS curve.
C)disposable income increases, and this leads to an increase in consumption and a right shift of the IS curve.
D)investment decreases, and this leads to a left shift in the IS curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
A fiscal policy contraction would lead to:
A)no reaction on the IS curve.
B)a movement along the IS curve.
C)a right shift in the IS curve.
D)a left shift in the IS curve.
A)no reaction on the IS curve.
B)a movement along the IS curve.
C)a right shift in the IS curve.
D)a left shift in the IS curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The U.S. imposed a tariff on solar panels produced in China. How did this affect China's IS curve?
A)Net exports decreased, leading to a left shift of the IS curve.
B)Net exports increased, leading to a right shift of the IS curve.
C)Government expenditure decreased, leading to a left shift of the IS curve.
D)Interest rates fell, leading to a left shift in the IS curve.
A)Net exports decreased, leading to a left shift of the IS curve.
B)Net exports increased, leading to a right shift of the IS curve.
C)Government expenditure decreased, leading to a left shift of the IS curve.
D)Interest rates fell, leading to a left shift in the IS curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
In June 2019, India imposed a tariff on almonds from the United States. How does this affect the IS curve in the U.S.?
A)Net exports decrease, leading to a left shift of the IS curve.
B)Net exports increase, leading to a right shift of the IS curve.
C)Government expenditure decreases, leading to a left shift of the IS curve.
D)Interest rates fall, leading to a left shift in the IS curve.
A)Net exports decrease, leading to a left shift of the IS curve.
B)Net exports increase, leading to a right shift of the IS curve.
C)Government expenditure decreases, leading to a left shift of the IS curve.
D)Interest rates fall, leading to a left shift in the IS curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which of the following shows the correct effect on the IS curve of an increase in the real interest rate?
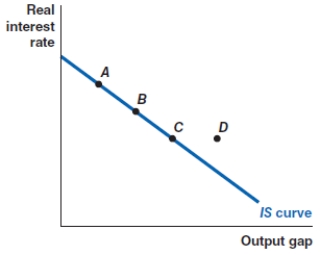
A)a movement from point A to point D
B)a movement from point A to point B
C)a movement from point C to point B
D)a movement from point D to point C

A)a movement from point A to point D
B)a movement from point A to point B
C)a movement from point C to point B
D)a movement from point D to point C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which of the following shows the correct effect on the IS curve of a decrease in the real interest rate?
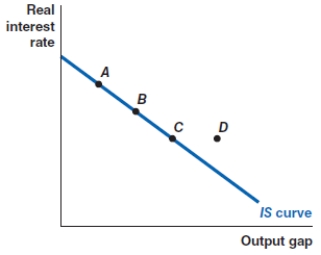
A)a movement from point A to point D
B)a movement from point A to point B
C)a movement from point C to point B
D)a movement from point D to point C

A)a movement from point A to point D
B)a movement from point A to point B
C)a movement from point C to point B
D)a movement from point D to point C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which of the following shows the correct effect on the IS curve of a decrease in personal income tax rates?
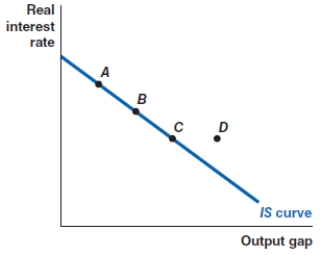
A)a movement from point A to point D
B)a movement from point A to point B
C)a movement from point C to point B
D)a movement from point C to point D

A)a movement from point A to point D
B)a movement from point A to point B
C)a movement from point C to point B
D)a movement from point C to point D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
In October 2019, the Federal Reserve lowered real interest rates in the economy. Which of the following shows the correct effect on the IS curve?
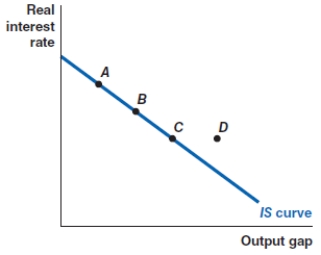
A)a movement from point A to point D
B)a movement from point A to point B
C)a movement from point C to point B
D)a movement from point C to point D

A)a movement from point A to point D
B)a movement from point A to point B
C)a movement from point C to point B
D)a movement from point C to point D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
After the inflationary period of 1979, Paul Volcker, chair of the Federal Reserve, raised real interest rates sharply. Which of the following shows the correct effect on the IS curve?
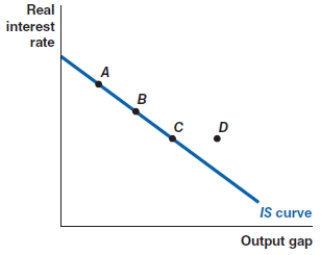
A)a movement from point A to point D
B)a movement from point A to point B
C)a movement from point C to point A
D)a movement from point C to point D

A)a movement from point A to point D
B)a movement from point A to point B
C)a movement from point C to point A
D)a movement from point C to point D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Suppose the U.S. dollar appreciates. Which of the following figures shows the correct effect on the IS curve?
A)
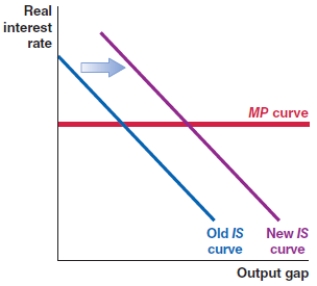
B)
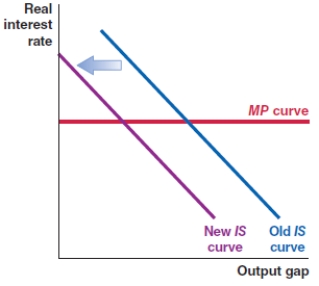
C)
D)
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which of the following cause shifts in the MP curve?
A)changes in tariffs
B)financial shocks
C)changes in tax rates
D)spending shocks
A)changes in tariffs
B)financial shocks
C)changes in tax rates
D)spending shocks

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Which of the following cause(s) shifts in the MP curve?
A)changes in monetary policy
B)consumer pessimism
C)business optimism
D)spending shocks
A)changes in monetary policy
B)consumer pessimism
C)business optimism
D)spending shocks

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The risk premium is the:
A)extra rise in interest rates when the Federal Reserve identifies an output gap.
B)extra interest charged by lenders to account for risk.
C)risk-free rate of interest.
D)federal funds rate.
A)extra rise in interest rates when the Federal Reserve identifies an output gap.
B)extra interest charged by lenders to account for risk.
C)risk-free rate of interest.
D)federal funds rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The MP curve is the:
A)current discount rate set by Fed.
B)current real interest rate as determined by monetary policy and the risk premium.
C)relationship between the real interest rate and real GDP.
D)relationship between the real interest rate and the exchange rate.
A)current discount rate set by Fed.
B)current real interest rate as determined by monetary policy and the risk premium.
C)relationship between the real interest rate and real GDP.
D)relationship between the real interest rate and the exchange rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Which of the figures shown here correctly represents the shape of the MP curve?
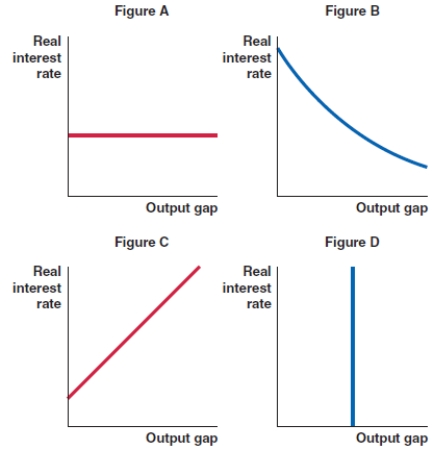
A)Figure A
B)Figure B
C)Figure C
D)Figure D

A)Figure A
B)Figure B
C)Figure C
D)Figure D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
If the nominal rate of interest is 4.8%, the rate of inflation is 2%, and the risk premium is 0.75%, the MP curve is at:
A)3.55%.
B)2.05%.
C)2.8%.
D)4.05%.
A)3.55%.
B)2.05%.
C)2.8%.
D)4.05%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
If the nominal rate of interest is 4.5%, the rate of inflation is 2%, and the risk premium is 1.5%, the risk-free rate is:
A)3.5%.
B)1.5%.
C)2.5%.
D)1%.
A)3.5%.
B)1.5%.
C)2.5%.
D)1%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
If the risk-free rate is 1.5% and the risk premium is 2%, the MP curve is at:
A)1.5%.
B)3.5%.
C)2%.
D)4%.
A)1.5%.
B)3.5%.
C)2%.
D)4%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
If the real rate of interest is 3.7% and the risk-free rate is 2%, the risk premium is:
A)1.7%.
B)5.7%.
C)3.7%.
D)2%.
A)1.7%.
B)5.7%.
C)3.7%.
D)2%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
If the real rate of interest is 2.7% and the risk-free rate is 1.5%, the risk premium is:
A)1.2%.
B)4.2%.
C)3.7%.
D)2%.
A)1.2%.
B)4.2%.
C)3.7%.
D)2%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
When the perceived financial risk rises in an economy, the:
A)lenders become less risk averse.
B)TED spread rises.
C)TED spread falls.
D)risk premiums fall.
A)lenders become less risk averse.
B)TED spread rises.
C)TED spread falls.
D)risk premiums fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
When the perceived financial risk falls in an economy, the:
A)lenders become more risk averse.
B)TED spread rises.
C)TED spread falls.
D)risk premiums rise.
A)lenders become more risk averse.
B)TED spread rises.
C)TED spread falls.
D)risk premiums rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The difference between the three-month interbank loan interest rate and the interest rate on short-term U.S. government debt is the:
A)risk-free rate.
B)federal funds rate.
C)MP curve.
D)TED spread.
A)risk-free rate.
B)federal funds rate.
C)MP curve.
D)TED spread.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
A good proxy for the risk-free interest rate is the interest rate on a:
A)loan to the U.S. government.
B)loan to a member of the public who has a good credit rating.
C)corporate bond.
D)junk bond.
A)loan to the U.S. government.
B)loan to a member of the public who has a good credit rating.
C)corporate bond.
D)junk bond.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
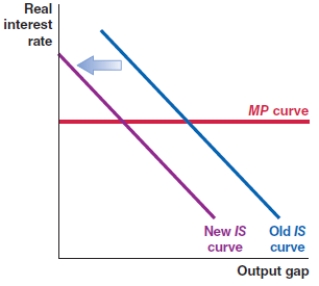
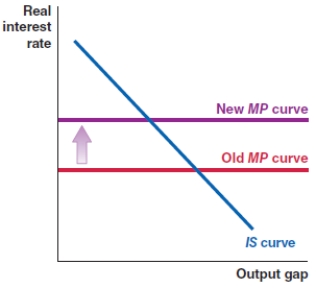
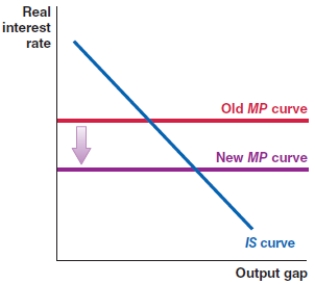
In October 2019, the Federal Reserve lowered the Federal Funds rate in the economy. Which of the following figures shows the correct effect on the MP curve?
A)
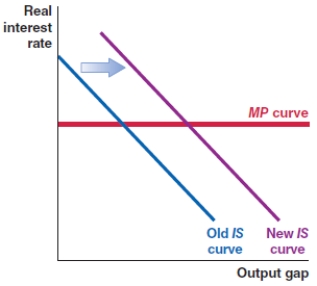
B)
C)
D)
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The intersection of the IS curve and the MP curve determine:
A)the federal funds rate.
B)the risk-free interest rate in the economy.
C)the largest output gap.
D)macroeconomic equilibrium.
A)the federal funds rate.
B)the risk-free interest rate in the economy.
C)the largest output gap.
D)macroeconomic equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
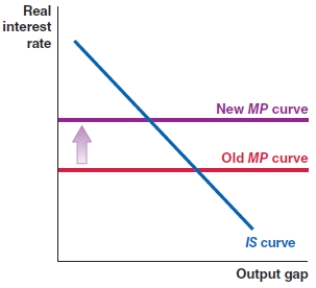
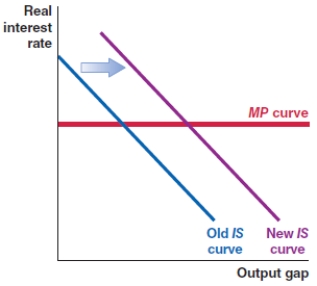
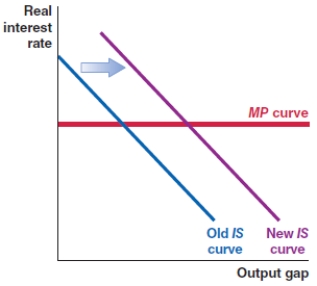
Which of the following shows the correct effect on the IS-MP framework if there is an increase in the risk premium in an economy?
A)
B)
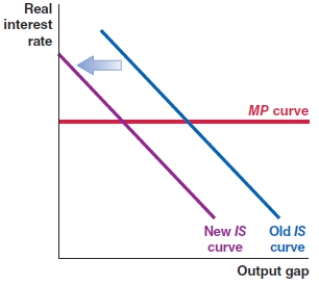
C)
D)
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
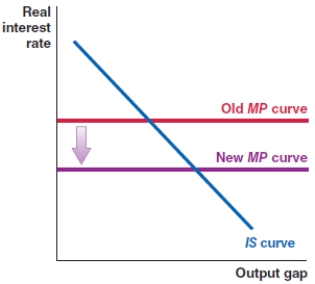
79
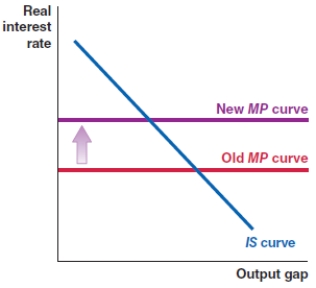
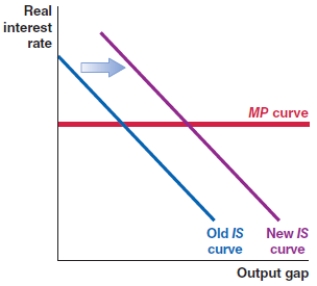
Which of the following shows the correct effect on the IS-MP framework if there is a sharp increase in loan default rates in an economy?
A)
B)
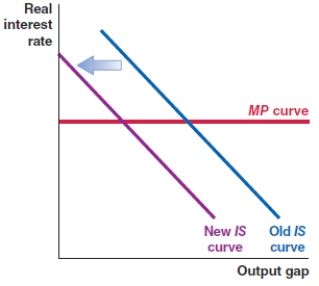
C)
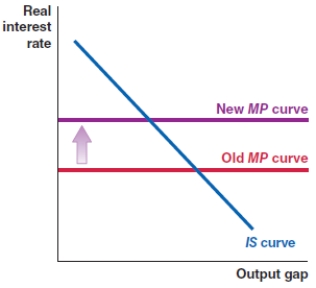
D)
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
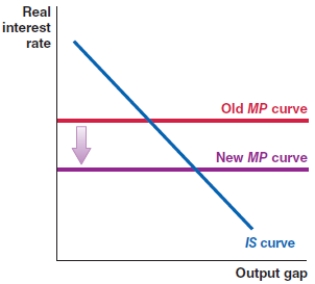
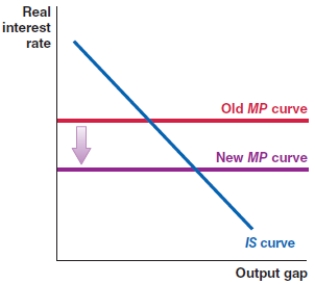
In 2008, the Federal Reserve committed funds to stabilize the banking system and lower the risk premium in the economy. Which of the following shows the correct effect on the IS-MP framework?
A)
B)
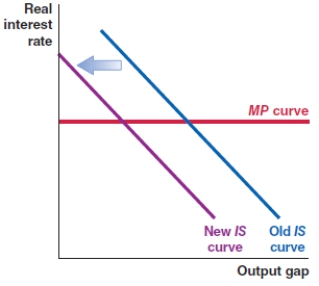
C)
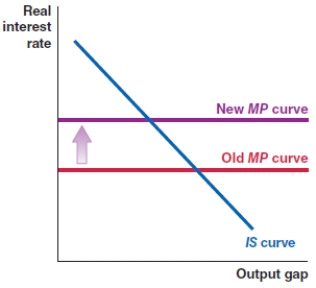
D)
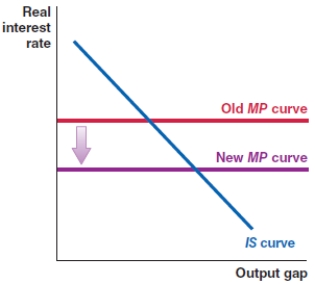
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



