Deck 25: Consumption and Saving
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/158
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 25: Consumption and Saving
1
Which of the following scenarios represents consumption spending?
A)You get a haircut at the local salon.
B)The local Ford dealership brings in a stock of new car models.
C)Your town gets a new fire truck.
D)Your university upgrades all its computers.
A)You get a haircut at the local salon.
B)The local Ford dealership brings in a stock of new car models.
C)Your town gets a new fire truck.
D)Your university upgrades all its computers.
A
2
Which of the scenarios represents consumption spending?
A)A new hospital is constructed in your town.
B)You take out a bank loan.
C)You eat at a fancy restaurant for Valentine's Day.
D)Your parents pay their income taxes.
A)A new hospital is constructed in your town.
B)You take out a bank loan.
C)You eat at a fancy restaurant for Valentine's Day.
D)Your parents pay their income taxes.
C
3
Which of the scenarios represents consumption spending?
A)Your roommate borrows $50 from you.
B)You and your date go on a balloon ride.
C)Your mayor approves the construction of a new city hall building.
D)The local high school upgrades its classrooms.
A)Your roommate borrows $50 from you.
B)You and your date go on a balloon ride.
C)Your mayor approves the construction of a new city hall building.
D)The local high school upgrades its classrooms.
B
4
Consumption spending is:
A)purchases of stocks and bonds by consumers.
B)money that is saved by consumers.
C)household spending on final goods and services.
D)business spending on inputs for producing consumer goods.
A)purchases of stocks and bonds by consumers.
B)money that is saved by consumers.
C)household spending on final goods and services.
D)business spending on inputs for producing consumer goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The consumption function is a plot of the:
A)level of consumption associated with each level of income.
B)average marginal propensity to consume over time.
C)level of government spending associated with each level of income.
D)price of consumer goods and services over time.
A)level of consumption associated with each level of income.
B)average marginal propensity to consume over time.
C)level of government spending associated with each level of income.
D)price of consumer goods and services over time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The marginal propensity to consume is the:
A)initial level of consumption after income is earned.
B)average level of consumption over time.
C)fraction of each dollar of extra income that households save.
D)fraction of each dollar of extra income that households spend on consumption.
A)initial level of consumption after income is earned.
B)average level of consumption over time.
C)fraction of each dollar of extra income that households save.
D)fraction of each dollar of extra income that households spend on consumption.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which statement correctly describes the relationship between consumption and income?
A)Consumption is always half of income.
B)Consumption and income are positively related.
C)Income is always less than consumption.
D)Total consumption is independent of income.
A)Consumption is always half of income.
B)Consumption and income are positively related.
C)Income is always less than consumption.
D)Total consumption is independent of income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The marginal propensity to consume is:
A)always 1.
B)positive.
C)negative.
D)zero.
A)always 1.
B)positive.
C)negative.
D)zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
If the average marginal propensity to consume is 0.75, then a $1 million increase in total income will lead to a _____ in consumption.
A)$250,000 increase
B)$75,000 increase
C)$750,000 decrease
D)$750,000 increase
A)$250,000 increase
B)$75,000 increase
C)$750,000 decrease
D)$750,000 increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
If the average marginal propensity to consume is 0.8, then a $10 million increase in total income will lead to a _____ increase in consumption.
A)$80 million
B)$0.8 million
C)$8 million
D)$2 million
A)$80 million
B)$0.8 million
C)$8 million
D)$2 million

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
If the average marginal propensity to consume is 0.68, then a $1 trillion increase in total income will lead to a _____ in consumption.
A)$3.2 trillion decrease
B)$3.2 trillion increase
C)$6.8 trillion increase
D)$0.68 trillion increase
A)$3.2 trillion decrease
B)$3.2 trillion increase
C)$6.8 trillion increase
D)$0.68 trillion increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
What is the marginal propensity to consume if a $10 million increase in total income leads to a $7.9 million increase in consumption?
A)0.79
B)7.9
C)0.079
D)0.21
A)0.79
B)7.9
C)0.079
D)0.21

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
What is the marginal propensity to consume if a $100 million increase in total income leads to a $58 million increase in consumption?
A)4.2
B)5.8
C)0.58
D)0.42
A)4.2
B)5.8
C)0.58
D)0.42

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
If a $100 million increase in total income leads to a $62 million increase in consumption, the slope of the consumption function is:
A)negative.
B)0.62.
C)zero.
D)0.38.
A)negative.
B)0.62.
C)zero.
D)0.38.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Total consumption is $1,800 when income is $2,000, and total consumption increases to $2,600 when income is $3,000. What is the marginal propensity to consume?
A)0.8
B)0.5
C)0.2
D)1.25
A)0.8
B)0.5
C)0.2
D)1.25

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Total consumption is $1,400 when income is $1,600, and total consumption increases to $1,900 when income is at $2,400. What is the marginal propensity to consume?
A)0.83
B)1.6
C)0.37
D)0.63
A)0.83
B)1.6
C)0.37
D)0.63

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
What is your permanent income marginal propensity to consume (MPC) if your income permanently changes by $20,000 and your consumption increases by $15,000?
A)0.75
B)0.25
C)0.2
D)1.33
A)0.75
B)0.25
C)0.2
D)1.33

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
What is your permanent income marginal propensity to consume (MPC) if your income permanently changes by $50,000 and your consumption increases by $45,000?
A)0.1
B)1.11
C)0.9
D)1.25
A)0.1
B)1.11
C)0.9
D)1.25

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
What is your permanent income marginal propensity to consume (MPC) if your income permanently changes by $5,000 and your consumption increases by $5,000?
A)0.1
B)1.11
C)1
D)0.5
A)0.1
B)1.11
C)1
D)0.5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Consider the following data. What is the marginal propensity to consume?
A)0.3
B)1
C)0.7
D)1.42
A)0.3
B)1
C)0.7
D)1.42

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Consider the following data. What is the marginal propensity to consume?
A)0.7
B)1
C)0.3
D)0.45
A)0.7
B)1
C)0.3
D)0.45

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Consider the following data. What is the marginal propensity to consume?
A)0.9
B)0.1
C)1.1
D)0.84
A)0.9
B)0.1
C)1.1
D)0.84

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Consider the following data. What is the marginal propensity to consume?
A)1.25
B)0.8
C)0.2
D)2.8
A)1.25
B)0.8
C)0.2
D)2.8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Consider the following data. What is the marginal propensity to consume?
A)1.67
B)0.6
C)0.75
D)0.4
A)1.67
B)0.6
C)0.75
D)0.4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of these statements is correct?
A)Savings plus consumption equals income.
B)Income plus consumption equals saving.
C)Dissaving equals consumption.
D)Dissaving plus saving plus consumption equals income.
A)Savings plus consumption equals income.
B)Income plus consumption equals saving.
C)Dissaving equals consumption.
D)Dissaving plus saving plus consumption equals income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Mark earns $3,800 in the current period. His consumption in this same period is $4,100. Which of the following is true?
A)He has borrowed $3,800.
B)His income is $7,900.
C)His dissaving is $300.
D)He saves $300.
A)He has borrowed $3,800.
B)His income is $7,900.
C)His dissaving is $300.
D)He saves $300.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Dissaving is:
A)excess income over and above consumption.
B)excess consumption over and above income.
C)saving plus interest earned.
D)consumption plus income.
A)excess income over and above consumption.
B)excess consumption over and above income.
C)saving plus interest earned.
D)consumption plus income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Dissaving is:
A)positive saving.
B)negative saving.
C)net wealth minus income.
D)saving plus interest earned.
A)positive saving.
B)negative saving.
C)net wealth minus income.
D)saving plus interest earned.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
How can dissaving in the current period be funded?
(i) borrowing from friends
(ii) bank loans
(iii) previous savings
(iv) current income earned
A)(ii) and (iii)
B)(i), (ii), and (iii)
C)(ii), (iii), and (iv)
D)(i), (ii), (iii), and (iv)
(i) borrowing from friends
(ii) bank loans
(iii) previous savings
(iv) current income earned
A)(ii) and (iii)
B)(i), (ii), and (iii)
C)(ii), (iii), and (iv)
D)(i), (ii), (iii), and (iv)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Net wealth is:
A)the amount by which income exceeds bills.
B)the real interest rate on saving.
C)equivalent to total consumption.
D)the amount by which assets exceed debts.
A)the amount by which income exceeds bills.
B)the real interest rate on saving.
C)equivalent to total consumption.
D)the amount by which assets exceed debts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
When real interest rates rise, consumption will shift:
A)downward if income rises as well.
B)upward if the income effect outweighs the substitution effect.
C)upward if the substitution effect outweighs the income effect.
D)downward if there is saving.
A)downward if income rises as well.
B)upward if the income effect outweighs the substitution effect.
C)upward if the substitution effect outweighs the income effect.
D)downward if there is saving.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
When real interest rates rise, consumption will shift:
A)only if income rises as well.
B)downward if the income effect outweighs the substitution effect.
C)downward if the substitution effect outweighs the income effect.
D)downward if there is saving.
A)only if income rises as well.
B)downward if the income effect outweighs the substitution effect.
C)downward if the substitution effect outweighs the income effect.
D)downward if there is saving.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
If Larry is a hand-to-mouth consumer and has just received a gift of $350, we can expect Larry to exhibit:
A)a large change in consumption.
B)a small change in consumption.
C)a large change in saving.
D)no change in MPC.
A)a large change in consumption.
B)a small change in consumption.
C)a large change in saving.
D)no change in MPC.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
If Frank is a hand-to-mouth consumer and he has just received a permanent 10% increase in salary, we can expect Frank to exhibit:
A)a large change in consumption.
B)a small change in consumption.
C)a large change in saving.
D)no change in MPC.
A)a large change in consumption.
B)a small change in consumption.
C)a large change in saving.
D)no change in MPC.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
If Derek is a consumption smoother and has just signed a contract for a new job that will increase his salary by 14%, we can expect Derek to exhibit:
A)a large change in consumption.
B)a small change in consumption.
C)zero change in saving.
D)no change in MPC.
A)a large change in consumption.
B)a small change in consumption.
C)zero change in saving.
D)no change in MPC.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
If Marios is a consumption smoother and has just won a prize of $12,000, we can expect Marios to exhibit:
A)a large change in consumption.
B)a small change in consumption.
C)zero change in saving.
D)no change in MPC.
A)a large change in consumption.
B)a small change in consumption.
C)zero change in saving.
D)no change in MPC.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
For consumption smoothers, the marginal propensity to consume out of anticipated changes in income is:
A)zero.
B)one.
C)negative.
D)always close to 1.
A)zero.
B)one.
C)negative.
D)always close to 1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Credit constraints limit the:
A)amount of saving that people can make.
B)interest rates that banks can charge.
C)amount of money that banks can accept as deposits.
D)amount of money that people can borrow.
A)amount of saving that people can make.
B)interest rates that banks can charge.
C)amount of money that banks can accept as deposits.
D)amount of money that people can borrow.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Hand-to-mouth consumers:
A)spend more on luxuries than on necessities.
B)have very high levels of consumption.
C)live paycheck to paycheck.
D)engage in a significant amount of spending.
A)spend more on luxuries than on necessities.
B)have very high levels of consumption.
C)live paycheck to paycheck.
D)engage in a significant amount of spending.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Hand-to-mouth consumers:
(i) spend more on necessities than on luxuries.
(ii) save very little or nothing at all.
(iii) purchase a large amount of luxury items.
(iv) live paycheck to paycheck.
A)(iv) only
B)(i), (ii), and (iv)
C)(iii) and (iv)
D)(i) and (ii)
(i) spend more on necessities than on luxuries.
(ii) save very little or nothing at all.
(iii) purchase a large amount of luxury items.
(iv) live paycheck to paycheck.
A)(iv) only
B)(i), (ii), and (iv)
C)(iii) and (iv)
D)(i) and (ii)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The opportunity cost of an extra dollar of consumption today is the:
A)same as the marginal benefit of consuming the dollar in the future.
B)marginal benefit of consumption today.
C)average benefit from consumption today and in the future.
D)marginal benefit of consuming a dollar-plus-interest in the future.
A)same as the marginal benefit of consuming the dollar in the future.
B)marginal benefit of consumption today.
C)average benefit from consumption today and in the future.
D)marginal benefit of consuming a dollar-plus-interest in the future.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The benefit of an extra dollar of consumption is called the:
A)marginal benefit of consumption.
B)average benefit of consumption.
C)average price of goods and services consumed.
D)real interest rate.
A)marginal benefit of consumption.
B)average benefit of consumption.
C)average price of goods and services consumed.
D)real interest rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The rational rule of consumption is to consume more today if the:
A)price of consumption today exceeds the dollar-plus-interest in the future.
B)marginal benefit of a dollar of consumption today is greater than (or equal to) the marginal benefit of spending a dollar plus interest in the future.
C)marginal benefit of a dollar of consumption today is less than the marginal benefit of spending a dollar plus interest in the future.
D)real interest rate in the future is expected to be higher than the real interest rate today.
A)price of consumption today exceeds the dollar-plus-interest in the future.
B)marginal benefit of a dollar of consumption today is greater than (or equal to) the marginal benefit of spending a dollar plus interest in the future.
C)marginal benefit of a dollar of consumption today is less than the marginal benefit of spending a dollar plus interest in the future.
D)real interest rate in the future is expected to be higher than the real interest rate today.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
When consumers receive more income, their spending:
A)increases.
B)increases.
C)decreases.
D)decreases.
E)stays the same, but their savings decreas
F)stays the same, but their savings decreas
G)and their savings both decrease.
H)and their savings both decrease.
A)increases.
B)increases.
C)decreases.
D)decreases.
E)stays the same, but their savings decreas
F)stays the same, but their savings decreas
G)and their savings both decrease.
H)and their savings both decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which of the following graphs shows the correct effect on the consumption function when there is a decrease in income?
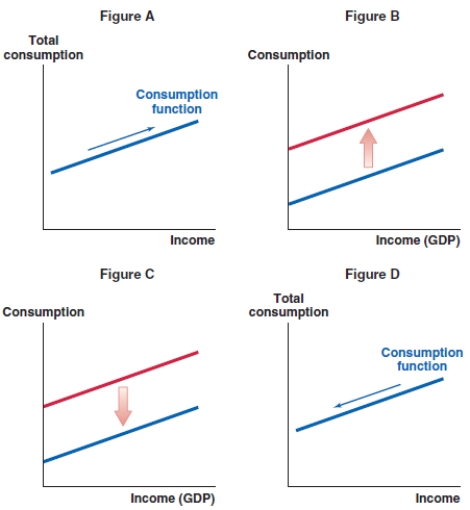
A)Figure A
B)Figure B
C)Figure C
D)Figure D

A)Figure A
B)Figure B
C)Figure C
D)Figure D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which of the following graphs shows the correct effect on the consumption function when there is an increase in real interest rates and the substitution effect is dominant?
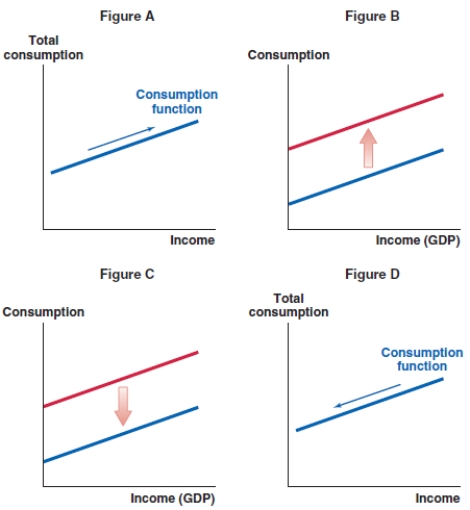
A)Figure A
B)Figure B
C)Figure C
D)Figure D

A)Figure A
B)Figure B
C)Figure C
D)Figure D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which of the following graphs shows the correct effect on the consumption function when there is a decrease in real interest rates and the substitution effect is dominant?
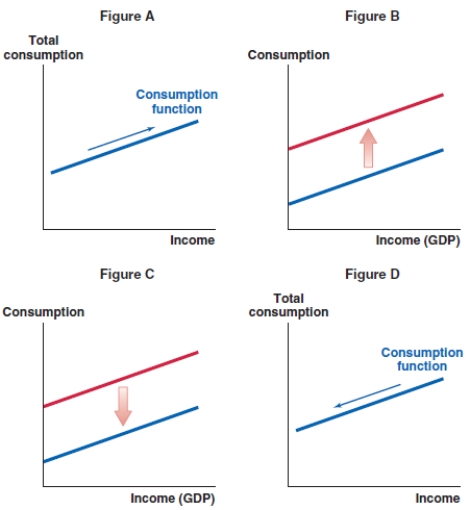
A)Figure A
B)Figure B
C)Figure C
D)Figure D

A)Figure A
B)Figure B
C)Figure C
D)Figure D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Why does a temporary change in income lead to only a small change in consumption for a consumption smoother?
A)The MPC always tends to be low.
B)The consumer prefers to focus on current consumption rather than future consumption.
C)Temporary increases in income are heavily taxed.
D)The consumer tends to spread a temporary spike in income over the lifetime of the consumer.
A)The MPC always tends to be low.
B)The consumer prefers to focus on current consumption rather than future consumption.
C)Temporary increases in income are heavily taxed.
D)The consumer tends to spread a temporary spike in income over the lifetime of the consumer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Why does an anticipated change in income lead to no change in consumption for a consumption smoother?
A)The consumer is not aware of anticipated changes in future income.
B)Consumption is based on permanent income, which is already factored into anticipated future changes in income.
C)There are high tax rates on anticipated changes in future income.
D)There is a failure of the permanent income hypothesis.
A)The consumer is not aware of anticipated changes in future income.
B)Consumption is based on permanent income, which is already factored into anticipated future changes in income.
C)There are high tax rates on anticipated changes in future income.
D)There is a failure of the permanent income hypothesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
When does an anticipated change in future income lead to a change in consumption for consumption smoothers?
A)when the permanent income hypothesis fails
B)when the anticipated future income arrives in the paycheck
C)It never leads to a change in consumption.
D)when the consumption smoother first learns of the anticipated future change in income
A)when the permanent income hypothesis fails
B)when the anticipated future income arrives in the paycheck
C)It never leads to a change in consumption.
D)when the consumption smoother first learns of the anticipated future change in income

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which of the following graphs shows the correct effect on the consumption function when taxes decrease in the economy?
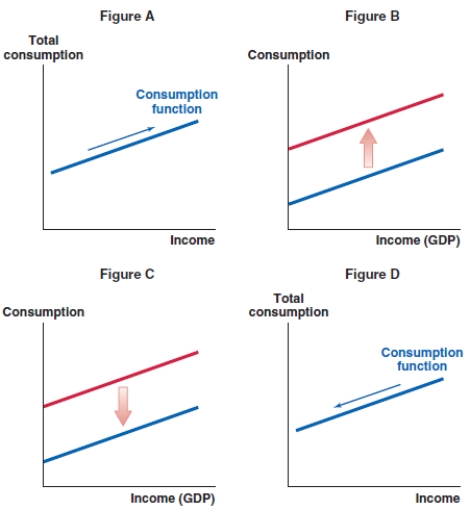
A)Figure A
B)Figure B
C)Figure C
D)Figure D

A)Figure A
B)Figure B
C)Figure C
D)Figure D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which of the following graphs shows the correct effect on the consumption function when taxes increase in the economy?
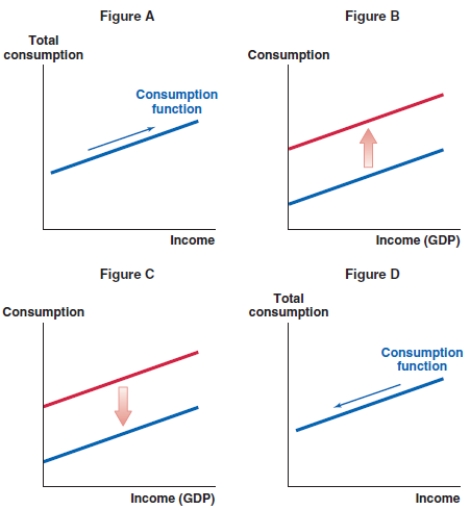
A)Figure A
B)Figure B
C)Figure C
D)Figure D

A)Figure A
B)Figure B
C)Figure C
D)Figure D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which of the following graphs shows the correct effect on the consumption function when consumers become optimistic about the state of the economy?
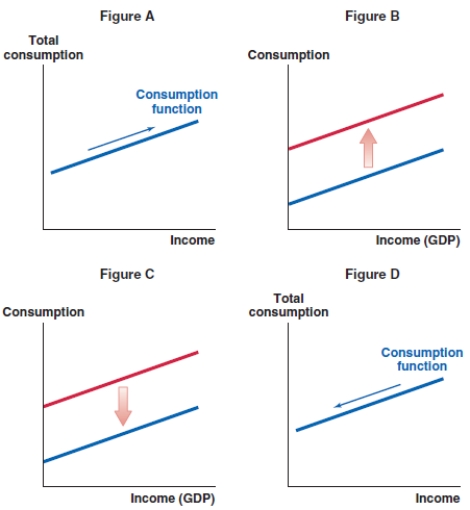
A)Figure A
B)Figure B
C)Figure C
D)Figure D

A)Figure A
B)Figure B
C)Figure C
D)Figure D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which of the following graphs shows the correct effect on the consumption function when consumers become pessimistic about the state of the economy?
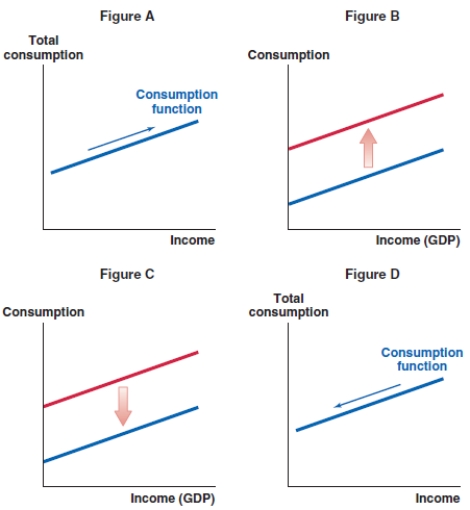
A)Figure A
B)Figure B
C)Figure C
D)Figure D

A)Figure A
B)Figure B
C)Figure C
D)Figure D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which of the following graphs shows the correct effect on the consumption function when consumer wealth decreases?
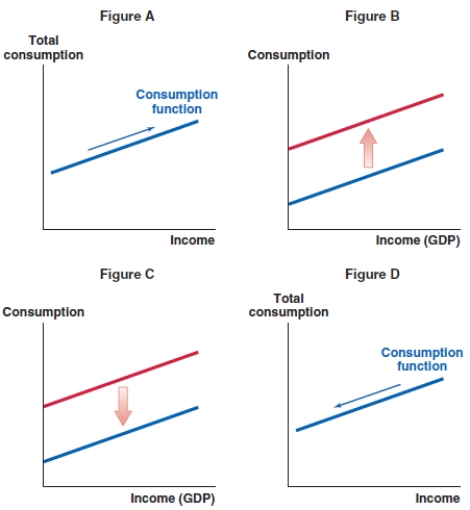
A)Figure A
B)Figure B
C)Figure C
D)Figure D

A)Figure A
B)Figure B
C)Figure C
D)Figure D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which of the following graphs shows the correct effect on the consumption function when consumer wealth increases?
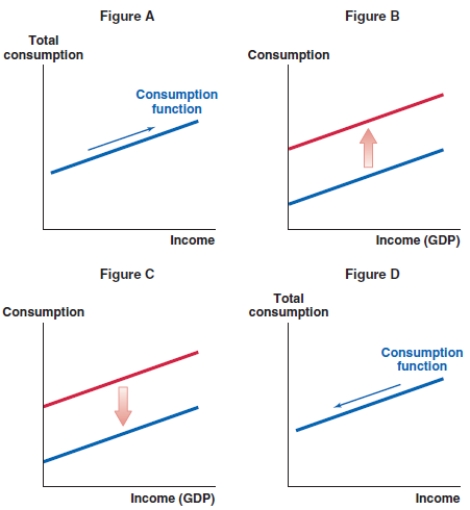
A)Figure A
B)Figure B
C)Figure C
D)Figure D

A)Figure A
B)Figure B
C)Figure C
D)Figure D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Suppose the federal minimum wage decreases in the United States. Which of the following graphs shows the correct effect on the consumption function?
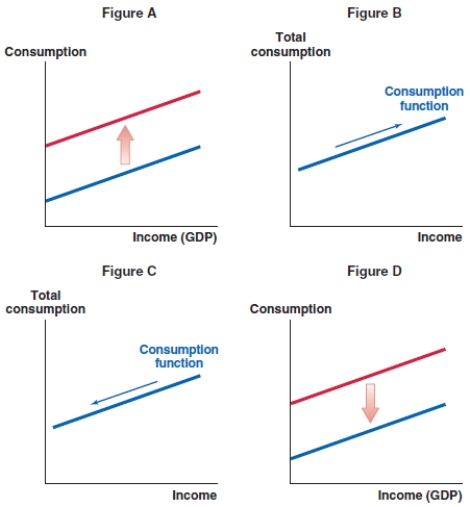
A)Figure A
B)Figure B
C)Figure C
D)Figure D

A)Figure A
B)Figure B
C)Figure C
D)Figure D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Suppose the London stock market experiences a significant boom. Which of the following graphs shows the correct effect on the consumption function in the United Kingdom?
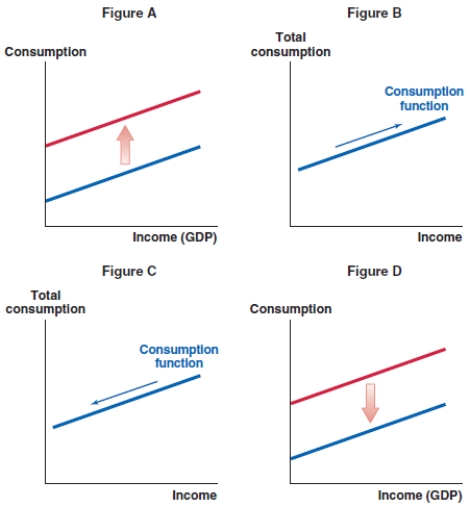
A)Figure A
B)Figure B
C)Figure C
D)Figure D

A)Figure A
B)Figure B
C)Figure C
D)Figure D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Suppose the Canadian job markets report is very strong and consumers begin to expect more economic growth and rising incomes. Which of the following graphs shows the correct effect on the consumption function in Canada?
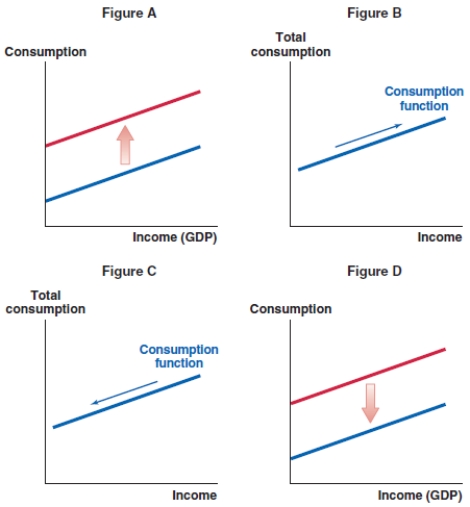
A)Figure A
B)Figure B
C)Figure C
D)Figure D

A)Figure A
B)Figure B
C)Figure C
D)Figure D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
What effect does a booming real estate market in China have on the consumption function in China?
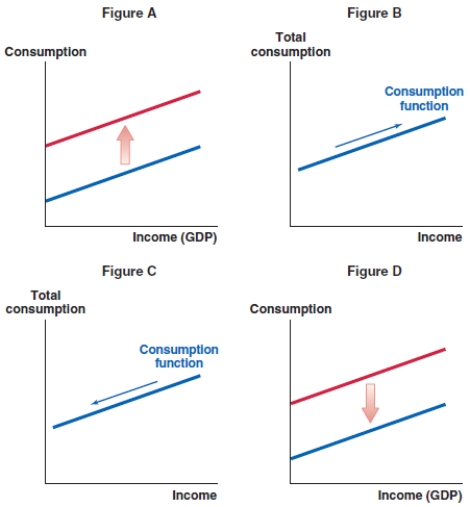
A)Figure A
B)Figure B
C)Figure C
D)Figure D

A)Figure A
B)Figure B
C)Figure C
D)Figure D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
If the real estate market in Kyiv, Ukraine, experiences a slump, what effect does this have on the consumption function in Ukraine?
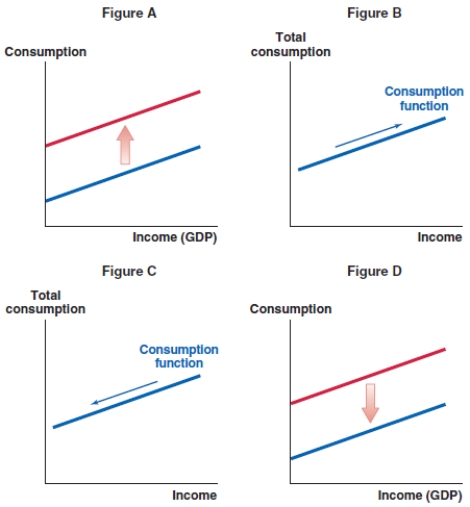
A)Figure A
B)Figure B
C)Figure C
D)Figure D

A)Figure A
B)Figure B
C)Figure C
D)Figure D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Suppose falling interest rates in Australia discourage saving. What effect does this have on the consumption function in Australia?
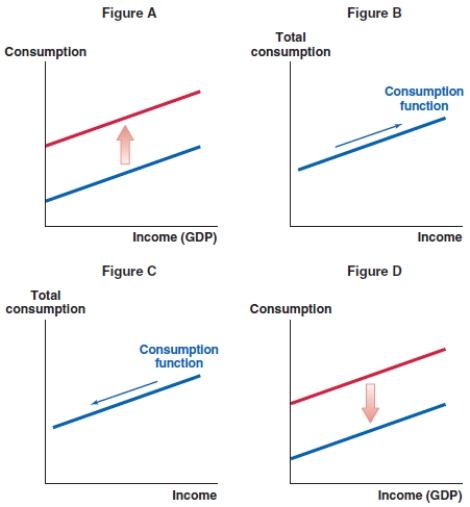
A)Figure A
B)Figure B
C)Figure C
D)Figure D

A)Figure A
B)Figure B
C)Figure C
D)Figure D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
What is the permanent income hypothesis?
A)the idea that the marginal propensity to consume does not change over time
B)the idea that consumption is based on permanent income rather than current income
C)the idea that temporary changes in income lead to the largest changes in total consumption
D)the idea that consumption is based on current income rather than permanent income
A)the idea that the marginal propensity to consume does not change over time
B)the idea that consumption is based on permanent income rather than current income
C)the idea that temporary changes in income lead to the largest changes in total consumption
D)the idea that consumption is based on current income rather than permanent income

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
What is the permanent income hypothesis?
A)the idea that the marginal propensity to consume does not change over time
B)the idea that people choose how much to consume based on their long-term average income
C)the idea that temporary changes in income lead to the largest changes in total consumption
D)the idea that people choose how much to consume based on their current income
A)the idea that the marginal propensity to consume does not change over time
B)the idea that people choose how much to consume based on their long-term average income
C)the idea that temporary changes in income lead to the largest changes in total consumption
D)the idea that people choose how much to consume based on their current income

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The permanent income hypothesis implies that young consumers with no savings and low income will fund permanent consumption by:
A)borrowing.
B)dissaving.
C)saving.
D)not paying taxes.
A)borrowing.
B)dissaving.
C)saving.
D)not paying taxes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The permanent income hypothesis implies that retired consumers with savings but no income will fund excess permanent consumption by:
A)borrowing.
B)dissaving.
C)saving.
D)not paying taxes.
A)borrowing.
B)dissaving.
C)saving.
D)not paying taxes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The permanent income hypothesis implies that consumers whose incomes exceed their permanent consumption will engage in:
A)borrowing.
B)dissaving.
C)saving.
D)not paying taxes.
A)borrowing.
B)dissaving.
C)saving.
D)not paying taxes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
If policy makers announce tax cuts, it is reasonable to expect that hand-to-mouth consumers will:
A)increase spending.
B)increase saving.
C)not pay taxes.
D)have less disposable income.
A)increase spending.
B)increase saving.
C)not pay taxes.
D)have less disposable income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
If there is a temporary rise in income, a consumption smoother will exhibit _____ in consumption, and a hand-to-mouth consumer will exhibit _____ in consumption.
A)a small increase; a large increase
B)a large increase; a large increase
C)no change; a large increase
D)a large increase; no change
A)a small increase; a large increase
B)a large increase; a large increase
C)no change; a large increase
D)a large increase; no change

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
If there is a permanent rise in income, a consumption smoother will exhibit _____ in consumption, and a hand-to-mouth consumer will exhibit _____ in consumption.
A)a small increase; a large increase
B)a large increase; a large increase
C)no change; a large increase
D)a large increase; no change
A)a small increase; a large increase
B)a large increase; a large increase
C)no change; a large increase
D)a large increase; no change

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
If there is an anticipated rise in income, a consumption smoother will exhibit _____ in consumption, and a hand-to-mouth consumer will exhibit _____ in consumption.
A)a small increase; a large increase
B)a large increase; a large increase
C)no change; a large increase
D)a large increase; no change
A)a small increase; a large increase
B)a large increase; a large increase
C)no change; a large increase
D)a large increase; no change

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
If there is news of a future rise in income, a consumption smoother will exhibit _____ in consumption, and a hand-to-mouth consumer will exhibit _____ in consumption.
A)a small increase; a large increase
B)a large increase; a large increase
C)no change; a large increase
D)a large increase; no change
A)a small increase; a large increase
B)a large increase; a large increase
C)no change; a large increase
D)a large increase; no change

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
If there is _____ rise in income, a hand-to-mouth consumer will exhibit no change in consumption.
A)a temporary
B)an announcement about a future
C)a permanent
D)an anticipated
A)a temporary
B)an announcement about a future
C)a permanent
D)an anticipated

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
If there is _____ rise in income, a consumption smoother will exhibit no change in consumption.
A)a temporary
B)an announced
C)a permanent
D)an anticipated
A)a temporary
B)an announced
C)a permanent
D)an anticipated

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
If a short-lived recession is expected, a consumption smoother will exhibit _____ in consumption.
A)a large increase
B)no change
C)a rising rate of increase
D)a large decrease
A)a large increase
B)no change
C)a rising rate of increase
D)a large decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
If there is _____ rise in income, a consumption smoother will exhibit a small change in consumption.
A)a temporary
B)an announced
C)a permanent
D)an anticipated
A)a temporary
B)an announced
C)a permanent
D)an anticipated

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Total consumption in the economy is composed of:
A)only permanent changes in consumption.
B)consumption by consumption smoothers only.
C)consumption by hand-to-mouth consumers only.
D)consumption by hand-to-mouth consumers and consumption by consumption smoothers.
A)only permanent changes in consumption.
B)consumption by consumption smoothers only.
C)consumption by hand-to-mouth consumers only.
D)consumption by hand-to-mouth consumers and consumption by consumption smoothers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
If there is _____ rise in income, there will be an intermediate increase in total consumption in the economy.
A)a permanent
B)zero
C)a temporary
D)no news of a
A)a permanent
B)zero
C)a temporary
D)no news of a

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
If there is _____ rise in income, there will be a large increase in total consumption in the economy.
A)a temporary
B)an announced
C)a permanent
D)an anticipated
A)a temporary
B)an announced
C)a permanent
D)an anticipated

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
If there is _____ rise in income, there will be an intermediate increase in total consumption in the economy.
A)no news of a
B)an announcement of a future
C)an anticipated
D)zero
A)no news of a
B)an announcement of a future
C)an anticipated
D)zero

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



