Deck 13: Augustine: God and the Soul
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/56
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 13: Augustine: God and the Soul
1
Although the glory of Rome faded as the early Middle Ages settled over western Europe, philosophy survived in Byzantium for another thousand years or so because
A) Persians invaded the Byzantium.
B) the Greek language predominated there, making it easy for the Byzantines to continue the study of Western philosophy.
C) Natives from Greece settled in Byzantium.
D) The Romans passed over the legacy of philosophy to the Byzantines.
A) Persians invaded the Byzantium.
B) the Greek language predominated there, making it easy for the Byzantines to continue the study of Western philosophy.
C) Natives from Greece settled in Byzantium.
D) The Romans passed over the legacy of philosophy to the Byzantines.
the Greek language predominated there, making it easy for the Byzantines to continue the study of Western philosophy.
2
The Abbasid caliphate united people of many different cultures and religions under a single ruler, which was instrumental in
A) the flowering of arts, science, and philosophy.
B) the consolidation of religious rule.
C) promoting fundamentalist ideas.
D) The suppression of religious sciences.
A) the flowering of arts, science, and philosophy.
B) the consolidation of religious rule.
C) promoting fundamentalist ideas.
D) The suppression of religious sciences.
the flowering of arts, science, and philosophy.
3
The word 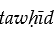 signifies
signifies
A) the absolute unity of God.
B) the superiority of Islam over other religions.
C) the principle of non-duality.
D) beliefs in duality.
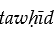 signifies
signifiesA) the absolute unity of God.
B) the superiority of Islam over other religions.
C) the principle of non-duality.
D) beliefs in duality.
the absolute unity of God.
4
To claim that Greek philosophy conveyed "the truth," 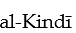 tried to show that it did not conflict
tried to show that it did not conflict
A) with common sense.
B) with the principles of philosophical demonstration.
C) with the principles of mathematics and astronomy.
D) with the teachings of Islam.
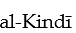 tried to show that it did not conflict
tried to show that it did not conflictA) with common sense.
B) with the principles of philosophical demonstration.
C) with the principles of mathematics and astronomy.
D) with the teachings of Islam.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
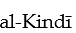 takes up the old problem of the one and the many in order to
takes up the old problem of the one and the many in order toA) prove that the universe is created.
B) show that God is the sole creator of the cosmos.
C) establish the tenets of Ptolemaic astronomy.
D) prove that the universe is eternal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
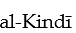 uses the tools of Aristotelian philosophy
uses the tools of Aristotelian philosophyA) to argue against the Aristotelian view of the eternity of the world, since Islam opposes it.
B) to show the world was created ex nihilo.
C) to establish the Platonic Forms.
D) to prove that geocentricism is false.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
According to 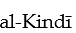 , the Active Intellect
, the Active Intellect
A) is a material intellect.
B) looks after the affairs of the celestial realm.
C) is a co-creator of the world.
D) thinks the abstract ideas.
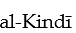 , the Active Intellect
, the Active IntellectA) is a material intellect.
B) looks after the affairs of the celestial realm.
C) is a co-creator of the world.
D) thinks the abstract ideas.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
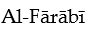 is called the "the Second Master"
is called the "the Second Master"A) because of his religious aspiration.
B) because of his logical and philosophical acumen.
C) because he was a great musician.
D) due to his Turkic or Persian ancestry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
According to 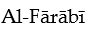 ,
,
A) religion hinders philosophical progress.
B) philosophy needs religion in order to affirm truth.
C) only philosophy can produce genuine knowledge.
D) both religion and philosophy can produce genuine knowledge.
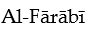 ,
,A) religion hinders philosophical progress.
B) philosophy needs religion in order to affirm truth.
C) only philosophy can produce genuine knowledge.
D) both religion and philosophy can produce genuine knowledge.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
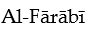 says that prophets come to know God
says that prophets come to know GodA) not through the rational demonstrations of philosophy, but
Through the revelatory visions of the imagination.
B) both through the rational demonstrations of philosophy and via
Revelatory visions.
C) through powerful intuitions.
D) through the rational demonstrations of philosophy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
For 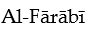 the highest form of knowledge is called
the highest form of knowledge is called
A) opinion.
B) absolute certitude.
C) divine inspiration.
D) Revelation.
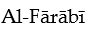 the highest form of knowledge is called
the highest form of knowledge is calledA) opinion.
B) absolute certitude.
C) divine inspiration.
D) Revelation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Avicenna's philosophical system can be characterized as
A) Aristotelian.
B) Aristotelianism suffused with Neoplatonic and Islamic elements.
C) Neoplatonic.
D) Platonic.
A) Aristotelian.
B) Aristotelianism suffused with Neoplatonic and Islamic elements.
C) Neoplatonic.
D) Platonic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
According to Avicenna, Aristotelian metaphysics overlooks the question of
A) form.
B) time.
C) essence.
D) existence.
A) form.
B) time.
C) essence.
D) existence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Aristotle's God, unlike that of Avicenna,
A) is a God of motion, not existence.
B) is a substance.
C) is a Platonic form.
D) is an immaterial intellect.
A) is a God of motion, not existence.
B) is a substance.
C) is a Platonic form.
D) is an immaterial intellect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
For Avicenna, the element of existence, whenever we find it in the external world,
A) is caused by the Active Intellect.
B) is uncaused.
C) is additional to a thing's essence.
D) is an active force of nature.
A) is caused by the Active Intellect.
B) is uncaused.
C) is additional to a thing's essence.
D) is an active force of nature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
To say that something's existence is possible in itself, as opposed to necessary in itself, is to say that
A) it is a combination of form and matter.
B) it requires both essence and existence from an external agency.
C) its essence does not require its existence.
D) its existence does not require its essence.
A) it is a combination of form and matter.
B) it requires both essence and existence from an external agency.
C) its essence does not require its existence.
D) its existence does not require its essence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
In Avicenna's view, God can
A) only know about universals.
B) only know about particulars.
C) know both particulars and universals.
D) know particulars by way of universals.
A) only know about universals.
B) only know about particulars.
C) know both particulars and universals.
D) know particulars by way of universals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The Flying Man thought experiment
A) proves the immateriality of the soul.
B) proves the separate existence of the soul.
C) Both A and B
D) shows the pre-existence of the soul before birth.
A) proves the immateriality of the soul.
B) proves the separate existence of the soul.
C) Both A and B
D) shows the pre-existence of the soul before birth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Methodic Experience is
A) is mode of perception.
B) experience of one thing following another over many repetitions, either always or with few exceptions.
C) is a sort of mystical experience.
D) a powerful epistemological tool to do philosophy.
A) is mode of perception.
B) experience of one thing following another over many repetitions, either always or with few exceptions.
C) is a sort of mystical experience.
D) a powerful epistemological tool to do philosophy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
For 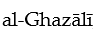 , certain knowledge is
, certain knowledge is
A) something in which there is no room for doubt, error or deception.
B) unattainable.
C) philosophical demonstration.
D) divine inspiration.
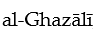 , certain knowledge is
, certain knowledge isA) something in which there is no room for doubt, error or deception.
B) unattainable.
C) philosophical demonstration.
D) divine inspiration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
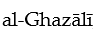
A) denies causality.
B) upholds occasionalism.
C) does not take a definite stance on the denial of causality.
D) affirms causality.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
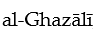 believes that
believes thatA) through mystical practice one can attain miraculous power.
B) Sufism has all the answers.
C) philosophy can help us discover God.
D) through mystical practices one can attain experiential knowledge of God and the world, which is ineffable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Islam departs from other religions in stating that the prophets are not divine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
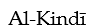 seems to have developed his fondness for the tactic of reductio ad absurdum by reading an Arabic translation of Euclid's geometrical treatise, the Elements.
seems to have developed his fondness for the tactic of reductio ad absurdum by reading an Arabic translation of Euclid's geometrical treatise, the Elements.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
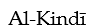 believes that the world is eternal.
believes that the world is eternal.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
According to 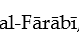 , the purpose of religion is to enable people who are incapable of philosophy to enter heaven and avoid hell by ensuring that they have right opinions about God, the universe, and the proper way to live.
, the purpose of religion is to enable people who are incapable of philosophy to enter heaven and avoid hell by ensuring that they have right opinions about God, the universe, and the proper way to live.
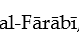 , the purpose of religion is to enable people who are incapable of philosophy to enter heaven and avoid hell by ensuring that they have right opinions about God, the universe, and the proper way to live.
, the purpose of religion is to enable people who are incapable of philosophy to enter heaven and avoid hell by ensuring that they have right opinions about God, the universe, and the proper way to live.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
For 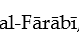 the material world emanates from God
the material world emanates from God
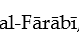 the material world emanates from God
the material world emanates from God
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The human intellect grasps universal forms only when the Active Intellect illuminates them.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
For 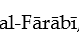 the highest form of knowledge involves scientific demonstrations of truths about abstract universals and the changeable, contingent features of the world.
the highest form of knowledge involves scientific demonstrations of truths about abstract universals and the changeable, contingent features of the world.
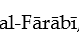 the highest form of knowledge involves scientific demonstrations of truths about abstract universals and the changeable, contingent features of the world.
the highest form of knowledge involves scientific demonstrations of truths about abstract universals and the changeable, contingent features of the world.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
From an Avicennan perspective, Aristotle takes existence for granted.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
For Avicenna, each person's soul comes into being when the person is born; it does not have pre-existence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
In Avicenna's view, induction can provide the foundations for genuine knowledge.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
For Avicenna, as for 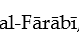 , the universe is both eternal and created.
, the universe is both eternal and created.
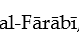 , the universe is both eternal and created.
, the universe is both eternal and created.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
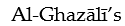 attack on philosophy successfully put an end to philosophy in the Islamic world.
attack on philosophy successfully put an end to philosophy in the Islamic world.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The Sufis were people who pursued knowledge of God through practices designed to achieve a higher state of consciousness.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
What is the principle of tawḥīd? How does it differ from the Christian doctrine of the Holy Trinity?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
How does al-Kindī explain the one-many relationship?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
How does al-Kindī prove that "multiplicity" is real?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
How does al-Kindī square the principle of tawḥīd with claim that the relationship of the one-many underpins all physical things?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
What is the role of religion in al-Fārābī's philosophy?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Describe al-Fārābī's concept of "absolute certitude."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
What is the role of the Active Intellect in ordinary and prophetic perception?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
How would you explain Avicenna's essence-existence distinction?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
What is the Flying Man argument supposed to prove?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
What is the difference between induction and methodic experience in Avicenna's philosophy?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
How does God know particulars according to Avicenna?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
What argument does al-Ghazālī give for doubting the things he learns by way of reasoning?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
What is the difference between Avicenna's and al-Ghazālī's way of understanding God's perfection?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The philosophers discussed in this chapter offer different views about the relationship between reason and revealed religion. Do you think any of them are correct? Why or why not?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Describe al-Fārābī's theory of emanation that features the Active Intellect as the tenth and the last intellect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Compare and contrast al-Kindī's, al-Fārābī's and Avicenna's views on the "eternity of the world."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Do you think al-Ghazālī denies causality? Would you consider him an occasionalist?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
What do you make of Avicenna's proof of the existence of God? Do you think it is defensible? Why or why not?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
How does Avicenna's essence-existence distinction reform Aristotle's hylomorphism?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The continuing importance of the basic outlooks of Plato and Aristotle can be illustrated through a comparison of Augustine and Aquinas, both Christians, but different in so many ways.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
After students have understood the proofs for God's existence in this chapter, you might ask them to choose one proof and write a half-page to a full page on it by way of critique. Your evaluation of their criticism should be a useful learning experience for them.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



