Deck 8: Tariffs
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/116
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 8: Tariffs
1
A revenue tariff is:
A) a tariff on domestically produced products.
B) a tariff levied on a product that is produced domestically that is designed to protect domestic industries.
C) a tariff levied on a product that is not domestically produced.
D) a tariff based on the profits of international firms doing business within a country.
E) only observed in developed countries.
A) a tariff on domestically produced products.
B) a tariff levied on a product that is produced domestically that is designed to protect domestic industries.
C) a tariff levied on a product that is not domestically produced.
D) a tariff based on the profits of international firms doing business within a country.
E) only observed in developed countries.
a tariff levied on a product that is not domestically produced.
2
The purpose of a protective tariff is:
A) to protect domestic consumers from harmful products.
B) to protect the international laws of commerce.
C) to protect the foreign country from anti-trust actions.
D) to protect the automobile industry
E) to protect domestic producers from foreign competition.
A) to protect domestic consumers from harmful products.
B) to protect the international laws of commerce.
C) to protect the foreign country from anti-trust actions.
D) to protect the automobile industry
E) to protect domestic producers from foreign competition.
to protect domestic producers from foreign competition.
3
Specific tariffs are collected:
A) only on industrial products.
B) only on pharmaceutical products.
C) only on products that arrive by train.
D) as a fixed amount of money per unit traded.
E) only on manufactured products.
A) only on industrial products.
B) only on pharmaceutical products.
C) only on products that arrive by train.
D) as a fixed amount of money per unit traded.
E) only on manufactured products.
as a fixed amount of money per unit traded.
4
A tariff levied as a certain amount per unit imported is known as:
A) a specific tariff.
B) a counter tariff.
C) a forgone tariff.
D) FAS
E) CIF.
A) a specific tariff.
B) a counter tariff.
C) a forgone tariff.
D) FAS
E) CIF.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A per unit tax on imported goods is called:
A) a specific tariff.
B) a per unit tariff.
C) an ad valorem tariff.
D) a compound tariff.
E) FAS.
A) a specific tariff.
B) a per unit tariff.
C) an ad valorem tariff.
D) a compound tariff.
E) FAS.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A tariff of 20% on imported goods is called:
A) a specific tariff.
B) a percentage tariff.
C) an ad valorem tariff.
D) a compound tariff.
E) a uniform tariff.
A) a specific tariff.
B) a percentage tariff.
C) an ad valorem tariff.
D) a compound tariff.
E) a uniform tariff.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
_____ is the barrier to trade that best distinguishes among gradations of a good or service.
A) Specific tariff
B) Voluntary export restraint
C) Ad valorem tariff
D) Import quota
E) F.A.S.
A) Specific tariff
B) Voluntary export restraint
C) Ad valorem tariff
D) Import quota
E) F.A.S.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Product "A" has an import value of $100. If a tariff of 10 percent of the product's value plus $10 per unit were imposed on "A", the result would be a(n) ____ of _____ .
A) ad valorem; $15
B) combined; $15
C) compound; $15
D) revenue; $17
E) compound; $20
A) ad valorem; $15
B) combined; $15
C) compound; $15
D) revenue; $17
E) compound; $20

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A tariff of 20% plus $1 per unit on imported goods is called:
A) a specific tariff.
B) a complex tariff.
C) an ad valorem tariff.
D) a compound tariff.
E) CIF.
A) a specific tariff.
B) a complex tariff.
C) an ad valorem tariff.
D) a compound tariff.
E) CIF.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
When a tariff is so high that imports are zero, the tariff is said to be:
A) effective.
B) exclusionary.
C) involuntary.
D) prohibitive.
E) excessive
A) effective.
B) exclusionary.
C) involuntary.
D) prohibitive.
E) excessive

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A tariff of ($250/import + 15% of the CIF value/import) is known as a(n) _____ tariff.
A) nonspecific
B) ad valorem
C) compound
D) specific
E) prohibitive
A) nonspecific
B) ad valorem
C) compound
D) specific
E) prohibitive

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The Free alongside (FAS) method of valuing imports:
A) defines the price of the imported good as the foreign market price before it is loaded into the ship, train, or plane for shipment to the importing country.
B) defines the imported price as the price in the foreign market including the cost of loading it onto the ship, train, or plane for shipment to the importing country.
C) defines the imported price as the price including all inter-country charges up to the importing country's port of entry.
D) All of the above
E) None of the above
A) defines the price of the imported good as the foreign market price before it is loaded into the ship, train, or plane for shipment to the importing country.
B) defines the imported price as the price in the foreign market including the cost of loading it onto the ship, train, or plane for shipment to the importing country.
C) defines the imported price as the price including all inter-country charges up to the importing country's port of entry.
D) All of the above
E) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The free on board (FOB) method of valuing imports:
A) defines the price of the imported good as the foreign market price before it is loaded into the ship, train, or plane for shipment to the importing country.
B) defines the imported price as the price in the foreign market including the cost of loading it onto the ship, train, or plane for shipment to the importing country.
C) defines the imported price as the price including all inter-country charges up to the importing country's port of entry.
D) All of the above
E) None of the above
A) defines the price of the imported good as the foreign market price before it is loaded into the ship, train, or plane for shipment to the importing country.
B) defines the imported price as the price in the foreign market including the cost of loading it onto the ship, train, or plane for shipment to the importing country.
C) defines the imported price as the price including all inter-country charges up to the importing country's port of entry.
D) All of the above
E) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The FOB value of imports includes:
A) the value of the product alongside the carrier.
B) the expense of loading for shipment.
C) all freight and insurance costs to transport the goods to the importing country.
D) the sum of a and b.
E) the sum of b and c.
A) the value of the product alongside the carrier.
B) the expense of loading for shipment.
C) all freight and insurance costs to transport the goods to the importing country.
D) the sum of a and b.
E) the sum of b and c.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
CIF stands for:
A) captain in front.
B) capital is free.
C) cost, insurance, and freight.
D) a form of grease payment.
E) None of the above
A) captain in front.
B) capital is free.
C) cost, insurance, and freight.
D) a form of grease payment.
E) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The cost, insurance and freight (CIF) method of valuing imports:
A) defines the price of the imported good as the foreign market price before it is loaded into the ship, train, or plane for shipment to the importing country.
B) defines the imported price as the price in the foreign market including the cost of loading it onto the ship, train, or plane for shipment to the importing country.
C) defines the imported price as the price including all inter-country charges up to the importing country's port of entry.
D) All of the above
E) None of the above
A) defines the price of the imported good as the foreign market price before it is loaded into the ship, train, or plane for shipment to the importing country.
B) defines the imported price as the price in the foreign market including the cost of loading it onto the ship, train, or plane for shipment to the importing country.
C) defines the imported price as the price including all inter-country charges up to the importing country's port of entry.
D) All of the above
E) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Almost all countries in the world use which of the following definitions to assess the value of an import?
A) TTK
B) JIT
C) CIF
D) JMK
E) FOB
A) TTK
B) JIT
C) CIF
D) JMK
E) FOB

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The availability of alternative definitions of "price" such as FAS, CIF, and FOB creates complications regarding the administration of the _____ tariff.
A) ad valorem
B) generic
C) export
D) specific
E) prohibitive
A) ad valorem
B) generic
C) export
D) specific
E) prohibitive

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following is not a method of valuing imports for tariff purposes?
A) Free alongside (FAS) price
B) Free on board (FOB) price
C) Cost, insurance and freight (CIF) price
D) WTO price
E) None of the above
A) Free alongside (FAS) price
B) Free on board (FOB) price
C) Cost, insurance and freight (CIF) price
D) WTO price
E) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The difference between the price producers are willing to accept for the product and the price producers actually receive for the product is known as:
A) producer surplus.
B) consumer surplus.
C) price discrimination.
D) the firm's profit.
E) market surplus.
A) producer surplus.
B) consumer surplus.
C) price discrimination.
D) the firm's profit.
E) market surplus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Consumer surplus is equal to the:
A) area under the demand curve and above the supply curve.
B) area under the demand curve.
C) area under the supply curve.
D) area under the demand curve and above the equilibrium price.
E) price times quantity.
A) area under the demand curve and above the supply curve.
B) area under the demand curve.
C) area under the supply curve.
D) area under the demand curve and above the equilibrium price.
E) price times quantity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The triangular area above the supply curve and below the market price is known as:
A) consumer surplus.
B) producer surplus.
C) oligopoly.
D) marginal revenue.
E) marginal cost.
A) consumer surplus.
B) producer surplus.
C) oligopoly.
D) marginal revenue.
E) marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Consumer surplus will tend to rise if:
A) the market price falls.
B) the market price rises.
C) there are absolutely no imports.
D) there are absolutely no exports.
E) autarky exists.
A) the market price falls.
B) the market price rises.
C) there are absolutely no imports.
D) there are absolutely no exports.
E) autarky exists.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A reduction in the price of a commodity due to an increase in supply will:
A) increase consumer surplus.
B) reduce consumer surplus.
C) leave consumer surplus unchanged.
D) cause the demand curve to shift to the right.
E) not change producer surplus.
A) increase consumer surplus.
B) reduce consumer surplus.
C) leave consumer surplus unchanged.
D) cause the demand curve to shift to the right.
E) not change producer surplus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The triangular area below the demand curve and above the market price is known as:
A) producer surplus.
B) consumer surplus.
C) average total cost.
D) marginal cost.
E) total revenue.
A) producer surplus.
B) consumer surplus.
C) average total cost.
D) marginal cost.
E) total revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Producer surplus is equal to the:
A) area under the demand curve and above the supply curve.
B) area above the supply curve and below the equilibrium price.
C) area under the demand curve.
D) area under the supply curve.
E) area above the demand curve.
A) area under the demand curve and above the supply curve.
B) area above the supply curve and below the equilibrium price.
C) area under the demand curve.
D) area under the supply curve.
E) area above the demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
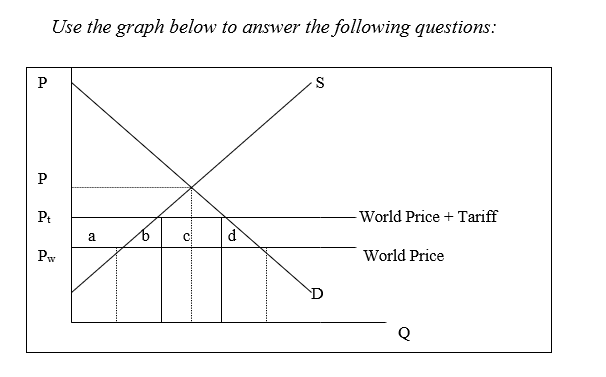
-The consumer surplus gained by moving from autarky to free trade is represented by:
A) a + b + c + d.
B) a + b.
C) a + c.
D) a only.
E) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28

-The producer surplus lost by moving from autarky to free trade is represented by:
A) a.
B) b.
C) c.
D) d
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29

-According to the graph, imports:
A) have caused the price to fall from P to Pw.
B) have caused consumer surplus to rise.
C) have caused producer surplus to fall.
D) all of the above
E) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30

-The introduction of a tariff would raise the price from:
A) Pw to Pt.
B) Pt to P.
C) Pw to P.
D) P to zero.
E) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31

-Without a tariff the price of imports would be:
A) a + b + c + d.
B) b + d.
C) P.
D) Pw.
E) zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32

-When a specific tariff is placed on an item, compared to free trade consumers lose:
A) only a.
B) only b.
C) only c.
D) only d.
E) a + b + c + d.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33

-The loss of consumer surplus due to the tariff is:
A) only a.
B) only b.
C) only c.
D) only d.
E) a + b + c + d.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34

-A tariff on imports would reduce consumer surplus by:
A) a + b.
B) b + c.
C) a + b + c.
D) a + b + c + d.
E) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35

-With the tariff, government revenue is:
A) a.
B) b.
C) c.
D) d.
E) is not represented in the graph.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36

-The imposition of a tariff would yield tariff revenue of:
A) a.
B) b.
C) c.
D) d.
E) a + b.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37

-The increase in producer surplus attributable to the tariff is:
A) a.
B) b.
C) c.
D) d.
E) b + d.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38

-The gain in producer's surplus that occurs because of the tariff is:
A) a.
B) b + c.
C) c.
D) a + b + c + d.
E) only d.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39

-The losses to society because of the inefficient allocation of resources attributable to the tariff is:
A) a.
B) b.
C) c.
D) b + c.
E) a + b.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40

-The dead weight loss of the tariff is:
A) a + d.
B) b + d.
C) c + d.
D) b + c.
E) only c.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
When a tariff is imposed on imported goods or services, the consumer surplus in the domestic market _____ and producer surplus in the domestic market _____ .
A) rises; falls
B) rises; rises
C) falls; falls
D) falls; rises
E) falls; stays the same
A) rises; falls
B) rises; rises
C) falls; falls
D) falls; rises
E) falls; stays the same

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
When a tariff is imposed on imported goods and services, the _____ in consumer surplus is _____ the ______ in producer surplus.
A) increase; less than, increase
B) increase; less than, decrease
C) decrease; greater than, increase
D) decrease; less than, increase
E) increase; the same as; decrease
A) increase; less than, increase
B) increase; less than, decrease
C) decrease; greater than, increase
D) decrease; less than, increase
E) increase; the same as; decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
When a tariff is imposed on imports, domestic producer surplus:
A) falls.
B) rises.
C) stays the same.
D) becomes negative.
E) is indeterminate.
A) falls.
B) rises.
C) stays the same.
D) becomes negative.
E) is indeterminate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Tariffs cause a redistribution of income from:
A) the government to producers and consumers.
B) consumers and the government to producers.
C) producers and consumers to the government.
D) consumers to producers and the government.
E) producers to governments.
A) the government to producers and consumers.
B) consumers and the government to producers.
C) producers and consumers to the government.
D) consumers to producers and the government.
E) producers to governments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
If a small country imposes a tariff:
A) the imported product price rises by more than the tariff.
B) the imported product price rises by exactly the amount of the tariff.
C) the imported product price rise by less than the amount of the tariff.
D) the imported product price falls by the amount of the tariff.
E) the effects are the same for a large country.
A) the imported product price rises by more than the tariff.
B) the imported product price rises by exactly the amount of the tariff.
C) the imported product price rise by less than the amount of the tariff.
D) the imported product price falls by the amount of the tariff.
E) the effects are the same for a large country.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
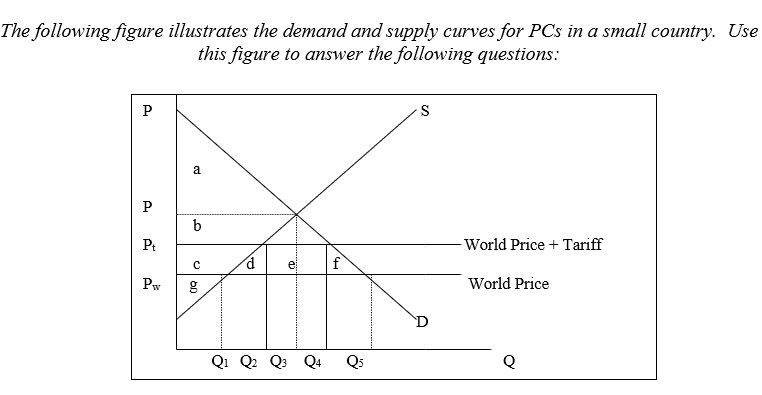
-With no trade the amount of domestically produced PCs is:
A) Q1.
B) Q2.
C) Q3.
D) Q4.
E) Q1 to Q3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47

-With no trade the country's producer surplus is:
A) area a.
B) area b.
C) area c.
D) areas b + c.
E) areas b + c + g.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48

-With no trade the country's consumer surplus is:
A) area a.
B) area a + b.
C) area b.
D) area c.
E) area a + b + c.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49

-With free trade the country imports:
A) Q1.
B) Q2.
C) Q3.
D) Q1 to Q2.
E) Q1 to Q5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50

-With free trade the country's producers surplus is:
A) area a.
B) area b.
C) area c.
D) area d.
E) area g.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51

-With a tariff imposed on PCs, the country imports:
A) Q1.
B) Q2.
C) Q3.
D) Q4.
E) Q2 to Q4.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52

-The loss of consumer surplus due to the tariff is:
A) area c.
B) area d.
C) area c + d.
D) area c + d + e.
E) area c + d + e + f.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53

-The amount of producer surplus domestic producers gain as a result of the tariff is:
A) area c.
B) area c + d.
C) area d.
D) area f.
E) area c + d + e.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54

-The amount of revenue the government collects as a result of the tariff is:
A) area c.
B) area d.
C) area e.
D) area f.
E) area e + f.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55

-The dead-weight loss of the tariff to the country is:
A) area c + d + e + f.
B) area d + e + f.
C) area d + f.
D) area d.
E) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
If a large country imposes a tariff:
A) the imported product price rises by more than the tariff.
B) the imported product price rises by exactly the amount of the tariff.
C) the imported product price rises by less than the amount of the tariff.
D) the imported product price falls by the amount of the tariff.
E) the effects are same as for a small country.
A) the imported product price rises by more than the tariff.
B) the imported product price rises by exactly the amount of the tariff.
C) the imported product price rises by less than the amount of the tariff.
D) the imported product price falls by the amount of the tariff.
E) the effects are same as for a small country.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The imposition of an import tariff by a large country can cause:
A) a decrease in imports.
B) an increase in the country's welfare.
C) a decrease in the country's welfare.
D) All of the above
E) None of the above
A) a decrease in imports.
B) an increase in the country's welfare.
C) a decrease in the country's welfare.
D) All of the above
E) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Assume that domestic calculators are made with foreign parts that cost $80 and that the calculators retail for $90. If in a small country situation if a tariff of $1 is placed on the foreign parts, then the effective rate of protection is:
A) -10%.
B) 10%.
C) 50%.
D) 80%.
E) 100%.
A) -10%.
B) 10%.
C) 50%.
D) 80%.
E) 100%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Assume that U.S.-assembled computers are made with $1,000 of components and sell for $2,000 in the U.S. Now, a $200 tariff is imposed on foreign computers. The nominal tariff is ______ and the effective rate of protection is ________ .
A) 10%; 10%
B) 5%; 20%
C) 20%; 50%
D) 10%; 20%
A) 10%; 10%
B) 5%; 20%
C) 20%; 50%
D) 10%; 20%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Consider three goods: raw leather, leather wallets, and tanned leather. Assume that an industrial country employs a tariff structure using these ad valorem tariff rates on imports of 0%, 4.5%, and 7.9%. If this hypothetical industrial country uses a tariff structure similar to most other industrial countries, these rates will be placed on _____, _____, and ____, respectively.
A) raw leather, leather wallets, tanned leather
B) leather wallets, raw leather, tanned leather
C) raw leather, tanned leather, leather wallets
D) tanned leather, leather wallets, raw leather
E) domestic producers, importers, exporters
A) raw leather, leather wallets, tanned leather
B) leather wallets, raw leather, tanned leather
C) raw leather, tanned leather, leather wallets
D) tanned leather, leather wallets, raw leather
E) domestic producers, importers, exporters

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
A domestically produced DVD player sells for $500, including $250 of imported components. A tariff of 20% is imposed on the imported DVD player. What is the effective rate of protection?
A) 20%
B) 30%
C) 40%
D) 60%
E) 62%
A) 20%
B) 30%
C) 40%
D) 60%
E) 62%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
A domestically produced DVD player sells for $500, including $250 of imported components. A tariff of 20% is imposed on the imported DVD player, and a tariff of 10% is imposed on the imported components. What is the effective rate of protection?
A) 20%
B) 25%
C) 30%
D) 40%
E) 52%
A) 20%
B) 25%
C) 30%
D) 40%
E) 52%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Which of the following components is not necessary to determine the effective rate of protection?
A) The tariff on the imported final product
B) The tariff on the imported components
C) The percentage of imported components used in producing the final product
D) All of the above
E) None of the above
A) The tariff on the imported final product
B) The tariff on the imported components
C) The percentage of imported components used in producing the final product
D) All of the above
E) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Tariff escalation encourages:
A) final processing of the product in the home country.
B) final processing of the product in developing countries.
C) final processing of the product and processing of component production in the home country.
D) final processing of the product and processing of component production in developing countries.
E) industrial development in developing countries.
A) final processing of the product in the home country.
B) final processing of the product in developing countries.
C) final processing of the product and processing of component production in the home country.
D) final processing of the product and processing of component production in developing countries.
E) industrial development in developing countries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Tariff escalation results from:
A) tariffs increasing as the percent of the value of product imported decreases.
B) low tariffs on imported inputs and high tariffs on imported final products.
C) tariffs increasing on fuel products whose value is higher than the products produced domestically.
D) high tariffs on imported inputs and low tariffs on imported final products.
E) The existence of FAS tariffs.
A) tariffs increasing as the percent of the value of product imported decreases.
B) low tariffs on imported inputs and high tariffs on imported final products.
C) tariffs increasing on fuel products whose value is higher than the products produced domestically.
D) high tariffs on imported inputs and low tariffs on imported final products.
E) The existence of FAS tariffs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Which of the following is not a common argument for tariffs?
A) National defense
B) Infant government
C) Senile industry
D) Senile government
E) Health and safety
A) National defense
B) Infant government
C) Senile industry
D) Senile government
E) Health and safety

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which of the following is not a common argument for tariffs?
A) Increase the number of jobs in the economy.
B) National defense.
C) Infant industry.
D) Senile industry.
E) None of the above
A) Increase the number of jobs in the economy.
B) National defense.
C) Infant industry.
D) Senile industry.
E) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
A production subsidy:
A) increases domestic output of the industry.
B) decreases domestic output of an industry.
C) is less efficient than an equivalent tariff.
D) is more costly than an equivalent tariff.
E) is always necessary.
A) increases domestic output of the industry.
B) decreases domestic output of an industry.
C) is less efficient than an equivalent tariff.
D) is more costly than an equivalent tariff.
E) is always necessary.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which method of valuation for tariffs includes transportation changes?
A) FAS
B) FOB
C) CIF
D) OMB
E) EXF
A) FAS
B) FOB
C) CIF
D) OMB
E) EXF

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Which type of tariff is easiest to administer?
A) specific
B) ad valorem
C) compound
D) FAS
E) FOB
A) specific
B) ad valorem
C) compound
D) FAS
E) FOB

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
A tariff is simply a tax on exported goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
A revenue tariff is a tax on goods that are not domestically produced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
In a developing country tariffs may be easier to collect than income or sales taxes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
During the nineteenth century, tariffs were the major source of revenue of the U.S. government.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Specific tariffs work best on products that essentially are homogeneous.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
A constant 4-cent tariff on gasoline would be referred to as a specific tariff.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Ad valorem tariffs are a regressive form of taxation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
A tariff levied as a percentage of the value of the imported item is known as an ad valorem tariff.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Ad valorem tariffs are most useful if the product category is characterized by vertical product differentiation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
A compound tariff is a theoretical possibility that never occurs in practice.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



