Deck 12: International Trade and Economic Growth
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/117
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 12: International Trade and Economic Growth
1
The goal of economic development is for the _____ countries to achieve a standard of living roughly equivalent to that of _____ countries.
A) developed, developing
B) developing, developed
C) middle-income, low income
D) high-income, middle income
E) middle-income, low-income
A) developed, developing
B) developing, developed
C) middle-income, low income
D) high-income, middle income
E) middle-income, low-income
developing, developed
2
In the low- and middle income countries _____ and _____ of the population respectively are illiterate.
A) 5%, 10%
B) 7%, 14%
C) 16%, 20%
D) 17%, 38%
E) 48%, 57%
A) 5%, 10%
B) 7%, 14%
C) 16%, 20%
D) 17%, 38%
E) 48%, 57%
17%, 38%
3
GDP per capita in the high-income countries is approximately:
A) $451.
B) $2,000.
C) $15,000.
D) $38,404.
A) $451.
B) $2,000.
C) $15,000.
D) $38,404.
$38,404.
4
GDP per capita in low-income countries is _____ per year.
A) $635
B) $2,000
C) $5,000
D) $7,500
A) $635
B) $2,000
C) $5,000
D) $7,500

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following is a precondition for economic growth?
A) a high level of technology
B) a high K/L ratio
C) the rule of law
D) free trade
E) a civil war
A) a high level of technology
B) a high K/L ratio
C) the rule of law
D) free trade
E) a civil war

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The rule of law is important to economic growth as it is necessary for the enforcement of.
A) free trade
B) emigration
C) contracts
D) industrial policy
E) social security
A) free trade
B) emigration
C) contracts
D) industrial policy
E) social security

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following is not one of the factors of production?
A) land
B) labor
C) capital
D) property rights
E) rule of law
A) land
B) labor
C) capital
D) property rights
E) rule of law

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following countries has a large amount of economic freedom?
A) Hong Kong
B) Libya
C) Zimbabwe
D) Laos
E) Cuba
A) Hong Kong
B) Libya
C) Zimbabwe
D) Laos
E) Cuba

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
In order for GDP per capita to grow, it is necessary for _____ growth to be in excess of _____ growth.
A) population, GDP
B) labor, capital
C) GDP, population
D) land, capital
E) land, labor
A) population, GDP
B) labor, capital
C) GDP, population
D) land, capital
E) land, labor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The graphical relationship between real GDP and the size of the labor force is known as:
A) the Kuznets curve.
B) the production function.
C) the technology curve.
D) the demand curve
E) the Kuznets curve..
A) the Kuznets curve.
B) the production function.
C) the technology curve.
D) the demand curve
E) the Kuznets curve..

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The production function:
A) is linear.
B) is undefined for low-income countries.
C) slopes downward and to the right.
D) slopes upward to the right.
E) has a negative slope.
A) is linear.
B) is undefined for low-income countries.
C) slopes downward and to the right.
D) slopes upward to the right.
E) has a negative slope.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
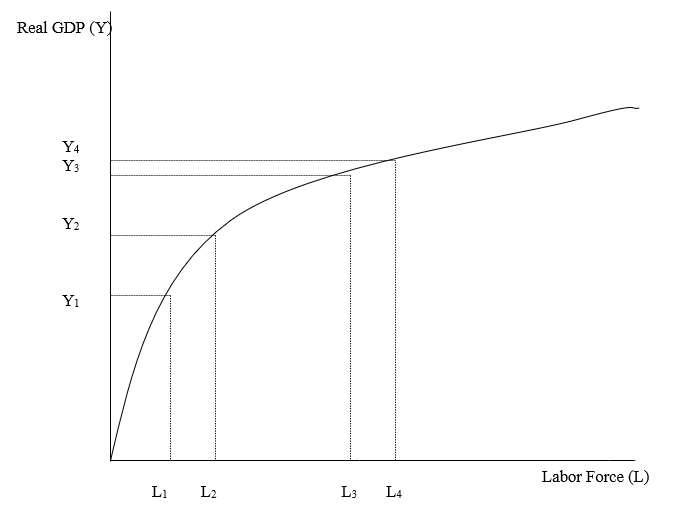
-In the figure above, an increase in the labor force:
A) increases real GDP.
B) decreases real GDP.
C) shifts the production function upward.
D) shifts the production function downward.
E) L never changes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13

-In the figure above, which of the following would cause an upward shift in the production function?
A) an increase in the labor force
B) a decrease in the labor force
C) an increase in the capital stock
D) a decrease in the capital stock
E) a decrease in technology.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14

-In the figure above, which of the following would cause an increase in real GDP?
A) a decline in the labor force
B) an improvement in technology
C) a decrease in the capital stock
D) a decline in technology
E) no change in the labor force or capital stock.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15

-In the figure above, an increase in real GDP with an unchanged labor force could happen as a result of:
A) a smaller capital stock.
B) a higher level of technology.
C) a lower level of technology.
D) higher oil prices.
E) high tariffs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
An improvement in technology would tend to:
A) cause a movement to the right along an existing production function.
B) cause a movement to the left along an existing production function.
C) cause an upward shift in the production function.
D) have no effect on the production function.
E) None of the above
A) cause a movement to the right along an existing production function.
B) cause a movement to the left along an existing production function.
C) cause an upward shift in the production function.
D) have no effect on the production function.
E) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The theory of comparative advantage indicates that international trade should increase the output of the economy by moving resources from _____ to _____ industries.
A) comparative advantage, comparative disadvantage
B) comparative disadvantage, comparative advantage
C) smaller, larger
D) efficient, inefficient
E) business to government
A) comparative advantage, comparative disadvantage
B) comparative disadvantage, comparative advantage
C) smaller, larger
D) efficient, inefficient
E) business to government

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
An increase in economic growth that cannot be accounted for by increases in either the labor force or the capital stock is known as an increase in:
A) inefficiency.
B) total factor productivity.
C) labor input.
D) managerial productivity.
E) government efficiency.
A) inefficiency.
B) total factor productivity.
C) labor input.
D) managerial productivity.
E) government efficiency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
FDI in a developing country would tend to cause:
A) a reduced level of technology.
B) exploitation of workers.
C) an upward shift of the production function.
D) lower tariff revenues.
E) higher tariffs.
A) a reduced level of technology.
B) exploitation of workers.
C) an upward shift of the production function.
D) lower tariff revenues.
E) higher tariffs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following is responsible for the largest movements of FDI into developing countries?
A) UNIDO
B) UNCTAD
C) MNCs
D) the WTO
E) the IMF
A) UNIDO
B) UNCTAD
C) MNCs
D) the WTO
E) the IMF

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following would not cause an upward shift in the production function in a developing country?
A) FDI
B) technology transfers
C) increasing openness
D) immigration
E) autarky
A) FDI
B) technology transfers
C) increasing openness
D) immigration
E) autarky

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Importing and exporting of goods and services can lead to increases in specialization and knowledge that can:
A) decrease GDP per capita.
B) increase total factor productivity.
C) shift the production function downwards.
D) cause an increase in population.
E) decrease total factor productivity.
A) decrease GDP per capita.
B) increase total factor productivity.
C) shift the production function downwards.
D) cause an increase in population.
E) decrease total factor productivity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following refers to natural resources or the ability to produce certain agricultural products?
A) primary products
B) cheap products
C) import substitution
D) total factor productivity promotion
E) trade policy
A) primary products
B) cheap products
C) import substitution
D) total factor productivity promotion
E) trade policy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The possession of primary products in a developing country could:
A) provide a convenient source of revenue for the government.
B) reduce the amount of foreign exchange available.
C) make the development of infrastructure more difficult.
D) not influence industrial development.
E) None of the above
A) provide a convenient source of revenue for the government.
B) reduce the amount of foreign exchange available.
C) make the development of infrastructure more difficult.
D) not influence industrial development.
E) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
In many cases, both the demand and supply of primary products are _____ .
A) elastic
B) inelastic
C) perfectly elastic
D) undefined
E) cannot be changed
A) elastic
B) inelastic
C) perfectly elastic
D) undefined
E) cannot be changed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
If primary products are a high percentage of a country's exports then large changes in the price of these commodities could influence the _____ .
A) tariff
B) terms of trade
C) effective rate of protection
D) structure of protection
E) industrial structure
A) tariff
B) terms of trade
C) effective rate of protection
D) structure of protection
E) industrial structure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following is a cartel that attempts to influence the world price of crude oil?
A) IEA
B) OPEC
C) UNOCAL
D) EXXON
E) BP
A) IEA
B) OPEC
C) UNOCAL
D) EXXON
E) BP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The development strategy based on developing industries that will reduce imports is known as:
A) primary production.
B) import substitution.
C) export promotion.
D) FDI intervention.
E) property rights protection
A) primary production.
B) import substitution.
C) export promotion.
D) FDI intervention.
E) property rights protection

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following is not associated with an import substitution development strategy?
A) high tariffs
B) quotas
C) government subsidies to manufacturing
D) replacing imports with domestic producton
E) lower prices for consumers
A) high tariffs
B) quotas
C) government subsidies to manufacturing
D) replacing imports with domestic producton
E) lower prices for consumers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
An import substitution strategy tends to lead to:
A) faster economic growth.
B) more jobs in the economy.
C) greater efficiency in the use of resources.
D) more rent seeking behavior.
E) less protectionism
A) faster economic growth.
B) more jobs in the economy.
C) greater efficiency in the use of resources.
D) more rent seeking behavior.
E) less protectionism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A development strategy based on developing industries in line with a country's comparative advantage is known as:
A) Dutch development.
B) import substitution.
C) export promotion.
D) WTO experiment.
E) industrial protection.
A) Dutch development.
B) import substitution.
C) export promotion.
D) WTO experiment.
E) industrial protection.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following regions has tended to grow fastest during the 1990s?
A) East Asia
B) Latin America
C) Central America
D) Africa
E) the Middle East
A) East Asia
B) Latin America
C) Central America
D) Africa
E) the Middle East

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following statements is incorrect?
A) Manufacturing requires very little infrastructure.
B) Manufacturing usually is more infrastructure intensive than agriculture.
C) Manufacturing doesn't require increases in human capital.
D) Low taxes on manufacturing will increase exports.
E) None of the above
A) Manufacturing requires very little infrastructure.
B) Manufacturing usually is more infrastructure intensive than agriculture.
C) Manufacturing doesn't require increases in human capital.
D) Low taxes on manufacturing will increase exports.
E) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
High tariffs are a feature of which of the following development strategies?
A) primary products
B) import substitution
C) export promotion
D) WTO promotion
E) industrial protection
A) primary products
B) import substitution
C) export promotion
D) WTO promotion
E) industrial protection

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Economies using an export promotion development strategy tend to:
A) grow more slowly.
B) create more jobs.
C) earn less foreign exchange.
D) not import products for which that country has a comparative disadvantage.
E) not import commodities.
A) grow more slowly.
B) create more jobs.
C) earn less foreign exchange.
D) not import products for which that country has a comparative disadvantage.
E) not import commodities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The correct term for "foreign aid" is:
A) foreign exchange.
B) unilateral transfers.
C) grants.
D) official development assistance (ODA).
E) IMF.
A) foreign exchange.
B) unilateral transfers.
C) grants.
D) official development assistance (ODA).
E) IMF.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following is not part of basic infrastructure in a developing country?
A) water systems
B) electricity systems
C) urban transportation systems
D) IT systems
E) UNIDO
A) water systems
B) electricity systems
C) urban transportation systems
D) IT systems
E) UNIDO

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
ODA in the world economy is approximately:
A) $20 billion.
B) $106 billion.
C) $500 billion.
D) $1 trillion.
E) $10 trillion
A) $20 billion.
B) $106 billion.
C) $500 billion.
D) $1 trillion.
E) $10 trillion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
ODA is less than _____ percent of the collective GDPs of the developing countries.
A) 1
B) 3
C) 5
D) 10
E) 13
A) 1
B) 3
C) 5
D) 10
E) 13

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
U.S. ODA is approximately _____ billion.
A) $1
B) $25
C) $50
D) $77
E) $83
A) $1
B) $25
C) $50
D) $77
E) $83

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
ODA as a percentage of GDP for all developed countries is approximately _____ .
A) 0.10
B) 0.29
C) 0.52
D) 0.86
E) 1.05
A) 0.10
B) 0.29
C) 0.52
D) 0.86
E) 1.05

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
A transfer of money from a developed country government to a developing country where there is no repayment involved is known as a _____ .
A) grant
B) loan
C) policy statement
D) nonofficial ODA
E) terms of trade
A) grant
B) loan
C) policy statement
D) nonofficial ODA
E) terms of trade

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
ODA that involves restrictions on how and where the aid may be spent is known as:
A) corrupt aid.
B) mislaid aid.
C) tied aid.
D) useless aid.
E) dead aid.
A) corrupt aid.
B) mislaid aid.
C) tied aid.
D) useless aid.
E) dead aid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which of the following part of the World Bank primarily makes loans to middle-income countries for infrastructure?
A) IBRD
B) IDA
C) MIGA
D) UNCTAD
E) UNIDO
A) IBRD
B) IDA
C) MIGA
D) UNCTAD
E) UNIDO

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which of the following part of the World Bank primarily makes loans to low-income countries?
A) IBRD
B) IDA
C) UN
D) IADB
E) UNCTAD
A) IBRD
B) IDA
C) UN
D) IADB
E) UNCTAD

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which part of the World Bank makes loans to private sector firms in developing countries?
A) IBRD
B) IDA
C) IFC
D) MIGA
E) IMF
A) IBRD
B) IDA
C) IFC
D) MIGA
E) IMF

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
During the 1980s and 1990s, the World Bank was criticized for not taking _____ concerns into account when making loans.
A) solvency
B) discrimination
C) environmental
D) business
E) property rights
A) solvency
B) discrimination
C) environmental
D) business
E) property rights

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The most recent World Bank initiatives involve the reduction of _____ in developing countries.
A) malaria
B) ebola
C) crime
D) corruption
E) aid misallocation
A) malaria
B) ebola
C) crime
D) corruption
E) aid misallocation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which of the following UN agencies was established to assist developing countries in the process of integrating into the world economy?
A) WHO
B) UNCTAD
C) UNIDO
D) UNDP
E) IMF
A) WHO
B) UNCTAD
C) UNIDO
D) UNDP
E) IMF

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which of the following UN agencies assists developing countries with problems associated with industrialization?
A) MIGA
B) UNCTAD
C) UNESCO
D) UNIDO
E) IMF
A) MIGA
B) UNCTAD
C) UNESCO
D) UNIDO
E) IMF

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which of the following UN agencies assists the developing countries with trade negotiations?
A) UNCTAD
B) UNDP
C) IFC
D) WTO
E) UNIDO
A) UNCTAD
B) UNDP
C) IFC
D) WTO
E) UNIDO

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which of the following is not a UN agency?
A) UNIDO
B) UNCTAD
C) UNDP
D) IFC
E) None of the above
A) UNIDO
B) UNCTAD
C) UNDP
D) IFC
E) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which institution makes loans for infrastructure projects in developing countries?
A) The IMF
B) The EU
C) The World Bank
D) ECLA
E) none of the above
A) The IMF
B) The EU
C) The World Bank
D) ECLA
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Economic development is unrelated to the concept of GDP per capita.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Access to basic health care is not part of the problem of economic development.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
GDP per capita in the low-income countries is approximately $1,877 per year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Mexico is a familiar example of a middle-income country.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The low-income countries contain over 37 percent of the world's population but produce only 0.7% of world output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The high-income countries are concentrated in North America and Western Europe.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Property rights are not a precondition for economic growth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Economic growth can be enhanced by a reduction in the size of the labor force.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
An example of a country with a substantial amount of economic freedom is North Korea.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Low-income countries usually have high birth rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
With respect to economic growth, only the capital stock in the private sector is important.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
A change in technology means that an economy can produce less output with more inputs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Because of the shape of the production function, an equal increase in the labor force in a developing versus developed country would tend to yield more economic growth in the latter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
An increase in the capital stock would tend to shift the production function upward while an increase in technology would tend to shift it downward.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Increases in the capital stock and improvements in technology are mutually exclusive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The theory of comparative advantage indicates that international trade should increase the total output of an economy by moving resources from comparative disadvantage to comparative advantage industries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Empirical tests of openness and economic growth usually show a positive correlation between the two.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
In order to show that openness causes faster economic growth, it is necessary to show that openness causes the production function to shift upward.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
More open economies tend to have faster rates of growth of total factor productivity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Empirical research on economic growth indicates that openness tends to increase real GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
It is difficult for a poor country to rapidly increase its stock of capital.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Technology transfers into developing countries tend to lead to an upward shift in the production function.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
International trade in goods and services can lead to technology transfers even in the absence of FDI.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The structure of protection in developed countries may make it difficult for some developing countries to develop a manufacturing industry based on primary products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Frequently, the prices of primary products are volatile because both the demand and supply curves are inelastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
If primary products are a high percentage of a country's GDP then instability in the prices of these products could translate into instability of GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Countries that possess primary products always grow faster than countries that do not.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



