Deck 1: Scarcity and Choice
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/78
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 1: Scarcity and Choice
1
Normative economics involve facts while while positive economics involves value judgments.
False
2
"The unemployment rate should be kept lower than 5 percent" is a normative economics statement.
True
3
"People are willing to work more hours if the federal minimum wage increases" is a positive economics statement.
True
4
A study of the effects of a decrease in income taxes on U.S. consumption spending would essentially be a microeconomics issue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
FedEx, founded by entrepreneur Frederick Smith, was an overnight success in 1971.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Money and capital mean the same thing to economists.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Points outside the production possibilities curve are unattainable, given existing resources and technology.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
If the U.S. reduced its unemployment rate by 2%, this would shift the U.S. production possibilities curve outward.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
If the U.S. is operating at a point on the production possibilities curve itself, we can say the U.S. is achieving economic efficiency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
As a factor of production, capital includes money that is used to finance the purchase of plants and equipment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Entrepreneurship is a special type of labor input.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The 4 factors of production are land, labor, capital, and entrepreneurship.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Economists believe people can make better choices by looking at the overall situation, rather than by "thinking at the margin."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Economic models are built from words, diagrams, and/or mathematical equations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A rational person will refrain from taking action if the marginal benefits exceed the marginal costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The law of increasing opportunity costs is illustrated by a production possibilities curve that is bowed outward from the origin of the diagram.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
If the supply of resources increases in the U.S., we can be sure that more goods and services will be produced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Economics is first and foremost the study of how to make a lot of money for housholds and businesses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
According to the "economic way of thinking," every choice has a cost, people make better choices by thinking at the margin, and people act as if they are motivated by self-interest.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Normative economics involves value judgments that cannot be empirically tested, while positive economics describes the facts of the economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The source of the scarcity problem is that people have unlimited resources to satisfy their limited material wants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
An entrepreneur is a person who organizes, manages, and assembles the other factors of production to produce goods and services.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
For a college student, the opportunity cost of attending a football game the night before an exam equals the ticket price plus the difference in her test score that the additional study time would have yielded.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
An economy's production possibilities curve assumes a high unemployment rate, fixed resources, and unchanged technology.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Economic growth occurs if an economy realizes an increasing resource base or technological advance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Capital goods are available for immediate use by households, while consumer goods are used for producing other goods and services in the future.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
All points along a production possibilities curve depict economic efficiency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The law of increasing opportunity cost occurs because resources are not completely adaptable to alternative uses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The terrorist attacks of September 11, 2001 led the U.S. to devote more of its resources to national security, creating an opportunity cost for society in terms of the other goods that were given up.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Economics is first and foremost the study of
A) choice under conditions of scarcity
B) how incomes are divided among the factors of production
C) the allocation of household incomes among various stocks and bonds
D) government ownership of economic resources
A) choice under conditions of scarcity
B) how incomes are divided among the factors of production
C) the allocation of household incomes among various stocks and bonds
D) government ownership of economic resources

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The branch of economics that focuses on the choices made by households and firms, and the effects that those choices have on particular markets, is
A) aggregate economics
B) expenditure economics
C) macroeconomics
D) microeconomics
A) aggregate economics
B) expenditure economics
C) macroeconomics
D) microeconomics

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Microeconomics includes all of the following questions except
A) How would a tax on movie tickets affect purchases by teenagers?
B) How would a ban on immigrant workers affect U.S. orange growers?
C) Will an increase in the federal minimum wage help the working poor?
D) Why do economies experience unemployment and inflation?
A) How would a tax on movie tickets affect purchases by teenagers?
B) How would a ban on immigrant workers affect U.S. orange growers?
C) Will an increase in the federal minimum wage help the working poor?
D) Why do economies experience unemployment and inflation?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The branch of economics that is concerned with the overall performance of the economy is
A) resource economics
B) contemporary economics
C) macroeconomics
D) microeconomics
A) resource economics
B) contemporary economics
C) macroeconomics
D) microeconomics

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Macroeconomics addresses all of the following questions except
A) What causes unemployment in the U.S. economy?
B) Should the U.S. government adopt policies to reduce consumption?
C) How does a decline in interest rates affect the U.S. economy?
D) Should I put my savings in a bank account or invest them in the stock market?
A) What causes unemployment in the U.S. economy?
B) Should the U.S. government adopt policies to reduce consumption?
C) How does a decline in interest rates affect the U.S. economy?
D) Should I put my savings in a bank account or invest them in the stock market?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The economic way of thinking includes all of the following principles except
A) limited human wants and unlimited resources cause scarcity of goods
B) every choice has a cost
C) people make better choices by thinking at the margin
D) economic incentives underlie the rational decisions of people
A) limited human wants and unlimited resources cause scarcity of goods
B) every choice has a cost
C) people make better choices by thinking at the margin
D) economic incentives underlie the rational decisions of people

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A question that positive economics would consider is
A) Should the federal minimum wage be increased to help the working poor?
B) Does free trade result in job losses for workers in import-competing industries?
C) Should all Americans have access to health care?
D) Should high school teachers receive an increase in pay?
A) Should the federal minimum wage be increased to help the working poor?
B) Does free trade result in job losses for workers in import-competing industries?
C) Should all Americans have access to health care?
D) Should high school teachers receive an increase in pay?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which is a question of normative economics?
A) Why do janitors earn less than engineers?
B) Does inflation impose hardships on people with fixed incomes?
C) What causes growth for the economy?
D) Should welfare payments be increased?
A) Why do janitors earn less than engineers?
B) Does inflation impose hardships on people with fixed incomes?
C) What causes growth for the economy?
D) Should welfare payments be increased?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Economists recognize all of the following as factors of production except
A) entrepreneurship
B) capital
C) money
D) land
A) entrepreneurship
B) capital
C) money
D) land

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A(n) ______ is a person who organizes, manages, and assembles the other factors of production to produce goods and services.
A) manager
B) capitalist
C) entrepreneur
D) innovator
A) manager
B) capitalist
C) entrepreneur
D) innovator

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Because of scarcity of factors of production,
A) only goods in relative abundance are free
B) all goods tend to be expensive
C) an economy cannot operate at maximum capacity
D) economic decisions usually entail opportunity costs
A) only goods in relative abundance are free
B) all goods tend to be expensive
C) an economy cannot operate at maximum capacity
D) economic decisions usually entail opportunity costs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which of the following is not an assumption that underlies an economy's production possibilities curve?
A) fixed income
B) fixed resources
C) unchanged technology
D) fully employed resources
A) fixed income
B) fixed resources
C) unchanged technology
D) fully employed resources

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
All points along a production possibilities curve depict the
A) maximum satisfaction that households receive from their purchases of goods
B) minimum satisfaction that households receive from their purchases of goods
C) maximum output that society can produce with given resources and technology
D) minimum output that society can produce with given resources and technology
A) maximum satisfaction that households receive from their purchases of goods
B) minimum satisfaction that households receive from their purchases of goods
C) maximum output that society can produce with given resources and technology
D) minimum output that society can produce with given resources and technology

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
A point outside the economy's production possibilities curve is
A) attainable when resources are fully employed
B) attainable if the law of increasing opportunity costs prevails
C) unattainable given the existing levels of resources and technology
D) unattainable given the existing levels of money income
A) attainable when resources are fully employed
B) attainable if the law of increasing opportunity costs prevails
C) unattainable given the existing levels of resources and technology
D) unattainable given the existing levels of money income

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The law of increasing opportunity costs is best explained by
A) resources not being completely adaptable to alternative uses
B) factors of production being limited and human wants for goods being unlimited
C) efficiencies generated by large-scale production
D) economic efficiency being possible only in the short run
A) resources not being completely adaptable to alternative uses
B) factors of production being limited and human wants for goods being unlimited
C) efficiencies generated by large-scale production
D) economic efficiency being possible only in the short run

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Economic growth would occur for all of the following reasons except
A) increasing resource base
B) increasing money income
C) technological advance
D) increasing productivity of labor
A) increasing resource base
B) increasing money income
C) technological advance
D) increasing productivity of labor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which of the following would not result in an outward shift of a nation's production possibilities curve?
A) a reduction in the unemployment rate
B) a rise in labor productivity
C) advances in technology
D) an expanding resource base
A) a reduction in the unemployment rate
B) a rise in labor productivity
C) advances in technology
D) an expanding resource base

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which of the following statements about consumer goods is false?
A) They are goods that are available for immediate use by households.
B) They include items such as clothing, food, and recreation.
C) They do not contribute to the future production of society.
D) They are a source of an economy's growth potential.
A) They are goods that are available for immediate use by households.
B) They include items such as clothing, food, and recreation.
C) They do not contribute to the future production of society.
D) They are a source of an economy's growth potential.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
When the U.S. and its allies imposed economic sanctions against Iraq in 1990, the hope was to
A) force Iraq to operate inside its existing production possibilities curve
B) cause Iraq's production possibilities curve to shift outward to the right
C) force Iraq to produce under conditions of increasing opportunity cost
D) cause Iraq to operate at maximum efficiency in the production of oil
A) force Iraq to operate inside its existing production possibilities curve
B) cause Iraq's production possibilities curve to shift outward to the right
C) force Iraq to produce under conditions of increasing opportunity cost
D) cause Iraq to operate at maximum efficiency in the production of oil

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which of the following is not a decision that every society, regardless of its wealth and power, must make regarding the production and distribution of goods and services?
A) How shall incomes be spent to make consumers as happy as possible?
B) What goods shall be produced and in what quantities?
C) How shall goods be produced?
D) For whom shall the goods be produced?
A) How shall incomes be spent to make consumers as happy as possible?
B) What goods shall be produced and in what quantities?
C) How shall goods be produced?
D) For whom shall the goods be produced?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
In the studying example given in the text, how was the relationship between study time and course grade depicted graphically?
A) by a bowed outward curve
B) by a bowed inward curve
C) by a positively-sloped straight line
D) by a negatively-sloped straight line
A) by a bowed outward curve
B) by a bowed inward curve
C) by a positively-sloped straight line
D) by a negatively-sloped straight line

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Suppose that one hour of additional studying would raise a students's score on an exam by an additional 5 points. What can we conclude from this?
A) it's not worth it for this student to study for the exam
B) the slope of the study time-grade line is +5
C) the study time-grade line has shifted to the right
D) the student's exam score is an independent variable
A) it's not worth it for this student to study for the exam
B) the slope of the study time-grade line is +5
C) the study time-grade line has shifted to the right
D) the student's exam score is an independent variable

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The opportunity cost of placing your savings in a bank account is the
A) transaction cost that you incur when withdrawing funds from your account
B) decrease in your satisfaction that results from consuming fewer goods now
C) anticipated higher inflation rates in the future
D) interest that you receive on your savings account
A) transaction cost that you incur when withdrawing funds from your account
B) decrease in your satisfaction that results from consuming fewer goods now
C) anticipated higher inflation rates in the future
D) interest that you receive on your savings account

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The bowed-out shape of a production possibilities curve illustrates
A) insufficient resources to produce the country's basic needs
B) free trade with a neighboring country
C) increasing opportunity costs
D) how an economy grows when resources are added
A) insufficient resources to produce the country's basic needs
B) free trade with a neighboring country
C) increasing opportunity costs
D) how an economy grows when resources are added

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Capacity utilization rates in the U.S.
A) are usually around 100 percent for all industries
B) vary across manufacturing, mining, and utilities industries
C) were much lower in 2006 than in the previous 30 years
D) cannot be calculated due to insufficient data
A) are usually around 100 percent for all industries
B) vary across manufacturing, mining, and utilities industries
C) were much lower in 2006 than in the previous 30 years
D) cannot be calculated due to insufficient data

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The opportunity cost of taking a trip to Disneyland includes the money you
A) save using a discount airfare coupon
B) give to your favorite charity each year
C) earn when you get back from Disneyland
D) could have earned if you stayed at home and worked
A) save using a discount airfare coupon
B) give to your favorite charity each year
C) earn when you get back from Disneyland
D) could have earned if you stayed at home and worked

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
A rational person does not act unless the action
A) yields marginal benefits that are greater than marginal costs
B) yields marginal costs that are greater than marginal benefits
C) results in taxes for the person
D) results in losses for the person
A) yields marginal benefits that are greater than marginal costs
B) yields marginal costs that are greater than marginal benefits
C) results in taxes for the person
D) results in losses for the person

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Assuming that rational people are motivated by incentives, what would occur if the average salary of finance majors rises by 30 percent and the average salary of philosophy majors remains constant?
A) Students will shift majors from philosophy to finance.
B) Students will shift majors from finance to philosophy.
C) Students will stop majoring in both finance and philosophy.
D) Students will drop out of college.
A) Students will shift majors from philosophy to finance.
B) Students will shift majors from finance to philosophy.
C) Students will stop majoring in both finance and philosophy.
D) Students will drop out of college.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Figure 1.1 U.S. Production Possibilities Curve
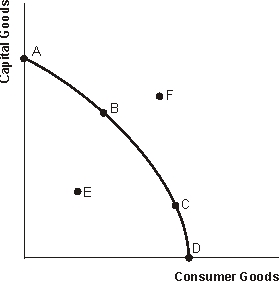
-Refer to Figure 1.1. The shape of the production possibilities curve suggests that the United States produces under conditions of
A) zero opportunity cost
B) constant opportunity cost
C) increasing opportunity cost
D) decreasing opportunity cost

-Refer to Figure 1.1. The shape of the production possibilities curve suggests that the United States produces under conditions of
A) zero opportunity cost
B) constant opportunity cost
C) increasing opportunity cost
D) decreasing opportunity cost

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Figure 1.1 U.S. Production Possibilities Curve

-Refer to Figure 1.1. Which current production alternative would best induce increases in the economy's future production capabilities in the long run?
A) alternative A
B) alternative B
C) alternative C
D) alternative D

-Refer to Figure 1.1. Which current production alternative would best induce increases in the economy's future production capabilities in the long run?
A) alternative A
B) alternative B
C) alternative C
D) alternative D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Figure 1.1 U.S. Production Possibilities Curve

-Refer to Figure 1.1. If the economy moves from point A to point B, it will produce
A) more capital goods, but fewer consumer goods
B) more consumer goods, but fewer capital goods
C) more capital goods, and more consumer goods
D) fewer capital goods, and fewer consumer goods

-Refer to Figure 1.1. If the economy moves from point A to point B, it will produce
A) more capital goods, but fewer consumer goods
B) more consumer goods, but fewer capital goods
C) more capital goods, and more consumer goods
D) fewer capital goods, and fewer consumer goods

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Figure 1.1 U.S. Production Possibilities Curve

-Refer to Figure 1.1. If the economy is located at point E,
A) the economy is operating at maximum capacity
B) economic growth has occurred in the economy
C) there must be unemployment in the economy
D) the quality of the economy's resources has deteriorated

-Refer to Figure 1.1. If the economy is located at point E,
A) the economy is operating at maximum capacity
B) economic growth has occurred in the economy
C) there must be unemployment in the economy
D) the quality of the economy's resources has deteriorated

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Figure 1.1 U.S. Production Possibilities Curve

-Refer to Figure 1.1. Which of the following could allow the economy to move from point B to point F over time?
A) a reduction in the unemployment rate
B) a decrease in the productivity of labor
C) an increase in sodas consumed
D) an advance in technology

-Refer to Figure 1.1. Which of the following could allow the economy to move from point B to point F over time?
A) a reduction in the unemployment rate
B) a decrease in the productivity of labor
C) an increase in sodas consumed
D) an advance in technology

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Table 1.1. U.S. Production Possibilities Curve Data
-Refer to Table 1.1. The data in the table show that the U.S. economy produces under conditions of
A) constant opportunity cost
B) increasing opportunity cost
C) decreasing opportunity cost
D) zero opportunity cost
-Refer to Table 1.1. The data in the table show that the U.S. economy produces under conditions of
A) constant opportunity cost
B) increasing opportunity cost
C) decreasing opportunity cost
D) zero opportunity cost

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Table 1.1. U.S. Production Possibilities Curve Data
-Refer to Table 1.1. If the economy were operating at point C, the opportunity cost of producing an additional capital good is
A) 6 consumer goods
B) 8 consumer goods
C) 10 consumer goods
D) 12 consumer goods
-Refer to Table 1.1. If the economy were operating at point C, the opportunity cost of producing an additional capital good is
A) 6 consumer goods
B) 8 consumer goods
C) 10 consumer goods
D) 12 consumer goods

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Table 1.1. U.S. Production Possibilities Curve Data
-Refer to Table 1.1. As we move from point A to point F, the
A) opportunity cost of consumer goods in terms of capital goods is unchanged
B) opportunity cost of consumer goods in terms of capital goods increases
C) economy becomes more productive in producing both goods
D) economy becomes less productive in producing both goods
-Refer to Table 1.1. As we move from point A to point F, the
A) opportunity cost of consumer goods in terms of capital goods is unchanged
B) opportunity cost of consumer goods in terms of capital goods increases
C) economy becomes more productive in producing both goods
D) economy becomes less productive in producing both goods

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Table 1.1. U.S. Production Possibilities Curve Data
-Refer to Table 1.1. If the economy produces 4 capital goods and 10 consumer goods, the economy
A) operates at a point outside of its production possibilities schedule
B) faces excess productive capacity
C) experiences price inflation
D) has realized economic growth
-Refer to Table 1.1. If the economy produces 4 capital goods and 10 consumer goods, the economy
A) operates at a point outside of its production possibilities schedule
B) faces excess productive capacity
C) experiences price inflation
D) has realized economic growth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Table 1.1. U.S. Production Possibilities Curve Data
-Refer to Table 1.1. Points A, B, C, D, E and F are
A) unattainable
B) positive
C) efficient
D) normative
-Refer to Table 1.1. Points A, B, C, D, E and F are
A) unattainable
B) positive
C) efficient
D) normative

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Table 1.1. U.S. Production Possibilities Curve Data
-Refer to Table 1.1. The economy would move from producing 3 capital goods and 20 consumer goods to 3 capital goods and 22 consumer goods if there was an
A) increase in the productivity of labor
B) advance in technology
C) increase in the labor force
D) elimination of unemployment
-Refer to Table 1.1. The economy would move from producing 3 capital goods and 20 consumer goods to 3 capital goods and 22 consumer goods if there was an
A) increase in the productivity of labor
B) advance in technology
C) increase in the labor force
D) elimination of unemployment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The ratio of an industry's production to its capacity is
A) the capacity utilization rate
B) always 100 percent
C) the economic growth rate
D) negative during a recession
A) the capacity utilization rate
B) always 100 percent
C) the economic growth rate
D) negative during a recession

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
In 2005, Hurricanes Katrina and Rita reduced the U.S. economy's output potential. This occurred primarily through the destruction of
A) crops such as tomatoes and oranges
B) homes and day care centers
C) oil and natural gas platforms
D) forestry industries
A) crops such as tomatoes and oranges
B) homes and day care centers
C) oil and natural gas platforms
D) forestry industries

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
In the 1970s, Japanese and European steel companies were able to increase their productivity relative to U.S. steel companies when they
A) brought in more immigrant workers at low wages
B) recyled and renovated their older obsolete equipment
C) invested in efficient new plant and equipment
D) took over companies producing unrelated products such as wool
A) brought in more immigrant workers at low wages
B) recyled and renovated their older obsolete equipment
C) invested in efficient new plant and equipment
D) took over companies producing unrelated products such as wool

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Payments made to resources include all of the following except
A) interest
B) profits
C) wages
D) welfare
A) interest
B) profits
C) wages
D) welfare

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Which of the following countries faced U.S. economic sanctions in the 1980's to fight discriminatory laws and practices?
A) India
B) South Africa
C) Russia
D) Iraq
A) India
B) South Africa
C) Russia
D) Iraq

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
When people act as if they are motivated by self-interest, and respond predictably to opportunities for gain, this is
A) inconsistent with the basic principles of economics
B) an example of macroeconomics, not microeconomics
C) rational self-interest
D) irrational because not all people want to increase their wealth
A) inconsistent with the basic principles of economics
B) an example of macroeconomics, not microeconomics
C) rational self-interest
D) irrational because not all people want to increase their wealth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
What tools do economists use to help understand, explain, and predict economic phenomena in the real world?
A) normative economics
B) opportunity cost
C) economic systems
D) economic models
A) normative economics
B) opportunity cost
C) economic systems
D) economic models

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The downward-sloping nature of production possibilities curves reflects which basic truth of economics?
A) Money can buy anything people want.
B) A lower price means people will buy more.
C) When people make choices, they have opportunity costs.
D) People are happiest when they have fewest goods.
A) Money can buy anything people want.
B) A lower price means people will buy more.
C) When people make choices, they have opportunity costs.
D) People are happiest when they have fewest goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
A point located on a production possibilities curve represents
A) an unattainable choice
B) efficient use of resources
C) inefficient production
D) changing technology
A) an unattainable choice
B) efficient use of resources
C) inefficient production
D) changing technology

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Suppose we know there is a direct relationship between two variables: the amount of candy given to a group of children and the number of times the children smile. Another way to say this is that there is a(n) _________ relationship between candy and smiles.
A) positive
B) negative
C) inverse
D) opportunity cost
A) positive
B) negative
C) inverse
D) opportunity cost

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



