Deck 11: Accounting for Economic Fluctuations: Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply Analysis
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/58
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 11: Accounting for Economic Fluctuations: Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply Analysis
1
What is gross domestic product? How is this calculation arrived at and what uses does it have as a macroeconomic measure?
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is a measure of the total economic output of a country. It represents the market value of all goods and services produced within a country's borders in a specific time period, usually annually or quarterly.
The calculation of GDP is arrived at by adding up the total value of all goods and services produced in the country, including consumption, investment, government spending, and net exports (exports minus imports). There are three main ways to calculate GDP: the production approach, the income approach, and the expenditure approach. Each of these methods provides a slightly different perspective on the economy, but they all ultimately aim to measure the total economic output of the country.
GDP has several important uses as a macroeconomic measure. It is used to gauge the overall health and size of an economy, as well as to compare the economic performance of different countries. It is also used to track economic growth over time and to identify periods of expansion or contraction in the economy. Additionally, GDP is used to inform government policy decisions, such as fiscal and monetary policy, and to assess the impact of these policies on the economy. Overall, GDP is a crucial tool for understanding and analyzing the economic performance of a country.
The calculation of GDP is arrived at by adding up the total value of all goods and services produced in the country, including consumption, investment, government spending, and net exports (exports minus imports). There are three main ways to calculate GDP: the production approach, the income approach, and the expenditure approach. Each of these methods provides a slightly different perspective on the economy, but they all ultimately aim to measure the total economic output of the country.
GDP has several important uses as a macroeconomic measure. It is used to gauge the overall health and size of an economy, as well as to compare the economic performance of different countries. It is also used to track economic growth over time and to identify periods of expansion or contraction in the economy. Additionally, GDP is used to inform government policy decisions, such as fiscal and monetary policy, and to assess the impact of these policies on the economy. Overall, GDP is a crucial tool for understanding and analyzing the economic performance of a country.
2
Explain the difference between GNP and GDP.
GNP (Gross National Product) and GDP (Gross Domestic Product) are both measures of a country's economic performance, but they differ in their scope and focus.
GDP measures the total economic output within a country's borders, regardless of whether the production is done by domestic or foreign entities. It includes the value of goods and services produced within the country, but excludes income earned by foreign residents and businesses operating within the country.
On the other hand, GNP measures the total economic output produced by the residents and businesses of a country, regardless of whether the production takes place within the country's borders or abroad. It includes the income earned by residents and businesses from foreign investments and excludes the income earned by foreign residents and businesses within the country.
In summary, GDP focuses on the economic activity that occurs within a country's borders, while GNP focuses on the economic activity generated by a country's residents and businesses, regardless of where it occurs. Both measures are important for understanding a country's economic performance and its impact on its residents.
GDP measures the total economic output within a country's borders, regardless of whether the production is done by domestic or foreign entities. It includes the value of goods and services produced within the country, but excludes income earned by foreign residents and businesses operating within the country.
On the other hand, GNP measures the total economic output produced by the residents and businesses of a country, regardless of whether the production takes place within the country's borders or abroad. It includes the income earned by residents and businesses from foreign investments and excludes the income earned by foreign residents and businesses within the country.
In summary, GDP focuses on the economic activity that occurs within a country's borders, while GNP focuses on the economic activity generated by a country's residents and businesses, regardless of where it occurs. Both measures are important for understanding a country's economic performance and its impact on its residents.
3
"GDP is a measure of output and not a measure of economic transactions. Consequently, many of our economic activities are neither calculated nor revealed in our GDP accounting." React to this statement.
While it is true that GDP is a measure of output, it is not accurate to say that it is not a measure of economic transactions. GDP includes the total value of all goods and services produced within a country's borders, which inherently involves economic transactions. However, it is important to acknowledge that GDP does have limitations in capturing the full scope of economic activities.
There are certain economic activities that are not fully captured in GDP accounting, such as informal or underground economic activities, volunteer work, and household production. These activities contribute to the overall economy but may not be included in official GDP calculations. Additionally, GDP does not account for the distribution of income or the impact of environmental degradation, which are important factors in assessing overall economic well-being.
It is important to consider alternative measures such as Gross National Income (GNI), Human Development Index (HDI), or Genuine Progress Indicator (GPI) to gain a more comprehensive understanding of economic well-being and sustainability. These measures take into account a broader range of economic activities and factors that contribute to overall welfare and progress.
In conclusion, while GDP is a valuable measure of economic output, it is essential to recognize its limitations and consider supplementary indicators to provide a more holistic view of economic activity and well-being.
There are certain economic activities that are not fully captured in GDP accounting, such as informal or underground economic activities, volunteer work, and household production. These activities contribute to the overall economy but may not be included in official GDP calculations. Additionally, GDP does not account for the distribution of income or the impact of environmental degradation, which are important factors in assessing overall economic well-being.
It is important to consider alternative measures such as Gross National Income (GNI), Human Development Index (HDI), or Genuine Progress Indicator (GPI) to gain a more comprehensive understanding of economic well-being and sustainability. These measures take into account a broader range of economic activities and factors that contribute to overall welfare and progress.
In conclusion, while GDP is a valuable measure of economic output, it is essential to recognize its limitations and consider supplementary indicators to provide a more holistic view of economic activity and well-being.
4
Explain why the conversion of nominal GDP to real GDP provides a more useful set of comparative data.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Sketch a "generalized" business cycle in which national output is graphed over time. Now label the important stages of the cycle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Compare and contrast the general economic conditions that are expected to characterize an economy near a) the peak of the business cycle, and b) the trough of the cycle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Summarize Joseph Schumpeter's explanation of the long waves in aggregate economic behavior. Compare Schumpeter's version of long wave analysis with that of Nikoli Kondratieff.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
What are the three principal macroeconomic measures used to gauge aggregate economic performance? Explain how, in a general way, government policy may be used to affect AD and AS and how, in turn, this will affect macroeconomic measures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Why is the AD curve downward sloping to the right and the AS curve upward sloping to the right?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Given an economy in equilibrium, but at below its potential output level, how would Keynesians and supply-siders differ on strategy for obtaining the potential output level?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Using the analytical tools of AD and AS, explain the coming and stubborn persistence of the recession of 2007-2009.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Answer the following questions using the aggregate supply diagram below.
a. Identify where potential output would be.
b. Illustrate how aggregate demand might increase, raising output, but not price level.
c. Illustrate how an increase in aggregate demand might increase both output and price level.
d. Illustrate how a change in aggregate demand increases only the price level.

a. Identify where potential output would be.
b. Illustrate how aggregate demand might increase, raising output, but not price level.
c. Illustrate how an increase in aggregate demand might increase both output and price level.
d. Illustrate how a change in aggregate demand increases only the price level.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A homeowner who married her gardener will by that action probably lower the GDP a small amount.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
GDP is a physical measure of national output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
GDP counts legal as well as illegal market sales.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
National Income is a measure of all payments made to factors of production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Personal Income is obtained by subtracting personal taxes from disposable income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Nominal GDP is national output adjusted for price changes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
In converting current GDP to real GDP, if the price index is over 100, we will be deflating current GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Inflating GDP refers to the fact that real GDP may be greater than nominal GDP if the price level for the year in question is less than 100.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
According to the Russian economist N. Kondratieff, long wave crisis in capitalist countries appears every 40 to 60 years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
John Maynard Keynes is best known for his elaborate study of business cycles in which he emphasized "long wave" theory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The slope of the AD curve is explained in precisely the same way we would explain the slope of the demand curve for a particular commodity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Stagflation refers to a situation in which both prices and output rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Decreasing corporate profit taxes should stimulate corporate profits which in turn will shift the AD curve to the left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The absolute level of AS or output is limited by the potential output constraint a nation faces.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The interest rate effect refers to the fact that we would expect individuals to consume less and save more when price levels rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Generally for producers of goods, a decline in resource prices will lead to action that will shift the AS curve to the right.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Proponents of the "New Economy" maintain that aggregate supply was increased through freer trade, advances in information technology, access to cheaper resources, and innovation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The difference between real GDP and nominal GDP is that nominal GDP measures output at current money levels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
GDP is widely regarded as a comprehensive and accurate measure of society's well-being.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The Employment Act of 1946 mandated that government undertake policies that would maintain both stable prices and high levels of employment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The stock market crash of 1929 was primarily caused by the excessive federal deficits runup during the Coolidge and Hoover administrations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Chain-type indexes are intended to offset the disadvantages of relying on fixed- weight versus current-weight indexes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Gross National Product:
A) has been replaced by GDP as the official measure of U.S. output
B) is no longer officially calculated
C) differs little from gross domestic product in the United States
D) a and c are correct
E) a and b are correct
F) none of the above
A) has been replaced by GDP as the official measure of U.S. output
B) is no longer officially calculated
C) differs little from gross domestic product in the United States
D) a and c are correct
E) a and b are correct
F) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
GDP is:
A) the current official measure of U.S. output
B) does not count the earnings of American business overseas
C) includes earnings of foreign businesses operating in the United States
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
A) the current official measure of U.S. output
B) does not count the earnings of American business overseas
C) includes earnings of foreign businesses operating in the United States
D) all of the above
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
GDP:
A) measures all market sales, even the sales of illegal goods
B) counts financial as well as output sales
C) tells us much about how income and output are distributed
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
A) measures all market sales, even the sales of illegal goods
B) counts financial as well as output sales
C) tells us much about how income and output are distributed
D) all of the above
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following will be counted in GDP?
A) Your sale of your 2001 Nissan
B) the value-added of a food wholesaler
C) illegal drug sales
D) mowing your lawn
E) a pimp's share of income from illegal prostitution
F) none of the above
A) Your sale of your 2001 Nissan
B) the value-added of a food wholesaler
C) illegal drug sales
D) mowing your lawn
E) a pimp's share of income from illegal prostitution
F) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Xn is obtained by:
A) counting up all exported goods
B) subtracting exports from government purchase
C) subtracting imports from exports
D) counting up all imported goods
A) counting up all exported goods
B) subtracting exports from government purchase
C) subtracting imports from exports
D) counting up all imported goods

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
To move to Disposable Income from Personal Income, we must:
A) subtract personal taxes
B) subtract Social Security contributions
C) subtract indirect business taxes
D) add personal taxes
A) subtract personal taxes
B) subtract Social Security contributions
C) subtract indirect business taxes
D) add personal taxes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The ordinary sequence of a business cycle runs
A) Trough to peak to contraction to expansion
B) Trough to contraction to peak to expansion
C) Trough to expansion to peak to contraction
D) Trough to expansion to peak to contraction to worsening contraction to crash
E) none of the above
A) Trough to peak to contraction to expansion
B) Trough to contraction to peak to expansion
C) Trough to expansion to peak to contraction
D) Trough to expansion to peak to contraction to worsening contraction to crash
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following have been offered by economists as explanations of business cycle behavior?
A) "laws of motion within capitalism"
B) sunspots
C) demographic shifts
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
A) "laws of motion within capitalism"
B) sunspots
C) demographic shifts
D) all of the above
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which economist is associated with the "sunspot theory" of business cycles?
A) Karl Marx
B) William S. Jevons
C) J. M. Keynes
D) Adam Smith
E) Al Gore
A) Karl Marx
B) William S. Jevons
C) J. M. Keynes
D) Adam Smith
E) Al Gore

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which of the following is not true?
A) price levels, employment levels, and rate of output growth are major measures of aggregate economic performance
B) price levels are principally determined by the interaction of AD and AS
C) monetary policy has little effect on AD
D) the chief determinant of levels of employment is the level of real output
A) price levels, employment levels, and rate of output growth are major measures of aggregate economic performance
B) price levels are principally determined by the interaction of AD and AS
C) monetary policy has little effect on AD
D) the chief determinant of levels of employment is the level of real output

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Answer questions 12-18 by choosing from the following answers:
A. AD shifts to the right
B. AD shifts to the left
C. AS shifts to the right
D. AS shifts to the left
-What will be the probable immediate effect of a decline in consumer spending?
A) AD shifts to the right
B) AD shifts to the left
C) AS shifts to the right
D) AS shifts to the left
A. AD shifts to the right
B. AD shifts to the left
C. AS shifts to the right
D. AS shifts to the left
-What will be the probable immediate effect of a decline in consumer spending?
A) AD shifts to the right
B) AD shifts to the left
C) AS shifts to the right
D) AS shifts to the left

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Answer questions 12-18 by choosing from the following answers:
A. AD shifts to the right
B. AD shifts to the left
C. AS shifts to the right
D. AS shifts to the left
-What will be the effect of a sudden increase in the price of petroleum?
A) AD shifts to the right
B) AD shifts to the left
C) AS shifts to the right
D) AS shifts to the left
A. AD shifts to the right
B. AD shifts to the left
C. AS shifts to the right
D. AS shifts to the left
-What will be the effect of a sudden increase in the price of petroleum?
A) AD shifts to the right
B) AD shifts to the left
C) AS shifts to the right
D) AS shifts to the left

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Answer questions 12-18 by choosing from the following answers:
A. AD shifts to the right
B. AD shifts to the left
C. AS shifts to the right
D. AS shifts to the left
-What would you expect of a personal income tax cut?
-------------------------------. AD shifts to the right
A) AD shifts to the right
B) AD shifts to the left
C) AS shifts to the right
D) AS shifts to the left
A. AD shifts to the right
B. AD shifts to the left
C. AS shifts to the right
D. AS shifts to the left
-What would you expect of a personal income tax cut?
-------------------------------. AD shifts to the right
A) AD shifts to the right
B) AD shifts to the left
C) AS shifts to the right
D) AS shifts to the left

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Answer questions 12-18 by choosing from the following answers:
A. AD shifts to the right
B. AD shifts to the left
C. AS shifts to the right
D. AS shifts to the left
-What happens if American exports are rising and imports are falling?
-------------------------------. AD shifts to the right
A) AD shifts to the right
B) AD shifts to the left
C) AS shifts to the right
D) AS shifts to the left
A. AD shifts to the right
B. AD shifts to the left
C. AS shifts to the right
D. AS shifts to the left
-What happens if American exports are rising and imports are falling?
-------------------------------. AD shifts to the right
A) AD shifts to the right
B) AD shifts to the left
C) AS shifts to the right
D) AS shifts to the left

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Answer questions 12-18 by choosing from the following answers:
A. AD shifts to the right
B. AD shifts to the left
C. AS shifts to the right
D. AS shifts to the left
-What would you expect to be the result of a decline in U.S. productivity?
A) AD shifts to the right
B) AD shifts to the left
C) AS shifts to the right
D) AS shifts to the left
A. AD shifts to the right
B. AD shifts to the left
C. AS shifts to the right
D. AS shifts to the left
-What would you expect to be the result of a decline in U.S. productivity?
A) AD shifts to the right
B) AD shifts to the left
C) AS shifts to the right
D) AS shifts to the left

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Answer questions 12-18 by choosing from the following answers:
A. AD shifts to the right
B. AD shifts to the left
C. AS shifts to the right
D. AS shifts to the left
-…Productivity rises?
A) AD shifts to the right
B) AD shifts to the left
C) AS shifts to the right
D) AS shifts to the left
A. AD shifts to the right
B. AD shifts to the left
C. AS shifts to the right
D. AS shifts to the left
-…Productivity rises?
A) AD shifts to the right
B) AD shifts to the left
C) AS shifts to the right
D) AS shifts to the left

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Answer questions 12-18 by choosing from the following answers:
A. AD shifts to the right
B. AD shifts to the left
C. AS shifts to the right
D. AS shifts to the left
-…Turmoil in the Middle East cuts off oil supplies?
A) AD shifts to the right
B) AD shifts to the left
C) AS shifts to the right
D) AS shifts to the left
A. AD shifts to the right
B. AD shifts to the left
C. AS shifts to the right
D. AS shifts to the left
-…Turmoil in the Middle East cuts off oil supplies?
A) AD shifts to the right
B) AD shifts to the left
C) AS shifts to the right
D) AS shifts to the left

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
If the supply curve is always horizontal in the short run until potential output is obtained:
A) increases in AD are always inflationary
B) aggregate supply is more important than aggregate demand in determining output
C) Keynesian theory is wrong
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
A) increases in AD are always inflationary
B) aggregate supply is more important than aggregate demand in determining output
C) Keynesian theory is wrong
D) all of the above
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which of the following price indices is based on a market basket of consumer goods?
A) the GDP deflator
B) the CPI
C) the PPI
D) the PCE
A) the GDP deflator
B) the CPI
C) the PPI
D) the PCE

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which of the following is not likely to be a usual characteristic of the peak stage of the business cycle?
A) High levels of employment
B) Low unemployment
C) High levels of investment
D) High levels of consumer spending
E) Falling prices
A) High levels of employment
B) Low unemployment
C) High levels of investment
D) High levels of consumer spending
E) Falling prices

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which country has the highest GDP in the world?
A) Germany
B) China
C) India
D) Russian Federation
E) United States
A) Germany
B) China
C) India
D) Russian Federation
E) United States

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Answer the next three questions based upon the following diagram.
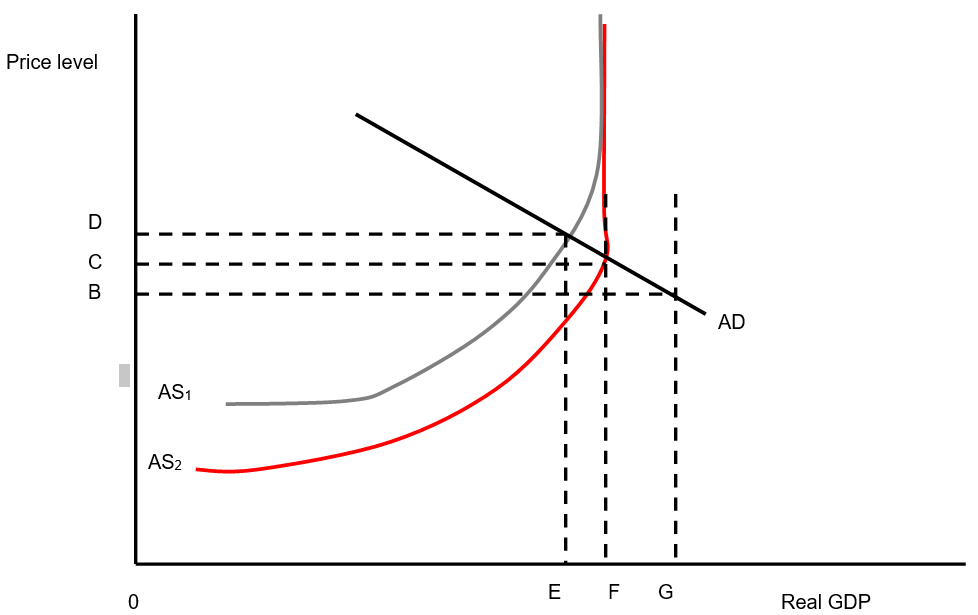
-If aggregate supply is AS1:
A) inflation is C and real GDP is F
B) price level is C and real GDP is F
C) price level is D and real GDP is E
D) price level is B and real GDP is G
E) the output gap is FG

-If aggregate supply is AS1:
A) inflation is C and real GDP is F
B) price level is C and real GDP is F
C) price level is D and real GDP is E
D) price level is B and real GDP is G
E) the output gap is FG

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Answer the next three questions based upon the following diagram.

-Potential real GDP is represented by:
A) F
B) E
C) G
D) C

-Potential real GDP is represented by:
A) F
B) E
C) G
D) C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Answer the next three questions based upon the following diagram.

-The shift of aggregate supply from AS1 to AS2:
A) results in price level rising from C to F
B) results in price level falling from C to F and real GDP rising from E to F
C) results in price level rising from C to F and real GDP rising from E to F
D) results in price level rising from C to F and real GDP falling from F to E

-The shift of aggregate supply from AS1 to AS2:
A) results in price level rising from C to F
B) results in price level falling from C to F and real GDP rising from E to F
C) results in price level rising from C to F and real GDP rising from E to F
D) results in price level rising from C to F and real GDP falling from F to E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



