Deck 2: User's Guide to the Sky
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/160
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 2: User's Guide to the Sky
1
What is the term for the point on the celestial sphere directly above an observer,no matter where on the Earth the observer is located?
A)north celestial pole
B)south celestial pole
C)zenith
D)nadir
A)north celestial pole
B)south celestial pole
C)zenith
D)nadir
zenith
2
If the apparent visual magnitude of a star is 7.3,what does this tell us about the brightness of the star?
A)It is one of the brighter stars in the sky.
B)It is bright enough that it would be visible even during the day.
C)It is not visible with the unaided eye.
D)It appears faint because of its great distance from the Earth.
A)It is one of the brighter stars in the sky.
B)It is bright enough that it would be visible even during the day.
C)It is not visible with the unaided eye.
D)It appears faint because of its great distance from the Earth.
It is not visible with the unaided eye.
3
Seen from Winnipeg (latitude 50 degrees North),where is the star Polaris in the sky?
A)directly overhead
B)40 degrees above the horizon
C)50 degrees above the horizon
D)the position depends on the time of day
A)directly overhead
B)40 degrees above the horizon
C)50 degrees above the horizon
D)the position depends on the time of day
50 degrees above the horizon
4
Which of the following is equivalent to one-3,600ᵗʰ of a degree?
A)precession
B)second of arc
C)minute of arc
D)angular diameter
A)precession
B)second of arc
C)minute of arc
D)angular diameter

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The star Vega has an apparent visual magnitude of 0.03 and the star HR 4374 has an apparent visual magnitude of 4.87.It has been determined that both stars are at the same distance from the Earth.What does this information tell us about the two stars?
A)Together the two stars would have a magnitude of 4.9.
B)Vega must produce less energy per second than HR 4374.
C)Vega must produce more energy per second than HR 4374.
D)Vega will appear fainter to us than HR 4374.
A)Together the two stars would have a magnitude of 4.9.
B)Vega must produce less energy per second than HR 4374.
C)Vega must produce more energy per second than HR 4374.
D)Vega will appear fainter to us than HR 4374.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Where in the sky would an observer at the Earth's equator see the celestial equator?
A)The celestial equator would be at 45 degrees above the northern horizon.
B)The celestial equator would be at 45 degrees above the southern horizon.
C)The celestial equator would coincide with the horizon.
D)The celestial equator would be directly overhead.
A)The celestial equator would be at 45 degrees above the northern horizon.
B)The celestial equator would be at 45 degrees above the southern horizon.
C)The celestial equator would coincide with the horizon.
D)The celestial equator would be directly overhead.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
What is the celestial equator?
A)the dividing line between the north and south celestial hemispheres
B)a line around the sky directly above the Earth's poles
C)the path that the Sun appears to follow on the celestial sphere as the Earth orbits the Sun
D)the path that the planets appear to follow in the sky
A)the dividing line between the north and south celestial hemispheres
B)a line around the sky directly above the Earth's poles
C)the path that the Sun appears to follow on the celestial sphere as the Earth orbits the Sun
D)the path that the planets appear to follow in the sky

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
What causes the precession of the Earth's rotation axis?
A)the force of gravity from the Sun and Moon on the Earth's equatorial bulge
B)the force of gravity from the Sun and Jupiter on the Earth-Moon system
C)the magnetic field of the Earth
D)the impacts of asteroids
A)the force of gravity from the Sun and Moon on the Earth's equatorial bulge
B)the force of gravity from the Sun and Jupiter on the Earth-Moon system
C)the magnetic field of the Earth
D)the impacts of asteroids

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
For an observer in New Delhi,India,at a latitude of 28° North,what is the angle between the northern horizon and the north celestial pole?
A)5°
B)28°
C)40°
D)62°
A)5°
B)28°
C)40°
D)62°

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following best describes the Big Dipper?
A)a constellation
B)another name for the Seven Sisters
C)an asterism
D)another name for the Great Bear
A)a constellation
B)another name for the Seven Sisters
C)an asterism
D)another name for the Great Bear

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Why are Venus and Mercury often called "morning star" and "evening star"?
A)They look more like stars than the other planets do.
B)They both rotate quite slowly and have long mornings and evenings.
C)They are both reddish in colour, like the Sun near the horizon.
D)They are only visible just before sunrise or just after sunset.
A)They look more like stars than the other planets do.
B)They both rotate quite slowly and have long mornings and evenings.
C)They are both reddish in colour, like the Sun near the horizon.
D)They are only visible just before sunrise or just after sunset.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
For an observer in Valdivia,Chile,at a latitude of 39° South,what is the angle between the southern horizon and the south celestial pole?
A)23.5°
B)39°
C)45°
D)51°
A)23.5°
B)39°
C)45°
D)51°

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
For an observer in Lusaka,Zambia,at a latitude of 16° South,what is the angle between the southern horizon and the south celestial pole?
A)16°
B)23.5°
C)74°
D)164°
A)16°
B)23.5°
C)74°
D)164°

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Where is an observer's nadir?
A)the point directly opposite the observer's zenith
B)the north point on the observer's horizon
C)the east point on the observer's horizon
D)the point directly opposite the north celestial pole
A)the point directly opposite the observer's zenith
B)the north point on the observer's horizon
C)the east point on the observer's horizon
D)the point directly opposite the north celestial pole

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
For an observer in Pond Inlet,Nunavut,at a latitude of 73° North,what is the angle between the northern horizon and the north celestial pole?
A)17°
B)23.5°
C)27°
D)73°
A)17°
B)23.5°
C)27°
D)73°

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
What languages do the standard constellation names come from?
A)Greek and Latin
B)Latin and Arabic
C)Greek and Arabic
D)Arabic and Sanskrit
A)Greek and Latin
B)Latin and Arabic
C)Greek and Arabic
D)Arabic and Sanskrit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
What language is the source of most star names,such as Aldebaran and Betelgeuse?
A)Latin
B)Greek
C)Arabic
D)Italian
A)Latin
B)Greek
C)Arabic
D)Italian

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
What is the purpose of the magnitude scale?
A)It measures the apparent location of celestial objects in the sky.
B)It measures the apparent size of a celestial object.
C)It measures the apparent brightness of a celestial object.
D)It measures the apparent speed of a celestial object.
A)It measures the apparent location of celestial objects in the sky.
B)It measures the apparent size of a celestial object.
C)It measures the apparent brightness of a celestial object.
D)It measures the apparent speed of a celestial object.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
An observer in the northern hemisphere watches the sky for several hours.Due to the motion of the Earth,this observer notices that the stars near the north celestial pole appear to move.What pattern does this apparent movement follow?
A)counter-clockwise around the celestial pole
B)clockwise around the celestial pole
C)from left to right
D)from right to left
A)counter-clockwise around the celestial pole
B)clockwise around the celestial pole
C)from left to right
D)from right to left

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
What aspect of an object depends on both the size of the object and the distance to the object?
A)apparent brightness
B)apparent magnitude
C)angular diameter
D)proper motion
A)apparent brightness
B)apparent magnitude
C)angular diameter
D)proper motion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
An observer in the southern hemisphere takes a time exposure photograph of the night sky.If the illustration depicts the photograph taken by the observer,which direction was the camera pointing?
A)due south
B)due east
C)due west
D)straight up, directly overhead
A)due south
B)due east
C)due west
D)straight up, directly overhead

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The star delta Cephei has a declination of about +58.5 degrees.Which observer will see it above their horizon for the longest fraction of one night?
A)an observer in Valdivia, Chile, at a latitude of 39° S
B)an observer in Windhoek, Namibia, at a latitude of 22.5° S
C)an observer in Zacatecas, Mexico, at a latitude of 22.5° N
D)an observer in Edmonton, Canada, at a latitude of 53.5° N
A)an observer in Valdivia, Chile, at a latitude of 39° S
B)an observer in Windhoek, Namibia, at a latitude of 22.5° S
C)an observer in Zacatecas, Mexico, at a latitude of 22.5° N
D)an observer in Edmonton, Canada, at a latitude of 53.5° N

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What is the approximate latitude of the observer in the diagram?
A)20° N
B)20° S
C)70° N
D)0°
A)20° N
B)20° S
C)70° N
D)0°

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Table 2-1
-Refer to Table 2-1.Which star in the table would appear brightest to an observer on Earth?
A)? Dra
B)? Cet
C)Nim
D) ? CMa
-Refer to Table 2-1.Which star in the table would appear brightest to an observer on Earth?
A)? Dra
B)? Cet
C)Nim
D) ? CMa

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
An observer in the northern hemisphere takes a time exposure photograph of the night sky.If the illustration depicts the photograph taken by the observer,which direction was the camera pointing?
A)due north
B)due south
C)due west
D)straight up, directly overhead
A)due north
B)due south
C)due west
D)straight up, directly overhead

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following statements correctly describes the relationship between stars and constellations?
A)Only stars close to the ecliptic (the Earth's orbital plane) are located in constellations.
B)Every star is located in a constellation.
C)Only the brighter stars are in constellations.
D)Only those stars that were visible to the ancient Greeks are located in constellations.
A)Only stars close to the ecliptic (the Earth's orbital plane) are located in constellations.
B)Every star is located in a constellation.
C)Only the brighter stars are in constellations.
D)Only those stars that were visible to the ancient Greeks are located in constellations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Do the constellations visible in the sky at a particular time of night (say 9 p.m.)follow a seasonal pattern?
A)No, the same constellations are visible at 9 p.m. on any clear night of the year.
B)No. As the year progresses, the constellations visible at 9 p.m. are the same, but their shapes change.
C)Yes, at 9 p.m. on a clear winter night, ALL of the constellations you can see are different from the ones that appear at the same time on a summer night.
D)Yes, at 9 p.m. on a summer night, MOST of the constellations you can see are different from those you can see on a winter night. Some constellations are visible all year long.
A)No, the same constellations are visible at 9 p.m. on any clear night of the year.
B)No. As the year progresses, the constellations visible at 9 p.m. are the same, but their shapes change.
C)Yes, at 9 p.m. on a clear winter night, ALL of the constellations you can see are different from the ones that appear at the same time on a summer night.
D)Yes, at 9 p.m. on a summer night, MOST of the constellations you can see are different from those you can see on a winter night. Some constellations are visible all year long.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Table 2-1
-Refer to Table 2-1.Which star in the table would be invisible to the unaided eye of an observer on Earth?
A)? Dra
B)? Cet
C)Nim
D) ? CMa
-Refer to Table 2-1.Which star in the table would be invisible to the unaided eye of an observer on Earth?
A)? Dra
B)? Cet
C)Nim
D) ? CMa

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
You want to observe the star Arcturus just as it crosses the meridian.If the meridian crossing happens at exactly 9:00 p.m.tonight,at what time will it occur 7 days from now,at the same location?
A)8:32 p.m.
B)9:00 p.m.
C)9:28 p.m.
D)6:00 a.m.
A)8:32 p.m.
B)9:00 p.m.
C)9:28 p.m.
D)6:00 a.m.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
You point your finger toward the zenith right now,and then point there again six hours later.At both times,your finger was pointing in the same direction relative to one of the options below.Which one?
A)your horizon
B)the Sun
C)the Moon
D)the fixed stars
A)your horizon
B)the Sun
C)the Moon
D)the fixed stars

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
How much of the night sky lies north of the celestial equator?
A)Less than half, because of the tilt of the equator to the ecliptic plane.
B)More than half, because of the precession of the poles.
C)Exactly half.
D)All of the night sky.
A)Less than half, because of the tilt of the equator to the ecliptic plane.
B)More than half, because of the precession of the poles.
C)Exactly half.
D)All of the night sky.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
An observer in the southern hemisphere takes a time exposure photograph of the night sky.If the illustration depicts the photograph taken by the observer,which direction was the camera pointing?
A)due north
B)due south
C)due east
D)due west
A)due north
B)due south
C)due east
D)due west

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
An observer in the northern hemisphere takes a time exposure photograph of the night sky.If the illustration depicts the photograph taken by the observer,which direction was the camera pointing?
A)due north
B)due south
C)due east
D)straight up, directly overhead
A)due north
B)due south
C)due east
D)straight up, directly overhead

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
An observer in the southern hemisphere takes a time exposure photograph of the night sky.If the illustration depicts the photograph taken by the observer,which direction was the camera pointing?
A)due north
B)due south
C)due east
D)due west
A)due north
B)due south
C)due east
D)due west

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
For an observer in Oberon Bay,Australia,at a latitude of 39° South,what is the angle between the southern horizon and the south celestial pole?
A)23.5°
B)39°
C)45°
D)51°
A)23.5°
B)39°
C)45°
D)51°

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
An observer in the northern hemisphere takes a time exposure photograph of the night sky.If the illustration depicts the photograph taken by the observer,which direction was the camera pointing?
A)due north
B)due south
C)due west
D)straight up, directly overhead
A)due north
B)due south
C)due west
D)straight up, directly overhead

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following measures time relative to the stars?
A)solar day
B)sidereal day
C)tropical year
D)synodic month
A)solar day
B)sidereal day
C)tropical year
D)synodic month

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
If the north celestial pole appears on your horizon,what is your latitude?
A)0°
B)45° N
C)90° N
D)90° S
A)0°
B)45° N
C)90° N
D)90° S

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
What is the approximate latitude of the observer in the diagram?
A)50° N
B)50° S
C)90° N
D)90° S
A)50° N
B)50° S
C)90° N
D)90° S

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
If an observer travels north,toward higher latitudes,how does the number of circumpolar stars that he or she sees in the sky change?
A)remains constant
B)decreases
C)increases
D)also depends on the longitude of the observer
A)remains constant
B)decreases
C)increases
D)also depends on the longitude of the observer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which of the following is 18 years and 11-1/3 days long?
A)sidereal period
B)synodic period
C)eclipse season
D)Saros cycle
A)sidereal period
B)synodic period
C)eclipse season
D)Saros cycle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
What do stars in the same constellation have in common?
A)They probably formed at the same time.
B)They must be part of the same cluster of stars in space.
C)They must have been discovered at about the same time.
D)They are in the same part of the sky as seen from the Earth.
A)They probably formed at the same time.
B)They must be part of the same cluster of stars in space.
C)They must have been discovered at about the same time.
D)They are in the same part of the sky as seen from the Earth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The second is defined as a fixed interval of time,with no reference to astronomical timescales.If the Earth's period of rotation doubled,but its period of revolution stayed the same,what would happen?
A)There would half as many seconds in the day.
B)There would be twice as many seconds in the day.
C)There would be half as many seconds in the year.
D)There would be twice as many seconds in the year.
A)There would half as many seconds in the day.
B)There would be twice as many seconds in the day.
C)There would be half as many seconds in the year.
D)There would be twice as many seconds in the year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
What is the ecliptic?
A)the centre line of the celestial sphere
B)the projection of the Earth's orbit on the sky
C)the apparent path of the Moon around the sky
D)the line between east and west, passing through the zenith
A)the centre line of the celestial sphere
B)the projection of the Earth's orbit on the sky
C)the apparent path of the Moon around the sky
D)the line between east and west, passing through the zenith

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
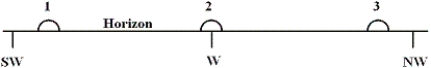
The diagram shows three approximate locations of the Sun along the western horizon.Which number indicates the location of the Sun at sunset on December 21st (winter solstice)for an observer at latitude 48° North?
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)The Sun will not set on December 21st at this latitude.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
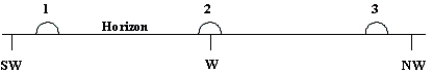
The diagram shows three approximate locations of the Sun along the western horizon.Which number indicates the location of the Sun at sunset on autumnal equinox (Sept.21)for an observer at a latitude of 45° North?
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)The Sun will not set on the autumnal equinox at this latitude.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
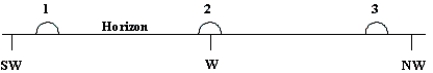
The diagram shows three approximate locations of the Sun along the western horizon.Which number indicates the location of the Sun at sunset on June 21 (summer solstice)for an observer at a latitude of 77° North?
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)The Sun will not set on June 21 at this latitude.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
If you see the Sun pass directly overhead on at least one day per year,then where are you on Earth?
A)within 23.5° latitude of the equator
B)within 66.5° latitude of the equator
C)exactly on the equator
D)could be anywhere, because this occurs at least once per year at any location on the Earth
A)within 23.5° latitude of the equator
B)within 66.5° latitude of the equator
C)exactly on the equator
D)could be anywhere, because this occurs at least once per year at any location on the Earth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
If you were standing on the Earth's equator,which of the following in the sky would pass through your zenith during the entire day (24 hours)?
A)the north celestial pole
B)the south celestial pole
C)the celestial equator
D)circumpolar constellations
A)the north celestial pole
B)the south celestial pole
C)the celestial equator
D)circumpolar constellations

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
What is the term for a set of beliefs that appears to be based on scientific ideas,but which fails to obey the most basic rules of science?
A)theory
B)hypothesis
C)pseudoscience
D)scientific model
A)theory
B)hypothesis
C)pseudoscience
D)scientific model

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
At which of the following times would you find the Sun on the celestial equator?
A)vernal equinox and summer solstice
B)autumnal equinox and vernal equinox
C)summer solstice and winter solstice
D)autumnal equinox and winter solstice
A)vernal equinox and summer solstice
B)autumnal equinox and vernal equinox
C)summer solstice and winter solstice
D)autumnal equinox and winter solstice

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Why are Northern Hemisphere winters colder than Northern Hemisphere summers?
A)The Earth is closer to the Sun during the summer than it is during the winter.
B)The snow that falls in the northern latitudes cools the Earth during the winter.
C)The light from the Sun shines more directly on the Northern Hemisphere during the summer.
D)The period of sunlight is shorter during the summer than during the winter.
A)The Earth is closer to the Sun during the summer than it is during the winter.
B)The snow that falls in the northern latitudes cools the Earth during the winter.
C)The light from the Sun shines more directly on the Northern Hemisphere during the summer.
D)The period of sunlight is shorter during the summer than during the winter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
If the perihelion of the Earth was significantly closer to the Sun than is currently the case,what would be the probable effect on the climate of the Southern Hemisphere?
A)The winter season would be much colder than at present.
B)The winter season would be much warmer than at present.
C)The summer season would be much colder than at present.
D)The summer season would be much warmer than at present.
A)The winter season would be much colder than at present.
B)The winter season would be much warmer than at present.
C)The summer season would be much colder than at present.
D)The summer season would be much warmer than at present.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
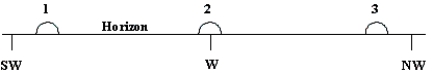
The diagram shows three approximate locations of the Sun along the western horizon.Which number indicates the location of the Sun at sunset on the vernal equinox (March 21)for an observer at a latitude of 48° South?
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)The Sun will not set on vernal equinox at this latitude.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
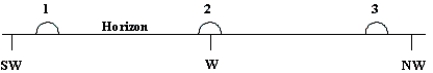
The diagram shows three approximate locations of the Sun along the western horizon.Which number indicates the location of the Sun at sunset on June 21 (summer solstice)for an observer at a latitude of 37° North?
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)The Sun will not set on June 21 at this latitude.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
In Brazil,in what month does the longest period of daylight occur?
A)March
B)June
C)September
D)December
A)March
B)June
C)September
D)December

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
If you were standing at the Earth's North Pole,which of the following would be located at the zenith?
A)the nadir
B)the star Vega
C)the celestial equator
D)the north celestial pole
A)the nadir
B)the star Vega
C)the celestial equator
D)the north celestial pole

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
During the month of June the north celestial pole points towards Polaris;where does it point during the month of December?
A)just south of Polaris
B)towards the star Vega
C)towards the star Thuban
D)still towards Polaris
A)just south of Polaris
B)towards the star Vega
C)towards the star Thuban
D)still towards Polaris

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
How far,and in what direction,does the Sun appear to move on the celestial sphere per day?
A)about one degree westward
B)about one degree eastward
C)about 360 degrees westward
D)about 360 degrees eastward
A)about one degree westward
B)about one degree eastward
C)about 360 degrees westward
D)about 360 degrees eastward

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
At what two celestial locations do the celestial equator and the ecliptic coincide?
A)winter solstice and summer solstice
B)vernal equinox and autumnal equinox
C)north celestial pole and south celestial pole
D)zenith and east point
A)winter solstice and summer solstice
B)vernal equinox and autumnal equinox
C)north celestial pole and south celestial pole
D)zenith and east point

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
What is the term for the Moon when it is visible above the eastern horizon a couple of hours before sunrise?
A)the waning gibbous Moon
B)the waxing gibbous Moon
C)the waxing crescent Moon
D)the waning crescent Moon
A)the waning gibbous Moon
B)the waxing gibbous Moon
C)the waxing crescent Moon
D)the waning crescent Moon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
When does a solar or lunar eclipse occur?
A)when the Sun is near the plane of the Moon's orbit, and the Moon is new or full
B)any time the Moon is new or full
C)half way through an eclipse year
D)when the Sun is near the equinox and the Moon is new or full
A)when the Sun is near the plane of the Moon's orbit, and the Moon is new or full
B)any time the Moon is new or full
C)half way through an eclipse year
D)when the Sun is near the equinox and the Moon is new or full

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Relative to the stars,the Moon moves eastward in the sky each night.About how far does it move?
A)1°
B)13°
C)27.3°
D)29.5°
A)1°
B)13°
C)27.3°
D)29.5°

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
What is the Saros cycle?
A)the pattern of repetition of solar and lunar eclipses
B)the time between annular eclipses at a particular location
C)the number of full Moons in a year
D)the pattern of events that happen in a single eclipse
A)the pattern of repetition of solar and lunar eclipses
B)the time between annular eclipses at a particular location
C)the number of full Moons in a year
D)the pattern of events that happen in a single eclipse

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
What is the term for a solar eclipse in which the Moon's umbra does not reach the Earth's surface?
A)a partial solar eclipse
B)an annular solar eclipse
C)a penumbral solar eclipse
D)an umbral solar eclipse
A)a partial solar eclipse
B)an annular solar eclipse
C)a penumbral solar eclipse
D)an umbral solar eclipse

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
On the autumnal equinox (Sept.21),where is the Sun on the celestial sphere?
A)23.5° north of the celestial equator
B)23.5° south of the celestial equator
C)on the celestial equator and moving north with respect to the equator
D)on the celestial equator and moving south with respect to the equator
A)23.5° north of the celestial equator
B)23.5° south of the celestial equator
C)on the celestial equator and moving north with respect to the equator
D)on the celestial equator and moving south with respect to the equator

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
What is the term for a solar eclipse in which the Moon's umbra reaches the Earth's surface?
A)a total solar eclipse
B)a partial solar eclipse
C)a penumbral solar eclipse
D)an umbral solar eclipse
A)a total solar eclipse
B)a partial solar eclipse
C)a penumbral solar eclipse
D)an umbral solar eclipse

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
What is the term for the point in the Earth's orbit where the Earth is farthest from the Sun?
A)aphelion
B)perihelion
C)precession
D)the winter solstice
A)aphelion
B)perihelion
C)precession
D)the winter solstice

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
What is the term for the point in the Earth's orbit where the Earth is closest to the Sun?
A)aphelion
B)perihelion
C)precession
D)the vernal equinox
A)aphelion
B)perihelion
C)precession
D)the vernal equinox

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
On the vernal equinox (March 21),where is the Sun on the celestial sphere?
A)23.5° north of the celestial equator
B)23.5° south of the celestial equator
C)on the celestial equator and moving north with respect to the equator
D)on the celestial equator and moving south with respect to the equator
A)23.5° north of the celestial equator
B)23.5° south of the celestial equator
C)on the celestial equator and moving north with respect to the equator
D)on the celestial equator and moving south with respect to the equator

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
What is the term for a lunar eclipse in which the Moon moves completely into the Earth's umbral shadow?
A)a partial lunar eclipse
B)an annular eclipse
C)a penumbral lunar eclipse
D)a total lunar eclipse
A)a partial lunar eclipse
B)an annular eclipse
C)a penumbral lunar eclipse
D)a total lunar eclipse

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
When and where is a third quarter Moon visible?
A)near the eastern horizon just after sunset
B)in the southern sky at sunrise
C)in the southern sky at sunset
D)from sunset until sunrise
A)near the eastern horizon just after sunset
B)in the southern sky at sunrise
C)in the southern sky at sunset
D)from sunset until sunrise

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
What is the sidereal period of the Moon?
A)the period of time between one full Moon and the next
B)the period of time for the Moon to orbit the Earth once with respect to the stars
C)the period of time between successive eclipses at a given location on Earth
D)the period of time from when the Moon rises until the Moon rises again the next night
A)the period of time between one full Moon and the next
B)the period of time for the Moon to orbit the Earth once with respect to the stars
C)the period of time between successive eclipses at a given location on Earth
D)the period of time from when the Moon rises until the Moon rises again the next night

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
What is apparent solar time?
A)the time between successive meridian crossings of a particular star
B)time measured relative to successive meridian crossings of the Sun
C)the period of time between successive solar eclipses at a given location on Earth
D)time measured relative to sunrise and sunset
A)the time between successive meridian crossings of a particular star
B)time measured relative to successive meridian crossings of the Sun
C)the period of time between successive solar eclipses at a given location on Earth
D)time measured relative to sunrise and sunset

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Which of the following describes a concept very similar to latitude?
A)right ascension
B)declination
C)magnitude
D)meridian
A)right ascension
B)declination
C)magnitude
D)meridian

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
What is the term for the Moon when it is visible above the western horizon a couple of hours before sunrise?
A)the waning gibbous Moon
B)the waxing gibbous Moon
C)the waxing crescent Moon
D)the waning crescent Moon
A)the waning gibbous Moon
B)the waxing gibbous Moon
C)the waxing crescent Moon
D)the waning crescent Moon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Which planet(s)in our solar system is (are)never visible to the naked eye?
A)Mercury and Neptune
B)Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune
C)Neptune
D)Mercury and Venus
A)Mercury and Neptune
B)Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune
C)Neptune
D)Mercury and Venus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
What is the term for the period of time it takes for the Moon to complete a cycle of the lunar phases that is approximately 29.5 days long?
A)sidereal period of the Moon
B)saros cycle of the Moon
C)synodic period of the Moon
D)eclipse season of the Moon
A)sidereal period of the Moon
B)saros cycle of the Moon
C)synodic period of the Moon
D)eclipse season of the Moon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
How does the Moon's appearance change during a total lunar eclipse?
A)The Moon goes from new to full.
B)The Moon disappears.
C)The Moon turns a dark red colour.
D)The Moon's far side is visible.
A)The Moon goes from new to full.
B)The Moon disappears.
C)The Moon turns a dark red colour.
D)The Moon's far side is visible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
When and where is a waxing crescent Moon visible?
A)near the eastern horizon just before sunrise
B)near the eastern horizon just after sunset
C)near the western horizon just before sunrise
D)near the western horizon just after sunset
A)near the eastern horizon just before sunrise
B)near the eastern horizon just after sunset
C)near the western horizon just before sunrise
D)near the western horizon just after sunset

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



