Deck 8: The Deaths of Stars
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/145
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 8: The Deaths of Stars
1
When mass is transferred toward a white dwarf in a binary system,the material forms a rapidly growing whirlpool of material.What is that whirlpool called?
A)an accretion disk
B)an Algol paradox
C)a planetary nebula
D)a supernova remnant
A)an accretion disk
B)an Algol paradox
C)a planetary nebula
D)a supernova remnant
an accretion disk
2
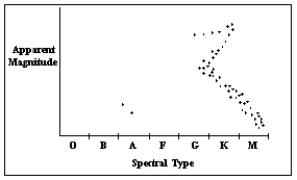
Refer to the H-R diagram.What type of star do the two data points above spectral type "A" represent?
A)massive main-sequence stars
B)massive supergiant stars
C)white dwarfs with mass less than the sun's mass
D)white dwarfs with mass greater than twice the sun's mass
white dwarfs with mass less than the sun's mass
3
As a star exhausts the hydrogen in its core,what happens?
A)It becomes hotter and more luminous.
B)It becomes hotter and less luminous.
C)It becomes cooler and less luminous.
D)It becomes cooler and more luminous.
A)It becomes hotter and more luminous.
B)It becomes hotter and less luminous.
C)It becomes cooler and less luminous.
D)It becomes cooler and more luminous.
It becomes cooler and more luminous.
4

What is the approximate age of the star cluster in the H-R diagram?
(Hint: Main sequence stars of spectral types O and B have a core supply of hydrogen that is sufficient to last about 250 million years;types A and F,about 2 billion years;type G about 10 billion years;types K and M about 30 billion years.The apparent magnitude scale means that larger numbers are toward the bottom of the vertical axis.)
A)200 million years
B)2 billion years
C)10 billion years
D)30 billion years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
What is the defining characteristic of stars within a cluster that are at the turnoff point?
A)They are just leaving the main sequence.
B)They are just becoming white dwarfs.
C)They are just entering the main sequence.
D)They are about to explode in supernovae.
A)They are just leaving the main sequence.
B)They are just becoming white dwarfs.
C)They are just entering the main sequence.
D)They are about to explode in supernovae.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
What is the term for a collection of 100 to 1000 young stars in a region about 80 light-years in diameter?
A)Herbig-Haro object
B)globular cluster
C)open cluster
D)giant cluster
A)Herbig-Haro object
B)globular cluster
C)open cluster
D)giant cluster

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7

Refer to the H-R diagram.How would the H-R diagram of a more distant star cluster look different?
A)The points would shift down, because all of the stars would have larger apparent magnitudes.
B)The points would shift to the right, because all of the stars would appear to be cooler.
C)The points would shift up, because all of the stars would have smaller apparent magnitudes.
D)The points would shift to the left, because all of the stars would appear to be hotter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
What is the term for the form of electromagnetic radiation produced by rapidly moving electrons spiralling through magnetic fields?
A)Lagrangian radiation
B)ultraviolet radiation
C)synchrotron radiation
D)infrared radiation
A)Lagrangian radiation
B)ultraviolet radiation
C)synchrotron radiation
D)infrared radiation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
What property is the same for all stars in a star cluster?
A)age
B)mass
C)luminosity
D)radius
A)age
B)mass
C)luminosity
D)radius

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
When does a star experience helium fusion?
A)when it is on the horizontal branch
B)after it has become a red giant star
C)just before it enters the main sequence
D)before it leaves the main sequence
A)when it is on the horizontal branch
B)after it has become a red giant star
C)just before it enters the main sequence
D)before it leaves the main sequence

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following correctly describes a relationship between pressure,temperature,and density in degenerate matter?
A)Pressure depends only on the temperature.
B)Pressure does not depend on temperature.
C)Temperature depends only on density.
D)Pressure does not depend on density.
A)Pressure depends only on the temperature.
B)Pressure does not depend on temperature.
C)Temperature depends only on density.
D)Pressure does not depend on density.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
What type of object is the Crab nebula?
A)a planetary nebula
B)an open cluster
C)an absorption nebula
D)a supernova remnant
A)a planetary nebula
B)an open cluster
C)an absorption nebula
D)a supernova remnant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
What do we call the region of the HR diagram that represents giant stars that are fusing helium in their cores and then in their shells?
A)turnoff point
B)horizontal branch
C)turn-on point
D)main sequence
A)turnoff point
B)horizontal branch
C)turn-on point
D)main sequence

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which nuclear fuels does a one solar mass star use over the course of its entire lifespan?
A)hydrogen
B)hydrogen and helium
C)hydrogen, helium, and carbon
D)hydrogen, helium, carbon, and oxygen
A)hydrogen
B)hydrogen and helium
C)hydrogen, helium, and carbon
D)hydrogen, helium, carbon, and oxygen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15

Refer to the H-R diagram.How would the H-R diagram of an older star cluster look different?
A)The points would shift to the right, because all of the stars would have lower temperatures.
B)The lower main sequence would look the same, but the turnoff would be at spectral type K or M.
C)The points would shift down, because all of the stars would have lower luminosities.
D)The lower main sequence would look the same, but the turnoff would be at spectral type F or A.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
What is the term for a collection of 10⁵ to 10⁶ old stars in a region 30 to 100 light-years in diameter?
A)Herbig-Haro object
B)globular cluster
C)open cluster
D)giant cluster
A)Herbig-Haro object
B)globular cluster
C)open cluster
D)giant cluster

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Why are giant and supergiant stars rare?
A)The giant and supergiant stages are very short.
B)The star blows up before the giant or supergiant stage is reached.
C)They do not form as often as main sequence stars.
D)The giant or supergiant stage is very long.
A)The giant and supergiant stages are very short.
B)The star blows up before the giant or supergiant stage is reached.
C)They do not form as often as main sequence stars.
D)The giant or supergiant stage is very long.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
If the stars at the turnoff point of a cluster have a mass of 3 times the mass of the Sun,what is the age of the cluster?
A)6.4×10⁸ years
B)3.3×10⁹ years
C)3.0×10¹⁰ years
D)1.6×10¹¹ years
A)6.4×10⁸ years
B)3.3×10⁹ years
C)3.0×10¹⁰ years
D)1.6×10¹¹ years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Why are star clusters important to our study of stars?
A)because all stars formed in star clusters
B)because they allow us to test our theories and models of stellar evolution
C)because the Sun was once a member of a globular cluster
D)because they are the only objects that contain Cepheid variables
A)because all stars formed in star clusters
B)because they allow us to test our theories and models of stellar evolution
C)because the Sun was once a member of a globular cluster
D)because they are the only objects that contain Cepheid variables

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
What principle explains why matter flowing from one star in a binary system to its companion forms an accretion disk?
A)conservation of tidal forces
B)conservation of temperature
C)conservation of angular momentum
D)conservation of energy
A)conservation of tidal forces
B)conservation of temperature
C)conservation of angular momentum
D)conservation of energy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
As a white dwarf cools,why does its radius NOT change?
A)because pressure due to nuclear reactions in a shell just below the surface keeps it from collapsing
B)because pressure does not depend on temperature for a white dwarf, since the electrons are degenerate
C)because pressure does not depend on temperature, since the star has exhausted all its nuclear fuels
D)because material accreting onto it from a companion maintains a constant radius
A)because pressure due to nuclear reactions in a shell just below the surface keeps it from collapsing
B)because pressure does not depend on temperature for a white dwarf, since the electrons are degenerate
C)because pressure does not depend on temperature, since the star has exhausted all its nuclear fuels
D)because material accreting onto it from a companion maintains a constant radius

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
When material expanding away from a star in a binary system reaches the edge of its Roche lobe,what happens?
A)The material will start to fall back toward the star.
B)All of the material will accrete on to the companion.
C)The material will no longer be gravitationally bound to the star.
D)The material will increase in temperature and eventually undergo thermonuclear fusion.
A)The material will start to fall back toward the star.
B)All of the material will accrete on to the companion.
C)The material will no longer be gravitationally bound to the star.
D)The material will increase in temperature and eventually undergo thermonuclear fusion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Where is synchrotron radiation produced?
A)in planetary nebulae
B)in the outer layers of red dwarfs
C)in the collapsing iron cores of massive stars
D)in supernova remnants
A)in planetary nebulae
B)in the outer layers of red dwarfs
C)in the collapsing iron cores of massive stars
D)in supernova remnants

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Why can't massive stars generate energy through iron fusion?
A)because iron fusion requires very high density
B)because no star can get hot enough for iron fusion
C)because both fusion and fission of iron nuclei absorb energy
D)because massive stars go supernova before they create an iron core
A)because iron fusion requires very high density
B)because no star can get hot enough for iron fusion
C)because both fusion and fission of iron nuclei absorb energy
D)because massive stars go supernova before they create an iron core

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What is a white dwarf composed of?
A)hydrogen nuclei and degenerate electrons
B)helium nuclei and normal electrons
C)carbon and oxygen nuclei and degenerate electrons
D)degenerate iron nuclei
A)hydrogen nuclei and degenerate electrons
B)helium nuclei and normal electrons
C)carbon and oxygen nuclei and degenerate electrons
D)degenerate iron nuclei

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
What does the Chandrasekhar-Landau limit tell us?
A)Accretion disks can grow hot through friction.
B)Neutron stars of more than 3 solar masses are not stable.
C)White dwarfs more massive than 1.4 solar masses are not stable.
D)Stars with a mass less than 0.5 solar masses will not go through helium flash.
A)Accretion disks can grow hot through friction.
B)Neutron stars of more than 3 solar masses are not stable.
C)White dwarfs more massive than 1.4 solar masses are not stable.
D)Stars with a mass less than 0.5 solar masses will not go through helium flash.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Why can't the lowest mass stars become giants?
A)Their centres never get hot enough.
B)Their rotation is too slow.
C)They do not contain helium.
D)They never use up their hydrogen.
A)Their centres never get hot enough.
B)Their rotation is too slow.
C)They do not contain helium.
D)They never use up their hydrogen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
After they leave the main sequence,what happens to stars with masses between 0.4 and 4 solar masses?
A)They undergo thermonuclear fusion of hydrogen and helium, but never get hot enough to ignite carbon.
B)They undergo thermonuclear fusion of hydrogen, but never get hot enough to ignite helium.
C)They produce type-I supernovae after they exhaust their nuclear fuels.
D)They produce type-II supernovae after they exhaust their nuclear fuels.
A)They undergo thermonuclear fusion of hydrogen and helium, but never get hot enough to ignite carbon.
B)They undergo thermonuclear fusion of hydrogen, but never get hot enough to ignite helium.
C)They produce type-I supernovae after they exhaust their nuclear fuels.
D)They produce type-II supernovae after they exhaust their nuclear fuels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
When does a type-II supernova occur?
A)when a white dwarf's mass exceeds the Chandrasekhar-Landau limit
B)when the iron core of a massive star collapses
C)directly following a helium flash
D)when two neutron stars collide
A)when a white dwarf's mass exceeds the Chandrasekhar-Landau limit
B)when the iron core of a massive star collapses
C)directly following a helium flash
D)when two neutron stars collide

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following is almost always associated with a nova?
A)a very massive star
B)a star undergoing helium burning
C)a white dwarf in a close binary system
D)a solar-like star that has exhausted its hydrogen and helium
A)a very massive star
B)a star undergoing helium burning
C)a white dwarf in a close binary system
D)a solar-like star that has exhausted its hydrogen and helium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
What is a planetary nebula?
A)the expelled outer envelope of a medium mass star
B)a cloud of hot gas produced by a supernova explosion
C)a nebula within which planets are forming
D)a cloud of hot gas surrounding a planet
A)the expelled outer envelope of a medium mass star
B)a cloud of hot gas produced by a supernova explosion
C)a nebula within which planets are forming
D)a cloud of hot gas surrounding a planet

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
What produces synchrotron radiation?
A)objects with temperatures below 10,000 K
B)high-velocity electrons moving through a magnetic field
C)cold hydrogen atoms in space
D)helium burning in a massive star
A)objects with temperatures below 10,000 K
B)high-velocity electrons moving through a magnetic field
C)cold hydrogen atoms in space
D)helium burning in a massive star

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
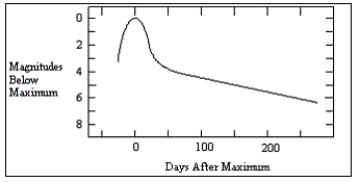
The diagram shows a light curve from a supernova.How many days after maximum light did it take for the supernova to decrease in brightness by 5 magnitudes?
A)less than 50
B)50
C)150
D)250

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
What does a planetary nebula do?
A)produces an absorption spectrum
B)produces an emission spectrum
C)contracts to form planets
D)contracts to form a star
A)produces an absorption spectrum
B)produces an emission spectrum
C)contracts to form planets
D)contracts to form a star

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35

The diagram shows a light curve from a supernova.About how long did it take for the supernova to reach its maximum luminosity?
A)25 days
B)50 days
C)100 days
D)200 days

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Suppose you discover a binary star system with a 0.7 solar mass giant star and a 2 solar mass main sequence star.Why is this surprising?
A)0.7 solar mass stars are not expected to become giants.
B)All 2 solar mass stars should have left the main sequence.
C)Giant stars are expected to destroy their companions, so the 2 solar mass star shouldn't exist.
D)The 2 solar mass star should have become a giant before the 0.7 solar mass star.
A)0.7 solar mass stars are not expected to become giants.
B)All 2 solar mass stars should have left the main sequence.
C)Giant stars are expected to destroy their companions, so the 2 solar mass star shouldn't exist.
D)The 2 solar mass star should have become a giant before the 0.7 solar mass star.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
If the hypothesis that novae occur in close binary systems is correct,then which of the following should novae do?
A)They should produce synchrotron radiation.
B)They should occur in regions of star formation.
C)They should all be visual binaries.
D)They should repeat after some interval.
A)They should produce synchrotron radiation.
B)They should occur in regions of star formation.
C)They should all be visual binaries.
D)They should repeat after some interval.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
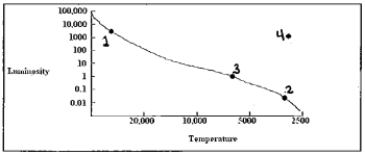
Which point indicates the location on the H-R diagram of a one-solar-mass star when it stars to fuse helium?
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following offered support for the theory that the collapse of a massive star's iron core produces neutrinos?
A)the detection of neutrinos from the supernova of 1987
B)the brightening of supernovae a few days after they are first visible
C)underground counts of solar neutrinos
D)laboratory measurements of the mass of the neutrino
A)the detection of neutrinos from the supernova of 1987
B)the brightening of supernovae a few days after they are first visible
C)underground counts of solar neutrinos
D)laboratory measurements of the mass of the neutrino

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Under what conditions are Type Ia supernovae believed to occur?
A)when the core of a massive star collapses
B)when a white dwarf exceeds the Chandrasekhar-Landau limit
C)when hydrogen detonation occurs
D)when neutrinos in a massive star form a shock wave that explodes the star
A)when the core of a massive star collapses
B)when a white dwarf exceeds the Chandrasekhar-Landau limit
C)when hydrogen detonation occurs
D)when neutrinos in a massive star form a shock wave that explodes the star

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
After what evolutionary stage does a star become a white dwarf?
A)protostar
B)pre-main sequence
C)main sequence
D)giant
A)protostar
B)pre-main sequence
C)main sequence
D)giant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
For a star with a mass similar to that of the Sun,what is the last stage of the nuclear fusion?
A)hydrogen to helium
B)helium to carbon and oxygen
C)carbon to magnesium
D)silicon to iron
A)hydrogen to helium
B)helium to carbon and oxygen
C)carbon to magnesium
D)silicon to iron

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
What happens when light travels out of a gravitational field,loses energy,and its wavelength grows longer?
A)a gravitational blue shift
B)the solar wind
C)a gravitational red shift
D)a pulsar wind
A)a gravitational blue shift
B)the solar wind
C)a gravitational red shift
D)a pulsar wind

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
What is the density of a neutron star?
A)about the same as that of a white dwarf
B)about the same as that of the Sun
C)about the same as that of an atomic nucleus
D)zero
A)about the same as that of a white dwarf
B)about the same as that of the Sun
C)about the same as that of an atomic nucleus
D)zero

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Why can't pulsars be spinning white dwarfs?
A)White dwarfs are not very common.
B)White dwarfs are not dense enough to produce bright pulses.
C)White dwarfs do not have magnetic fields.
D)White dwarfs are too large to produce such short pulses.
A)White dwarfs are not very common.
B)White dwarfs are not dense enough to produce bright pulses.
C)White dwarfs do not have magnetic fields.
D)White dwarfs are too large to produce such short pulses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
What are the two longest stages in the life of a one solar mass star?
A)protostar, pre-main sequence
B)protostar, white dwarf
C)protostar, main sequence
D)main sequence, white dwarf
A)protostar, pre-main sequence
B)protostar, white dwarf
C)protostar, main sequence
D)main sequence, white dwarf

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
What is the source of the energy radiated by a white dwarf?
A)the proton-proton chain
B)the CNO cycle
C)gravitational contraction after becoming a white dwarf
D)gravitational contraction during the white dwarf formation phase
A)the proton-proton chain
B)the CNO cycle
C)gravitational contraction after becoming a white dwarf
D)gravitational contraction during the white dwarf formation phase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
About how long will a 0.5 solar mass star spend on the main sequence?
A)5 million years
B)570 million years
C)5 billion years
D)57 billion years
A)5 million years
B)570 million years
C)5 billion years
D)57 billion years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
If you had an extremely sensitive radio telescope,could you detect every pulsar in the Milky Way galaxy?
A)Yes, because all pulsars emit radio waves.
B)Yes, because all pulsars are nearby.
C)No, some pulsars don't flash all of the time.
D)No, some pulsar beams don't point in the direction of Earth.
A)Yes, because all pulsars emit radio waves.
B)Yes, because all pulsars are nearby.
C)No, some pulsars don't flash all of the time.
D)No, some pulsar beams don't point in the direction of Earth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which of the following has a radius of about 10 kilometres and is supported by the pressure associated with degenerate neutrons?
A)black hole
B)neutron star
C)white dwarf
D)supernova remnant
A)black hole
B)neutron star
C)white dwarf
D)supernova remnant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
What happens to stars that have ejected a planetary nebula?
A)They become protostars.
B)They become brown dwarfs.
C)They become white dwarfs.
D)They become red giants.
A)They become protostars.
B)They become brown dwarfs.
C)They become white dwarfs.
D)They become red giants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
In the year 10⁵4 CE,Chinese astronomers observed the appearance of a new star.What occupies that location now?
A)a molecular cloud
B)a planetary nebula with a white dwarf in the centre
C)a supernova remnant with a pulsar in the centre
D)nothing
A)a molecular cloud
B)a planetary nebula with a white dwarf in the centre
C)a supernova remnant with a pulsar in the centre
D)nothing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
What does the explosion of a type II supernova typically leave behind?
A)a planetary nebula
B)a shell of hot, expanding gas with a white dwarf at the centre
C)a shell of hot, expanding gas with a pulsar at the centre
D)nothing is ever left behind
A)a planetary nebula
B)a shell of hot, expanding gas with a white dwarf at the centre
C)a shell of hot, expanding gas with a pulsar at the centre
D)nothing is ever left behind

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
What are hypernovae?
A)supernovae that occur when two red dwarfs collide
B)supernovae that occur when 10 solar mass stars explode
C)supernovae that occur when stars more massive than 25 solar masses explode
D)supernovae that occur when two black holes collide
A)supernovae that occur when two red dwarfs collide
B)supernovae that occur when 10 solar mass stars explode
C)supernovae that occur when stars more massive than 25 solar masses explode
D)supernovae that occur when two black holes collide

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Why are neutron stars expected to spin rapidly?
A)They conserve angular momentum when they collapse.
B)They have high orbital velocities.
C)They have high densities.
D)The energy from the supernova explosion that formed them makes them spin faster.
A)They conserve angular momentum when they collapse.
B)They have high orbital velocities.
C)They have high densities.
D)The energy from the supernova explosion that formed them makes them spin faster.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Why do astronomers sometimes say "black holes don't suck"?
A)Black holes can have accretion disks around them.
B)The distance between a black hole event horizon and singularity is not very large.
C)Material that falls into a black hole can come out later.
D)A black hole's gravity is the same as that of any other object of the same mass.
A)Black holes can have accretion disks around them.
B)The distance between a black hole event horizon and singularity is not very large.
C)Material that falls into a black hole can come out later.
D)A black hole's gravity is the same as that of any other object of the same mass.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
What is the term that describes the slowing of clocks in strongly curved space-time?
A)gravitational radiation
B)time dilation
C)gravitational red shift
D)hyperspace drag
A)gravitational radiation
B)time dilation
C)gravitational red shift
D)hyperspace drag

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Although neutron stars are very hot,they are faint and not easy to see at visual wavelengths.Why is this?
A)Light does not escape from their event horizon.
B)Most neutron stars lie beyond dense dust clouds.
C)They have only a small surface area from which to emit light.
D)The peak of their thermal emission is at infrared wavelengths.
A)Light does not escape from their event horizon.
B)Most neutron stars lie beyond dense dust clouds.
C)They have only a small surface area from which to emit light.
D)The peak of their thermal emission is at infrared wavelengths.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
What is the term for the distance from a black hole at which the escape velocity is approximately equal to the speed of light?
A)Lagrangian point
B)Chandrasekhar-Landau limit
C)Hubble radius
D)Schwarzschild radius
A)Lagrangian point
B)Chandrasekhar-Landau limit
C)Hubble radius
D)Schwarzschild radius

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Observations from the Compton Gamma Ray Observatory showed that gamma ray bursts were located all over the sky.What did astronomers conclude from this?
A)The bursts were produced by stars in the disk of our galaxy.
B)The bursts were associated with planets in our solar system.
C)The bursts were produced by sources in distant galaxies.
D)The bursts were produced in our Sun.
A)The bursts were produced by stars in the disk of our galaxy.
B)The bursts were associated with planets in our solar system.
C)The bursts were produced by sources in distant galaxies.
D)The bursts were produced in our Sun.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
What has greater density than a white dwarf?
A)a neutron star
B)a red dwarf
C)a brown dwarf
D)a red giant
A)a neutron star
B)a red dwarf
C)a brown dwarf
D)a red giant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The rotation speed of pulsars slows down over time.What is believed to be the reason for this?
A)They are losing angular momentum into space via outward streaming particles.
B)They are dragging companion stars around in their magnetic fields.
C)They are conserving angular momentum.
D)Their mass is increasing.
A)They are losing angular momentum into space via outward streaming particles.
B)They are dragging companion stars around in their magnetic fields.
C)They are conserving angular momentum.
D)Their mass is increasing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Why is the material that accretes onto a neutron star or black hole expected to emit X-rays?
A)The material contains magnetic fields that will produce synchrotron radiation.
B)Hydrogen nuclei begin to fuse and emit high energy photons.
C)The material will become hot enough that it will radiate most strongly at X-ray wavelengths.
D)As the material slows down it converts thermal energy to gravitational potential energy.
A)The material contains magnetic fields that will produce synchrotron radiation.
B)Hydrogen nuclei begin to fuse and emit high energy photons.
C)The material will become hot enough that it will radiate most strongly at X-ray wavelengths.
D)As the material slows down it converts thermal energy to gravitational potential energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
How are millisecond pulsars unusual compared to other pulsars?
A)Their spin rates are fast for their age.
B)They only emit millimetre-wave radiation.
C)They have strong magnetic fields.
D)They are all X-ray binaries.
A)Their spin rates are fast for their age.
B)They only emit millimetre-wave radiation.
C)They have strong magnetic fields.
D)They are all X-ray binaries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
What is interesting about the orbit of the binary pulsar,PSR 1936+16,studied by Taylor and Hulse?
A)It is so small that the orbital period is smaller than the pulsar period.
B)It is growing smaller, presumably by emitting gravitational waves.
C)It provides evidence that it is being orbited by at least 6 planets the size of Jupiter.
D)It shows large changes each time an X-ray burst is emitted from the system.
A)It is so small that the orbital period is smaller than the pulsar period.
B)It is growing smaller, presumably by emitting gravitational waves.
C)It provides evidence that it is being orbited by at least 6 planets the size of Jupiter.
D)It shows large changes each time an X-ray burst is emitted from the system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
What is the approximate size of the Schwarzschild radius of a one solar mass black hole?
A)3 kilometres
B)1,500,000 kilometres, the size of the Sun
C)150,000,000 kilometres, or 1 AU
D)1013 kilometres, or 1 light-year
A)3 kilometres
B)1,500,000 kilometres, the size of the Sun
C)150,000,000 kilometres, or 1 AU
D)1013 kilometres, or 1 light-year

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Cygnus X-1 and LMC X-3 are binary systems with one component not visible.What must the unseen component masses be for astronomers to be certain that these systems contain a black hole?
A)less than 0.4 solar masses
B)between 0.4 and 1.4 solar masses
C)less than 5 solar masses
D)more than 5 solar masses
A)less than 0.4 solar masses
B)between 0.4 and 1.4 solar masses
C)less than 5 solar masses
D)more than 5 solar masses

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Which of the following would be most likely to indicate the presence of an isolated black hole?
A)bending of light from background stars
B)emission of light from within an event horizon
C)gravitational effects on a binary companion
D)X-ray emission from an accretion disk
A)bending of light from background stars
B)emission of light from within an event horizon
C)gravitational effects on a binary companion
D)X-ray emission from an accretion disk

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which of the following is NOT a property of pulsars?
A)strong magnetic field
B)rapid rotation
C)radius of at least 100 km
D)association with supernova remnants
A)strong magnetic field
B)rapid rotation
C)radius of at least 100 km
D)association with supernova remnants

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Do all supernova remnants contain pulsars?
A)Yes, pulsars are visible in all supernova remnants.
B)No, some supernova explosions form white dwarfs instead of the neutron stars necessary for pulsars.
C)No: all supernova remnants start out having pulsars but the pulsars can disappear before the supernova remnant dissipates.
D)Yes, but some pulsars' pulses are not visible from Earth because of the direction of their rotational axis.
A)Yes, pulsars are visible in all supernova remnants.
B)No, some supernova explosions form white dwarfs instead of the neutron stars necessary for pulsars.
C)No: all supernova remnants start out having pulsars but the pulsars can disappear before the supernova remnant dissipates.
D)Yes, but some pulsars' pulses are not visible from Earth because of the direction of their rotational axis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Which of the following mechanisms would be involved in extracting energy from compact objects?
A)time dilation
B)white holes
C)gravitational redshifts
D)jets and accretion disks
A)time dilation
B)white holes
C)gravitational redshifts
D)jets and accretion disks

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Which of the following objects is believed to possibly contain a black hole?
A)the central star of the Crab nebula
B)the Orion nebula
C)LMC X-3
D)PSR 1257+12
A)the central star of the Crab nebula
B)the Orion nebula
C)LMC X-3
D)PSR 1257+12

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Why is the name pulsar a poor description of the object?
A)Pulsars are neutron stars.
B)Pulsars' radio emissions are irregular.
C)Pulsars vibrate rather than pulsate.
D)Pulsars flash rather than pulsate.
A)Pulsars are neutron stars.
B)Pulsars' radio emissions are irregular.
C)Pulsars vibrate rather than pulsate.
D)Pulsars flash rather than pulsate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Who discovered the first pulsar,in November of 1967?
A)Jocelyn Bell
B)Russel Hulse and Joseph Taylor
C)Walter Baade
D)Edwin Hubble
A)Jocelyn Bell
B)Russel Hulse and Joseph Taylor
C)Walter Baade
D)Edwin Hubble

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
What is odd about the existence of planets around PSR J1257+12?
A)The gravitational pull of the pulsar should have pulled the planets down onto it.
B)Planets would not be expected to survive the supernova explosion that created the pulsar.
C)The planets should have been destroyed by the radiation from the pulsar.
D)The pulsar is rotating so fast that the planets should have been flung into space.
A)The gravitational pull of the pulsar should have pulled the planets down onto it.
B)Planets would not be expected to survive the supernova explosion that created the pulsar.
C)The planets should have been destroyed by the radiation from the pulsar.
D)The pulsar is rotating so fast that the planets should have been flung into space.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
What is the Schwarzschild radius?
A)the distance between a neutron star's centre and its surface
B)the distance between a black hole and its event horizon
C)the inner boundary of a planetary nebula
D)the point where synchrotron radiation is created around a pulsar
A)the distance between a neutron star's centre and its surface
B)the distance between a black hole and its event horizon
C)the inner boundary of a planetary nebula
D)the point where synchrotron radiation is created around a pulsar

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Which of the following factors does the escape velocity from the surface of an object depend on?
A)the object's mass and radius
B)the object's mass only
C)the object's radius and the mass of the object trying to escape
D)the object's radius and the speed of light
A)the object's mass and radius
B)the object's mass only
C)the object's radius and the mass of the object trying to escape
D)the object's radius and the speed of light

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
When searching for black holes,what associated phenomena do astronomers search for?
A)single stars that emit large quantities of X-rays
B)X-ray binaries where the compact companion has a mass in excess of 3 solar masses
C)large spherical regions from which no light is detected
D)pulsars with periods of less than one millisecond
A)single stars that emit large quantities of X-rays
B)X-ray binaries where the compact companion has a mass in excess of 3 solar masses
C)large spherical regions from which no light is detected
D)pulsars with periods of less than one millisecond

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Where is the singularity of a black hole found?
A)It is found outside the event horizon.
B)It is located within the event horizon.
C)It is located at the Lagrangian point if the black hole is in a binary system.
D)It doesn't exist, since all black holes have a finite size.
A)It is found outside the event horizon.
B)It is located within the event horizon.
C)It is located at the Lagrangian point if the black hole is in a binary system.
D)It doesn't exist, since all black holes have a finite size.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Which of the following is an example of time dilation?
A)As material approaches a black hole event horizon, it appears redder and redder.
B)The time that a star spends as a giant is much shorter than its main-sequence lifetime.
C)Pulsars' pulsation periods slow down as they age.
D)As a star approaches a black hole's event horizon, it appears to move more and more slowly.
A)As material approaches a black hole event horizon, it appears redder and redder.
B)The time that a star spends as a giant is much shorter than its main-sequence lifetime.
C)Pulsars' pulsation periods slow down as they age.
D)As a star approaches a black hole's event horizon, it appears to move more and more slowly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



