Deck 22: Neonatal and Pediatric Ventilation
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/40
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 22: Neonatal and Pediatric Ventilation
1
The pressure manometer in-line with a bubble CPAP setup is reading higher than the depth of the expiratory limb in the liquid-filled bottle.This is most likely caused by which of the following?
A) Set flow rate above 5 L/min
B) Set flow rate below 5 L/min
C) Fluid in the inspiratory line
D) Improperly placed manometer
A) Set flow rate above 5 L/min
B) Set flow rate below 5 L/min
C) Fluid in the inspiratory line
D) Improperly placed manometer
A
The set flow rate for a bubble CPAP setup is 5 L/min.Flow rates above 5 L/min result in higher pressures than those anticipated by the submersion depth of the distal tubing.Flow rates lower than 5 L/min would not be able to maintain the bubble CPAP level needed for a given depth.Improper placement of the manometer could result in lower pressures than expected,because the manometer would not be reading pressure on exhalation.Fluid in the inspiratory line may drop the pressure reading by the manometer,because it would cause back pressure behind the fluid.
The set flow rate for a bubble CPAP setup is 5 L/min.Flow rates above 5 L/min result in higher pressures than those anticipated by the submersion depth of the distal tubing.Flow rates lower than 5 L/min would not be able to maintain the bubble CPAP level needed for a given depth.Improper placement of the manometer could result in lower pressures than expected,because the manometer would not be reading pressure on exhalation.Fluid in the inspiratory line may drop the pressure reading by the manometer,because it would cause back pressure behind the fluid.
2
The mode of ventilation that allows a neonate to breathe at a high and a low CPAP setting is which of the following?
A) SiPAP
B) HFOV
C) Nasal IMV
D) Nasal HFV
A) SiPAP
B) HFOV
C) Nasal IMV
D) Nasal HFV
A
Nasal SiPAP allows the neonate to breathe continuously at CPAP and during a sustained "sigh" breath to recruit lung units at two different lung volumes.It allows the neonate to breathe at a high and a low CPAP setting.
Nasal SiPAP allows the neonate to breathe continuously at CPAP and during a sustained "sigh" breath to recruit lung units at two different lung volumes.It allows the neonate to breathe at a high and a low CPAP setting.
3
Neonatal patients are more vulnerable to rapid deterioration because of ________________.
A) high chest wall compliance
B) low functional residual capacity
C) smaller surface area for gas exchange
D) presence of fetal hemoglobin
A) high chest wall compliance
B) low functional residual capacity
C) smaller surface area for gas exchange
D) presence of fetal hemoglobin
C
Neonatal and pediatric patients have smaller lungs,higher airway resistance,lower lung compliance,less surface area for gas exchange,and lower cardiovascular reserve than do adults; all of these factors make them more vulnerable to rapid deterioration.Although neonates have high chest wall compliance,this is not the reason for their vulnerability to rapid deterioration.It is the reason for the presence of retractions when the WOB is elevated.
Neonatal and pediatric patients have smaller lungs,higher airway resistance,lower lung compliance,less surface area for gas exchange,and lower cardiovascular reserve than do adults; all of these factors make them more vulnerable to rapid deterioration.Although neonates have high chest wall compliance,this is not the reason for their vulnerability to rapid deterioration.It is the reason for the presence of retractions when the WOB is elevated.
4
A 5-year-old patient diagnosed with tracheomalacia after a long intubation has had numerous failures to wean and extubate.What should the respiratory therapist recommend to help alleviate spontaneous breathing problems associated with tracheomalacia until a stent can be placed in the airway?
A) BiPAP
B) Nasal HFV
C) Nasal SiPAP
D) Tracheostomy and CPAP
A) BiPAP
B) Nasal HFV
C) Nasal SiPAP
D) Tracheostomy and CPAP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Nasal CPAP should be administered to a neonate with _______________.
A) cleft palate
B) choanal atresia
C) apnea of prematurity
D) tracheoesophageal fistula
A) cleft palate
B) choanal atresia
C) apnea of prematurity
D) tracheoesophageal fistula

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Respiratory failure is imminent in infants who demonstrate which of the following?
A) Substernal retractions
B) Tachypnea
C) Grunting
D) Nasal flaring
A) Substernal retractions
B) Tachypnea
C) Grunting
D) Nasal flaring

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A newborn of 32 weeks' gestation is currently receiving nasal CPAP.The respiratory therapist recently increased the CPAP level from 8 to 10 cm H₂O; the FɪO₂ is 0.6.On the new setting,the PₐO₂ is 52 mm Hg and the PₐCO₂ increased from 48 to 55 mm Hg.The most likely cause of this is which of the following?
A) Barotrauma
B) Alveolar overdistention
C) Ventilator-induced lung injury
D) Increased pulmonary vascular resistance
A) Barotrauma
B) Alveolar overdistention
C) Ventilator-induced lung injury
D) Increased pulmonary vascular resistance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Oxygen delivery and tissue perfusion may be evaluated clinically by which of the following?
A) Mucous membrane color
B) Skin color and tone
C) Capillary refill
D) Chest X-ray
A) Mucous membrane color
B) Skin color and tone
C) Capillary refill
D) Chest X-ray

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The minimum acceptable pH for a premature or term newborn is which of the following?
A) 7.20
B) 7.25
C) 7.30
D) 7.35
A) 7.20
B) 7.25
C) 7.30
D) 7.35

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A full-term neonate shows signs of respiratory distress after delivery by cesarean section.The baby is placed on nasal CPAP at 4 cm H₂O with an FɪO₂ of 0.6.The ABG results on these settings are: pH = 7.32,PₐCO₂ = 45 mm Hg,PₐO₂ = 48 mm Hg,SₐO₂ = 70%,HCO₃⁻ = 22 mEq/L.The respiratory therapist should recommend which of the following?
A) Intubate and mechanically ventilate.
B) Increase the FɪO₂ to 0.7.
C) Increase the CPAP to 6 cm H₂O.
D) Intubate and use ventilator CPAP.
A) Intubate and mechanically ventilate.
B) Increase the FɪO₂ to 0.7.
C) Increase the CPAP to 6 cm H₂O.
D) Intubate and use ventilator CPAP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Potential harmful effects of nasal CPAP include which of the following?
A) Volutrauma
B) CO₂ retention
C) Oxygen toxicity
D) Ventilator-induced lung injury
A) Volutrauma
B) CO₂ retention
C) Oxygen toxicity
D) Ventilator-induced lung injury

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A newborn with which of the following clinical manifestations should receive nasal CPAP?
A) Substernal retractions, PₐCO₂ = 65 mm Hg, PₐCO₂ = 48 mm Hg, FɪO₂ = 0.4
B) Tachypnea, nasal flaring, PₐCO₂ = 50 mm Hg, PₐCO₂ = 50 mm Hg, FɪO₂ = 0.6
C) Grunting, substernal retractions, pH = 7.20, PₐCO₂ = 70 mm Hg, PₐCO₂ = 40 mm Hg, FɪO₂ = 0.7
D) Tachypnea, pale skin, pH = 7.32, PₐCO₂ = 45 mm Hg, PₐCO₂ = 75 mm Hg, FɪO₂ = 0.21
A) Substernal retractions, PₐCO₂ = 65 mm Hg, PₐCO₂ = 48 mm Hg, FɪO₂ = 0.4
B) Tachypnea, nasal flaring, PₐCO₂ = 50 mm Hg, PₐCO₂ = 50 mm Hg, FɪO₂ = 0.6
C) Grunting, substernal retractions, pH = 7.20, PₐCO₂ = 70 mm Hg, PₐCO₂ = 40 mm Hg, FɪO₂ = 0.7
D) Tachypnea, pale skin, pH = 7.32, PₐCO₂ = 45 mm Hg, PₐCO₂ = 75 mm Hg, FɪO₂ = 0.21

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
NIV can be used successfully in neonates for which of the following?
A) Severe ventilatory impairment
B) Persistent apnea
C) After extubation
D) Cleft palate
A) Severe ventilatory impairment
B) Persistent apnea
C) After extubation
D) Cleft palate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following are contraindications for the use of pressure support in neonates receiving nasal IMV?
1)Large airway leaks
2)Ineffectiveness of triggering
3)Increased risk of volutrauma
4)Hypocapnia from excessive triggering
A) 1 and 2 only
B) 1 and 3 only
C) 2 and 3 only
D) 2 and 4 only
1)Large airway leaks
2)Ineffectiveness of triggering
3)Increased risk of volutrauma
4)Hypocapnia from excessive triggering
A) 1 and 2 only
B) 1 and 3 only
C) 2 and 3 only
D) 2 and 4 only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Bubble CPAP should_________________________________.
A) bubble only on expiration
B) bubble only on inspiration
C) bubble on inspiration and expiration
D) have a gas flow setting of 10 L/min
A) bubble only on expiration
B) bubble only on inspiration
C) bubble on inspiration and expiration
D) have a gas flow setting of 10 L/min

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The most common interface for infants receiving CPAP is which of the following?
A) Nasopharyngeal tube
B) Binasal prongs
C) Nasal mask
D) Endotracheal tube
A) Nasopharyngeal tube
B) Binasal prongs
C) Nasal mask
D) Endotracheal tube

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The primary goals of mechanical ventilatory support in newborns and pediatric patients include all of the following except ____________________.
A) improving lung compliance
B) eliminating airway resistance
C) achieving adequate lung volume
D) limiting lung injury
A) improving lung compliance
B) eliminating airway resistance
C) achieving adequate lung volume
D) limiting lung injury

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A neonate of 30 weeks' gestation shows signs of respiratory distress after delivery,including grunting,nasal flaring,and cyanosis.The baby is placed on nasal CPAP at 6 cm H₂O with an FɪO₂ of 0.6.The grunting and nasal flaring are alleviated,and the ABG results on these settings are: pH = 7.20,PₐCO₂ = 64 mm Hg,PₐO₂ = 48 mm Hg,SₐO₂ = 70%,HCO₃⁻ = 21 mEq/L.The respiratory therapist should recommend which of the following?
A) Increase the CPAP to 8 cm H₂O and the FɪO₂ to 0.7.
B) Switch to nasal IMV, an inspiratory pressure of 18 cm H₂O, PEEP of 4 cm H₂O, and an FɪO₂ of 0.8.
C) Continue with the current settings and monitor the patient closely.
D) Intubate and use PC-IMV, an inspiratory pressure of 16 cm H₂O, PEEP of 5 cm H₂O, and an FɪO₂ of 0.8.
A) Increase the CPAP to 8 cm H₂O and the FɪO₂ to 0.7.
B) Switch to nasal IMV, an inspiratory pressure of 18 cm H₂O, PEEP of 4 cm H₂O, and an FɪO₂ of 0.8.
C) Continue with the current settings and monitor the patient closely.
D) Intubate and use PC-IMV, an inspiratory pressure of 16 cm H₂O, PEEP of 5 cm H₂O, and an FɪO₂ of 0.8.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Infants with which of the following problems would benefit from nasal CPAP?
A) Cleft palate
B) Choanal atresia
C) Patent ductus arteriosus
D) Tracheoesophageal fistula
A) Cleft palate
B) Choanal atresia
C) Patent ductus arteriosus
D) Tracheoesophageal fistula

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The gas flow rate for a noncommercial bubble CPAP device should be set at _______ L/min.
A) 3
B) 5
C) 8
D) 10
A) 3
B) 5
C) 8
D) 10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The inspiratory time setting for an infant with RDS,airway resistance of 30 cm H₂O/L/sec,and lung compliance of 0.002 L/cm H₂O should be which of the following?
A) 0.25 sec
B) 0.30 sec
C) 0.45 sec
D) 0.55 sec
A) 0.25 sec
B) 0.30 sec
C) 0.45 sec
D) 0.55 sec

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The pressure manometer should be placed at which point in the following CPAP system?
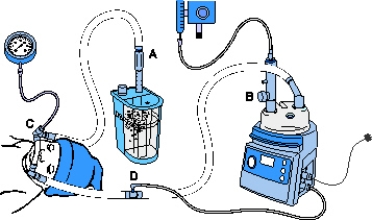
A) Point A
B) Point B
C) Point C
D) Point D

A) Point A
B) Point B
C) Point C
D) Point D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The maximum percent leak that may be allowed around a cuffless endotracheal tube is which of the following?
A) 6%
B) 12%
C) 19%
D) 25%
A) 6%
B) 12%
C) 19%
D) 25%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A pediatric patient with a 5-mm ET tube is ready to be switched to PSV.What minimum PS level should be used for this patient?
A) 4 cm H₂O
B) 6 cm H₂O
C) 8 cm H₂O
D) 10 cm H₂O
A) 4 cm H₂O
B) 6 cm H₂O
C) 8 cm H₂O
D) 10 cm H₂O

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The inspiratory time setting for an infant with bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD),airway resistance of 45 cm H₂O/L/sec,and lung compliance of 0.004 L/cm H₂O should be which of the following?
A) 0.25 second
B) 0.45 second
C) 0.6 second
D) 0.9 second
A) 0.25 second
B) 0.45 second
C) 0.6 second
D) 0.9 second

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The number of time constants for almost complete equilibration of alveolar pressure in a normal infant's lungs is___________.
A) 1-3
B) 2-4
C) 3⁻⁵
D) 4-7
A) 1-3
B) 2-4
C) 3⁻⁵
D) 4-7

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A pediatric patient with air leak syndrome is being ventilated with PC-CMV.The settings are: rate = 20 breaths/min,TI = 0.8 sec,PIP = 30 cm H₂O,PEEP = 8 cm H₂O,FɪO₂ = 0.8,MAP = 14 cm H₂O.The patient is to be switched to HFOV.What MAP range is appropriate for this patient?
A) 8-10 cm H₂O
B) 10-12 cm H₂O
C) 12-14 cm H₂O
D) 14-16 cm H₂O
A) 8-10 cm H₂O
B) 10-12 cm H₂O
C) 12-14 cm H₂O
D) 14-16 cm H₂O

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A pediatric patient intubated with a 3.5-mm endotracheal tube is receiving pressure support ventilation.The respiratory therapist notes patient-ventilator asynchrony and a rapid deceleration of flow that prematurely ends inspiration.The most appropriate action to alleviate this is which of the following?
A) Increase the PS level.
B) Increase the rise time.
C) Decrease the PS level.
D) Increase the flow cycle.
A) Increase the PS level.
B) Increase the rise time.
C) Decrease the PS level.
D) Increase the flow cycle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Neurally adjusted ventilator assist (NAVA)is particularly useful with newborns because it ___________________.
A) reduces gas trapping
B) is not affected by leaks
C) decreases the development of VILA
D) is sensitive to changes in respiratory drive
A) reduces gas trapping
B) is not affected by leaks
C) decreases the development of VILA
D) is sensitive to changes in respiratory drive

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
An 835-g newborn is receiving HFOV with the following settings: MAP = 10 cm H₂O; FɪO₂ = 0.6; frequency = 10 Hz; amplitude (P)= 20 cm H₂O.The ABG values are: pH = 7.35,PₐCO₂ = 40 mm Hg,PₐO₂ = 40 mm Hg.Based on these data,which of the following is the most appropriate action?
A) Increase the frequency.
B) Increase the MAP.
C) Decrease the amplitude.
D) Decrease the bias flow.
A) Increase the frequency.
B) Increase the MAP.
C) Decrease the amplitude.
D) Decrease the bias flow.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A preterm neonate is being supported with nasal SiPAP.The baseline CPAP level is set at 6 cm H₂O,the high CPAP level at 10 cm H₂O,the rate is 20 "sigh" breaths,and the FɪO₂ is 0.8.The baby's PₐO₂ on these settings has been steadily declining and is now 48 mm Hg.The physician and respiratory therapist decided to use nasal HFV before intubating and using mechanical ventilation.The initial settings for NHFV for this patient should include which of the following?
A) MAP = 10 cm H₂O; frequency = 8 Hz; FɪO₂ = 1.0
B) MAP = 10 cm H₂O; frequency = 10 Hz; FɪO₂ = 0.8
C) MAP = 6 cm H₂O; frequency = 8 Hz; FɪO₂ = 0.8
D) MAP = 6 cm H₂O; frequency = 10 Hz; FɪO₂ = 1.0
A) MAP = 10 cm H₂O; frequency = 8 Hz; FɪO₂ = 1.0
B) MAP = 10 cm H₂O; frequency = 10 Hz; FɪO₂ = 0.8
C) MAP = 6 cm H₂O; frequency = 8 Hz; FɪO₂ = 0.8
D) MAP = 6 cm H₂O; frequency = 10 Hz; FɪO₂ = 1.0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following is the term used to describe the exchange of gas between lung units with different time constants?
A) Streaming
B) Pendelluft
C) Taylor-type dispersion
D) Diffusion
A) Streaming
B) Pendelluft
C) Taylor-type dispersion
D) Diffusion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Newer ventilators allow neonates to use what type of trigger for better synchronization with the ventilator?
A) Time
B) Flow
C) Pressure
D) Volume
A) Time
B) Flow
C) Pressure
D) Volume

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A mechanically ventilated pediatric patient in the process of being weaned is switched to PC-IMV with PS.The respiratory therapist notes that every PS breath is being time cycled.The most likely cause of this is which of the following?
A) The PS setting is too high.
B) The flow cycle setting is too low.
C) This is the normal cycle for PS.
D) A large leak is present around the cuffless ET tube.
A) The PS setting is too high.
B) The flow cycle setting is too low.
C) This is the normal cycle for PS.
D) A large leak is present around the cuffless ET tube.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
A neonate is being ventilated with PRVC.The respiratory therapist responds to a low volume alarm.After checking the patient and the ventilator,the respiratory therapist finds no disconnects.The most appropriate action is which of the following?
A) DRₐᴡa sample for arterial blood gas evaluation.
B) Increase the target volume.
C) Put the patient in the PC-CMV mode.
D) Recommend surfactant replacement therapy.
A) DRₐᴡa sample for arterial blood gas evaluation.
B) Increase the target volume.
C) Put the patient in the PC-CMV mode.
D) Recommend surfactant replacement therapy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The patient with which of the following conditions should be considered for HFV?
A) Status asthmaticus
B) Bronchopleural fistula
C) Meconium aspiration
D) Cystic fibrosis
A) Status asthmaticus
B) Bronchopleural fistula
C) Meconium aspiration
D) Cystic fibrosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
During HFOV,oxygenation can be improved by making which of the following changes?
1)Increasing the FɪO₂
2)Decreasing the amplitude
3)Increasing the MAP
4)Increasing the frequency
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) 2 and 4
1)Increasing the FɪO₂
2)Decreasing the amplitude
3)Increasing the MAP
4)Increasing the frequency
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) 2 and 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A 3-month-old,6.4-kg infant with ARDS is receiving ventilatory support.The initial settings are: PC-CMV,PIP = 22 cm H₂O,PEEP = 5 cm H₂O,rate = 30 breaths/min,FɪO₂ = 0.6.The ABG results show a PₐO₂ of 48 mm Hg.The respiratory therapist increases the PEEP to 8 cm H₂O.The pressure-volume loops below show the change that occurs after this increase.(Loop A [solid line] was generated from the initial settings.Loop B [dashed line] was generated from the increase in PEEP.)The respiratory therapist's most appropriate action is which of the following?
A) Decrease the PEEP to 5 cm H₂O.
B) Keep the PEEP at 8 cm H₂O.
C) Decrease the PIP to 20 cm H₂O.
D) Increase the PIP to 24 cm H₂O.
A) Decrease the PEEP to 5 cm H₂O.
B) Keep the PEEP at 8 cm H₂O.
C) Decrease the PIP to 20 cm H₂O.
D) Increase the PIP to 24 cm H₂O.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Both inspiration and expiration are active in which type of high-frequency ventilation?
A) High-frequency positive pressure ventilation
B) High-frequency oscillatory ventilation
C) High-frequency jet ventilation
D) High-frequency percussive ventilation
A) High-frequency positive pressure ventilation
B) High-frequency oscillatory ventilation
C) High-frequency jet ventilation
D) High-frequency percussive ventilation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which type of trigger allows for better synchronization during neonatal ventilation?
A) Flow
B) Time
C) Volume
D) Pressure
A) Flow
B) Time
C) Volume
D) Pressure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



