Deck 26: Metabolism
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/18
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 26: Metabolism
1
Which is the third stage of catabolism?
A) Glycolysis
B) Digestion
C) Formation of acetyl CoA
D) Fatty acid oxidation
E) Citric acid cycle
A) Glycolysis
B) Digestion
C) Formation of acetyl CoA
D) Fatty acid oxidation
E) Citric acid cycle
Citric acid cycle
2
Step 6 of the citric acid cycle is shown. Which statement best describes the role of FAD in this reaction? 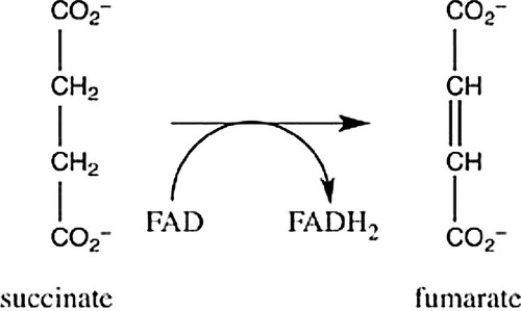
A) FAD causes the oxidation of succinate to form fumarate.
B) FAD causes the isomerication of succinate to form fumarate.
C) FAD causes the reduction of succinate to form fumarate.
D) FAD causes succinate to undergo hydration to form fumarate.

A) FAD causes the oxidation of succinate to form fumarate.
B) FAD causes the isomerication of succinate to form fumarate.
C) FAD causes the reduction of succinate to form fumarate.
D) FAD causes succinate to undergo hydration to form fumarate.
FAD causes the oxidation of succinate to form fumarate.
3
Which is the second stage of catabolism?
A) Glycolysis
B) Fatty acid oxidation
C) Citric acid cycle
D) Digestion
E) Formation of acetyl CoA
A) Glycolysis
B) Fatty acid oxidation
C) Citric acid cycle
D) Digestion
E) Formation of acetyl CoA
Formation of acetyl CoA
4
The second step of the citric acid cycle, the isomerization of citrate to isocitrate, is shown. What is the structure of isocitrate? 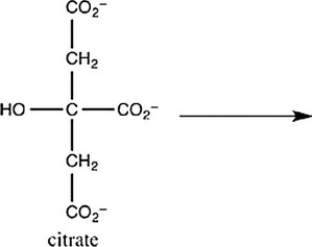
A)
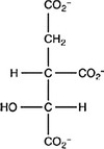
B)
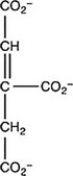
C)
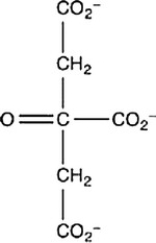
D)
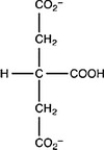

A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
What is the classification of the reaction shown? 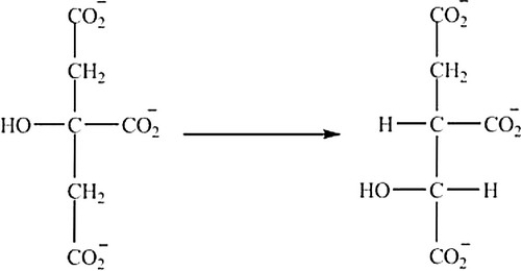
A) Hydrolysis
B) Decarboxylation
C) Isomerization
D) Reduction
E) Oxidation

A) Hydrolysis
B) Decarboxylation
C) Isomerization
D) Reduction
E) Oxidation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Oxaloacetate is the starting material in the first step of the citric acid cycle and the product of the last step. The last step of the citric acid cycle, the oxidation of malate to oxaloacetate, is shown. What is the structure of oxaloacetate? 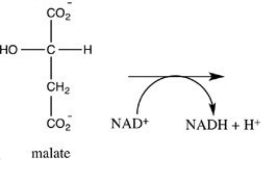
A)
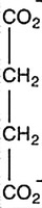
B)
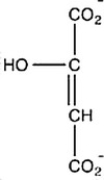
C)
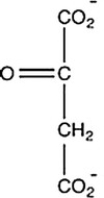
D)
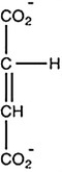

A)
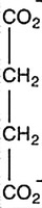
B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which statement best describes how the interconversion of ATP and ADP is responsible for storing and providing energy for cellular reactions? 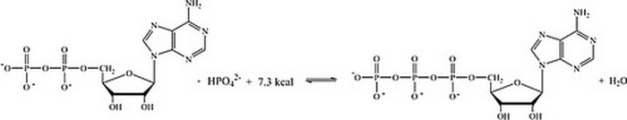
A) The energy required to phosphorylate ADP is stored in ATP, and released when ATP undergoes hydrolysis.
B) The energy required to hydrolyze ATP comes from the energy producing reactions in the cell; the energy lost is then stored in ATP.
C) The energy stored in ADP is released when ATP is synthesized.
D) The energy released in the phosphorylation of ADP can be coupled with unfavorable reactions within the cell.

A) The energy required to phosphorylate ADP is stored in ATP, and released when ATP undergoes hydrolysis.
B) The energy required to hydrolyze ATP comes from the energy producing reactions in the cell; the energy lost is then stored in ATP.
C) The energy stored in ADP is released when ATP is synthesized.
D) The energy released in the phosphorylation of ADP can be coupled with unfavorable reactions within the cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which coupled reaction properly indicates the role of the coenzyme as an oxidizing agent?
A)
B)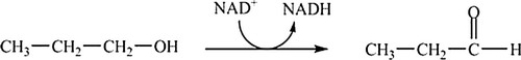
C)
D)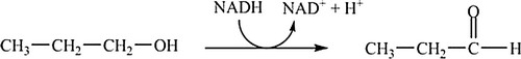
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The conversion of Fe3+ to Fe2+ in the electron transport chain is an example of Fe3+ acting as a (an) ________ agent.
A) oxidizing
B) oxidizing and reducing
C) catalytic
D) reducing
A) oxidizing
B) oxidizing and reducing
C) catalytic
D) reducing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
FAD is the abbreviation for
A) fluorine adenine dinucleotide.
B) flavin adenine dinucleotide.
C) fluorine amino dinucleotide.
D) flavin amino dinucleotide.
A) fluorine adenine dinucleotide.
B) flavin adenine dinucleotide.
C) fluorine amino dinucleotide.
D) flavin amino dinucleotide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
What is the classification of the reaction shown? 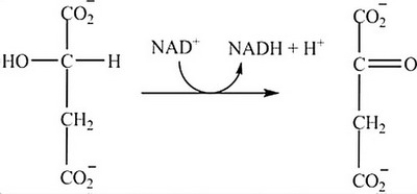
A) Isomerization
B) Hydrolysis
C) Redox
D) Decarboxylation

A) Isomerization
B) Hydrolysis
C) Redox
D) Decarboxylation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which intermediate in the citric acid cycle is a secondary alcohol?
A)
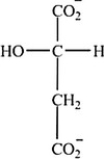
B) Two of the intermediates are secondary alcohols.
C)
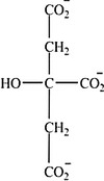
D)
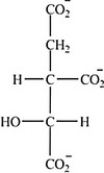
E)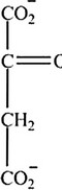
A)

B) Two of the intermediates are secondary alcohols.
C)

D)

E)
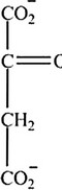

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
How many electrons are donated by each NADH in the electron transport chain?
A) 0
B) 3
C) 2
D) 1
A) 0
B) 3
C) 2
D) 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which is the abbreviated structure of acetyl CoA?
A)
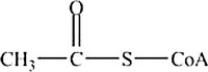
B)
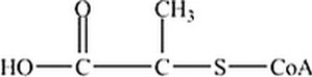
C)
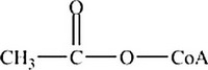
D)
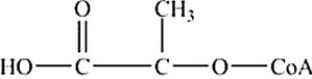
A)
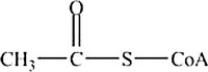
B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Step 7 of the citric acid cycle is shown. Which statement best describes what occurs in this step? 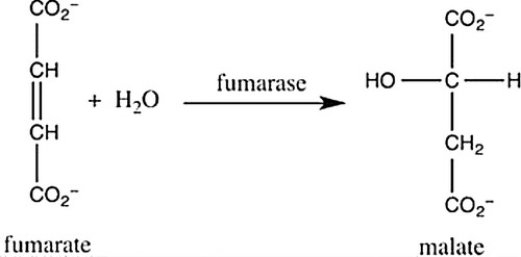
A) Fumarate undergoes reduction with the aid of the cofactor fumarase.
B) Fumarate undergoes hydrogenation with hydrogens and electrons provided by the enzyme fumarase.
C) Fumarate undergoes hydrolysis with the aid of the enzyme fumarase.
D) Fumarate undergoes hydration with the aid of the enzyme fumarase.

A) Fumarate undergoes reduction with the aid of the cofactor fumarase.
B) Fumarate undergoes hydrogenation with hydrogens and electrons provided by the enzyme fumarase.
C) Fumarate undergoes hydrolysis with the aid of the enzyme fumarase.
D) Fumarate undergoes hydration with the aid of the enzyme fumarase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which intermediate in the citric acid cycle contains two chirality centers?
A)
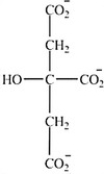
B)
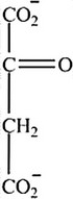
C)
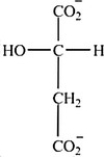
D)
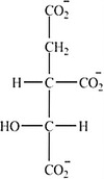
A)

B)
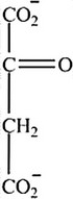
C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which molecule contains the largest amount of stored energy?
A)
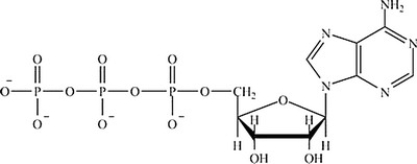
B)
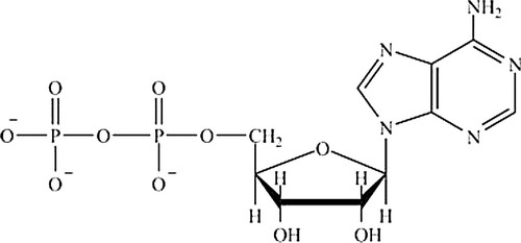
C)
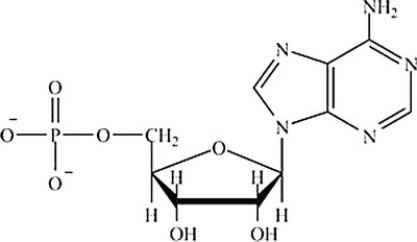
D)
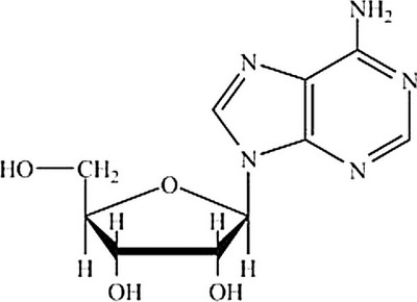
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
What is the primary function of the citric acid cycle in metabolism?
A) To break down food molecules into smaller components so they can be absorbed by the blood
B) To synthesize ATP from the energy produced in the hydrolysis of citric acid
C) To convert acetyl groups to CO2 molecules and provide reduced coenzymes for the electron transport chain
D) To provide the enzymes necessary to aid in the hydrolysis of carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids
A) To break down food molecules into smaller components so they can be absorbed by the blood
B) To synthesize ATP from the energy produced in the hydrolysis of citric acid
C) To convert acetyl groups to CO2 molecules and provide reduced coenzymes for the electron transport chain
D) To provide the enzymes necessary to aid in the hydrolysis of carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



