Deck 25: Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/18
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 25: Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis
1
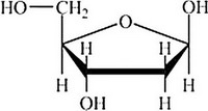
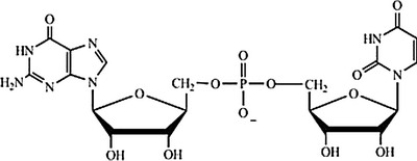
Which structure represents a nucleotide?
A)
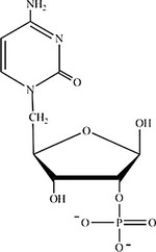
B)
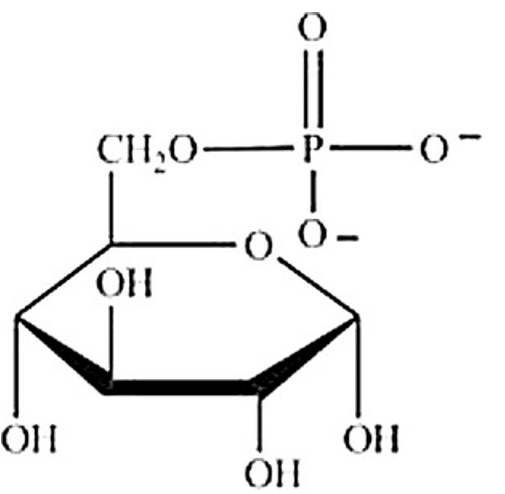
C)
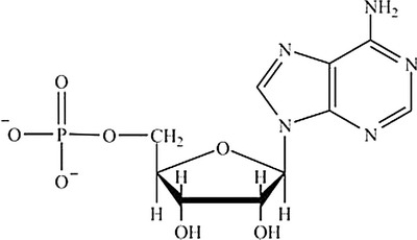
D)
A)

B)

C)

D)


2
In the transcription "cartoon" shown, the direction of transcription is from 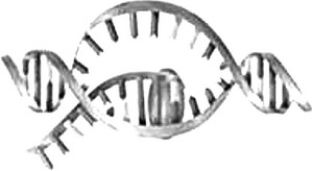
A) top to bottom.
B) right to left.
C) bottom to top.
D) left to right.

A) top to bottom.
B) right to left.
C) bottom to top.
D) left to right.
left to right.
3
Each individual tRNA contains ________.
A) an anticodon complementary to any of the three stop codons
B) the sequence of codons that determines the order of amino acids in the protein
C) an anticodon of three nucleotides that is complementary to the codon in mRNA and identifies individual amino acids
D) a base sequence that is identical to the informational strand of DNA
A) an anticodon complementary to any of the three stop codons
B) the sequence of codons that determines the order of amino acids in the protein
C) an anticodon of three nucleotides that is complementary to the codon in mRNA and identifies individual amino acids
D) a base sequence that is identical to the informational strand of DNA
an anticodon of three nucleotides that is complementary to the codon in mRNA and identifies individual amino acids
4
The "cartoon" shown below is an example of an 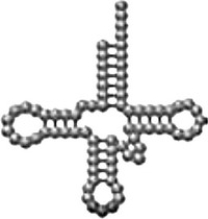
A) tRNA cloverleaf.
B) mRNA cloverleaf.
C) DNA cloverleaf.
D) rRNA cloverleaf.

A) tRNA cloverleaf.
B) mRNA cloverleaf.
C) DNA cloverleaf.
D) rRNA cloverleaf.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following best describes the primary function of mRNA in a cell?
A) To serve as the template strand in the synthesis of DNA
B) To transport amino acids to the ribosomes for protein synthesis
C) To transcribe the instructions for protein synthesis from DNA and carry this information to the ribosomes
D) To serve as a coenzyme in the enzyme-catalyzed hydrolysis of proteins
A) To serve as the template strand in the synthesis of DNA
B) To transport amino acids to the ribosomes for protein synthesis
C) To transcribe the instructions for protein synthesis from DNA and carry this information to the ribosomes
D) To serve as a coenzyme in the enzyme-catalyzed hydrolysis of proteins

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which is the structure of ATP?
A)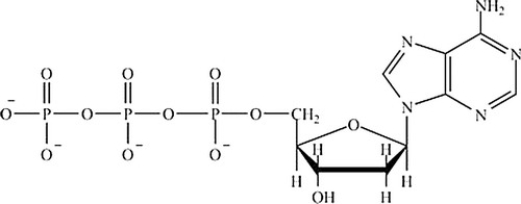
B)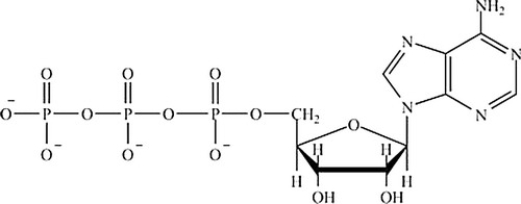
C)
D)
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which component is not part of a nucleotide?
A) An amino acid
B) A phosphate group
C) A nitrogen-containing base
D) A monosaccharide
A) An amino acid
B) A phosphate group
C) A nitrogen-containing base
D) A monosaccharide

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which is not one of the elements needed to amplify DNA by polymerase chain reaction (PCR)?
A) Nucleoside triphosphates that serve as the source of the nucleotides A, T, C, and G needed in the synthesis of the new strands of DNA
B) A DNA polymerase enzyme that will catalyze the synthesis of a complementary strand of DNA from a template strand
C) The segment of DNA that must be copied
D) A restriction endonuclease enzyme that cleaves DNA at specific locations
E) Two primers-short polynucleotides that are complementary to the two ends of the segment to be amplified
A) Nucleoside triphosphates that serve as the source of the nucleotides A, T, C, and G needed in the synthesis of the new strands of DNA
B) A DNA polymerase enzyme that will catalyze the synthesis of a complementary strand of DNA from a template strand
C) The segment of DNA that must be copied
D) A restriction endonuclease enzyme that cleaves DNA at specific locations
E) Two primers-short polynucleotides that are complementary to the two ends of the segment to be amplified

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
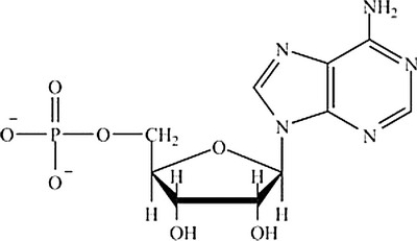
Which base is at the 5' end of the structure shown? 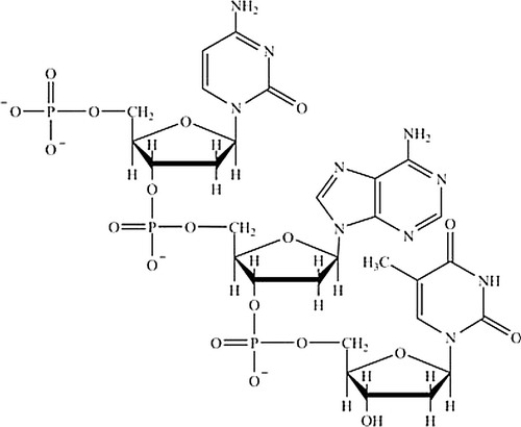
A) Cytosine
B) Uracil
C) Adenine
D) Thymine
E) Guanine

A) Cytosine
B) Uracil
C) Adenine
D) Thymine
E) Guanine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The correct order of steps in each cycle of the polymerase chain reaction are:
I. The DNA sample is heated to unwind the double helix into two single stands.
II. Primers are added to form a short segment of double-stranded DNA on each strand
III. DNA polymerase is used to add nucleotides to lengthen the DNA segment
A) II III I
B) II I III
C) III I II
D) I II III
I. The DNA sample is heated to unwind the double helix into two single stands.
II. Primers are added to form a short segment of double-stranded DNA on each strand
III. DNA polymerase is used to add nucleotides to lengthen the DNA segment
A) II III I
B) II I III
C) III I II
D) I II III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which statement concerning the replication of DNA is not true?
A) A new phosphodiester bond is formed between the 5'-phosphate of the nucleoside triphosphate and the 3'-OH group of the new DNA strand.
B) In replication, the lagging strand is synthesized in small fragments which are then joined together by a DNA ligase enzyme.
C) The first step in replication is unwinding the DNA to expose the bases on each strand.
D) Replication occurs in only one direction on the template strand, from the 5' end to the 3' end.
A) A new phosphodiester bond is formed between the 5'-phosphate of the nucleoside triphosphate and the 3'-OH group of the new DNA strand.
B) In replication, the lagging strand is synthesized in small fragments which are then joined together by a DNA ligase enzyme.
C) The first step in replication is unwinding the DNA to expose the bases on each strand.
D) Replication occurs in only one direction on the template strand, from the 5' end to the 3' end.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A virus lacks which of the following molecules?
A) Free Nucleotides
B) DNA
C) Enzymes
D) Two of these are correct.
A) Free Nucleotides
B) DNA
C) Enzymes
D) Two of these are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following is an example of a virus?
A) Herpes
B) All of these are correct.
C) Influenza
D) Common cold
A) Herpes
B) All of these are correct.
C) Influenza
D) Common cold

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which structure correctly represents the dinucleotide sequence GU that is found in RNA?
A)
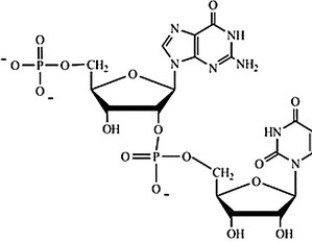
B)
C)
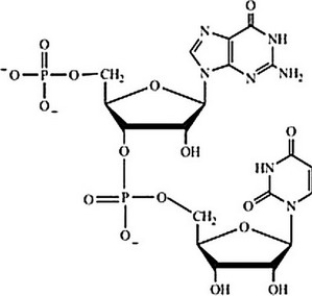
D)
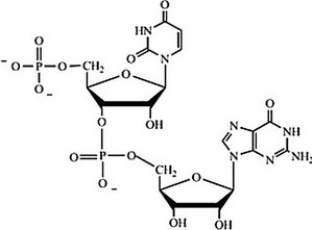
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following part of cocktail of drugs used to fight HIV?
A) AZT
B) RNA
C) DNA
D) PCR
A) AZT
B) RNA
C) DNA
D) PCR

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A virus that contains RNA is called a
A) retrovirus.
B) AZT.
C) RNA virus.
D) reverse transcription.
A) retrovirus.
B) AZT.
C) RNA virus.
D) reverse transcription.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which statement about RNA codons is not true?
A) Three codons are "start" codons, signaling the start of protein synthesis.
B) There are 64 different codons.
C) It is possible for two different codons to code for the same amino acid.
D) Three codons are "stop" codons, signaling the termination of protein synthesis.
A) Three codons are "start" codons, signaling the start of protein synthesis.
B) There are 64 different codons.
C) It is possible for two different codons to code for the same amino acid.
D) Three codons are "stop" codons, signaling the termination of protein synthesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
How are the correct amino acids brought to the ribosomes for protein synthesis?
A) By the transport protein coenzyme A
B) By reduced coenzymes that match the codons found on the DNA template strand
C) Amino acids are synthesized at the ribosomes by the hydrolysis of proteins
D) By tRNA molecules that contain the complementary sequence of an mRNA codon in their anticodon loop
A) By the transport protein coenzyme A
B) By reduced coenzymes that match the codons found on the DNA template strand
C) Amino acids are synthesized at the ribosomes by the hydrolysis of proteins
D) By tRNA molecules that contain the complementary sequence of an mRNA codon in their anticodon loop

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



