Deck 22: The Shoulder Complex
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/40
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 22: The Shoulder Complex
1
Identify the bone that supports the anterior portion of the shoulder, keeping it free from the thoracic cage.
A) The clavicle
B) The sternum
C) The scapula
D) The humerus
E) The calcaneus
A) The clavicle
B) The sternum
C) The scapula
D) The humerus
E) The calcaneus
The clavicle
2
Which of the following statements is true of the clavicle?
A) It lacks muscle or fat protection.
B) It is the only shoulder bone that does not join the acromion process of the scapula.
C) It serves mainly as an articulating surface for the head of the humerus.
D) It serves as a site of attachment for the ribs via the costal cartilage.
E) It connects the anterior portion of the shoulder to the thoracic cage.
A) It lacks muscle or fat protection.
B) It is the only shoulder bone that does not join the acromion process of the scapula.
C) It serves mainly as an articulating surface for the head of the humerus.
D) It serves as a site of attachment for the ribs via the costal cartilage.
E) It connects the anterior portion of the shoulder to the thoracic cage.
It lacks muscle or fat protection.
3
Which of the following statements is true of the glenohumeral joint?
A) It is extremely weak because it is surrounded by a tight, unsupported capsule.
B) It is not a true joint and is stabilized by the scapula.
C) It is an ellipsoidal joint that is the only direct connection between the upper extremity and the trunk.
D) It is a gliding articulation of the lateral end of the clavicle with the acromion process.
E) It is an enarthrodial joint in which the round head of the humerus articulates with the shallow glenoid cavity of the scapula.
A) It is extremely weak because it is surrounded by a tight, unsupported capsule.
B) It is not a true joint and is stabilized by the scapula.
C) It is an ellipsoidal joint that is the only direct connection between the upper extremity and the trunk.
D) It is a gliding articulation of the lateral end of the clavicle with the acromion process.
E) It is an enarthrodial joint in which the round head of the humerus articulates with the shallow glenoid cavity of the scapula.
It is an enarthrodial joint in which the round head of the humerus articulates with the shallow glenoid cavity of the scapula.
4
Which of the following bones of the shoulder complex provides the only axial skeleton attachment for the entire upper extremity?
A) The sternum
B) The clavicle
C) The scapula
D) The humerus
E) The calcaneus
A) The sternum
B) The clavicle
C) The scapula
D) The humerus
E) The calcaneus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following statements is true of the sternum?
A) It serves as a site of attachment for the ribs via the costal cartilage.
B) It serves mainly as an articulating surface for the head of the humerus.
C) It supports the anterior portion of the shoulder, keeping it free from the thoracic cage.
D) It extends from the sternum to the tip of the shoulder, where it joins the acromion process of the scapula.
E) It serves as a site of attachment for all of the muscles that move the shoulder complex.
A) It serves as a site of attachment for the ribs via the costal cartilage.
B) It serves mainly as an articulating surface for the head of the humerus.
C) It supports the anterior portion of the shoulder, keeping it free from the thoracic cage.
D) It extends from the sternum to the tip of the shoulder, where it joins the acromion process of the scapula.
E) It serves as a site of attachment for all of the muscles that move the shoulder complex.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following is a flat, triangular bone that serves mainly as an articulating surface for the head of the humerus?
A) The scapula
B) The clavicle
C) The sternum
D) The humerus
E) The talus
A) The scapula
B) The clavicle
C) The sternum
D) The humerus
E) The talus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following statements is true of the scapula?
A) It provides for the only axial skeleton attachment for the entire upper extremity.
B) It supports the anterior portion of the shoulder, keeping it free from the thoracic cage.
C) It serves as a site of attachment for many of the muscles that move the shoulder complex.
D) It provides an attachment for the clavicle at the sternoclavicular joint.
E) It serves as a site of attachment for the ribs via the costal cartilage.
A) It provides for the only axial skeleton attachment for the entire upper extremity.
B) It supports the anterior portion of the shoulder, keeping it free from the thoracic cage.
C) It serves as a site of attachment for many of the muscles that move the shoulder complex.
D) It provides an attachment for the clavicle at the sternoclavicular joint.
E) It serves as a site of attachment for the ribs via the costal cartilage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
At what location of the clavicle is it more susceptible to fracture?
A) Lateral end, acromioclavicular joint
B) Medial end, sternoclavicular joint
C) Lateral one-third, flattened shape
D) Middle one-third, point which clavicle changes shape
E) Medial one-third, circular or bowed-shape
A) Lateral end, acromioclavicular joint
B) Medial end, sternoclavicular joint
C) Lateral one-third, flattened shape
D) Middle one-third, point which clavicle changes shape
E) Medial one-third, circular or bowed-shape

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
What structural support attaches on the anatomical neck of the humerus?
A) Articular capsule of the glenohumeral joint
B) Rotator cuff
C) Glenoid labrum
D) Latissimus dorsi muscle
E) Coracoacromial ligament
A) Articular capsule of the glenohumeral joint
B) Rotator cuff
C) Glenoid labrum
D) Latissimus dorsi muscle
E) Coracoacromial ligament

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Identify the test for supraspinatus muscle strength that has a patient bring his or her arm into 90 degrees of forward flexion and 30 degrees of horizontal abduction.
A) The drop arm test
B) The empty can test
C) The Hawkins-Kennedy test
D) The clunk test
E) The sulcus test
A) The drop arm test
B) The empty can test
C) The Hawkins-Kennedy test
D) The clunk test
E) The sulcus test

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following statements is true of the drop arm test?
A) It is designed to determine tears of the rotator cuff, primarily of the supraspinatus muscle.
B) It requires a patient to bring his or her arm into 90 degrees of forward flexion and 30 degrees of horizontal abduction.
C) It is designed to test for glenohumeral instability.
D) It is designed to determine whether there is any displacement of the acromion process and the distal head of the clavicle.
E) It requires the forced flexion of the humerus in the overhead position.
A) It is designed to determine tears of the rotator cuff, primarily of the supraspinatus muscle.
B) It requires a patient to bring his or her arm into 90 degrees of forward flexion and 30 degrees of horizontal abduction.
C) It is designed to test for glenohumeral instability.
D) It is designed to determine whether there is any displacement of the acromion process and the distal head of the clavicle.
E) It requires the forced flexion of the humerus in the overhead position.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Of the special tests for the articulations of the shoulder girdle, which one involves stress load applied and translation of the humerus is assessed in both an anterior and posterior direction?
A) Glenohumeral Translation Test
B) Anterior and Posterior Drawer Test
C) Sternoclavicualr Joint Instability Test
D) Clunk Test
E) Apprehension Test
A) Glenohumeral Translation Test
B) Anterior and Posterior Drawer Test
C) Sternoclavicualr Joint Instability Test
D) Clunk Test
E) Apprehension Test

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following is a step that an athletic trainer would take while performing the sulcus test on an athlete?
A) The athletic trainer should grasp the elbow of the athlete and apply traction in an inferior direction.
B) The athletic trainer should place one hand over the athlete's shoulder to stabilize the scapula.
C) The athletic trainer should grasp the humeral head of the athlete between his or her thumb and index finger.
D) The athletic trainer should apply downward pressure over the distal forearm of the athlete.
E) The athletic trainer should take the patient's radial pulse while his or her elbow is flexed to 90 degrees.
A) The athletic trainer should grasp the elbow of the athlete and apply traction in an inferior direction.
B) The athletic trainer should place one hand over the athlete's shoulder to stabilize the scapula.
C) The athletic trainer should grasp the humeral head of the athlete between his or her thumb and index finger.
D) The athletic trainer should apply downward pressure over the distal forearm of the athlete.
E) The athletic trainer should take the patient's radial pulse while his or her elbow is flexed to 90 degrees.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Of the special tests for the articulations of the shoulder girdle, which one involves passively abducting and externally rotating the arm with an anterior force applied to the humeral head?
A) Load and Shift Test
B) Anterior Drawer Test
C) Sternoclavicualr Joint Instability Test
D) Clunk Test
E) Crank Test
A) Load and Shift Test
B) Anterior Drawer Test
C) Sternoclavicualr Joint Instability Test
D) Clunk Test
E) Crank Test

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following is a test for biceps tendon irritation that is performed with a patient in a seated position with the hands clasped behind the head?
A) Roo's test
B) Neer's test
C) Yergason's test
D) Ludington's test
E) Speed's test
A) Roo's test
B) Neer's test
C) Yergason's test
D) Ludington's test
E) Speed's test

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
In the history section of a shoulder assessment, what would be considered an inappropriate question to ask the patient?
A) What is your professional occupation?
B) Is there a weakness or a sense of fatigue with the arm?
C) Have you ever had this injury before?
D) Do you think this is related to a possible heart attack?
E) Is there a distortion in temperature such as a cold or warm feeling?
A) What is your professional occupation?
B) Is there a weakness or a sense of fatigue with the arm?
C) Have you ever had this injury before?
D) Do you think this is related to a possible heart attack?
E) Is there a distortion in temperature such as a cold or warm feeling?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
In the observation section of a shoulder assessment, what would be difficult to observe without performing a special test?
A) Symmetrical height of the acromion
B) Laxity of the joint capsule
C) Kyphosis, lordosis, or scoliosis
D) Sprengel's deformity
E) Winged scapula
A) Symmetrical height of the acromion
B) Laxity of the joint capsule
C) Kyphosis, lordosis, or scoliosis
D) Sprengel's deformity
E) Winged scapula

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following structures would be unable to be palpated?
A) Subscapular fossa
B) Bicipital groove
C) Scapula spine
D) Serratus anterior
E) Rotator cuff tendons
A) Subscapular fossa
B) Bicipital groove
C) Scapula spine
D) Serratus anterior
E) Rotator cuff tendons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
In the prevention of a shoulder injury, what could be done to prevent athletes from falling with an outstretched arm?
A) Add a cowboy collar for a football player
B) Fit a figure-eight brace for a volleyball player
C) Teach the soccer player to fall backwards
D) Instruct a baseball player to make a fist when sliding
E) Demonstrate a shoulder front roll for a ballerina
A) Add a cowboy collar for a football player
B) Fit a figure-eight brace for a volleyball player
C) Teach the soccer player to fall backwards
D) Instruct a baseball player to make a fist when sliding
E) Demonstrate a shoulder front roll for a ballerina

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
What ligament along with the acromion forms the coracoacromial arch?
A) Anterior sternoclavicular ligament
B) Coracoacromial ligament
C) Coracoclavicular ligament
D) Superior glenohumeral ligament
E) Middle glenohumeral ligament
A) Anterior sternoclavicular ligament
B) Coracoacromial ligament
C) Coracoclavicular ligament
D) Superior glenohumeral ligament
E) Middle glenohumeral ligament

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
What is an incorrect statement about the muscles that produce movement of the scapula on the thorax to help maintain the position of the glenoid relative to the humerus?
A) The serratus anterior abducts and downwardly rotates the scapula.
B) The middle trapezius adducts the scapula.
C) The lower trapezius adducts and depresses the scapula.
D) The upper trapezius elevates the scapula.
E) The levator scapula elevates the scapula.
A) The serratus anterior abducts and downwardly rotates the scapula.
B) The middle trapezius adducts the scapula.
C) The lower trapezius adducts and depresses the scapula.
D) The upper trapezius elevates the scapula.
E) The levator scapula elevates the scapula.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
What is the CORRECT title of the highlighted peripheral nerve? 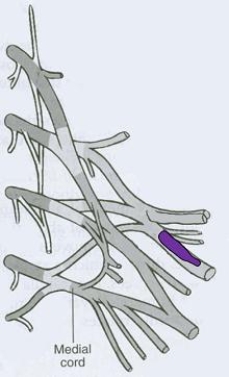
A) Pectoral nerve
B) Dorsal scapular nerve
C) Axillary nerve
D) Radial nerve
E) Suprascapular nerve

A) Pectoral nerve
B) Dorsal scapular nerve
C) Axillary nerve
D) Radial nerve
E) Suprascapular nerve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What is the CORRECT title of the highlighted peripheral nerve? 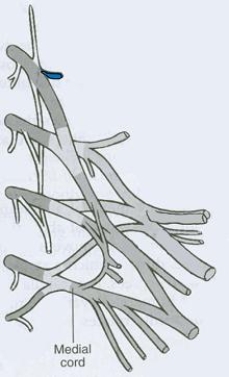
A) Pectoral nerve
B) Posterior scapular nerve
C) Axillary nerve
D) Radial nerve
E) Suprascapular nerve

A) Pectoral nerve
B) Posterior scapular nerve
C) Axillary nerve
D) Radial nerve
E) Suprascapular nerve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
What is the CORRECT title of the highlighted peripheral nerve? 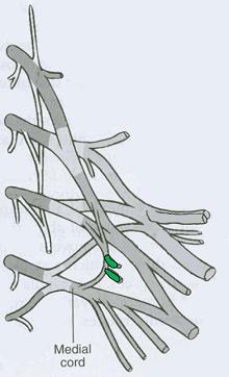
A) Pectoral nerve (medial and lateral)
B) Dorsal scapular nerve (posterior)
C) Axillary nerve
D) Musculocutaneous nerve
E) Suprascapular nerve

A) Pectoral nerve (medial and lateral)
B) Dorsal scapular nerve (posterior)
C) Axillary nerve
D) Musculocutaneous nerve
E) Suprascapular nerve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What is the CORRECT title of the highlighted peripheral nerve? 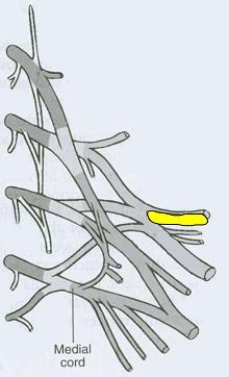
A) Pectoral nerve
B) Dorsal scapular nerve
C) Axillary nerve
D) Musculocutaneous nerve
E) Suprascapular nerve

A) Pectoral nerve
B) Dorsal scapular nerve
C) Axillary nerve
D) Musculocutaneous nerve
E) Suprascapular nerve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
What is the CORRECT title of the highlighted peripheral nerve? 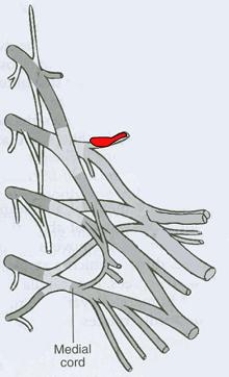
A) Pectoral nerve
B) Dorsal scapular nerve
C) Axillary nerve
D) Musculocutaneous nerve
E) Suprascapular nerve

A) Pectoral nerve
B) Dorsal scapular nerve
C) Axillary nerve
D) Musculocutaneous nerve
E) Suprascapular nerve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following injuries is managed with the use of immobilization with a figure-eight brace?
A) A scapular fracture
B) A clavicular fracture
C) A humeral fracture
D) A sternoclavicular sprain
E) An acromioclavicular sprain
A) A scapular fracture
B) A clavicular fracture
C) A humeral fracture
D) A sternoclavicular sprain
E) An acromioclavicular sprain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
What additional structure could be compromised with a fracture of the humerus?
A) Rotator cuff
B) Median nerve
C) Radial nerve
D) Clavicle bone
E) Brachial plexus
A) Rotator cuff
B) Median nerve
C) Radial nerve
D) Clavicle bone
E) Brachial plexus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following injuries has an etiology of indirect force transmitted through the humerus of the shoulder joint by direct violence such as a blow that strikes a poorly padded clavicle?
A) Scapular fracture
B) Clavicular fracture
C) Humeral fracture
D) Sternoclavicular sprain
E) Acromioclavicular sprain
A) Scapular fracture
B) Clavicular fracture
C) Humeral fracture
D) Sternoclavicular sprain
E) Acromioclavicular sprain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
If a patient exhibits posterior separation of the clavicle with complete disruption of the acromioclavicular ligament, what grade sprain was sustained?
A) Grade 2
B) Grade 3
C) Grade 4
D) Grade 5
E) Grade 6
A) Grade 2
B) Grade 3
C) Grade 4
D) Grade 5
E) Grade 6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following statements is true of a Bankart lesion?
A) It is an anterior defect on the labrum.
B) It is a defect found on the posterior lateral aspect of the humeral head.
C) It is caused by the compression of the cancellous bone of the head of the humerus against the anterior glenoid rim.
D) It is caused by an injury to the superior aspect of the labrum.
E) It is created by a divot in the humeral head.
A) It is an anterior defect on the labrum.
B) It is a defect found on the posterior lateral aspect of the humeral head.
C) It is caused by the compression of the cancellous bone of the head of the humerus against the anterior glenoid rim.
D) It is caused by an injury to the superior aspect of the labrum.
E) It is created by a divot in the humeral head.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
What type of shoulder condition affects the attachment of the long head of the biceps to the superior labrum?
A) A Bankart lesion
B) A SLAP lesion
C) A Hill-Sachs lesion
D) A rotator cuff tear
E) A reverse Hill-Sachs lesion
A) A Bankart lesion
B) A SLAP lesion
C) A Hill-Sachs lesion
D) A rotator cuff tear
E) A reverse Hill-Sachs lesion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The acronym GIRD stands for which of the following?
A) Glenoid internal retract downward
B) Getting internal restricts dips
C) Glenohumeral in restrictive devices
D) Glenohumeral internal rotation deficit
E) Glenoid internally rotates downward
A) Glenoid internal retract downward
B) Getting internal restricts dips
C) Glenohumeral in restrictive devices
D) Glenohumeral internal rotation deficit
E) Glenoid internally rotates downward

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
If a patient were suffering from thoracic outlet syndrome, which of the following symptoms is not inapplicable?
A) Pain
B) Paresthesia
C) Muscles hypertrophy
D) Radial nerve palsy
E) A sensation of cold
A) Pain
B) Paresthesia
C) Muscles hypertrophy
D) Radial nerve palsy
E) A sensation of cold

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Upon viewing an MRI it is noted that the patient has an anterior defect on the labrum. What is this defect called?
A) A Bankart lesion
B) A SLAP lesion
C) A Hill-Sachs lesion
D) A rotator cuff tear
E) A reverse Hill-Sachs lesion
A) A Bankart lesion
B) A SLAP lesion
C) A Hill-Sachs lesion
D) A rotator cuff tear
E) A reverse Hill-Sachs lesion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
What muscle or muscle group is responsible for decelerating the humerus in the deceleration phase of throwing?
A) Internal rotators of the rotator cuff
B) External rotators of the rotator cuff
C) Rhomboids
D) Shoulder flexors
E) Shoulder extensors
A) Internal rotators of the rotator cuff
B) External rotators of the rotator cuff
C) Rhomboids
D) Shoulder flexors
E) Shoulder extensors

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
During what phase of throwing are both shoulders adducted, externally rotated and horizontally abducted?
A) Windup
B) Cocking
C) Acceleration
D) Deceleration
E) Follow-through
A) Windup
B) Cocking
C) Acceleration
D) Deceleration
E) Follow-through

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
What is the clinical premise for completing a Subjective Shoulder Scale Assessment?
A) To establish patient quality of dermatomes
B) To establish patient range of motion
C) To establish patient efficiency of myotomes
D) To establish patient pain and function
E) To establish patient mental and emotional status
A) To establish patient quality of dermatomes
B) To establish patient range of motion
C) To establish patient efficiency of myotomes
D) To establish patient pain and function
E) To establish patient mental and emotional status

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
What direction is the acromion process forced with an acromioclavicular joint sprain?
A) Upward and anterior
B) Downward, backward and inward
C) Upward, backward and outward
D) Downward, forward and inward
E) Downward and posterior
A) Upward and anterior
B) Downward, backward and inward
C) Upward, backward and outward
D) Downward, forward and inward
E) Downward and posterior

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A baseball pitcher suffered an anterior shoulder subluxation last season and is returning as the starting pitcher this season. During what phase of throwing would concerned be the greatest of a re-injury?
A) Windup
B) Cocking
C) Acceleration
D) Deceleration
E) Follow-through
A) Windup
B) Cocking
C) Acceleration
D) Deceleration
E) Follow-through

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



