Deck 20: The Knee and Related Structures
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/49
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 20: The Knee and Related Structures
1
Please check all of the factors that may contribute to patellofemoral stress syndrome.
A) Tightness in the gastrocnemius
B) Decreased Q angle
C) Supination of the foot
D) Tightness of the iliotibial band
E) Patella baja
F) Weak hip adductors
G) Vastus medialis oblique insufficiency
A) Tightness in the gastrocnemius
B) Decreased Q angle
C) Supination of the foot
D) Tightness of the iliotibial band
E) Patella baja
F) Weak hip adductors
G) Vastus medialis oblique insufficiency
Tightness in the gastrocnemius
Tightness of the iliotibial band
Weak hip adductors
Vastus medialis oblique insufficiency
Tightness of the iliotibial band
Weak hip adductors
Vastus medialis oblique insufficiency
2
Please check all of the therapeutic exercises that would be appropriate for a person who is in the acute injury phase of surgical repair of an anterior cruciate ligament.
A) Insert quad sets video with no audio (strengthening hip and thigh folder)
B) Insert hamstring curls on NK video with no audio (strengthening hip and thigh folder)
C) Insert video hip flexor strengthening with no audio (strengthening hip and thigh folder)
D) Insert straight leg lift adduction video with no audio from strengthening hip and thigh folder
E) Insert machine squat video with no audio from strengthening hip and thigh folder
F) Insert posterior tibial glides distal with no audio from joint mobilizations folder
G) Insert patellar glides video with no audio from joint mobilizations folder
A) Insert quad sets video with no audio (strengthening hip and thigh folder)
B) Insert hamstring curls on NK video with no audio (strengthening hip and thigh folder)
C) Insert video hip flexor strengthening with no audio (strengthening hip and thigh folder)
D) Insert straight leg lift adduction video with no audio from strengthening hip and thigh folder
E) Insert machine squat video with no audio from strengthening hip and thigh folder
F) Insert posterior tibial glides distal with no audio from joint mobilizations folder
G) Insert patellar glides video with no audio from joint mobilizations folder
Insert quad sets video with no audio (strengthening hip and thigh folder)
Insert straight leg lift adduction video with no audio from strengthening hip and thigh folder
Insert patellar glides video with no audio from joint mobilizations folder
Insert straight leg lift adduction video with no audio from strengthening hip and thigh folder
Insert patellar glides video with no audio from joint mobilizations folder
3
Which of the following statements about the knee and related structures is INCORRECT?
A) The patella is the largest sesamoid bone in the human body.
B) The knee joint consists of four articulations between the femur and the tibia, the femur and the patella, the femur and the fibula, and the tibia and the fibula.
C) The articular surface of the medial condyle is shorter from front to back than is the surface of the lateral condyle.
D) The medial meniscus is C-shaped, where the lateral meniscus is more O-shaped.
E) The anterior cruciate ligament comprises three twisted bands: the anteromedial, intermediate, and posterolateral bands.
A) The patella is the largest sesamoid bone in the human body.
B) The knee joint consists of four articulations between the femur and the tibia, the femur and the patella, the femur and the fibula, and the tibia and the fibula.
C) The articular surface of the medial condyle is shorter from front to back than is the surface of the lateral condyle.
D) The medial meniscus is C-shaped, where the lateral meniscus is more O-shaped.
E) The anterior cruciate ligament comprises three twisted bands: the anteromedial, intermediate, and posterolateral bands.
The articular surface of the medial condyle is shorter from front to back than is the surface of the lateral condyle.
4
From the following descriptive statements of the patella, select the INCORRECT statement.
A) The patella is the largest sesamoid bone in the human body.
B) The lateral aspect of the patella is wider than the medial aspect.
C) Tracking within this groove depends on the pull of the quadriceps muscle and patellar tendon.
D) The patella articulates between the concavity provided by the tibial plateaus.
E) The patella is located in the tendon of the quadriceps femoris muscle and divided into three medial facets and a lateral facet.
A) The patella is the largest sesamoid bone in the human body.
B) The lateral aspect of the patella is wider than the medial aspect.
C) Tracking within this groove depends on the pull of the quadriceps muscle and patellar tendon.
D) The patella articulates between the concavity provided by the tibial plateaus.
E) The patella is located in the tendon of the quadriceps femoris muscle and divided into three medial facets and a lateral facet.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following is a characteristic of the medial meniscus?
A) It is a round, fibrous cord that is about the size of a pencil.
B) It is a horseshoe-shaped fat pad.
C) It is attached to the lateral articular facet on the superior aspect of the tibia.
D) It is attached to fibers of the semimembranous muscle posteriorly.
E) It is an O-shaped fibrocartilage.
A) It is a round, fibrous cord that is about the size of a pencil.
B) It is a horseshoe-shaped fat pad.
C) It is attached to the lateral articular facet on the superior aspect of the tibia.
D) It is attached to fibers of the semimembranous muscle posteriorly.
E) It is an O-shaped fibrocartilage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The major purpose of the medial collateral ligament is:
A) to prevent hyperextension of the knee.
B) to limit anterior translation of the tibia in non-weight bearing.
C) to prevent the knee from valgus and external rotating forces.
D) to work in conjunction with the thigh muscles to stabilize the knee joint.
E) to attach the medial meniscus to the femur and to allow the tibia to move on the meniscus inferiorly.
A) to prevent hyperextension of the knee.
B) to limit anterior translation of the tibia in non-weight bearing.
C) to prevent the knee from valgus and external rotating forces.
D) to work in conjunction with the thigh muscles to stabilize the knee joint.
E) to attach the medial meniscus to the femur and to allow the tibia to move on the meniscus inferiorly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Identify a function of a bursa.
A) To supply blood to the knee
B) To maintain spacing between the femoral condyles and tibial plateau
C) To act as a separator between the patellar tendon and the joint capsule
D) To reduce the friction between anatomical structures
E) To produce external tibial rotation as the knee moves into extension
A) To supply blood to the knee
B) To maintain spacing between the femoral condyles and tibial plateau
C) To act as a separator between the patellar tendon and the joint capsule
D) To reduce the friction between anatomical structures
E) To produce external tibial rotation as the knee moves into extension

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
In the context of bony palpation, which of the following structures is palpated on the lateral aspect by an athletic trainer?
A) Inferior patellar border
B) Intercondylar fossa
C) Tibial tuberosity
D) Head of the fibula
E) Adductor tubercle
A) Inferior patellar border
B) Intercondylar fossa
C) Tibial tuberosity
D) Head of the fibula
E) Adductor tubercle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
At what degree of knee flexion are the mensci the most helpful in stabilizing the knee?
A) 15°
B) 35°
C) 90°
D) 125°
E) 180°
A) 15°
B) 35°
C) 90°
D) 125°
E) 180°

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
What structure within the knee attaches to the superior fibers of the semimembranosus muscle?
A) The posterior cruciate ligament
B) The lateral meniscus
C) The anterior cruciate ligament
D) The medial meniscus
E) Pes anserine
A) The posterior cruciate ligament
B) The lateral meniscus
C) The anterior cruciate ligament
D) The medial meniscus
E) Pes anserine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The anterior cruciate ligament prevents the femur from moving posteriorly during weight bearing. What is its role in non-weight bearing?
A) Limits anterior translation of the tibia
B) Limits posterior translation of the tibia
C) Limits anterior translation of the femur
D) Limits the tibia against excessive external rotation
E) Limits the tibia against excessive internal rotation
A) Limits anterior translation of the tibia
B) Limits posterior translation of the tibia
C) Limits anterior translation of the femur
D) Limits the tibia against excessive external rotation
E) Limits the tibia against excessive internal rotation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Why are the cruciate ligaments "extrasynovial"?
A) The synovial membrane lines the inner surface of the joint capsule.
B) The cruciate ligaments consist of two or more multidirectional fibrous bands.
C) The synovial membrane passes in front of the cruciate ligaments.
D) The collateral ligaments are intrasynovial.
E) The synovium attaches to only the collateral ligaments.
A) The synovial membrane lines the inner surface of the joint capsule.
B) The cruciate ligaments consist of two or more multidirectional fibrous bands.
C) The synovial membrane passes in front of the cruciate ligaments.
D) The collateral ligaments are intrasynovial.
E) The synovium attaches to only the collateral ligaments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Why does the tibia externally rotate with extension of the knee during the "screw-home" mechanism?
A) It occurs because the lateral femoral condyle is larger than the medial condyle.
B) It occurs because the medial femoral condyle is larger than the lateral condyle.
C) It occurs to unlock the knee.
D) It occurs to lock the knee.
E) It occurs to allow the anterior cruciate ligament to loosen.
A) It occurs because the lateral femoral condyle is larger than the medial condyle.
B) It occurs because the medial femoral condyle is larger than the lateral condyle.
C) It occurs to unlock the knee.
D) It occurs to lock the knee.
E) It occurs to allow the anterior cruciate ligament to loosen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Where does the patella lie on the femur when the knee is in full extension?
A) The patella lies slightly medial and proximal to the trochlea.
B) The patella lies slightly distal to the intercondylar eminence and proximal to the tibial tuberosity.
C) The patella lies slightly lateral and distal to the trochlea.
D) The patella lies slightly medial and superior to the femoral groove.
E) The patella lies slightly lateral and proximal to the trochlea.
A) The patella lies slightly medial and proximal to the trochlea.
B) The patella lies slightly distal to the intercondylar eminence and proximal to the tibial tuberosity.
C) The patella lies slightly lateral and distal to the trochlea.
D) The patella lies slightly medial and superior to the femoral groove.
E) The patella lies slightly lateral and proximal to the trochlea.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
In the history section of a knee assessment, what would be considered an inappropriate question to ask the patient?
A) What were you doing when the knee was hurt?
B) Did your ankle also give out?
C) What is your major complaint?
D) Was the pain in your knee from side-to-side?
E) What position was your body when it was injured?
A) What were you doing when the knee was hurt?
B) Did your ankle also give out?
C) What is your major complaint?
D) Was the pain in your knee from side-to-side?
E) What position was your body when it was injured?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
In the observation section of a knee assessment, what would be considered an inappropriate action to perform?
A) Assessing leg alignment
B) Assessing the gait pattern
C) Assessing if the patient can do a half-squat to extension
D) Assessing a sacral shift
E) Assessing the way the patellar sit
A) Assessing leg alignment
B) Assessing the gait pattern
C) Assessing if the patient can do a half-squat to extension
D) Assessing a sacral shift
E) Assessing the way the patellar sit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following would be unable to be discovered during the palpation section of a knee assessment?
A) Bursitis
B) Tendinosis
C) Joint effusion
D) Muscle soreness
E) Ligament sprain
A) Bursitis
B) Tendinosis
C) Joint effusion
D) Muscle soreness
E) Ligament sprain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
What does a ballotable patella indicate?
A) Intracapsular swelling
B) Displaced fracture
C) Bursitis
D) Tendinitis
E) Extracapsular swelling
A) Intracapsular swelling
B) Displaced fracture
C) Bursitis
D) Tendinitis
E) Extracapsular swelling

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
According to the different knee stability tests, a positive Apley's grinding test indicates a torn
A) medial meniscus.
B) posterior cruciate ligament.
C) lateral meniscus.
D) anterior cruciate ligament.
E) lateral collateral ligament.
A) medial meniscus.
B) posterior cruciate ligament.
C) lateral meniscus.
D) anterior cruciate ligament.
E) lateral collateral ligament.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following tests is similar to the flexion-rotation drawer test but is done in a side-lying position?
A) The posterior drawer test
B) The jerk test
C) The Thessaly test
D) Godfrey's Test
E) Losee's test
A) The posterior drawer test
B) The jerk test
C) The Thessaly test
D) Godfrey's Test
E) Losee's test

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following is an advantage of the Lachman drawer test?
A) It tests the knee at a comfortable 90-degree position.
B) It reduces the restriction created by the hamstring muscles.
C) It can be performed easily on very large patients.
D) It is performed when a patient is in a comfortable, side-lying position.
E) It helps in determining a torn meniscus easily.
A) It tests the knee at a comfortable 90-degree position.
B) It reduces the restriction created by the hamstring muscles.
C) It can be performed easily on very large patients.
D) It is performed when a patient is in a comfortable, side-lying position.
E) It helps in determining a torn meniscus easily.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following is true of the external rotation recurvatum test?
A) An athletic trainer uses one hand to press against the head of the fibula and the other to grasp a patient's ankle.
B) An athletic trainer places one hand on the foot and one hand over the top of the knee, fingers touching the medial joint line.
C) An athletic trainer grasps the great toe of a patient and lifts his or her leg off a table.
D) A clinician stands in front of and supports a patient by holding his or her outstretched hands.
E) An athletic trainer stands facing the anterior aspect of a patient's leg, with both hands encircling the upper portion of the leg immediately below the knee joint.
A) An athletic trainer uses one hand to press against the head of the fibula and the other to grasp a patient's ankle.
B) An athletic trainer places one hand on the foot and one hand over the top of the knee, fingers touching the medial joint line.
C) An athletic trainer grasps the great toe of a patient and lifts his or her leg off a table.
D) A clinician stands in front of and supports a patient by holding his or her outstretched hands.
E) An athletic trainer stands facing the anterior aspect of a patient's leg, with both hands encircling the upper portion of the leg immediately below the knee joint.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
In the context of special tests for assessment of knee joint instability, the patient stands flatfooted on the floor in
A) the Thessaly test.
B) mcMurray's meniscal test.
C) the Apley compression test.
D) the pivot-shift test.
E) the Lachman drawer test.
A) the Thessaly test.
B) mcMurray's meniscal test.
C) the Apley compression test.
D) the pivot-shift test.
E) the Lachman drawer test.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Why are there several alternate methods to perform the Lachman drawer test?
A) Because many different physicians have found more valid methods
B) Because the alternate methods involve testing for rotator instabilities
C) Because many different athletic trainers have found more valid methods
D) Because the female population within the profession created alternate methods
E) Because larger patients are difficult to assess using the original Lachman drawer test
A) Because many different physicians have found more valid methods
B) Because the alternate methods involve testing for rotator instabilities
C) Because many different athletic trainers have found more valid methods
D) Because the female population within the profession created alternate methods
E) Because larger patients are difficult to assess using the original Lachman drawer test

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A patient presents with an increased Q angle, pain on the lateral facet of the patella, tightness in their hamstrings, patella alta, and a tight iliotibial band. What is the patient's assessment?
A) Patellar subluxation
B) Chondromalacia patella
C) Patellofemoral stress syndrome
D) Patellofemoral arthralgia
E) Hemarthrosis
A) Patellar subluxation
B) Chondromalacia patella
C) Patellofemoral stress syndrome
D) Patellofemoral arthralgia
E) Hemarthrosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
What is the normal Q angle for both male and female patients?
A) 15 degrees male, 15 degrees female
B) 15 degrees male, 10 degrees female
C) 10 degrees male, 10 degrees female
D) 10 degrees male, 15 degrees female
E) 20 degrees male, 15 degrees female
A) 15 degrees male, 15 degrees female
B) 15 degrees male, 10 degrees female
C) 10 degrees male, 10 degrees female
D) 10 degrees male, 15 degrees female
E) 20 degrees male, 15 degrees female

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
If the verbal cue "soft knees" were used, what should that mean to the patient?
A) Hip flexion to aid in impact absorption
B) Try not to make a sound when landing
C) Landing on forefoot
D) Landing with knee in flexion
E) Rolling into heel contact
A) Hip flexion to aid in impact absorption
B) Try not to make a sound when landing
C) Landing on forefoot
D) Landing with knee in flexion
E) Rolling into heel contact

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
What type of brace is used to protect grade 1 or 2 sprains of the ACL?
A) Prophylactic
B) Hinge brace
C) Functional brace
D) Post-operative brace
E) Rehabilitation brace
A) Prophylactic
B) Hinge brace
C) Functional brace
D) Post-operative brace
E) Rehabilitation brace

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
When the anterior cruciate ligament is torn, what signs and symptoms could the patient experience?
A) A snapping sound, immediate pain and rapid swelling at the joint line
B) A pop followed by immediate disability, and rapid swelling at the joint line
C) A snapping sound, delayed pain and rapid swelling at the joint line
D) A popping sound, delayed pain and no swelling at the joint line
E) A snapping sound, delayed pain and no swelling at the joint line
A) A snapping sound, immediate pain and rapid swelling at the joint line
B) A pop followed by immediate disability, and rapid swelling at the joint line
C) A snapping sound, delayed pain and rapid swelling at the joint line
D) A popping sound, delayed pain and no swelling at the joint line
E) A snapping sound, delayed pain and no swelling at the joint line

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
In the context of a knee plica, the characteristics of locking and snapping could be misinterpreted as a
A) meniscal tear.
B) patella subluxation.
C) patella femoral stress syndrome.
D) patellar tendonitis.
E) joint contusion.
A) meniscal tear.
B) patella subluxation.
C) patella femoral stress syndrome.
D) patellar tendonitis.
E) joint contusion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Why should this rehabilitative exercise be performed following an anterior cruciate ligament repair?
A) To mobilize the patella
B) To mobilize the fibula
C) To mobilize the femur
D) To mobilize the lateral meniscus
E) To mobilize the medial meniscus
A) To mobilize the patella
B) To mobilize the fibula
C) To mobilize the femur
D) To mobilize the lateral meniscus
E) To mobilize the medial meniscus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which brace would be the most appropriate to wear for an athlete recovering from a grade 3 medial collateral ligament tear?
A)
B)
C)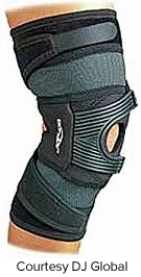
D)
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
If a patient is found to have loose bodies within the knee, what would be the appropriate management?
A) Surgical removal
B) Immobilization
C) Rest and anti-inflammatory agents
D) RICE
E) Rest and the application of heat
A) Surgical removal
B) Immobilization
C) Rest and anti-inflammatory agents
D) RICE
E) Rest and the application of heat

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A patient complains of diffuse pain along the joint line after a direct force to the knee. The pain is localized and with immediate joint effusion and pain with weight bearing when standing or walking. What is most likely the problem?
A) Joint contusion
B) Osteochondritis dissecans
C) Osteochondral knee fracture
D) Knee plica
E) Patellar fracture
A) Joint contusion
B) Osteochondritis dissecans
C) Osteochondral knee fracture
D) Knee plica
E) Patellar fracture

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following conditions may cause an increase in a patient's Q angle?
A) Genu valgum
B) Genu varum
C) Genu recurvatum
D) Shallow femoral grooves
E) Externally rotated fibulas
A) Genu valgum
B) Genu varum
C) Genu recurvatum
D) Shallow femoral grooves
E) Externally rotated fibulas

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
An injury to the intrapatella fat pad can occur when the pad becomes wedged between which of the following?
A) Tibia and fibula
B) Femur and tibia
C) Patella and femur
D) Tibia and patella
E) Patella and fibula
A) Tibia and fibula
B) Femur and tibia
C) Patella and femur
D) Tibia and patella
E) Patella and fibula

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following involves correction of foot and leg alignment problems as part of its management process?
A) Runner's knee
B) Larsen-Johansson disease
C) Osgood-Schlatter disease
D) Osteochondritis dissecans
E) Jumper's knee
A) Runner's knee
B) Larsen-Johansson disease
C) Osgood-Schlatter disease
D) Osteochondritis dissecans
E) Jumper's knee

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
In the context of jumper's knee, when chronic inflammation develops in the patellar tendon at the superior patellar pole, it is usually referred to as
A) patellar tendinitis.
B) quadriceps tendinitis.
C) pes anserinus tendinitis.
D) an apophysitis.
E) an eccentric contraction.
A) patellar tendinitis.
B) quadriceps tendinitis.
C) pes anserinus tendinitis.
D) an apophysitis.
E) an eccentric contraction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
In the context of jumper's knee, the shock-absorbing function that the quadriceps provides upon landing from a jump is known as
A) an isometric contraction.
B) straight instability.
C) rotatory instability.
D) translation.
E) an eccentric contraction.
A) an isometric contraction.
B) straight instability.
C) rotatory instability.
D) translation.
E) an eccentric contraction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Please identify the correct location of a baker's cyst.
A)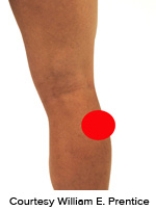
B)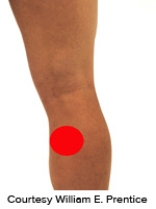
C)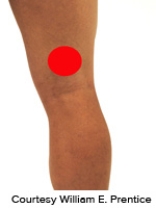
D)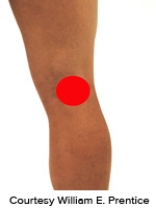
E)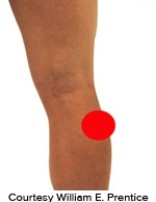
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
In the context of knee joint rehabilitation, which of the following is an example of a closed kinetic chain activity?
A) Walking
B) Rock climbing
C) Exercise tubing
D) Running
E) Jumping
A) Walking
B) Rock climbing
C) Exercise tubing
D) Running
E) Jumping

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
In the context of knee joint rehabilitation, when regaining neuromuscular control of joint motion after injury, which of the following can be used to improve proprioception and balance?
A) The Genucom
B) DynaDisc
C) An orthotic device
D) Cryotherapy
E) A soft posterior splint
A) The Genucom
B) DynaDisc
C) An orthotic device
D) Cryotherapy
E) A soft posterior splint

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
If a doctor were to perform a pivot-shift test, a jerk test, and an Apley's compression test, what are the involved structures?
A) ACL and LCL
B) PCL and MM
C) ACL, PCL, MM
D) MCL, LCL, MM
E) ACL, PCL, MCL
A) ACL and LCL
B) PCL and MM
C) ACL, PCL, MM
D) MCL, LCL, MM
E) ACL, PCL, MCL

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
What does this apparatus measure? 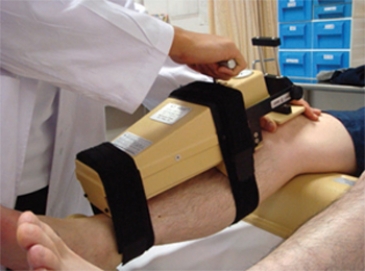
A) Quad strength
B) Displacement of the knee
C) Joint effusion
D) Proprioception ability of the knee
E) Nerve conduction

A) Quad strength
B) Displacement of the knee
C) Joint effusion
D) Proprioception ability of the knee
E) Nerve conduction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
What is being measured in this illustration? 
A) The girth of the femur.
B) The length of the femur.
C) The diameter of the patella.
D) The A angle.
E) The Q angle.

A) The girth of the femur.
B) The length of the femur.
C) The diameter of the patella.
D) The A angle.
E) The Q angle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
When bracing a Grade 3 medial collateral ligament sprain, conservative initial treatment would involve setting a hinge brace to allow what degrees of motion?
A) 30 to 90 degrees
B) 0 to 90 degrees
C) 90 to 120 degrees
D) 0 to 30 degrees
E) 0 to 45 degrees
A) 30 to 90 degrees
B) 0 to 90 degrees
C) 90 to 120 degrees
D) 0 to 30 degrees
E) 0 to 45 degrees

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A sustained noncontact anterolateral rotary instability injury is caused by which of the following motions?
A) Deceleration with a valgus stress and rotation
B) Acceleration with a valgus stress and rotation
C) Deceleration with a varus stress and rotation
D) Acceleration with a varus stress and rotation
E) Acceleration with a valgus stress and no rotation
A) Deceleration with a valgus stress and rotation
B) Acceleration with a valgus stress and rotation
C) Deceleration with a varus stress and rotation
D) Acceleration with a varus stress and rotation
E) Acceleration with a valgus stress and no rotation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
What surgical repair of this structure requires no postoperative bracing?
A) Anterior cruciate repair
B) Posterior cruciate repair
C) Partial menisectomy
D) Meniscal repair
E) Osteochondral fracture repair
A) Anterior cruciate repair
B) Posterior cruciate repair
C) Partial menisectomy
D) Meniscal repair
E) Osteochondral fracture repair

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Based on this picture, what is the patient's condition? 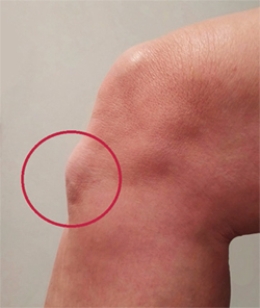
A) Osgood Schlatter's disease
B) Larsen-Johansson disease
C) Jumper's knee
D) Cyclist's knee
E) Patellofemoral stress syndrome

A) Osgood Schlatter's disease
B) Larsen-Johansson disease
C) Jumper's knee
D) Cyclist's knee
E) Patellofemoral stress syndrome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



