Deck 4: Computed Tomography
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/10
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 4: Computed Tomography
1
When viewing an axial CT image of the spine:
A) The spinous process points down and the patient's left side is to the left on the image
B) The spinous process points down and the patient's right side is to the left on the image
C) The spinous process points up and the patient's left side is to the left on the image
D) There are no fixed conventions for viewing these images
A) The spinous process points down and the patient's left side is to the left on the image
B) The spinous process points down and the patient's right side is to the left on the image
C) The spinous process points up and the patient's left side is to the left on the image
D) There are no fixed conventions for viewing these images
The spinous process points down and the patient's right side is to the left on the image
2
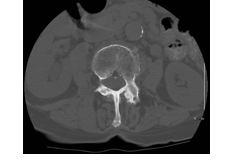
-Refer to the figure. What imaging method is displayed in this axial scan of the lower thoracic spine?
A) CT, soft tissue window
B) CT myelogram
C) CT, bone window
D) 3D CT
CT, bone window
3

-In CT scans, which improves spatial resolution (visible details in the image)?
A) Small matrix size
B) Thick slices
C) Small field of view
D) Low bone density
Small field of view
4

-In CT images:
A) Cortical bone appears dark
B) Fat appears light gray
C) Dense structures appear white
D) Muscles have a lighter shade than do tendons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5

-Windowing (typically expressed in terms of Hounsfield units) refers to the:
A) Size of the field of view in the images
B) Pixel density displayed in the images
C) Range of radiodensities displayed in an image
D) Collimation used when producing the images

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6

-Cone beam CT has which characteristic?
A) It constructs images from a large number of slices
B) It has longer scanning times but greater image detail
C) It is associated with less radiation exposure
D) It has less spatial resolution than conventional scanners

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7

-What is true of resolution in CT images?
A) Contrast resolution distinguishes between tissues that have very different radiodensities
B) Spatial resolution improves with larger matrix size
C) Higher contrast resolution always improves the image quality
D) Spatial resolution improves the larger the field of view

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8

-Musculoskeletal CT scanning is typically done with:
A) A slice thickness of 0.5 mm or less
B) Contrast-enhanced CT
C) Slices of less than 3 mm
D) Comparison with MRI

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9

-The main advantages of CT lie in:
A) Displaying fine detail of cortical bone
B) Its ability to differentiate between malignant and benign tumors
C) Showing the histological makeup of tissues
D) Low radiation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
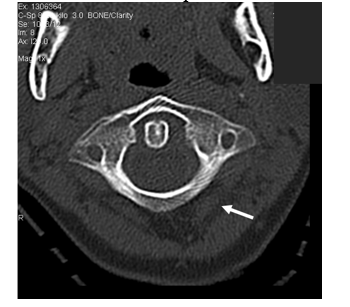
-Refer to the figure. In this image, the arrow points to:
A) Muscle
B) Tendon
C) Entrapped air
D) Intermuscular fat plane

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



