Deck 19: Working Capital Management
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/92
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 19: Working Capital Management
1
A company's cash on hand and the rate that cash is used in operations due to negative operating cash flows is best described as:
A) liquidity.
B) cash burn.
C) productivity.
D) financial leverage.
E) operational efficiency.
A) liquidity.
B) cash burn.
C) productivity.
D) financial leverage.
E) operational efficiency.
cash burn.
2
How long a company can operate before it has to raise funds, either by issuing stock or borrowing is best described as:
A) liquidity.
B) burn rate.
C) cash burn.
D) financial leverage.
E) operational efficiency.
A) liquidity.
B) burn rate.
C) cash burn.
D) financial leverage.
E) operational efficiency.
burn rate.
3
The sum of a company's current assets is best described as:
A) liquidity.
B) cash burn.
C) total assets.
D) working capital.
E) net working capital.
A) liquidity.
B) cash burn.
C) total assets.
D) working capital.
E) net working capital.
working capital.
4
Current assets minus current liabilities is best described as:
A) liquidity.
B) cash burn.
C) total assets.
D) working capital.
E) net working capital.
A) liquidity.
B) cash burn.
C) total assets.
D) working capital.
E) net working capital.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following is the correct formula to determine cash?
A) Beginning cash balance + collections from customers - payments to suppliers = ending cash balance
B) Beginning cash balance - collections from customers + payments to suppliers = ending cash balance
C) Beginning cash balance + collections from customers + payments to suppliers = ending cash balance
D) Beginning cash balance - collections from customers - payments to suppliers = ending cash balance
A) Beginning cash balance + collections from customers - payments to suppliers = ending cash balance
B) Beginning cash balance - collections from customers + payments to suppliers = ending cash balance
C) Beginning cash balance + collections from customers + payments to suppliers = ending cash balance
D) Beginning cash balance - collections from customers - payments to suppliers = ending cash balance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The ending cash balance for a company with the following financial information:
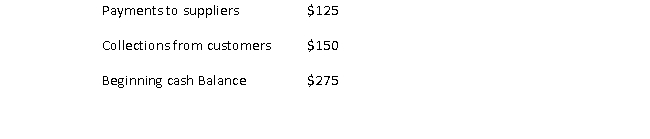 is closest to:
is closest to:
A) $0
B) $250
C) $300
D) $325
E) $550
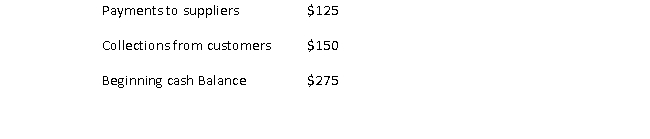 is closest to:
is closest to:A) $0
B) $250
C) $300
D) $325
E) $550

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The terms under which a company grants credit to its customers is best described as:
A) credit policy.
B) liquidity policy.
C) payment policy.
D) inventory policy.
A) credit policy.
B) liquidity policy.
C) payment policy.
D) inventory policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
How quickly a company pays off the credit it receives from other companies is best described as:
A) credit policy.
B) liquidity policy.
C) payment policy.
D) inventory policy.
A) credit policy.
B) liquidity policy.
C) payment policy.
D) inventory policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Determining whether to use EOQ, MRP or JIT is part of what type of policy?
A) Credit policy
B) Liquidity policy
C) Payment policy
D) Inventory policy
A) Credit policy
B) Liquidity policy
C) Payment policy
D) Inventory policy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following is the correct current ratio calculation?
A) Current assets / Current liabilities
B) Current assets - Current liabilities
C) Current liabilities - Current assets
D) Current liabilities / Current assets
A) Current assets / Current liabilities
B) Current assets - Current liabilities
C) Current liabilities - Current assets
D) Current liabilities / Current assets

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following is the correct quick ratio calculation?
A) Current assets / Current liabilities
B) (Cash + Accounts receivable) / Current liabilities
C) (Cash + Marketable securities) / Current liabilities
D) (Cash + Marketable securities + Accounts receivable) / Current liabilities
A) Current assets / Current liabilities
B) (Cash + Accounts receivable) / Current liabilities
C) (Cash + Marketable securities) / Current liabilities
D) (Cash + Marketable securities + Accounts receivable) / Current liabilities

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following is the correct accounts receivable turnover calculation?
A) Revenues / Accounts receivable
B) Accounts receivable /Revenues
C) Accounts receivable / Current liabilities
D) Accounts receivable / Average daily sales
E) (Cash + Marketable securities + Accounts receivable) / Current liabilities
A) Revenues / Accounts receivable
B) Accounts receivable /Revenues
C) Accounts receivable / Current liabilities
D) Accounts receivable / Average daily sales
E) (Cash + Marketable securities + Accounts receivable) / Current liabilities

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following is the correct days sales outstanding calculation?
A) Revenues / Accounts receivable
B) Accounts receivable/ Revenues
C) Average daily sales/ Accounts receivable
D) Accounts receivable/Average daily sales
A) Revenues / Accounts receivable
B) Accounts receivable/ Revenues
C) Average daily sales/ Accounts receivable
D) Accounts receivable/Average daily sales

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following is the correct inventory turnover calculation?
A) Inventory / Cost of goods sold
B) Cost of goods sold /Inventory
C) Inventory / Average days cost of goods sold
D) Average days cost of goods sold / Inventory
A) Inventory / Cost of goods sold
B) Cost of goods sold /Inventory
C) Inventory / Average days cost of goods sold
D) Average days cost of goods sold / Inventory

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following is the correct days sales in inventory calculation?
A) 365 / Inventory turnover
B) Inventory turnover / 365
C) Inventory / Cost of goods sold
D) Cost of goods sold /Inventory
A) 365 / Inventory turnover
B) Inventory turnover / 365
C) Inventory / Cost of goods sold
D) Cost of goods sold /Inventory

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following is the correct accounts payable turnover calculation?
A) Inventory Turnover / 365
B) Inventory / Accounts Payable
C) Purchases / Accounts Payable
D) Accounts Payable /Purchases
E) Accounts Payable / Average Days' Purchases
A) Inventory Turnover / 365
B) Inventory / Accounts Payable
C) Purchases / Accounts Payable
D) Accounts Payable /Purchases
E) Accounts Payable / Average Days' Purchases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The average time it takes a company to acquire inventory, sell it, and collect the sale proceeds is best described as:
A) liquidity.
B) cash burn.
C) operating cycle.
D) cash conversion cycle.
E) days sales outstanding.
A) liquidity.
B) cash burn.
C) operating cycle.
D) cash conversion cycle.
E) days sales outstanding.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The measure of the average time between when a company pays cash for its inventory purchases and when it receives cash for its sales is best described as the:
A) liquidity.
B) cash burn.
C) operating cycle.
D) cash conversion cycle.
E) days sales outstanding.
A) liquidity.
B) cash burn.
C) operating cycle.
D) cash conversion cycle.
E) days sales outstanding.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Using the following financial statements,
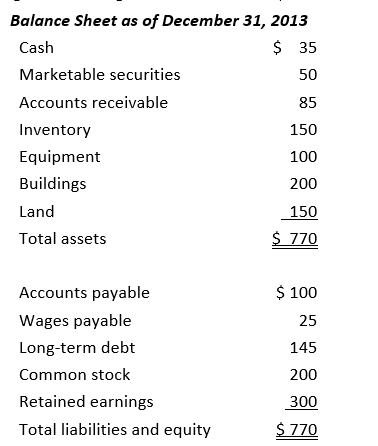
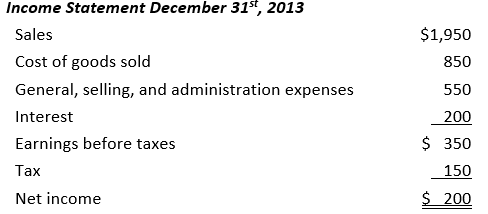 the quick ratio is closest to:
the quick ratio is closest to:
A) 0.28
B) 0.68
C) 1.36
D) 2.56

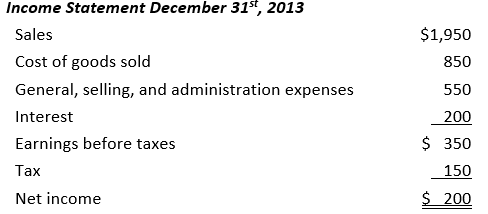 the quick ratio is closest to:
the quick ratio is closest to:A) 0.28
B) 0.68
C) 1.36
D) 2.56

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Using the following financial statements
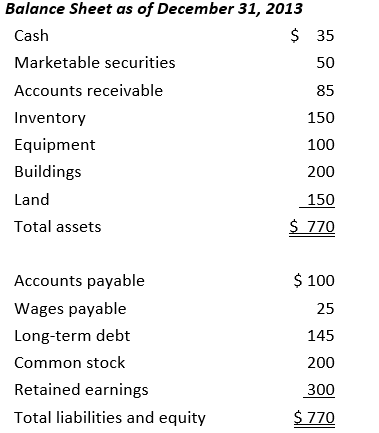 the current ratio is closest to:
the current ratio is closest to:
A) 0.29
B) 2.56
C) 3.20
 the current ratio is closest to:
the current ratio is closest to:A) 0.29
B) 2.56
C) 3.20

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Using the following financial statements:
 the accounts receivable turnover ratio is closest to:
the accounts receivable turnover ratio is closest to:
A) 14.4
B) 22.9
C) 28.9
D) 34.1
 the accounts receivable turnover ratio is closest to:
the accounts receivable turnover ratio is closest to:A) 14.4
B) 22.9
C) 28.9
D) 34.1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Using the following financial statements
 the days sales outstanding is closest to:
the days sales outstanding is closest to:
A) 15.9
B) 36.5
C) 59.9
D) 137.4
 the days sales outstanding is closest to:
the days sales outstanding is closest to:A) 15.9
B) 36.5
C) 59.9
D) 137.4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Using the following financial statement information,
 the inventory turnover ratio is closest to:
the inventory turnover ratio is closest to:
A) 0.14
B) 0.18
C) 5.67
D) 7.33
 the inventory turnover ratio is closest to:
the inventory turnover ratio is closest to:A) 0.14
B) 0.18
C) 5.67
D) 7.33

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Using the following financial statements
 the days sales in inventory is closest to:
the days sales in inventory is closest to:
A) 28.1
B) 64.4
C) 71.1
D) 137.4
 the days sales in inventory is closest to:
the days sales in inventory is closest to:A) 28.1
B) 64.4
C) 71.1
D) 137.4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Using the following financial statements,
 the accounts payable turnover, assuming that beginning inventory is equal to ending inventory, is closest to:
the accounts payable turnover, assuming that beginning inventory is equal to ending inventory, is closest to:
A) 6.8
B) 8.5
C) 10.0
D) 19.5
 the accounts payable turnover, assuming that beginning inventory is equal to ending inventory, is closest to:
the accounts payable turnover, assuming that beginning inventory is equal to ending inventory, is closest to:A) 6.8
B) 8.5
C) 10.0
D) 19.5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Using the following financial statements,
 the days payables outstanding is closest to:
the days payables outstanding is closest to:
A) 18.9
B) 36.7
C) 42.9
D) 53.8
 the days payables outstanding is closest to:
the days payables outstanding is closest to:A) 18.9
B) 36.7
C) 42.9
D) 53.8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Using the following financial statements
 the operating cycle is closest to:
the operating cycle is closest to:
A) 80.3
B) 88.0
C) 173.9
D) 208.5
 the operating cycle is closest to:
the operating cycle is closest to:A) 80.3
B) 88.0
C) 173.9
D) 208.5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Using the following financial statement information,
 the cash conversion cycle (CCC), assuming all sales on credit and that beginning inventory is equal to ending inventory, is closest to:
the cash conversion cycle (CCC), assuming all sales on credit and that beginning inventory is equal to ending inventory, is closest to:
A) 34.2
B) 37.4
C) 137.2
D) 189.6
 the cash conversion cycle (CCC), assuming all sales on credit and that beginning inventory is equal to ending inventory, is closest to:
the cash conversion cycle (CCC), assuming all sales on credit and that beginning inventory is equal to ending inventory, is closest to:A) 34.2
B) 37.4
C) 137.2
D) 189.6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Using the following financial statement information,
 the quick ratio is closest to:
the quick ratio is closest to:
A) 0.33
B) 0.67
C) 1.33
D) 2.33
 the quick ratio is closest to:
the quick ratio is closest to:A) 0.33
B) 0.67
C) 1.33
D) 2.33

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Using the following financial statement information,
 the current ratio is closest to:
the current ratio is closest to:
A) 0.19
B) 2.33
C) 3.50
 the current ratio is closest to:
the current ratio is closest to:A) 0.19
B) 2.33
C) 3.50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Using the following financial statement information,
 the accounts receivable turnover ratio, assuming all sales are for credit, is closest to:
the accounts receivable turnover ratio, assuming all sales are for credit, is closest to:
A) 20.0
B) 35.0
C) 40.0
 the accounts receivable turnover ratio, assuming all sales are for credit, is closest to:
the accounts receivable turnover ratio, assuming all sales are for credit, is closest to:A) 20.0
B) 35.0
C) 40.0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Using the following financial statement information,
 the days sales outstanding, assuming all sales on credit, is closest to:
the days sales outstanding, assuming all sales on credit, is closest to:
A) 10.4
B) 21.5
C) 36.5
D) 75.1
 the days sales outstanding, assuming all sales on credit, is closest to:
the days sales outstanding, assuming all sales on credit, is closest to:A) 10.4
B) 21.5
C) 36.5
D) 75.1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Using the following financial statement information,
 the inventory turnover ratio is closest to:
the inventory turnover ratio is closest to:
A) 0.08
B) 0.09
C) 11.33
D) 12.00
 the inventory turnover ratio is closest to:
the inventory turnover ratio is closest to:A) 0.08
B) 0.09
C) 11.33
D) 12.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Using the following financial statement information,
 the days sales in inventory is closest to:
the days sales in inventory is closest to:
A) 15.6
B) 32.2
C) 68.4
D) 75.2
 the days sales in inventory is closest to:
the days sales in inventory is closest to:A) 15.6
B) 32.2
C) 68.4
D) 75.2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Using the following financial statement information,
 the accounts payable turnover, assuming that beginning inventory is equal to ending inventory, is closest to:
the accounts payable turnover, assuming that beginning inventory is equal to ending inventory, is closest to:
A) 11.3
B) 17.0
C) 18.0
D) 35.0
 the accounts payable turnover, assuming that beginning inventory is equal to ending inventory, is closest to:
the accounts payable turnover, assuming that beginning inventory is equal to ending inventory, is closest to:A) 11.3
B) 17.0
C) 18.0
D) 35.0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Using the following financial statement information,
 the days payables outstanding is closest to:
the days payables outstanding is closest to:
A) 10.5
B) 21.5
C) 21.6
D) 32.3
 the days payables outstanding is closest to:
the days payables outstanding is closest to:A) 10.5
B) 21.5
C) 21.6
D) 32.3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Using the following financial statement information,
 the operating cycle, assuming all sales on credit, is closest to:
the operating cycle, assuming all sales on credit, is closest to:
A) 42.6
B) 52.1
C) 96.6
D) 143.6
 the operating cycle, assuming all sales on credit, is closest to:
the operating cycle, assuming all sales on credit, is closest to:A) 42.6
B) 52.1
C) 96.6
D) 143.6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Using the following financial statement information,

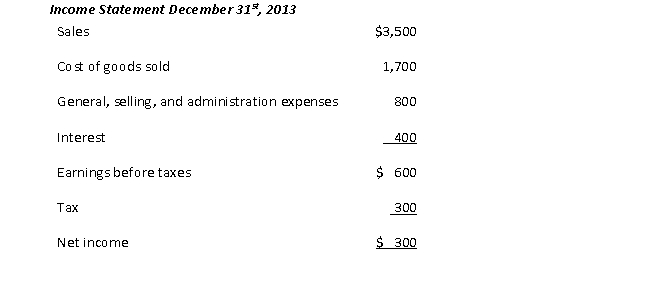 the cash conversion cycle (CCC), assuming all sales are on credit and that beginning inventory is equal to ending inventory, is closest to:
the cash conversion cycle (CCC), assuming all sales are on credit and that beginning inventory is equal to ending inventory, is closest to:
A) 19.9
B) 21.1
C) 75.0
D) 133.4

 the cash conversion cycle (CCC), assuming all sales are on credit and that beginning inventory is equal to ending inventory, is closest to:
the cash conversion cycle (CCC), assuming all sales are on credit and that beginning inventory is equal to ending inventory, is closest to:A) 19.9
B) 21.1
C) 75.0
D) 133.4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Using the following financial statement information,

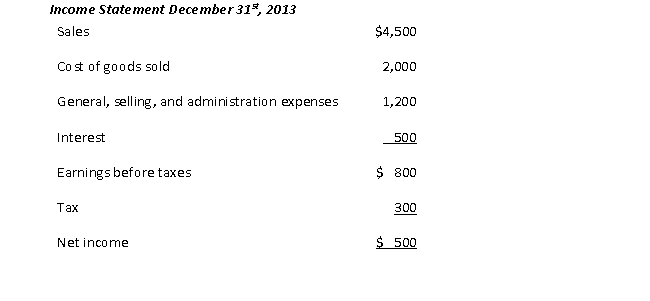 the quick ratio is closest to:
the quick ratio is closest to:
A) 0.38
B) 0.50
C) 1.25
D) 2.00

 the quick ratio is closest to:
the quick ratio is closest to:A) 0.38
B) 0.50
C) 1.25
D) 2.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Using the following financial statement information,
 the current ratio is closest to:
the current ratio is closest to:
A) 0.16
B) 2.00
C) 2.67
 the current ratio is closest to:
the current ratio is closest to:A) 0.16
B) 2.00
C) 2.67

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Using the following financial statement information,
 the accounts receivable turnover ratio is closest to:
the accounts receivable turnover ratio is closest to:
A) 18.0
B) 30.0
C) 36.0
 the accounts receivable turnover ratio is closest to:
the accounts receivable turnover ratio is closest to:A) 18.0
B) 30.0
C) 36.0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Using the following financial statement information,
 The days sales outstanding, assuming all sales are on credit, is closest to:
The days sales outstanding, assuming all sales are on credit, is closest to:
A) 12.2
B) 27.4
C) 32.4
D) 73.0
 The days sales outstanding, assuming all sales are on credit, is closest to:
The days sales outstanding, assuming all sales are on credit, is closest to:A) 12.2
B) 27.4
C) 32.4
D) 73.0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Using the following financial statement information,
 the inventory turnover ratio is closest to:
the inventory turnover ratio is closest to:
A) 0.06
B) 0.08
C) 13.33
D) 16.67
 the inventory turnover ratio is closest to:
the inventory turnover ratio is closest to:A) 0.06
B) 0.08
C) 13.33
D) 16.67

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Using the following financial statement information,
 the days sales in inventory is closest to:
the days sales in inventory is closest to:
A) 12.7
B) 27.4
C) 64.4
D) 73.0
 the days sales in inventory is closest to:
the days sales in inventory is closest to:A) 12.7
B) 27.4
C) 64.4
D) 73.0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Using the following financial statement information,
 the accounts payable turnover, assuming that beginning inventory is equal to ending inventory, is closest to:
the accounts payable turnover, assuming that beginning inventory is equal to ending inventory, is closest to:
A) 10.0
B) 13.3
C) 16.7
D) 30.0
 the accounts payable turnover, assuming that beginning inventory is equal to ending inventory, is closest to:
the accounts payable turnover, assuming that beginning inventory is equal to ending inventory, is closest to:A) 10.0
B) 13.3
C) 16.7
D) 30.0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Using the following financial statement information,
 the days payables outstanding is closest to:
the days payables outstanding is closest to:
A) 12.3
B) 22.0
C) 27.4
D) 36.6
 the days payables outstanding is closest to:
the days payables outstanding is closest to:A) 12.3
B) 22.0
C) 27.4
D) 36.6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Using the following financial statement information,
 the operating cycle is closest to:
the operating cycle is closest to:
A) 39.6
B) 44.6
C) 100.4
D) 137.4
 the operating cycle is closest to:
the operating cycle is closest to:A) 39.6
B) 44.6
C) 100.4
D) 137.4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Using the following financial statement information,
 the cash conversion cycle (CCC), assuming all sales on credit and assuming that beginning inventory is equal to ending inventory, is closest to:
the cash conversion cycle (CCC), assuming all sales on credit and assuming that beginning inventory is equal to ending inventory, is closest to:
A) 8.0
B) 12.2
C) 78.4
D) 125.2
 the cash conversion cycle (CCC), assuming all sales on credit and assuming that beginning inventory is equal to ending inventory, is closest to:
the cash conversion cycle (CCC), assuming all sales on credit and assuming that beginning inventory is equal to ending inventory, is closest to:A) 8.0
B) 12.2
C) 78.4
D) 125.2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The reason for holding cash required for a company's normal operations is best described as:
A) finance motive.
B) speculative motive.
C) transactions motive.
D) precautionary motive.
A) finance motive.
B) speculative motive.
C) transactions motive.
D) precautionary motive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The reason that companies keep cash on hand to take care of unanticipated required outlays, such as unexpected repairs on equipment is best described as:
A) finance motive
B) speculative motive
C) transactions motive
D) precautionary motive
A) finance motive
B) speculative motive
C) transactions motive
D) precautionary motive

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The reason that companies will accumulate cash in anticipation of any major outlays, such as lump-sum loan repayments or dividend payments is best described as:
A) finance motive.
B) speculative motive.
C) transactions motive.
D) precautionary motive.
A) finance motive.
B) speculative motive.
C) transactions motive.
D) precautionary motive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The fact that companies may keep extra cash available to take advantage of unexpected "bargains", such as the opportunity to purchase raw materials very cheaply is best described as:
A) finance motive.
B) speculative motive.
C) transactions motive.
D) precautionary motive.
A) finance motive.
B) speculative motive.
C) transactions motive.
D) precautionary motive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which of the following is not one of the four C's of credit?
A) Cost
B) Capacity
C) Character
D) Conditions
A) Cost
B) Capacity
C) Character
D) Conditions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
A company is considering the purchase of one of its inputs from supplier A. The credit terms are 1.5/10 net 30. What is the effective annual cost of forgoing the discount and paying on day 30?
A) 20.19%
B) 31.76%
C) 73.61%
A) 20.19%
B) 31.76%
C) 73.61%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A company is considering the purchase of one of its inputs from supplier A. The credit terms are 2/10 net 30. What is the effective annual cost of forgoing the discount and paying on day 30?
A) 27.86%
B) 44.59%
C) 109.05%
A) 27.86%
B) 44.59%
C) 109.05%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which of the following inventory management approaches attempts to find the optimal inventory level that minimizes the total of shortage and carrying costs?
A) The ABC Approach
B) Just-in-time (JIT) inventory system
C) Material Requirement Planning (MRP)
D) Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) Model
A) The ABC Approach
B) Just-in-time (JIT) inventory system
C) Material Requirement Planning (MRP)
D) Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) Model

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which of the following inventory management systems works in conjunction with production schedules to determine the exact level of raw materials and work-in-process that must be on hand to meet finished goods demand?
A) The ABC Approach
B) Just-in-time (JIT) inventory system
C) Material Requirement Planning (MRP)
D) Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) Model
A) The ABC Approach
B) Just-in-time (JIT) inventory system
C) Material Requirement Planning (MRP)
D) Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) Model

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which of the following inventory management systems fine-tunes the receipt of raw materials so that they arrive exactly when they are required in the production process?
A) The ABC Approach
B) Just-in-time (JIT) inventory system
C) Material Requirement Planning (MRP)
D) Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) Model
A) The ABC Approach
B) Just-in-time (JIT) inventory system
C) Material Requirement Planning (MRP)
D) Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) Model

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which of the following inventory management approaches attempts to divide inventory into several categories based on the value of the inventory items, their overall level of importance to the company's operations, and their profitability?
A) The ABC Approach
B) Just-in-time (JIT) inventory system
C) Material Requirement Planning (MRP)
D) Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) Mode
A) The ABC Approach
B) Just-in-time (JIT) inventory system
C) Material Requirement Planning (MRP)
D) Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) Mode

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
A company orders 240,000 windows per year. Every time a company orders windows from its suppliers, the supplier charges $1,000 in shipping and handling. The cost of keeping windows on hand, in terms of storage and maintenance costs, is $.25 per window. What quantity of windows should the company order?
A) 20,000
B) 30,984
C) 43,818
D) 60,000
A) 20,000
B) 30,984
C) 43,818
D) 60,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The important method of financing that occurs when a company finances its purchases through credit terms offered by their suppliers is best described as:
A) bank loan.
B) trade credit.
C) commercial paper.
D) factor arrangement.
E) bankers' acceptance.
A) bank loan.
B) trade credit.
C) commercial paper.
D) factor arrangement.
E) bankers' acceptance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which of the following statements is correct?
A) Operating loans are long-term financing arrangements.
B) Operating loans are typically secured by accounts receivable and inventory.
C) Operating loans are only available to large institutions with excellent credit ratings.
D) Banks generally offer an operating line for 100% of accounts receivable less than 90 days and 100% of the company's inventory value.
A) Operating loans are long-term financing arrangements.
B) Operating loans are typically secured by accounts receivable and inventory.
C) Operating loans are only available to large institutions with excellent credit ratings.
D) Banks generally offer an operating line for 100% of accounts receivable less than 90 days and 100% of the company's inventory value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
First Bank offers XYZ Company a 1-year variable rate loan at a rate of prime plus ½%. Prime rate is 3%. Payments must be made monthly and there are no other fees. What is the effective annual cost of this loan?
A) .29%
B) 3.00%
C) 3.50%
D) 3.56%
A) .29%
B) 3.00%
C) 3.50%
D) 3.56%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Which kind of short-term financing is likely to be used by a small firm with average credit?
A) Bank loan
B) Commercial paper
C) Bankers' acceptance
D) Money market instrument
A) Bank loan
B) Commercial paper
C) Bankers' acceptance
D) Money market instrument

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
A short-term financing instrument, which is issued at a discount in large denominations, with a maturity date of 30, 60, or 90 days, in which a bank guarantees the payments is best described as:
A) bank loan.
B) commercial paper.
C) bankers' acceptance.
D) money market instrument.
A) bank loan.
B) commercial paper.
C) bankers' acceptance.
D) money market instrument.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
A large ski manufacturer issues $50 million face value 60-day commercial paper for net proceeds of $49.75 million. The ski manufacturer must maintain a $50 million credit line, on which it must pay a standby fee of .1 percent. The effective annual cost to the ski manufacturer of this financing arrangement is nearest to:
A) .50%
B) .60%
C) 3.04%
D) 3.73%
A) .50%
B) .60%
C) 3.04%
D) 3.73%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
A large ski manufacturer issues $50 million face value 60-day commercial paper for net proceeds of $49.75 million. The ski manufacturer must maintain a $50 million credit line, on which it must pay a standby fee of .1 percent. The quoted yield of this commercial paper is closest to:
A) .50%
B) .60%
C) 3.04%
D) 3.73%
A) .50%
B) .60%
C) 3.04%
D) 3.73%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
A conduit for packaging portfolios of receivables and selling them to investors in the money market is best described as:
A) Bank loan
B) Trade paper
C) Commercial paper
D) Bankers' acceptance
E) Special purpose vehicle (SPV)
A) Bank loan
B) Trade paper
C) Commercial paper
D) Bankers' acceptance
E) Special purpose vehicle (SPV)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which of the following statements is incorrect?
A) Special purpose vehicles are usually formed as sole proprietorships.
B) The credit risk of the seller of the receivables or loans is not directly involved in the securitization.
C) To improve the credit quality of SPVs, credit enhancements such as requiring collateral, insurance, or other agreements are often added.
D) Companies that offer financing for purchases sell the loans directly to the capital market through SPVs so that neither the loans nor the financing appear on their balance sheets.
A) Special purpose vehicles are usually formed as sole proprietorships.
B) The credit risk of the seller of the receivables or loans is not directly involved in the securitization.
C) To improve the credit quality of SPVs, credit enhancements such as requiring collateral, insurance, or other agreements are often added.
D) Companies that offer financing for purchases sell the loans directly to the capital market through SPVs so that neither the loans nor the financing appear on their balance sheets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The tests a credit rating agency performs to gauge the effect of changing economic conditions to see how it affects the ability of the SPV to pay off its securities is best described as:
A) stress tests.
B) ratio analysis.
C) prepayments.
D) credit enhancement.
A) stress tests.
B) ratio analysis.
C) prepayments.
D) credit enhancement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Working capital refers to a company's cash on hand and the rate that cash is used in operations due to negative operating cash flows.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Companies use the finance motive to keep cash on hand for unanticipated required outlays of cash such as unexpected repairs on equipment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
A company can use a lock-box system to reduce the float time of customer payments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Credit analysis is the process designed to assess the risk of nonpayment by potential customers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
A company should borrow funds at a rate of 10% to take advantage of credit terms offered to them of 1/10 net 30 if the company normally does not pay until the 30th day.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Trade credit is usually one of a company's most important sources of short-term financing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Factor arrangements are usually one of the most cost effective forms of financing for companies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
A company is considering the purchase of one of its inputs from supplier

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
A company is considering the purchase of one of its inputs from supplier

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
A company orders 120,000 windows per year. Every time a company orders windows from its suppliers, the supplier charges $1,000 in shipping and handling. The cost of keeping windows on hand, in terms of storage and maintenance costs, is $.25 per window. What quantity of windows should the company order?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



