Deck 15: Capital Structure Decisions
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/84
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 15: Capital Structure Decisions
1
What is not one of the three primary sources of uncertainty regarding a company's earnings?
A) Sales risk
B) Financial risk
C) Operating risk
D) Environment risk
A) Sales risk
B) Financial risk
C) Operating risk
D) Environment risk
Environment risk
2
The uncertainty regarding the price and quantity of goods a company will produce and sell is best described as:
A) financial risk.
B) business risk.
C) operating risk.
A) financial risk.
B) business risk.
C) operating risk.
business risk.
3
The uncertainty arising from the mix of fixed and variable costs in the production and sale of goods is best described as:
A) financial risk.
B) business risk.
C) operating risk.
A) financial risk.
B) business risk.
C) operating risk.
operating risk.
4
The uncertainty arising from the capital structure decisions is best described as:
A) financial risk.
B) business risk.
C) operating risk.
A) financial risk.
B) business risk.
C) operating risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Operating risk is best defined as uncertainty regarding:
A) the price and quantity of goods and services sold.
B) operating earnings based on the mix of fixed and variable operating costs.
C) the earnings to owners, influenced by the degree to which assets are financed by debt (relative to equity).
A) the price and quantity of goods and services sold.
B) operating earnings based on the mix of fixed and variable operating costs.
C) the earnings to owners, influenced by the degree to which assets are financed by debt (relative to equity).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The greater the operating leverage, the greater the
A) operating earnings.
B) volatility of operating earnings.
C) uncertainty in the number of goods produced and sold.
A) operating earnings.
B) volatility of operating earnings.
C) uncertainty in the number of goods produced and sold.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Green Company's contribution margin of $5 per unit and fixed operating costs of $45,000 breaks even, in terms of operating earnings, at:
A) 5,000 units.
B) 9,000 units.
C) 45,000 units.
D) 225,000 units.
A) 5,000 units.
B) 9,000 units.
C) 45,000 units.
D) 225,000 units.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Skate and Snowboard Unlimited has a contribution margin of $20 per unit and fixed operating costs of $25,000. What is the break even in terms of operating earnings for Skate and Snowboard Unlimited?
A) 1,250 units
B) 5,000 units
C) 20,000 units
D) 25,000 units
E) 500,000 units
A) 1,250 units
B) 5,000 units
C) 20,000 units
D) 25,000 units
E) 500,000 units

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The local golf range sells its product for $9 per unit. The variable cost per unit is $2 and the fixed operating costs are $3,000. The degree of operating leverage at 20,000 units produced and sold is closest to:
A) 1.022.
B) 7.000.
C) 10.218.
D) 2857.142.
A) 1.022.
B) 7.000.
C) 10.218.
D) 2857.142.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Consider a business that has a variable cost per unit of $2, a sales price per unit of $4.50, and fixed operating costs of $5,000. The degree of operating leverage at 10,000 units produced and sold is closest to:
A) 0.80
B) 1.00
C) 1.25
A) 0.80
B) 1.00
C) 1.25

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Consider a business that has a variable cost per unit of $2, a sales price per unit of $4.50, and fixed operating costs of $5,000. The contribution margin is closest to:
A) $0.44
B) $1.25
C) $2.50
A) $0.44
B) $1.25
C) $2.50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Consider a business that has a variable cost per unit of $4, a sales price per unit of $8, and fixed operating costs of $15,000. The degree of operating leverage at 20,000 units produced and sold is closest to:
A) 0.81
B) 1.00
C) 1.23
D) 2.50
A) 0.81
B) 1.00
C) 1.23
D) 2.50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Lexington Company with a degree of operating leverage of 1.40 and a degree of financial leverage of 1.90 has a degree of total leverage closest to:
A) 0.500.
B) 1.400.
C) 2.660.
D) 3.300.
A) 0.500.
B) 1.400.
C) 2.660.
D) 3.300.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The Gearing Company with a degree of operating leverage of 1.5 and a degree of total leverage of 4.2 has a degree of financial leverage closest to:
A) 0.4
B) 2.7.
C) 2.8.
A) 0.4
B) 2.7.
C) 2.8.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The Gearing Company with a degree of operating leverage of 1.6 and a degree of total leverage of 5 has a degree of financial leverage closest to:
A) 0.320
B) 3.125
C) 3.400
A) 0.320
B) 3.125
C) 3.400

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Suppose a company has the following:
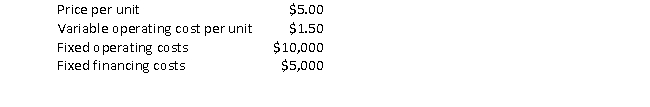 The degree of total leverage at 10,000 units produced and sold is closest to:
The degree of total leverage at 10,000 units produced and sold is closest to:
A) 0.43
B) 1.75.
C) 2.33.
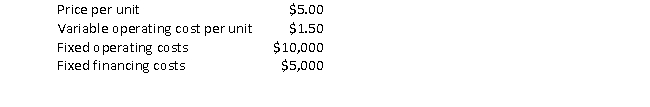 The degree of total leverage at 10,000 units produced and sold is closest to:
The degree of total leverage at 10,000 units produced and sold is closest to:A) 0.43
B) 1.75.
C) 2.33.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Suppose a company has the following:
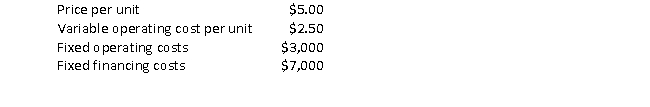 The degree of total leverage at 5,000 units produced and sold is closest to:
The degree of total leverage at 5,000 units produced and sold is closest to:
A) 0.20.
B) 0.50.
C) 1.31.
D) 3.80.
E) 5.00.
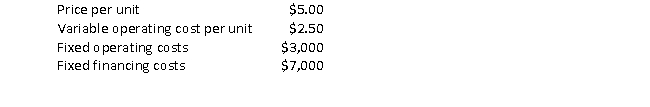 The degree of total leverage at 5,000 units produced and sold is closest to:
The degree of total leverage at 5,000 units produced and sold is closest to:A) 0.20.
B) 0.50.
C) 1.31.
D) 3.80.
E) 5.00.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Verde Company has a degree of operating leverage of 3.5. This means that a:
A) 1 percent change in operating earnings will result in a 3.5 percent change in net income.
B) 1 percent change in units produced and sold will result in a 3.5 percent change in net income.
C) 1 percent change in units produced and sold will result in a 3.5 percent change in earnings per share.
D) 1 percent change in units produced and sold will result in a 3.5 percent change in operating earnings.
A) 1 percent change in operating earnings will result in a 3.5 percent change in net income.
B) 1 percent change in units produced and sold will result in a 3.5 percent change in net income.
C) 1 percent change in units produced and sold will result in a 3.5 percent change in earnings per share.
D) 1 percent change in units produced and sold will result in a 3.5 percent change in operating earnings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Doberman Company has a degree of financial leverage of 2.5. This means that a:
A) 1 percent change in operating earnings will result in a 2.5 percent change in net income.
B) 1 percent change in units produced and sold will result in a 2.5 percent change in net income.
C) 1 percent change in units produced and sold will result in a 2.5 percent change in earnings per share.
D) 1 percent change in units produced and sold will result in a 2.5 percent change in operating earnings.
A) 1 percent change in operating earnings will result in a 2.5 percent change in net income.
B) 1 percent change in units produced and sold will result in a 2.5 percent change in net income.
C) 1 percent change in units produced and sold will result in a 2.5 percent change in earnings per share.
D) 1 percent change in units produced and sold will result in a 2.5 percent change in operating earnings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Umbrella Company has a degree of total leverage of 4.0. This means that a:
A) 1 percent change in operating earnings will result in a 4.0 percent change in net income.
B) 1 percent change in units produced and sold will result in a 4.0 percent change in net income.
C) 1 percent change in units produced and sold will result in a 4.0 percent change in earnings per share.
D) 1 percent change in units produced and sold will result in a 4.0 percent change in operating earnings.
A) 1 percent change in operating earnings will result in a 4.0 percent change in net income.
B) 1 percent change in units produced and sold will result in a 4.0 percent change in net income.
C) 1 percent change in units produced and sold will result in a 4.0 percent change in earnings per share.
D) 1 percent change in units produced and sold will result in a 4.0 percent change in operating earnings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The sensitivity of net income to changes in operating earnings, influenced by the use of debt, relative to equity, as a source of capital is best described as:
A) indifference point.
B) degree of total leverage.
C) degree of financial leverage.
D) degree of operating leverage.
A) indifference point.
B) degree of total leverage.
C) degree of financial leverage.
D) degree of operating leverage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The number of units produced and sold at which the operating profit is zero is best described as:
A) indifference point.
B) EPS indifference point.
C) financial break-even point.
D) operating break-even point.
A) indifference point.
B) EPS indifference point.
C) financial break-even point.
D) operating break-even point.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A company experiences a 60 percent change in net income for every 10 percent change in operating profit. What is this company's degree of financial leverage?
A) 0.166
B) 6.0
C) 16.6
D) 60.0
A) 0.166
B) 6.0
C) 16.6
D) 60.0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
ABC Company's net income went up 5 percent change in response to a 1 percent increase in operating profit. What is ABC Company's degree of financial leverage?
A) 0.20
B) 2
C) 5
D) 20
A) 0.20
B) 2
C) 5
D) 20

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Fox Company expects to sell 10,000 units of its product at a price of $20 per unit. The variable cost to produce a unit is $7, and the company has fixed operating costs of $10,000. The break-even units produced and sold is nearest to:
A) 76.92.
B) 500.
C) 769.23.
D) 10,000.
A) 76.92.
B) 500.
C) 769.23.
D) 10,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Amarillo Company expects to sell 20,000 units of its product at a price of $15 per unit. The variable cost to produce a unit is $9, and the company has fixed operating costs of $14,000. The break-even units produced and sold is closest to:
A) 1,000.
B) 2,333.
C) 20,000.
D) 23,333.
A) 1,000.
B) 2,333.
C) 20,000.
D) 23,333.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The return on investment at which the return on equity is zero is best described as the:
A) indifference point.
B) financial break-even.
C) operating break-even.
A) indifference point.
B) financial break-even.
C) operating break-even.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following statements is incorrect?
A) Debt is almost always the most expensive form of capital.
B) The amount of debt a company can carry depends on the underlying business risk of the asset being financed.
C) The more a company relies on debt financing, relative to equity financing, the greater the variation of returns to equity.
D) Financial leverage tends to increase returns at the expense of increased variability and increased risk of financial distress.
A) Debt is almost always the most expensive form of capital.
B) The amount of debt a company can carry depends on the underlying business risk of the asset being financed.
C) The more a company relies on debt financing, relative to equity financing, the greater the variation of returns to equity.
D) Financial leverage tends to increase returns at the expense of increased variability and increased risk of financial distress.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Business risk is comprised of all of the following except:
A) sales risk.
B) economic risk.
C) operating risk.
A) sales risk.
B) economic risk.
C) operating risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Pirates, Inc. is examining two different financing strategies (1) 50% debt and 50% equity, and (2) 75% debt and 25% equity. At 750 units produced and sold, the ROE is the same for both financing methods. The point at which 750 units are produced and sold is best described as the:
A) ROE equality.
B) indifference point.
C) EPS indifference point.
D) finance flexibility point.
A) ROE equality.
B) indifference point.
C) EPS indifference point.
D) finance flexibility point.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following is not one of the scenarios that the Modigliani and Miller Theories comprise?
A) A world with taxes and costs of financial distress
B) A world without taxes or costs of financial distress
C) A world with costs of financial distress, but no taxes
D) A world with taxes, but no costs of financial distress
A) A world with taxes and costs of financial distress
B) A world without taxes or costs of financial distress
C) A world with costs of financial distress, but no taxes
D) A world with taxes, but no costs of financial distress

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Costs of financial distress include all of the following except:
A) direct costs.
B) bankruptcy costs.
C) opportunity costs.
D) losses prior to bankruptcy.
A) direct costs.
B) bankruptcy costs.
C) opportunity costs.
D) losses prior to bankruptcy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Under which, Modigliani and Miller assumption is the value of the company not affected by the capital structure?
A) Taxes and costs to financial distress
B) No taxes, no costs of financial distress
C) Taxes, but no costs to financial distress
A) Taxes and costs to financial distress
B) No taxes, no costs of financial distress
C) Taxes, but no costs to financial distress

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
What is the conclusion of part 2 of Modigliani and Miller - taxes, but no costs to financial distress?
A) The more debt, the greater value of the company
B) There is some optimal capital structure for a company
C) Management should be indifferent in how to finance the company
A) The more debt, the greater value of the company
B) There is some optimal capital structure for a company
C) Management should be indifferent in how to finance the company

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
If there are no costs to financial distress, but there are taxes, the optimal capital structure, according to the Modigliani and Miller theory, is:
A) no debt.
B) almost all debt.
C) 50% debt, 50% equity.
A) no debt.
B) almost all debt.
C) 50% debt, 50% equity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The theory where a company uses debt to maximize its tax advantages up to the point where these benefits are outweighed by the associated estimated costs of financial distress and bankruptcy is best described as the:
A) agency theory.
B) bankruptcy theory.
C) pecking order theory.
D) static trade-off theory.
A) agency theory.
B) bankruptcy theory.
C) pecking order theory.
D) static trade-off theory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
An individual seeks to finance a home addition. This individual takes out a home equity line, due to the tax benefits of this type of financing, but only takes the loan in the amount in which she feels will not be over borrowing or too much debt for her financial situation. This would be an example of:
A) agency theory.
B) signaling theory.
C) pecking order theory.
D) static trade-off theory.
A) agency theory.
B) signaling theory.
C) pecking order theory.
D) static trade-off theory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The correct order in which companies prefer to raise financing according to pecking order theory is:
A) internal cash flow, debt, issuing common equity.
B) issuing common equity, debt, internal cash flow.
C) issuing common equity, internal cash flow, debt.
D) debt, internal cash flow, issuing common equity
E) internal cash flow, issuing common equity, debt.
A) internal cash flow, debt, issuing common equity.
B) issuing common equity, debt, internal cash flow.
C) issuing common equity, internal cash flow, debt.
D) debt, internal cash flow, issuing common equity
E) internal cash flow, issuing common equity, debt.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following is not a direct cost of financial distress?
A) The loss of the use of tax loss carryovers
B) Legal and accounting costs experienced in a bankruptcy liquidation
C) Losses related to liquidation from reduced asset prices in distress sales
D) Opportunity cost of company making decisions to meet short-term cash needs instead of decisions it otherwise would have made
A) The loss of the use of tax loss carryovers
B) Legal and accounting costs experienced in a bankruptcy liquidation
C) Losses related to liquidation from reduced asset prices in distress sales
D) Opportunity cost of company making decisions to meet short-term cash needs instead of decisions it otherwise would have made

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following is not an assumption of Modigliani and Miller irrelevance theory?
A) No taxes
B) No transaction costs
C) No asymmetric information
D) No costs to financial distress
E) All of the above are assumptions of the Modigliani and Miller irrelevance theory
A) No taxes
B) No transaction costs
C) No asymmetric information
D) No costs to financial distress
E) All of the above are assumptions of the Modigliani and Miller irrelevance theory

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The rule that the assets of a company are distributed to creditors, in order of seniority, in the case of liquidation is best described as the:
A) bankruptcy rule.
B) absolute priority rule.
C) financial leverage rule.
A) bankruptcy rule.
B) absolute priority rule.
C) financial leverage rule.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Earnings before interest and taxes divided by interest is best described as the:
A) equity multiplier.
B) debt-equity ratio.
C) times interest earned.
D) cash flow to debt ratio.
A) equity multiplier.
B) debt-equity ratio.
C) times interest earned.
D) cash flow to debt ratio.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which of the following statements is incorrect?
A) As companies issue more debt, their ratios deteriorate and their credit rating weakens.
B) Large, profitable firms tend to carry less debt because of using cash from operations for financing.
C) Investment -grade companies have higher coverage and less debt than companies with non-investment grade bonds.
D) Companies with investment -grade companies tend to have larger cash flow to debt and less liquidity, than companies with non-investment grade bonds.
A) As companies issue more debt, their ratios deteriorate and their credit rating weakens.
B) Large, profitable firms tend to carry less debt because of using cash from operations for financing.
C) Investment -grade companies have higher coverage and less debt than companies with non-investment grade bonds.
D) Companies with investment -grade companies tend to have larger cash flow to debt and less liquidity, than companies with non-investment grade bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which financial ratio shows how much debt is used to finance the company for every dollar of equity?
A) Debt ratio
B) Debt-equity ratio
C) Equity multiplier
D) Cash flow to debt ratio
A) Debt ratio
B) Debt-equity ratio
C) Equity multiplier
D) Cash flow to debt ratio

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Consider the following information for the AppleTree Company:
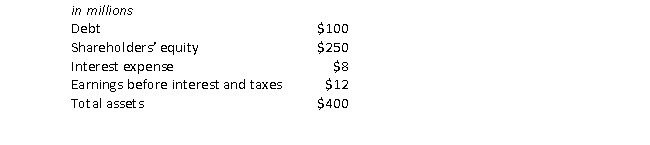 The debt-equity ratio for AppleTree is closest to:
The debt-equity ratio for AppleTree is closest to:
A) 0.25.
B) 0.29.
C) 0.40.
D) 0.60
E) 2.50.
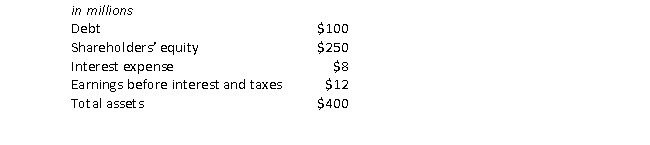 The debt-equity ratio for AppleTree is closest to:
The debt-equity ratio for AppleTree is closest to:A) 0.25.
B) 0.29.
C) 0.40.
D) 0.60
E) 2.50.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Consider the following information for the AppleTree Company:
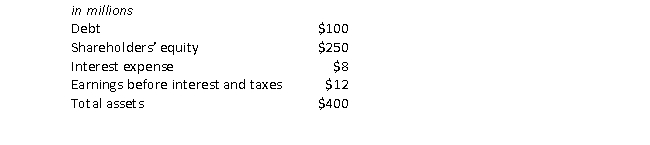 The times interest earned for AppleTree is closest to:
The times interest earned for AppleTree is closest to:
A) 0.25
B) 1.5.
C) 2.5.
D) 3.0.
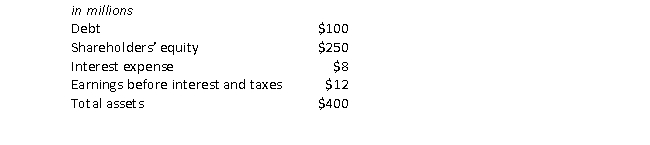 The times interest earned for AppleTree is closest to:
The times interest earned for AppleTree is closest to:A) 0.25
B) 1.5.
C) 2.5.
D) 3.0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Consider the following information for the AppleTree Company:
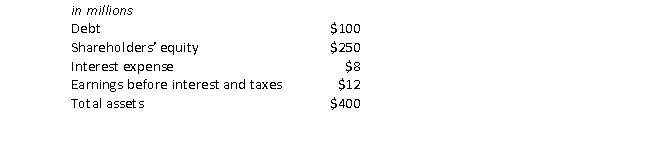 The debt ratio for AppleTree is closest to:
The debt ratio for AppleTree is closest to:
A) 0.25.
B) 0.29.
C) 0.40.
D) 0.60
E) 2.50.
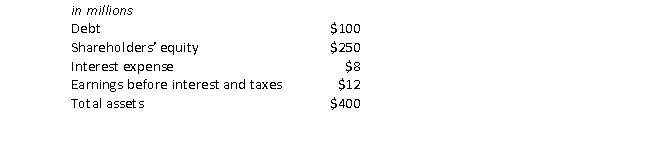 The debt ratio for AppleTree is closest to:
The debt ratio for AppleTree is closest to:A) 0.25.
B) 0.29.
C) 0.40.
D) 0.60
E) 2.50.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Altman's Z score is predictor of:
A) liquidation.
B) absolute priority.
C) financial distress.
A) liquidation.
B) absolute priority.
C) financial distress.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Financial risk is defined as uncertainty regarding operating earnings based on the mix of fixed and variable operating costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The lower the use of fixed costs relative to variable costs within a company, the greater the operating leverage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A degree of operating leverage of 2.50 means that a 1 percent change in the quantity of units produced and sold will result in a 2.5 percent change in net income or earnings per share.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The use of debt normally increases the expected ROE.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
A firm can have high sales risk and low operating risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Debt is almost always the most expensive form of capital.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Enterprise risk management looks at the risk of the company as a whole.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The state of business failing where bankruptcy seems imminent if dramatic action is not taken is best described as fiscal cliff.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The conflict of interest between creditors and shareholders when a company is in financial distress is an example of agency issues.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The fact that management makes decisions regarding capital structure on behalf of the shareholders, but they have their own interests at stake as well is best described as an information asymmetry problem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Pecking order theory would indicate that a large profitable firm would be the least likely to use debt financing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Generic Company's cash flow to debt ratio is 1.83. This means that Generic Company can satisfy its interest obligations from operating earnings 1.83 times.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Altman Z-score is used to predict the likelihood of bankruptcy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The lower the Altman Z-score, the less likely a firm is to file bankruptcy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
A company that is not profitable is more likely to finance with equity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Companies with hard tangible assets that could be sold are able to secure debt from lenders without as much focus on cash flow as companies with fewer tangible assets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Trinity, Inc. has an Altman's Z-score of 3.50. Westlake, Inc. has an Altman's Z-score of 2.15. Trinity, Inc. is more likely to go bankrupt.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Sunflower Company sells its product for $4 per unit. The variable cost per unit is $1 and the fixed operating costs are $500. What is the degree of operating leverage at 5,000 units produced and sold at Sunflower Company? What does this mean?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Phoenix Company has a degree of operating leverage of 1.75 and a degree of financial leverage of 2.10. What is the degree of total leverage of Phoenix Company? What does that mean?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The Fireworks Company sells packs of sparklers for $2.00 each. It costs $.50 per pack to manufacture and distribute the sparklers. The Fireworks Company has fixed operating costs of $8,000 and fixed financing costs of $2,000. What is the Fireworks Company's degree of operating leverage at 25,000 packs of sparklers produced and sold? What does this mean?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The Fireworks Company sells packs of sparklers for $2.00 each. It costs $.50 per pack to manufacture and distribute the sparklers. The Fireworks Company has fixed operating costs of $8,000 and fixed financing costs of $2,000. What is the Fireworks Company's degree of financial leverage at 25,000 packs of sparklers produced and sold? What does this mean?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The Fireworks Company sells packs of sparklers for $2.00 each. It costs $.50 per pack to manufacture and distribute the sparklers. The Fireworks Company has fixed operating costs of $8,000 and fixed financing costs of $2,000. What is the Fireworks Company's degree of total leverage at 25,000 packs of sparklers produced and sold? What does this mean?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Why is part two of Modigliani and Miller's Theory not realistic?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
List at least three factors that affect a company's capital structure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Consider the following information on Company XYZ:
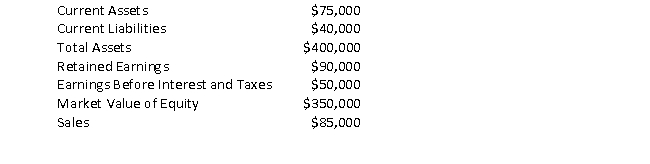 Calculate Altman's Z-score for Company XYZ.
Calculate Altman's Z-score for Company XYZ.
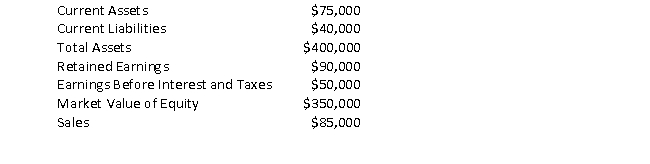 Calculate Altman's Z-score for Company XYZ.
Calculate Altman's Z-score for Company XYZ.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Consider the following information on Company Alpha:
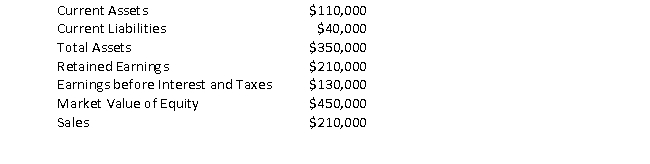 Calculate Altman's Z-score for Company Alpha.
Calculate Altman's Z-score for Company Alpha.
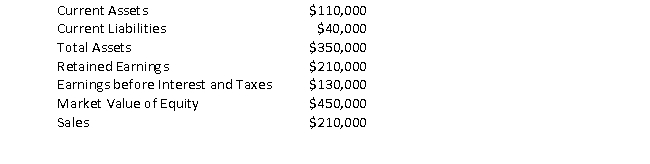 Calculate Altman's Z-score for Company Alpha.
Calculate Altman's Z-score for Company Alpha.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Business risk is the combined effect of:
A) sales risk and financial risk.
B) sales risk and operating risk.
C) operating risk and financial risk.
A) sales risk and financial risk.
B) sales risk and operating risk.
C) operating risk and financial risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
If a company produces and sells 100 million units per year, has a contribution margin of $5 per unit, and has $300 fixed operating costs, its degree of operating leverage is closest to:
A) 0.6.
B) 2.5.
C) 3.3.
A) 0.6.
B) 2.5.
C) 3.3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
A degree of operating leverage of 1.5 means that a:
A) 1.5 percent change in operating earnings results in a 1.5 percent change in net income.
B) 1 percent change in operating earnings results in a 1.5 percent change in units produced and sold.
C) 1 percent change in units produced and sold results in a 1.5 percent change in operating earnings.
A) 1.5 percent change in operating earnings results in a 1.5 percent change in net income.
B) 1 percent change in operating earnings results in a 1.5 percent change in units produced and sold.
C) 1 percent change in units produced and sold results in a 1.5 percent change in operating earnings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
A company with a degree of operating leverage of 2.0 and a degree of financial leverage of 3.0, has a degree of total leverage closest to:
A) 0.7
B) 1.0.
C) 5.0.
D) 6.0
A) 0.7
B) 1.0.
C) 5.0.
D) 6.0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
According to the Modigliani and Miller capital structure theory, in a world with interest deductibility but no costs to financial distress,
A) there is no optimal capital structure.
B) the optimal capital structure is 99.99 percent debt.
C) there is an optimal capital structure around 50 percent.
A) there is no optimal capital structure.
B) the optimal capital structure is 99.99 percent debt.
C) there is an optimal capital structure around 50 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The bottom line of the Modigliani and Miller capital structure theory is that:
A) companies should not use debt.
B) companies should use as much debt as possible.
C) there is tradeoff between the benefits of debt (i.e., interest deductibility) and the costs of debt (i.e., costs to financial distress).
A) companies should not use debt.
B) companies should use as much debt as possible.
C) there is tradeoff between the benefits of debt (i.e., interest deductibility) and the costs of debt (i.e., costs to financial distress).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



